Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (2): 289-302.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20240203.007
Previous Articles Next Articles
Efficacy of Sailuotong (塞络通) on neurovascular unit in amyloid precursor protein/presenilin-1 transgenic mice with Alzheimer’s disease
SUN Linjuan1, LI Chengfu2, LIU Jiangang1, LI Nannan1, HAN Fuhua5, QIAO Dandan1, TAO Zhuang4, ZHAN Min1, CHEN Wenjie1, ZHANG Xiaohui1, TONG Chenguang1, CHEN Dong1, Qi Jiangxia1, LIU Yang1, LIANG Xiao1, ZHENG Xiaoying3( ), ZHANG Yunling1(
), ZHANG Yunling1( )
)
- 1 Department of Neurology, Xiyuan Hospital, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100091, China
2 China Population and Development Research Center, Beijing 100081, China
3 Department of Institute of Population Research, Peking University, Beijing 100087, China
4 Graduate School of China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100700, China
5 Graduate School of Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100029, China
-
Received:2022-12-22Accepted:2023-04-08Online:2024-04-15Published:2024-03-05 -
Contact:ZHANG Yunling, Department of Neurology, Xiyuan Hospital, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100091, China.ling_zhangyun@yeah.net ; ZHENG Xiaoying, Department of Institute of Population Research, Peking University, Beijing 100087, China.zhengxiaoying@sph.pumc.edu.cn Telephone: +86-13910764257 -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China: Experimental study on the treatment of transgenic mice with Alzheimer's disease by protecting neurovascular unit by supplementing Qi and activating blood circulation investigate(81503450)
Cite this article
SUN Linjuan, LI Chengfu, LIU Jiangang, LI Nannan, HAN Fuhua, QIAO Dandan, TAO Zhuang, ZHAN Min, CHEN Wenjie, ZHANG Xiaohui, TONG Chenguang, CHEN Dong, Qi Jiangxia, LIU Yang, LIANG Xiao, ZHENG Xiaoying, ZHANG Yunling. Efficacy of Sailuotong (塞络通) on neurovascular unit in amyloid precursor protein/presenilin-1 transgenic mice with Alzheimer’s disease[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(2): 289-302.
share this article
| Group | Dose (mg·kg-1·d-1) | n | Number of crossings | Swimming time (s) | Swimming distance (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C57 sham-operated | - | 16 | 7.1±1.3 | 46.9±12.2 | 318.3±89.2 |
| C57 ischemia | - | 16 | 5.2±1.3a | 39.1±10.4a | 252.1±101.4a |
| APP/PS1 model | - | 16 | 4.2±2.1a | 37.2± 9.9a | 275.2±97.3e |
| APP/PS1 ischemia | - | 16 | 3.4±1.7a | 33.0±11.2a | 237.2±98.3e |
| C57BL ischaemic + aspirin | 32 | 16 | 6.1±1.7b | 45.4±12.4b | 198.3±124.8b |
| C57BL ischaemic + SLT | 32 | 16 | 6.4±1.7b | 43.3±13.4b | 298.2±69.9f |
| APP/PS1 + SLT | 32 | 16 | 5.7±2.1c | 46.3±9.3d | 305.3±89.5d |
| APP/PS1 ischaemic + donepezil hydrochloride | 20 | 16 | 5.3±2.2c | 45.5±11.3c | 333.6±76.7c |
| APP/PS1 ischaemic + SLT | 32 | 16 | 6.8±2.2f | 44.2±8.0f | 341.3±81.1f |
Table 1 Effect of the method of replenishing Qi and activating blood on the spatial learning and memory ability of APP/PS1 double transgenic ischemic mice ($\bar{x}±s$)
| Group | Dose (mg·kg-1·d-1) | n | Number of crossings | Swimming time (s) | Swimming distance (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C57 sham-operated | - | 16 | 7.1±1.3 | 46.9±12.2 | 318.3±89.2 |
| C57 ischemia | - | 16 | 5.2±1.3a | 39.1±10.4a | 252.1±101.4a |
| APP/PS1 model | - | 16 | 4.2±2.1a | 37.2± 9.9a | 275.2±97.3e |
| APP/PS1 ischemia | - | 16 | 3.4±1.7a | 33.0±11.2a | 237.2±98.3e |
| C57BL ischaemic + aspirin | 32 | 16 | 6.1±1.7b | 45.4±12.4b | 198.3±124.8b |
| C57BL ischaemic + SLT | 32 | 16 | 6.4±1.7b | 43.3±13.4b | 298.2±69.9f |
| APP/PS1 + SLT | 32 | 16 | 5.7±2.1c | 46.3±9.3d | 305.3±89.5d |
| APP/PS1 ischaemic + donepezil hydrochloride | 20 | 16 | 5.3±2.2c | 45.5±11.3c | 333.6±76.7c |
| APP/PS1 ischaemic + SLT | 32 | 16 | 6.8±2.2f | 44.2±8.0f | 341.3±81.1f |
| Group | Dose (mg·kg-1·d-1) | n | Number of errors (times) | Incubation period (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C57 sham-operated | - | 15 | 1.3±1.2 | 226.5±53.1 |
| C57 ischemia | - | 15 | 2.2±1.4a | 179.2±55.3a |
| APP/PS1 model | - | 14 | 2.6±1.3 | 167.7±61.2a |
| APP/PS1 ischemia | - | 15 | 3.1±1.7a | 156.8±54.9a |
| C57BL ischaemic + aspirin | 32 | 15 | 1.3±1.3 | 217.5±64.4 |
| C57BL ischaemic + SLT | 32 | 15 | 1.2±1.5b | 226.8±66.2b |
| APP/PS1 + SLT | 32 | 14 | 1.5±1.1c | 213.4±49.8d |
| APP/PS1 ischaemic + donepezil hydrochloride | 20 | 15 | 1.5±1.6c | 206.2±73.6e |
| APP/PS1 ischaemic + SLT | 32 | 16 | 1.6±1.5c | 239.5±62.5e |
Table 2 Effect of the method of replenishing Qi and activating blood on step-down test of APP/PS1 double transgenic ischemic mice ($\bar{x}±s$)
| Group | Dose (mg·kg-1·d-1) | n | Number of errors (times) | Incubation period (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C57 sham-operated | - | 15 | 1.3±1.2 | 226.5±53.1 |
| C57 ischemia | - | 15 | 2.2±1.4a | 179.2±55.3a |
| APP/PS1 model | - | 14 | 2.6±1.3 | 167.7±61.2a |
| APP/PS1 ischemia | - | 15 | 3.1±1.7a | 156.8±54.9a |
| C57BL ischaemic + aspirin | 32 | 15 | 1.3±1.3 | 217.5±64.4 |
| C57BL ischaemic + SLT | 32 | 15 | 1.2±1.5b | 226.8±66.2b |
| APP/PS1 + SLT | 32 | 14 | 1.5±1.1c | 213.4±49.8d |
| APP/PS1 ischaemic + donepezil hydrochloride | 20 | 15 | 1.5±1.6c | 206.2±73.6e |
| APP/PS1 ischaemic + SLT | 32 | 16 | 1.6±1.5c | 239.5±62.5e |
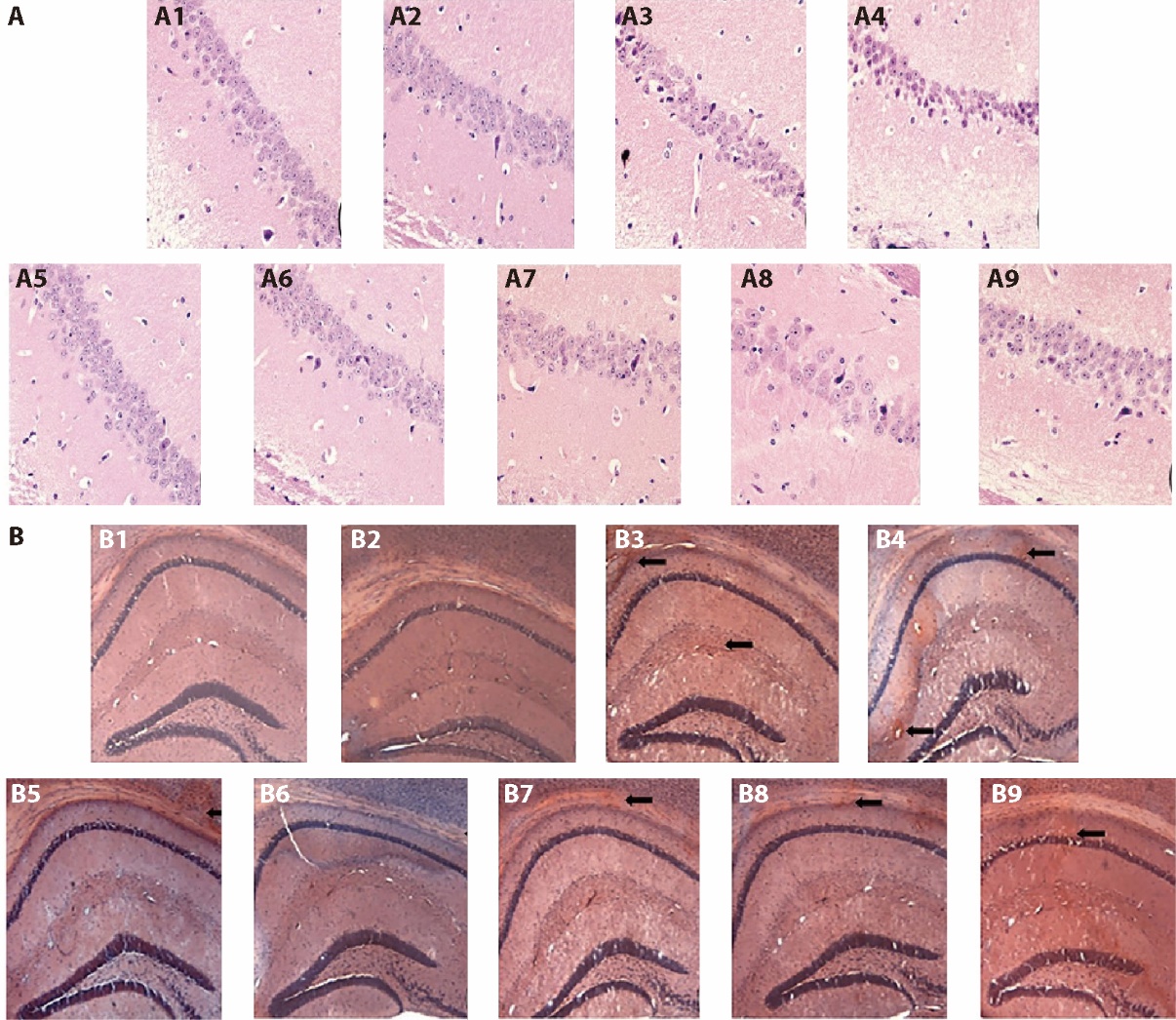
Figure 1 Effect of replenishing Qi and activating blood on pathological morphology and amyloid in the brain of APP/PS1 double transgenic ischemic mice A: HE pathological staining × 400; B: Congo red staining × 40. A1/B1: C57 sham-operated group; A2/B2: C57 ischemia group; A3/B3: APP/PS1 model group; A4/B4: APP/PS1 ischemia group; A5/B5: C57BL ischaemic + aspirin group at dose of 20 mg·kg-1·d-1 A6/B6: C57BL ischaemic + SLT group at dose of 32 mg·kg-1·d-1; A7/B7: APP/PS1 + SLT group at dose of 32 mg·kg-1·d-1; A8/B8: APP/PS1 ischaemic + donepezil hydrochloride group at dose of 32 mg·kg-1·d-1; A9/B9: APP/PS1 ischaemic + SLT group at dose of 32 mg·kg-1·d-1. Ischaemic treatment: both right and left common carotid arteries were separated, and the arterial blood vessel was stimulated with a temperature-controlled current of 80 mu A using an in vivo thrombometer to cause thrombosis. Duration: two months. SLT: Sailuotong; APP: amyloid precursor protein; PS1: presenilin-1presenilin-1.
