Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (5): 885-895.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20240806.006
Previous Articles Next Articles
Regulatory effects of the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase-myosin light chain kinase pathway on the intestinal epithelial mechanical barrier and the mechanism of modified Pulsatilla decoction (加味白头翁汤) in the treatment of ulcerative colitis
WU Tingting1, YANG Xin1,2, ZHU Huiping1, GUO Jinwei1, ZHU Hui1, ZHANG Peipei1, WANG Meng1, LIANG Guoqiang1,3( ), SUN Hongwen1(
), SUN Hongwen1( )
)
- 1 Department of Internal Medicine, Suzhou TCM Hospital Affiliated to Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Suzhou 215003, China
2 Department of Internal Medicine, The Affiliated Suzhou Science and Technology Town Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Suzhou 215153, China
3 Suzhou Academy of Wumen Chinese Medicine, Suzhou Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital Affiliated to Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Suzhou 215003, China
-
Received:2023-06-11Accepted:2023-11-15Online:2024-10-15Published:2024-08-06 -
Contact:SUN Hongwen, Department of Internal Medicine, Suzhou TCM Hospital Affiliated to Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Suzhou 215003, China. shw8101@163.com; LIANG Guoqiang, Suzhou Academy of Wumen Chinese Medicine, Suzhou TCM Hospital Affiliated to Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Suzhou 215003, China. 616250366@qq.com Telephone: +86-512-67872371 -
Supported by:Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province-funded Project: Regulation of Intestinal Epithelial Tight Junction Proteins Through the p38 Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase-Myosin Light Chain kinase Signaling Pathway in Ulcerative Colitis Treatment by Modified Pulsatilla Decoction(BK20201179);Jiangsu Health Commission-funded Project: Study on the Prevention of Postoperative Recurrence in Patients with Colorectal Adenoma and High Triglyceride based on the Theory of “Treating the Disease Before It Gets Worse” by Modified Jisheng Wumei Pill(BJ23039);Suzhou