Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (2): 335-347.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20220419.001
• Original articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Efficacy of electro-acupuncture at “Weizhong” (BL40) on macrophage polarization in rats with injured lumbar multifidus
TIAN Yuan1,2, BU He2, WANG Tieshan3, YANG Dongliang4, ZHANG Wei7, LIU Tong5,6, ZHANG Li1( ), HUO Zejun8(
), HUO Zejun8( )
)
- 1 Department of Acupuncture-Moxibustion and Tuina, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100029, China
2 Department of Acupuncture-Moxibustion and Tuina, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Baotou Medical College, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, Baotou 014030, China
3 Beijing Research Institute of Chinese Medicine, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100029, China
4 Cangzhou Medical College, Cangzhou 061000, China
5 the Fifth College of Clinical Medicine, Guangzhou University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510006, China
6 Department of Acupuncture and Rehabilitation, Guangdong Second Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510095, China
7 Department of Pathology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Baotou Medical College, Inner Mongolia University of Science and Technology, Inner Mongolia 014010, China
8 Department of Chinese Medicine, