Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (4): 786-795.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2025.04.009
• Original Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of pestle needle therapy on the posterior cervical muscle in a rabbit model of cervical spondylosis
WU Haoyang1, Liu Yuan1, CHEN Yuzhou1, XIE Yizhou1, ZHONG Lei2, YU Yang2( ), FAN Xiaohong2(
), FAN Xiaohong2( )
)
- 1 College of Clinical Medicine, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu 610032, China
2 Department of Orthopaedics, Affiliated Hospital of Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu 610075, China
-
Received:2024-10-22Accepted:2025-02-28Online:2025-08-15Published:2025-07-25 -
Contact:YU Yang,FAN Xiaohong -
About author:Prof. YU Yang, Department of Orthopaedics, Affiliated Hospital of Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu 610075, China. spine_yy@163.com,Telephone: +86-13981888850
Prof. FAN Xiaohong, Department of Orthopaedics, Affiliated Hospital of Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu 610075, China. fxh202010@2980.com;
-
Supported by:Sichuan Provincial Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine Key Project of Scientific Research in Traditional Chinese Medicine: Deep Learning-based Three-dimensional Finite Element Analysis of Pestle Needle Therapy for the Treatment of Cervical Spine Physiologic Curvature Abnormalities(2023zd025);Scientific Research Project of Sichuan Provincial Science and Technology Department: Improvement of cartilage Degeneration in Knee Osteoarthritis by Regulating Zn2+ Homeostasis via Autophagy in Duhuo Jisheng Decoction(23NFSC2298)
Cite this article
WU Haoyang, Liu Yuan, CHEN Yuzhou, XIE Yizhou, ZHONG Lei, YU Yang, FAN Xiaohong. Effect of pestle needle therapy on the posterior cervical muscle in a rabbit model of cervical spondylosis[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(4): 786-795.
share this article

Figure 1 PNT exerts a positive effect on PCM injury in CS rabbit A: pain threshold; B: HE staining (× 200, scale bar: 100 μm). Yellow arrow: degenerated and necrotic cells; Red arrow: inflammatory cells; Green arrow: fibrous hyperplasia. C: Masson staining (× 400, scale bar: 50 μm); D: calculation of Masson staining PA %; E: IHC staining of Col1α1 (× 200, scale bar: 40 μm). B1, C1, E1: CON; B2, C2, E2: CS1; B3, C3, E3: EA; B4, C4, E4: PN1. F: calculation of Col1α1 PA %. CON group: normal healthy rabbits were immobilized without any restriction on the neck for 42 d; CS1 group: rabbits subjected to CS model induce for 42 d without treatment; EA group: CS model rabbits treated with electroacupuncture once 30 min daily for 21 d; PN1 group: CS model rabbits treated with PNT once 35 min daily for 21 d. PNT: pestle needle therapy; HE: hematoxylin-eosin; CON: control group; CS1: cervical spondylosis group 1; EA: electroacupuncture group; PN1: pestle needle thrapy group 1; IHC: immunohistochemistry; Col1α1: collagen type I alpha 1; PA: positive area. Statistical analyses were measured using one-way analysis of variance followed by Fisher’s least significant difference post hoc test, and the data were expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (n = 6 for each group). Compared with the CON group, aP < 0.001, cP < 0.01; compared with the CS group, eP < 0.001, bP < 0.01, dP < 0.05.

Figure 2 PNT promote PCM apoptosis and promote autophagy in CS rabbits A: TUNEL staining (× 400; scale bar: 50 μm). A1-4: merge; A5-8: DAPI; A9-12: TUNEL. A1, A5, A9: CON; A2, A6, A10: CS1; A3, A7, A11: EA; A4, A8, A12: PN1. Red circle: bright band; green circle: dark band; yellow arrow: M line; light blue arrow: Z line; red arrow: mitochondria; dark blue arrow: sarcoplasmic reticulum; purple arrow: autophagosome. B: calculation of TUNEL-positive cells percentage. C: WB bands for Bax, Bcl-2, and Caspase-3; D: relative protein expression of Bax, Bcl-2, and Caspase-3; E: TEM observation (× 30 000, scale bar: 500 nm). E1: CON; E2: CS1; E3: EA; E4: PN1. F: WB bands for P62, LC3-I, and LC3-II. G: relative protein expression of P62, and LC3-II/I. H: relative mRNA level of ATG5, ATG7. CON group: normal healthy rabbits were immobilized without any restriction on the neck for 42 d; CS1 group: rabbits subjected to CS model induce for 42 d without treatment; EA group: CS model rabbits treated with electroacupuncture once 30 min daily for 21 d; PN1 group: CS model rabbits treated with PNT once 35 min daily for 21 d. TUNEL: terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated DUTP nick end labeling; DAPI: 4',6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole; CON: control group; CS1: cervical spondylosis group 1; EA: electroacupuncture group; PN1: pestle needle therapy group 1; WB: Western bolt; Bax: Bcl-2 associated X protein; Bcl-2: B-cell lymphoma-2; Caspase-3: cysteine aspartate-specific protease-3; TEM: transmission electron microscope; P62: sequestosome-1; LC3: microtubule-associated protein light chain 3; ATG: autophagy protein; mRNA: messenger ribonucleic acid; PNT: pestle needle therapy; CON: control; CS: cervical spondylosis; EA: electroacupuncture; PN: pestle needle. Statistical analyses were measured using one-way analysis of variance followed by Fisher’s least significant difference post hoc test, and the data were expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (n = 6 for each group). Compared with the CON group, aP < 0.001, eP < 0.01; compared with the CS group, cP < 0.001, bP < 0.01, and dP < 0.05.