Health Commission-funded Project: Study on the Technical Application of Xu Jingfan's “Eliminating Stasis and Protecting Membrane” Method to Regulate Recombinant NLR Family, Pyrin Domain Containing Protein 3 to Repair Esophageal Mucosa in Reflux Esophagitis treatment(SS202080);Suzhou Health Commission-funded Project(SKY2022015);Suzhou Health Commission-funded Project: Clinical Diagnostic and Therapeutic Techniques for Reflux Esophagitis Treatment with Graded Step-down Therapy by Combining Traditional Chinese and Western medicine(LCZX201817)
Cite this article
WU Tingting, YANG Xin, ZHU Huiping, GUO Jinwei, ZHU Hui, ZHANG Peipei, WANG Meng, LIANG Guoqiang, SUN Hongwen. Regulatory effects of the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase-myosin light chain kinase pathway on the intestinal epithelial mechanical barrier and the mechanism of modified Pulsatilla decoction (加味白头翁汤) in the treatment of ulcerative colitis[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(5): 885-895.
share this article
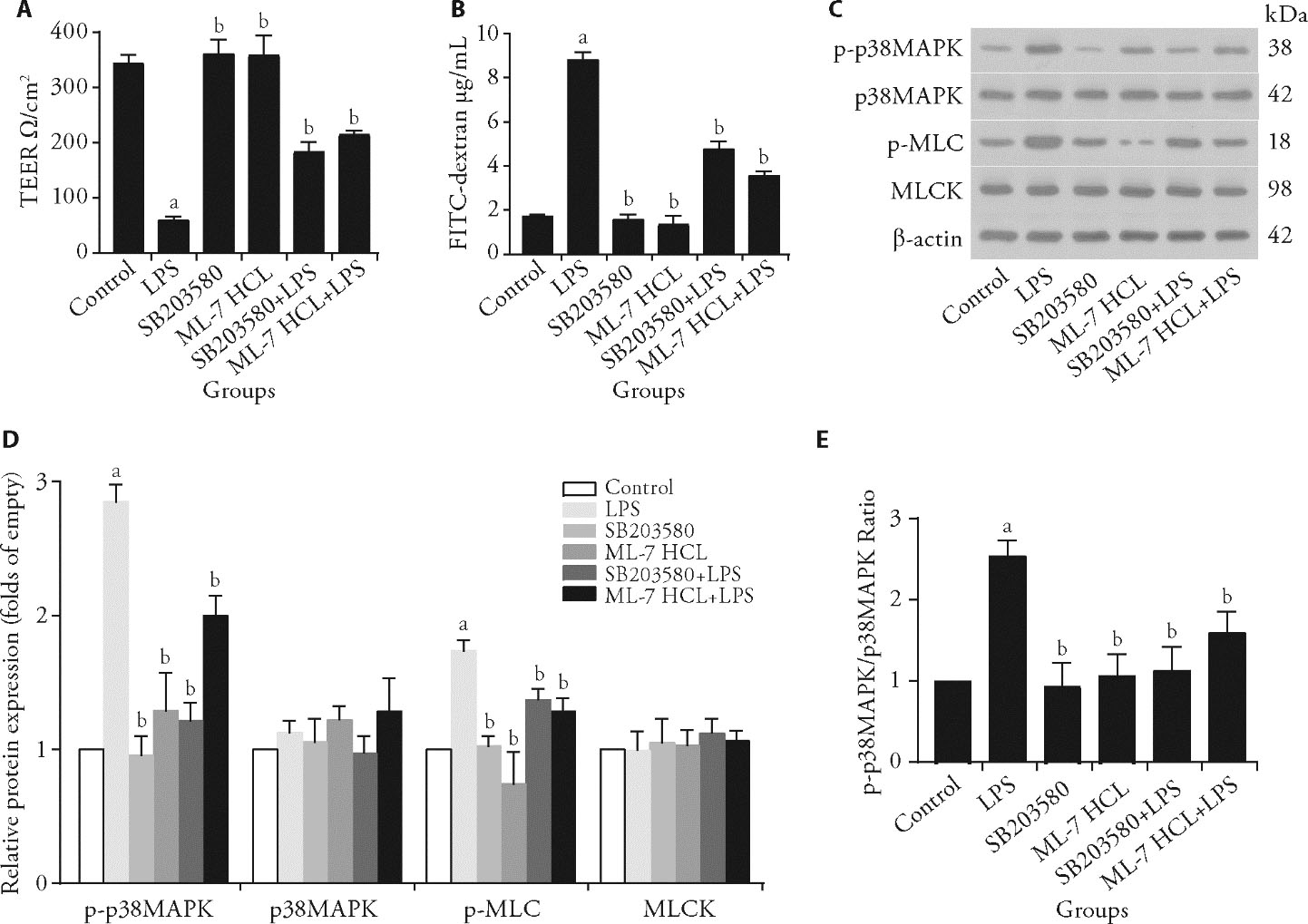
Figure 1 The p38MAPK-MLCK pathway regulates intestinal mechanical barrier function A: analysis of TEER in IEC-6 cells after exposure to LPS, SB203580, and ML-7 HCL for 24 h; B: analysis of permeability in IEC-6 cells; C: yhe p-p38MAPK, p38MAPK, p-MLC, and MLCK proteins were detected by western blotting analysis; D: band intensity was quantitated using densitometry; E: bar graphs showed the relative quantification of p-p38MAPK/p38MAPK. Control group: basal medium. LPS group: LPS (30 μg/mL). SB203580 group: SB203580 (10 μm /L). ML-7 HCL group: ML-7 HCL (10 μm/L) SB203580 + LPS group: LPS group + SB203580 (10 μm /L). ML-7 HCL + LPS group: LPS group + ML-7 HCL (10 μm/L) and LPS (30 μg/mL). LPS: lipopolysaccharide; SB203580: p38MAPK inhibitor; ML-7 HCL: ML-7 hydrochloride, MLCK inhibitor; TEER: transepithelial electronic resistance. Statistical analyses were measured using one-way or two-way analysis of variance for multimal comparisons. Data were presented as mean ± standard deviation (n = 3). Compared with the control group, aΡ<0.01; compared with the LPS group, bΡ<0.01.
