Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (5): 1059-1066.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2025.05.012
• Original Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Jingui Shenqi pill (金匮肾气丸 ) treats cardiorenal syndrome by inhibiting mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway and reducing inflammatory response
HUANG Shuyan, DING Xinyue, ZHANG Hui, LIU Zongjun, LUAN Yuling( ), XING Lina(
), XING Lina( )
)
- Institute of Cardiovascular Translational Medicine, Putuo Hospital, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200300, China
-
Received:2024-09-02Accepted:2024-11-29Online:2025-10-15Published:2025-09-15 -
Contact:LUAN Yuling, Putuo Hospital, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Shanghai 200300, China. luanyuling0311@163.com;
XING Lina, Putuo Hospital, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Shanghai 200300, China. ptgcp4404@126.com,Telephone: +86-19821250291; +86-13918035850 -
Supported by:Shanghai Putuo District Health System Science and Technology Innovation Project: Study on the Effect and Mechanism of Jinkui Shenqi Pills on Renal Water Metabolism via provirus integration site for moloney murine leukemia virus 3/aquaporin 2 Regulation(PTKWS202104);Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine "Xinglin Scholar" Discipline Talent Research Enhancement Plan: Based on provirus integration site for moloney murine leukemia virus 3 to Explore the Molecular Mechanism of Jingui Shenqi pill in Regulating Water Metabolism in Renal Tubular Cells(YYZX2022165);Clinical Advantage Discipline of Health System of Putuo District in Shanghai(2019ysxk01)
