Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (6): 1215-1227.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2025.06.004
• Original Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of improved Yupingfeng powder prescription (玉屏风散加味) on interleukin-33/suppression of tumorigenicity 2 pathway in mice with ovalbumins-induced allergic rhinitis
LEI Xiaochun1, LIU Cuizhen1, LIN Xiujuan1, XIE Xiangyu1, KE Wei1, QIU Zhenwen2, TANG Hongmei2, HUANG Yushen3, ZHANG Lijuan4, HUANG Baoyuan2, WAN Xin1,2( ), LI Detang2,5(
), LI Detang2,5( )
)
- 1 The First Clinical Medical School of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, China
2 Department of Pharmacy, the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, China
3 Lingnan Medical Research Center, the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, China
4 Department of otorhinolaryngology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, China
5 Department of Pharmacy, Chongqing Hospital of the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine (Chongqing Beibei Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine), Chongqing 400700, China
-
Received:2024-11-22Accepted:2025-04-11Online:2025-12-15Published:2025-11-24 -
Contact:Prof. WAN Xin, Department of Pharmacy, The First Clinical Medical School of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, China, wanxin145@163.com, Telephone: + 86-19928311931;
Prof. LI Detang, Department of Pharmacy, Chongqing Hospital of the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine (Chongqing Beibei Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine), Chongqing 400700, China, lidetang2002@163.com -
Supported by:Exploring the Mechanism of Improved Yupingfeng Powder in Treating Allergic Rhinitis Based on the Nucleotide-Binding Oligomerization Domain, Leucine-rich Repeat and Pyrin Domain-containing Protein 3/Interleukin-33-Mediated Activation Pathway of Pulmonary Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cells in Airway Epithelial Cells(82374526);Mechanism of Shikonin in Treating Acute Lung Injury Through Regulating M1 