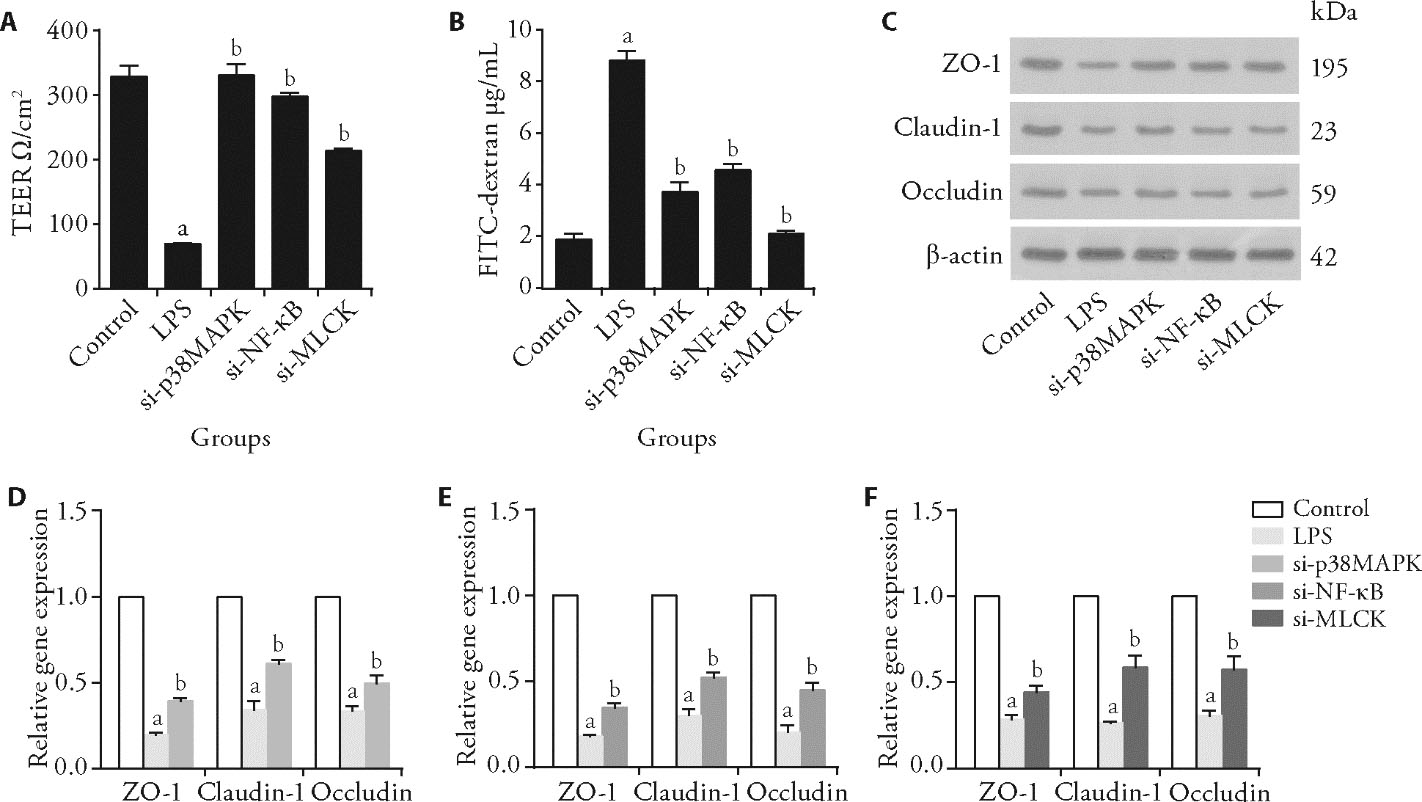
Figure 2 Regulation of tight junctions (TJ) protein by p38MAPK-MLCK pathway A: analysis of TEER and in IEC-6 cells after silencing p38MAPK, NF-κB, and MLCK gene; B: analysis of permeability in IEC-6 cells; C: ZO-1, Claudin-1, and Occludin proteins were detected by western blotting analysis; D: relative gene expression level of ZO-1 in IEC-6 cells; E: relative gene expression level of Claudin-1 in IEC-6 cells; F: relative gene expression level of Occludin in IEC-6 cells; LPS: lipopolysaccharide; MPD: modified Pulsatilla decoction; TEER: transepithelial electronic resistance; p38MAPK: p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase; NF-κB: nuclear factor kappa-B; MLCK: myosin light chain kinase. Statistical analyses were measured using one-way analysis of variance for multimal comparisons. Data were presented as mean ± standard deviation (n = 3). Compared with the control group, aΡ<0.01; compared with the LPS group, bΡ<0.01.