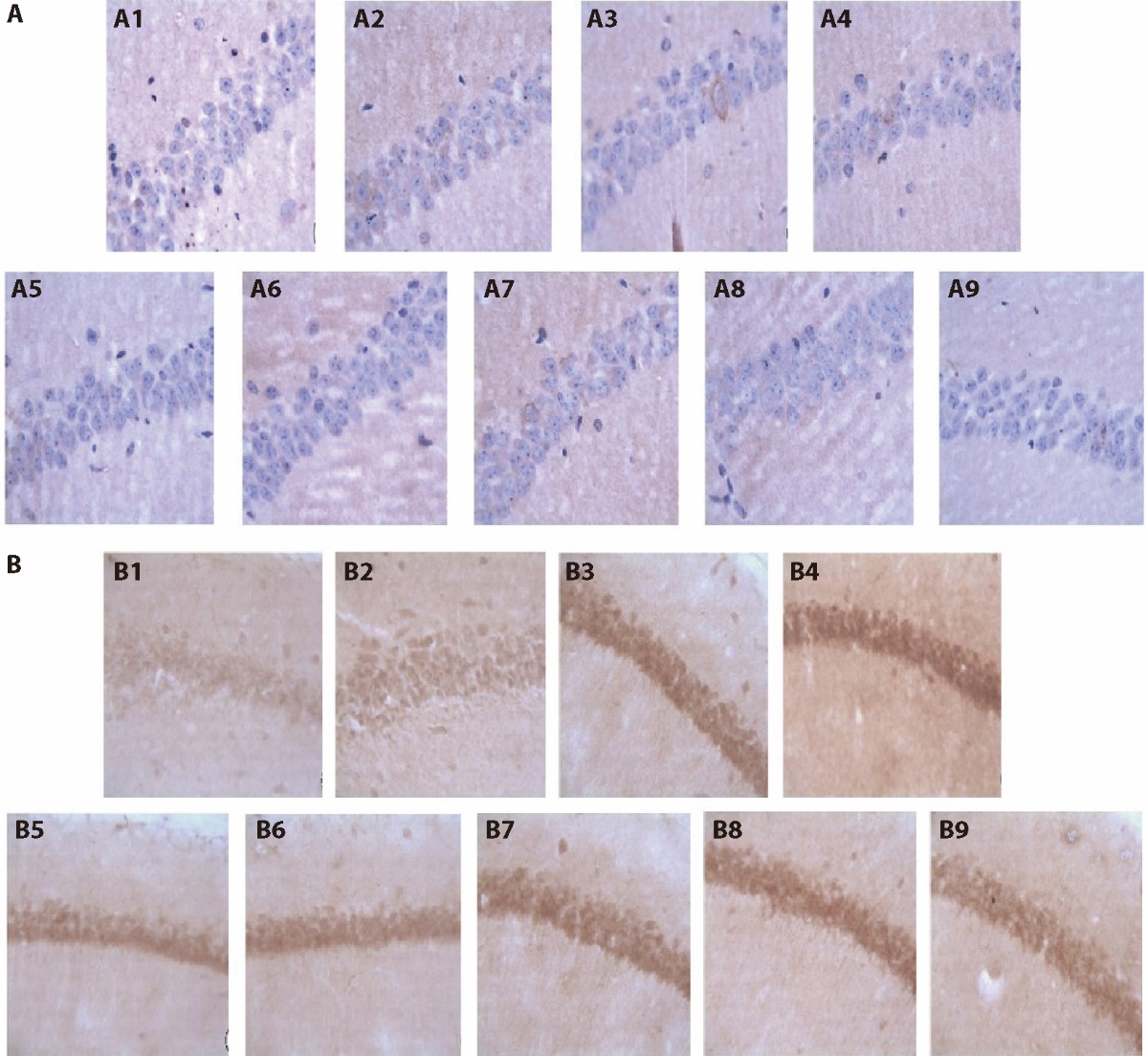
Figure 2 Effects of Invigorating Qi and Activating blood circulation on APP and Aβ1-42 brain tissue of APP/PS1 double transgenic ischemic mice A: APP positive expression × 400; B: Aβ1-42 positive expression × 400. A1/B1: C57 sham-operated group; A2/B2: C57 ischemia group; A3/B3: APP/PS1 model group; A4/B4: APP/PS1 ischemia group; A5/B5: C57BL ischaemic + aspirin group at dose of 20 mg·kg-1·d-1 A6/B6: C57BL ischaemic + SLT group at dose of 32 mg·kg-1·d-1; A7/B7: APP/PS1 + SLT group at dose of 32 mg·kg-1·d-1; A8/B8: APP/PS1 ischaemic + donepezil hydrochloride group at dose of 32 mg·kg-1·d-1; A9/B9: APP/PS1 ischaemic + SLT group at dose of 32 mg·kg-1·d-1. Ischaemic treatment: both right and left common carotid arteries were separated, and the arterial blood vessel was stimulated with a temperature-controlled current of 80 mu A using an in vivo thrombometer to cause thrombosis. Duration: two months. SLT: Sailuotong; APP: amyloid precursor protein; PS1: presenilin-1presenilin-1.
| Group | Dose (mg/kg·d) | Visual field number (n) | APP | Aβ1-42 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C57 sham-operated | - | 12 | 1.15±0.5 | 3.75±1.2 |
| C57 ischemia | - | 12 | 1.46±0.5 | 8.12±1.0d |
| APP/PS1 model | - | 12 | 5.53±0.8a | 19.12±5.2d |
| APP/PS1 ischemia | - | 12 | 9.77±0.6a | 31.43±9.2a |
| C57BL ischaemic + aspirin | 32 | 12 | 1.28±0.4 | 7.18±3.2 |
| C57BL ischaemic + SLT | 32 | 12 | 1.14±0.5 | 5.12±4.4e |
| APP/PS1 + SLT | 32 | 12 | 3.38±0.5b | 14.38±5.4b |
| APP/PS1 ischaemic + donepezil hydrochloride | 20 | 12 | 6.23±0.6c | 16.24±6.4c |
| APP/PS1 ischaemic + SLT | 32 | 12 | 7.18±0.4c | 19.38±6.0c |
Table 3 Effect of replenishing Qi and activating blood on APP and Aβ1-42 expression in hippocampal CA1 region of APP/PS1 double transgenic ischemic mice ($\bar{x}±s$)
| Group | Dose (mg/kg·d) | Visual field number (n) | APP | Aβ1-42 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C57 sham-operated | - | 12 | 1.15±0.5 | 3.75±1.2 |
| C57 ischemia | - | 12 | 1.46±0.5 | 8.12±1.0d |
| APP/PS1 model | - | 12 | 5.53±0.8a | 19.12±5.2d |
| APP/PS1 ischemia | - | 12 | 9.77±0.6a | 31.43±9.2a |
| C57BL ischaemic + aspirin | 32 | 12 | 1.28±0.4 | 7.18±3.2 |
| C57BL ischaemic + SLT | 32 | 12 | 1.14±0.5 | 5.12±4.4e |
| APP/PS1 + SLT | 32 | 12 | 3.38±0.5b | 14.38±5.4b |
| APP/PS1 ischaemic + donepezil hydrochloride | 20 | 12 | 6.23±0.6c | 16.24±6.4c |
| APP/PS1 ischaemic + SLT | 32 | 12 | 7.18±0.4c | 19.38±6.0c |
| Group | Dose (mg·kg-1·d-1) | n | Aβ |
|---|---|---|---|
| C57 sham-operated | - | 10 | 0.79±0.25 |
| C57 ischemia | - | 10 | 1.06±0.16 |
| APP/PS1 model | - | 10 | 1.22±0.27a |
| APP/PS1 ischemia | - | 10 | 1.52±0.13b |
| C57BL ischaemic + aspirin | 32 | 10 | 0.75±0.29 |
| C57BL ischaemic + SLT | 32 | 10 | 0.79±0.29 |
| APP/PS1 + SLT | 32 | 10 | 0.75±0.29 |
| APP/PS1 ischaemic + donepezil hydrochloride | 20 | 10 | 0.82±0.30c |
| APP/PS1 ischaemic + SLT | 32 | 10 | 0.79±0.26c |
Table 4 Effect of replenishing Qi and activating blood on Aβ protein content in the cerebrospinal fluid in APP/PS1 double transgenic ischemic mice of each group (ng/mL, $\bar{x}±s$)
| Group | Dose (mg·kg-1·d-1) | n | Aβ |
|---|---|---|---|
| C57 sham-operated | - | 10 | 0.79±0.25 |
| C57 ischemia | - | 10 | 1.06±0.16 |
| APP/PS1 model | - | 10 | 1.22±0.27a |
| APP/PS1 ischemia | - | 10 | 1.52±0.13b |
| C57BL ischaemic + aspirin | 32 | 10 | 0.75±0.29 |
| C57BL ischaemic + SLT | 32 | 10 | 0.79±0.29 |
| APP/PS1 + SLT | 32 | 10 | 0.75±0.29 |
| APP/PS1 ischaemic + donepezil hydrochloride | 20 | 10 | 0.82±0.30c |
| APP/PS1 ischaemic + SLT | 32 | 10 | 0.79±0.26c |

Figure 3 Effect of the method of replenishing Qi and activating blood on the ultrastructure of hippocampus and cortical blood vessels in APP/PS1 double transgenic ischemic mice A: ultrastructure of brain tissue hippocampus; B: ultrastructure of cortical blood vessels. Scale bars = 500 nm. A1/B1: C57 sham-operated group; A2/B2: C57 ischemia group; A3/B3: APP/PS1 model group; A4/B4: APP/PS1 ischemia group; A5/B5: C57BL ischaemic + aspirin group at dose of 20 mg·kg-1·d-1 A6/B6: C57BL ischaemic + SLT group at dose of 32 mg·kg-1·d-1; A7/B7: APP/PS1 + SLT group at dose of 32 mg·kg-1·d-1; A8/B8: APP/PS1 ischaemic + donepezil hydrochloride group at dose of 32 mg·kg-1·d-1; A9/B9: APP/PS1 ischaemic + SLT group at dose of 32 mg·kg-1·d-1. Ischaemic treatment: both right and left common carotid arteries were separated, and the arterial blood vessel was stimulated with a temperature-controlled current of 80 mu A using an in vivo thrombometer to cause thrombosis. Duration: two months. SLT: Sailuotong; APP: amyloid precursor protein; PS1: presenilin-1.
| Group | n | VEGF | Ang | bFGF |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C57 sham-operated | 10 | 9.6±1.2 | 1.6±0.5 | 6.4±2.1 |
| C57 ischemia | 10 | 12.4±2.4a | 1.5±0.2 | 6.6±0.5 |
| APP/PS1 model | 10 | 6.8±1.7a | 1.2±0.8 | 5.8±2.4 |
| APP/PS1 ischemia | 10 | 10.5±3.0 | 1.4±0.5 | 5.6±1.6 |
| C57BL ischaemic + aspirin | 10 | 10.4±2.3 | 1.9±0.6 | 8.7±2.5 |
| C57BL ischaemic + SLT | 10 | 14.3±1.5b | 2.9±0.7b | 9.6±2.5b |
| APP/PS1 + SLT | 10 | 13.6±4.1c | 1.9±0.7 | 9.8±1.6 |
| APP/PS1 ischaemic + donepezil hydrochloride | 10 | 10.4±2.0c | 2.0±0.3c | 5.8±1.4 |
| APP/PS1 ischaemic + SLT | 10 | 13.7±1.3c | 2.0±0.4c | 7.0±1.9c |
Table 5 Effects of supplementing Qi and Activating blood circulation on VEGF, Ang, bFGF content in APP/PS1 double transgenic ischemic mice (ng/mg, $\bar{x}±s$)
| Group | n | VEGF | Ang | bFGF |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C57 sham-operated | 10 | 9.6±1.2 | 1.6±0.5 | 6.4±2.1 |
| C57 ischemia | 10 | 12.4±2.4a | 1.5±0.2 | 6.6±0.5 |
| APP/PS1 model | 10 | 6.8±1.7a | 1.2±0.8 | 5.8±2.4 |
| APP/PS1 ischemia | 10 | 10.5±3.0 | 1.4±0.5 | 5.6±1.6 |
| C57BL ischaemic + aspirin | 10 | 10.4±2.3 | 1.9±0.6 | 8.7±2.5 |
| C57BL ischaemic + SLT | 10 | 14.3±1.5b | 2.9±0.7b | 9.6±2.5b |
| APP/PS1 + SLT | 10 | 13.6±4.1c | 1.9±0.7 | 9.8±1.6 |
| APP/PS1 ischaemic + donepezil hydrochloride | 10 | 10.4±2.0c | 2.0±0.3c | 5.8±1.4 |
| APP/PS1 ischaemic + SLT | 10 | 13.7±1.3c | 2.0±0.4c | 7.0±1.9c |
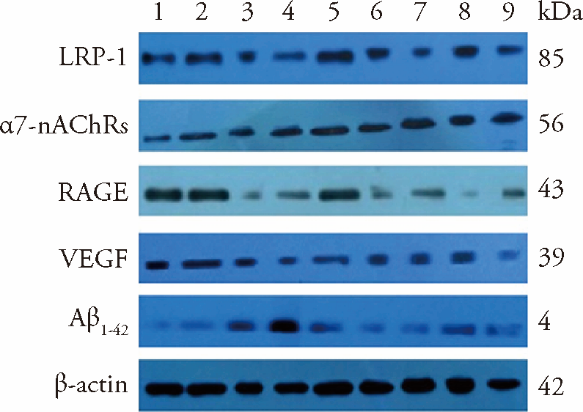
Figure 4 Effect of replenishing Qi and activating blood on the expression of related proteins in APP/PS1 ischemia model mice ($\bar{x}±s$, n = 10) 1: C57 sham-operated group; 2: C57 ischemia group; 3: APP/PS1 model group; 4: APP/PS1 ischemia group; 5: C57BL ischaemic + aspirin group at dose of 20 mg·kg-1·d-1; 6: C57BL ischaemic + SLT group at dose of 32 mg·kg-1·d-1; 7: APP/PS1 + SLT group at dose of 32 mg·kg-1·d-1; 8: APP/PS1 ischaemic + donepezil hydrochloride group at dose of 32 mg·kg-1·d-1; 9: APP/PS1 ischaemic + SLT group at dose of 32 mg·kg-1·d-1. Ischaemic treatment: both right and left common carotid arteries were separated, and the arterial blood vessel was stimulated with a temperature-controlled current of 80 mu A using an in vivo thrombometer to cause thrombosis. Duration: two months. SLT: Sailuotong; APP: amyloid precursor protein; PS1: presenilin-1.
| Group | n | VEGF | Aβ1-42 | α7-nAChRs | RAGE | LRP-1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C57 sham-operated | 10 | 1.000±0.172 | 1.000±0.073 | 1.000±0.131 | 1.000±0.074 | 1.000±0.203 |
| C57 ischemia | 10 | 1.710±0.088a | 0.930±0.122 | 1.410±0.153a | 1.052±0.091 | 0.970±0.072 |
| APP/PS1 model | 10 | 0.620±0.045a | 1.550±0.124d | 1.560±0.065a | 1.150±0.116 | 0.800±0.103 |
| APP/PS1 ischemia | 10 | 0.500±0.046a | 2.730±0.270a | 2.250±0.083a | 1.518±0.077a | 0.600±0.054d |
| C57BL ischaemic + aspirin | 10 | 1.330±0.022b | 1.040±0.111 | 1.380±0.142 | 1.050±0.062 | 1.160±0.104 f |
| C57BL ischaemic + SLT | 10 | 1.880±0.042 | 0.960±0.115 | 1.110±0.144 | 1.010±0.052 | 1.050±0.200 |
| APP/PS1 + SLT | 10 | 1.040±0.081c | 1.200±0.132c | 1.160±0.120c | 1.020±0.079c | 1.260±0.064c |
| APP/PS1 ischaemic + donepezil hydrochloride group | 10 | 0.580±0.084 | 1.560±0.127c | 1.250±0.256c | 1.230±0.075e | 1.180±0.085c |
| APP/PS1 ischaemic + SLT | 10 | 0.839±0.095c | 1.460±0.273c | 1.480±0.135ac | 1.240±0.151ac | 1.220±0.032c |
Table 6 Effect of replenishing Qi and activating blood on VEGF, Aβ1-42, α7-nAChRs, RAGE and LRP-1 protein content in the brain tissues in APP/PS1 double transgenic ischemic mice of each group ($\bar{x}±s$)
| Group | n | VEGF | Aβ1-42 | α7-nAChRs | RAGE | LRP-1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C57 sham-operated | 10 | 1.000±0.172 | 1.000±0.073 | 1.000±0.131 | 1.000±0.074 | 1.000±0.203 |
| C57 ischemia | 10 | 1.710±0.088a | 0.930±0.122 | 1.410±0.153a | 1.052±0.091 | 0.970±0.072 |
| APP/PS1 model | 10 | 0.620±0.045a | 1.550±0.124d | 1.560±0.065a | 1.150±0.116 | 0.800±0.103 |
| APP/PS1 ischemia | 10 | 0.500±0.046a | 2.730±0.270a | 2.250±0.083a | 1.518±0.077a | 0.600±0.054d |
| C57BL ischaemic + aspirin | 10 | 1.330±0.022b | 1.040±0.111 | 1.380±0.142 | 1.050±0.062 | 1.160±0.104 f |
| C57BL ischaemic + SLT | 10 | 1.880±0.042 | 0.960±0.115 | 1.110±0.144 | 1.010±0.052 | 1.050±0.200 |
| APP/PS1 + SLT | 10 | 1.040±0.081c | 1.200±0.132c | 1.160±0.120c | 1.020±0.079c | 1.260±0.064c |
| APP/PS1 ischaemic + donepezil hydrochloride group | 10 | 0.580±0.084 | 1.560±0.127c | 1.250±0.256c | 1.230±0.075e | 1.180±0.085c |
| APP/PS1 ischaemic + SLT | 10 | 0.839±0.095c | 1.460±0.273c | 1.480±0.135ac | 1.240±0.151ac | 1.220±0.032c |
| Group | n | VEGF | APP | α7-nAChRs | RAGE | LRP-1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C57 sham-operated | 10 | 0.800±0.150 | 0.720±0.392 | 1.200±0.291 | 1.090±0.392 | 1.160±0.713 |
| C57 ischemia | 10 | 1.450±0.730a | 0.680±5.254 | 1.120±3.022 | 0.730±2.991 | 1.570±0.959a |
| APP/PS1 model | 10 | 0.180±0.080a | 1.070±0.045a | 0.190±0.040a | 2.090±0.031a | 0.380±0.191a |
| APP/PS1 ischemia | 10 | 0.540±0.481a | 2.730±1.132a | 0.320±0.903a | 2.670±0.675a | 0.850±1.052a |
| C57BL ischaemic + aspirin | 10 | 0.860±0.421b | 0.680±5.250 | 0.400±0.212d | 0.480±0.214b | 1.380±2.053b |
| C57BL ischaemic + SLT | 10 | 1.490±0.111 | 0.150±0.190d | 0.320±0.192d | 0.110±0.091d | 1.250±0.312c |
| APP/PS1 + SLT | 10 | 0.630±0.450c | 0.580±0.626 | 0.700±0.580 | 0.501±0.455 | 1.680±0.523e |
| APP/PS1 ischaemic + donepezil hydrochloride | 10 | 0.160±0.121 | 0.420±0.480 | 0.630±0.002 | 1.240±0.244 | 1.490±0.422e |
| APP/PS1 ischaemic + SLT | 10 | 0.930±0.345c | 0.690±0.242 | 1.180±1.591 | 2.090±0.915 | 1.420±0.560e |
Table 7 Effect of replenishing Qi and activating blood on mRNA expressions of VEGF, APP, α7-nAChRs, RAGE and LRP-1 in APP/PS1 double transgenic ischemic mice of each group ($\bar{x}±s$)
| Group | n | VEGF | APP | α7-nAChRs | RAGE | LRP-1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C57 sham-operated | 10 | 0.800±0.150 | 0.720±0.392 | 1.200±0.291 | 1.090±0.392 | 1.160±0.713 |
| C57 ischemia | 10 | 1.450±0.730a | 0.680±5.254 | 1.120±3.022 | 0.730±2.991 | 1.570±0.959a |
| APP/PS1 model | 10 | 0.180±0.080a | 1.070±0.045a | 0.190±0.040a | 2.090±0.031a | 0.380±0.191a |
| APP/PS1 ischemia | 10 | 0.540±0.481a | 2.730±1.132a | 0.320±0.903a | 2.670±0.675a | 0.850±1.052a |
| C57BL ischaemic + aspirin | 10 | 0.860±0.421b | 0.680±5.250 | 0.400±0.212d | 0.480±0.214b | 1.380±2.053b |
| C57BL ischaemic + SLT | 10 | 1.490±0.111 | 0.150±0.190d | 0.320±0.192d | 0.110±0.091d | 1.250±0.312c |
| APP/PS1 + SLT | 10 | 0.630±0.450c | 0.580±0.626 | 0.700±0.580 | 0.501±0.455 | 1.680±0.523e |
| APP/PS1 ischaemic + donepezil hydrochloride | 10 | 0.160±0.121 | 0.420±0.480 | 0.630±0.002 | 1.240±0.244 | 1.490±0.422e |
| APP/PS1 ischaemic + SLT | 10 | 0.930±0.345c | 0.690±0.242 | 1.180±1.591 | 2.090±0.915 | 1.420±0.560e |
| 1. |
Tripathi SM, Murray AD. Alzheimer's dementia: the emerging role of positron emission tomography. Neuroscientist 2022; 28: 507-19.
DOI URL |
| 2. |
Scheltens P, De Strooper B, Kivipelto M, et al. Alzheimer's disease. Lancet 2021; 397: 1577-90.
DOI PMID |
| 3. | Button EB, Robert J, Caffrey TM, et al. Hdl from an Alzheimer’s disease perspective. Curr Opin Lipidol 2019; 30: 224-34. |
| 4. |
Lane CA, Hardy J, Schott JM. Alzheimer's disease. Eur J Neurol 2018; 25: 59-70.
