Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (2): 251-259.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2024.02.002
Previous Articles Next Articles
Polyphyllin I enhances tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-induced inhibition of human osteosarcoma cell growth via downregulating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway
CHANG Junli1, ZHAO Fulai1, SUN Xingyuan1, MA Xiaoping1, ZHAO Peng1, ZHOU Chujie1, SHI Binhao1, GU Wenchao2, WANG Yongjun1, YANG Yanping1( )
)
- 1 Spine Disease Institute, Longhua Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200032, China
2 Department of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology, University of Tsukuba, Ibaraki 315-0114, Japan
-
Received:2023-01-11Accepted:2023-04-27Online:2024-04-15Published:2024-03-05 -
Contact:YANG Yanping, Spine Disease Institute, Longhua Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200032, China.yanpingyang@shutcm.edu.cn Telephone: +86-13391142018 -
Supported by:National Key R&D Program of China: Cooperating Studies on Measurement Technologies of Human Phenome and Cross-scale Correlation of Phenotypic Data(2020YFE0201600);National Nature Science Foundation: Study on LncRNA-CCDC18-AS1 Mediated Osteosarcoma Occurrence by Activating YAP/TAZ and Tumor Microenvironment M2 TAM-dependent Lung Metastasis, and Efficacy/mechanism of Removing Blood Stasis/clearing heat/eliminating Toxic Material Principle(81973877);Mechanism Study on m6A Methyltransferase RBM15 Mediated YAP Epigenetic Modification to Promote Osteosarcoma Lung Metastasis through Lymphatic System and Management with Qichong Powder(82174408);Shanghai Collaborative Innovation Center of Industrial Transformation of Hospital TCM Preparation: Preclinical Study on the Treatment of Osteosarcoma with Qingre Jiedu Granules;Research Projects within Budget of Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine: the Research on the Mechanism of the HIPK3 Activation of Wnt/β-catenin Induction the Osteosarcoma and the Intervention of Banmao Decoction(2021LK047)
Cite this article
CHANG Junli, ZHAO Fulai, SUN Xingyuan, MA Xiaoping, ZHAO Peng, ZHOU Chujie, SHI Binhao, GU Wenchao, WANG Yongjun, YANG Yanping. Polyphyllin I enhances tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-induced inhibition of human osteosarcoma cell growth via downregulating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(2): 251-259.
share this article
| Group | n | MG-63 | U-2 OS |
|---|---|---|---|
| TRAIL-Ctrl | 3 | 97.32±0.61 | 97.06±0.17 |
| TRAIL-12.5 ng/mL | 3 | 98.99±0.39 | 98.51±0.97 |
| TRAIL-25 ng/mL | 3 | 98.33±0.58 | 97.99±0.59 |
| TRAIL-50 ng/mL | 3 | 84.58±3.71 | 85.99±0.65 |
| TRAIL-100 ng/mL | 3 | 40.72±5.56a | 67.78±4.25a |
| TRAIL-200 ng/mL | 3 | 17.96±2.98a | 38.62±0.39a |
