Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (2): 303-310.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2025.02.005
• Original articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of Huoxue Chubi decoction (活血除痹汤) on protein kinase B-mammalian target of rapamycin autophagy pathway in scleroderma Balb/c model mice
CHEN Xi1, QU Tiange1, JIA Hui2, DUAN Xingwu1, LI Jianhong1, ZHANG Kaihui1, ZHANG Runtian1( ), WANG Ruijie3(
), WANG Ruijie3( )
)
- 1 Department of Dermatology, Dongzhimen Hospital Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100107, China
2 Department of Surgery, Shunyi Hospital, Beijing Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Beijing 101300, China
3 Department of Dermatology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Hangzhou 310060, China
-
Received:2024-03-06Accepted:2024-08-20Online:2025-04-15Published:2025-03-10 -
Contact:Dr. ZHANG Runtian, Department of Dermatology, Dongzhimen Hospital Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100107, China, dermatology@126.com; Dr. WANG Ruijie, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Hangzhou 310060, China, wangruijie62@163.com, Telephone: +86-10-84013167 -
Supported by:Natural Science Foundation-funded Project: Exploration the Mechanism of Yiqi Huoxue Therapy in Treating Scleroderma Fibrosis based on Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase (PI3K)-Protein Kinase B (Akt)-Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) Signal Pathway about Autophagy(81804106);2023 Science and Technology Innovation Project Dongzhimen Hospital Beijing University of Chinese Medicine: Exploration the Mechanism of Radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae Components in Treating Scleroderma Fibrosis Based on PI3K-Akt-mTOR Signal Pathway about Autophagy(DZMKJCX-2023-009)
Cite this article
CHEN Xi, QU Tiange, JIA Hui, DUAN Xingwu, LI Jianhong, ZHANG Kaihui, ZHANG Runtian, WANG Ruijie. Effects of Huoxue Chubi decoction (活血除痹汤) on protein kinase B-mammalian target of rapamycin autophagy pathway in scleroderma Balb/c model mice[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(2): 303-310.
share this article
| Group | n | Skin thickness (μm) | ROS (IOD/mg) | Collagen level (IOD/μm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 7 | 333.91±29.44a | 1616.40±295.02 a | 0.26±0.05c |
| BLM | 7 | 544.36±77.19 | 9311.22±1790.95 | 0.43±0.09 |
| Colchicine | 7 | 436.81±50.84b | 3495.15±1976.69c | 0.28±0.03c |
| HXCB-H | 7 | 443.82±42.65b | 4681.03±1020.88c | 0.28±0.04 c |
| HXCB-M | 7 | 465.59±69.88 | 8346.29±4142.16 | 0.34±0.08 |
| HXCB-L | 7 | 485.71±75.95 | 8723.89±4255.77 | 0.36±0.05 |
Table 1 Comparison of skin thickness, ROS and collagen levels in each group ($\bar{x}±s$)
| Group | n | Skin thickness (μm) | ROS (IOD/mg) | Collagen level (IOD/μm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 7 | 333.91±29.44a | 1616.40±295.02 a | 0.26±0.05c |
| BLM | 7 | 544.36±77.19 | 9311.22±1790.95 | 0.43±0.09 |
| Colchicine | 7 | 436.81±50.84b | 3495.15±1976.69c | 0.28±0.03c |
| HXCB-H | 7 | 443.82±42.65b | 4681.03±1020.88c | 0.28±0.04 c |
| HXCB-M | 7 | 465.59±69.88 | 8346.29±4142.16 | 0.34±0.08 |
| HXCB-L | 7 | 485.71±75.95 | 8723.89±4255.77 | 0.36±0.05 |

Figure 1 Effect of HXCB on skin thickness in scleroderma mice A: control group (× 400); B: BLM group (× 400); C: Colchicine group (× 400); D: HXCB-H group (× 400); E: HXCB-M group (× 400); F: HXCB-L group (× 400). n = 7. The scleroderma model mice were received subcutaneous 0.1 mL injections of 400 μg/mL BLM at the center of the depilated area, and intervention began 4 weeks after model was established. Colchicine (0.13 mg·kg-1·d-1), HXCB-H (4.6 g·kg-1·d-1), HXCB-M (2.3 g·kg-1·d-1) and HXCB-L (1.15 g·kg-1·d-1) were used for gavage once per day for 33-60 d, and mice were euthanized on day 61. BLM: bleomycin; HXCB-H: high-dose Huoxue Chubi decoction; HXCB-M: middle-dose Huoxue Chubi decoction; HXCB-L: low-dose Huoxue Chubi decoction. Dyeing method of all pictures were the Hematoxylin and eosin.

