Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (4): 806-816.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20250318.002
• Original Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Exploration of the mechanism of Danggui Buxue decoction (当归补血汤) for the treatment of gastric ulcer based on network pharmacology, molecular docking, and in vivo experiment
SONG Mingming1, MEN Bo1, CHEN Mei1, LIU Rui1, MO Hongping1, ZHANG Da2( ), PAN Tao1, WEN Xudong1(
), PAN Tao1, WEN Xudong1( )
)
- 1 Department of Gastroenterology, Integrated TCM & Western Medicine Affiliated Hospital of Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu 610041, China
2 Sichuan Integrative Medicine Hospital, Chengdu 610041, China
-
Received:2024-03-12Accepted:2024-10-21Online:2025-08-15Published:2025-03-18 -
Contact:ZHANG Da,WEN Xudong -
About author:WEN Xudong, Department of Gastroenterology, Integrated TCM & Western Medicine Affiliated Hospital of Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu 610041, China. xudongwen@cdutcm.edu.cn
ZHANG Da, Sichuan Integrative Medicine Hospital, Chengdu 610041, China. 1150930045@qq.com;
First author contact:SONG Mingming and MEN Bo are co-first authors and contributed equally to this work
-
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China: Mechanism of Danggui Buxue Decoction in Promoting Liver Regulation by Modulating Kupffer Cell Glycolysis-Mediated Histone Lactylation in Hepatocytes(82474299);XingLin Scholars Program of Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine: Study on the Role and Mechanism of Electrospun Astragalus Polysaccharide and Angelica Polysaccharide in Promoting Liver Regeneration(YYZX2020036)
Cite this article
