Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (6): 1227-1235.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2024.06.009
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Moxibustion inhibits the macrophage M1 polarization toll-like receptor 4/myeloid differentiation factor 88/nuclear factor kappa B signaling pathway by regulating T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin-containing protein-3 in rheumatoid arthritis
LUO Kun1, ZHONG Yumei2, GUO Yanding1, ZHANG Linlin1, HU Danhui1, MA Wenbin1, YANG Xin3, ZHOU Haiyan1( )
)
- 1 Acupuncture and Tuina School, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu 610075, China
2 Department of Painology, Chengdu Integrated TCM & Western Medicine Hospital/Chengdu First People's Hospital, Chengdu 610095, China
3 Health Rehabilitation School, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu 610075, China
-
Received:2023-09-11Accepted:2023-12-05Online:2024-12-15Published:2024-11-12 -
Contact:Prof. ZHOU Haiyan, Acupuncture and Tuina School, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu 610075, China. zhouhaiyan@cdutcm.edu.cn Telephone: +86-13551039390 -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China: Study on Immunoregulatory Mechanism of Moxibustion "Regulating Weiqi" to Regulate the Intrasynovial Environment Steady State in Rheumatoid Arthritis Model Rats based on the Skin-resident Memory T cells- Growth Arrest-specific 6/ Mer Tyrosine Kinase(82374587);National Natural Science Foundation of China: Study on the Immune Mechanisms of Macrophage M1/M2 Polarization in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis by Moxibustion "Strengthening Body Resistance and Eliminating Evil"(81973959);National Key R&D Program of China: Research on the Functional Characteristics of "Special Effects" and "Common Effects" of Acupoints(2019YFC1709001);Science and Technology Innovation Seedling Project of Sichuan Province: based on Macrophage M1 Polarization Signaling Pathway Toll-like receptor 4/Myeloid differentiation factor 88/Nuclear factor kappa B and its Regulatory Molecule T-cell Immunoglobulin and Mucin-containing Protein-3 Exploring the Effect Mechanism of Moxibustion on Experimental Rheumatoid Arthritis Model(2022037)
Cite this article
LUO Kun, ZHONG Yumei, GUO Yanding, ZHANG Linlin, HU Danhui, MA Wenbin, YANG Xin, ZHOU Haiyan. Moxibustion inhibits the macrophage M1 polarization toll-like receptor 4/myeloid differentiation factor 88/nuclear factor kappa B signaling pathway by regulating T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin-containing protein-3 in rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(6): 1227-1235.
share this article

Figure 1 Investigation of the effect of moxibustion on reducing foot swell and inflammatory responses in rats with rheumatoid arthritis A: photo of footpads of rats in the control group; B: photo of footpads of rats in the rheumatoid arthritis group; C: photo of footpads of rats in the moxibustion group; D: HE stained image of ankle of control groups, magnification:× 20; E: HE stained image of ankle of rheumatoid arthritis groups, magnification:× 20; F: HE stained image of ankle of moxibustion groups, magnification:× 20; G: HE stained image of ankle of control groups, magnification:× 200; H: HE stained image of ankle of rheumatoid arthritis groups, magnification:× 200; I: HE stained image of ankle of moxibustion groups, magnification:× 200. The control group received 0.5 mL/kg of saline with bilateral foot pads; the rheumatoid arthritis group received 0.5 mL/kg of FCA with bilateral foot pads; the moxibustion group received 0.5 mL/kg of FCA with bilateral foot pads for three cycles of moxibustion treatment. HE: hematoxylin-eosin staining; FCA: Freund's Adjuvant Complete.
