Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (5): 944-953.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20240515.003
Previous Articles Next Articles
Neuroprotective effect of Naochuxue prescription (脑出血方) on intracerebral hemorrhage: inhibition of autophagy via downregulating high mobility group box-1
JIN Hong1, WANG Xinna2, WANG Ruonan3, LI Jinjian2, YU Junchao2, ZHAO Dexi2( ), ZHAI Lu4(
), ZHAI Lu4( )
)
- 1 College of Chinese medicine, Changchun University of Chinese Medicine, Changchun 13000, China
2 Department of Encephalopathy, the Affiliated Hospital of Changchun University of Chinese Medicine, Changchun 130000, China
3 College of nursing, Changchun University of Chinese Medicine, Changchun 13000, China
4 Research Center of Traditional Chinese Medicine, the First Affiliated Hospital of Changchun University of Chinese Medicine, Changchun 13000, China
-
Received:2023-03-22Accepted:2023-09-05Online:2024-10-15Published:2024-05-15 -
Contact:ZHAO Dexi, Department of Encephalopathy, the Affiliated Hospital of Changchun University of Chinese Medicine, Changchun 130000, China. dexizhao1006@163.com;ZHAI Lu, Research Center of Traditional Chinese Medicine, the First Affiliated Hospital of Changchun University of Chinese Medicine, Changchun 13000, China. 174759250@qq.com Telephone: +86-18844305875 -
Supported by:Study on the Mechanism of Cerebral Hematoma Resorption by Intervening Cerebral Hemorrhage Prescription based on the Method of Breaking Blood and Removing Blood Stasis(81774224);Anti-inflammatory Mechanism of Naochuxue Prescription based on Toll-like Receptor 4/AKT/Forkhead Box O3 Pathway Regulation of Microglia Autophagy(2021JC070)
Cite this article
JIN Hong, WANG Xinna, WANG Ruonan, LI Jinjian, YU Junchao, ZHAO Dexi, ZHAI Lu. Neuroprotective effect of Naochuxue prescription (脑出血方) on intracerebral hemorrhage: inhibition of autophagy via downregulating high mobility group box-1[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(5): 944-953.
share this article

Figure 1 HPLC chromatogram of NCXP A: HPLC mixed standard chromatograms of Typhaneoside, Isorhamnetin-3-O-neohespeidoside, Aloe-Emodin, Rhein, Emodin, and Chrysophanol with DAD detection at 254 nm are shown. B: HPLC chromatogram of NCXP with DAD detection at 254 nm is shown. C: HPLC fingerprint chromatogram of ten batches of NCXP (S1-10) and similarity was analyzed using the Chinese Medicine Chromatographic Fingerprint Similarity Evaluation System (2012 Edition). HPLC: high-performance liquid chromatography; NCXP: Naochuxue prescription; DAD: diode array detector.
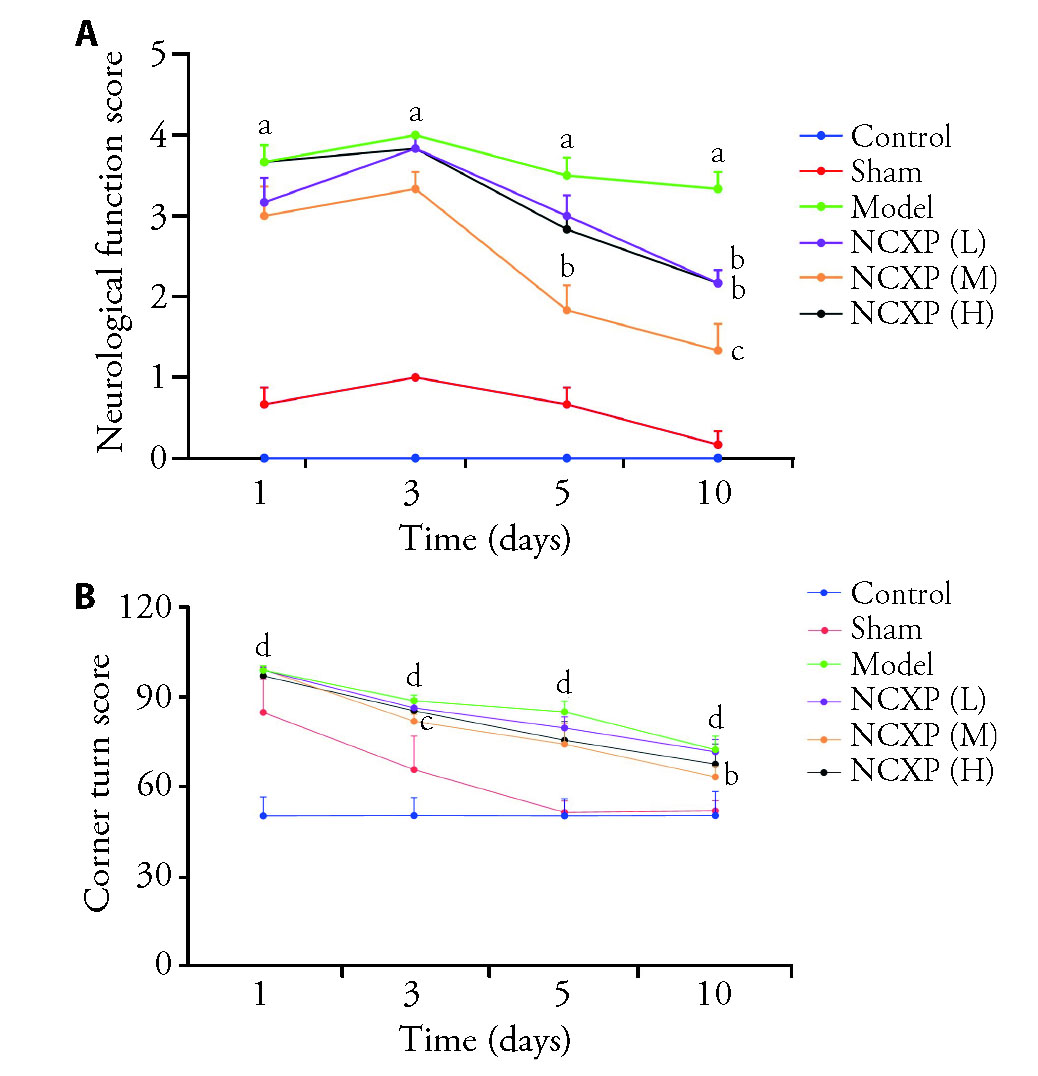
Figure 2 Effects of NCXP on neurobehavioral outcomes after ICH A: neurological deficit scores (Zea Longa 5) on the 1st, 3rd, 5th, and 10th days after ICH; B: corner turn test on the 1st, 3rd, 5th, and 10th days after ICH. Control: control group; Sham: sham-operated group; Model: ICH model group; NCXP (L): low-dose Naochuxue prescription (0.13 g/kg); NCXP (M): medium-dose Naochuxue prescription (0.26 g/kg); NCXP (H): high-dose Naochuxue prescription (0.52 g/kg). The drug was administered by once daily for 10 d. NCXP: Naochuxue prescription; ICH: intracerebral hemorrhage. One-way analysis of variance, and Tukey's multiple comparisons test. Results are presented as mean ± standard deviation. aP<0.01, vs sham group; bP<0.05,cP<0.01, vs model group; dP<0.01, vs control group, n = 6 in each group.