Figure 2 Effect of HXCB on collagen levels in scleroderma mice A: control group (× 400); B: BLM group (× 400); C: Colchicine group (× 400); D: HXCB-H group (× 400); E: HXCB-M group (× 400); F: HXCB-L group (× 400). n = 7. The scleroderma model mice were received subcutaneous 0.1 mL injections of 400 μg/mL BLM at the center of the depilated area, and intervention began 4 weeks after model was established. Colchicine (0.13 mg·kg-1·d-1), HXCB-H (4.6 g·kg-1·d-1), HXCB-M (2.3 g·kg-1·d-1) and HXCB-L (1.15 g·kg-1·d-1) were used for gavage once per day for 33-60 d, and mice were euthanized on day 61. BLM: bleomycin; HXCB-H: high-dose Huoxue Chubi decoction; HXCB-M: middle-dose Huoxue Chubi decoction; HXCB-L: low-dose Huoxue Chubi decoction. Dyeing method of all pictures were the Masson-trichrome. Masson-trichrome staining sections showed that muscle fibers were red and collagen fibers were blue.
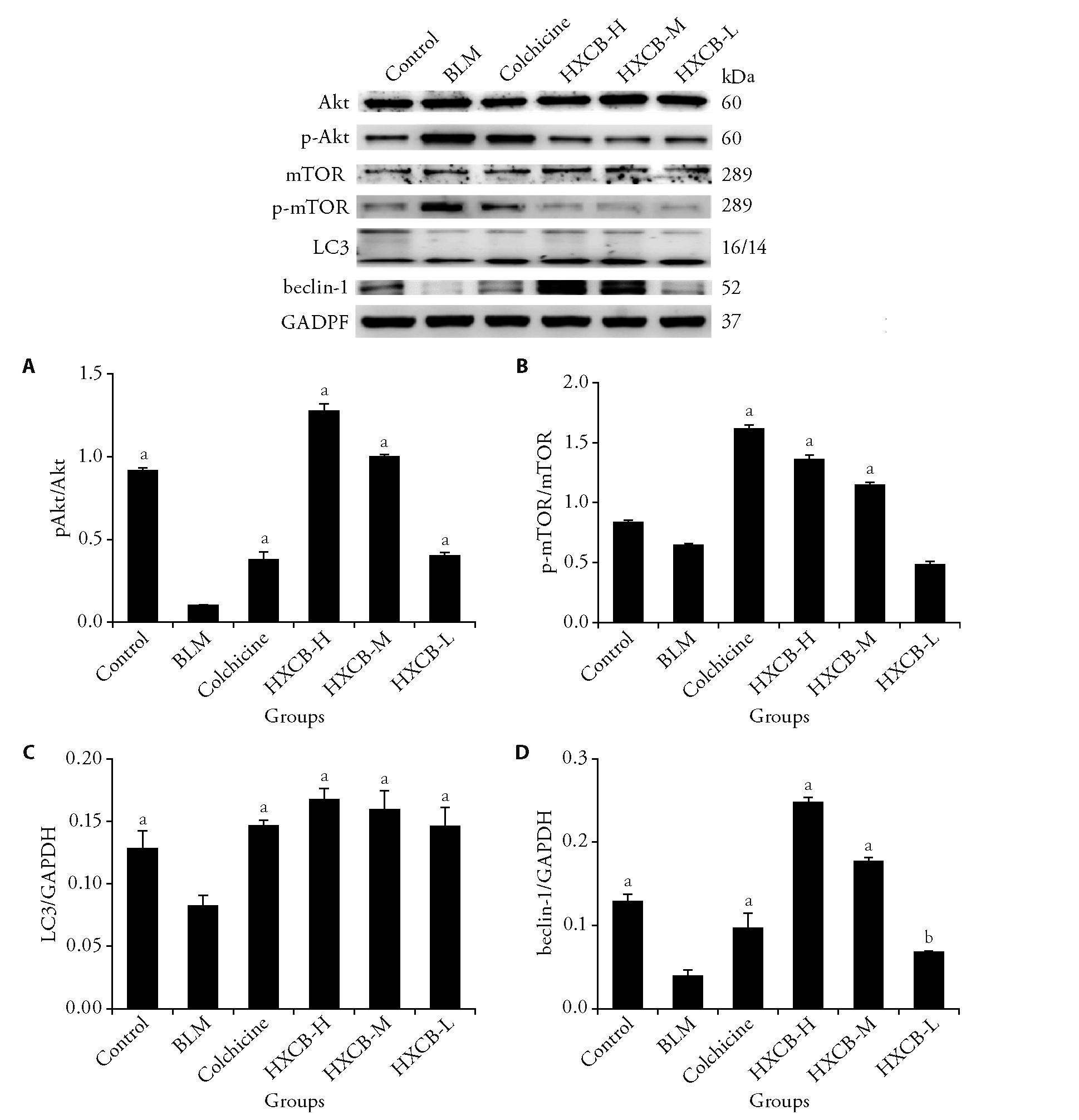
Figure 3 Protein relative expression of p-Akt/Akt, p-mTOR/mTOR and LC3, Beclin-1 in each group A: p-Akt/Akt expression level in the groups; B: p-mTOR/mTOR expression level in the groups; C: LC3 expression level in the groups; D: Beclin-1 expression level in the groups. n = 3. The scleroderma model mice were received subcutaneous 0.1 mL injections of 400 μg/mL BLM at the center of the depilated area, and intervention began 4 weeks after model was