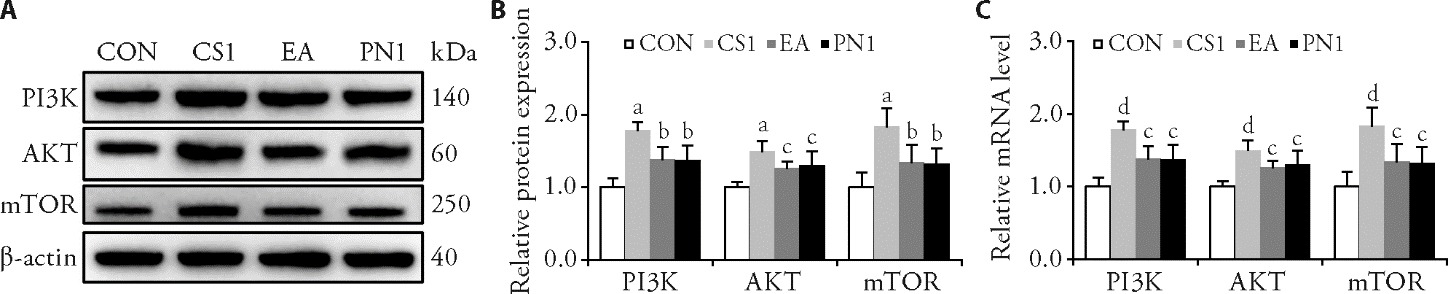
Figure 3 PNT inhibit the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in CS rabbits A: WB bands for PI3K, AKT, and mTOR; B: relative protein expression of PI3K, AKT, and mTOR; C: relative mRNA level of PI3K, AKT, and mTOR. CON group: normal healthy rabbits were immobilized without any restriction on the neck for 42 d; CS1 group: rabbits subjected to CS model induce for 42 d without treatment; EA group: CS model rabbits treated with electroacupuncture once 30 min daily for 21 d; PN1 group: CS model rabbits treated with PNT once 35 min daily for 21 d. CON: control group; CS1: cervical spondylosis group 1; EA: electroacupuncture group; PN1: pestle needle therapy group 1; WB: Western bolt; mRNA: messenger ribonucleic acid; PI3K: phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; AKT: protein kinase B; mTOR: mammalian target of rapamycin; PNT: pestle needle therapy; CON: control; CS: cervical spondylosis; EA: electroacupuncture; PN: pestle needle. Statistical analyses were measured using one-way analysis of variance followed by Fisher’s least significant difference post hoc test, and the data were expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (n = 6 for each group). Compared with the CON group, aP < 0.001, dP < 0.01; compared with the CS group, bP < 0.01, dP < 0.05.