Table 1 Change of viability in MG-63 and U-2 OS cells were treated with various concentrations of TRAIL for 24 h (%,$\bar{x}±s$)
| Group | n | MG-63 | U-2 OS |
|---|---|---|---|
| TRAIL-Ctrl | 3 | 97.32±0.61 | 97.06±0.17 |
| TRAIL-12.5 ng/mL | 3 | 98.99±0.39 | 98.51±0.97 |
| TRAIL-25 ng/mL | 3 | 98.33±0.58 | 97.99±0.59 |
| TRAIL-50 ng/mL | 3 | 84.58±3.71 | 85.99±0.65 |
| TRAIL-100 ng/mL | 3 | 40.72±5.56a | 67.78±4.25a |
| TRAIL-200 ng/mL | 3 | 17.96±2.98a | 38.62±0.39a |
| Group | n | MG-63 | U-2 OS |
|---|---|---|---|
| PPI-Ctrl | 3 | 95.18±0.19 | 98.52±0.12 |
| PPI-200 nM | 3 | 91.66±1.62 | 97.32±0.18 |
| PPI-400 nM | 3 | 88.27±0.89 | 90.64±1.39 |
| PPI-600 nM | 3 | 72.03±3.51a | 80.52±0.79a |
Table 2 Change of viability in MG-63 and U-2 OS cells were treated with various concentrations of PPI for 24 h (%, $\bar{x}±s$)
| Group | n | MG-63 | U-2 OS |
|---|---|---|---|
| PPI-Ctrl | 3 | 95.18±0.19 | 98.52±0.12 |
| PPI-200 nM | 3 | 91.66±1.62 | 97.32±0.18 |
| PPI-400 nM | 3 | 88.27±0.89 | 90.64±1.39 |
| PPI-600 nM | 3 | 72.03±3.51a | 80.52±0.79a |
| Group | n | MG-63 | U-2 OS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ctrl | 3 | 95.18±0.19 | 98.52±0.12 |
| PPI | 3 | 88.27±0.89 | 90.64±1.39 |
| TRAIL | 3 | 88.55±0.66 | 87.52±1.53 |
| PPI+TRAIL | 3 | 48.18±2.58abc | 55.78±1.81ade |
Table 3 Change of viability in MG-63 and U-2 OS cells (%,$\bar{x}±s$)
| Group | n | MG-63 | U-2 OS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ctrl | 3 | 95.18±0.19 | 98.52±0.12 |
| PPI | 3 | 88.27±0.89 | 90.64±1.39 |
| TRAIL | 3 | 88.55±0.66 | 87.52±1.53 |
| PPI+TRAIL | 3 | 48.18±2.58abc | 55.78±1.81ade |

Figure 1 PPI sensitizes TRAIL-induced osteosarcoma cells apoptosis MG-63 and U-2 OS cells were treated with 400 nM PPI, 50 ng/mL TRAIL or a combination (400 nM PPI plus 50 ng/mL TRAIL) for 24 h, then detected the apoptosis by flow cytometry. A: representative images of apoptosis. A1: control group of MG-63 cell lines; A2: PPI group of MG-63 cell lines; A3: TRAIL group of MG-63 cell lines; A4: PPI + TRAIL group of MG-63 cell lines; A5: control group of U-2 OS cell lines; A6: PPI group of U-2 OS cell lines; A7: TRAIL group of U-2 OS cell lines; A8: PPI + TRAIL group of U-2 OS cell lines. B: morphological images under an inverted phase contrast microscope (magnification, × 40). B1: control group of MG-63 cell lines; B2: PPI group of MG-63 cell lines; B3: TRAIL group of MG-63 cell lines; B4: PPI+TRAIL group of MG-63 cell lines; B5: control group of U-2 OS cell lines; B6: PPI group of U-2 OS cell lines; B7: TRAIL group of U-2 OS cell lines; B8: PPI + TRAIL group of U-2 OS cell lines. C: expressions of apoptosis-related proteins (total PARP and cleaved-PARP) were detected by Western blotting analysis. The β-actin was used as a loading control for Western blotting analysis. 