established. Colchicine (0.13 mg·kg-1·d-1), HXCB-H (4.6 g·kg-1·d-1), HXCB-M (2.3 g·kg-1·d-1) and HXCB-L (1.15 g·kg-1·d-1) were used for gavage once per day for 33-60 d, and mice were euthanized on day 61. BLM: bleomycin; HXCB-H: high-dose Huoxue Chubi decoction; HXCB-M: middle-dose Huoxue Chubi decoction; HXCB-L: low-dose Huoxue Chubi decoction. Akt: protein kinase B; mTOR: mammalian target of rapamycin; p-Akt: phosphorylated Akt; p-mTOR: phosphorylated mTOR; Beclin-1: B-celllymphoma-2-interacting myosin-like coiled-coil protein 1; LC3: microtubule-associated protein A/B-light chain 3. The single factor analysis of variance of completely randomized design was used for parameter comparison between groups, aP < 0.001, bP < 0.01 vs BLM group.
| Group | n | Akt | mTOR | LC3 | Beclin-1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 7 | 0.955±0.051a | 0.780±0.119a | 0.938±0.071a | 0.959±0.057a |
| BLM | 7 | 2.563±0.215 | 2.419±0.172 | 0.600±0.042 | 0.392±0.033 |
| Colchicine | 7 | 2.017±0.189a | 1.800±0.142a | 1.295±0.096a | 0.778±0.043a |
| HXCB-H | 7 | 0.812±0.059a | 0.449±0.030a | 1.824±0.046a | 2.563±0.208a |
| HXCB-M | 7 | 1.055±0.023a | 0.740±0.044a | 1.697±0.039a | 2.051±0.068a |
| HXCB-L | 7 | 1.184±0.065a | 0.891±0.051a | 1.693±0.064a | 0.690±0.035a |
Table 2 mRNA relative expression of Akt-mTOR signals and LC3, Beclin-1 in each group ($\bar{x}±s$)