Cite this article
HUANG Shuyan, DING Xinyue, ZHANG Hui, LIU Zongjun, LUAN Yuling, XING Lina. Jingui Shenqi pill (金匮肾气丸 ) treats cardiorenal syndrome by inhibiting mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway and reducing inflammatory response[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(5): 1059-1066.
share this article
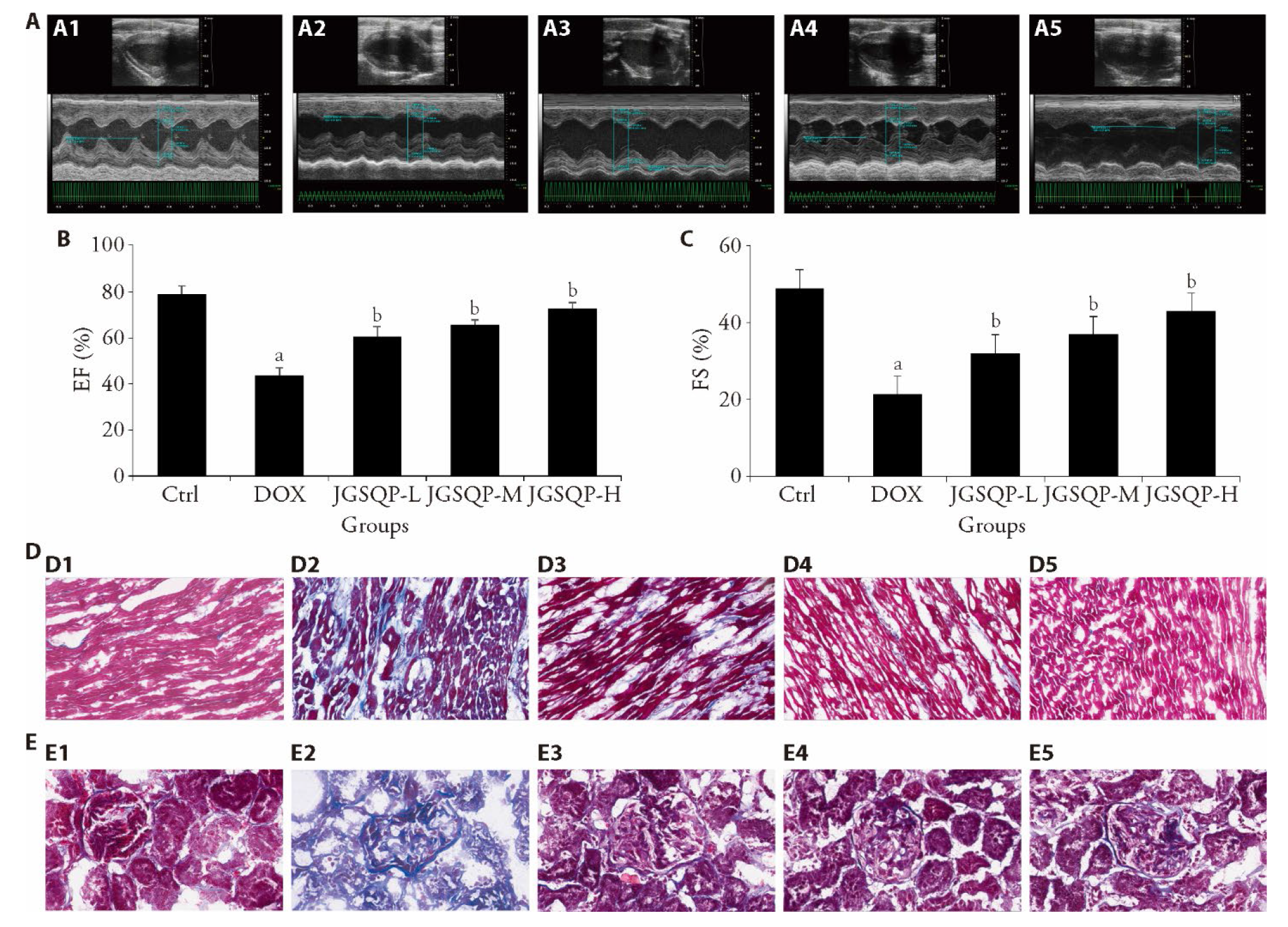
Figure 1 Effect of JGSQP on rats injury and fibrosis A: cardiac ultrasound results of rats treated with JGSQP; B: rats EF statistical column; C: rats FS statistical column; D: results of heart masson staining after intervention with JGSQP (× 20); E: results of kidney masson staining after intervention with JGSQP (× 40). A1, D1, E1: control group; A2, D2, E2: DOX group; A3, D3, E3: JGSQP-L group; A4, D4, E4: JGSQP-M group; A5, D5, E5: JGSQP-H group. DOX: doxorubicin group (3 mg/kg doxorubicin was injected intraperitoneally once/week for 6 weeks); JGSQP-L: JGSQP low-dose group (0.5 g/kg JGSQP were administered by gavage for 8 weeks); JGSQP-M: JGSQP medium-dose group (1.0 g/kg JGSQP were administered by gavage for 8 weeks); JGSQP-H: JGSQP high-dose group (2.0 g/kg JGSQP were administered by gavage for 8 weeks). JGSQP: Jingui Shenqi pill; EF: ejection fraction; DOX: doxorubicin. Differences were evaluated by one-way analysis of variance. Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation (n = 8). aP < 0.05, compared with the control group, bP < 0.05, compared with the DOX group.
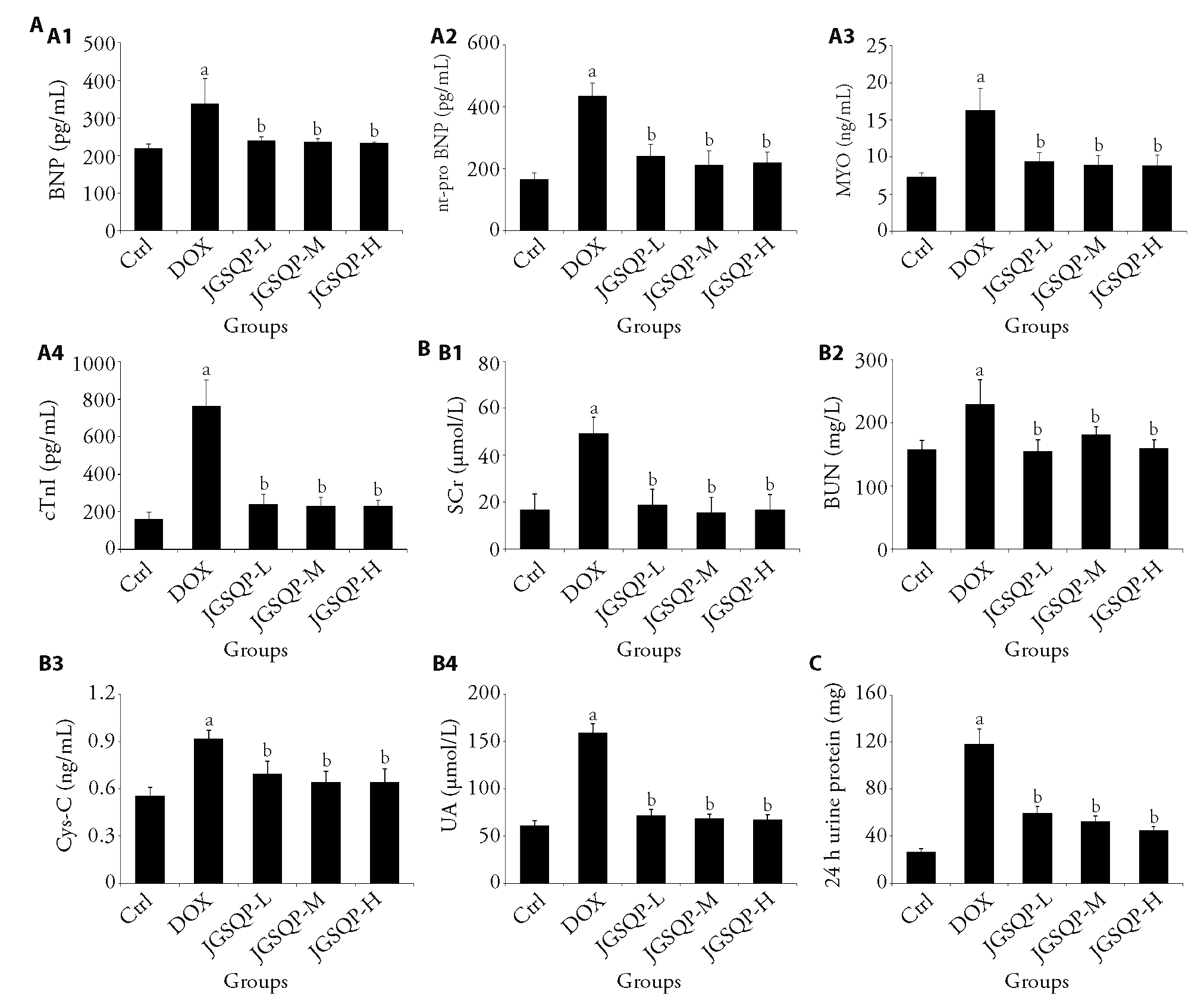
Figure 2 Effect of JGSQP on improving cardiorena function in rats A: ELISA of BNP, nt-pro BNP, MYO, cTNI expression in rats serum; A1: BNP; A2: nt-pro BNP; A3: MYO; A4: cTNI; B: rats serum SCr, BUN, Cys-C, UA expression; B1: SCr; B2: BUN; B3: Cys-C; B4: UA; C: rats 24 h urine protein. DOX: doxorubicin group (3 mg/kg doxorubicin was injected intraperitoneally once/week for 6 weeks); JGSQP-L: JGSQP low-dose group (0.5 g/kg JGSQP were administered by gavage for 8 weeks); JGSQP-M: JGSQP medium-dose group (1.0 g/kg JGSQP were administered by gavage for 8 weeks); JGSQP-H: JGSQP high-dose group (2.0 g/kg JGSQP were administered by gavage for 8 weeks). JGSQP: Jingui Shenqi pill; ELISA: enzyme linked immunosorbent assay; BNP: brain natriuretic peptide; nt-pro BNP: N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide; MYO: myoglobin; Ctn-I:cardiac troponin Ⅰ; Scr: serum creatinine; BUN: blood urea nitrogen; Cys-C: cystatin C; UA: uric acid; DOX: doxorubicin. Differences were evaluated by one-way analysis of variance. Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation (n = 8). aP < 0.05, compared with the control group, bP < 0.05, compared with the DOX group.