| Item | Group | n | Day 0 | Day 7 | Day 14 | Day 21 | Day 28 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Right | Control | 6 | 0.35±0.03 | 0.35±0.03 | 0.34±0.02 | 0.33±0.02 | 0.34±0.02 |
| RA | 6 | 0.37±0.03 | 0.63±0.02a | 0.66±0.05a | 0.62±0.04a | 0.59±0.03a | |
| Mox | 6 | 0.37±0.02 | 0.62±0.03a | 0.51±0.04ab | 0.49±0.05ab | 0.50±0.02ab | |
| Left | Control | 6 | 0.36±0.02 | 0.39±0.02 | 0.36±0.03 | 0.36±0.03 | 0.36±0.02 |
| RA | 6 | 0.37±0.03 | 0.71±0.12a | 0.69±0.10a | 0.71±0.08a | 0.68±0.06a | |
| Mox | 6 | 0.37±0.02 | 0.71±0.03a | 0.55±0.04ab | 0.52±0.02ab | 0.52±0.03ab |
Table 1 Thicknesses of the left and right foot pads (cm,
| Item | Group | n | Day 0 | Day 7 | Day 14 | Day 21 | Day 28 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Right | Control | 6 | 0.35±0.03 | 0.35±0.03 | 0.34±0.02 | 0.33±0.02 | 0.34±0.02 |
| RA | 6 | 0.37±0.03 | 0.63±0.02a | 0.66±0.05a | 0.62±0.04a | 0.59±0.03a | |
| Mox | 6 | 0.37±0.02 | 0.62±0.03a | 0.51±0.04ab | 0.49±0.05ab | 0.50±0.02ab | |
| Left | Control | 6 | 0.36±0.02 | 0.39±0.02 | 0.36±0.03 | 0.36±0.03 | 0.36±0.02 |
| RA | 6 | 0.37±0.03 | 0.71±0.12a | 0.69±0.10a | 0.71±0.08a | 0.68±0.06a | |
| Mox | 6 | 0.37±0.02 | 0.71±0.03a | 0.55±0.04ab | 0.52±0.02ab | 0.52±0.03ab |
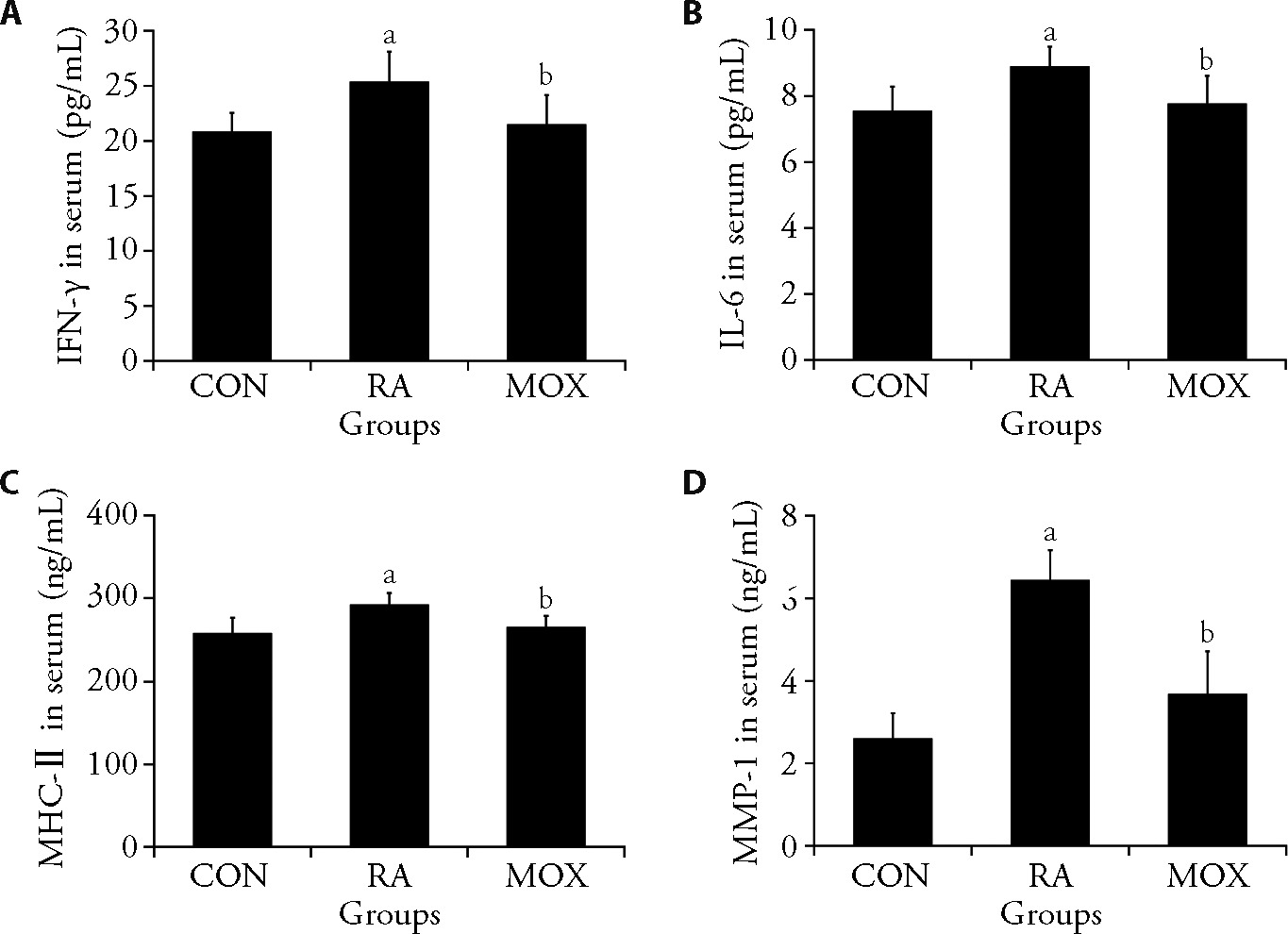
Figure 2 Inflammatory responses in rats with RA can be improved by moxibustion A: levels of IFN-γ in serum of rats in each group; B: levels of IL-6 in serum of rats in each group; C: levels of MHC-Ⅱ in serum of rats in each group; D: levels of MMP-1 in serum of rats in each group. The rheumatoid arthritis and moxibustion groups injected 0.5 mL/kg of FCA, the control group received an equal amount of normal saline, and three cycles of moxibustion treatment for the moxibustion group. IFN-γ: interferon gamma; IL-6: interleukin-6; MHC-Ⅱ: major histocompatibility complex Ⅱ; MMP-1: matrix metallopeptidase 1; FCA: Freund's Adjuvant Complete. The Data represent the mean ± standard deviation using one-way analysis of variance (n = 6). aP < 0.05 vs the control group; bP < 0.05 vs the rheumatoid arthritis group.

