Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (5): 954-962.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20240806.003
Previous Articles Next Articles
Qingfei Zhisou oral liquid (清肺止嗽口服液) alleviates fever-induced inflammation by regulating arachidonic acid and lysophospholipids metabolism and inhibiting hypothalamus transient receptor potential ion channels expression
GAO Jiaming1, ZHANG Yehao1, Chen Yuanyuan1, JIN Long1, ZHAO Jianfeng2, GUO Hao1( ), FU Jianhua1(
), FU Jianhua1( )
)
- 1 Institute of Basic Medical Sciences, Xiyuan Hospital of China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100091, China
2 Pharmaceutical R&D Department, Taiyuan Yidavike Medical Technology Development Co., Ltd., Taiyuan 030006, China
-
Received:2023-05-06Accepted:2023-09-05Online:2024-10-15Published:2024-08-06 -
Contact:Prof. GUO Hao, Institute of Basic Medical Sciences, Xiyuan Hospital of China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100091, China. g0502g@163.com;Prof. FU Jianhua, Institute of Basic Medical Sciences, Xiyuan Hospital of China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100091, China. jianhuaffcn@263.net Telephone: +86-10-62835636; +86-10-62835016 -
Supported by:Beijing Traditional Chinese Medicine Foundation for Science and Technology(JJ-2020-78);Research on the Protection of Intellectual Property Rights of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Scientific and Technological Innovation Project of China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences(CI2021A00912);Basic and Translational Research on the Application of Traditional Chinese Medicine; the Research Foundation of Major New Drug Creation, from the Ministry of Science and Technology of China(2018ZX09721003-009-022);Research on Key Technologies and Industrialization of Traditional Chinese Medicine Preparations for Children;National Natural Science Foundation of China(82074060);Study on the Effect of Tanyu Tongzhi Fang in Maintaining Vascular Homeostasis in the Treatment of Atherosclerosis
Cite this article
GAO Jiaming, ZHANG Yehao, Chen Yuanyuan, JIN Long, ZHAO Jianfeng, GUO Hao, FU Jianhua. Qingfei Zhisou oral liquid (清肺止嗽口服液) alleviates fever-induced inflammation by regulating arachidonic acid and lysophospholipids metabolism and inhibiting hypothalamus transient receptor potential ion channels expression[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(5): 954-962.
share this article
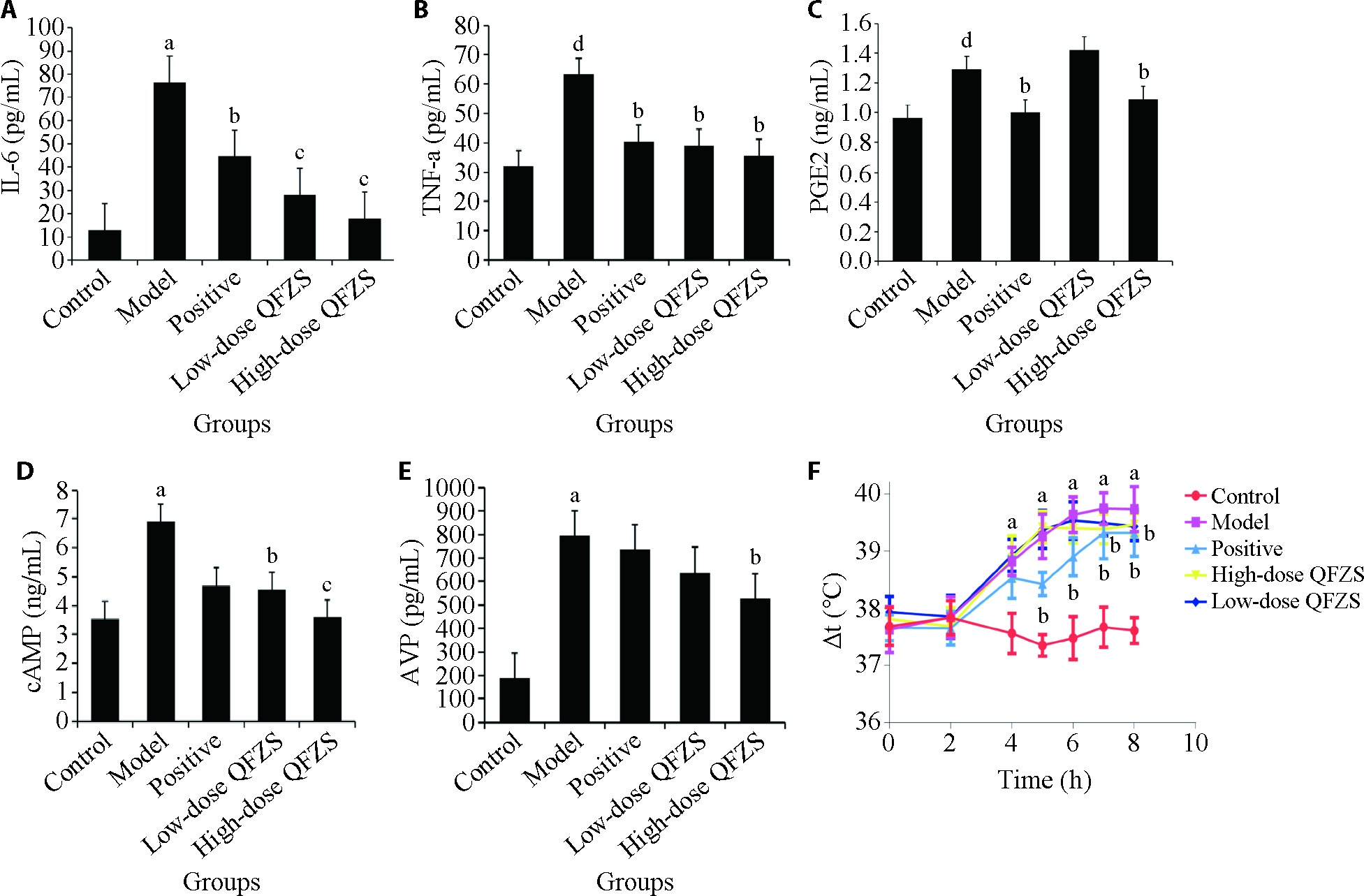
Figure 1 Differences in inflammatory cytokines and hypothalamic-releasing factors A: IL-6 level; B: TNF-α level; C: PGE-2 level; D: cAMP level; E: AVP; F: rectal temperature of the rats in each group. Control group: sham operated; Model group: Yeast-induced fever model without treatment; Positive group: Yeast-induced fever model with Aspirin (100 mg/kg); Lose-dose QFZS group: Yeast-induced fever model with low-dose QFZS (2.82 g/kg); High-dose QFZS group: Yeast-induced fever model with high-dose QFZS (5.64 g/kg). IL-6: interleukin-6; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor-α; AVP: arginine vasopressin; cAMP: cyclic adenosine monophosphate; PGE-2: prostaglandin E-2; QFZS: Qingfei Zhisou oral liquid. Data represent the mean ± standard deviation using one-way analysis of variance (n = 4). Compared with the control group, aP < 0.01, dP < 0.05; compared with the model group, bP < 0.05, cP < 0.01.