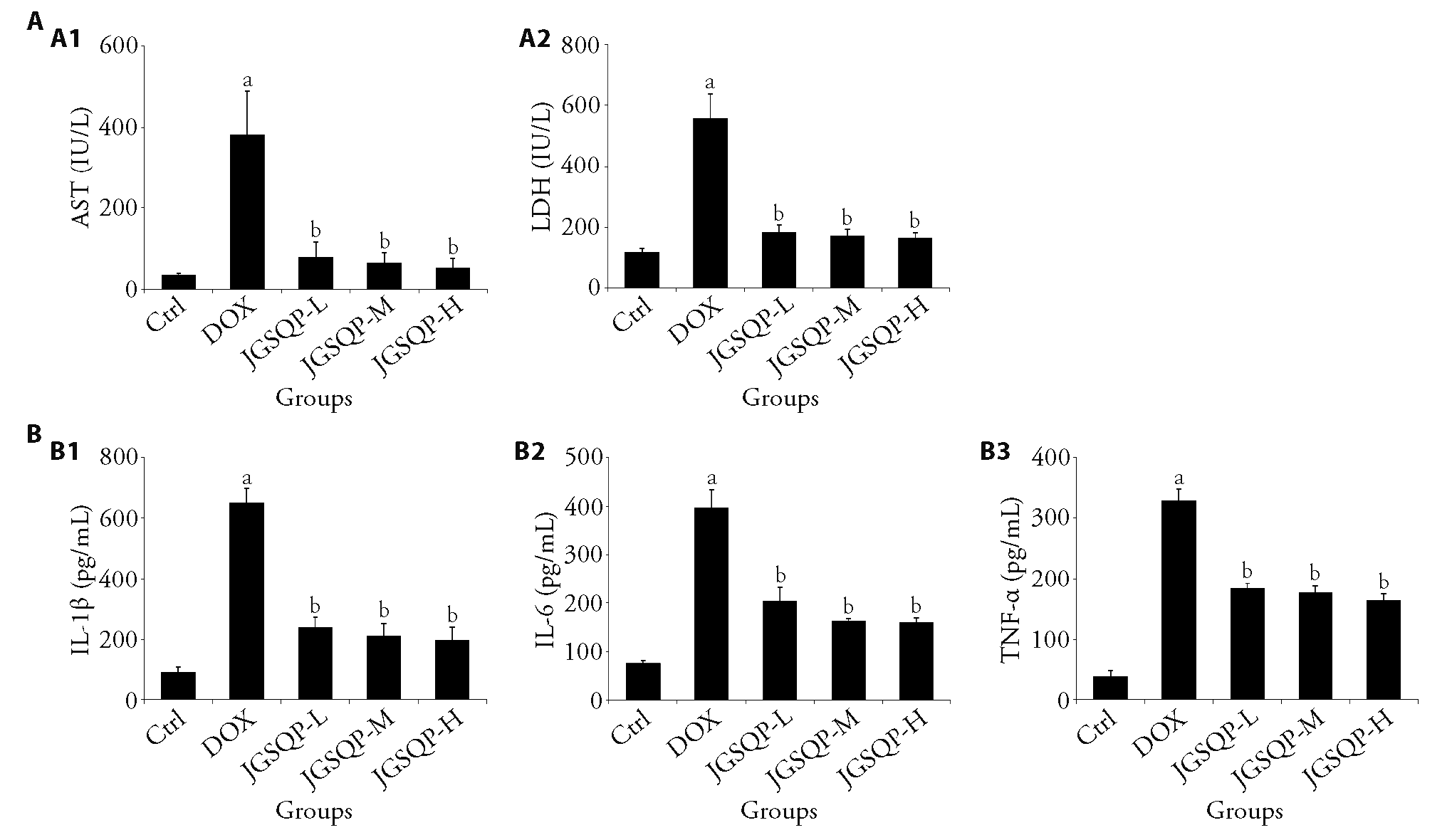
Figure 3 JGSQP for the treatment of inflammation in rats A: expression of AST and LDH in serum of rats treated with JGSQP; B: ELISA of IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α expression in rats serum. A1: AST; A2: LDH; B1: IL-1β; B2: IL-6; B3: TNF-α. DOX: doxorubicin group (3 mg/kg doxorubicin was injected intraperitoneally once/week for 6 weeks); JGSQP-L: JGSQP low-dose group (0.5 g/kg JGSQP were administered by gavage for 8 weeks); JGSQP-M: JGSQP medium-dose group (1.0 g/kg JGSQP were administered by gavage for 8 weeks); JGSQP-H: JGSQP high-dose group (2.0 g/kg JGSQP were administered by gavage for 8 weeks). JGSQP: Jingui Shenqi pill; ELISA: enzyme linked immunosorbent assay; AST: aspartate transaminase; LDH: lactate dehydrogenase assay; IL-1β: interleukin-1β; IL-6: interleukin-6; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor-α; DOX: doxorubicin. Differences were evaluated by one-way analysis of variance. Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation (n = 8). aP < 0.05, compared with the control group; bP < 0.05, compared with the DOX group.