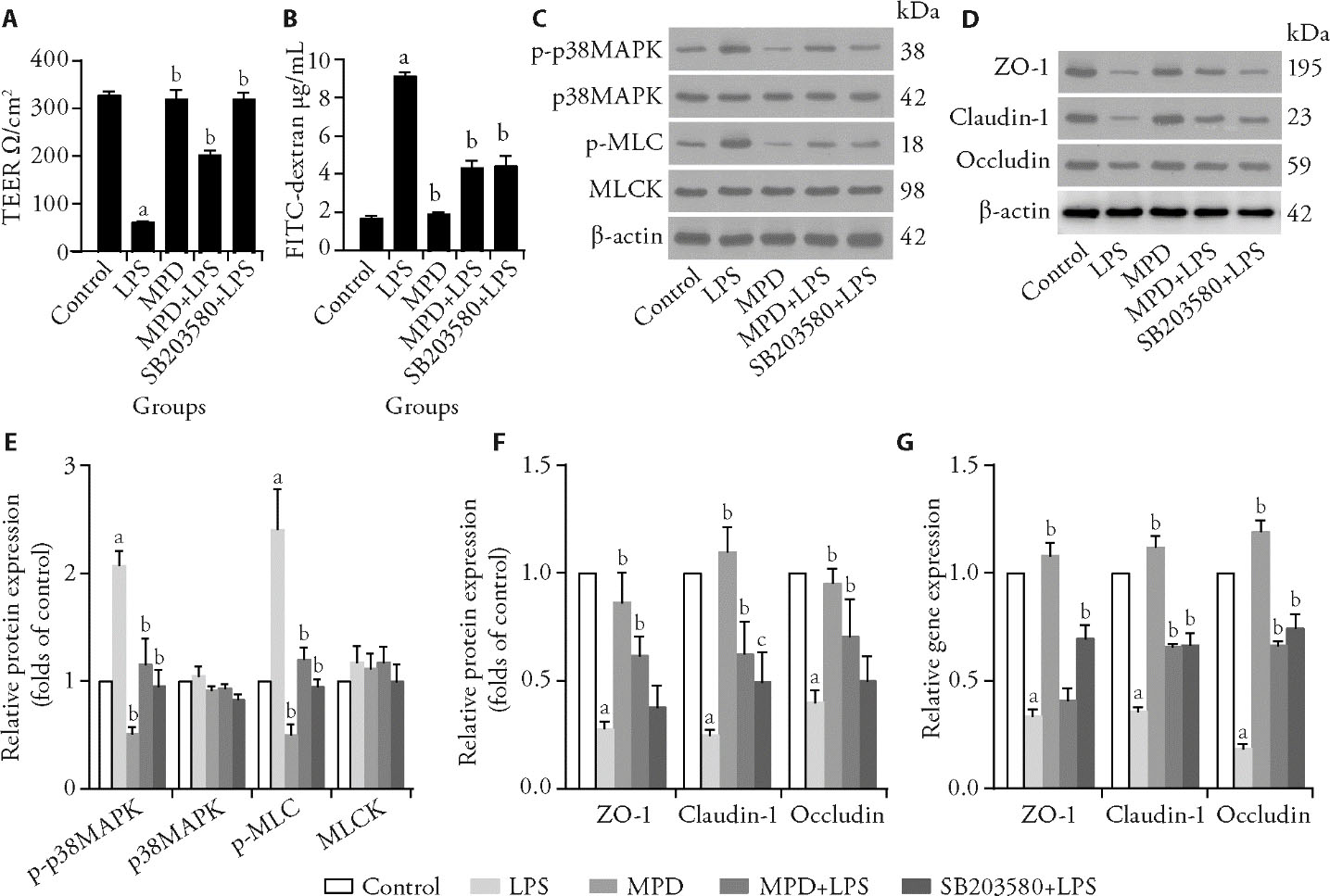
Figure 3 MPD protects against LPS-induced damage to the epithelial barrier of the intestine via the inhibition of the p38MAPK-MLCK pathway A: analysis of TEER and in IEC-6 cells after exposure to LPS, MPD and SB203580 for 24 h; B: analysis of permeability in IEC-6 cells; C: TJ proteins were detected by western blotting analysis; D: p38MAPK-MLCK pathway related proteins were detected by western blotting analysis; E: relative protein expression of p38MAPK-MLCK pathway related proteins in IEC-6 cells; F: relative protein expression of TJ related proteins in IEC-6 cells; G: relative gene levels of TJ proteins in IEC-6 cells. Control group: basal medium; LPS group: LPS (30 μg/mL); MPD group: 10%MPD-containing serum; MPD + LPS group: LPS group + 10%MPD-containing serum; SB203580 + LPS group: LPS group + SB203580 (10 μm/L). LPS: lipopolysaccharide; MPD: modified Pulsatilla decoction; TJ: tight junction; TEER: transepithelial electronic resistance; SB203580: p38MAPK inhibitor; p38MAPK: p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase; MLCK: myosin light chain kinase. Statistical analyses were measured using one-way or two-way analysis of variance for multimal comparisons. Data were presented as mean ± standard deviation (n = 3). Compared with the control group, aΡ<0.01; compared with the LPS group, bΡ<0.01; compared with the LPS group, cΡ<0.05.