SONG Mingming, MEN Bo, CHEN Mei, LIU Rui, MO Hongping, ZHANG Da, PAN Tao, WEN Xudong. Exploration of the mechanism of Danggui Buxue decoction (当归补血汤) for the treatment of gastric ulcer based on network pharmacology, molecular docking, and in vivo experiment[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(4): 806-816.
share this article
| Herbs | Mol ID | Molecule name | OB (%) | DL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Danggui (Radix Angelicae Sinensis) | MOL000358 | Beta-sitosterol | 36.91 | 0.75 |
| MOL000449 | Stigmasterol | 43.83 | 0.76 | |
| Huangqi (Radix Astragali Mongolici) | MOL000211 | Mairin | 55.38 | 0.78 |
| MOL000239 | Jaranol | 50.83 | 0.29 | |
| MOL000296 | Hederagenin | 36.91 | 0.75 | |
| MOL000033 | (3S,8S,9S,10R,13R,14S,17R)-10,13-dimethyl-17-[(2R,5S)-5-propan-2-yloctan-2-yl]-2,3,4,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-dodecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-ol | 36.23 | 0.78 | |
| MOL000354 | Isorhamnetin | 49.6 | 0.31 | |
| MOL000371 | 3,9-di-O-methylnissolin | 53.74 | 0.48 | |
| MOL000374 | 5'-hydroxyiso-muronulatol-2',5'-di-O-glucoside | 41.72 | 0.69 | |
| MOL000378 | 7-O-methylisomucronulatol | 74.69 | 0.3 | |
| MOL000379 | 9,10-dimethoxypterocarpan-3-O-β-D-glucoside | 36.74 | 0.92 | |
| MOL000380 | (6aR,11aR)-9,10-dimethoxy-6a,11a-dihydro-6H-benzofurano[3,2-c]chromen-3-ol | 64.26 | 0.42 | |
| MOL000387 | Bifendate | 31.1 | 0.67 | |
| MOL000392 | Formononetin | 69.67 | 0.21 | |
| MOL000398 | Isoflavanone | 109.99 | 0.3 | |
| MOL000417 | Calycosin | 47.75 | 0.24 | |
| MOL000422 | Kaempferol | 41.88 | 0.24 | |
| MOL000433 | FA | 68.96 | 0.71 | |
| MOL000438 | (3R)-3-(2-hydroxy-3,4-dimethoxyphenyl) chroman-7-ol | 67.67 | 0.26 | |
| MOL000439 | Isomucronulatol-7,2'-di-O-glucosiole | 49.28 | 0.62 | |
| MOL000442 | 1,7-Dihydroxy-3,9-dimethoxy pterocarpene | 39.05 | 0.48 | |
| MOL000098 | Quercetin | 46.43 | 0.28 |
Table 1 Active ingredients of Danggui Buxue decoction