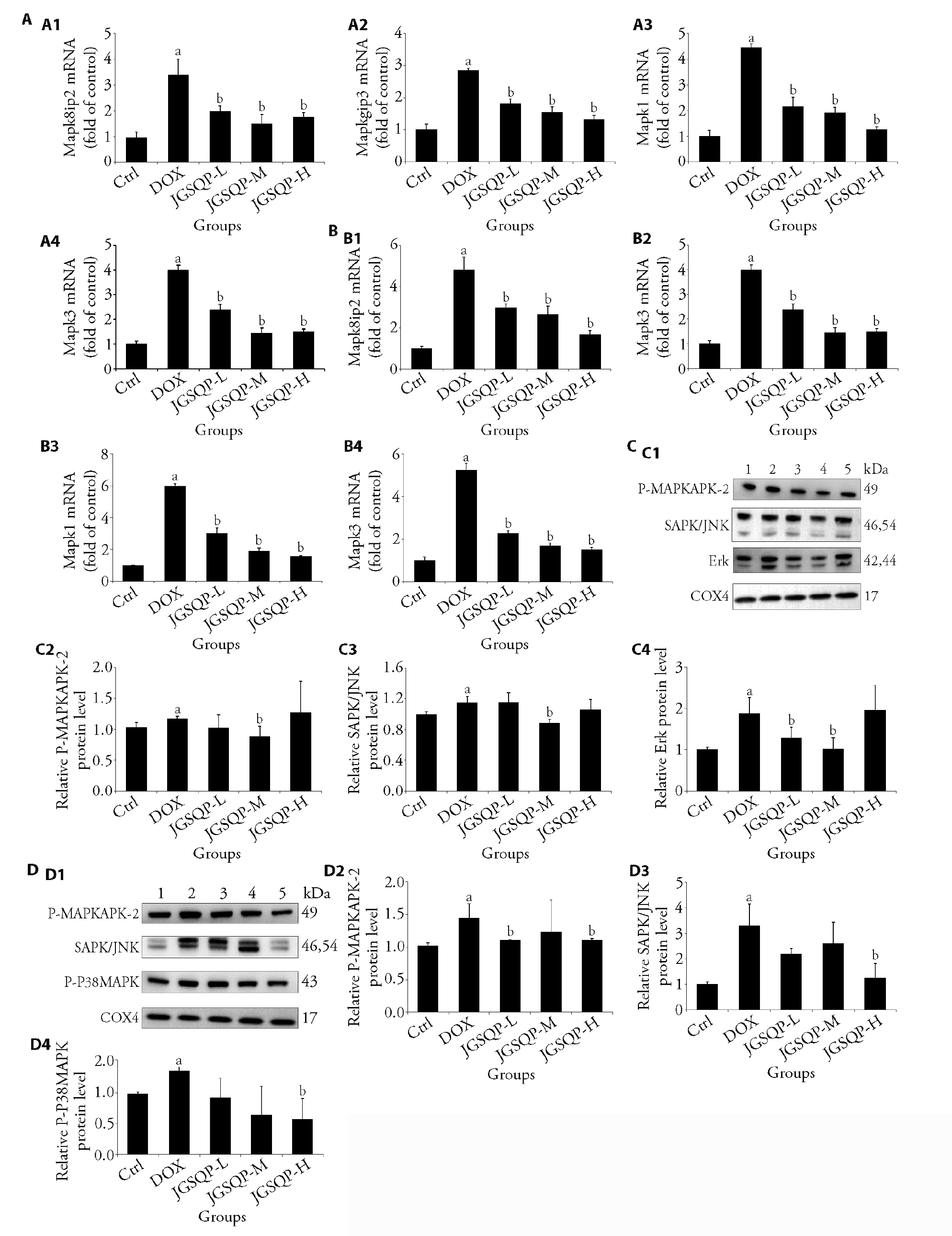
Figure 4 JGSQP can inhibit the activation of MAPK pathway A: PCR results of Mapk8ip2, Mapk8ip3, Mapk1, Mapk3 in rat heart; A1: Mapk8ip2; A2: Mapk8ip3; A3: Mapk1; A4: Mapk3; B: PCR results of Mapk8ip2, Mapk8ip3, Mapk1, Mapk3 in rat kidney; B1: Mapk8ip2; B2: Mapk8ip3; B3: Mapk1; B4: Mapk3; C: Western blot measured rats heart P-MAPK-2, SAPK/JNK, Erk protein expression. The column shows protein expression. C1: Western blot image of rats heart P-MAPK-2, SAPK/JNK, Erk protein expression; C2: P-MAPK-2 protein expression; C3: SAPK/JNK protein expression; C4: Erk protein expression; D: Western blotting measured rats kidney P-MAPK-2, SAPK/JNK, P-P38 MAPK protein expression; D1: Western blotting image of rats kidney P-MAPK-2, SAPK/JNK, P-P38 MAPK protein expression; D2: P-MAPK-2 protein expression; D3: SAPK/JNK protein expression; D4: P-P38 MAPK protein expression; 1: control group; 2: DOX group; 3: JGSQP-L group; 4: JGSQP-M group; 5: JGSQP-H group. DOX: doxorubicin group (3 mg/kg doxorubicin was injected intraperitoneally once/week for 6 weeks); JGSQP-L: JGSQP low-dose group (0.5 g/kg JGSQP were administered by gavage for 8 weeks); JGSQP-M: JGSQP medium-dose group (1.0 g/kg JGSQP were administered by gavage for 8 weeks); JGSQP-H: JGSQP high-dose group (2.0 g/kg JGSQP were administered by gavage for 8 weeks). JGSQP: Jingui Shenqi pill; PCR: quantitative real?time polymerase chain reaction ; Mapk8ip2: mitogen-activated protein kinase 8 interacting protein 2; Mapk8ip3: mitogen-activated protein kinase 8 interacting protein 3; Mapk1: mitogen-activated protein kinase 1; Mapk3: mitogen-activated protein kinase 3; P-MAPKAPK-2: phospho-mitogen-activated protein kinase-activated protein kinase 2; SAPK/JNK: stress-activated protein kinase/c-jun N-terminal kinase; Erk: extracellular signal-regulated kinase; P-P38 MAPK: phospho-p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase; COX4: cytochrome c oxidase subunit 4; DOX: doxorubicin. Differences were evaluated by one-way analysis of variance. Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation (n = 8). aP < 0.05, compared with the control group; bP < 0.05, compared with the DOX group.