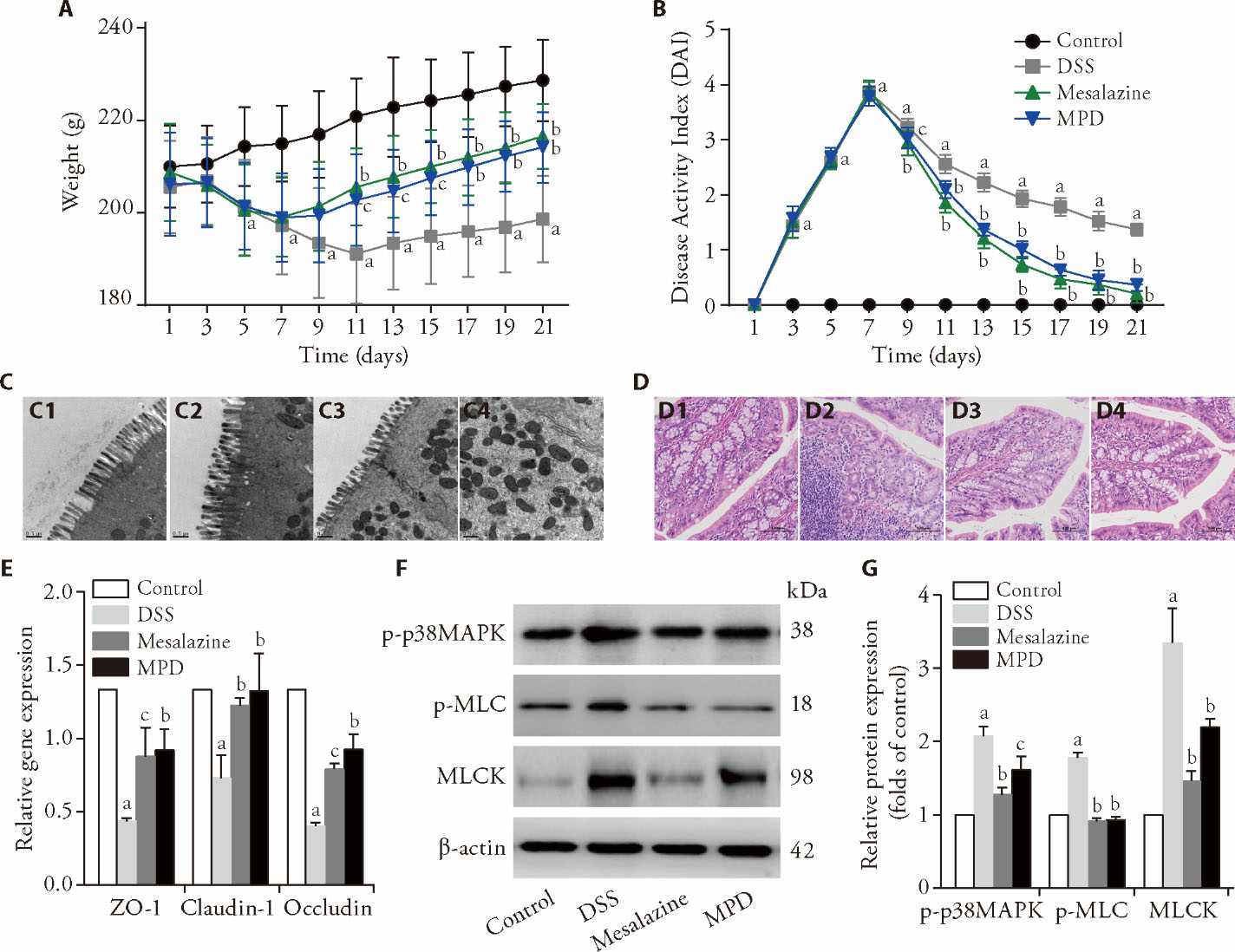
Figure 4 MPD is protective against DSS-induced colitis in vivo A: body weight changes of rats; B: DAI scores of rats; C: representative transmission electron microscope picture of colon tissue from each group. C1: Control group; C2: DSS group; C3: Mesalazine group; 4: MPD group. Scale bar = 0.5 μm, × 20 000; D: representative hematoxylin-eosin staining of colon tissue from each group. D1: Control group; D2: DSS group; D3: Mesalazine group; D4: MPD group. Scale bar = 100 μm, × 200; E: relative gene levels of TJ in the rat colonic tissue. F: the p-p38MAPK, p-MLC, and MLCK proteins were detected using Western blotting. G: band intensity was quantitated using densitometry. Control group: NS via enema. UC group: NS via enema, Mesalazine group: mesalazine 0.42 g/kg via enema. MPD group: MPD 17.28 g/kg via enema. MPD: modified Pulsatilla decoction; DSS: dextran sodium sulfate; p38MAPK: p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase; MLCK: myosin light chain kinase. Statistical analyses were measured using one-way analysis of variance for multimal comparisons. Data were presented as mean ± standard deviation (n = 3). Compared with the control group, aΡ<0.01; Compared with the DSS group, bΡ<0.01; compared with the DSS group, cΡ<0.05.
| 1. | Kotze PG, Underwood FE, Damião AOMC, et al. Progression of inflammatory bowel diseases throughout Latin America and the Caribbean: a systematic review. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2020; 18: 304-12. |
| 2. | Taft TH, Keefer L. A systematic review of disease-related stigmatization in patients living with inflammatory bowel disease. Clin Exp Gastroenter 2016; 9: 49-58. |
| 3. |
Ahluwalia B, Moraes L, Magnusson MK, Öhman L. Immunopathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease and mechanisms of biological therapies. Scand J Gastroentero 2018; 53: 379-89.