| Herbs | Mol ID | Molecule name | OB (%) | DL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Danggui (Radix Angelicae Sinensis) | MOL000358 | Beta-sitosterol | 36.91 | 0.75 |
| MOL000449 | Stigmasterol | 43.83 | 0.76 | |
| Huangqi (Radix Astragali Mongolici) | MOL000211 | Mairin | 55.38 | 0.78 |
| MOL000239 | Jaranol | 50.83 | 0.29 | |
| MOL000296 | Hederagenin | 36.91 | 0.75 | |
| MOL000033 | (3S,8S,9S,10R,13R,14S,17R)-10,13-dimethyl-17-[(2R,5S)-5-propan-2-yloctan-2-yl]-2,3,4,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-dodecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-ol | 36.23 | 0.78 | |
| MOL000354 | Isorhamnetin | 49.6 | 0.31 | |
| MOL000371 | 3,9-di-O-methylnissolin | 53.74 | 0.48 | |
| MOL000374 | 5'-hydroxyiso-muronulatol-2',5'-di-O-glucoside | 41.72 | 0.69 | |
| MOL000378 | 7-O-methylisomucronulatol | 74.69 | 0.3 | |
| MOL000379 | 9,10-dimethoxypterocarpan-3-O-β-D-glucoside | 36.74 | 0.92 | |
| MOL000380 | (6aR,11aR)-9,10-dimethoxy-6a,11a-dihydro-6H-benzofurano[3,2-c]chromen-3-ol | 64.26 | 0.42 | |
| MOL000387 | Bifendate | 31.1 | 0.67 | |
| MOL000392 | Formononetin | 69.67 | 0.21 | |
| MOL000398 | Isoflavanone | 109.99 | 0.3 | |
| MOL000417 | Calycosin | 47.75 | 0.24 | |
| MOL000422 | Kaempferol | 41.88 | 0.24 | |
| MOL000433 | FA | 68.96 | 0.71 | |
| MOL000438 | (3R)-3-(2-hydroxy-3,4-dimethoxyphenyl) chroman-7-ol | 67.67 | 0.26 | |
| MOL000439 | Isomucronulatol-7,2'-di-O-glucosiole | 49.28 | 0.62 | |
| MOL000442 | 1,7-Dihydroxy-3,9-dimethoxy pterocarpene | 39.05 | 0.48 | |
| MOL000098 | Quercetin | 46.43 | 0.28 |
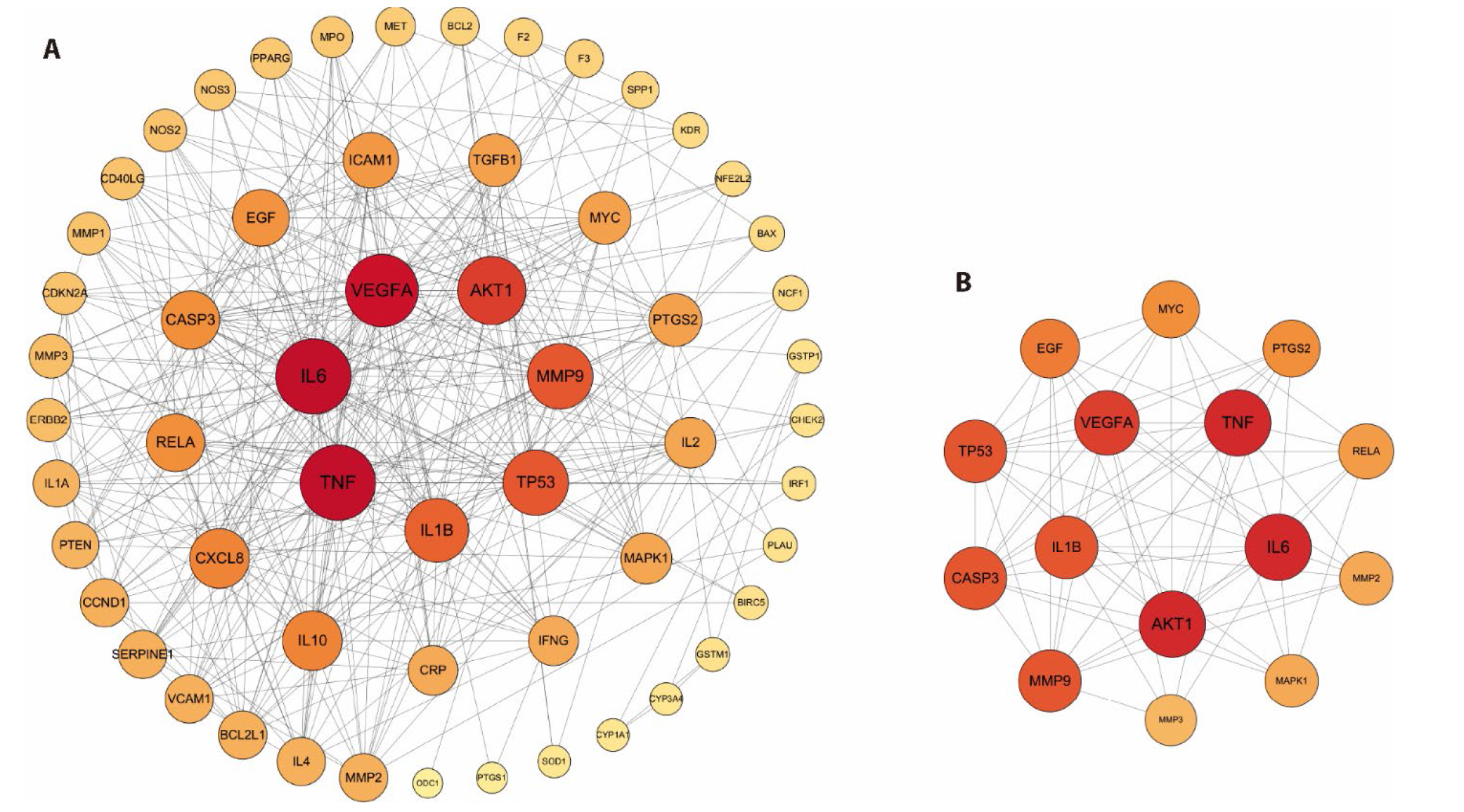
Figure 1 Network pharmacology analysis of DBD on GU A: PPI network for 57 potential targets; B: PPI network for the 14 key targets. DBD: Danggui Buxue decoction; GU: gastric ulcer; PPI: protein-protein interaction.