| Group | n | Akt | mTOR | LC3 | Beclin-1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 7 | 0.955±0.051a | 0.780±0.119a | 0.938±0.071a | 0.959±0.057a |
| BLM | 7 | 2.563±0.215 | 2.419±0.172 | 0.600±0.042 | 0.392±0.033 |
| Colchicine | 7 | 2.017±0.189a | 1.800±0.142a | 1.295±0.096a | 0.778±0.043a |
| HXCB-H | 7 | 0.812±0.059a | 0.449±0.030a | 1.824±0.046a | 2.563±0.208a |
| HXCB-M | 7 | 1.055±0.023a | 0.740±0.044a | 1.697±0.039a | 2.051±0.068a |
| HXCB-L | 7 | 1.184±0.065a | 0.891±0.051a | 1.693±0.064a | 0.690±0.035a |
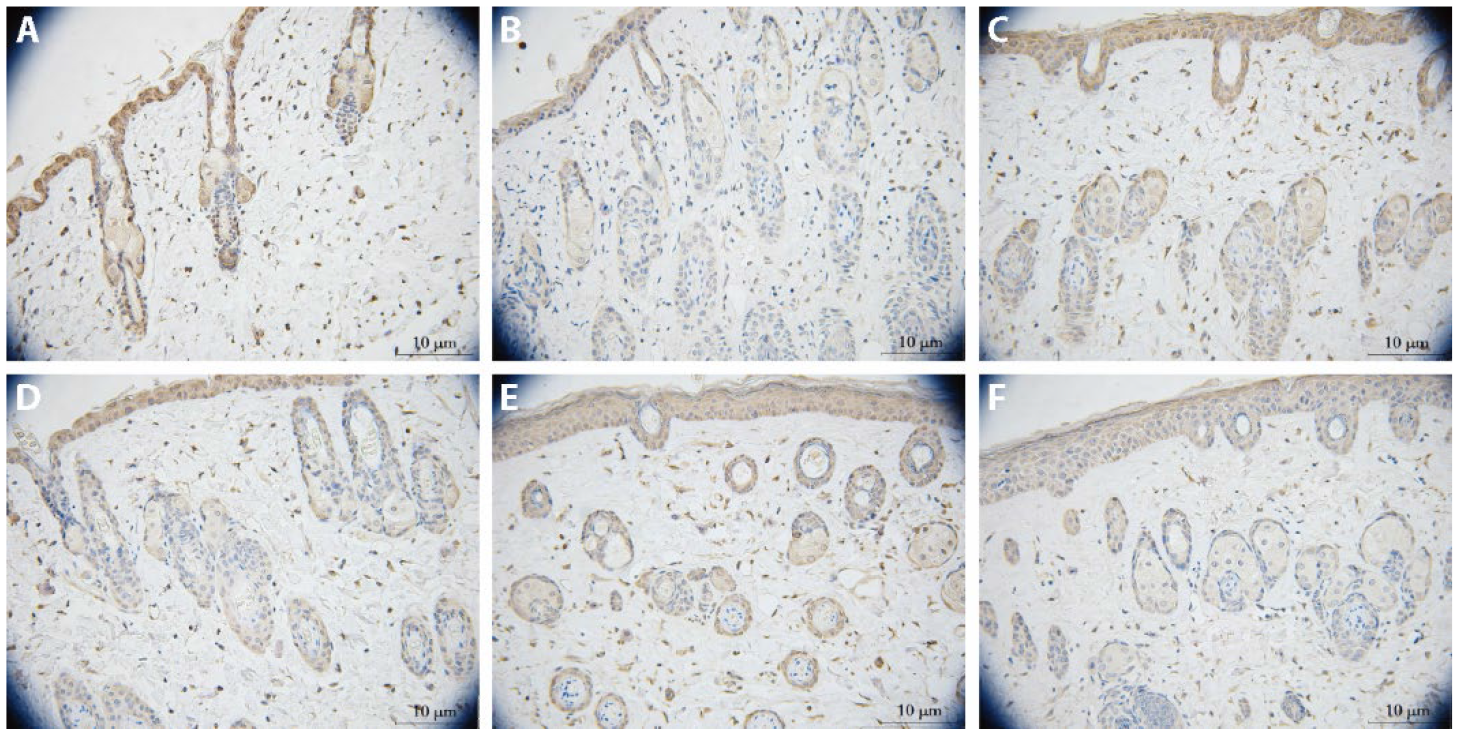
Figure 4 Effect of HXCB on LC3 in scleroderma mice A: control group (× 400); B: BLM group (× 400); C: Colchicine group (× 400); D: HXCB-H group (× 400); E: HXCB-M group (× 400); F: HXCB-L group (× 400). n = 7. The scleroderma model mice were received subcutaneous 0.1 mL injections of 400 μg/mL BLM at the center of the depilated area, and intervention began 4 weeks after model was established. Colchicine (0.13 mg·kg-1·d-1), HXCB-H (4.6 g·kg-1·d-1), HXCB-M (2.3 g·kg-1·d-1) and HXCB-L (1.15 g·kg-1·d-1) were used for gavage once per day for 33-60 d, and mice were euthanized on day 61. LC3: microtubule-associated protein A/B-light chain 3; BLM: bleomycin; HXCB-H: high-dose Huoxue Chubi decoction; HXCB-M: middle-dose Huoxue Chubi decoction; HXCB-L: low-dose Huoxue Chubi decoction. Dyeing method of all pictures were the immunohistochemical.
| 1. | Zhao B. China Clinical Dermatology. Jiangsu: Jiangsu Science and Technology Press, 2017: 878-85. |
| 2. | Chen X, Zhang RT, Duan XW. Research progress in TCM treatment of scleroderma. Zhong Guo Ma Feng Pi Fu Bing Za Zhi 2013; 29: 331-3. |
| 3. |
Domenico DP, Rosa V, Luciana G. Defective autophagy in fibroblasts may contribute to fibrogenesis in autoimmune processes. Curr Pharm Design 2011; 17: 3878-87.
DOI PMID |
| 4. | Yang JH, Gao XG, Fu ZR. Role of autophagy in the mechanism of liver immune tolerance. Jie Fang Jun Yi Xue Za Zhi 2014; 39: 503-6. |
| 5. | Zhao H, Wang Y, Qiu T, Liu W, Yao P. Autophagy, an important therapeutic target for pulmonary fibrosis diseases. Clini Chim Acta 2020; 502: 139-47. |
| 6. | Zhou X, Liu CF, Lu JH, Zhu LB, Li M. 2-Methoxyestradiol inhibits hypoxia-induced scleroderma fibroblast collagen synthesis by phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt/mTOR signaling. Rheumatology 2018; 57: 1675-84. |
| 7. | Ruth SS, Zvulun E. Regulation of autophagy by ROS: physiology and pathology. Trends Biochem Sci 2011; 36: 30-8. |
| 8. |
Lei LF, Yan C, Bo L. Beclin-1: autophagic regulator and therapeutic target in cancer. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2013; 45: 921-4.
DOI PMID |
| 9. | Jiang YQ, Kou JY, Han XB, et al. ROS-dependent activation of autophagy through the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway is induced by hydroxysafflor yellow a-sonodynamic hherapy in THP-1 macrophages. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2017; 1: 1-16. |
| 10. | Chen X, Zhang RT, Xia M, Duan XW. Introduction of Duan Xingwu's experience in treating localized scleroderma. Zhong Guo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Pi Fu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi 2015; 14: 164-6. |
| 11. | Wang WY. Study on medication rules of Professor Duan Xingwu in the treatment of scleroderma based on data mining. Beijing: Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, 2021: 1-72. |
| 12. | Qu X. Dermatology and venereology of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Beijing: China Traditional Chinese Medicine Press, 2009: 212-6. |
| 13. | Duan XW. Interpretation of classic Chinese medical cases-dermatology. Beijing: China Medical Science and Technology Press, 2016: 198-212. |
| 14. | Bogna GG, Mariusz P. Oxidative damage and antioxidative therapyin systemic sclerosis. Mediat Inflamm 2014; 9: 1-11. |
| 15. | Jiang XW, Wang YC, Chang C. Regulation of autophagy by Traditional Chinese Medicine. Zhong Yi Za Zhi 2017; 58: 1566-8. |
| 16. | Huang GH, Ji XY, Wu DL, et al. Relationship between autophagy and Qi deficiency and phlegm stasis in Traditional Chinese Medicine. Zhong Yi Za Zhi 2011; 52: 1717-19. |
| 17. |
Laplante M, Sabatini DM. mTOR signaling in growth control and disease. Cell 2012; 149: 274-93.
DOI PMID |
| 18. |
Wesselborg S, Stork B. Autophagy signal transduction by ATG proteins: from hierarchies to networks. Cell Mol Life Sci 2015; 72: 4721-57.
DOI PMID |
| 19. | Deretic V. Autophagy in leukocytes and other cells: mechanisms, subsystem organization, selectivity and links to innate immunity. J Leukoc Biol 2016; 100: 969-78. |
| 20. |
Yu L, Chen Y, Tooze SA. Autophagy pathway: cellular and molecular mechanisms. Autophagy 2018; 14: 207-15.
DOI PMID |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

