Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (5): 987-997.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2025.05.006
• Original Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Mechanism of Tiaogeng decoction (调更汤) in a cognitive dysfunction mouse model
NI Shuang1, LIU Xiaofei1, GUO Xiaoyan1, GU Zuxi2, WU Panqing1, CONG Chao1, LI Shengnan1, GAO Xianwei1, XU Lianwei1( )
)
- 1 Department of Gynecology, Longhua Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200032, China
2 Experimental Animal Center, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 201203, China
-
Received:2024-10-22Accepted:2025-01-25Online:2025-10-15Published:2025-09-15 -
Contact:Prof. XU Lianwei, Department of Gynecology, Longhua Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200032, China. doctorsherryxlw@163.com, Telephone: +86-18917763165 -
Supported by:Natural Science Foundation-funded Project: Mechanism of Tiaogeng Decoction improving Cognitive Function via Regulating Nuclear Factor-erythroid 2-related Factor 2/c-Jun N-terminal kinase/Aβ Oxidative Stress Network in Hippocampus Neurons(81874482)
Cite this article
NI Shuang, LIU Xiaofei, GUO Xiaoyan, GU Zuxi, WU Panqing, CONG Chao, LI Shengnan, GAO Xianwei, XU Lianwei. Mechanism of Tiaogeng decoction (调更汤) in a cognitive dysfunction mouse model[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(5): 987-997.
share this article
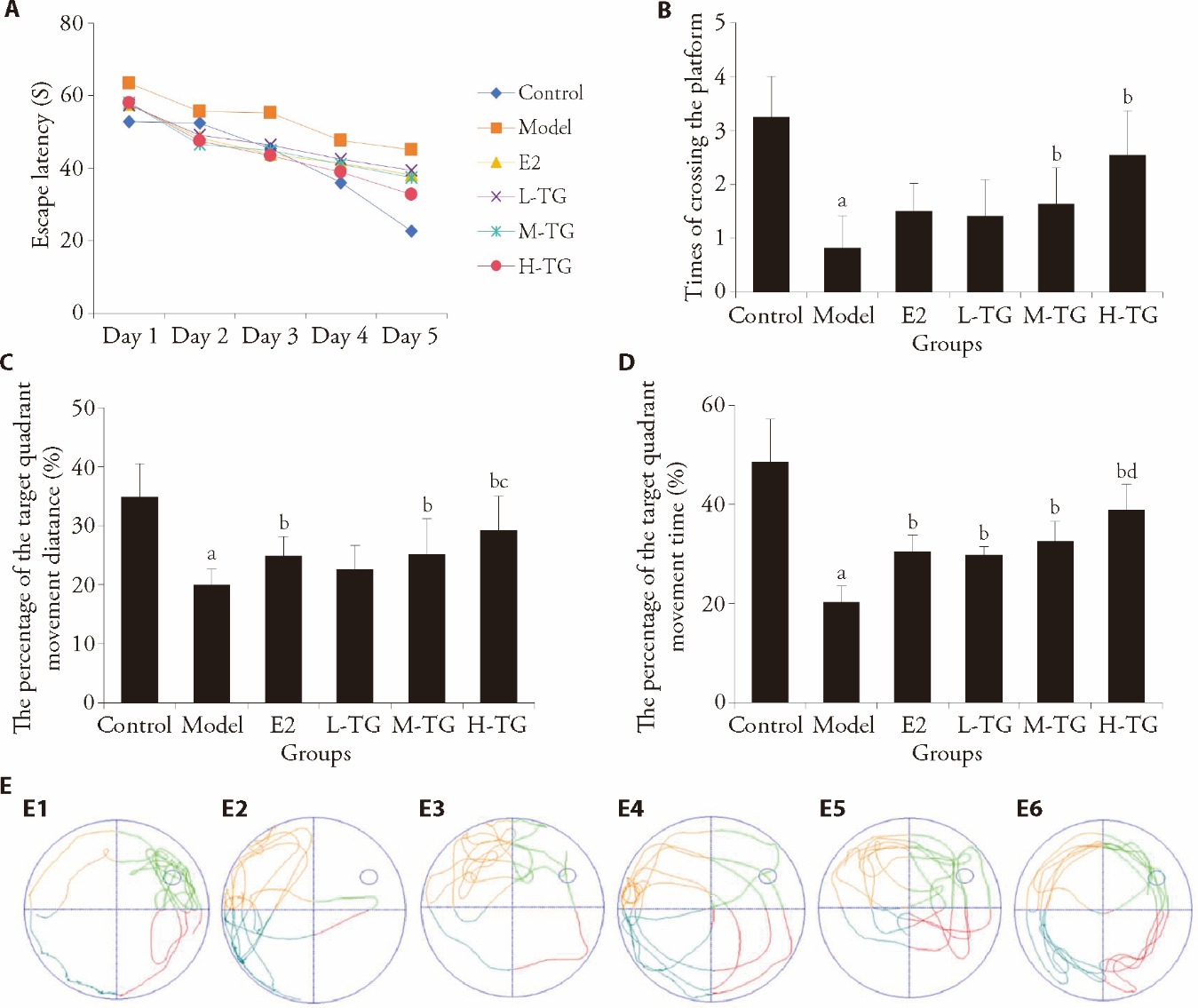
Figure 1 Water maze test results A: comparison of escape latency; B: times of crossing the platform; C: percentage of the target quadrant movement distance; D: percentage of the target quadrant movement time; E: track chart for comparison of times of crossing platforms in each group. E1: control group; E2: model group; E3: E2 group; E4: L-TG group; E5: M-TG group; E6: H-TG group. Control group: give purified water 0.3 mL/d; Model group: give purified water 0.3 mL/d; E2 group: give estradiol valerate 0.152 mg·kg?1·d?1; L-TG group: give Tiaogeng decoction 0.82 g·kg?1·d?1; M-TG group: give Tiaogeng decoction 1.64 g·kg?1·d?1; H-TG group: give Tiaogeng decoction 3.28 g·kg?1·d?1. Statistical analyses were measured by using one-way analysis of variance to analyze the differences between the groups. The data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (n = 12). Compared with control group, aP < 0.01; compared with model group, bP < 0.05; compared with L-TG group, cP < 0.05; compared with E2 group, dP < 0.05.

Figure 2 Observation on the structure of hippocampal neuronal organelles in each group under electron microscope A: control group; A1: magnified 4500 times, green arrow indicates neuron nucleus; A2: magnified 11500 times, green arrow indicates mitochondrion; B: model group; B1: magnified 4500 times, green arrow indicates cell nuclear membrane; B2: magnified 11500 times, green arrow indicates mitochondrion; C: E2 group; C1: magnified 4500 times; C2: magnified 11500 times, Green arrow indicates mitochondrion; D: L-TG group; D1: magnified 4500 times; D2: magnified 11500 times, green arrow indicates mitochondrion; E: M-TG group; E1: magnified 4500 times; E2: magnified 11500 times, green arrow indicates mitochondrion; F: H-TG group; F1: magnified 4500 times; F2: magnified 11500 times, green arrow indicates mitochondrion. Control group: give purified water 0.3 mL/d; Model group: give purified water 0.3 mL/d; E2 group: give estradiol valerate 0.152 mg·kg-1·d?1; L-TG group: give Tiaogeng decoction 0.82 g·kg-1·d?1; M-TG group: give Tiaogeng decoction 1.64 g·kg-1·d?1; H-TG group: give Tiaogeng decoction 3.28 g·kg-1·d?1.
