Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (5): 998-1008.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2025.05.007
• Original Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of Chang’an decoction (肠安方) on ulcerative colitis by regulating T helper 17 cells and regulatory T cells via Rab27 in the p53/high mobility group box 1 pathway
ZHENG Li1, JIN Ting1, WANG Xiaojing2, WANG Yingqi1, LIU Fengbin2,3,4, MI Hong2( )
)
- 1 the First Clinical College, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, China
2 Department of Gastroenterology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, China
3 Department of Gastroenterology, Baiyun Hospital of the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, China
4 Lingnan Medical Research Centre, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, China
-
Received:2024-08-22Accepted:2025-01-12Online:2025-10-15Published:2025-09-15 -
Contact:MI Hong, Department of Gastroenterology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, China. mihong1123@163.com, Telephone: +86-20-18702090846 -
Supported by:Lingnan Medical Research Center of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine;National Natural Science Foundation of China: Mechanism of Chang’an Decoction in Intestinal Mucosal Immunity of Ulcerative Colitis on Exocrine Mediated Rab27(81903963);Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province: the Role of the Neuropeptide Spexin-associated Gycogen Synthase Kinase-3β Signaling Pathway in Regulating the Enteric Nervous-immune Network in Ulcerative Colitis and the Intervention Mechanism of Chang’an Formula(2018A030310614)
Cite this article
ZHENG Li, JIN Ting, WANG Xiaojing, WANG Yingqi, LIU Fengbin, MI Hong. Effect of Chang’an decoction (肠安方) on ulcerative colitis by regulating T helper 17 cells and regulatory T cells via Rab27 in the p53/high mobility group box 1 pathway[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(5): 998-1008.
share this article
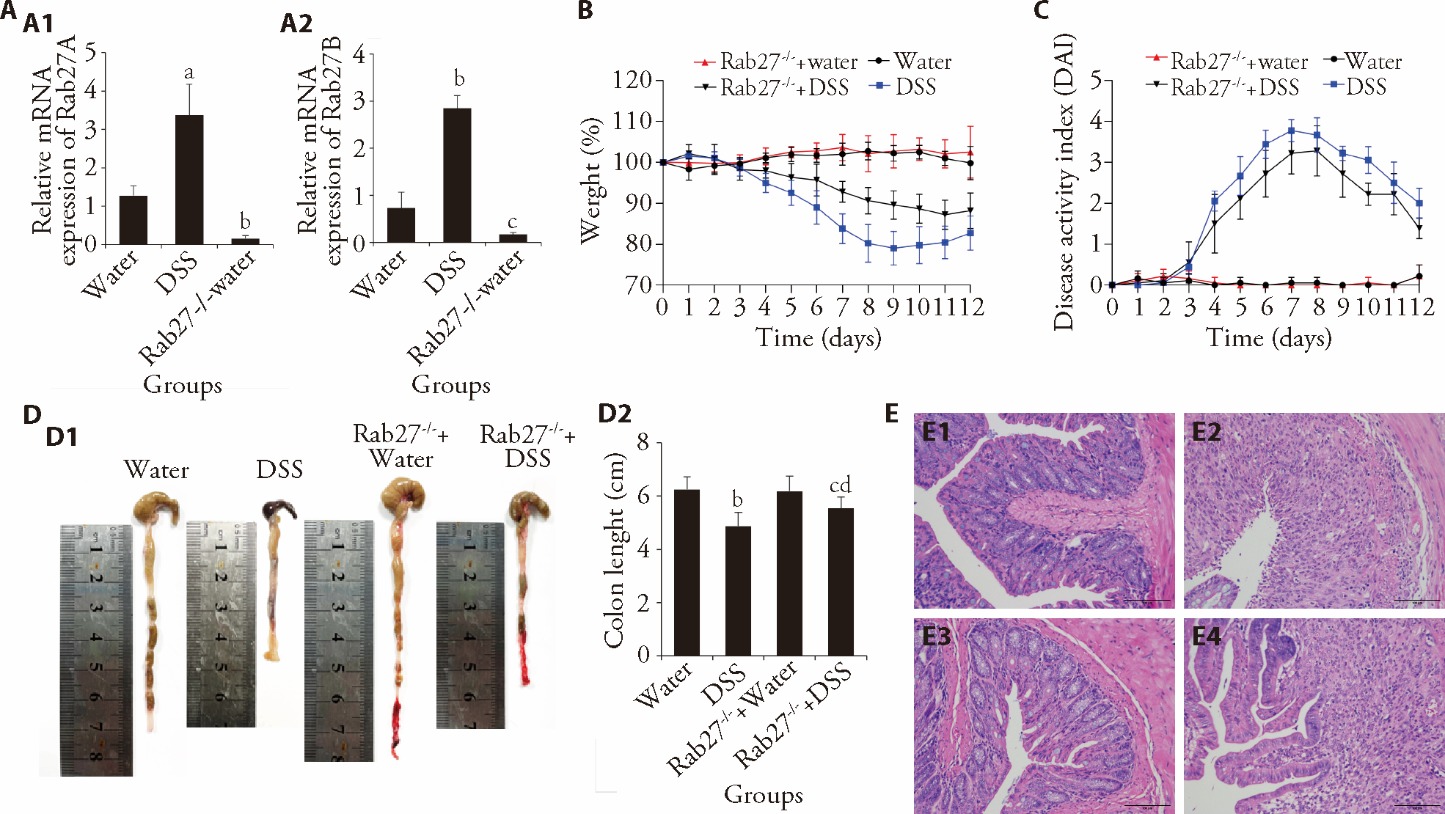
Figure 1 The intestinal inflammation of DSS-induced mice could be alleviated by Rab27 knockout A: mRNA expression (n = 3); A1: Rab27A; A2: Rab27B; B: weight change (n = 6); C: DAI scores (n = 6); D: colon length (n = 6); D1: measurement of the colon; D2: statistical graph of colon length; E: HE staining (scale bar: 100 μm × 200); E1: Water; E2: DSS; E3: Rab27-/-+Water; E4: Rab27-/-+DSS; Water: control group; DSS: ulcerative colitis group; Rab27-/-+Water: Rab27 knock out mice with normal drinking water; Rab27-/-+DSS: Rab27 knock out mice with ulcerative colitis. DAI: disease activity index; HE: hematoxylin and eosin. One-way analysis of variance was utilized. Results are presented as mean ± standard deviation. aP < 0.01, cP < 0.05 vs water; bP < 0.001, dP < 0.05 vs DSS.

Figure 2 Th17/Treg cell balance could be regulated by CAD A: number of Th17 and Treg cells in mesenteric lymph nodes (n = 3); A1:Th17 cells in the Water group; A2: Th17 cells in the DSS group; A3: Th17 cells in the DSS + CAD group; A4: Treg cells in the Water group; A5: Treg cells in the DSS group; A6: Treg cells in the DSS + CAD group; A7: statistical graph of Th17 cells; A8: statistical graph of Treg cells; B: protein expressions of RORγt and Foxp3 in colon tissues (n = 3); B1: protein band; B2: statistical graph of RORγt; B3: statistical graph of Foxp3; C: immunofluorescence results of RORγt and Foxp3 in colon tissues (scale bars: 100 μm × 200); C1: RORγt in the Water group; C2: RORγt in the DSS group; C3: RORγt in the DSS + CAD group; C4: Foxp3 in the Water group; C5: Foxp3 in the DSS group; C6: Foxp3 in the DSS + CAD group; CAD-H: high-dose Chang’an decoction (26 g·kg-1·d-1); Water: control group; DSS: ulcerative colitis group; DSS + CAD: ulcerative colitis mice with high-dose Chang’an decoction (26 g·kg-1·d-1); CAD: Chang’an decoction. The drug was administered for 6 d. Th17: T helper 17 cells; Treg: regulatory T cells; UC: ulcerative colitis; RORγt: RAR-related orphan receptor γt; Foxp3: forkhead box protein 3; MLNs: mesenteric lymph nodes. One-way analysis of variance was utilized. Results are presented as mean ± standard deviation. aP < 0.01, cP < 0.001 vs water; bP < 0.01, dP < 0.05, eP < 0.001 vs DSS.