Figure 3 Moxibustion inhibits M1 polarization of macrophages. Expression of factors related to TLR4-MyD88-NF-κB pathway A: expression of TLR4mRNA; B: expression of MyD88mRNA. C: Western blot results showing expression level of NF-κB protein; D: Western blot analysis; E: expression of TIM-3mRNA; F: expression of TIM-3mRNA after lentivirus interference. qPCR was performed on spleens from rheumatoid arthritis rats to determine mRNA expression levels. Measurement of NF-κB expression in synovium by Weston blot. The rheumatoid arthritis, moxibustion groups and TIM-3 lentiviral intervention groups injected 0.5 mL/kg of FCA, the control group received an equal amount of normal saline, and three cycles of moxibustion treatment for the moxibustion group. Lentiviral was injected into the rat foot pads of the TIM-3 lentiviral intervention group. TLR4: Toll-like receptor 4; MyD88: Myeloid differentiation factor 88; NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa B; TIM-3: T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin-containing protein-3. The Data represent the mean ± standard deviation using one-way analysis of variance (n = 6). aP < 0.01, cP < 0.05 vs the control group; bP < 0.01, dP < 0.05 vs the rheumatoid arthritis group.

Figure 4 Moxibustion modulates TIM-3 to inhibit macrophage M1 polarization Expression of factors related to Tim-3/TLR4-MyD88-NF-κB pathway. A: levels of IL-12 in serum of rats in each group; B: Levels of TNF-α in serum of rats in each group; C: levels of TNF-β in serum of rats in each group; D: expression of MyD88mRNA; E: expression of NF-κBmRNA. The rheumatoid arthritis, moxibustion groups, TIM-3 lentiviral intervention and TIM-3 lentiviral intervention + moxibustion intervention groups injected 0.5 mL/kg of FCA, the control group received an equal amount of normal saline, and three cycles of moxibustion treatment for the moxibustion and TIM-3 lentiviral intervention + moxibustion intervention groups. Lentiviral was injected into the rat foot pads of the TIM-3 lentiviral intervention and TIM-3 lentiviral intervention + moxibustion intervention groups. IL-12: interleukin-12; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor alpha; TNF-β: tumor necrosis factor beta; MyD88: Myeloid differentiation factor 88; NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa B; TIM-3: T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin-containing protein-3; FCA: Freund's Adjuvant Complete. The Data represent the mean ± standard deviation using one-way analysis of variance (n = 6). aP < 0.01, dP < 0.05 vs the control group; bP < 0.01, cP < 0.05 vs the rheumatoid arthritis group.
| 1. |
Smith MH, Berman JR. What is rheumatoid arthritis? JAMA 2022; 327: 1194.