| 1. |
Ricci Z, Romagnoli S, Ronco C. Cardiorenal syndrome. Crit Care Clin 2021; 37: 335-47.
DOI PMID |
| 2. |
Alprecht-Quiroz P, Zúñiga-Pineda B, Lara-Terán JJ, Cáceres-Vinueza SV, Duarte-Vera YC. Cardiorenal syndrome: clinical and echocardiographic aspects. Arch Cardiol Mex 2020; 90: 503-10.
DOI PMID |
| 3. | Orvalho JS, Cowgill LD. Cardiorenal syndrome: diagnosis and management. Vet Clin N Am-small 2017; 47: 1083-102. |
| 4. | Chávez-Iñiguez JS, Sánchez-Villaseca SJ, García-Macías LA. Cardiorenal syndrome: classification, pathophysiology, diagnosis and management. Literature review. Arch Cardiol Mex 2022; 92: 253-63. |
| 5. | Junho CVC, Trentin-Sonoda M, Panico K, et al. Cardiorenal syndrome: long road between kidney and heart. Heart Fall Rev 2022; 27: 2137-53. |
| 6. | Brandenburg V, Heine GH. The cardiorenal syndrome. Deut Med Wochenschr 2019; 144: 382-6. |
| 7. | Lyu TJ, FA JJ, Xing LN. Research progress of Jinkui Shenqi pill in treatment of chronic kidney disease. Shi Jie Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi 2019; 19: 1270-2. |
| 8. | Liang XW, Lai H, Wu J, et al. Effect of Jinkui shenqi pills on the level of monoamine neurotransmitters in kidney-Yang deficiency rats. Zhong Guo Zhong Yi Ji Chu Yi Xue Za Zhi 2024; 30: 1-15. |
| 9. | Kao ST, Wang SD, Lin CC, Lin LJ. Jin Gui Shen Qi Wan. A Traditional Chinese Medicine, alleviated allergic airway hypersensitivity and inflammatory cell infiltration in a chronic asthma mouse model. J Ethnopharmacol 2018; 227: 181-90. |
| 10. |
Xiong X, Wang P, Li X, Zhang Y. Shenqi pill, a traditional Chinese herbal formula, for the treatment of hypertension: a systematic review. Complement Ther Med 2015; 23: 484-93.
DOI PMID |
| 11. |
Liang D, Qi Y, Liu L, et al. Jin-gui-shen-qi Wan ameliorates diabetic retinopathy by inhibiting apoptosis of retinal ganglion cells through the Akt/HIF-1α pathway. Chin Med-UK 2023; 18: 130.
DOI PMID |
| 12. |
Patel KP, Katsurada K, Zheng H. Cardiorenal syndrome: the role of neural connections between the heart and the kidneys. Circ Res 2022; 130: 1601-17.
DOI PMID |
| 13. |
Kosiorek A, Biegus J, Rozentryt P, Hurkacz M, Zymliński R. Cardiorenal syndrome: decongestion in heart failure across wide spectrum of kidney pathophysiology. Adv Clin Exp Med 2022; 31: 445-55.