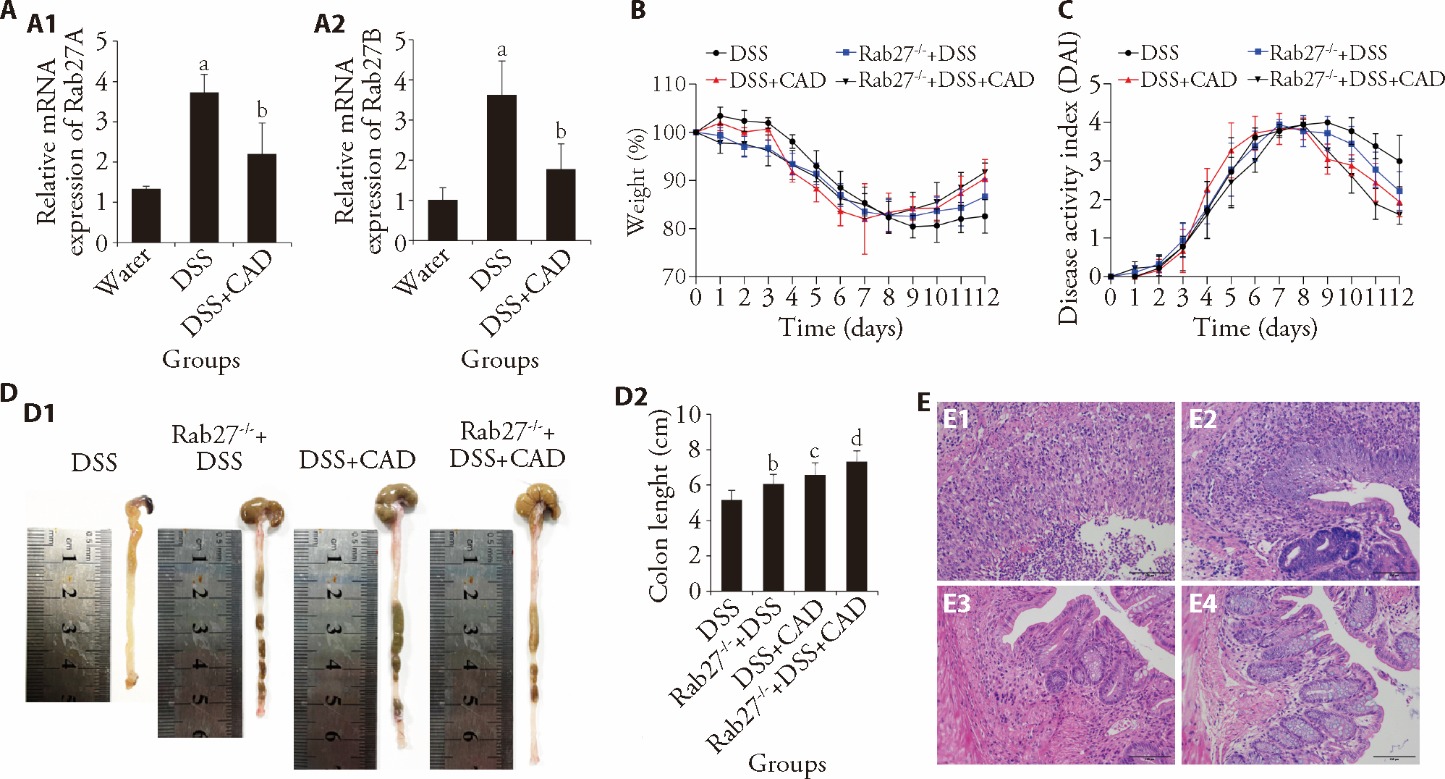
Figure 3 The inflammation of DSS-induced mice could be alleviated by CAD via affecting Rab27 A: mRNA expression (n = 3); A1: Rab27A; A2: Rab27B; B: weight change (n = 6); C: DAI scores (n = 6); D: colon length (n = 6); D1: measurement of colon; D2: statistical graph of colon length; E: HE staining (scale bar: 100 μm × 200); E1: DSS; E2: Rab27-/- + DSS; E3: DSS + CAD; E4: Rab27-/- + DSS + CAD; DSS: ulcerative colitis group; Rab27-/- + DSS: Rab27 knock out mice with ulcerative colitis; DSS + CAD: ulcerative colitis mice with high-dose Chang’an decoction (26 g·kg-1·d-1); Rab27-/- + DSS + CAD: Rab27 knock out mice with ulcerative colitis were given high-dose Chang’an decoction (26 g·kg-1·d-1); CAD: Chang’an decoction. The drug was administered for 6 d. DAI: disease activity index; HE: hematoxylin and eosin; PCR: polymerase chain reaction. One-way analysis of variance was utilized. Results are presented as mean ± standard deviation. aP < 0.01 vs water, bP < 0.05 vs DSS, cP < 0.01 vs DSS, dP < 0.001 vs DSS.
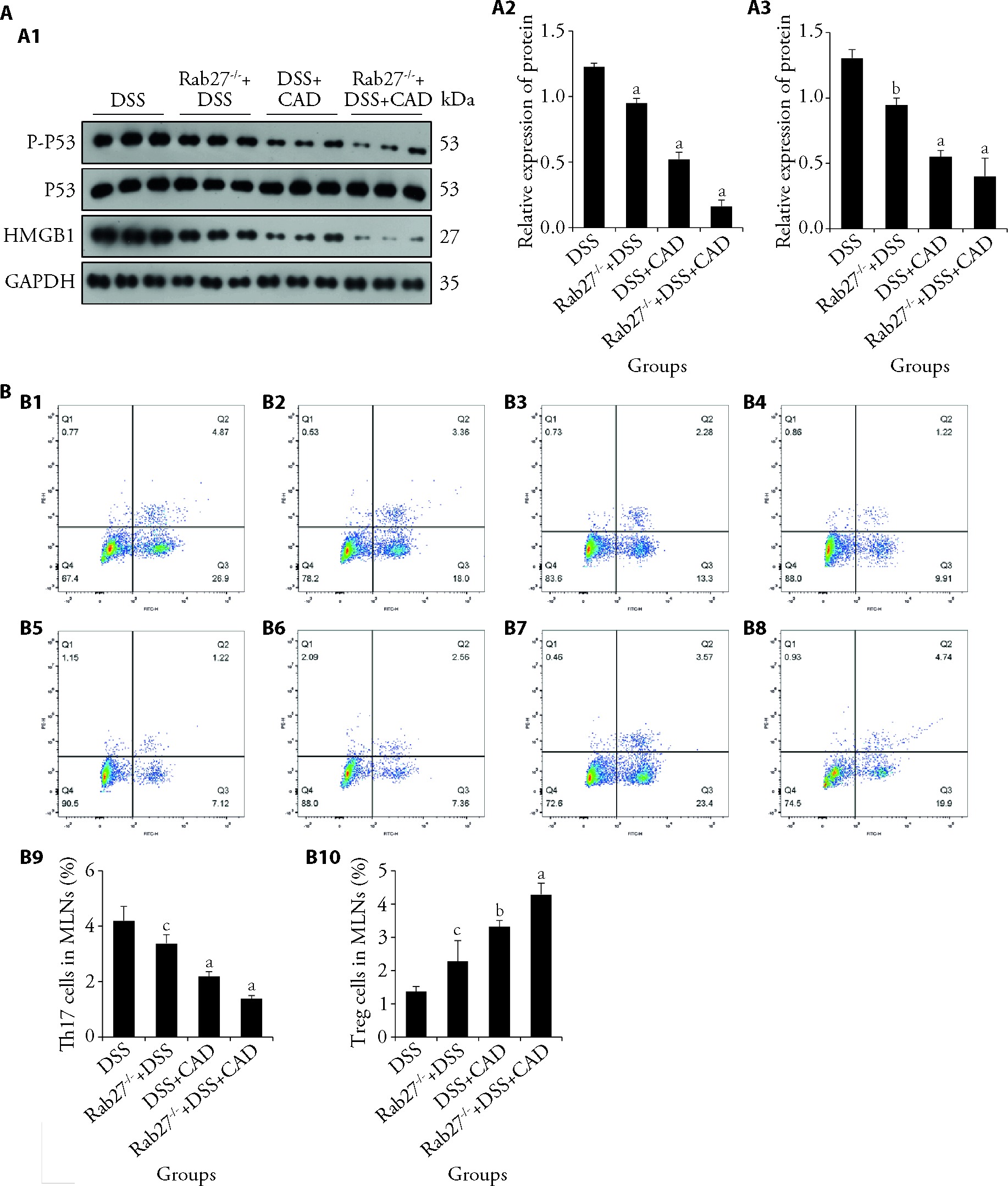
Figure 4 Th17/Treg balance could be regulated by CAD via effecting Rab27 in P53/HMGB1 pathway A: protein expression levels of P-P53, P53 and HMGB1 in colon tissues (n = 3); A1: protein band; A2: statistical graph of HMGB1; A3: statistical graph of P-P53; B: number of Th17 and Treg cells in mesenteric lymph nodes of each group (n = 3). B1:Th17 cells in the DSS group; B2: Th17 cells in the Rab27-/- + DSS group; B3: Th17 cells in the DSS + CAD group; B4: Th17 cells in the Rab27-/- + DSS + CAD group; B5: Treg cells in the DSS group; B6: Treg cells in the Rab27-/- + DSS group; B7: Treg cells in the DSS + CAD group; B8: Treg cells in the Rab27-/- + DSS + CAD group; B9: statistical graph of Th17 cells; B10: statistical graph of Treg cells; DSS: ulcerative colitis group; Rab27-/- + DSS: Rab27 knock out mice with ulcerative colitis; DSS + CAD: ulcerative colitis mice with high-dose Chang’an decoction (26 g·kg-1·d-1); Rab27-/- + DSS + CAD: Rab27 knock out mice with ulcerative colitis were given high-dose Chang’an decoction (26 g·kg-1·d-1); CAD: Chang’an decoction (26 g·kg-1·d-1). The drug was administered for 6 d. HMGB1: high mobility group box 1; P-P53: phospho- P53; IL-17: interleukin 17; IL-21: interleukin 21; IL-22: interleukin 22; TGF-β: transforming growth factor β; IL-10: interleukin 10; PCR: polymerase chain reaction; MLNs: mesenteric lymph nodes; UC: ulcerative colitis; Th17: T helper 17 cells; Treg: regulatory T cells; NF-κB: nuclear factor kappa-B. One-way analysis of variance was utilized. Results are presented as mean ± standard deviation. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001 vs DSS.