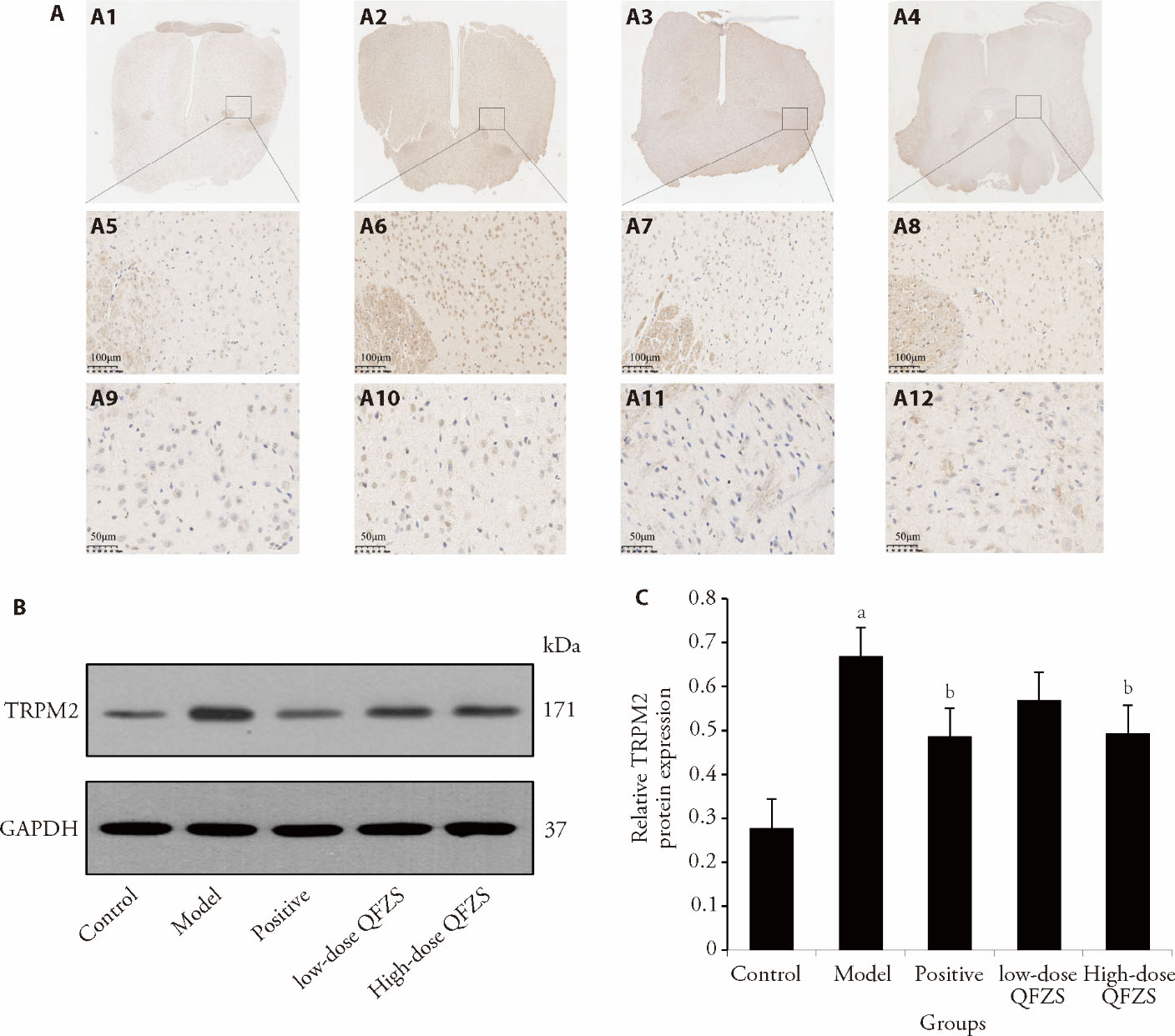
Figure 2 Effects of QFZS on TRPM2 expression A: the immunohistochemistry staining of TRPM2, A1-A4: images of control (A1), model (A2), Lose-dose QFZS (A3), High-dose QFZS(A4) (× 1); A5-A8: images of control (A5), model (A6), Lose-dose QFZS (A7), High-dose QFZS(A8) (× 200, bar = 100 μm); A9-A12: images of control (A9), model (A10), Lose-dose QFZS (A11), High-dose QFZS(A12) (× 400, bar = 50 μm). B: Western blotting representative images of TRPM2 respective quantification in the hypothalamus; C: protein expression levels of TRPM2. Control group: sham operated; Model group: Yeast-induced fever model without treatment; Positive group: Yeast-induced fever model with Aspirin (100 mg/kg); Lose-dose QFZS group: Yeast-induced fever model with low-dose QFZS (2.82 g/kg); High-dose QFZS group: Yeast-induced fever model with high-dose QFZS (5.64 g/kg). TRPM2: transient receptor potential melastatin 2; GAPDH: glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; QFZS: Qingfei Zhisou oral liquid. Data represent the mean ± standard deviation using one-way analysis of variance (n = 5). Compared with the sham group, aP < 0.05; compared with the model group, bP < 0.05.