Macrophage Polarization via Adenosine 5'-monophosphate-Activated Protein Kinase/Dynamin-Related Protein 1-mediated Mitochondrial Dynamics(2024A04J4334);Exemplary Study on Process Optimization and Quality Standard Enhancement of Hospital Preparations Such as Gangmei Qingyan Mixture(2023A03J0299);Anti-Allergic Mechanism of Improved Yupingfeng Powder in Alleviating Nasal Mucosal Inflammation in Allergic Rhinitis via Interleukin-33/Suppression of Tumorigenicity 2-Regulated Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cells Suppression(202201020457);Elite Talent Program of the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine by 2023 Years and Guangdong Province Lingnan Characteristic Hospital Preparation Transformation Engineering Technology Research Center(2023A170)
Cite this article
LEI Xiaochun, LIU Cuizhen, LIN Xiujuan, XIE Xiangyu, KE Wei, QIU Zhenwen, TANG Hongmei, HUANG Yushen, ZHANG Lijuan, HUANG Baoyuan, WAN Xin, LI Detang. Effect of improved Yupingfeng powder prescription (玉屏风散加味) on interleukin-33/suppression of tumorigenicity 2 pathway in mice with ovalbumins-induced allergic rhinitis[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(6): 1215-1227.
share this article
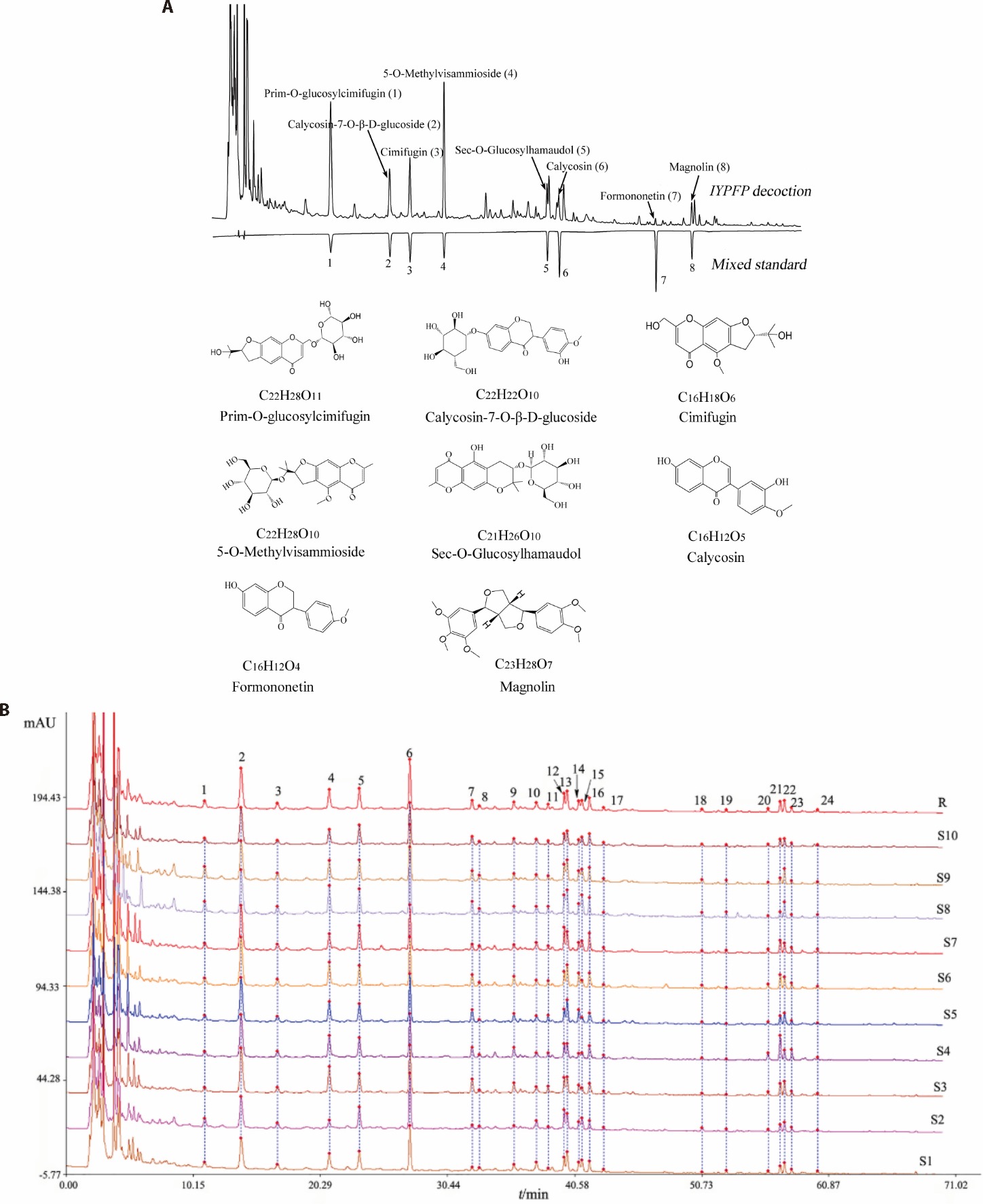
Figure 1 Chemical profiling of IYPFP: plasma component identification by UPLC-Q-exactive orbitrap-MS/MS and quality evaluation through HPLC fingerprinting and content analysis A: establishment of high-performance liquid chromatogram and identification of 8 chemical components in IYPFP and chemical structure and formulae of 8 chemical ingredients; B: the eight major chemical compounds of IYPFP: prim-O-glucosylcimifugin (peak 2), calycosin-7-O-β-D-glucoside (peak 4), cimifugin (peak 5), 5-O-methylvisammioside (peak 6), sec-O-glucosylhamaudol (peak 12), calycosin (peak 15), formononetin (peak 19), and magnolin (peak 21). IYPFP: improved Yupingfeng Powder prescription; UPLC-Q-Exactive Orbitrap-MS/MS: ultra high performance liquid chromatography quadrupole exactive orbitrap mass spectrometry; HPLC: high performance liquid chromatography.