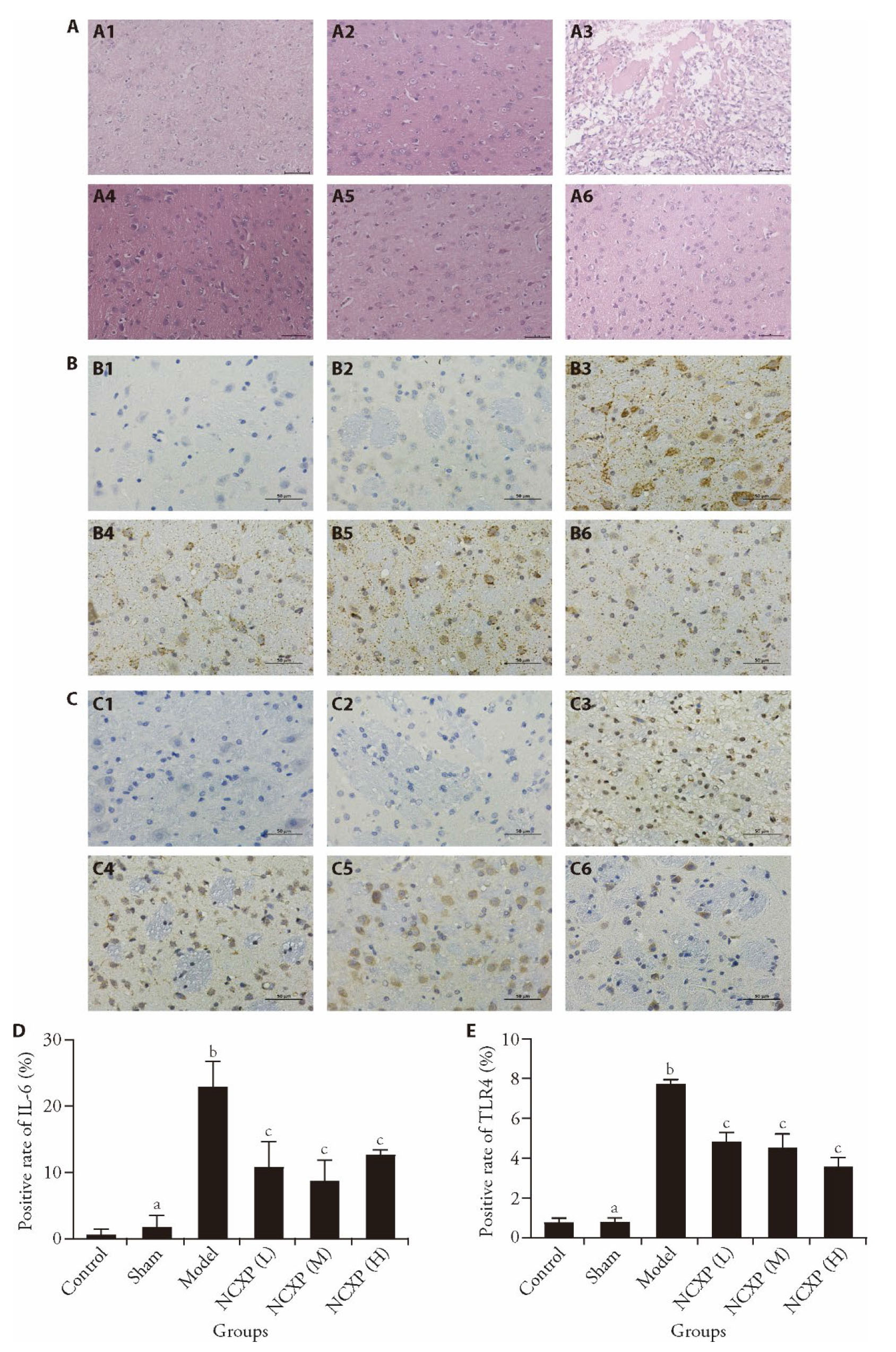
Figure 3 Pathological effects and the expression of IL-6 and TLR4 of NCXP on the brain tissue after ICH A: pathological effects of each group tissue (× 200). The dyeing method of the pictures is the hematoxylin-eosin staining method. A1: control group; A2: sham group; A3: model group; A4: NCXP (L) group; A5: NCXP (M) group; A6: NCXP (H) group; B: effect of different doses of NCXP on the expression of IL-6 (× 400). B1: control group; B2: sham group; B3: model group; B4: NCXP (L) group; B5: NCXP (M) group; B6: NCXP (H) group; C: effect of different doses of NCXP on the expression of TLR4 (× 400). C1: control group; C2: sham group; C3: model group; C4: NCXP (L) group; C5: NCXP (M) group; C6: NCXP (H) group. The Dyeing method of the Figures B-C is the immunohistochemistry method; D: statistical graph of IL-6 expression; E: statistical graph of TLR4 expression. Control: control group; Sham: sham-operated group; Model: ICH model group; NCXP (L): low-dose Naochuxue prescription (0.13 g/kg); NCXP (M): medium-dose Naochuxue prescription (0.26 g/kg); NCXP (H): high-dose Naochuxue prescription (0.52 g/kg). The drug was administered by once daily for 10 d. NCXP: Naochuxue prescription; ICH: intracerebral hemorrhage; IL-6: interleukin 6; TLR4: toll-like receptor 4. One-way analysis of variance, and Tukey's multiple comparisons test. Results are presented as mean ± standard deviation. aP>0.05, bP<0.01, vs Control; cP<0.01 vs Model, n = 6 in each group.