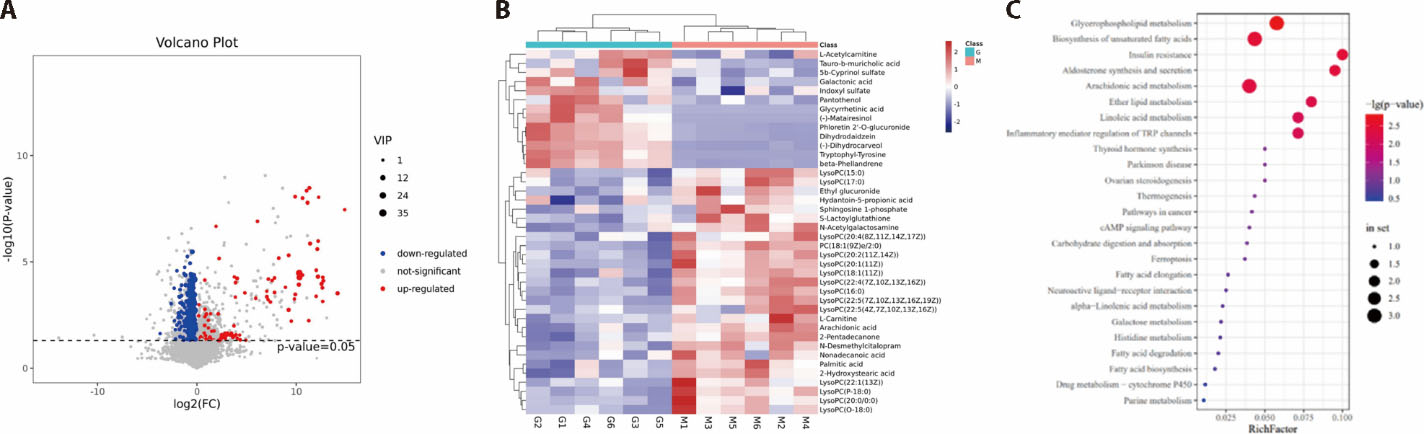
Figure 3 Screening, pathway analysis, and enrichment of differential metabolites A: summary analysis of differential metabolites volcano plot, B; heat map of metabolisms, C: pathway enrichment of differential metabolites.
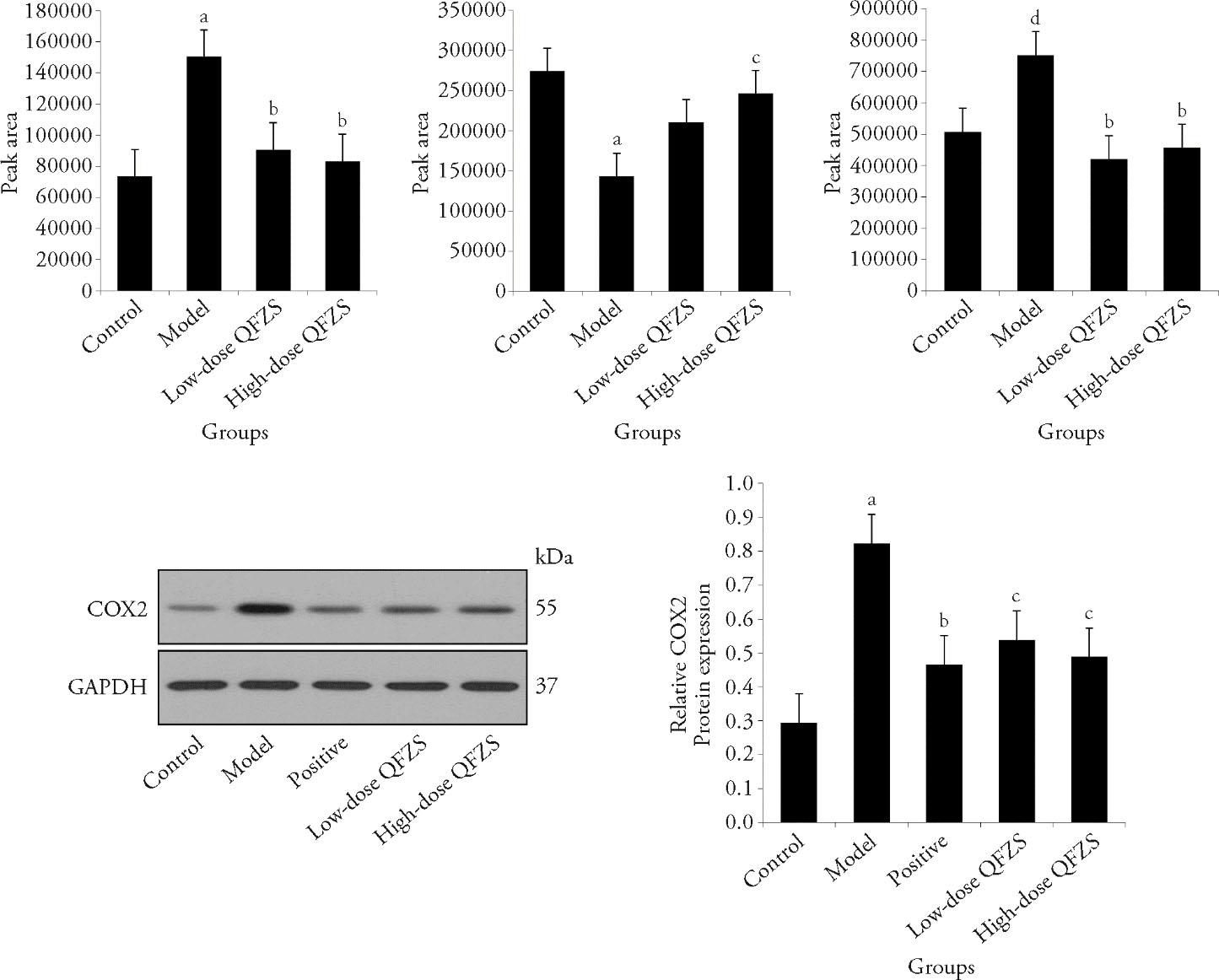
Figure 4 Relative levels of common metabolites A: arachidonic acid; B: galactonic acid; C: N-desmethylcitalopram; D: Western blotting representative images of COX-2; E: protein expression levels of COX-2. Control group: sham operated; model group: Yeast-induced fever model without treatment; positive group: Yeast-induced fever model with Aspirin (100 mg/kg); Lose-dose QFZS group: Yeast-induced fever model with low-dose QFZS (2.82 g/kg); High-dose QFZS group: Yeast-induced fever model with high-dose QFZS (5.64 g/kg). COX-2: cyclooxygenase-2; GAPDH: glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; QFZS: Qingfei Zhisou oral liquid. Data represent the mean ± standard deviation using one-way analysis of variance (n = 5). Compared with the control, aP < 0.01, dP < 0.001; compared with the model, bP < 0.001, cP < 0.01.
| 1. |
Evans SS, Repasky EA, Fisher DT. Fever and the thermal regulation of immunity: the immune system feels the heat. Nat Rev Immunol 2015; 15: 335-49.
DOI PMID |
| 2. | Caterina MJ. Transient receptor potential ion channels as participants in thermosensation and thermoregulation. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 2007; 292: 64-76. |
| 3. | Morrison SF. Central neural control of thermoregulation and brown adipose tissue. Auton. Neurosci 2016; 196: 14-24. |
| 4. |
Heller HC. The thermostat of vertebrate animals. Sci Am 1978; 239: 102-12.
PMID |
| 5. | Song K, Wang H, Kamm GB, et al. The TRPM2 channel is a hypothalamic heat sensor that limits fever and can drive hypothermia. Science 2016; 353: 1393-8. |
| 6. | Tan CH. The TRPM2 ion channel is required for sensitivity to warmth. Nature 2016; 536: 460-3. |
| 7. |
Beck A, Kolisek M, Bagley LA, et al. Nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide phosphate and cyclic ADP-ribose regulate TRPM2 channels in T lymphocytes. FASEB J 2006; 20: 962-4.
PMID |
| 8. |
Heiner I, Eisfeld J, Warnstedt M, et al. Endogenous ADP-ribose enables calcium-regulated cation currents through TRPM2 channels in neutrophil granulocytes. Biochem J 2006; 398: 225-32.
PMID |
| 9. |
Kolisek M, Beck A, Fleig A, et al. Cyclic ADP-ribose and hydrogen peroxide synergize with ADP-ribose in the activation of TRPM2 channels. Mol Cell 2005; 18: 61-9.
PMID |
| 10. | Wang B, Wu L, Chen J, et al. Metabolism pathways of arachidonic acids: mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets. Signal Transduct Target Ther 2021; 6: 94. |
| 11. | Huang Y, Yao P, Leung KW, et al. The Chinese medicinal herbs of spleen-meridian property regulate body temperature in yeast-induced fever rats. Phytomedicine 2020; 74: 152815. |
| 12. | Sharma V, Bhatia P, Alam O, et al. Recent advancement in the discovery and development of COX-2 inhibitors: insight into biological activities and SAR studies (2008-2019). Bioorg Chem 2019; 89: 103007. |
| 13. | Zhu M. 284 cases of lung fever and cough treated with clear lungs and anti-cough decoction. Yao Wu Zi Xun 2011; 24: 3795. |
| 14. | Yang D. 87 cases of cough after treatment of infection. Zhong Yi Yao Yan Jiu Qian Yan 2010; 16: 76. |
| 15. | Qiu YZ. Efficacy of lung cleansing and anti-drinking in the treatment of acute onset of chronic bronchitis. Zhong Yi Yao Xue Kan 2006; 24: 160-1. |
| 16. |
Qi T, Li H, Li S, et al. Indirubin improves antioxidant and anti-inflammatory functions in lipopolysaccharide-challenged mice. Oncotarget 2017; 8: 36658-63.
DOI PMID |
| 17. | Zhou Y, Gao C, Vong CT, et al. Rhein regulates redox-mediated activation of NLRP3 inflammasomes in intestinal inflammation through macrophage-activated crosstalk. Br J Pharmacol 2022; 179: 1978-97. |
| 18. | Ge H, Tang H, Liang Y, et al. Rhein attenuates inflammation through inhibition of NF-κB and NALP3 inflammasome in vivo and in vitro. Drug Des Devel Ther 2017; 6: 1663-71. |
| 19. |
Zhu T, Zhang W, Feng SJ, et al. Emodin suppresses LPS-induced inflammation in RAW264.7 cells through a PPARγ-dependent pathway. Int Immunopharmacol 2016; 34: 16-24.
DOI PMID |
| 20. | Gao X, Huang C, Geng T, et al. Serum and urine metabolomics based on UPLC-Q-TOF/MS reveals the antipyretic mechanism of Reduning injection in a rat model. J Ethnopharmacol 2020; 25: 112429. |
| 21. | Zhang X, Wang Y, Li S, et al. The potential antipyretic mechanism of gardeniae fructus and its heat-processed products with plasma metabolomics using rats with yeast-induced fever. Front Pharmacol 2019; 9: 491. |
| 22. | Zhao A, Ma B, Xu L, et al. Jiedu Tongluo granules ameliorates post-stroke depression rat model via regulating NMDAR/BDNF signaling pathway. Front Pharmacol 2021; 20: 662003. |
| 23. |
Lu B, Zhao J, Xu L, et al. Identification of molecular target proteins in Berberine-treated cervix adenocarcinoma HeLa cells by proteomic and bioinformatic analyses. Phytother Res 2012; 26: 646-56.
DOI PMID |
| 24. |
Wang X, Wang R, Xing D, et al. Kinetic difference of berberine between hippocampus and plasma in rat after intravenous administration of Coptidis rhizoma extract. Life Sci 2005; 77: 3058-67.