| S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | S7 | S8 | S9 | S10 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 1 | 0.970 | 0.978 | 0.965 | 0.982 | 0.982 | 0.983 | 0.990 | 0.992 | 0.988 |
| S2 | 0.970 | 1 | 0.931 | 0.920 | 0.950 | 0.944 | 0.966 | 0.964 | 0.974 | 0.969 |
| S3 | 0.978 | 0.931 | 1 | 0.988 | 0.992 | 0.994 | 0.978 | 0.973 | 0.976 | 0.986 |
| S4 | 0.965 | 0.920 | 0.988 | 1 | 0.975 | 0.986 | 0.977 | 0.953 | 0.958 | 0.977 |
| S5 | 0.982 | 0.950 | 0.992 | 0.975 | 1 | 0.997 | 0.982 | 0.976 | 0.984 | 0.991 |
| S6 | 0.982 | 0.944 | 0.994 | 0.986 | 0.997 | 1 | 0.986 | 0.974 | 0.981 | 0.991 |
| S7 | 0.983 | 0.966 | 0.978 | 0.977 | 0.982 | 0.986 | 1 | 0.969 | 0.978 | 0.991 |
| S8 | 0.990 | 0.964 | 0.973 | 0.953 | 0.976 | 0.974 | 0.969 | 1 | 0.996 | 0.984 |
| S9 | 0.992 | 0.974 | 0.976 | 0.958 | 0.984 | 0.981 | 0.978 | 0.996 | 1 | 0.988 |
| S10 | 0.988 | 0.969 | 0.986 | 0.977 | 0.991 | 0.991 | 0.991 | 0.984 | 0.988 | 1 |
| Similarity results | 0.993 | 0.968 | 0.991 | 0.981 | 0.994 | 0.995 | 0.991 | 0.989 | 0.993 | 0.997 |
Table 1 IYPFP decoction Results of similarity evaluation and analysis of 10 batches of samples
| S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | S7 | S8 | S9 | S10 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 1 | 0.970 | 0.978 | 0.965 | 0.982 | 0.982 | 0.983 | 0.990 | 0.992 | 0.988 |
| S2 | 0.970 | 1 | 0.931 | 0.920 | 0.950 | 0.944 | 0.966 | 0.964 | 0.974 | 0.969 |
| S3 | 0.978 | 0.931 | 1 | 0.988 | 0.992 | 0.994 | 0.978 | 0.973 | 0.976 | 0.986 |
| S4 | 0.965 | 0.920 | 0.988 | 1 | 0.975 | 0.986 | 0.977 | 0.953 | 0.958 | 0.977 |
| S5 | 0.982 | 0.950 | 0.992 | 0.975 | 1 | 0.997 | 0.982 | 0.976 | 0.984 | 0.991 |
| S6 | 0.982 | 0.944 | 0.994 | 0.986 | 0.997 | 1 | 0.986 | 0.974 | 0.981 | 0.991 |
| S7 | 0.983 | 0.966 | 0.978 | 0.977 | 0.982 | 0.986 | 1 | 0.969 | 0.978 | 0.991 |
| S8 | 0.990 | 0.964 | 0.973 | 0.953 | 0.976 | 0.974 | 0.969 | 1 | 0.996 | 0.984 |
| S9 | 0.992 | 0.974 | 0.976 | 0.958 | 0.984 | 0.981 | 0.978 | 0.996 | 1 | 0.988 |
| S10 | 0.988 | 0.969 | 0.986 | 0.977 | 0.991 | 0.991 | 0.991 | 0.984 | 0.988 | 1 |
| Similarity results | 0.993 | 0.968 | 0.991 | 0.981 | 0.994 | 0.995 | 0.991 | 0.989 | 0.993 | 0.997 |
| Chemical constituents | Molecular formula | Linear range | Concentration (μg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prim-O-glucosylcimifugin | C22H28O11 | y=2299.0x-4.6027 | 12.123±0.358 |
| Cimifugin | C16H18O6 | y=3952.2x-6.781 | 3.857±0.102 |
| Sec-O-Glucosylhamaudol | C21H26O10 | y=2113.5x-4.8354 | 3.809±0.034 |
| 5-O-Methylvisammioside | C22H28O10 | y=2469.8x-5.2983 | 11.137±0.079 |
| Calycosin-7-O-β-D-glucoside | C22H22O10 | y=3262.4x-3.2236 | 5.372±0.046 |
| Calycosin | C22H22O10 | y=5330.7x-9.1153 | 1.313±0.052 |
| Formononetin | C16H12O4 | y=7421.5x-10.649 | 0.288±0.014 |
| Magnolin | C23H28O7 | y=2893.5x-5.7248 | 2.068±0.041 |
Table 2 Concentration of IYPFP of eight major chemical compositions ($\bar{x}$ ± s, n = 3)
| Chemical constituents | Molecular formula | Linear range | Concentration (μg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prim-O-glucosylcimifugin | C22H28O11 | y=2299.0x-4.6027 | 12.123±0.358 |
| Cimifugin | C16H18O6 | y=3952.2x-6.781 | 3.857±0.102 |
| Sec-O-Glucosylhamaudol | C21H26O10 | y=2113.5x-4.8354 | 3.809±0.034 |
| 5-O-Methylvisammioside | C22H28O10 | y=2469.8x-5.2983 | 11.137±0.079 |
| Calycosin-7-O-β-D-glucoside | C22H22O10 | y=3262.4x-3.2236 | 5.372±0.046 |
| Calycosin | C22H22O10 | y=5330.7x-9.1153 | 1.313±0.052 |
| Formononetin | C16H12O4 | y=7421.5x-10.649 | 0.288±0.014 |
| Magnolin | C23H28O7 | y=2893.5x-5.7248 | 2.068±0.041 |

Figure 2 Comparison of the nasal mucosa tissues pathology of mice in each group A: HE staining of nasal mucosa tissues from mice (A1: × 2, scale bar = 1000 μm; A2-A6: × 100, scale bar = 20 μm); B: statistical analysis results of thickness of nasal mucosa; C: HE staining of nasal mucosa tissues from mice (C1: × 2, scale bar = 1000 μm; C2-C6: × 40, scale bar = 50 μm); D: statistical analysis results of goblet cells in nasal mucosa. A1: observation of nasal mucosa thickness; C1: observation of goblet cells; A2, C2: blank control group; A3, C3: OVA model group; A4, C4: OVA + DEX group; A5, C5: OVA + 1.5 g/kg IYPFP group; A6, C6: OVA + 4.5 g/kg IYPFP group; Control group: injected with 200 μL saline on days 0, 7 and 14 and administered 20 μL saline per nostril daily from days 22 to 28; Model group: injected of 200 μL of saline containing 50 μg of OVA and 2 mg of aluminium hydroxide on days 0, 7 and 14, and challenged intranasally with 20 μL saline containing 25 mg/mL OVA per nostril daily from days 22 to 28; DEX group: injected of 200 μL of saline containing 50 μg of OVA and 2 mg of aluminium hydroxide on days 0, 7 and 14, and challenged intranasally with 20 μL saline containing 25 mg/mL OVA per nostril daily from days 22 to 28, then intraperitoneally administered with 200 μL saline containing 0.5 mg Dex daily from day 15 to 28; IYPFP 1.5 g/kg group and IYPFP 4.5 g/kg group: injected of 200 μL of saline containing 50 μg of OVA and 2 mg of aluminium hydroxide on days 0, 7 and 14, and challenged intranasally with 20 μL saline containing 25 mg/mL OVA per nostril daily from days 22 to 28, then intragastrically administered 200 μL of IYPFP at 1.5 or 4.5 g/kg daily from day 15 to 28. Control: blank control group; Model: OVA model group; DEX: OVA + DEX group; IYPFP 1.5 g/kg: OVA + 1.5 g/kg IYPFP group; IYPFP 4.5 g/kg: OVA+4.5 g/kg IYPFP group. Differences in means between groups were examined using one-way analysis of variance, with the Dunnett’s T3 test used for the data in this table. Data were presented as mean ± standard deviation (n = 3). Compared with the Control group, aP < 0.01; compared with the Model group, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.05.
| Group | n | IgE | Histamine | IL-33 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 3 | 16.02±0.21 | 12.73±0.27 | 99.46±6.00 |
| Model | 3 | 18.01±0.45a | 15.14±0.52a | 152.55±5.23a |
| DEX | 3 | 14.27±0.33b | 12.05±0.21b | 127.87±3.18b |
| IYPFP 1.5 g/kg | 3 | 15.48±0.29b | 13.16±0.31b | 133.28±1.48b |
| IYPFP 4.5 g/kg | 3 | 14.76±0.55b | 12.84±0.78b | 119.90±5.47b |
Table 3 The expression of OVA-specific IgE, histamine and IL-33 in serum was detected by ELISA ($\bar{x}$ ± s)
| Group | n | IgE | Histamine | IL-33 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 3 | 16.02±0.21 | 12.73±0.27 | 99.46±6.00 |
| Model | 3 | 18.01±0.45a | 15.14±0.52a | 152.55±5.23a |
| DEX | 3 | 14.27±0.33b | 12.05±0.21b | 127.87±3.18b |
| IYPFP 1.5 g/kg | 3 | 15.48±0.29b | 13.16±0.31b | 133.28±1.48b |
| IYPFP 4.5 g/kg | 3 | 14.76±0.55b | 12.84±0.78b | 119.90±5.47b |

Figure 3 real-time PCR analysis to evaluate the expression of IFN-γ, IL-5, IL-13 and TNF-α mRNA in lung tissue A: IFN-γ mRNA level in lung; B: IL-5 mRNA level in lung; C: IL-13 mRNA level in lung; D: TNF-α mRNA level in lung; E: the ratio of IL-5 to IFN-g produced by the individual variations in T-cell is expressed as Th2/Th1; F: the ratio of IL-13 to IFN-γ produced by the individual variations in T-cell is expressed as Th2/Th1. Control group: injected with 200 μL saline on days 0, 7 and 14 and administered 20 μL saline per nostril daily from days 22 to 28; Model group: injected of 200 μL of saline containing 50 μg of OVA and 2 mg of aluminium hydroxide on days 0, 7 and 14, and challenged intranasally with 20 μL saline containing 25 mg/mL OVA per nostril daily from days 22 to 28; DEX group: injected of 200 μL of saline containing 50 μg of OVA and 2 mg of aluminium hydroxide on days 0, 7 and 14, and challenged intranasally with 20 μL saline containing 25 mg/mL OVA per nostril daily from days 22 to 28, then intraperitoneally administered with 200 μL saline containing 0.5 mg Dex daily from day 15 to 28; IYPFP 1.5 g/kg group and IYPFP 4.5 g/kg group: injected of 200 μL of saline containing 50 μg of OVA and 2 mg of aluminium hydroxide on days 0, 7 and 14, and challenged intranasally with 20 μL saline containing 25 mg/mL OVA per nostril daily from days 22 to 28, then intragastrically administered 200 μL of IYPFP at 1.5 or 4.5 g/kg daily from day 15 to 28. Control: blank control group; Model: OVA model group; DEX: OVA + DEX group; IYPFP 1.5 g/kg: OVA + 1.5 g/kg IYPFP group; IYPFP 4.5 g/kg: OVA + 4.5 g/kg IYPFP group. IFN-γ: interferon γ; IL-5: interleukin-5; IL-13: interleukin-13; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor-α; OVA: ovalbumin; DEX: dexamethasone; IYPFP: improved Yupingfeng powder prescription. The 2-△△CT method was used to analyse relative gene expression. All data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (n = 6). Differences in means between groups were examined using one-way analysis of variance, with the Dunnett’s T3 test used for the data in this table. Compared with the Control group, aP < 0.01, cP < 0.05; compared with the Model group, bP < 0.01, dP < 0.05.

Figure 4 influence of IYPFP on the IL-33/ST2 signaling pathway and Th1/Th2 cytokines A-B: all pictures were stained by immunohistochemical method to observe the expression of the IL-33 and ST2 protein in nasal mucosa. The brown color was positive (× 63, scale bar = 20 μm); C: the average density value of IL33 proteins in nasal mucosa (n = 3); D: the average density value of ST2 proteins in nasal mucosa (n = 3); E: real-time PCR analysis to evaluate the mRNA expression of IL-33 in the lung tissues (n = 6); F: real-time PCR analysis to evaluate the mRNA expression of ST2 in the lung tissues (n = 6); G: Western blot analysis for expression of IL-33 and ST2 in the lung tissues in each group of mice. The graph showed relative density was calculated using β-actin as a control. All data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (n = 3); H: protein expression of IL-33 in lung tissues of mice; I: protein expression of ST2 in lung tissues of mice; A1, B1: blank Control group; A2, B2: OVA model group; A3, B3: OVA + DEX group; A4, B4: OVA + 1.5 g/kg IYPFP group; A5, B5: OVA + 4.5 g/kg IYPFP group. Control group: injected with 200 μL saline on days 0, 7 and 14 and administered 20 μL saline per nostril daily from days 22 to 28; Model group: injected of 200 μL of saline containing 50 μg of OVA and 2 mg of aluminium hydroxide on days 0, 7 and 14, and challenged intranasally with 20 μL saline containing 25 mg/mL OVA per nostril daily from days 22 to 28; DEX group: injected of 200 μL of saline containing 50 μg of OVA and 2 mg of aluminium hydroxide on days 0, 7 and 14, and challenged intranasally with 20 μL saline containing 25 mg/mL OVA per nostril daily from days 22 to 28, then intraperitoneally administered with 200 μL saline containing 0.5 mg Dex daily from day 15 to 28; IYPFP 1.5 g/kg group and IYPFP 4.5 g/kg group: injected of 200 μL of saline containing 50 μg of OVA and 2 mg of aluminium hydroxide on days 0, 7 and 14, and challenged intranasally with 20 μL saline containing 25 mg/mL OVA per nostril daily from days 22 to 28, then intragastrically administered 200 μL of IYPFP at 1.5 or 4.5 g/kg daily from day 15 to 28. IL-33: interleukin-33; ST2: suppression of tumorigenicity 2; OVA: ovalbumin; DEX: dexamethasone; IYPFP: Improved Yupingfeng Powder Prescription. The 2-△△CT method was used to analyse relative gene expression. Differences in means between groups were examined using one-way analysis of variance, with the Dunnett’s T3 test used for the data in this table. Compared with the Control group, aP < 0.01, dP < 0.05; compared with the Model group, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.05.