Figure 4 mRNA and protein expression of HMGB1, Beclin1, LC3, and p62 of NCXP on the brain tissue after ICH A: mRNA expression of HMGB1, Beclin1, LC3B, and p62; A1: mRNA expression of HMGB1, A2: mRNA expression of Beclin1, A3: mRNA expression of LC3B, A4: mRNA expression of p62. B: protein images and expression of HMGB1, Beclin1, LC3Ⅱ/Ⅰ, and p62. B1: Western blotting representative images of HMGB1, Beclin1, LC3Ⅱ/Ⅰ, and p62, B2: protein expression of HMGB1, B3: protein expression of Beclin1, B4: protein expression of LC3Ⅱ/Ⅰ, B5: protein expression of p62. Control: control group, Sham: sham-operated group, Model: ICH model group, NCXP (L): low-dose Naochuxue prescription (0.13 g/kg), NCXP (M): medium-dose Naochuxue prescription (0.26 g/kg), NCXP (H): high-dose Naochuxue prescription (0.52 g/kg). The drug was administered by once daily for 10 d. NCXP: Naochuxue prescription; ICH: intracerebral hemorrhage; HMGB1: high mobility group box-1; LC3: microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3 beta; p62: sequestosome 1. One-way analysis of variance, and Tukey's multiple comparisons test. Results are presented as mean ± standard deviation. aP>0.05, bP<0.01, fP<0.05, vs Control; cP<0.05, dP<0.01, eP>0.05, vs Model, n = 6 in each group.
| 1. | Krishnamurthi RV, Feigin VL, Forouzanfar MH, et al. Global and regional burden of first-ever ischaemic and haemorrhagic stroke during 1990-2010: findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet Glob Health 2013; 1: e259-81. |
| 2. |
Li X, Huang X, Tang Y, et al. Assessing the pharmacological and therapeutic efficacy of Traditional Chinese Medicine Liangxue Tongyu prescription for intracerebral hemorrhagic stroke in neurological disease models. Front Pharmacol 2018; 9: 1169.
DOI PMID |
| 3. |
Rodriguez-Luna D, Stewart T, Dowlatshahi D, et al. Perihematomal edema is greater in the presence of a spot sign but does not predict intracerebral hematoma expansion. Stroke 2016; 47: 350-55.
DOI PMID |
| 4. |
Dang G, Yang Y, Wu G, Hua Y, Keep RF, Xi G. Early erythrolysis in the hematoma after experimental intracerebral hemorrhage. Transl Stroke Res 2017; 8: 174-82.
DOI PMID |
| 5. | Babi MA, James ML. Peri-hemorrhagic edema and secondary hematoma expansion after intracerebral hemorrhage: from benchwork to practical aspects. Front Neurol 2017; 8: 4. |
| 6. |
Mendelow A, Gregson B, Fernandes H, et al. Early surgery versus initial conservative treatment in patients with spontaneous supratentorial intracerebral haematomas in the International Surgical Trial in Intracerebral Haemorrhage (STICH): a randomised trial. Lancet 2005; 365: 387-97.
DOI PMID |
| 7. |
Mendelow AD, Gregson BA, Rowan EN, Murray GD, Gholkar A, Mitchell PM. Early surgery versus initial conservative treatment in patients with spontaneous supratentorial lobar intracerebral haematomas (STICH Ⅱ): a randomised trial. Lancet 2013; 382: 397-408.
DOI PMID |
| 8. | Zhao D, Yu L. Clinical study on the treatment of hemorrhagic stroke based on the method of “breaking blood and resolving blood stasis". Changchun Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue Xue Bao 2012; 28: 974-75. |
| 9. |
Tschoe C, Bushnell CD, Duncan PW, Alexander-Miller MA, Wolfe SQ. Neuroinflammation after intracerebral hemorrhage and potential therapeutic targets. J Stroke 2020; 22: 29-46.
DOI PMID |
| 10. |
Andersson U, Tracey KJ. HMGB1 is a therapeutic target for sterile inflammation and infection. Annu Rev Immunol 2011; 29: 139-62.
DOI PMID |
| 11. |
Shen X, Ma L, Dong W, et al. Autophagy regulates intracerebral hemorrhage induced neural damage via apoptosis and NF-κB pathway. Neurochem Int 2016; 96: 100-12.
DOI PMID |
| 12. | Li H, Wu J, Shen H, et al. Autophagy in hemorrhagic stroke: mechanisms and clinical implications. Prog Neurobiol 2018; 163-4: 79-97. |
| 13. |
Kang R, Zeh HJ, Lotze MT, Tang D. The Beclin 1 network regulates autophagy and apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 2011; 18: 571-80.
DOI PMID |
| 14. |
Tang D, Kang R, Livesey KM, et al. Endogenous HMGB1 regulates autophagy. J Cell Biol 2010; 190: 881-92.
DOI PMID |
| 15. |
Rosenberg GA, Mun-Bryce S, Wesley M, Kornfeld M. Collagenase-induced intracerebral hemorrhage in rats. Stroke 1990; 21: 801-7.
DOI PMID |
| 16. |
Fang H, Chen J, Lin S, et al. CD36-mediated hematoma absorption following intracerebral hemorrhage: negative regulation by TLR4 signaling. J Immunol 2014; 192: 5984-92.
DOI PMID |
| 17. |
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S, Cummins R. Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke 1989; 20: 84-91.
DOI PMID |
| 18. |
Hua Y, Schallert T, Keep RF, Wu J, Hoff JT, Xi G. Behavioral tests after intracerebral hemorrhage in the rat. Stroke 2002; 33: 2478-84.
DOI PMID |
| 19. | Lin W, Hou J, Han T, Zheng L, Liang H, Zhou X. Efficacy and safety of Traditional Chinese Medicine for intracranial hemorrhage by promoting blood circulation and removing blood stasis: a systematic review and Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front Pharmacol 2022; 13: 942657. |
| 20. | Li HQ, Wei JJ, Xia W, et al. Promoting blood circulation for removing blood stasis therapy for acute intracerebral hemorrhage: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2015; 36: 659-75. |
| 21. | Zeng L, Tang G, Wang J, et al. Safety and efficacy of herbal medicine for acute intracerebral hemorrhage (CRRICH): a multicentre randomised controlled trial. BMJ Open 2019; 9: e024932. |
| 22. | Liu H, Ren J, Wang J, et al. Pharmacoeconomic evaluation of herbal decoctions for activating blood circulation to remove blood stasis and filling essence and nourishing marrow to treat cerebral hemorrhage at the acute stage. Beijing Zhong Yi Yao 2015; 34: 513-16. |
| 23. | Ma Y, Zhang D, Lyu Z, et al. Optimal intervention time and risk of the activating blood and removing stasis method in acute cerebral hemorrhage patients: a randomized placebo-controlled trial. Medicine 2021; 100: e24214. |
| 24. |
Ren J, Zhou X, Wang J, Zhao J, Zhang P. Poxue Huayu and Tianjing Busui decoction for cerebral hemorrhage (upregulation of neurotrophic factor expression): upregulation of neurotrophic factor expression. Neural Regen Res 2013; 8: 2039-49.
DOI PMID |
| 25. | Dong H, Ren JX, Wang JJ, et al. Chinese medicinal leech: ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry, and pharmacological activities. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2016; 2016: 1-11. |
| 26. | Komatsu K, Nagayama Y, Tanaka K, Ling Y, Basnet P, Meselhy MR. Development of a high performance liquid chromatographic method for systematic quantitative analysis of chemical constituents in rhubarb. Chem Pharm Bull 2006; 54: 941-7. |
| 27. |
Hu B, Zhang H, Meng X, Wang F, Wang P. Aloe-emodin from rhubarb (Rheum rhabarbarum) inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses in RAW264.7 macrophages. J Ethnopharmacol 2014; 153: 846-53.
