Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (6): 1201-1214.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20250923.001
Previous Articles Next Articles
Moxibustion for human immunodeficiency virus and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome and its complications: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials
KONG Lingyao1, ZHANG Xiaowen1, WANG Xuehui1, WANG Zhijie2, Robinson Nicola3, LIU Jianping1( )
)
- 1 Centre for Evidence-Based Chinese Medicine, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100029, China
2 Oncology Department, Shanxi Province Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Taiyuan 030012, China
3 Institute of Health and Social Care, London South Bank University, London SE1 0AA, United Kingdom
-
Received:2025-04-10Accepted:2025-06-04Online:2025-12-15Published:2025-09-23 -
Contact:Prof. LIU Jianping, Professor and Director, Centre for Evidence-Based Chinese Medicine, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100029, China. liujp@bucm.edu.cn, Telephone: +86-18801396070 -
Supported by:High-level Traditional Chinese Medicine key subjects construction project of National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine-Evidence-based Traditional Chinese Medicine(zyyzdxk-2023249);Guest Professor of Beijing University of Chinese Medicine(20210017)
Cite this article
KONG Lingyao, ZHANG Xiaowen, WANG Xuehui, WANG Zhijie, Robinson Nicola, LIU Jianping. Moxibustion for human immunodeficiency virus and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome and its complications: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(6): 1201-1214.
share this article
| Study ID | Country | Condition | Course of condition (month, T/C) | Sample size (T/C) | Gender (%) (male, T/C) | Age (years, T/C) | Intervention | Control | Outcome | Duration | Funding | Follow up |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guo Y, Qian BY 2005 | Eritrea | HIV-related diarrhea | 120 d- 5 years/ 150 d- 5 years | 60/30 | 60/70 | 21-53 (range)/19-58 (range) | Moxa stick moxibustion+ginger/salt-insulated moxibustion (ST36, CV8, CV4, ST25; Qi deficiency of the spleen and lung pattern: BL13, BL25. Deficiency of the spleen and stomach pattern: BL20, BL21, CV12. Yang deficiency of the spleen and kidney pattern: BL23, GV4. Watery stools occurring 5 to 10 times per day: CV8 (ginger-insulated moxibustion). Stool with mucus, CV8 (salt-insulated moxibustion). 5-10 min, QD) | Western Medicine (oral administration of berberine tablets and oral sugar-salt solution for fluid replenishment. Fluid replenishment should be adjusted based on the severity of the condition, with a daily dosage ranging from 500 to 2500 mL. Each 500 mL of solution should contain 25 g of glucose and 4.5 g of sodium chloride.) | Symptom resolution | 7 d | NR | NR |
| Wang JD et al 2006 | China | HIV-related diarrhea | NR | 50/50 | 47 | 43.1 (15-66) | Moxa stick moxibustion (ST36, CV8, CV4. 10 min, BID)+Western Medicine | Western Medicine (conventional treatment (anti-pathogenic therapy, fluid resuscitation, electrolyte and fluid replacement)) | Symptom resolution | 15 d | Yes | NR |
| Zhou LH et al 2007 | China | HIV-related diarrhea | 11.75 years/ 11.75 years | 41/34 | 54/21 | 45.24± 9.13/ 42.79± 11.65 | Moxa stick moxibustion (ST36, CV4, CV8. 20 min, QD)+Western Medicine | Western Medicine (Flupentixol 0.2 g, TID; Smecta, 1 sachet, TID. Treatment duration is 1 week. Discontinue flupentixol and continue taking Smecta for 2 months.) | NHP, symptom resolution, adverse events | 2 months | Yes | 4 months |
| Liu ZW et al 2013 | China | HIV-positive | 32.52±18.29 /33.68±17.57 | 50/50 | 46/48 | 35.0±0.5/ 34.0±0.6 | Moxa stick moxibustion (ST36, SP6, BL18, KI3, LR3, IL4 Moxibustion therapy done with a partner, once daily for the first 3 days, then 3 times per week.) | Health education (including television lectures on HIV prevention and control, and distribution of informational pamphlets) | KPS, CD4+ | 3 months | Yes | 9 months |
| Zhang X et al 2014 | China | HIV patients with peripheral neuropathy | 5.9/6.6 | 30/30 | 40/53 | 45 months/ 44 months | Moxibustion (ST36, ST37, GB34. QD)+Western Medicine | Western Medicine (ART+methylcobalamin tablets, vitamin B1 tablets, and gabapentin capsules.) | symptom resolution | 1 month | Yes | NR |
| Nkomo O et al 2016 | Gabon | AIDS lung infection | NR | 18/18 | 58 | 42.67±12.68/ 41.80±15.20 | Wheat-grain sized cone moxibustion (GV14, ST36. 10 Zhuang. 2 times one week)+Western Medicine | Western Medicine (routine anti-infection treatment, ART) | CD4+, WHOQOL-HIV, symptom resolution | 4 weeks | NR | NR |
| Nong HL, Shi ZZ et al 2016 | China | HIV-related diarrhea | 5.7± 1.9 years/ 6.5±1.5 years | 26/26 | 65/69 | 40.4±10.2/ 39.6±11.3 | Ginger-insulated moxibustion (CV8, CV4, ST25, CV12. 10 min, BID) | Western Medicine (oral berberine tablets and oral sugar-saline rehydration solution (each 500 mL of rehydration solution contains 25 g of glucose and 4.5 g of sodium chloride) are given. Depending on the severity of the condition, 500 to 2000 mL of rehydration solution is given daily.) | MOS-HIV, symptom resolution | 14 d | Yes | NR |
| Yuan HZ et al 2017 | China | HIV-related diarrhea | NR | 25/25 | 52/56 | 43.3±10.8/ 45.1±10.3 | Moxa stick moxibustion (ST36, CV8, CV4, ST25, CV12. 10 min, BID) + Western Medicine | Western Medicine (pathogenic treatment should be given as appropriate, while oral berberine tablets and oral sugar-salt water rehydration are administered. The amount of fluid supplementation should be 500-2500 mL/d depending on the severity of the patient's condition, with each 500 mL solution containing 25 g of glucose and 4.5 g of sodium chloride.) | symptom resolution | 14 d | NR | NR |
| Liu ZW et al 2018 | China | HIV-positive | 33.5± 17.3/ 34.7±17.5 | 50/50 | 52/54 | 36.5±4.5/ 35.6±5.6 | Moxa stick moxibustion (ST36, CV8, CV4, ST25, SP6, BL20, BL18, CV12 once a day for the first 3 d, then once every 3d)+ Western Medicine | Western Medicine (the following 3 types: ①TDF: 0.3 g, once a night, 3TC: 0.3 g, once a night, EFV: 0.6 g, once a night; ②AZT: 0.3 g, once every 12 h, 3TC: 0.3 g, QD, NVP: 0.2 g, Once every 12 h; ③AZT: 0.3 g, once every 12 h, 3TC: 0.3 g, QD, LPV/r: 0.5 g every 12 h) | CD4+, CD4+/CD8+, IL-2, IL-7, WHOQOL-BREF, adverse events | 1.5 years | Yes | NR |
| Liu ZW et al 2018 | China | People with HIV with negative emotions | 28.25±9.12/30.68±8.76 | 50/50 | 48/46 | 35.5±1.5/ 34.5±1.6 | Moxa stick moxibustion (ST36, SP6, BL18, KI13, LR3, LI4. 5-10 min, TID) | Health education (including the explanation of AIDS related knowledge, the latest progress of AIDS prevention and treatment) | CD4+, CD4+/CD8+, | 6 months | Yes | NR |
| Ao Wen et al 2024 | China | HIV-positive | NR | 35/36 | 83/86 | 42.31± 11.05/ 51.25± 7.88 | Moxa stick moxibustion (RN6, RN4, 15 min, QD) | Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate tablets, 0.3 g, QD; Lamivudine tablets, 0.3 g, QD; Efavirenz tablets, 600 mg, QD | CD4+, WHOQOL-BREF, adverse events | 12 weeks | Yes | 3 months |
Table 1 Characteristics of included studies
| Study ID | Country | Condition | Course of condition (month, T/C) | Sample size (T/C) | Gender (%) (male, T/C) | Age (years, T/C) | Intervention | Control | Outcome | Duration | Funding | Follow up |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guo Y, Qian BY 2005 | Eritrea | HIV-related diarrhea | 120 d- 5 years/ 150 d- 5 years | 60/30 | 60/70 | 21-53 (range)/19-58 (range) | Moxa stick moxibustion+ginger/salt-insulated moxibustion (ST36, CV8, CV4, ST25; Qi deficiency of the spleen and lung pattern: BL13, BL25. Deficiency of the spleen and stomach pattern: BL20, BL21, CV12. Yang deficiency of the spleen and kidney pattern: BL23, GV4. Watery stools occurring 5 to 10 times per day: CV8 (ginger-insulated moxibustion). Stool with mucus, CV8 (salt-insulated moxibustion). 5-10 min, QD) | Western Medicine (oral administration of berberine tablets and oral sugar-salt solution for fluid replenishment. Fluid replenishment should be adjusted based on the severity of the condition, with a daily dosage ranging from 500 to 2500 mL. Each 500 mL of solution should contain 25 g of glucose and 4.5 g of sodium chloride.) | Symptom resolution | 7 d | NR | NR |
| Wang JD et al 2006 | China | HIV-related diarrhea | NR | 50/50 | 47 | 43.1 (15-66) | Moxa stick moxibustion (ST36, CV8, CV4. 10 min, BID)+Western Medicine | Western Medicine (conventional treatment (anti-pathogenic therapy, fluid resuscitation, electrolyte and fluid replacement)) | Symptom resolution | 15 d | Yes | NR |
| Zhou LH et al 2007 | China | HIV-related diarrhea | 11.75 years/ 11.75 years | 41/34 | 54/21 | 45.24± 9.13/ 42.79± 11.65 | Moxa stick moxibustion (ST36, CV4, CV8. 20 min, QD)+Western Medicine | Western Medicine (Flupentixol 0.2 g, TID; Smecta, 1 sachet, TID. Treatment duration is 1 week. Discontinue flupentixol and continue taking Smecta for 2 months.) | NHP, symptom resolution, adverse events | 2 months | Yes | 4 months |
| Liu ZW et al 2013 | China | HIV-positive | 32.52±18.29 /33.68±17.57 | 50/50 | 46/48 | 35.0±0.5/ 34.0±0.6 | Moxa stick moxibustion (ST36, SP6, BL18, KI3, LR3, IL4 Moxibustion therapy done with a partner, once daily for the first 3 days, then 3 times per week.) | Health education (including television lectures on HIV prevention and control, and distribution of informational pamphlets) | KPS, CD4+ | 3 months | Yes | 9 months |
| Zhang X et al 2014 | China | HIV patients with peripheral neuropathy | 5.9/6.6 | 30/30 | 40/53 | 45 months/ 44 months | Moxibustion (ST36, ST37, GB34. QD)+Western Medicine | Western Medicine (ART+methylcobalamin tablets, vitamin B1 tablets, and gabapentin capsules.) | symptom resolution | 1 month | Yes | NR |
| Nkomo O et al 2016 | Gabon | AIDS lung infection | NR | 18/18 | 58 | 42.67±12.68/ 41.80±15.20 | Wheat-grain sized cone moxibustion (GV14, ST36. 10 Zhuang. 2 times one week)+Western Medicine | Western Medicine (routine anti-infection treatment, ART) | CD4+, WHOQOL-HIV, symptom resolution | 4 weeks | NR | NR |
| Nong HL, Shi ZZ et al 2016 | China | HIV-related diarrhea | 5.7± 1.9 years/ 6.5±1.5 years | 26/26 | 65/69 | 40.4±10.2/ 39.6±11.3 | Ginger-insulated moxibustion (CV8, CV4, ST25, CV12. 10 min, BID) | Western Medicine (oral berberine tablets and oral sugar-saline rehydration solution (each 500 mL of rehydration solution contains 25 g of glucose and 4.5 g of sodium chloride) are given. Depending on the severity of the condition, 500 to 2000 mL of rehydration solution is given daily.) | MOS-HIV, symptom resolution | 14 d | Yes | NR |
| Yuan HZ et al 2017 | China | HIV-related diarrhea | NR | 25/25 | 52/56 | 43.3±10.8/ 45.1±10.3 | Moxa stick moxibustion (ST36, CV8, CV4, ST25, CV12. 10 min, BID) + Western Medicine | Western Medicine (pathogenic treatment should be given as appropriate, while oral berberine tablets and oral sugar-salt water rehydration are administered. The amount of fluid supplementation should be 500-2500 mL/d depending on the severity of the patient's condition, with each 500 mL solution containing 25 g of glucose and 4.5 g of sodium chloride.) | symptom resolution | 14 d | NR | NR |
| Liu ZW et al 2018 | China | HIV-positive | 33.5± 17.3/ 34.7±17.5 | 50/50 | 52/54 | 36.5±4.5/ 35.6±5.6 | Moxa stick moxibustion (ST36, CV8, CV4, ST25, SP6, BL20, BL18, CV12 once a day for the first 3 d, then once every 3d)+ Western Medicine | Western Medicine (the following 3 types: ①TDF: 0.3 g, once a night, 3TC: 0.3 g, once a night, EFV: 0.6 g, once a night; ②AZT: 0.3 g, once every 12 h, 3TC: 0.3 g, QD, NVP: 0.2 g, Once every 12 h; ③AZT: 0.3 g, once every 12 h, 3TC: 0.3 g, QD, LPV/r: 0.5 g every 12 h) | CD4+, CD4+/CD8+, IL-2, IL-7, WHOQOL-BREF, adverse events | 1.5 years | Yes | NR |
| Liu ZW et al 2018 | China | People with HIV with negative emotions | 28.25±9.12/30.68±8.76 | 50/50 | 48/46 | 35.5±1.5/ 34.5±1.6 | Moxa stick moxibustion (ST36, SP6, BL18, KI13, LR3, LI4. 5-10 min, TID) | Health education (including the explanation of AIDS related knowledge, the latest progress of AIDS prevention and treatment) | CD4+, CD4+/CD8+, | 6 months | Yes | NR |
| Ao Wen et al 2024 | China | HIV-positive | NR | 35/36 | 83/86 | 42.31± 11.05/ 51.25± 7.88 | Moxa stick moxibustion (RN6, RN4, 15 min, QD) | Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate tablets, 0.3 g, QD; Lamivudine tablets, 0.3 g, QD; Efavirenz tablets, 600 mg, QD | CD4+, WHOQOL-BREF, adverse events | 12 weeks | Yes | 3 months |
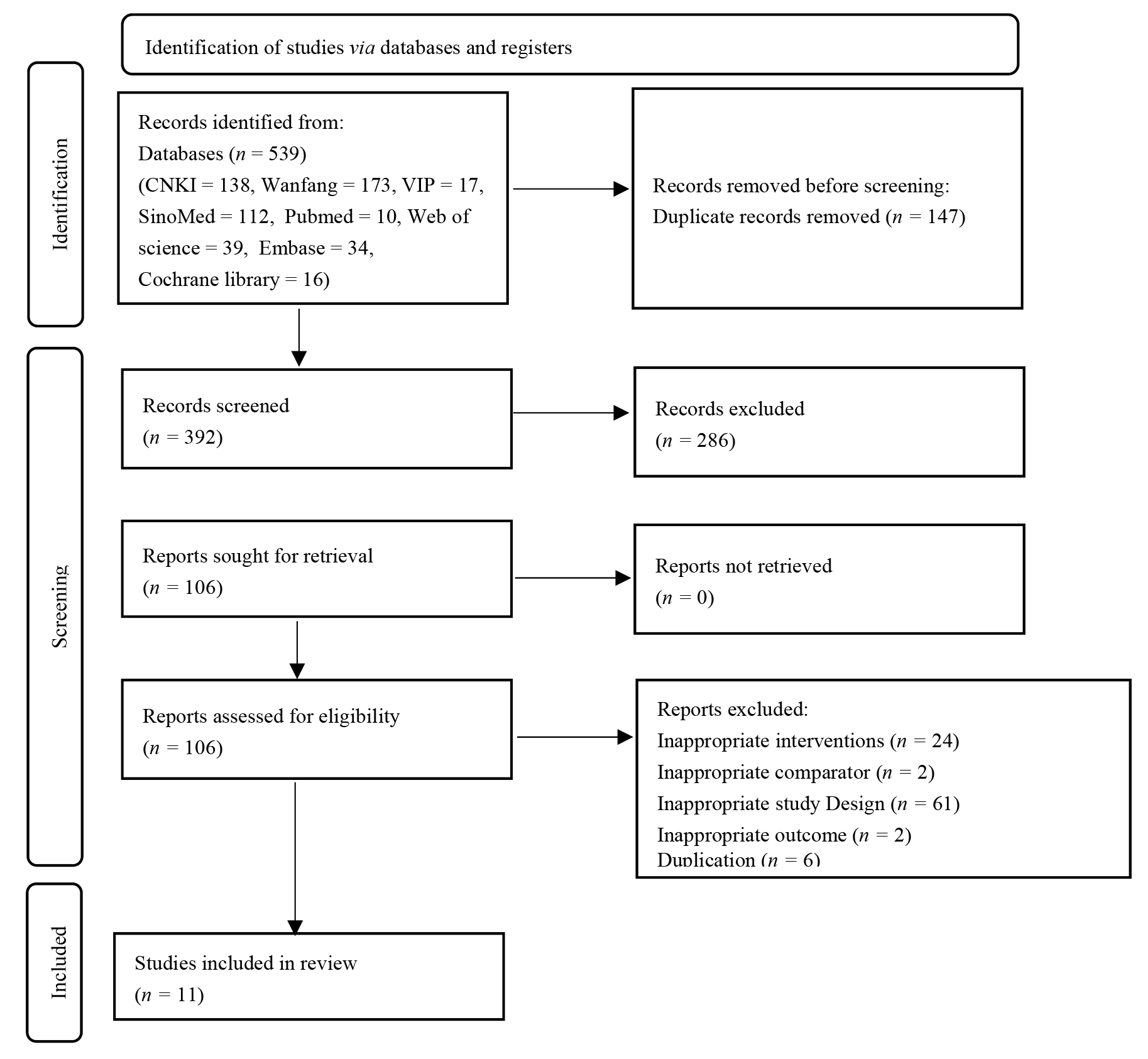
Figure 1 Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and Meta-analysis flow diagram CNKI: China National Knowledge Infrastructure Database; VIP: China Science and Technology Journal Database

Figure 2 Risk of bias of included studies A: risk of bias summary for each individual outcome within the included studies; B: risk of bias graph summarizing the overall percentage of judgments. CD: cluster of differentiation; HAD: hospital anxiety and depression scale; IL: interleukin; KPS: karnofsky performance status; MOS-HIV: medical outcomes study-HIV health survey; NHP: Nottingham health profile; WHOQOL-BREF: world health organization quality of life-brief version; WHOQOL-HIV: world health organization quality of life for HIV; HIV: human immunodeficiency virus.
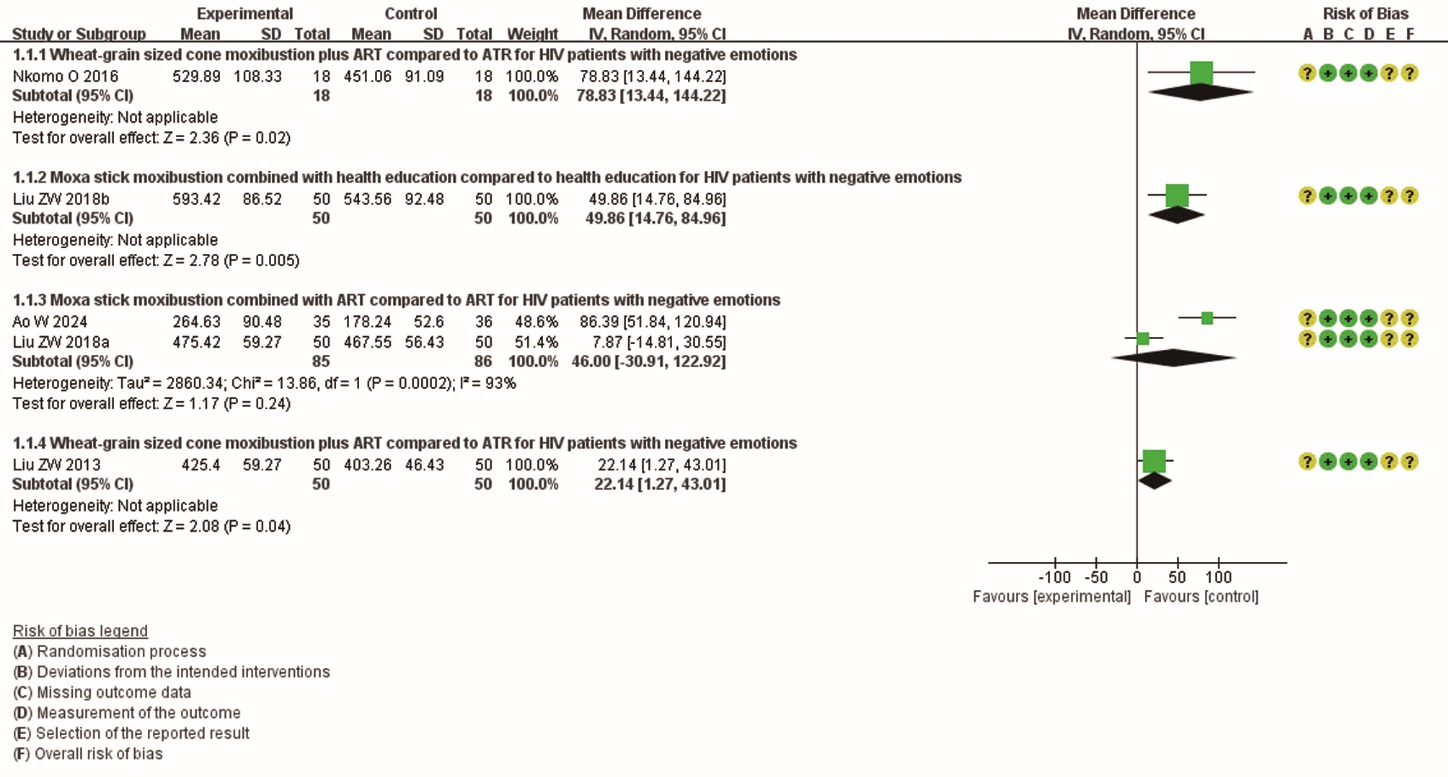
Figure 3 Meta-analysis of CD4+ count of patients with HIV HIV: human immunodeficiency virus; ART: antiretroviral therapy; SD: standard deviation; CI: confidence interval; IV: inverse variance; df: degrees of freedom.
| Condition | Study | Criterion | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| HIV-related diarrhea | Nong HL, Shi ZZ 2016 Wang JD et al 2006 Guo Y, Qian BY 2005 | Criteria A: reduction in stool frequency by at least 2 times compared to before treatment, but stools remain unformed; slight improvement in other associated symptoms. | Guiding Principle of Clinical Research on New Drugs of Traditional Chinese Medicine |
| HIV-related diarrhea | Yuan HZ et al 2017 Zhou LH et al 2007 | Criteria B: slight improvement in stool consistency and frequency, partial improvement in TCM symptoms, and a reduction in symptom score of ≥ 30% and < 70%. | Guiding Principle for Treating Diarrhea with New Drugs of Traditional Chinese Medicine |
| AIDS lung infection | Baptiste O 2016 | Criteria C: clinical symptoms have significantly improved, with a symptom score improvement rate of ≥ 30% and < 70% | NR |
| HIV patients with peripheral neuropathy | Zhang X et al 2014 | Criteria D: clinical symptoms and signs show improvement, with a symptom score reduction of > 30%. | NR |
Table 2 The criterion of symptom resolution
| Condition | Study | Criterion | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| HIV-related diarrhea | Nong HL, Shi ZZ 2016 Wang JD et al 2006 Guo Y, Qian BY 2005 | Criteria A: reduction in stool frequency by at least 2 times compared to before treatment, but stools remain unformed; slight improvement in other associated symptoms. | Guiding Principle of Clinical Research on New Drugs of Traditional Chinese Medicine |
| HIV-related diarrhea | Yuan HZ et al 2017 Zhou LH et al 2007 | Criteria B: slight improvement in stool consistency and frequency, partial improvement in TCM symptoms, and a reduction in symptom score of ≥ 30% and < 70%. | Guiding Principle for Treating Diarrhea with New Drugs of Traditional Chinese Medicine |
| AIDS lung infection | Baptiste O 2016 | Criteria C: clinical symptoms have significantly improved, with a symptom score improvement rate of ≥ 30% and < 70% | NR |
| HIV patients with peripheral neuropathy | Zhang X et al 2014 | Criteria D: clinical symptoms and signs show improvement, with a symptom score reduction of > 30%. | NR |
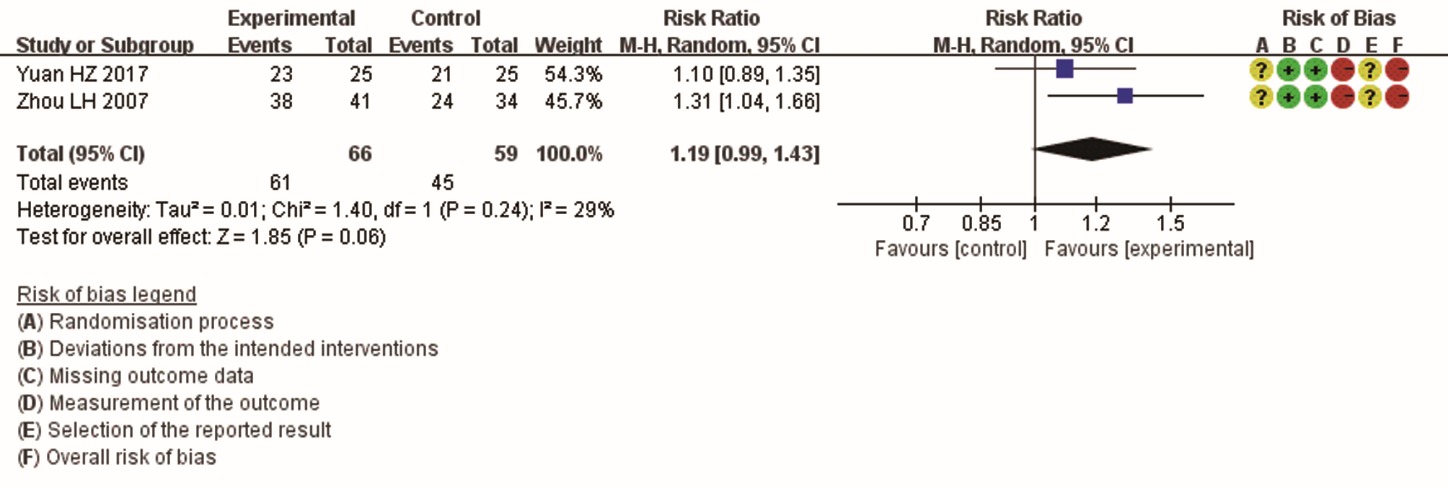
Figure 4 Meta-analysis of symptom resolution of HIV-related diarrhea after treatment: moxa stick moxibustion combined with Western Medicine versus Western Medicine alone CI: confidence interval; df: degrees of freedom; HIV: human immunodeficiency virus; M-H: Mantel-Haenszel.