| Compound | IL-33 | ST2 | IL-5 | IL-13 | IFN-γ | Histamine | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prim-O-glucosylcimifugin | -4.88 | -4.49 | -4.31 | -3.67 | -3.70 | -4.79 | -25.84 |
| Calycosin-7-O-β-D-glucoside | -7.09 | -8.26 | -7.50 | -6.42 | -7.27 | -8.16 | -44.70 |
| Cimifugin | -6.18 | -6.15 | -5.74 | -5.62 | -6.70 | -7.99 | -38.38 |
| 5-O-methylvisammioside | -5.62 | -7.25 | -6.08 | -5.98 | -6.84 | -7.91 | -39.68 |
| sec-O-Glucosylhamaudol | -6.30 | -8.05 | -6.77 | -6.47 | -6.44 | -7.57 | -41.60 |
| Calycosin | -6.24 | -8.12 | -6.64 | -6.29 | -6.74 | -7.83 | -41.86 |
| formononetin | -6.00 | -7.93 | -6.59 | -5.56 | -6.49 | -7.77 | -40.34 |
| Magnolin | -6.64 | -7.43 | -6.82 | -6.31 | -7.16 | -8.89 | -43.25 |
| Total | -48.95 | -57.68 | -50.45 | -46.32 | -51.34 | -60.91 |
Table 4 Binding energies between the key ingredients of IYPFP and the target gene
| Compound | IL-33 | ST2 | IL-5 | IL-13 | IFN-γ | Histamine | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prim-O-glucosylcimifugin | -4.88 | -4.49 | -4.31 | -3.67 | -3.70 | -4.79 | -25.84 |
| Calycosin-7-O-β-D-glucoside | -7.09 | -8.26 | -7.50 | -6.42 | -7.27 | -8.16 | -44.70 |
| Cimifugin | -6.18 | -6.15 | -5.74 | -5.62 | -6.70 | -7.99 | -38.38 |
| 5-O-methylvisammioside | -5.62 | -7.25 | -6.08 | -5.98 | -6.84 | -7.91 | -39.68 |
| sec-O-Glucosylhamaudol | -6.30 | -8.05 | -6.77 | -6.47 | -6.44 | -7.57 | -41.60 |
| Calycosin | -6.24 | -8.12 | -6.64 | -6.29 | -6.74 | -7.83 | -41.86 |
| formononetin | -6.00 | -7.93 | -6.59 | -5.56 | -6.49 | -7.77 | -40.34 |
| Magnolin | -6.64 | -7.43 | -6.82 | -6.31 | -7.16 | -8.89 | -43.25 |
| Total | -48.95 | -57.68 | -50.45 | -46.32 | -51.34 | -60.91 |
| 1. |
Bernstein JA, Bernstein JS, Makol R, Ward S. Allergic rhinitis: a review. JAMA 2024; 331: 866-77.
DOI PMID |
| 2. |
Bousquet J, Anto JM, Bachert C, et al. Allergic rhinitis. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2020; 6: 95.
DOI PMID |
| 3. |
Kucuksezer UC, Ozdemir C, Yazici D, et al. The epithelial barrier theory: development and exacerbation of allergic and other chronic inflammatory diseases. Asia Pac Allergy 2023; 13: 28-39.
DOI PMID |
| 4. |
Zhang R, Zhang L, Li P, et al. Epithelial barrier in the nasal mucosa, related risk factors and diseases. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 2023; 184: 481-501.
DOI URL |
| 5. |
Wheatley LM, Togias A. Clinical practice. Allergic rhinitis. N Engl J Med 2015; 372: 456-63.
DOI URL |
| 6. | Drazdauskaite G, Layhadi JA, Shamji MH. Mechanisms of allergen immunotherapy in allergic rhinitis. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep 2020; 21: 2. |
| 7. |
Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Gu W, Sun B. TH1/TH2 cell differentiation and molecular signals. Adv Exp Med Biol 2014; 841: 15-44.
DOI PMID |
| 8. |
Cayrol C, Girard JP. IL-33: an alarmin cytokine with crucial roles in innate immunity, inflammation and allergy. Curr Opin Immunol 2014; 31: 31-7.
DOI PMID |
| 9. |
Cayrol C, Girard JP. Interleukin-33 (IL-33): a nuclear cytokine from the IL-1 family. Immunol Rev 2018; 281: 154-68.
DOI PMID |
| 10. | Hong H, Liao S, Chen F, Yang Q, Wang DY. Role of IL-25, IL-33, and TSLP in triggering united airway diseases toward type 2 inflammation. Allergy 2020; 75: 2794-804. |
| 11. | Shani O, Vorobyov T, Monteran L, et al. Fibroblast-derived IL33 facilitates breast cancer metastasis by modifying the immune microenvironment and driving Type 2 immunity. Cancer Res 2020; 80: 5317-29. |
| 12. |
Toki S, Goleniewska K, Zhang J, et al. TSLP and IL-33 reciprocally promote each other's lung protein expression and ILC2 receptor expression to enhance innate type-2 airway inflammation. Allergy 2020; 75: 1606-17.
DOI PMID |
| 13. |
Yin C, Liu B, Li Y, et al. IL-33/ST2 induces neutrophil-dependent reactive oxygen species production and mediates gout pain. Theranostics 2020; 10: 12189-203.
DOI PMID |
| 14. | Ma Q, Qian Y, Jiang J, et al. IL-33/ST2 axis deficiency exacerbates neutrophil-dominant allergic airway inflammation. Clin Transl Immunology 2021; 10: e1300. |
| 15. |
Breiteneder H, Peng YQ, Agache I, et al. Biomarkers for diagnosis and prediction of therapy responses in allergic diseases and asthma. Allergy 2020; 75: 3039-68.
DOI URL |
| 16. |
Korppi M, Terasjarvi J, Lauhkonen E, et al. IL 33 rs1342326 gene variation is associated with allergic rhinitis at school age after infant bronchiolitis. Acta Paediatr 2020; 109: 2112-6.
DOI URL |
| 17. |
Tamasauskiene L, Sitkauskiene B. Systemic and local cytokine profile and risk factors for persistent allergic airway inflammation in patients sensitised to house dust mite allergens. BMC Pulm Med 2021; 21: 424.
DOI PMID |
| 18. | Jin LM (Ming dynasty). Yi Fang Lei Ju. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House, 2006: 5. |
| 19. | Zhu ZH (Yuan dynasty). Dan Xi Xin Fa. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House, 2005: 86-7. |
| 20. | Zhang L, Li D, Pang Z, et al. Effect of ModifiedYupingfeng San of lung deficieney-cold type AR patients with the clinical efficacy and IL-17A, TGF-β1 expression. Yunnan Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue Xue Bao 2018; 41: 41-6. |
| 21. | Liu C, Feng S, Lin X, et al. Identification of chemical constituents of modified Yupingfengsan formula. Zhong Guo Yao Fang 2024; 35: 2225-31. |
| 22. | Wan X, Li DT, Zhang LJ, et al. Establishment of characteristic chromatogram and content determination of 4 index components in Jianpiyifei biyan prescription standard decoction. Zhong Guo Yao Fang 2022; 33: 1980-5. |
| 23. |
Hui C, Wei F, Ye L, et al. Effects and mechanism of Chinese medicine Jiawei Yupingfeng in a mouse model of allergic rhinitis. J Integr Med 2021; 19: 354-61.
DOI PMID |
| 24. | Xu J, Zhang L, Xie S, et al. Effect of astragalus polysaccharide on Th1/Th2 immune balance in rats with allergic rhinitis. Shi Zhen Guo Yi Guo Yao 2020; 31: 2613-16. |
| 25. | Xu J, Zhang Q, Li Z, et al. Astragalus polysaccharides attenuate ovalbumin-induced allergic rhinitis in rats by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation and NOD2-mediated NF-κB activation. J Med Food 2021; 24: 1-9. |
| 26. | Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China. 2020 ed. Beijing: China Medical Science Press; 2020: 15-315. |
| 27. | Liu HL, Chen HF, Liu QD, et al. HDAC downregulation of Xiaoqinglong decoction in the treatment of allergic rhinitis. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 2023; 184: 376-90. |
| 28. | Zhang JJ, He XC, Zhou M, et al. Xiao-qing-long-tang ameliorates OVA-induced allergic rhinitis by inhibiting ILC2s through the IL-33/ST2 and JAK/STAT pathways. Phytomedicine 2023; 119: 155012. |
| 29. |
Xu Q, Bauer R, Hendry BM, et al. The quest for modernisation of Traditional Chinese Medicine. BMC Complement Altern Med 2013; 13: 132.
DOI URL |
| 30. | Liu SH, Chen PS, Huang CC, et al. Unlocking the mystery of the therapeutic effects of Chinese medicine on cancer. Front Pharmacol 2020; 11: 601785. |
| 31. | Bernstein DI, Schwartz G, Bernstein JA. Allergic rhinitis: mechanisms and treatment. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am 2016; 36: 261-78. |
| 32. |
Steelant B, Seys SF, Van Gerven L, et al. Histamine and T helper cytokine-driven epithelial barrier dysfunction in allergic rhinitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2018; 141: 951-63.
DOI PMID |
| 33. | Sogut A, Yilmaz O, Kirmaz C, et al. Regulatory-T, T-helper 1, and T-helper 2 cell differentiation in nasal mucosa of allergic rhinitis with olive pollen sensitivity. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 2012; 157: 349-53. |
| 34. |
Haenuki Y, Matsushita K, Futatsugi-Yumikura S, et al. A critical role of IL-33 in experimental allergic rhinitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2012; 130: 184-94.
DOI PMID |
| 35. |
Akasaki S, Matsushita K, Kato Y, et al. Murine allergic rhinitis and nasal Th2 activation are mediated via TSLP- and IL-33-signaling pathways. Int Immunol 2016; 28: 65-76.
DOI PMID |
| 36. | Peng YQ, Chen DH, Xu ZB, et al. IL-33 receptor expression on myeloid and plasmacytoid dendritic cells after allergen challenge in patients with allergic rhinitis. Int Immunopharmacol 2021; 101: 108233. |
| 37. | Chen Z, Liu L, Gao C, et al. Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz. (Huangqi): a promising edible immunomodulatory herbal medicine. J Ethnopharmacol 2020; 258: 112895. |
| 38. | Zhang CH, Yang X, Wei JR, et al. Ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry, pharmacology, toxicology and clinical applications of Radix Astragali. Chin J Integr Med 2021; 27: 229-40. |
| 39. | Yan X, Yu A, Zheng H, et al. Calycosin-7-O-beta-D-glucoside attenuates OGD/R-induced damage by preventing oxidative stress and neuronal apoptosis via the SIRT1/FOXO1/PGC-1alpha pathway in HT 22 cells. Neural Plast 2019; 2019: 8798069. |
| 40. |
Tsai CC, Wu HH, Chang CP, Lin CH, Yang HH. Calycosin-7-O-beta-D-glucoside reduces myocardial injury in heat stroke rats. J Formos Med Assoc 2019; 118: 730-8.
DOI URL |
| 41. |
Dong L, Yin L, Chen R, et al. Anti-inflammatory effect of calycosin glycoside on lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses in RAW 264.7 cells. Gene 2018; 675: 94-101.
DOI PMID |
| 42. |
Yi L, Cui J, Wang W, et al. Formononetin attenuates airway inflammation and oxidative stress in murine allergic asthma. Front Pharmacol 2020; 11: 533841.
DOI URL |
| 43. |
Zhou J, Sun YY, Sun MY, et al. Prim-O-glucosylcimifugin attenuates lipopolysaccharide induced inflammatory response in RAW 264.7 macrophages. Pharmacogn Mag 2017; 13: 378-84.
DOI PMID |
| 44. |
Yin Y, Liu K, Li G. Protective effect of Prim-O-Glucosylcimifugin on ulcerative colitis and its mechanism. Front Pharmacol 2022; 13: 882924.
DOI URL |
| 45. | Wang X, Jiang X, Yu X, et al. Cimifugin suppresses allergic inflammation by reducing epithelial derived initiative key factors via regulating tight junctions. J Cell Mol Med 2017; 21: 2926-36. |
| 46. |
Koh GH, Song H, Kim SH, et al. Effect of sec-O-glucosylhamaudol on mechanical allodynia in a rat model of postoperative pain. Korean J Pain 2019; 32: 87-96.
DOI URL |
| 47. |
Yoo OK, Keum YS. 4'-O-β-D-Glucosyl-5-O-methylvisamminol attenuates pro-inflammatory responses and protects against oxidative damages. Biomol Ther 2019; 27: 381-5.
DOI URL |
| 48. |
Oh SH, Kim SW, Kim DJ, et al. Sec-O-glucosylhamaudol mitigates inflammatory processes and autophagy via p38/JNK MAPK signaling in a rat neuropathic pain model. Korean J Pain 2021; 34: 405-16.
DOI URL |
| 49. | Ma P, Che D, Zhao T, et al. Magnolin inhibits IgE/Ag-induced allergy in vivo and in vitro. Int Immunopharmacol 2019; 76: 105867. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