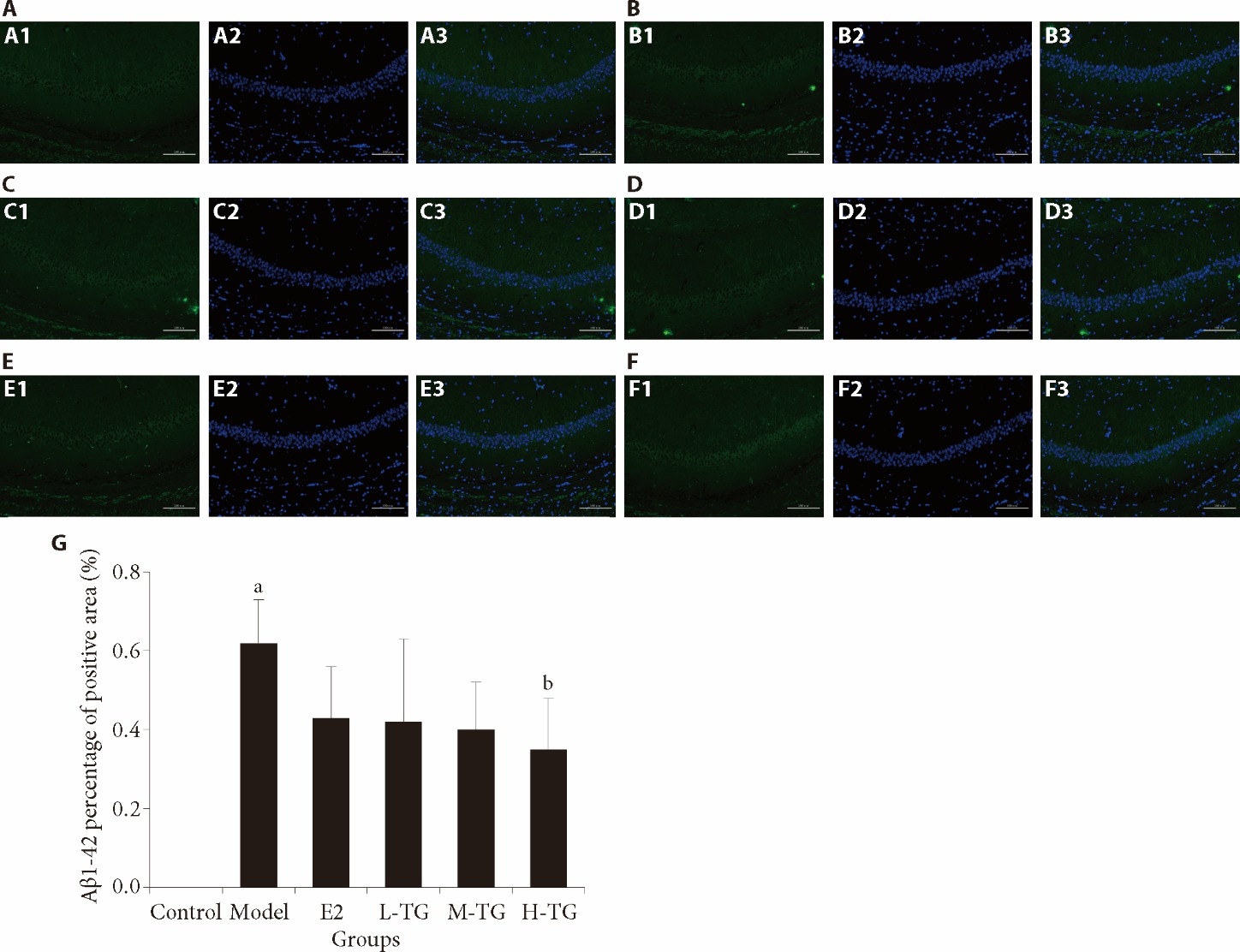
Figure 3 Immunofluorescence detection of hippocampal CA1 area Aβ1-42 A: control group; A1: Aβ1-42 expression; A2: cell nuclear blue fluorescence staining; A3: merge; B: model group; B1: Aβ1-42 expression; B2: cell nuclear blue fluorescence staining; B3: merge; C: E2 group; C1: Aβ1-42 expression; C2: cell nuclear blue fluorescence staining; C3: merge; D: L-TG group; D1: Aβ1-42 expression; D2: cell nuclear blue fluorescence staining; D3: merge; E: M-TG group; E1: Aβ1-42 expression; E2: cell nuclear blue fluorescence staining; E3: merge; F: H-TG group; F1: Aβ1-42 expression; F2: cell nuclear blue fluorescence staining; F3: merge; G: Aβ1-42 percentage of positive area. Control group: give purified water 0.3 mL/d; Model group: give purified water 0.3 mL/d; E2 group: give estradiol valerate 0.152 mg·kg-1·d?1; L-TG group: give Tiaogeng decoction 0.82 g·kg-1·d?1; M-TG group: give Tiaogeng decoction 1.64 g·kg-1·d?1; H-TG group: give Tiaogeng decoction 3.28 g·kg-1·d?1. Statistical analyses were measured by using one-way analysis of variance to analyze the differences between the groups. The data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (n = 3). Compared with control group, aP < 0.05; compared with model group, bP < 0.05.

Figure 4 Oxidative stress indicators in the hippocampus A: SOD; B: MDA; C: ROS; D: HO-1. Control group: give purified water 0.3 mL/d; Model group: give purified water 0.3 mL/d; E2 group: give estradiol valerate 0.152 mg·kg-1·d?1; L-TG group: give Tiaogeng decoction 0.82 g·kg-1·d?1; M-TG group: give Tiaogeng decoction 1.64 g·kg-1·d?1; H-TG group: give Tiaogeng decoction 3.28 g·kg-1·d?1. SOD: superoxide dismutase; MDA: malondialdehyde; ROS: reactive oxygen species; HO-1: heme oxygenase-1. Statistical analyses were measured by using one-way analysis of variance to analyze the differences between the groups. The data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (n = 6). Compared with control group, aP < 0.01; compared with model group, bP < 0.05.
| 1. | Gaugler J, James B, Johnson T, et al. 2022 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement 2022; 18: 700-89. |
| 2. |
Chan KY, Wang W, Wu JJ, et al. Epidemiology of Alzheimer’s disease and other forms of dementia in China, 1990-2010: a systematic review and analysis. Lancet 2013; 381: 2016-23.
DOI PMID |
| 3. | Karlamangla AS, Lachman ME, Han W, Huang M, Greendale GA. Evidence for cognitive aging in midlife women: study of women’s health across the nation. PLoS One 2017; 12: e0169008. |
| 4. | Mosconi L, Berti V, Quinn C, et al. Perimenopause and emergence of an Alzheimer’s bioenergetic phenotype in brain and periphery. PLoS One 2017; 12: e0185926. |
| 5. |
Sperling RA, Karlawish J, Johnson KA. Preclinical Alzheimer disease-the challenges ahead. Nat Rev Neurol 2013; 9: 54-8.
DOI PMID |
| 6. |
Luine VN. Estradiol and cognitive function: past, present and future. Horm Behav 2014; 66: 602-18.
DOI PMID |
| 7. |
Scheyer O, Rahman A, Hristov H, et al. Female sex and Alzheimer’s risk: the menopause connection. J Prev Alzheimers Dis 2018; 5: 225-30.
DOI PMID |
| 8. |
Roberts R, Knopman DS. Classification and epidemiology of MCI. Clin Geriatr Med 2013; 29: 753-72.
DOI PMID |
| 9. | Li K, Wei Q, Liu FF, et al. Synaptic dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease: Aβ, tau, and epigenetic alterations. Mol Neurobiol 2018; 55: 3021-32. |
| 10. | Yao J, Irwin RW, Zhao L, Nilsen J, Hamilton RT, Brinton RD. Mitochondrial bioenergetic deficit precedes Alzheimer’s pathology in female mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2009; 106: 14670-75. |
| 11. |
Cheignon C, Tomas M, Bonnefont-Rousselot D, Faller P, Hureau C, Collin F. Oxidative stress and the amyloid beta peptide in Alzheimer’s disease. Redox Biol 2018; 14: 450-64.
DOI PMID |
| 12. | Wang X, Li B, Yu X, Zhou Y, Gao Y. The neuroprotective effect of GM-1 ganglioside on the amyloid-beta-induced oxidative stress in PC-12 cells mediated by Nrf-2/ARE signaling pathway. Neurochem Res 2022; 47: 2405-15. |
| 13. | Buendia I, Michalska P, Navarro E, Gameiro I, Egea J, León R. Nrf2-ARE pathway: an emerging target against oxidative stress and neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative diseases. Pharmacol Ther 2016; 157: 84-104. |
| 14. |
Dinkova-Kostova AT, Kostov RV, Kazantsev AG. The role of Nrf2 signaling in counteracting neurodegenerative diseases. FEBS Journal 2018; 285: 3576-90.
DOI PMID |
| 15. | Li Q, Xiang Y, Chen Y, Tang Y, Zhang Y. Ginsenoside Rg1 protects cardiomyocytes against hypoxia/reoxygenation injury via activation of Nrf2/HO-1 signaling and inhibition of JNK. Cell Physiol Biochem 2017; 44: 21-37. |
| 16. |
Rojo AI, Pajares M, Rada P, et al. NRF 2 deficiency replicates transcriptomic changes in Alzheimer’s patients and worsens APP and TAU pathology. Redox Biol 2017; 13: 444-51.
DOI PMID |
| 17. | Kaneto H, Nakatani Y, Kawamori D, et al. Role of oxidative stress, endoplasmic reticulum stress, and c-Jun N-terminal kinase in pancreatic beta-cell dysfunction and insulin resistance. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2005; 37: 1595-608. |
| 18. |
Abdelli S, Abderrahmani A, Hering BJ, Beckmann JS, Bonny C. The c-Jun N-terminal kinase JNK participates in cytokine- and isolation stress-induced rat pancreatic islet apoptosis. Diabetologia 2007; 50: 1660-9.
PMID |
| 19. |
Weston CR, Davis RJ. The JNK signal transduction pathway. Curr Opin Cell Biol 2007; 19: 142-9.
DOI PMID |
| 20. |
Morishima Y, Gotoh Y, Zieg J, et al. Beta-amyloid induces neuronal apoptosis via a mechanism that involves the c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathway and the induction of Fas ligand. J Neurosci 2001; 21: 7551-60.
PMID |
| 21. | Sun A, Liu M, Nguyen XV, Bing G. P 38 MAP kinase is activated at early stages in Alzheimer’s disease brain. Exp Neurol 2003; 183: 394-405. |
| 22. |
Thakur A, Wang X, Siedlak SL, Perry G, Smith MA, Zhu X. C-Jun phosphorylation in Alzheimer disease. J Neurosci Res 2007; 85: 1668-73.
PMID |
| 23. | Jia M, Kluwe L, Liu HC, et al. Efficacy and side-effects of a semi-individualized Chinese herb mixture “Tiáo Gēng Tāng” for menopausal syndrome in China. In vivo 2015; 29: 109-15. |
| 24. | Ni S, Xu LW. Clinical study on the effect of Tiaogeng decoction on the memory ability of menopausal women. Tianjin Zhong Yi Yao 2021; 38: 727-31. |
| 25. | Li S, Cong C, Liu Y, et al. Tiao Geng decoction for treating menopausal syndrome exhibits anti-aging effects likely via suppressing ASK1/MKK7/JNK mediated apoptosis in ovariectomized rats. J Ethnopharmacol 2020; 261: 113061. |
| 26. | Gao X, Li S, Liu X, et al. Neuroprotective effects of Tiaogeng decoction against H2O2-induced oxidative injury and apoptosis in PC 12 cells via Nrf2 and JNK signaling pathways. J Ethnopharmacol 2021; 279: 114379. |
| 27. |
Savonenko A, Xu GM, Melnikova T, et al. Episodic-like memory deficits in the APPswe/PS1dE9 mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease: relationships toβ-amyloid deposition and neurotransmitter abnormalities. Neurobiol Dis 2005; 18: 602-17.
DOI PMID |
| 28. | Lebrun CE, van der Schouw YT, de Jong FH, Pols HA, Grobbee DE, Lamberts SW. Endogenous oestrogens are related to cognition in healthy elderly women. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2005; 63: 50-5. |
| 29. |
Nilsen J, Irwin RW, Gallaher TK, Brinton RD. Estradiol in vivo regulation of brain mitochondrial proteome. J Neurosci 2007; 27: 14069-77.