| 1. |
Gallo RC, Montagnier L. The discovery of HIV as the cause of AIDS. N Engl J Med 2003; 349: 2283-5.
DOI URL |
| 2. | World Health Organization. HIV. cited 2024-06-12. Available from URL: https://www.who.int/health-topics/hiv-aids#tab=tab_1. |
| 3. |
Zhu Z, Zhao R, Hu Y. Symptom Clusters in People Living With HIV: A Systematic Review. J Pain Symptom Manage 2019; 58: 115-33.
DOI URL |
| 4. | United Nations. AIDS. Global Issues. cited 2024-06-12; 2 screens. Available from URL: : https://www.un.org/en/global-issues/aids#:-:text= According%20to%20UNAIDS%2C%20since%20the,them%20were%20women%20and%20girls. |
| 5. |
Gilks CF, Crowley S, Ekpini R, et al. The WHO public-health approach to antiretroviral treatment against HIV in resource-limited settings. Lancet 2006; 368: 505-10.
DOI PMID |
| 6. | World Health Organization. Global health sector strategies on, respectively, HIV, viral hepatitis and sexually transmitted infections for the period 2022-2030. 2022-07-18, cited 2024-12-08; 4. Available from URL: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240053779. |
| 7. | United Nations General Assembly. Political declaration on HIV and AIDS: Ending inequalities and getting on track to end AIDS by 2030. 2021-06-09, cited 2024-12-08. Available from URL: https://www.unaids.org/en/resources/documents/2021/2021_political-declaration-on-hiv-and-aids. |
| 8. |
Matza LS, Chung KC, Kim KJ, et al. Risks associated with antiretroviral treatment for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV): qualitative analysis of social media data and health state utility valuation. Qual Life Res 2017; 26: 1785-98.
DOI PMID |
| 9. | World Health Organization.HIV drug resistance:brief report 2024. 2024-2-29, cited 2024-12-08; 2. Available from URL: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240086319. |
| 10. |
Greenwald MK, Akcasu N, Baal P, Outlaw AY, Cohn JA, Lundahl LH. Cannabis and complementary/alternative self-treatment approaches for symptom management among African American persons living with HIV. AIDS Care 2023; 35: 78-82.
DOI URL |
| 11. |
Lorenc A, Robinson N. A review of the use of complementary and alternative medicine and HIV: issues for patient care. AIDS Patient Care STDS 2013; 27: 503-10.
DOI URL |
| 12. |
Weber R, Christen L, Loy M, et al. Randomized, placebo-controlled trial of Chinese herb therapy for HIV-1-infected individuals. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 1999; 22: 56-64.
DOI URL |
| 13. | Han G. The TCM remedies for treatment of AIDS--a clinical report of 60 cases. J Tradit Chin Med 2007; 27: 33-6. |
| 14. |
Jocelyn, Nasution FM, Nasution NA, et al. HIV/AIDS in Indonesia: current treatment landscape, future therapeutic horizons, and herbal approaches. Front Public Health 2024; 12: 1298297.
DOI URL |
| 15. |
Swaminathan S, Padmapriyadarsini C, Yoojin L, et al. Nutritional supplementation in HIV-infected individuals in South India: a prospective interventional study. Clin Infect Dis 2010; 51: 51-7.
DOI PMID |
| 16. | Olsen MF, Abdissa A, Kæstel P, et al. Effects of nutritional supplementation for HIV patients starting antiretroviral treatment: randomised controlled trial in Ethiopia. BMJ 2014; 348: g3187. |
| 17. |
Rodkjaer LO, Laursen T, Seeberg K, et al. The effect of a mind-body intervention on mental health and coping self-efficacy in HIV-infected individuals: a feasibility study. J Altern Complement Med 2017; 23: 326-30.
DOI URL |
| 18. |
Ramirez-Garcia MP, Gagnon MP, Colson S, Côté J, Flores-Aranda J, Dupont M. Mind-body practices for people living with HIV: a systematic scoping review. BMC Complement Altern Med 2019; 19: 125.
DOI |
| 19. | Hillier SL, Louw Q, Morris L, Uwimana J, Statham S. Massage therapy for people with HIV/AIDS. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2010; 2010: Cd007502. |
| 20. | Ge S, Dune L, Liu M, et al. Feasibility of therapeutic Chinese massage (Tui Na) for peripheral neuropathy among people with human immunodeficiency virus: findings of a pilot randomized controlled trial. Front Neurol 2023; 14: 1148150. |
| 21. | Littlewood RA, Vanable PA. A global perspective on complementary and alternative medicine use among people living with HIV/AIDS in the era of antiretroviral treatment. Curr HIV/AIDS Rep 2011; 8: 257-68. |
| 22. | Deng H, Shen X. The mechanism of moxibustion: ancient theory and modern research. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2013; 2013: 379291. |
| 23. |
Yin S, Zhu F, Li Z, et al. An overview of systematic reviews of moxibustion for knee osteoarthritis. Front Physiol 2022; 13: 822953.