DOI PMID |
| 28. | Zeng P, Wang XM, Su HF, et al. Protective effects of Da-cheng-qi decoction in rats with intracerebral hemorrhage. Phytomedicine 2021; 90: 153630. |
| 29. | Jadaun KS, Mehan S, Sharma A, Siddiqui EM, Kumar S, Alsuhaymi N. Neuroprotective effect of Chrysophanol as a PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling inhibitor in an experimental model of autologous blood-induced intracerebral hemorrhage. Curr Med Sci 2022; 42: 249-66. |
| 30. | Feng L, Li M, Ren J, et al. Proteomic analysis reveals that Di Dang decoction protects against acute intracerebral hemorrhage stroke in rats by regulating S100a8, S100a9 Col1a1, and Col1a2. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 2021; 17: 3301-14. |
| 31. | Luo L, Wu S, Chen R, Rao H, Peng W, Su W. The study of neuroprotective effects and underlying mechanism of Naoshuantong capsule on ischemia stroke mice. Chin Med 2020; 15: 119. |
| 32. | Yang ZQ, Zhao DX. Discussion on the mechanism of cerebral hemorrhage recipe on cerebral hemorrhage treatment based on network pharmacology. Jilin Zhong Yi Yao 2021; 41: 363-7. |
| 33. | Yang Z, Liu B, Zhong L, et al. Toll-like receptor-4-mediated autophagy contributes to microglial activation and inflammatory injury in mouse models of intracerebral haemorrhage: TLR4-mediated microglial autophagy. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 2015; 41: e95-106. |
| 34. | Tian X, Sun L, Feng D, et al. HMGB1 promotes neurovascular remodeling via rage in the late phase of subarachnoid hemorrhage. Brain Research 2017; 1670: 135-45. |
| 35. |
Bahadar GA, Shah ZA. Intracerebral hemorrhage and diabetes mellitus: blood-brain barrier disruption, pathophysiology and cognitive impairments. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 2021; 20: 312-26.
DOI PMID |
| 36. | Lei C, Geng J, Zhong L. The association between plasma HMGB1 and sRAGE and clinical outcome in intracerebral hemorrhage. J Neuroimmunol 2020; 345: 577266. |
| 37. | Liu RY, Wang JJ, Qiu X, Wu JM. Acute hyperglycemia together with hematoma of high-glucose blood exacerbates neurological injury in a rat model of intracerebral hemorrhage. Neurosci Bull 2014; 30: 90-8. |
| 38. | He Y, Wan S, Hua Y, Keep RF, Xi G. Autophagy after experimental intracerebral hemorrhage. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2008; 28: 897-905. |
| 39. | Xiao H, Chen H, Jiang R, et al. NLRP6 contributes to inflammation and brain injury following intracerebral haemorrhage by activating autophagy. J Mol Med 2020; 98: 1319-31. |
| 40. | Yoshii SR, Mizushima N. Monitoring and measuring autophagy. Int J Mol Sci 2017; 18: 1865. |
| 41. |
Klionsky DJ, Abdel-Aziz AK, Abdelfatah S, et al. Guidelines for the use and interpretation of assays for monitoring autophagy (4th edition). Autophagy 2021; 17: 1-382.
DOI PMID |
| 42. |
Shi H, Wang J, Wang J, Huang Z, Yang Z. IL-17A induces autophagy and promotes microglial neuroinflammation through ATG5 and ATG7 in intracerebral hemorrhage. J Neuroimmunol 2018; 323: 143-51.
DOI PMID |
| 43. | Levine B, Mizushima N, Virgin HW. Autophagy in immunity and inflammation. Nature 2011; 469: 323-35. |
| 44. | Lei C, Li Y, Zhu X, Li H, Chang X. HMGB1/TLR4 induces autophagy and promotes neuroinflammation after intracerebral hemorrhage. Brain Res 2022; 1792: 148003. |
| 45. |
Durocher M, Knepp B, Yee A, et al. Molecular correlates of hemorrhage and edema volumes following human intracerebral hemorrhage implicate inflammation, autophagy, mRNA splicing, and T cell receptor signaling. Transl Stroke Res 2021; 12: 754-77.
DOI PMID |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 53
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 37
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