DOI PMID |
| 4. |
Danese S, Vuitton L, Peyrin-Biroulet L. Biologic agents for IBD: practical insights. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2015; 12: 537-45.
DOI PMID |
| 5. | Lu A, Jia H, Xiao C, Lu Q. Theory of Traditional Chinese Medicine and therapeutic method of diseases. World J Gastroentero 2004; 10: 1854-6. |
| 6. | Hu T, Wen P, Linhardt RJ, Liao S, Wu H, Zou Y. Mulberry: a review of bioactive compounds and advanced processing technology. Trends Food Sci Tech 2018; 83: 138-58. |
| 7. |
Wenzheng S, Guangrong S. General principle of high-quality academic development of Traditional Chinese Medicine: "carrying on the essence, while pursuing innovations". J Tradit Chin Med 2023; 43: 1-2.
DOI |
| 8. | Han D. Adhesion of Bifidobacteria and related inflammatory factors in ulcerative colitis with Pingkui Enema. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2019: 1-46. |
| 9. | Han D, Yun H, Jin Y, Sun H. Effects of Pingkui enema on adhesion of Bifidobacteria and related inflammatory factors in ulcerative colitis. Guo Ji Zhong Yi Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2019; 41: 969-75. |
| 10. | Jin Y, Sun H. Effect and mechanism of Pingkui enema on ulcerative colitis model rats. Zhong Yi Yao Dao Bao 2019; 25: 51-4. |
| 11. | Anbazhagan AN, Priyamvada S, Alrefai WA, Dudeja PK. Pathophysiology of IBD associated diarrhea. Tissue Barriers 2018; 6: e1463897. |
| 12. | Elamin E, Masclee A, Troost F, et al. Ethanol impairs intestinal barrier function in humans through mitogen activated protein kinase signaling: a combined in vivo and in vitro approach. PLoS One 2014; 9: e107421. |
| 13. | Wu T, Yang X, Xu B, et al. Using network pharmacology and molecular docking technology to explore the mechanism of modified Pulsatilla decoction in the treatment of ulcerative colitis. Nat Prod Commun 2022; 17: 1-14. |
| 14. | Li H, Wei Y, Li X, et al. Diosmetin has therapeutic efficacy in colitis regulating gut microbiota, inflammation, and oxidative stress via the circ-Sirt1/Sirt1 axis. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2022; 43: 919-32. |
| 15. |
Niederlechner S, Baird C, Wischmeyer PE. P38MAP kinase, but not phosphoinositol-3 kinase, signal downstream of glutamine-mediated fibronectin-integrin signaling after intestinal injury. Nutr J 2013; 12: 88.
DOI PMID |
| 16. | Wu L, Peng W, Kuo W, et al. Commensal bacterial endocytosis in epithelial cells is dependent on myosin light chain kinase-activated brush border fanning by interferon-gamma. Am J Pathol 2014; 184: 2260-74. |
| 17. |
Chen S, Einspanier R, Schoen J. Transepithelial electrical resistance (TEER): a functional parameter to monitor the quality of oviduct epithelial cells cultured on filter supports. Histochem Cell Biol 2015; 144: 509-15.
DOI PMID |
| 18. | Tatsuta M, Kan-O K, Ishii Y, et al. Effects of cigarette smoke on barrier function and tight junction proteins in the bronchial epithelium: protective role of cathelicidin LL-37. Resp Res 2019; 20: 251. |
| 19. | Rodriguez-Canales M, Martinez-Galero E, Nava-Torres AD, et al. Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities of the methanolic extract of cyrtocarpa procera bark reduces the severity of ulcerative colitis in a chemically induced colitis model. Mediat Inflamm 2020; 2020: 5062506. |
| 20. | Yun HF, Liu R, Han D, et al. Pingkui Enema alleviates TNBS-induced ulcerative colitis by regulation of inflammatory factors, gut Bifidobacterium, and intestinal mucosal barrier in rats. Evid-Based Compl Alt 2020; 2020: 3896948. |
| 21. |
Cooper HS, Murthy SN, Shah RS, Sedergran DJ. Clinico-pathologic study of dextran sulfate sodium experimental murine colitis. Lab Invest 1993; 69: 238-49.
PMID |
| 22. | Ullah M, Sun Z. Klotho deficiency accelerates stem cells aging by impairing telomerase activity. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 2019; 74: 1396-407. |
| 23. | Jiang Y, Song J, Xu Y, et al. Piezol regulates intestinal epithelial function by affecting the tight junction protein claudin-1 via the ROCK pathway. Life Sci 2021; 275: 119254. |
| 24. | Perše M, Cerar A. Dextran sodium sulphate colitis mouse model: traps and tricks. J Biomed Biotechnol 2012; 2012: 718617. |
| 25. |
Chen G, Yang Y, Hu C, et al. Protective effects of Huangqin decoction against ulcerative colitis and associated cancer in mice. Oncotarget 2016; 7: 61643-55.