| Key targets | Betweenness centrality | Closeness centrality | Degree |
|---|---|---|---|
| TNF | 0.07224798 | 0.65882353 | 33 |
| IL-6 | 0.06024239 | 0.65116279 | 33 |
| VEGF | 0.09232003 | 0.66666667 | 31 |
| AKT1 | 0.1051178 | 0.64367816 | 28 |
| TP53 | 0.08365778 | 0.62921348 | 26 |
| MMP9 | 0.07389262 | 0.62222222 | 26 |
| IL-1β | 0.01989997 | 0.58947368 | 25 |
| CASP3 | 0.0375621 | 0.57731959 | 21 |
| RELA | 0.03861559 | 0.57142857 | 21 |
| EGF | 0.03017289 | 0.56565657 | 20 |
| MYC | 0.05219103 | 0.56 | 17 |
| PTGS2 | 0.0320954 | 0.54368932 | 17 |
| MAPK1 | 0.0283965 | 0.54368932 | 16 |
| MMP2 | 0.0200976 | 0.53846154 | 14 |
Table 2 Details of the key targets
| Key targets | Betweenness centrality | Closeness centrality | Degree |
|---|---|---|---|
| TNF | 0.07224798 | 0.65882353 | 33 |
| IL-6 | 0.06024239 | 0.65116279 | 33 |
| VEGF | 0.09232003 | 0.66666667 | 31 |
| AKT1 | 0.1051178 | 0.64367816 | 28 |
| TP53 | 0.08365778 | 0.62921348 | 26 |
| MMP9 | 0.07389262 | 0.62222222 | 26 |
| IL-1β | 0.01989997 | 0.58947368 | 25 |
| CASP3 | 0.0375621 | 0.57731959 | 21 |
| RELA | 0.03861559 | 0.57142857 | 21 |
| EGF | 0.03017289 | 0.56565657 | 20 |
| MYC | 0.05219103 | 0.56 | 17 |
| PTGS2 | 0.0320954 | 0.54368932 | 17 |
| MAPK1 | 0.0283965 | 0.54368932 | 16 |
| MMP2 | 0.0200976 | 0.53846154 | 14 |

Figure 2 Molecular docking: The hydrogen bond lengths, amino acid residues, and the active pockets between active components and proteins A: TNF-quercetin; B: TNF-kaempferol; C: IL-6-quercetin; D: VEGF-quercetin. TNF: tumor necrosis factor; IL-6: interleukin-6, VEGF: vascular endothelial growth factor.

Figure 3 Effect of DBD on gastric lesions induced by ethanol A: macroscopic examination of the gastric mucosa in mice of different groups; B: the average ulcer index of stomach samples in each group; C: results of HE staining of gastric mucosa (scale bar = 100 μm). A1, C1: Control group; A2, C2: Model group; A3, C3: Ranitidine group; A4, C4: DBD-H group; A5, C5: DBD-M group; A6, C6: DBD-L group. Control (distilled water, 1 week); Model (distilled water, 1 week); Ranitidine (ranitidine, 30 mg/kg body weight, 1 week); DBD-H (DBD, 2.34 g/kg, dry weight, 1 week); DBD-M (DBD, 1.17 g/kg, dry weight, 1 week); DBD-L (DBD, 0.59 g/kg, dry weight, 1 week). Statistical analyses were measured using one-way analysis of variance for multimal comparisons. Data were presented as mean ± standard deviation (n = 6). aP < 0.001 vs control group; bP < 0.001, cP < 0.05 vs model group. DBD: Danggui Buxue decoction.

Figure 4 Comparison of protein expression and mRNA expression levels A: representative results of protein phosphorylation levels in each group; B: quantitative results of protein phosphorylation levels in each group; C: relative mRNA expression of TNF-α; D: relative mRNA expression of IL-6; E: relative mRNA expression of VEGF; F: relative mRNA expression of IL-1β; G: relative mRNA expression of AKT1. Control (distilled water, 1 week); Model (distilled water, 1 week); Ranitidine (ranitidine, 30 mg/kg body weight, 1 week); DBD-H (DBD, 2.34 g/kg, dry weight, 1 week); DBD-M (DBD, 1.17 g/kg, dry weight, 1 week); DBD-L (DBD, 0.59 g/kg, dry weight, 1 week). DBD: Danggui Buxue decoction; TNF: tumor necrosis factor; AKT1: AKT serine/threonine kinase 1; IL-6: interleukin-6, VEGF: vascular endothelial growth factor; IL-1β: interleukin-1 beta. Statistical analyses were measured using one-way analysis of variance for multimal comparisons. Data were presented as mean ± standard deviation (n = 6). aP < 0.001 vs control group; bP < 0.001, cP < 0.01, dP < 0.05 vs model group.
| 1. | He Y, Koido M, Sutoh Y, et al. East Asian-specific and cross-ancestry genome-wide Meta-analyses provide mechanistic insights into peptic ulcer disease. Nat Genet 2023; 55: 2129-38. |
| 2. |
Xie X, Ren K, Zhou Z, Dang C, Zhang H. The global, regional and national burden of peptic ulcer disease from 1990 to 2019: a population-based study. BMC Gastroenterol 2022; 22: 58.
DOI PMID |
| 3. | Ford AC, Gurusamy KS, Delaney B, Forman D, Moayyedi P. Eradication therapy for peptic ulcer disease in Helicobacter pylori-positive people. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2016; 4: CD003840. |
| 4. |
Li Z, Zou D, Ma X, et al. Epidemiology of peptic ulcer disease: endoscopic results of the systematic investigation of gastrointestinal disease in China. Am J Gastroenterol 2010; 105: 2570-7.
DOI PMID |
| 5. |
Lanas A, Chan FKL. Peptic ulcer disease. Lancet 2017; 390: 613-24.
DOI PMID |
| 6. |
Lau JY, Sung J, Hill C, Henderson C, Howden CW, Metz DC. Systematic review of the epidemiology of complicated peptic ulcer disease: incidence, recurrence, risk factors and mortality. Digestion 2011; 84: 102-13.
DOI PMID |
| 7. | Leow AH, Lim YY, Liew WC, Goh KL. Time trends in upper gastrointestinal diseases and Helicobacter pylori infection in a multiracial Asian population--a 20-year experience over three time periods. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2016; 43: 831-7. |
| 8. | Sverden E, Agreus L, Dunn JM, Lagergren J. Peptic ulcer disease. BMJ 2019; 367: l5495. |
| 9. | Gupta A, Shetty S, Mutalik S, et al. Treatment of H. pylori infection and gastric ulcer: need for novel Pharmaceutical formulation. Heliyon 2023; 9: e20406. |
| 10. |
Kavitt RT, Lipowska AM, Anyane-Yeboa A, Gralnek IM. Diagnosis and treatment of peptic ulcer disease. Am J Med 2019; 132: 447-56.
DOI PMID |
| 11. | Haastrup PF, Thompson W, Sondergaard J, Jarbol DE. Side effects of long-term proton pump inhibitor use: a review. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 2018; 123: 114-21. |
| 12. | Haenisch B, von Holt K, Wiese B, et al. Risk of dementia in elderly patients with the use of proton pump inhibitors. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 2015; 265: 419-28. |
| 13. | Kuna L, Jakab J, Smolic R, Raguz-Lucic N, Vcev A, Smolic M. Peptic ulcer disease: a brief review of conventional therapy and herbal treatment options. J Clin Med 2019; 8: 179. |
| 14. | Gong AG, Li N, Lau KM, et al. Calycosin orchestrates the functions of Danggui Buxue Tang, a Chinese herbal decoction composing of Astragali Radix and Angelica Sinensis Radix: an evaluation by using calycosin-knock out herbal extract. J Ethnopharmacol 2015; 168: 150-7. |
| 15. | Xia LF, Hao ZH, Wang J. Analysis of the effect of Danggui Buxue Jiawei decoction on the treatment of refractory gastric ulcer in the elderly. Zhong Guo She Qu Yi Shi 2018; 34: 99-100. |
| 16. | Yang FX, Wang Y, Xia PF, et al. Review of chemical constituents,pharmacological effects and clinical applications of Danggui Buxue decoction and prediction and analysis of its Q-markers. Zhong Guo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2021; 46: 2677-85. |
| 17. | Li C, Zhu F, Wang S, Wang J, Wu B. Danggui Buxue decoction ameliorates inflammatory bowel disease by improving inflammation and rebuilding intestinal mucosal barrier. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2021; 2021: 8853141. |
| 18. | Bi WP, Man HB, Man MQ. Efficacy and safety of herbal medicines in treating gastric ulcer: a review. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20: 17020-8. |
| 19. | Chen Z, Liu L, Gao C, et al. Astragali Radix (Huangqi): a promising edible immunomodulatory herbal medicine. J Ethnopharmacol 2020; 258: 112895. |
| 20. |
Kim A, Lim JW, Kim H, Kim H. Supplementation with Angelica keiskei inhibits expression of inflammatory mediators in the gastric mucosa of Helicobacter pylori-infected mice. Nutr Res 2016; 36: 488-97.