DOI PMID |
| 25. |
Korbecki J, Bajdak-Rusinek K. The effect of palmitic acid on inflammatory response in macrophages: an overview of molecular mechanisms. Inflamm Res 2019; 68: 915-32.
DOI PMID |
| 26. |
Ciapaite J, Bakker SJ, Diamant M, et al. Metabolic control of mitochondrial properties by adenine nucleotide translocator determines palmitoyl-CoA effects. Implications for a mechanism linking obesity and type 2 diabetes. FEBS J 2006; 273: 5288-302.
DOI PMID |
| 27. | Wang YM, Liu HX, Fang NY, et al. High glucose concentration impairs 5-PAHSA activity by inhibiting AMP-activated protein kinase activation and promoting nuclear factor-kappa-B-mediated inflammation. Front Pharmacol 2019; 7: 1491. |
| 28. | Wan LM, Tan Jie, Wan SH, et al. Anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative effects of dexpanthenol on lipopolysaccharide induced acute lung injury in mice. Inflammation 2016; 39: 1757-63. |
| 29. | Bochkov VN, Oskolkova OV, Birukov KG, et al. Generation and biological activities of oxidized phospholipids. Antioxid Redox Signal 2010; 12: 1009-59. |
| 30. | Handl J, Meloun M, Mužáková V, et al. Inflammatory markers in dependence on the plasma concentration of 37 fatty acids after the coronary stent implantation. J Pharm Biomed Anal 2018; 5: 96-105. |
| 31. | Hannun YA, Obeid LM. Sphingolipids and their metabolism in physiology and disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2018; 19: 175-91. |
| 32. |
Tilley SL, Coffman TM, Koller BH. Mixed messages: modulation of inflammation and immune responses by prostaglandins and thromboxanes. J Clin Invest 2001; 108: 15-23.
DOI PMID |
| 33. | Tanaka S, Watanabe H, Nakano T, et al. Indoxyl sulfate contributes to adipose tissue inflammation through the activation of NADPH oxidase. Toxins (Basel) 2020; 12: 502. |
| 34. | Rapa SF, Prisco F, Popolo A, et al. Pro-inflammatory effects of indoxyl sulfate in mice: impairment of intestinal homeostasis and immune response. Int J Mol Sci 2021; 22: 1135. |
| 35. | Yin H, Brooks JD, Gao L, et al. Identification of novel autoxidation products of the omega-3 fatty acid eicosapentaenoic acid in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem 2007; 282: 29890-901. |
| 36. | Hamers A, Primus CP, Whitear C, et al. 20-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid (20-HETE) is a pivotal endogenous ligand for TRPV1-mediated neurogenic inflammation in the skin. Br J Pharmacol 2022; 179: 1450-69. |
| 37. |
Romanovsky AA. The thermoregulation system and how it works. Handb Clin Neurol 2018; 156: 43.
DOI |
| 38. |
Togashi K, Hara Y, Tominaga T, et al. TRPM2 activation by cyclic ADP-ribose at body temperature is involved in insulin secretion. EMBO J 2006; 25: 1804-15.
DOI PMID |
| 39. |
Knowles H, Li Y, Perraud AL. The TRPM2 ion channel, an oxidative stress and metabolic sensor regulating innate immunity and inflammation. Immunol Res 2013; 55: 241-8.
DOI PMID |
| 40. |
Yamamoto S, Shimizu S, Kiyonaka S, et al. TRPM2-mediated Ca2+ influx induces chemokine production in monocytes that aggravates inflammatory neutrophil infiltration. Nat Med 2008; 14: 738-47.
DOI PMID |
| 41. | Kashio M, Tominaga M. The TRPM2 channel: a thermo-sensitive metabolic sensor. Channels (Austin) 2017; 11: 426-33. |
| 42. |
Zhang Y, Sreekrishna K, Lin Y, et al. Modulation of transient receptor potential (TRP) channels by Chinese herbal extracts. Phytother Res 2011; 25: 1666-70.
DOI PMID |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 69
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 51
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