DOI PMID |
| 30. | Tian H, Ding N, Guo M, et al. Analysis of learning and memory ability in an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model using the morris water maze. J Vis Exp 2019; 152: 1-6. |
| 31. | Viña J, Lloret A, Ortí R, Alonso D. Molecular bases of the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease with antioxidants: prevention of oxidative stress. Mol Aspects Med 2004; 25: 117-23. |
| 32. | Liu G, Liao E, Zhong GC, et al. Dynamic pathological changes in the brain of female APP/PS1 double transgenic mice with different ages. Chongqing Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 2015; 40: 13-7. |
| 33. |
Uttara B, Singh AV, Zamboni P, Mahajan RT. Oxidative stress and neurodegenerative diseases: a review of upstream and downstream antioxidant therapeutic options. Curr Neuropharmacol 2009; 7: 65-74.
DOI PMID |
| 34. | Jiang T, Sun Q, Chen S. Oxidative stress: a major pathogenesis and potential therapeutic target of antioxidative agents in Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease. Prog Neurobiol 2016; 147: 1-19. |
| 35. | Guo XD, Sun GL, Zhou TT, et al. LX2343 alleviates cognitive impairments in AD model rats by inhibiting oxidative stress-induced neuronal apoptosis and tauopathy. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2017; 38: 1104-19. |
| 36. | Qaid EYA, Abdullah Z, Zakaria R, Long I. Minocycline protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced cognitive impairment and oxidative stress: possible role of the CREB-BDNF signaling pathway. Neurochem Res 2023; 48: 1480-90. |
| 37. |
Casado A, Encarnación López-Fernández M, Concepción Casado M, de La Torre R. Lipid peroxidation and antioxidant enzyme activities in vascular and Alzheimer dementias. Neurochem Res 2008; 33: 450-8.
DOI PMID |
| 38. | Qu Z, Sun J, Zhang W, Yu J, Zhuang C. Transcription factor NRF2 as a promising therapeutic target for Alzheimer’s disease. Free Radic Biol Med 2020; 159: 87-102. |
| 39. | Ramsey CP, Glass CA, Montgomery MB, et al. Expression of Nrf2 in neurodegenerative diseases. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2007; 66: 75-85. |
| 40. |
Kanninen K, Malm TM, Jyrkkänen HK, et al. Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 protects against beta amyloid. Mol Cell Neurosci 2008; 39: 302-13.
DOI PMID |
| 41. | Kanninen K, Heikkinen R, Malm T, et al. Intrahippocampal injection of a lentiviral vector expressing Nrf2 improves spatial learning in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2009; 106: 16505-10. |
| 42. | Sharma V, Kaur A, Singh TG. Counteracting role of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 pathway in Alzheimer’s disease. Biomed Pharmacother 2020; 129: 110373. |
| 43. | Cuadrado A, Rojo AI. Heme oxygenase-1 as a therapeutic target in neuro-degenerative diseases and brain infections. Curr Pharm Des 2008; 14: 429-42. |
| 44. | Shih AY, Imbeault S, Barakauskas V, et al. Induction of the Nrf2-driven antioxidant response confers neuroprotection during mitochondrial stress in vivo. J Biol Chem 2005; 280: 22925-36. |
| 45. | Yang LM, Yang Q, Liu PG, et al. Cloning and characterization analysis of superoxide dismutase gene from Trichoderma harzianum. J Chin Bioinform 2007; 5: 148-150. |
| 46. |
Harris CA, Deshmukh M, Tsui-Pierchala B, Maroney AC, Johnson EM. Inhibition of the c-Jun N-terminal kinase signaling pathway by the mixed lineage kinase inhibitor CEP-1347 (KT7515) preserves metabolism and growth of trophic factor-deprived neurons. J Neurosci 2002; 22: 103-13.
PMID |
| 47. | Feng Z, Bao S, Kong L, Chen X. MicroRNA-378 inhibits hepatocyte apoptosis during acute liver failure by targeting caspase-9 in mice. Gastroenterol Hepatol 2023; 46: 124-34. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