1, 9: control group; 2, 10: 200 nM PPI group; 3, 11: 400 nM PPI group; 4, 12: 600 nM PPI group; 5, 13: 50 ng/mL TRAIL group; 6, 14: 200 nM PPI + 50 ng/mL TRAIL group; 7, 15: 400 nM PPI+50 ng/mL TRAIL group; 8, 16: 600 nM PPI + 50 ng/mL TRAIL group. Ctrl: treated with PBS; PPI: treated with 400 nM PPI; TRAIL: treated with 50 ng/mL TRAIL; PPI+TRAIL: treated with 400 nM PPI plus 50 ng/mL TRAIL. Cells were treated for 24 h. FITC: fluorescein isothiocyanate; PPI: polyphyllin I; TRAIL: tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand; PARP: poly (adenosine diphosphate-ribose) polymerase.
| Group | n | MG-63 | U-2 OS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ctrl | 3 | 3.81±0.66 | 4.16±0.16 |
| PPI | 3 | 30.4±1.08 | 16.81±0.19 |
| TRAIL | 3 | 13.6±0.58 | 9.93±0.12 |
| PPI+TRAIL | 3 | 79.48±1.05abc | 42.17±0.14abc |
Table 4 Statistics of apoptosis rates (%,$\bar{x}±s$)
| Group | n | MG-63 | U-2 OS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ctrl | 3 | 3.81±0.66 | 4.16±0.16 |
| PPI | 3 | 30.4±1.08 | 16.81±0.19 |
| TRAIL | 3 | 13.6±0.58 | 9.93±0.12 |
| PPI+TRAIL | 3 | 79.48±1.05abc | 42.17±0.14abc |
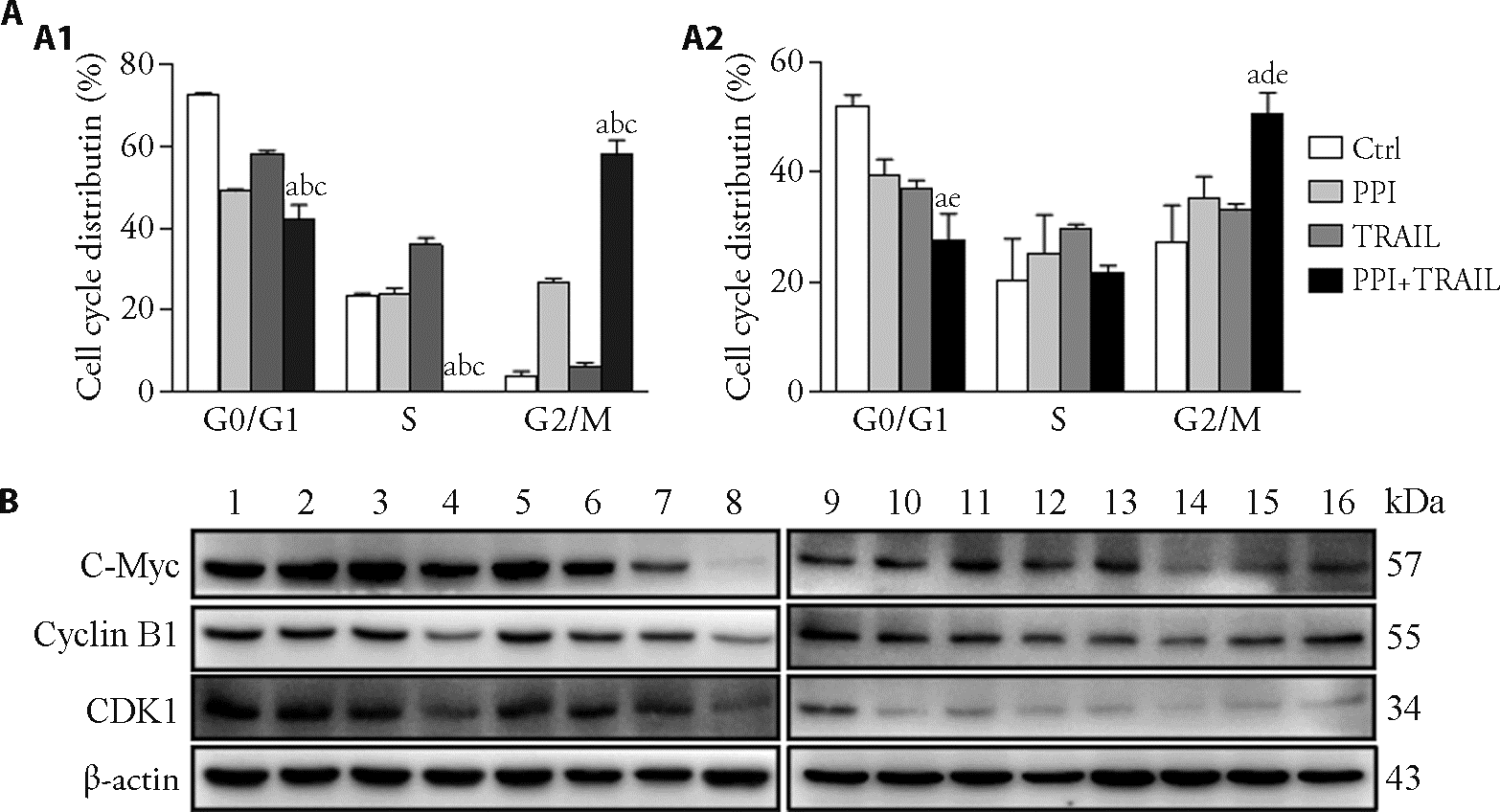
Figure 2 PPI and TRAIL synergistically arrest the cell cycle of osteosarcoma cells at G2/M MG-63 and U-2 OS cells were treated with 400 nM PPI, 50 ng/mL TRAIL or a combination (400 nM PPI plus 50 ng/mL TRAIL) for 24 h, then detected the cell cycle by flow cytometry. A: percent distribution of specific phases in the cell cycle. A1: ratio of G0/G1, S and G2/M period of MG-63 cell; A2: ratio of G0/G1, S and G2/M period of U-2 OS cell. B: expression levels of key proteins involved in cell cycle (C-Myc, Cyclin B1 and CDK1) were detected by Western blotting analysis. The β-actin was used as a loading control for Western blotting analysis. 1, 9: control group; 2, 10: 200 nM PPI group; 3, 11: 400 nM PPI group; 4, 12: 600 nM PPI group; 5, 13: 50 ng/mL TRAIL group; 6, 14: 200 nM PPI + 50 ng/mL TRAIL group; 7 and 15: 400 nM PPI + 50 ng/mL TRAIL group; 8, 16: 600 nM PPI + 50 ng/mL TRAIL group. Ctrl: treated with PBS; PPI: treated with 400 nM PPI; TRAIL: treated with 50 ng/mL TRAIL; PPI + TRAIL: treated with 400 nM PPI plus 50 ng/mL TRAIL. Cells were treated for 24 h. G0/G1: gap0/gap1, the gap time from the completion of mitosis to the start of DNA replication; S: synthesis phase, the period of DNA replication; G2/M: gap2/mitosis, the ratio of the period from the completion of DNA replication to the beginning of mitosis and mitosis; CDK1: cyclin-dependent kinases 1; PPI: polyphyllin I; TRAIL: tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand. Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation of three independent experiments. aP < 0.001 versus the control group; bP < 0.001, dP < 0.01 versus the PPI group; cP < 0.001, eP < 0.01 versus the TRAIL group.
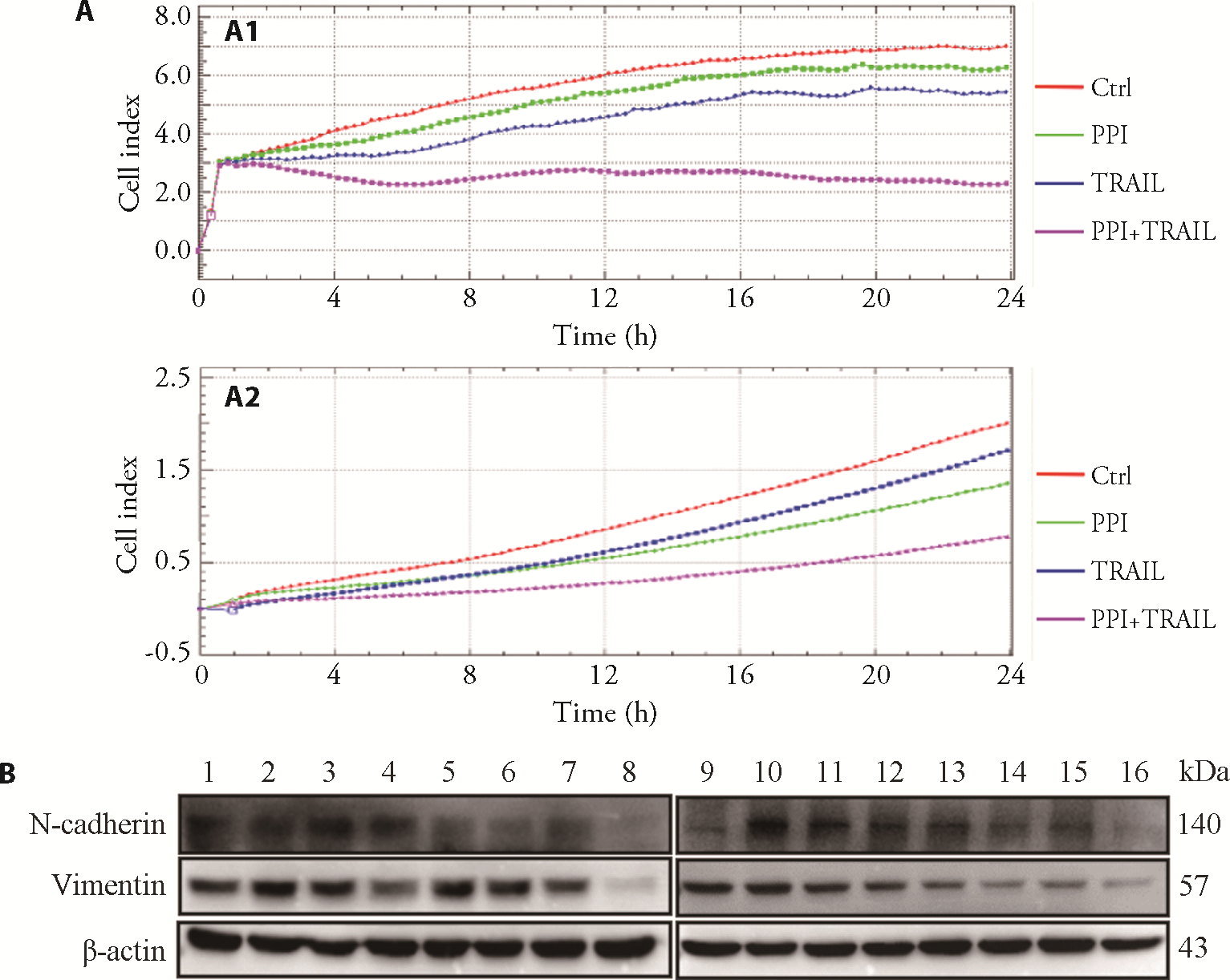
Figure 3 PPI sensitizes TRAIL-inhibited osteosarcoma cell migration and invasion A: migration of MG-63 and U-2 OS cells were assessed by the xCELLigence RTCA DP system respectively, as described in Materials and Methods. A1: MG-63; A2: U-2 OS. B: The expressions of proteins involved in EMT (N-cadherin and vimentin) were detected by Western blotting analysis. The β-actin was used as a loading control for Western blotting analysis. 1, 9: control group; 2, 10: 200 nM PPI group; 3, 11: 400 nM PPI group; 4, 12: 600 nM PPI group; 5, 13: 50 ng/mL TRAIL group; 6, 14: 200 nM PPI + 50 ng/mL TRAIL group; 7, 15: 400 nM PPI + 50 ng/mL TRAIL group; 8, 16: 600 nM PPI + 50 ng/mL TRAIL group. Ctrl: treated with PBS; PPI: treated with 400 nM PPI; TRAIL: treated with 50 ng/mL TRAIL; PPI + TRAIL: treated with 400 nM PPI plus 50 ng/mL TRAIL. Cells were treated for 24 h. RTCA: real time cell analysis; EMT: epithelial-mesenchymal transition; PPI: polyphyllin I; TRAIL: tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand.