DOI PMID |
| 14. | Langlo KAR, Lundgren KM, Zanaboni P, et al. Cardiorenal syndrome and the association with fitness: data from a telerehabilitation randomized clinical trial. ESC Heart Fail 2022; 9: 2215-24. |
| 15. | McCallum W, Sarnak MJ. Cardiorenal syndrome in the hospital. Clin Jam Soc Nephro: CJASN 2023; 18: 933-45. |
| 16. |
Jefferies JL, Kovesdy CP, Ronco C. Contemporary laboratory assessment of acute cardiorenal syndrome for early diagnosis - a call for action. AM Heart J 2023; 261: 75-84.
DOI PMID |
| 17. |
Mei SB, Hong L, Cai XY, Xiao B, Zhang P, Shao L. Oxidative stress injury in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Toxicol Lett 2019; 307: 41-8.
DOI PMID |
| 18. | Wang L, Hao D, Li X, et al. Advances in animal models of cardiorenal syndrome. Zhong Guo Yao Li Xue Tong Bao 2013; 29: 1496-8. |
| 19. | Oremek GM, Passek K, Holzgreve F, von der Eltz V, Dröge J. The biomarkers BNP and NT-proBNP. Zhi Ye Yi Xue Zhi Ye An Quan Yu Ren Ti Gong Cheng Xue Zhong Yang Za Zhi 2023; 73: 89-5. |
| 20. | Nougué H, Michel T, Picard F, et al. Deconvolution of BNP and NT-proBNP immunoreactivities by mass spectrometry in heart failure and sacubitril/valsartan treatment. Clin Chem 2023; 69: 350-62. |
| 21. | Myhre PL, Vaduganathan M, Claggett BL, et al. Influence of NT-proBNP on efficacy of dapagliflozin in heart failure with mildly reduced or preserved ejection fraction. JACC Heart failure 2022; 10: 902-13. |
| 22. | Xie C, Zhan Y, Wu Y, et al. Expression and clinical significance of serum sST2, BDNF, CTnI, and BUN/Cr in patients with heart failure. Altern Ther Health M 2023; 29: 176-81. |
| 23. | Miao Y, Liu Y, Liu C, Yao L, Kang X, Lyu M. Diagnostic value of echocardiography combined with serum h-FABP and cTnI in myocardial infarction and its evaluation value in left ventricular function. Evid-based Compl Alt: eCAM 2022; 2022: 8809708. |
| 24. | Lu P, Lin D, Chen N, et al. CNN-assisted SERS enables ultra-sensitive and simultaneous detection of Scr and BUN for rapid kidney function assessment. Anal Methods 2023; 15: 322-32. |
| 25. | Xu X, Ye B, Li M, Xia Y, Wu Y, Cheng W. The UA doppler index, plasma HCY, and Cys C in pregnancies complicated by congenital heart disease of the fetus. J Clin Med 2022; 11: 59-62. |
| 26. | Huang W, Wang L, Wan X. Monocyte to high density lipoprotein ratio in patients with acute kidney injury after cardiac surgery. Perfusion 2023; 38: 172-7. |
| 27. | Chung EYM, Trinh K, Li J, et al. Biomarkers in cardiorenal syndrome and potential insights into novel therapeutics. Front Cardiovasc Med 2022; 9: 868658. |
| 28. | Chen W, Fan Z, Huang C, Liu J. Poricoic acid A inhibits the NF-κB/MAPK pathway to alleviate renal fibrosis in rats with cardiorenal syndrome. Evid-based Compl Alt: eCAM 2022; 2022: 8644353. |
| 29. | Alasmari WA, Faruk E, Fouad H, Radi R, El-Wafaey DI. Adipose-derived stem cell and their extracellular vesicles ameliorates immune function, and cardiac markers in experimental model of cardiorenal syndrome type Ⅲ: TNF-α, IFN-γ and IL-10 cytokine production and their correlation with genotype. Transpl immunol 2022; 72: 101586. |
| 30. | Ma L, Wu F, Shao Q, et al. Baicalin alleviates oxidative stress and inflammation in diabetic nephropathy via Nrf2 and MAPK signaling pathway. Drug Des Dev Ther 2021; 15: 3207-21. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