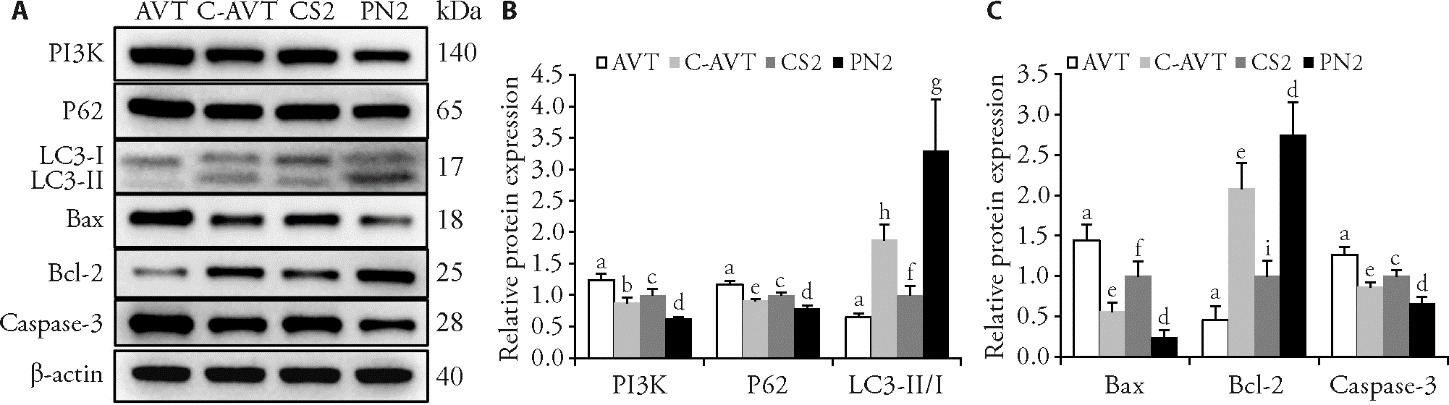
Figure 4 Rescue experiment A: WB bands for PI3K, P62, LC3-I, LC3-Ⅱ, Bax, Bcl-2 and Caspase-3 staining in PCM tissues; B: relative protein expression of PI3K, P62, and LC3-Ⅱ/Ⅰ; C: relative protein expression of Bax, Bcl-2 and Caspase-3. AVT group: CS model inducing by LNI for 42 d and received a 2 mL 740 Y-P (0.2 g/L) injection in the PCM for 5 d; C-AVT group: CS model rabbits treated with PNT for 21 d and received a 2 mL 740 Y-P (0.2 g/L) injection in the PCM for 5 d; CS2 group: CS model inducing by LNI for 42 d without treatment; PN2 group: CS model rabbits treated with PNT once 35 min daily for 21 d. AVT: activators group; C-AVT: pestle needle combined activators group; CS2: cervical spondylosis group 2; PN2: pestle needle therapy group 2; LNI: long-term neck immobilization; WB: Western bolt; PI3K: phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; P62: sequestosome-1; LC3: microtubule-associated protein light chain 3; Bax: Bcl-2 associated X protein; Bcl-2: B-cell lymphoma-2; Caspase-3: cysteine aspartate-specific protease-3. The data were expressed as the mean ± standard deviation of the mean (n = 5 for each group). Compared with the C-AVT group, aP < 0.001; compared with the PN2 group, bP < 0.001, eP < 0.01, hP < 0.05; compared with the AVT group cP < 0.001, fP < 0.01, iP < 0.05; compared with the CS2 group, dP < 0.001, gP < 0.01.
| 1. |
Rao RD, Currier BL, Albert TJ, et al. Degenerative cervical spondylosis: clinical syndromes, pathogenesis, and management. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2007; 89: 1360-78.
DOI PMID |
| 2. | Kazeminasab S, Nejadghaderi SA, Amiri P, et al. Neck pain: global epidemiology, trends and risk factors. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 2022; 23: 26. |
| 3. | Theodore N. Degenerative cervical spondylosis. N Engl J Med 2020; 383: 159-68. |
| 4. | Blanpied PR, Gross AR, Elliott JM, et al. Neck pain: revision 2017. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther 2017; 47: A1-83. |
| 5. | Yeh ML, Chung YC, Chen KM, et al. Acupoint electrical stimulation reduces acute postoperative pain in surgical patients with patient-controlled analgesia: a randomized controlled study. Altern Ther Health Med 2010; 16: 10-8. |
| 6. |
Dingyue W, Yana YU, Yiyuan W, et al. Musculoskeletal ultrasound to evaluate the efficacy of acupuncture: a review. J Tradit Chin Med 2024; 44: 629-32.
DOI |
| 7. |
Bingyu W, Fangfang J, Jiawei G, et al. Acupuncture reduces sedative and anaesthetic consumption and improves pain tolerance in patients undergoing colonoscopy: a Meta-analysis. J Tradit Chin Med 2024; 44: 1091-103.
DOI |
| 8. |
Wang X, Yin X, Guo XT, et al. Effects of the pestle needle therapy, a type of acupoint stimulation, on post-hemorrhoidectomy pain: a randomized controlled trial. J Integr Med 2020; 18: 492-8.