| Group | n | MG-63 | U-2 OS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ctrl | 3 | 449±36 | 659±48 |
| PPI | 3 | 201±6 | 297±18 |
| TRAIL | 3 | 245±13 | 367±27 |
| PPI+TRAIL | 3 | 104±7abc | 178±17acd |
Table 5 Statistics of invasion cell numbers ($\bar{x}±s$)
| Group | n | MG-63 | U-2 OS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ctrl | 3 | 449±36 | 659±48 |
| PPI | 3 | 201±6 | 297±18 |
| TRAIL | 3 | 245±13 | 367±27 |
| PPI+TRAIL | 3 | 104±7abc | 178±17acd |
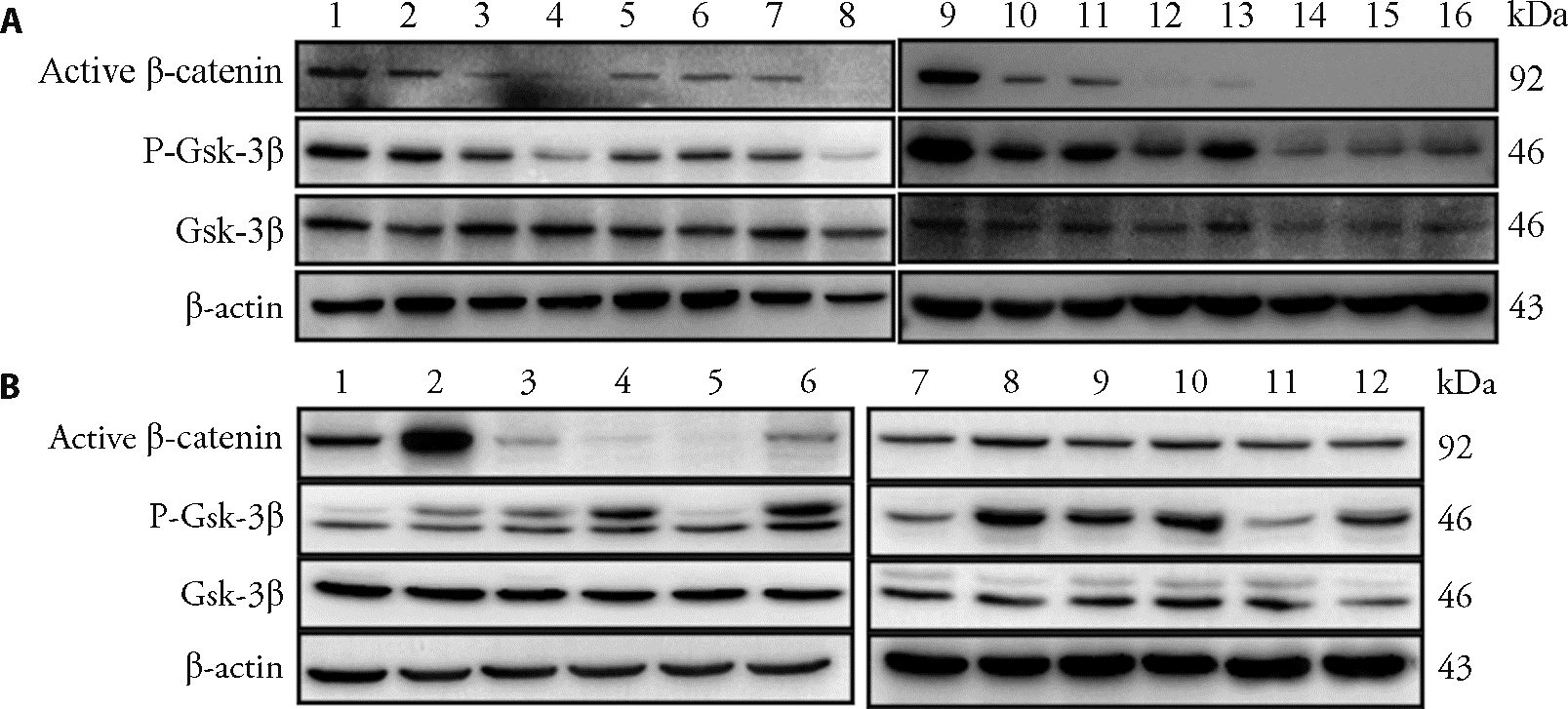
Figure 4 Combination of PPI and TRAIL inhibits osteosarcoma development by downregulating the activity of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway A: MG-63 and U-2 OS cells were exposed to different concentrations of PPI, 50 ng/mL TRAIL or their combination for 24 h. The expression levels of active-β-catenin, p-GSK-3β and total GSK-3β proteins were detected by Western blotting analysis. 1, 9: control group; 2, 10: 200 nM PPI group; 3, 11: 400 nM PPI group; 4, 12: 600 nM PPI group; 5, 13: 50 ng/mL TRAIL group; 6, 14: 200 nM PPI+50 ng/mL TRAIL group; 7, 15: 400 nM PPI + 50 ng/mL TRAIL group; 8, 16: 600 nM PPI + 50 ng/mL TRAIL group. B: MG-63 and U-2 OS cells pretreated with 4 μM BIO (the specific GSK-3β inhibitor that is a Wnt/β-catenin pathway activator) for 24 h were exposed to 400 nM PPI, 50 ng/mL TRAIL or a combination (400 nM PPI plus 50 ng/mL TRAIL) for 24 h. The expression levels of active-β-catenin, p-GSK-3β and total GSK-3β proteins were detected by Western blotting analysis. 1, 7: control group; 2, 8: 4 μM BIO group; 3, 9: 400 nM PPI group; 4, 10: 50 ng/mL TRAIL group; 5, 11: 400 nM PPI + 50 ng/mL TRAIL group; 6, 12: 4 μM BIO + 400 nM PPI + 50 ng/mL TRAIL group. The β-actin was used as a loading control for Western blotting analysis. GSK-3β: glycogen synthase kinase 3β; PPI: polyphyllin I; TRAIL: tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand; BIO: 6-Bromoindirubin-3'-oxime.
| 1. |
Saraf AJ, Fenger JM, Roberts RD. Osteosarcoma: accelerating progress makes for a hopeful future. Front Oncol 2018; 8: 4.
DOI PMID |
| 2. |