DOI PMID |
| 21. | Schottker B, Adamu MA, Weck MN, Brenner H. Helicobacter pylori infection is strongly associated with gastric and duodenal ulcers in a large prospective study. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2012; 10: 487-93 e1. |
| 22. | Lee YC, Dore MP, Graham DY. Diagnosis and treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection. Annu Rev Med 2022; 73: 183-95. |
| 23. | Tarnawski AS, Ahluwalia A. The critical role of growth factors in gastric ulcer healing: the cellular and molecular mechanisms and potential clinical implications. Cells 2021; 10: 1964. |
| 24. |
Lian YZ, Lin IH, Yang YC, Chao JC. Gastroprotective effect of Lycium barbarum polysaccharides and C-phycocyanin in rats with ethanol-induced gastric ulcer. Int J Biol Macromol 2020; 165: 1519-28.
DOI PMID |
| 25. | Formiga RO, Alves Junior EB, Vasconcelos RC, et al. Effect of p-cymene and rosmarinic acid on gastric ulcer healing-involvement of multiple endogenous curative mechanisms. Phytomedicine 2021; 86: 153497. |
| 26. | Hsieh HL, Yu MC, Cheng LC, et al. Quercetin exerts anti-inflammatory effects via inhibiting tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression in normal human gastric epithelial cells. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28: 1139-58. |
| 27. | Shams SGE, Eissa RG. Amelioration of ethanol-induced gastric ulcer in rats by quercetin: implication of Nrf2/HO1 and HMGB1/TLR4/NF-kappaB pathways. Heliyon 2022; 8: e11159. |
| 28. | Fatima SF, Ishtiaq S, Lashkar MO, Youssef FS, Ashour ML, Elhady SS. Metabolic profiling of heliotropium crispum aerial parts using HPLC and FTIR and in vivo evaluation of its anti-ulcer activity using an ethanol induced acute gastric ulcer model. Metabolites 2022; 12: 750. |
| 29. | Olaitan BS, Sabino DA, Pavan E, et al. Evidence for the involvement of cytokines modulation and prokinetic properties in gastric ulcer healing effects of helicteres sacarolha A. St.-Hil. A. Juss. Chem Biodivers 2022; 19: e202200322. |
| 30. |
Robinson K, Letley DP, Kaneko K. The human stomach in health and disease: infection strategies by Helicobacter pylori. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 2017; 400: 1-26.