DOI PMID |
| 26. | Li M, Luo H, Wu X, et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of Huangqin decoction on dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis in mice through regulation of the gut microbiota and suppression of the Ras-PI3K-Akt-HIF-1alpha and NF-kappa B pathways. Front Pharmacol 2019; 10: 1552. |
| 27. | Hua Y, Ma Q, Zhang X, et al. Pulsatilla decoction can treat the dampness-heat diarrhea rat model by regulating Glycer-inphospholipid metabolism based lipidomics approach. Front Pharmacol 2020; 11: 197. |
| 28. | Liu X, Li Y, Jiang H, Li H, Xiao L, Zhao Y. Comparison between Ye Tianshi and Xue Shengbai in treatment of diarrfea with damp-heat. Zhong Guo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2018; 43: 1720-5. |
| 29. | Jin Y. Clinical observation and mechanism study of Pingkui Enema in the treatment of ulcerative colitis. Nanjing: Nanjing University of traditional Chinese Medicine, 2019: 1-45 |
| 30. |
Turner JR. Intestinal mucosal barrier function in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol 2009; 9: 799-809.
DOI PMID |
| 31. |
Cui L, Guan X, Ding W, et al. Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi polysaccharide ameliorates DSS-induced ulcerative colitis by improving intestinal barrier function and modulating gut microbiota. Int J Biol Macromol 2021; 166: 1035-45.
DOI PMID |
| 32. | Maria-Ferreira D, Nascimento AM, Cipriani TR, et al. Rhamnogalacturonan, a chemically-defined polysaccharide, improves intestinal barrier function in DSS-induced colitis in mice and human Caco-2 cells. Sci Rep-Uk 2018; 8: 12261. |
| 33. | Li C, Ai G, Wang Y, et al. Oxyberberine, a novel gut microbiota-mediated metabolite of berberine, possesses superior anti-colitis effect: impact on intestinal epithelial barrier, gut microbiota profile and TLR4-MyD88-NF-kappaB pathway. Pharmacol Res 2020; 152: 104603. |
| 34. | Wang Y, Liu J, Huang Z, et al. Coptisine ameliorates DSS-induced ulcerative colitis via improving intestinal barrier dysfunction and suppressing inflammatory response. Eur J Pharmaco 2021; 896: 173912. |
| 35. |
Pastorelli L, De Salvo C, Mercado JR, Vecchi M, Pizarro TT. Central role of the gut epithelial barrier in the pathogenesis of chronic intestinal inflammation: lessons learned from animal models and human genetics. Front Immunol 2013; 4: 280.
DOI PMID |
| 36. | Van Itallie CM, Anderson JM. Architecture of tight junctions and principles of molecular composition. Semin Cell De Biol 2014; 36: 157-65. |
| 37. |
Lee SH. Intestinal permeability regulation by tight junction: implication on inflammatory bowel diseases. Intest Res 2015; 13: 11-8.
DOI PMID |
| 38. | Buckley A, Turner JR. Cell biology of tight junction barrier regulation and mucosal disease. Csh Perspect Biol 2018; 10: a29314. |
| 39. | Tsukita S, Furuse M, Itoh M. Multifunctional strands in tight junctions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2001; 2: 285-93. |
| 40. |
Van Itallie CM, Anderson JM. Claudins and epithelial paracellular transport. Annu Rev Physiol 2006; 68: 403-29.
PMID |
| 41. | Li Y, Xiao H, Hu D, et al. Berberine ameliorates chronic relapsing dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in C57BL/6 mice by suppressing Th17 responses. Pharmacol Res 2016; 110: 227-39. |
| 42. | Chi JH, Kim YH, Sohn DH, Seo GS, Lee SH. Ameliorative effect of Alnus japonica ethanol extract on colitis through the inhibition of inflammatory responses and attenuation of intestinal barrier disruption in vivo and in vitro. Biomed Pharmacother 2018; 108: 1767-74. |
| 43. |
Barton GM, Medzhitov R. Toll-like receptor signaling pathways. Science 2003; 300: 1524-5.
DOI PMID |
| 44. |
Kanemaru K, Nakamura Y, Totoki K, et al. Phospholipase Cdelta1 regulates p38 MAPK activity and skin barrier integrity. Cell Death Differ 2017; 24: 1079-90.