DOI PMID |
| 5. |
Fan L, Mao C, Hu X, et al. New insights into the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Front Neurol 2019; 10: 1312.
DOI URL |
| 6. |
Jean L, Foley AC, Vaux DJT. The physiological and pathological implications of the formation of hydrogels, with a specific focus on amyloid polypeptides. Biomolecules 2017; 7: 70.
DOI URL |
| 7. | Dauberman WN, Xu S. Alzheimer's disease pathogenesis: the denied access model. OMICS International 2017; 7: 1-10. |
| 8. |
Kocahan S, Doğan Z. Mechanisms of Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis and prevention: The brain, neural pathology, n-methyl-d-aspartate receptors, tau protein and other risk factors. Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci 2017; 15: 1-8.
DOI URL |
| 9. |
Carvey PM, Hendey B, Monahan AJ. The blood-brain barrier in neurodegenerative disease: a rhetorical perspective. J Neurochem 2009; 111: 291-314.
DOI PMID |
| 10. | Zlokovic BV. Neurovascular pathways to neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease and other disorders. Nat Rev Neurosci 2011; 12: 723-38. |
| 11. |
Ouellette J, Lacoste B. From neurodevelopmental to neurodegenerative disorders: the vascular continuum. Front Aging Neurosci 2021; 13: 749026.
DOI URL |
| 12. |
Chen CL, Young SH, Gan HH, et al. Chinese medicine neuroaid efficacy on stroke recovery: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized study. Stroke 2013; 44: 2093-100.
DOI PMID |
| 13. |
Wu B, Liu M, Liu H, et al. Meta-analysis of traditional chinese patent medicine for ischemic stroke. Stroke 2007; 38: 1973-9.
PMID |
| 14. |
Yao W, Yang H, Ding G. Mechanisms of Qi-blood circulation and Qi deficiency syndrome in view of blood and interstitial fluid circulation. J Tradit Chin Med 2013; 33: 538-44.
DOI URL |
| 15. | Zhang Y, Liu J, Yao M, et al. Sailuotong capsule prevents the cerebral ischaemia-induced neuroinflammation and impairment of recognition memory through inhibition of lcn2 expression. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2019; 2019: 8416105. |
| 16. |
Shi L, Zheng C, Shen Y, et al. Optical imaging of metabolic dynamics in animals. Nat Commun 2018; 9: 2995.
DOI PMID |
| 17. |
Obafemi TO, Owolabi OV, Omiyale BO, et al. Combination of donepezil and gallic acid improves antioxidant status and cholinesterases activity in aluminum chloride-induced neurotoxicity in wistar rats. Metab Brain Dis 2021; 36: 2511-9.
DOI PMID |
| 18. |
Lian W, Jia H, Xu L, et al. Multi-protection of dl0410 in ameliorating cognitive defects in d-galactose induced aging mice. Front Aging Neurosci 2017; 9: 409.
DOI PMID |
| 19. |
Chung CY, Licznerski P, Alavian KN, et al. The transcription factor orthodenticle homeobox 2 influences axonal projections and vulnerability of midbrain dopaminergic neurons. Brain 2010; 133: 2022-31.
DOI PMID |
| 20. |
Li P, Lu M, Shi J, et al. Lung mesenchymal cells elicit lipid storage in neutrophils that fuel breast cancer lung metastasis. Nat Immunol 2020; 21: 1444-55.
DOI |
| 21. |
Wang J, Sun BL, Xiang Y, et al. Capsaicin consumption reduces brain amyloid-beta generation and attenuates Alzheimer’s disease-type pathology and cognitive deficits in app/ps1 mice. Transl Psychiatry 2020; 10: 230.
DOI |
| 22. |
Wang Z, Liu CY, Zhao Y, Dean J. Figla, lhx8 and sohlh1 transcription factor networks regulate mouse oocyte growth and differentiation. Nucleic Acids Res 2020; 48: 3525-41.
DOI PMID |
| 23. |
Kou J, Yang J, Lim JE, et al. Catalytic immunoglobulin gene delivery in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease: prophylactic and therapeutic applications. Mol Neurobiol 2015; 51: 43-56.
DOI URL |
| 24. |
Kaczmarczyk A, Hempel AM, Von Arx C, et al. Precise timing of transcription by c-di-gmp coordinates cell cycle and morphogenesis in caulobacter. Nat Commun 2020; 11: 816.
DOI PMID |
| 25. |
Guttenplan KA, Weigel MK, Adler DI, et al. Knockout of reactive astrocyte activating factors slows disease progression in an als mouse model. Nat Commun 2020; 11: 3753.
DOI PMID |
| 26. |
Reiss AB, Arain HA, Stecker MM, Siegart NM, Kasselman LJ. Amyloid toxicity in Alzheimer’s disease. Rev Neurosci 2018; 29: 613-27.
DOI URL |
| 27. |
O'brien RJ, Wong PC. Amyloid precursor protein processing and Alzheimer’s disease. Annu Rev Neurosci 2011; 34: 185-204.
DOI URL |
| 28. | Jia J, Wei C, Chen S, et al. Efficacy and safety of the compound chinese medicine sailuotong in vascular dementia: a randomized clinical trial. Alzheimers Dement (N Y) 2018; 4: 108-17. |
| 29. |
Steiner GZ, Yeung A, Liu JX, et al. The effect of sailuotong (slt) on neurocognitive and cardiovascular function in healthy adults: a randomised, double-blind, placebo controlled crossover pilot trial. BMC Complement Altern Med 2016; 16: 15.
DOI URL |
| 30. | Vickrey BG, Brott TG, Koroshetz WJ. Research priority setting:a summary of the 2012 ninds stroke planning meeting report. Stroke 2013; 44: 2338-42. |
| 31. |
Iadecola C. The neurovascular unit coming of age: a journey through neurovascular coupling in health and disease. Neuron 2017; 96: 17-42.