DOI PMID |
| 31. | Xiao ZP, Wang XD, Peng ZY, et al. Molecular docking, kinetics study, and structure-activity relationship analysis of quercetin and its analogous as Helicobacter pylori urease inhibitors. J Agric Food Chem 2012; 60: 10572-7. |
| 32. | Yi L, Lu Y, Yu S, Cheng Q, Yi L. Formononetin inhibits inflammation and promotes gastric mucosal angiogenesis in gastric ulcer rats through regulating NF-kappa B signaling pathway. J Recept Signal Transduct Res 2022; 42: 16-22. |
| 33. | Ding K, Tan YY, Ding Y, et al. beta-Sitosterol improves experimental colitis in mice with a target against pathogenic bacteria. J Cell Biochem 2019; 120: 5687-94. |
| 34. | Zhang S, Shen Y, Liu H, et al. Inflammatory microenvironment in gastric premalignant lesions: implication and application. Front Immunol 2023; 14: 1297101. |
| 35. | Sugimoto M, Yamaoka Y, Furuta T. Influence of interleukin polymorphisms on development of gastric cancer and peptic ulcer. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16: 1188-200. |
| 36. | Zou Y, Cui X, Xiang Q, et al. Protective effect of against ethanol-induced gastric ulcer and its mechanism. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban 2021; 50: 561-7. |
| 37. | Arakawa T, Watanabe T, Tanigawa T, Tominaga K, Fujiwara Y, Morimoto K. Quality of ulcer healing in gastrointestinal tract: its pathophysiology and clinical relevance. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18: 4811-22. |
| 38. |
Tourani M, Habibzadeh M, Karkhah A, Shokri-Shirvani J, Barari L, Nouri HR. Association of TNF-alpha but not IL-1beta levels with the presence of Helicobacter pylori infection increased the risk of peptic ulcer development. Cytokine 2018; 110: 232-6.
DOI PMID |
| 39. | Moezi L, Heidari R, Amirghofran Z, Nekooeian AA, Monabati A, Dehpour AR. Enhanced anti-ulcer effect of pioglitazone on gastric ulcers in cirrhotic rats: the role of nitric oxide and IL-1beta. Pharmacol Rep 2013; 65: 134-43. |
| 40. | McKenna M, Balasuriya N, Zhong S, Li SS, O'Donoghue P. Phospho-form specific substrates of protein kinase B (AKT1). Front Bioeng Biotechnol 2020; 8: 619252. |
| 41. | Siddika T, Balasuriya N, Frederick MI, Rozik P, Heinemann IU, O'Donoghue P. Delivery of active AKT1 to human cells. Cells 2022; 11: 3834. |
| 42. | Tarnawski AS, Ahluwalia A, Jones MK. Angiogenesis in gastric mucosa: an important component of gastric erosion and ulcer healing and its impairment in aging. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2014; 29 Suppl 4: 112-23. |
| 43. | Ivyna de Araujo Rego R, Guedes Silvestre GF, Ferreira de Melo D, et al. Flavonoids-rich plant extracts against Helicobacter pylori infection as prevention to gastric cancer. Front Pharmacol 2022; 13: 951125. |
| 44. | Zhang S, Huang J, Xie X, He Y, Mo F, Luo Z. Quercetin from polygonum capitatum protects against gastric inflammation and apoptosis associated with Helicobacter pylori infection by affecting the levels of p38MAPK, BCL-2 and BAX. Molecules 2017; 22: 744. |
| 45. |
Zheng Y, Liu Z, Cai A, et al. Study on the mechanism of Ginseng-Gegen for mesenteric lymphadenitis based on network pharmacology. Transl Pediatr 2022; 11: 1534-43.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | Kanae Umemoto, SHAN Xiyao, Takuro Ishikawa, Tadashi Watsuji, Yasuharu Watanabe, Munekazu Naito. Novel insight into the site-specificity of Hegu (LI4): morphological, biomechanical, and histological analyses [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(4): 867-872. |
| [2] | LI Yue, DENG Jinyan, PI Shanshan, ZHANG Yingjuan, ZHAO Dan, GUO Yi, YE Yong’an, ZAO Xiaobin, DU Hongbo. Weifuchun (胃复春 ) exerts therapeutic effects on gastric fundic gland polyps by promoting ferroptosis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(3): 618-627. |
| [3] | HUANG Jiaen, LUO Qing, DONG Gengting, PENG Weiwen, HE Jianhong, DAI Weibo. Xiahuo Pingwei San (夏藿平胃散) attenuated intestinal inflammation in dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis mice through inhibiting the receptor for advanced glycation end-products signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(2): 311-325. |