Ligon JA, Choi W, Cojocaru G, et al. Pathways of immune exclusion in metastatic osteosarcoma are associated with inferior patient outcomes. J Immunother Cancer 2021; 9: e001772.
DOI URL |
| 3. | Miwa S, Shirai T, Yamamoto N, et al. Current and emerging targets in immunotherapy for osteosarcoma. J Oncol 2019; 2019: 7035045. |
| 4. | Tsukamoto S, Errani C, Angelini A, Mavrogenis AF. Current treatment considerations for osteosarcoma metastatic at presentation. Orthopedics 2020; 43: e345-8. |
| 5. |
Anderson ME. Update on survival in osteosarcoma. Orthop Clin North Am 2016; 47: 283-92.
DOI URL |
| 6. |
Eaton BR, Schwarz R, Vatner R, et al. Osteosarcoma. Pediatr Blood Cancer 2021; 68: e28352.
DOI URL |
| 7. |
Gamie Z, Kapriniotis K, Papanikolaou D, et al. TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) for bone sarcoma treatment: Pre-clinical and clinical data. Cancer Lett 2017; 409: 66-80.
DOI PMID |
| 8. |
Zhao J, Lu Y, Shen HM. Targeting p53 as a therapeutic strategy in sensitizing TRAIL-induced apoptosis in cancer cells. Cancer Lett 2012; 314: 8-23.
DOI PMID |
| 9. |
Deng X, Yi X, Huang D, et al. ROCK2 mediates osteosarcoma progression and TRAIL resistance by modulating O-GlcNAc transferase degradation. Am J Cancer Res 2020; 10: 781-98.
PMID |
| 10. |
Singh D, Prasad CB, Biswas D, et al. TRAIL receptors are differentially regulated and clinically significant in gallbladder cancer. Pathology 2020; 52: 348-58.
DOI URL |
| 11. |
Moon MH, Jeong JK, Seo JS, et al. Bisphosphonate enhances TRAIL sensitivity to human osteosarcoma cells via death receptor 5 upregulation. Exp Mol Med 2011; 43: 138-45.
DOI URL |
| 12. |
Shankar S, Ganapathy S, Srivastava RK. Sulforaphane enhances the therapeutic potential of TRAIL in prostate cancer orthotopic model through regulation of apoptosis, metastasis, and angiogenesis. Clin Cancer Res 2008; 14: 6855-66.
DOI PMID |
| 13. |
Tian Y, Gong GY, Ma LL, Wang ZQ, Song D, Fang MY. Anti-cancer effects of polyphyllin I: an update in 5 years. Chem Biol Interact 2020; 316: 108936.
DOI URL |
| 14. |
Wang Q, Zhou X, Zhao Y, et al. Polyphyllin I ameliorates collagen-induced arthritis by suppressing the inflammation response in macrophages through the NF-κB pathway. Front Immunol 2018; 9: 2091.