DOI PMID |
| 32. |
Echeverria V, Barreto GE, Avila-Rodriguezc M, Tarasov VV, Aliev G. Is vegf a key target of cotinine and other potential therapies against alzheimer disease? Curr Alzheimer Res 2017; 14: 1155-63.
DOI PMID |
| 33. |
Li W, Li P, Hua Q, et al. The impact of paracrine signaling in brain microvascular endothelial cells on the survival of neurons. Brain Res 2009; 1287: 28-38.
DOI PMID |
| 34. |
Religa P, Cao R, Religa D, et al. Vegf significantly restores impaired memory behavior in Alzheimer’s mice by improvement of vascular survival. Sci Rep 2013; 3: 2053.
DOI PMID |
| 35. |
Patel P, Shah J. Role of vitamin d in amyloid clearance via lrp-1 upregulation in Alzheimer’s disease: a potential therapeutic target? J Chem Neuroanat 2017; 85: 36-42.
DOI URL |
| 36. |
Donahue JE, Flaherty SL, Johanson CE, et al. Rage, lrp-1, and amyloid-beta protein in Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol 2006; 112: 405-15.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | ZHAO Ming, LUO Yimiao, WANG Huichan, CAO Yu, MA Lina, PEI Hui, LI Hao. Guilingji capsule (龟龄集胶囊) for Alzheimer's disease: secondary analysis of a randomized non-inferiority controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 1019-1025. |
| [2] | ZHANG Xiaoying, WANG Ruixuan, WANG Yiqing, XU Fanxing, YAN Tingxu, WU Bo, ZHANG Ming, JIA Ying. Spinosin protects Neuro-2a/APP695 cells from oxidative stress damage by inactivating p38 [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 868-875. |
| [3] | TIAN Meijing, HE Yannan, ZHENG Mingcui, QIN Gaofeng, GONG Zhuoyan, HUANG Shuaiyang, WANG Pengwen. Chinese herbal compound Jinsiwei (金思维) improves synaptic plasticity in mice with sporadic Alzheimer’s disease induced by streptozotocin [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(1): 78-86. |
| [4] | Wang Xu, Li Zhaolong, Li Chunri, Wang Yue, Yu Song, Ren Lu. Electroacupuncture with Bushen Jiannao improves cognitive deficits in senescence-accelerated mouse prone 8 mice by inhibiting neuroinflammation [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020, 40(5): 812-819. |
| [5] | Ren Beida, Cheng Fafeng, Wang Xueqian, Wan Yuxiang, Ji Wenting, Du Xin, Zhang Shuang, Liu Shuling, Ma Chongyang, Xiong Yiliang, Hao Gaoting, Wang Qingguo. Possible mechanisms underlying treatment of Alzheimer's disease with Traditional Chinese Medicine: active components, potential targets and synthetic pathways of Bulao Elixir [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020, 40(3): 484-496. |
| [6] | Chi Huiying, Liu Te, Pan Weidong, Chen Jiulin, Wu Beiling, Yu Zhihua, Chen Chuan. Shen-Zhi-Ling oral solution improves learning and memory ability in Alzheimer's disease mouse model [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2019, 39(05): 667-677. |
| [7] | Liu Lijuan, Yu Chen, Liu Junbao. Effect of Cuzhi liquid on learning and memory dysfunction in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2018, 38(06): 890-895. |
| [8] | Yu Chaochao, Wang Li, Kong Lihong, Shen Feng, Ma Chaoyang, Du Yanjun, Zhou Hua. Acupoint combinations used for treatment of Alzheimer's disease: A data mining analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2018, 38(06): 943-952. |
| [9] | Wang Jing, Cheng Kai, Qin Zhuo, Wang Yanping, Zhai Lijing, You Min, Wu Juanjiao. Effects of electroacupuncture at Guanyuan(CV 4) or Sanyinjiao (SP 6) on hypothalamus-pituitary-ovary axis and spatial learning and memory in female SAMP8 mice [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2017, 37(01): 96-100. |
| [10] | Hu Haiyan, Wang Yiyu, Zhang Yihui, Wang Wenhua, Xu Dongmei, Chen Zhiyu, Zhang Xiaoyan, Mao Dandan. Effect of Qingxinkaiqiao compound on cortical mRNA expression of the apoptosis-related genes Bcl-2, BAX, caspase-3, and Aβ in an Alzheimer's disease rat model [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2016, 36(05): 654-662. |
| [11] | Chen Songlin, Yao Xiaoli, Liang Yinying, Mei Weiyi, Liu Xiaoyun, Zhang Changran. Alzheimer's disease treated with combined therapy based on nourishing marrow and reinforcing Qi [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2015, 35(03): 255-259. |
| [12] | Jing Teng, Zhexue Xu, Jing Zhang, Jingmin Li. Effect of Yizhitongxuan decoction on learning and memory ability,Gαq/11 expression and Na~+-K~+-ATP enzyme activity in rat models of Alzheimer's Disease [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2014, 34(04): 470-476. |
| [13] | Yongchang Diwu, Jinzhou Tian, Jing Shi. Effect of Xixin decoction on phosphorylation toxicity at specific sites of tau protein in brains of rats with sporadic Alzheimer disease [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2013, 33(06): 787-793. |
| [14] | Ping Liu, Mingwang Kong, Songlin Liu, Gang Chen, Ping Wang. Effect of reinforcing kidney-essence, removing phlegm, and promoting mental therapy on treating Alzheimer's disease [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2013, 33(04): 449-454. |
| [15] | Yongchang Diwu, Jinzhou Tian, Jing Shi. Effect of Xixin decoction on O-linked N-acetylglucosamine Glycosylation of tau proteins in rat brain with sporadic Alzheimer disease [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2013, 33(03): 367-372. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