| [4] | HAN Shuai, Du Zhikang, WANG Zirui, HUANG Tianfeng, GE Yali, SHI Jianwen, GAO Ju. Network pharmacology approach to unveiling the mechanism of berberine in the amelioration of morphine tolerance [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(2): 376-384. |
| [5] | TAN Xiying, GU Ruxin, TAO Jing, ZHANG Yu, SUN RuiQian, YIN Gang, ZHANG Shuo, TANG Decai. Integrating network pharmacology and experimental validation to uncover the synergistic effects of Huangqi (Radix Astragali Mongolici)-Ezhu (Rhizoma Curcumae Phaeocaulis) with 5-fluorouracil in colorectal cancer models [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(2): 385-398. |
| [6] | SHI Jinyu, PAN Fuwei, GE Haiya, YANG Zongrui, ZHAN Hongsheng. Mechanism of Qigu capsule (芪骨胶囊) as a treatment for sarcopenia based on network pharmacology and experimental validation [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(2): 399-407. |
| [7] | HU Huiming, WENG Jiajun, TANG Fangrui, WANG Yaqi, FAN Shengxian, WANG Xuecheng, CUI Can, SHAO Feng, ZHU Yanchen. Hypolipidemic effect and mechanism of Hedan tablet (荷丹片) based on network pharmacology [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(2): 408-421. |
| [8] | YUAN Jianan, CHENG Kunming, LI Chao, ZHANG Xiang, DING Zeyu, LI Bing, ZHENG Yongqiu. Atractylenolide I ameliorates post-infectious irritable bowel syndrome by inhibiting the polymerase I and transcript release factor and c-Jun N-terminal kinase/inducible nitric oxide synthase pathway [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(1): 57-65. |
| [9] | YAN Kai, WANG Wei, WANG Yan, GAO Huijuan, FENG Xingzhong. Network pharmacology-based study on the mechanism of Tangfukang formula (糖复康方) against type 2 diabetes mellitus [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(1): 76-88. |
| [10] | ZHU Peixuan, SU Zeqi, FAN Qiongyin, ZHANG Cai, WANG Ting. Network pharmacology and animal experiments revealed the protective effects of Guilong prescription (归龙方) on chronic prostatitis and its possible mechanisms [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(1): 89-99. |
| [11] | YANG Chunyan, LUO Jia, PENG Weijie, DAI Weibo. Huaiyu pill (槐榆片) alleviates inflammatory bowel disease in mice via blocking toll like receptor 4/ myeloid differentiation primary response gene 88/ nuclear factor kappa B subunit 1 pathway [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(5): 916-925. |
| [12] | YU Siyun, ZHANG Shiwen, XIA Yu, LIU Xiaoqing, LIU Yajie, FU Jinrong. Network-based pharmacology and experimental validation to explore the mechanism of action of the Jiawei Pentongling formula (加味盆痛灵方) for the treatment of endometriosis-related pain [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(5): 991-999. |
| [13] | SONG Zhenguang, YANG Bin, WANG Fei, YAN Dongmei, ZHOU Xiaoqing, HUANG Liping, GAO Xuemei, LI Bin, HUANG Luqi. Study on the four Qi of Pfaffia glomerata based on the metabolomics technology and comparison of Dangshen (Radix Codonopsis) in the equivalent substitution prescription [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(4): 713-721. |
| [14] | YANG Qinjun, YIN Dandan, WANG Hui, GAO Yating, WANG Xinheng, WU Di, TONG Jiabing, WANG Chuanbo, LI Zegeng. Uncovering the action mechanism of Shenqi Tiaoshen formula (参芪调肾方) in the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease through network pharmacology, molecular docking, and experimental verification [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(4): 770-783. |
| [15] | HU Yuanyuan, LIU Xinguang, ZHAO Peng, WU Jinyan, YAN Xinhua, HOU Runsu, WANG Xiangcheng, YANG Fan, TIAN Xinrong, LI Jiansheng. Integration of serum pharmacochemistry with network pharmacology to reveal the potential mechanism of Yangqing Chenfei formula (养清尘肺方) for the treatment of silicosis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(4): 784-793. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