DOI URL |
| 24. |
Li Y, Hong E, Ye W, You J. Moxibustion as an adjuvant therapy for cancer pain: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. J Pain Res 2023; 16: 515-25.
DOI PMID |
| 25. |
Yin Z, Li Y, Zhang X, et al. Moxibustion ameliorates cognitive function in older adults with mild cognitive impairment: a systematic review and Meta-analysis of randomized controlled clinical trial. Eur J Integr Med 2022; 53: 102133.
DOI URL |
| 26. | Chen YY. Discussion on regulative effects of moxibustion on immune functions of HIV /AIDS patients. Zhong Guo Zhong Yi Ji Chu Yi Xue Za Zhi 2011; 17: 1256-7. |
| 27. | Yuan HZ, Hou MJ, Zhang X, et al. Clinical observation on treating diarrhea in AIDS in TCM. Zhong Yi Lin Chuang Yan Jiu 2017; 9: 54-6. |
| 28. | Liu ZW, Pang J, Jiang F, et al. Clinical observation of moxibustion therapy under the mode of peer education in the treatment of negative emotions in HIV infected patients. Shi Zhen Guo Yi Yi Yao 2018; 29: 136-7. |
| 29. | Liu ZW, Deng X, Mo JH, et al. Moxibustion combined with highly active antiretroviral therapy for CD4+ and γ chain cytokines of HIV infected patients. Zhong Guo Zhen Jiu 2018; 38. |
| 30. | Nong HL, Shi ZZ. Clinical research of moxibustion insulated by ginger in the treatment of AIDS diarrhea. Zhong Guo Yi Yao Dao Bao 2016; 13: 101-3+11. |
| 31. | Page MJ, Mckenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021; 372: n71. |
| 32. | From the Centers for Disease Control and prevention. 1993 revised classification system for HIV infection and expanded surveillance case definition for AIDS among adolescents and adults. JAMA 1993; 269: 460. |
| 33. | Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Revised surveillance case definition for HIV infection-United States, 2014. MMWR Recomm Rep 2014; 63: 1-10. |
| 34. |
Saldanha IJ, Li T, Yang C, Ugarte-Gil C, Rutherford GW, Dickersin K. Social network analysis identified central outcomes for core outcome sets using systematic reviews of HIV/AIDS. J Clin Epidemiol 2016; 70: 164-75.
DOI PMID |
| 35. | Sterne JAC, Savović J0 Page MJ, et al. RoB 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2019; 366: l4898. |
| 36. | Higgins JPT, Li T, Deeks JJ (editors). Chapter 6:Choosing effect measures and computing estimates of effect. In: Higgins JPT, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Welch VA (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 6.3 (updated February 2022). Cochrane, 2022. Available from URL: www.training.cochrane.org/handbook. |
| 37. |
Murad MH, Chu H, Lin L, Wang Z. The effect of publication bias magnitude and direction on the certainty in evidence. BMJ Evid Based Med 2018; 23: 84-6.
DOI PMID |
| 38. |
Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Schünemann HJ, Tugwell P, Knottnerus A. GRADE guidelines: a new series of articles in the Journal of Clinical Epidemiology. J Clin Epidemiol 2011; 64: 380-2.
DOI PMID |
| 39. | Baptiste ONJ. Clinical grain moxibustion AIDS lung infection CD4+T lymphocytes and impact studies. Nanjing: Nanjing TCM University, 2016: 13-23. |
| 40. | Guo Y, Qian BY. A clinical observation on 60 cases of treating diarrhea caused by AIDS with moxibustion. Henan Zhong Yi Xue Yuan Xue Bao 2005; 20: 6-7. |
| 41. | Liu ZW, Deng X, Mo JH, et al. Clinical observation on moxibustion for 50 cases of hiv infection under the peer education. Zhong Yi Za Zhi 2013; 54: 1119-21+1126. |
| 42. | Zhang X, Sun Y, Yang X, et al. Clinical research of ai-moxibustion therapy in treating peripheral neuropathy complicated by AIDS. Zhong Yi Xue Bao 2014; 29: 1703-4. |
| 43. | Zhou LH, Tang Y, Yang YH, et al. Clinical study of AIDS associated diarrhea treated with TCM therapy. Zhong Guo Zhong Yi Yao Xin Xi Za Zhi 2007: 10-2. |
| 44. | Wang JD, Huang GE, Zhai JQ, Zhou LH. Observation of the curative effect of treating 50 cases of diarrhea of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome with moxa roll moxibustion. Henan Zhong Yi XUe Yuan Xue Bao 2006; 21: 14. |
| 45. | Ao W, Chen YH, Chen W, Li Q. Thirty-five cases of AIDS were treated with moxibustion combined with antiviral therapy. Fujian Zhong Yi Yao 2024; 5: 59-60+63. |
| 46. | Luo G, Liu Z, Mo D, Kong F. Exploring the mechanism of moxibustion in the treatment of immune reconstitution insufficiency in HIV-infected patients based on "intestinal flora - immune inflammatory response. Zhong Guo Ai Zi Bing Xing Bing 2023; 29: 1059-62. |
| 47. | Tao Z, Huang XJ, Liu Y, et al. Efficacy of integrated Traditional Chinese Medicine and anti-retroviral therapy on immunological nonresponse in patients with human immunodeficiency virus/acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: a Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trial. J Tradit Chin Med 2021; 41: 669-76. |