DOI PMID |
| 2. | Gravallese EM, Firestein GS. Rheumatoid arthritis-common origins, divergent mechanisms. N Engl J Med 2023; 388: 529-42. |
| 3. | Pagliano O, Morrison RM, Chauvin JM, et al. Tim-3 mediates T cell trogocytosis to limit antitumor immunity. J Clin Invest 2022; 132: e152864. |
| 4. | Zhao L, Cheng S, Fan L, et al. TIM-3: an update on immunotherapy. Int Immunopharmacol 2021; 99: 107933. |
| 5. |
Li S, Peng D, He Y, et al. Expression of TIM-3 on CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in the peripheral blood and synovial fluid of rheumatoid arthritis. APMIS 2014; 122: 899-904.
DOI PMID |
| 6. |
Zhang W, Zhang Y, He Y, et al. Lipopolysaccharide mediates time-dependent macrophage M1/M2 polarization through the Tim-3/galectin-9 signalling pathway. Exp Cell Res 2019; 376: 124-32.
DOI PMID |
| 7. | Razi B, Reykandeh SE, Alizadeh S, et al. TIM family gene polymorphism and susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis: systematic review and Meta-analysis. PLoS One 2019; 14: e0211146. |
| 8. |
Kurowska-Stolarska M, Alivernini S. Synovial tissue macrophages in joint homeostasis, rheumatoid arthritis and disease remission. Nat Rev Rheumatol 2022; 18: 384-97.
DOI PMID |
| 9. | Chung SJ, Yoon HJ, Youn H, et al. 18F-FEDAC as a targeting agent for activated macrophages in DBA/1 mice with collagen-induced arthritis: comparison with 18F-FDG. J Nucl Med 2018; 59: 839-45. |
| 10. |
Roberts CA, Dickinson AK, Taams LS. The interplay between monocytes/macrophages and CD4(+) T cell subsets in rheumatoid arthritis. Front Immunol 2015; 6: 571.
DOI PMID |
| 11. |
Yu A, Zhang X, Li M, et al. Tim-3 enhances brain inflammation by promoting M1 macrophage polarization following intracerebral hemorrhage in mice. Int Immunopharmacol 2017; 53: 143-8.
DOI PMID |
| 12. | Cutolo M, Campitiello R, Gotelli E, et al. The role of M1/M2 macrophage polarization in rheumatoid arthritis synovitis. Front Immunol 2022; 13: 867260. |
| 13. | Han C, Yang Y, Sheng Y, et al. Glaucocalyxin B inhibits cartilage inflammatory injury in rheumatoid arthritis by regulating M1 polarization of synovial macrophages through NF-κB pathway. Aging 2021; 13: 22544-55. |
| 14. |
Kung CC, Dai SP, Chiang H, et al. Temporal expression patterns of distinct cytokines and M1/M2 macrophage polarization regulate rheumatoid arthritis progression. Mol Biol Rep 2020; 47: 3423-37.
DOI PMID |
| 15. | Zhang YH, He M, Wang Y, et al. Modulators of the balance between M1 and M2 macrophages during pregnancy. Front Immunol 2017; 8: 120. |
| 16. | Mantovani A, Biswas SK, Galdiero MR, et al. Macrophage plasticity and polarization in tissue repair and remodelling. J Pathol 2013; 229: 176-85. |
| 17. | Pang YZ, Luo ZH, Tang QQ, et al. Chinese medicine pathogenesis syndrome element of rheumatoid arthritis: discussion on Bi-syndrome pathological factors. Zhong Yi Za Zhi 2018; 59: 390-93. |
| 18. | Shen B, Sun Q, Chen H, et al. Effects of moxibustion on pain behaviors in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a Meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore) 2019; 98: e16413. |
| 19. | Wang Y, Tao S, Yu Z, et al. Effect of moxibustion on β-EP and dyn levels of pain-related indicators in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2021; 2021: 6637554. |
| 20. | Zhou HY, Zhong YM, Gao XH, et al. Efficacy of Moxa-burning heat stimulating Zusanli (ST36) and Shenshu (BL23) on expressions of macrophage migration inhibitory factor and macrophage apoptosis in rabbits with adjuvant-induced arthritis. J Tradit Chin Med 2022;42: 980-87. |
| 21. | Zhang L, Zhong Y, Lu W, et al. Moxibustion of Zusanli (ST36) and Shenshu (BL23) alleviates the inflammation of rheumatoid arthritis in rats through regulating macrophage migration inhibitory factor/ glucocorticoids signaling. J Tradit Chin Med 2024; 44: 353-61. |
| 22. | Zhong YM, Zhang LL, Lu WT, et al. Moxibustion regulates the polarization of macrophages through the IL-4/STAT6 pathway in rheumatoid arthritis. Cytokine 2022; 152: 155835. |
| 23. | Zhong YM, Wu F, Luo XC, et al. Mechanism on moxibustion for rheumatoid arthritis based on PD-1/PD-L1 signaling pathway. Zhong Guo Zhen Jiu 2020; 40: 976-82. |
| 24. | Chen Y, Li H, Luo X, et al. Moxibustion of Zusanli (ST36) and Shenshu (BL23) alleviates cartilage degradation through RANKL/OPG signaling in a rabbit model of rheumatoid arthritis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2019; 2019: 6436420. |
| 25. | Li Z. Experimental acupuncture. Beijing: China press of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2003: 314-6. |
| 26. |
Pan H, Guo R, Ju Y, et al. A single bacterium restores the microbiome dysbiosis to protect bones from destruction in a rat model of rheumatoid arthritis. Microbiome 2019; 7: 107.
DOI PMID |
| 27. |
Jannat A, John P, Bhatti A, et al. Tomorou attenuates progression of rheumatoid arthritis through alteration in ULK-1 independent autophagy pathway in collagen induced arthritis mice model. Cell Death Discov 2019; 5: 142.
DOI PMID |
| 28. | Coras R, Murillo-Saich JD, Guma M. Circulating pro- and anti-inflammatory metabolites and its potential role in rheumatoid arthritis pathogenesis. Cells 2020; 9: 827. |
| 29. | Tang L, Li G, Zheng Y, et al. Tim-3 relieves experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by suppressing MHC-II. Front Immunol 2022; 12: 770402. |
| 30. |
Zhuo Y, Zhang YF, Wu HJ, et al. Interaction between galectin-9/TIM-3 pathway and follicular helper CD4+ T cells contributes to viral persistence in chronic hepatitis C. Biomed Pharmacother 2017; 94: 386-93.
DOI PMID |
| 31. | Zhu Y, Yu HW, Pan YZ, et al. Effect of moxibustion at “Zusanli” (ST36) and “Shenshu” (BL23) on miR-155-mediated TLR4/NF-κB signaling involving amelioration of synovitis in rheumatoid arthritis rats. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu 2021; 46: 194-200. |
| 32. | Zhao C, Li XY, Li ZY, et al. Moxibustion regulates T-regulatory/T-helper 17 cell balance by modulating the microRNA-221/suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 axis in a mouse model of rheumatoid arthritis. J Integr Med 2022; 20: 453-62. |
| 33. | Yu Z, Wang Y, Li Y, et al. Effect of moxibustion on the serum levels of MMP-1, MMP-3, and VEGF in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2020; 2020: 7150605. |
| 34. | Yang T, Wang R, Liu H, et al. Berberine regulates macrophage polarization through IL-4-STAT6 signaling pathway in helicobacter pylori-induced chronic atrophic gastritis. Life Sci 2021; 266: 118903. |
| 35. | Chen YN, Hu MR, Wang L, et al. Macrophage M1/M2 polarization. Eur J Pharmacol 2020; 877: 173090. |
| 36. |
Elshabrawy HA, Essani AE, Szekanecz Z, et al. TLRs, future potential therapeutic targets for RA. Autoimmun Rev 2017; 16: 103-13.
DOI PMID |
| 37. | Yuan J, Hu L, Song XG, et al. Influence of moxibustion on TLR4-MyD88-NF-κB signal transduction pathway of synovial tissue in rheumatoid arthritis rats. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu 2015; 40: 199-204. |
| 38. | Zhang CY, Hu L, Cai RL, et al. Toll-like receptor 4/nuclear factor-κB signaling in synovial tissue is involved in the anti-inflammatory effect of moxibustion in rats with rheumatoid arthritis. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu 2018; 43: 687-91. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 149
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 37
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