DOI PMID |
| 9. | Shen ZF, Yu SY, Hu YP. Theory and clinical application of pestle needle therapy. Shanghai Zhen Jiu Za Zhi 2015; 34: 575-8. |
| 10. | Zhong SC. The pestle needle. Beijing: China Press of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2006: 83-5. |
| 11. | Zhong L, Zhong SC. Diagram of Sichuan Li's clinical experience on pestle needling. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House, 2017: 23-5. |
| 12. | Hu Y, Jiang YL, Li YX, et al. Systematic evaluation of the effectiveness and safety of pestle and mortar therapy in the treatment of cervical spondylosis. Chengdu Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue Xue Bao 2018; 41: 112-8. |
| 13. | Wang YZ, Zhong L, Wu ZJ, et al. Efficacy study on pestle needle combined with Chinese herbal fumigation for cervical spondylosis. Zhen Jiu Tui Na Yi Xue (Yin Wen Ban) 2016; 14: 284-9. |
| 14. | Jiang ZY, Li CD. Clinical observationon treatment of cervical spondylosis with poking dazhui bazhen points. Zhong Guo Zhen Jiu 2001: 21: 30-2. |
| 15. | Li HT, Wang JK, Li J, et al. Clinical researches on the treatment of cervical spondylosis with pestle needle. Zhen Jiu Lin Chuang Za Zhi 2021; 37: 85-9. |
| 16. | Gao H, Zhao ZY, Chen JL, et al. Effect of electroacupuncture combined with scraping on cervical muscle inflammatory factors and NF-κB/IκB/IKKβ signaling pathway in rabbits with cervical spondylosis. Hua Zhong Ke Ji Da Xue Xue Bao 2023; 52: 458-65. |
| 17. | Li YC, Song ZQ, Wan CY, et al. Establishment of an animal model for cervical spondylosis by prolonged low head position and cold - damp stimulation. Zhong Hua Zhong Yi Yao Xue Kan 2022; 40: 210-5+279-82. |
| 18. | Zhang X, Li DN, Li KP, et al. Establishment of animal model of rabbit cervical type cervical spondylosis. Zhong Hua Zhong Yi Yao Xue Kan 2015; 33: 913-6. |
| 19. | Guo Y. Experimental acupuncture. Beijing: China Press of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2016: 40-3. |
| 20. | Zhen YL, Xu ZX, ZHEN XC, et al. Objective detection and labeling of the common acupoints in rabbits. Shanghai Zhen Jiu Za Zhi 2003; 26-9. |
| 21. | Jin S. Pestle needle therapy and sports injuries. Chengdu: Sichuan Publishing House of Science and Technology, 2019: 80-3. |
| 22. | Ma HF, Ren Q, Chen WM, et al. Effects of Sanhuang gel on wound healing, basic fibroblast growth factor and interleukin 17 levels of auricular skin defect in rabbits. Zhong Guo Zu Zhi Gong Cheng Yan Jiu 2023; 27: 1842-7. |
| 23. | Shi HM, Xu YQ, Wang GY. Experiment of acupoint catgut embedding therapy on rabbits suffered from neck type of cervical spondylosis. Shi Zhen Guo Yi Guo Yao 2019; 30: 1526-28. |
| 24. | Liu JY, Liu T, Qian X, et al. Research progress of signal pathway related to cervical spondylosis. Zhong Guo Lin Chuang Yan Jiu Za Zhi 2023; 36: 134-8. |
| 25. | Xu SD, Kong LJ, Zhu QG, et al. Research on the kinematics characteristic of ‘Jingu imbalance’ of cervical spondylosis neck type. Zhong Hua Zhong Yi Yao Za Zhi 2020; 35: 4739-42. |
| 26. | Zhang GL, Zhang ZS, Fan XH. Effects of pestle needle combined with microwave treatment on serum pain medium for lumbar disc herniation. Shi Jie Zui Xin Yi Xue Xin Xi Wen Zhai 2019; 19: 142-3. |
| 27. | Xu Q, Hu J, Zhu Y, et al. Clinical observation on 70 cases of migraine with hyperactivity of liver Yang treated by pestle needle combined with massage manipulation. Minerva Pediatr 2023; 75: 930-2. |
| 28. |
Japaries W, Wen B, Zhang H. Pestle needle (Chu Zhen) treatment for neck pain. Med Acupunct 2022; 34: 400-4.
DOI PMID |
| 29. |
Cagnie B, Dhooge F, Van AJ, et al. Changes in microcirculation of the trapezius muscle during a prolonged computer task. Eur J Appl Physiol 2012; 112: 3305-12.
DOI PMID |
| 30. |
Strøm V, Røe C, Knardahl S. Work-induced pain, trapezius blood flux, and muscle activity in workers with chronic shoulder and neck pain. Pain 2009; 144: 147-55.