| 1. | Wei YY, Fan YM, Ga Y, et al. Shaoyao decoction attenuates DSS-induced ulcerative colitis, macrophage and NLRP 3 inflammasome activation through the MKP1/NF-kappa B pathway. Phytomedicine 2021; 92: 153743. |
| 2. | Deng B, Liao F, Liu Y, et al. Comprehensive analysis of endoplasmic reticulum stress-associated genes signature of ulcerative colitis. Front Immunol 2023; 14: 1158648. |
| 3. |
Wu Y, Liu X, Li G. Integrated bioinformatics and network pharmacology to identify the therapeutic target and molecular mechanisms of Huangqin decoction on ulcerative Colitis. Sci Rep 2022; 12: 159.
DOI PMID |
| 4. | Wu J, Luo Y, Shen Y, et al. Integrated metabonomics and network pharmacology to reveal the action mechanism effect of Shaoyao decoction on ulcerative colitis. Drug Des Devel Ther 2022; 16: 3739-76. |
| 5. |
Alexander M, Hu R, Runtsch MC, et al. Exosome-delivered microRNAs modulate the inflammatory response to endotoxin. Nat Commun 2015; 6: 7321.
DOI PMID |
| 6. |
Koh HM, Jang BG, Kim DC. Prognostic significance of Rab27 expression in solid cancer: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. Sci Rep 2020; 10: 14136.
DOI PMID |
| 7. | Wang H, Teng J, Wang M, et al. Expression and significant roles of the lncRNA NEAT1/miR-493-5p/Rab27A axis in ulcerative colitis. Immun Inflamm Dis 2023; 11: e814. |
| 8. |
Brusilovsky M, Rochman M, Azouz NP, et al. Uncovering the secretes of allergic inflammation. J Clin Invest 2020; 130: 3419-21.
DOI PMID |
| 9. |
Alexander M, Ramstead AG, Bauer KM, et al. Rab27-dependent exosome production inhibits chronic inflammation and enables acute responses to inflammatory stimuli. J Immunol 2017; 199: 3559-70.
DOI PMID |
| 10. | Luo Y, Yu MH, Yan YR, et al. Rab27A promotes cellular apoptosis and ROS production by regulating the miRNA-124-3p/STAT3/RelA signalling pathway in ulcerative colitis. J Cell Mol Med 2020; 24: 11330-42. |
| 11. | Pellegrini L, Foglio E, Pontemezzo E, et al. HMGB1 and repair: focus on the heart. Pharmacol Ther 2019; 196: 160-82. |
| 12. | Moraes TR, Veras FP, Barchuk AR, et al. Spinal HMGB 1 participates in the early stages of paclitaxel-induced neuropathic pain via microglial TLR4 and RAGE activation. Front Immunol 2024; 15: 1303937. |
| 13. | Vitali R, Mancuso AB, Palone F, et al. PARP 1 activation induces HMGB1 secretion promoting intestinal inflammation in mice and human intestinal organoids. Int J Mol Sci 2023; 24: 7096. |
| 14. |
Chen J, Lu P, Liu J, et al. 20(S)- Protopanaxadiol saponins isolated from Panax notoginseng target the binding of HMGB1 to TLR4 against inflammation in experimental ulcerative colitis. Phytother Res 2023; 37: 4690-705.
DOI PMID |
| 15. | Mi H, Liu FB, Li HW, et al. Anti-inflammatory effect of Chang-An-Shuan on TNBS-induced experimental colitis in rats. BMC Complement Altern Med 2017; 17: 315. |
| 16. | Ma H, Zhou M, Duan W, et al. Anemoside B4 prevents acute ulcerative colitis through inhibiting of TLR4/NF-kappa B/MAPK signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol 2020; 87: 106794. |
| 17. |
Zhu L, Gu P, Shen H. Protective effects of berberine hydrochloride on DSS-induced ulcerative colitis in rats. Int Immunopharmacol 2019; 68: 242-51.
DOI PMID |
| 18. | Su J, Li C, Yu X, et al. Protective effect of pogostone on 2,4,6-trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid-induced experimental colitis via inhibition of T helper cell. Front Pharmacol 2017; 8: 829. |
| 19. |
Vancamelbeke M, Vanuytsel T, Farre R, et al. Genetic and transcriptomic bases of intestinal epithelial barrier dysfunction in inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2017; 23: 1718-29.
DOI PMID |
| 20. |
Youlan C, Mingming D, Chaoyuan H, et al. Chang'an decoction alleviates endoplasmic reticulum stress by regulating mitofusin 2 to improve colitis. J Tradit Chin Med 2024; 44: 427-36.
DOI |
| 21. |
Lyu Q, Shi C, Qiao S, et al. Alpinetin exerts anti-colitis efficacy by activating AhR, regulating miR-302/DNMT-1/CREB signals, and therefore promoting Treg differentiation. Cell Death Dis 2018, 9: 890.
DOI PMID |
| 22. |
Wu D, Zhang Y, Zou B, et al. Shaoyao decoction alleviates TNBS-induced ulcerative colitis by decreasing inflammation and balancing the homeostasis of Th17/Treg cells. BMC Complement Med Ther 2023; 23: 424.
DOI PMID |
| 23. | Liu B, Qian Y, Li Y, et al. Circulating levels of cytokines and risk of inflammatory bowel disease: evidence from genetic data. Front Immunol 2023; 14: 1310086. |
| 24. | Yang Y, Hua Y, Zheng H, et al. Biomarkers prediction and immune landscape in ulcerative colitis: findings based on bioinformatics and machine learning. Comput Biol Med 2024; 168: 107778. |
| 25. |
Swedik SM, Madola A, Cruz MA, et al. Th17-derived cytokines synergistically enhance IL-17C production by the colonic epithelium. J Immunol 2022; 209: 1768-77.
DOI PMID |
| 26. | Chen X, Zhang M, Zhou F, et al. SIRT 3 activator honokiol inhibits Th17 cell differentiation and alleviates colitis. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2023; 29: 1929-40. |
| 27. | Li X, Sun L, Chen L, Xu Y, et al. Upregulation of microRNA-219-5p relieves ulcerative colitis through balancing the differentiation of Treg/Th 17 cells. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2020; 32: 813-20. |
| 28. | Fan Y, Fan Y, Liu K, et al. Edible bird's nest ameliorates dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis in C57BL/6J mice by restoring the Th17/Treg Cell balance. Front Pharmacol 2021; 12: 632602. |
| 29. | Yu J, Wang S, Yuan H, et al. Expression of Th17/Treg cells in peripheral blood and related cytokines of patients with ulcerative colitis of different syndrome types and correlation with the disease. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2021; 2021: 4600947. |
| 30. | Xu AT, Lu JT, Ran ZH, et al. Exosome in intestinal mucosal immunity. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2016; 31: 1694-99. |
| 31. |
Yang L, Liu G, Lian K, et al. Dietary leonurine hydrochloride supplementation attenuates lipopolysaccharide challenge-induced intestinal inflammation and barrier dysfunction by inhibiting the NF-kappaB/MAPK signaling pathway in broilers. J Anim Sci 2019; 97: 1679-92.
DOI PMID |
| 32. |
Wei J, Chen C, Feng J, et al. Muc2 mucin O-glycosylation interacts with enteropathogenic Escherichia coli to influence the development of ulcerative colitis based on the NF-kB signaling pathway. J Transl Med 2023; 21: 793.
DOI PMID |
| 33. | Ciprandi G, Bellussi LM, Passali GC, et al. HMGB 1 in nasal inflammatory diseases: a reappraisal 30 years after its discovery. Expert Rev Clin Immunol 2020; 16: 457-63. |
| 34. | Wu Y, Zhao Y, Yang HZ, et al. HMGB 1 regulates ferroptosis through Nrf2 pathway in mesangial cells in response to high glucose. Biosci Rep 2021; 41: BSR20202924. |
| 35. | Ghoneim ME, Abdallah DM, Shebl AM, et al. The interrupted cross-talk of inflammatory and oxidative stress trajectories signifies the effect of artesunate against hepatic ischemia/reperfusion-induced inflammasomopathy. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 2020; 409: 115309. |
| 36. | Zha C, Meng X, Li L, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps mediate the crosstalk between glioma progression and the tumor microenvironment via the HMGB1/RAGE/IL-8 axis. Cancer Biol Med 2020; 17: 154-68. |
| 37. | Arab HH, Eid AH, Mahmoud AM, et al. Linagliptin mitigates experimental inflammatory bowel disease in rats by targeting inflammatory and redox signaling. Life Sci 2021; 273: 119295. |
| 38. | Liang WJ, Yang HW, Liu HN, et al. HMGB 1 upregulates NF-kB by inhibiting IKB-alpha and associates with diabetic retinopathy. Life Sci 2020; 241: 117146. |
| 39. | Sun T, Xu W, Wang J, et al. Paeonol ameliorates diabetic erectile dysfunction by inhibiting HMGB1/RAGE/NF-kB pathway. Andrology 2023; 11: 344-57. |
| 40. |
Chen D, Liang X, Zhang JJ, et al. Analysis of changes in high-mobility group box 1, receptor for advanced glycation endproducts, and T helper 17/regulatory T balance in severe preeclampsia with acute heart failure. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich) 2024; 26: 431-40.
DOI PMID |
| 41. | Mo J, Ni J, Zhang M, et al. Mulberry anthocyanins ameliorate DSS-induced ulcerative colitis by improving intestinal barrier function and modulating gut microbiota. Antioxidants (Basel) 2022; 11: 1674. |
| [1] | GAO Changjiu, DING Song, Shadi A.D. Mohammed, LU Fang, LIU Changfeng, TENG Zhan, XU Peng, LIU Shumin. Cardioprotective mechanism of Qixuan Yijianing (芪玄抑甲宁) formula in Graves’ disease mice using miRNA sequencing approach [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(6): 1127-1136. |
| [2] | ZHOU Hua, LI Hui, WANG Haihua. Potential protective effects of the water-soluble Chinese propolis on experimental ulcerative colitis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 925-933. |
| [3] | WANG Bochuan, ZHANG Yong, ZHANG Qiuyun, ZHANG Zhiqiang, LUO Changyong, WANG Zhendong, BAI Chen, WANG Yuhan, GE Xueyi, QIAN Ying, YU He, GU Xiaohong. Reveal the mechanisms of prescriptions for liver cancer' treatment based on two illustrious senior TCM physicians [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(1): 188-197. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