DOI PMID |
| 15. |
Li K, Zhang J, Tian Y, et al. The Wnt/β-catenin/VASP positive feedback loop drives cell proliferation and migration in breast cancer. Oncogene 2020; 39: 2258-74.
DOI PMID |
| 16. |
Zhang LN, Zhao L, Yan XL, Huang YH. Loss of G3BP1 suppresses proliferation, migration, and invasion of esophageal cancer cells via Wnt/β-catenin and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways. J Cell Physiol 2019; 234: 20469-84.
DOI URL |
| 17. |
Zhang Y, Wang X. Targeting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in cancer. J Hematol Oncol 2020; 13: 165.
DOI |
| 18. |
He S, Tang S. WNT/β-catenin signaling in the development of liver cancers. Biomed Pharmacother 2020; 132: 110851.
DOI PMID |
| 19. |
Gajos-Michniewicz A, Czyz M. WNT signaling in melanoma. Int J Mol Sci 2020; 21: 4852.
DOI URL |
| 20. |
Liu Y, Liu YZ, Zhang RX, et al. Oridonin inhibits the proliferation of human osteosarcoma cells by suppressing Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Int J Oncol 2014; 45: 795-803.
DOI PMID |
| 21. |
Nusse R, Clevers H. Wnt/β-catenin signaling, disease, and emerging therapeutic modalities. Cell 2017; 169: 985-99.
DOI PMID |
| 22. |
Wiese KE, Nusse R, van Amerongen R. Wnt signalling: conquering complexity. Development 2018; 145: dev165902.
DOI URL |
| 23. |
Ono M, Yin P, Navarro A, et al. Paracrine activation of WNT/β-catenin pathway in uterine leiomyoma stem cells promotes tumor growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2013; 110: 17053-58.
DOI PMID |
| 24. |
Chang J, Wang H, Wang X, et al. Molecular mechanisms of polyphyllin I-induced apoptosis and reversal of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human osteosarcoma cells. J Ethnopharmacol 2015; 170: 117-27.
DOI PMID |
| 25. |
Chang J, Li Y, Wang X, et al. Polyphyllin I suppresses human osteosarcoma growth by inactivation of Wnt/β-catenin pathway in vitro and in vivo. Sci Rep 2017; 7: 7605.
DOI |
| 26. |
Gallego-Lleyda A, De Miguel D, Anel A, Martinez-Lostao L. Lipid nanoparticles decorated with TNF-related aptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) are more cytotoxic than soluble recombinant TRAIL in sarcoma. Int J Mol Sci 2018; 19: 1449.
DOI URL |
| 27. |
Kretz AL, von Karstedt S, Hillenbrand A, et al. Should we keep walking along the trail for pancreatic cancer treatment? Revisiting TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand for anticancer therapy. Cancers (Basel) 2018; 10: 77.
DOI URL |
| 28. |
Matsui TA, Sowa Y, Yoshida T, et al. Sulforaphane enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis through the induction of DR5 expression in human osteosarcoma cells. Carcinogenesis 2006; 27: 1768-77.
DOI URL |
| 29. |
Liu G, Yu MY, Huang X, et al. Synergistic effect of celecoxib in tumor necrosis factor‑related apoptosis‑inducing ligand treatment in osteosarcoma cells. Mol Med Rep 2014; 10: 2198-202.
DOI PMID |
| 30. |
Qian H, Chen Y, Huang T, et al. Combined application of embelin and tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand inhibits proliferation and invasion in osteosarcoma cells via caspase-induced apoptosis. Oncol Lett 2018; 15: 6931-40.
DOI PMID |
| 31. |
Li B, Chen R, Chen L, et al. Effects of DDIT4 in Methamphetamine-induced autophagy and apoptosis in dopaminergic neurons. Mol Neurobiol 2017; 54: 1642-60.
DOI PMID |
| 32. |
Meazza C, Scanagatta P. Metastatic osteosarcoma: a challenging multidisciplinary treatment. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 2016; 16: 543-56.
DOI URL |
| 33. |
Jiang X, Zhang Z, Song C, et al. Glaucocalyxin a reverses EMT and TGF-β1-induced EMT by inhibiting TGF-β1/Smad2/ 3 signaling pathway in osteosarcoma. Chem Biol Interact 2019; 307: 158-66.
DOI URL |
| 34. |
Shen S, Huang K, Wu Y, et al. A miR-135b-TAZ positive feedback loop promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and tumorigenesis in osteosarcoma. Cancer Lett 2017; 407: 32-44.
DOI PMID |
| 35. |
Ghosh N, Hossain U, Mandal A, Sil PC. The Wnt signaling pathway: a potential therapeutic target against cancer. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2019; 1443: 54-74.
DOI URL |
| 36. |
Vijayakumar S, Liu G, Rus IA, et al. High-frequency canonical Wnt activation in multiple sarcoma subtypes drives proliferation through a TCF/β-catenin target gene, CDC25A. Cancer Cell 2011; 19: 601-12.