| 48. | Jiang Y, Zheng RX, Yu ZY, et al. Traditional Chinese Medicine for HIV-associated acute herpes zoster: a systematic review and Meta-analysis of randomized trials. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2022; 2022: 8674648. |
| [1] | Hyungsun Jun, Nahyun Cho, Wonbae Ha, Junghan Lee, Mi Mi Ko, Young-Eun Kim, Jeeyoun Jung, Jungtae Leem. Key elements for screening kidney deficiency pattern in Traditional Chinese and Korean Medicine: a systematic review and Delphi study [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(6): 1169-1177. |
| [2] | WANG Ci, CAO Yawen, WANG Jiaying, CHEN Jixin, MA Xue, WANG Xianliang, MAO Jingyuan. Efficacy and safety of acupuncture for arrythmias: an overview of systematic reviews and Meta-analyses [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(6): 1178-1190. |
| [3] | FENG Chuwen, LI Chaoran, Yang Yan, QU Yuanyuan, SUN Zhongren, SUN Weibo, LIU Tingting, LI Shulin, Yang Tiansong. Identifying potential biomarkers in the hippocampus of chronic fatigue syndrome rats treated with moxibustion at Zusanli (ST36): a proteomics study [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(3): 571-585. |
| [4] | WANG Yiying, DONG Shuai, LI Bo, HAN Mei, CAO Huijuan. Update evidence of effectiveness on pain relieving of cupping therapy: a systematic review and Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(2): 234-253. |
| [5] | PENG Guangbin, LI Han, ZHU Lu, QI Qin, ZHENG Shiyu, ZHANG Linshan, LIN Yaying, MA Zhe, WU Luyi, HUANG Yan, WU Huangan. Regulation of mild moxibustion on non-neuronal cholinergic system in ulcerative colitis rats [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(2): 368-375. |
| [6] | LUO Kun, ZHONG Yumei, GUO Yanding, ZHANG Linlin, HU Danhui, MA Wenbin, YANG Xin, ZHOU Haiyan. Moxibustion inhibits the macrophage M1 polarization toll-like receptor 4/myeloid differentiation factor 88/nuclear factor kappa B signaling pathway by regulating T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin-containing protein-3 in rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(6): 1227-1235. |
| [7] | XU Yingshan, WU Chunxiao, YU Wei, GUO Hongji, LU Liming, XU Nenggui, TANG Chunzhi. Systematic review and Meta-analysis of brain plasticity associated with electroacupuncture in experimental ischemic stroke [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(5): 859-870. |
| [8] | DENG Yasheng, HAN Siyin, XI Lanhua, HUANG Hui, LIANG Tianwei, ZHENG Yiqing, FAN Yanping, LIN Jiang. Traditional Chinese Medicine in the treatment of recurrent respiratory tract infections in children: an overview of systematic reviews and Meta-analyses [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(5): 871-884. |
| [9] | CHEN Dandan, JIN Qianhong, SHEN Yuanjuan, WANG Qing, DAI Zhengxiang. Scraping therapy for knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(4): 633-641. |
| [10] | SHEN Jie, YIN Yaoli, LI Hongxiao, LU Ge, ZHU Yaoyao, QIN Yantong, JIN Xun, CHENG Jie, SHEN Meihong. Effect of moxibustion on expression profile of miRNAs in Tripterygium glycoside-induced decreased ovarian reserve [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(4): 745-752. |
| [11] | GUO Yanding, LUO Kun, ZHANG Linlin, LU Wenting, SHANG Yanan, ZHONG Yumei, HU Danhui, YANG Xin, ZHOU Haiyan. Study on the anti-inflammatory mechanism of moxibustion in rheumatoid arthritis in rats based on phospholipaseA2 signaling inhibition by Annexin 1 [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(4): 753-761. |
| [12] | WANG Yuhuang, ZHANG Le, ZHANG Zhengshan, YAO Zhi, LI Xiyao, SUN Luying, LIAO Xing. Characteristics and quality of clinical practice guidelines for diabetic kidney disease: a systematic review [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(3): 609-619. |
| [13] | ZHANG Linlin, ZHONG Yumei, LU Wenting, SHANG Yanan, GUO Yanding, LUO Xiaochao, CHEN Yang, LUO Kun, HU Danhui, YU Huiling, ZHOU Haiyan. Moxibustion of Zusanli (ST36) and Shenshu (BL23) alleviates the inflammation of rheumatoid arthritis in rats through regulating macrophage migration inhibitory factor/glucocorticoids signaling [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(2): 353-361. |
| [14] | LIU Tingting, LIU Tongou, LIU Mingfu. Effectiveness and safety of acupuncture in treatment of pregnancy-related symptoms: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 16-26. |
| [15] | WANG Jiabao, ZHANG Lishuang, NIU Baihan, YU Yajun, YANG Fengwen, MIAO Lin, CHAI Lijuan, DING Xinya, SUN Yingjie, WANG Yujing, WANG Lin, ZHANG Han, WANG Yi, LI Lin. Efficacy and safety of Weichang’ an pill (胃肠安丸) combined with Western Medicine on gastrointestinal diseases: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1057-1067. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