DOI PMID |
| 31. | Ji Y, Li M, Chang M, et al. Inflammation: roles in skeletal muscle atrophy. Antioxidants 2022; 11: 1686. |
| 32. |
Bo LZ, Zhang J, Wagner KR. Inhibition of myostatin reverses muscle fibrosis through apoptosis. J Cell Sci 2012; 125: 3957-65.
DOI PMID |
| 33. |
Mahdy MAA. Skeletal muscle fibrosis: an overview. Cell Tissue Res 2019; 375: 575-88.
DOI PMID |
| 34. | Wang YX, Rudnicki MA. Satellite cells, the engines of muscle repair. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2011; 13: 127-33. |
| 35. | Goh Q, Millay DP. Requirement of myomaker-mediated stem cell fusion for skeletal muscle hypertrophy. Elife 2017; 6: e20007. |
| 36. | Almada AE, Wagers AJ. Molecular circuitry of stem cell fate in skeletal muscle regeneration, ageing and disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2016; 17: 267-79. |
| 37. | García-Prat L, Martínez-Vicente M, Perdiguero E, et al. Autophagy maintains stemness by preventing senescence. Nature 2016; 529: 37-42. |
| 38. |
Fiacco E, Castagnetti F, Bianconi V, et al. Autophagy regulates satellite cell ability to regenerate normal and dystrophic muscles. Cell Death Differ 2016; 23: 1839-49.
DOI PMID |
| 39. |
Wang Y, Nartiss Y, Steipe B, et al. ROS-induced mitochondrial depolarization initiates PARK2/PARKIN-dependent mitochondrial degradation by autophagy. Autophagy 2012; 8: 1462-76.
DOI PMID |
| 40. |
Kim I, Rodriguez-Enriquez S, Lemasters JJ. Selective degradation of mitochondria by mitophagy. Arch Biochem Biophys 2007; 462: 245-53.
DOI PMID |
| 41. |
Li B, Sun C, Sun J, et al. Autophagy mediates serum starvation-induced quiescence in nucleus pulposus stem cells by the regulation of P27. Stem Cell Res Ther 2019; 10: 118.
DOI PMID |
| 42. |
Fernando P, Kelly JF, Balazsi K, et al. Caspase 3 activity is required for skeletal muscle differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002; 99: 11025-30.
DOI PMID |
| 43. |
Xu H, Xiong S, Wang H, et al. The evidence and the possible significance of autophagy in degeneration model of human cervical end-plate cartilage. Exp Ther Med 2014; 7: 537-42.
PMID |
| 44. | Xiong SL, Xu HG, Wang H, et al. Autophagy expression and its significance in chondrocytes from a degenerate model of human cervical endplate. Zhong Hua Yi Xue Za Zhi 2013; 93: 2474-77. |
| 45. | Chu Y, Yuan X, Tao Y, et al. Autophagy in muscle regeneration: mechanisms, targets, and therapeutic perspective. Int J Mol Sci 2024; 25: 11901. |
| 46. |
Romanov J, Walczak M, Ibiricu I, et al. Mechanism and functions of membrane binding by the Atg5-Atg12/Atg16 complex during autophagosome formation. EMBO J 2012; 31: 4304-17.
DOI PMID |
| 47. |
Schaaf MBE, Keulers TG, Vooijs MA, et al. LC3/GABARAP family proteins: autophagy-(un)related functions. FASEB J 2016; 30: 3961-78.
PMID |
| 48. |
Harrington JS, Ryter SW, Plataki M, et al. Mitochondria in health, disease, and aging. Physiol Rev 2023; 103: 2349-422.
DOI PMID |
| 49. | McArthur K, Whitehead LW, Heddleston JM, et al. BAK/BAX macropores facilitate mitochondrial herniation and mtDNA efflux during apoptosis. Science 2018; 359: eaao6047. |
| 50. |
Nagata S. Apoptosis and clearance of apoptotic cells. Annu Rev Immunol 2018; 36: 489-517.
DOI PMID |
| 51. | Singh R, Letai A, Sarosiek K. Regulation of apoptosis in health and disease: the balancing act of BCL-2 family proteins. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2019; 20: 175-93. |
| 52. | Liu FS, Fang T, Hong T, et al. Effects of acupotomy therapy on PI3K/Akt signaling pathway of posterior cervical extensor muscles cells in cervical spondylosis rabbits. Zhong Hua Zhong Yi Yao Za Zhi 2020; 35: 918-22. |
| 53. | Liu FS. Effects of acupotomy therapy on apoptosis in posterior cervical extensor muscles in rabbit cervical spondylosis model. Beijing: Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, 2012: 43-91. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