DOI PMID |
| 37. |
Zhang W, Duan N, Zhang Q, et al. DNA methylation mediated down-regulation of miR-370 regulates cell growth through activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in human osteosarcoma cells. Int J Biol Sci 2017; 13: 561-73.
DOI PMID |
| 38. |
Zimmerman ZF, Kulikauskas RM, Bomsztyk K, Moon RT, Chien AJ. Activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling increases apoptosis in melanoma cells treated with trail. PLoS One 2013; 8: e69593.
DOI URL |
| 39. |
Danieau G, Morice S, Rédini F, Verrecchia F, Royer BB. New insights about the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in primary bone tumors and their microenvironment: a promising target to develop therapeutic strategies. Int J Mol Sci 2019; 20: 3751.
DOI URL |
| 40. |
Hsieh CH, Hsu HH, Shibu MA, et al. Down-regulation of β-catenin and the associated migration ability by Taiwanin C in arecoline and 4-NQO-induced oral cancer cells via GSK-3β activation. Mol Carcinog 2017; 56: 1055-67.
DOI URL |
| 41. |
Cai Y, Mohseny AB, Karperien M, Hogendoorn PC, Zhou G, Cleton-Jansen AM. Inactive Wnt/beta-catenin pathway in conventional high-grade osteosarcoma. J Pathol 2010; 220: 24-33.
DOI URL |
| 42. |
Clevers H. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in development and disease. Cell 2006; 127: 469-80.
DOI PMID |
| 43. | Sha L, Ma D, Chen C. Exosome-mediated Hic-5 regulates proliferation and apoptosis of osteosarcoma via Wnt/β-catenin signal pathway. Aging (Albany NY) 2020; 12: 23598-608. |
| 44. |
Pai SG, Carneiro BA, Mota JM, et al. Wnt/beta-catenin pathway: modulating anticancer immune response. J Hematol Oncol 2017; 10: 101.
DOI URL |
| 45. |
Yadav PS, Feng S, Cong Q, Kim H, Liu Y, Yang Y. Stat3 loss in mesenchymal progenitors causes Job syndrome-like skeletal defects by reducing Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2021; 118: e2020100118.
DOI URL |
| [1] | WU Jieya, HOU Li, ZHANG Xiaoyuan, Elizabeth Gullen, GAO Chong, WANG Jing. Efficacy of Yisui granule (益髓颗粒) on myelodysplastic syndromes in SKM-1 mouse xenograft model through suppressing Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 78-87. |
| [2] | YAO Nan, CHEN Guocai, LU Yanyan, XU Xuemeng, ZHAO Chuanxi, HUANG Xuejun, LIU Wengang, PENG Sha, WU Huai. Bushen Qiangjin capsule(补肾强筋胶囊) inhibits the Wnt/β-catenin pathway to ameliorate papain-induced knee osteoarthritis in rats [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(6): 935-942. |
| [3] | XU Qian, QIN Wei, WU Fangzhen, LIN Yao, HONG Liting, CHEN Dan, HU Xuefeng, CAI Jing. Effect of Roucongrong(Herba Cistanches Deserticolae) decoction on the substantia nigra through Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in rats with Parkinson's disease induced by 6-hydroxydopamine hydrochloride [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(5): 762-770. |
| [4] | DONG Lei, XU Pei. Danzhi Jiangtang capsule (丹蛭降糖胶囊) alleviate hyperglycemiaand periodontitis via Wnt/β-catenin signaling in diabetic rats [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(4): 608-616. |
| [5] | Zheng Lixiang, Zheng Qing, Yu Zhipeng, Wang Jian, Ren Xiaoying, Gong Yan, Yang Xue, Hunag Ping, Weng Meizhi, Liu Hongning, Liu Haizhou. Liuwei Dihuang pill suppresses metastasis by regulating the wnt pathway and disrupting β-catenin/T cell factor interactions in a murine model of triple-negative breast cancer [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2019, 39(06): 826-832. |
| [6] | Guan Huiting, Xie Su, Liu Shangyi, Xie Qing, Hou Shengkai, Liu Huarong, Zhang Yunjie, Hu Yaqing, Zhang Chenyu. Effects of Jiazhu decoction in combination with cyclophosphamide on breast cancer in mice [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2019, 39(05): 642-648. |
| [7] | Fu Shuping, Yang Li, Hong Hao, Zhang Ronghua. Wnt/β-catenin signaling is involved in the Icariin induced proliferation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2016, 36(03): 360-368. |
| [8] | Yini Jiang, Daobing Liu, Xiangying Kong, Ying Xu, Weiheng Chen, Na Lin. HuoguⅠformula prevents steroid-induced osteonecrosis in rats by down-regulating PPARγ expression and activating Wnt/LRP5/β-catenin signaling [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2014, 34(03): 342-350. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