DOI PMID |
| 45. |
Birukova AA, Meng F, Tian Y, et al. Prostacyclin post-treatment improves LPS-induced acute lung injury and endothelial barrier recovery via Rap1. Biochimica Et Biophysica Acta 2015; 1852: 778-91.
DOI PMID |
| 46. | Stepanovska B, Lange AI, Schwalm S, Pfeilschifter J, Coldewey SM, Huwiler A. Downregulation of S1P lyase improves barrier function in human cerebral microvascular endothelial cells following an inflammatory challenge. Intl J Mol Sci 2020; 21: 1240. |
| 47. |
James J, Srivastava A, Varghese MV, et al. Heme induces rapid endothelial barrier dysfunction via the MKK3/p38MAPK axis. Blood 2020; 136: 749-54.
DOI PMID |
| 48. | Yang Z, Duan X, Wang X, et al. The effect of Q-switched 1064-nm Nd: YAG laser on skin barrier and collagen synthesis via miR-663a to regulate TGFbeta1/smad3/p38MAPK pathway. Photo-dermatol Photoimmunol Photomed 2021; 37: 412-21. |
| 49. | Hu T, Ju J, Mo L, et al. Anti-inflammation action of xanthones from Swertia chirayita by regulating COX-2/NF-kappaB/MAPKs/ Akt signaling pathways in RAW 264.7 macrophage cells. Phytomedicine 2019; 55: 214-21. |
| 50. | Hao G, Zhai J, Jiang H, et al. Acetylshikonin induces apoptosis of human leukemia cell line K 562 by inducing S phase cell cycle arrest, modulating ROS accumulation, depleting Bcr-Abl and blocking NF-kappa B signaling. Biomed Pharmacother 2020; 122: 109677. |
| 51. |
Yang K, Qiu B, Yan J, et al. Blockade of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway ameliorates delayed gastric emptying in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Int Immunopharmacol 2014; 23: 696-700.
DOI PMID |
| 52. | He X, Shu J, Xu L, Lu C, Lu A. Inhibitory effect of Astragalus polysaccharides on lipopolysaccharide-induced TNF-a and IL-1beta production in THP-1 cells. Molecules 2012; 17: 3155-64. |
| 53. | Shin M, Park H, Seo B, Roh S. New approach of medicinal herbs and sulfasalazine mixture on ulcerative colitis induced by dextran sodium sulfate. World J Gastroentero 2020; 26: 5272-86. |
| 54. | Ye X, Sun M. AGR2 ameliorates tumor necrosis factor-α-induced epithelial barrier dysfunction via suppression of NF-κB p65-mediated MLCK/p-MLC pathway activation. Int J Mol Med 2017; 39: 1206-14. |
| 55. |
Drolia R, Amalaradjou MAR, Ryan V, et al. Receptor-targeted engineered probiotics mitigate lethal Listeria infection. Nat Commun 2020; 11: 6344.
DOI PMID |
| 56. |
Al-Sadi R, Boivin M, Ma T. Mechanism of cytokine modulation of epithelial tight junction barrier. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed) 2009; 14: 2765-78.
PMID |
| 57. |
Broom OJ, Widjaya B, Troelsen J, Olsen J, Nielsen OH. Mitogen activated protein kinases: a role in inflammatory bowel disease? Clin Exp Immunol 2009; 158: 272-80.
DOI PMID |
| 58. |
Zhao X, Kang B, Lu C, et al. Evaluation of p38 MAPK pathway as a molecular signature in ulcerative colitis. J Proteome Res 2011; 10: 2216-25.
DOI PMID |
| 59. | Sun Y, Zhang Z, Peng Z. Observation on the therapeutic effects of modified Pulsatilla decoction enemaon damp-heat type ulcerative colitis and its effect on serum IL-17 and TNF-α. Zhong Guo Zhong Yi Yao Ke Ji 2022; 29: 71-3. |
| [1] | PANG Fengtao, LI Kesong, ZHANG Yi, TANG Xiaopo, ZHOU Xinyao. Efficacy of Lushi Runzao decoction (路氏润燥汤) on ameliorating Sjogren's syndrome: a network pharmacology and experimental verification-based study [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(4): 751-759. |
| [2] | ZHOU Zhenghua, JI Jianbin, WANG Hongxia, YAN Lin, KANG Hongchang. Qingchi San (青赤散) treats ulcerative colitis in mice by inhibiting the nuclear factor-kappa B signaling pathway and Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain, leucine-rich repeat and pyrin domain-containing 3 inflammasome formation [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(1): 68-77. |
| [3] | Zhou Peijuan, Wang Aicheng, Li Bai, Liu Chunyan, Wang Yu. Effect of acupuncture at Fengchi(GB 20)on the activity of myosin light chain kinase in the middle meningeal artery of migraine modeled rats [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2015, 35(03): 301-305. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 234
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 169
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

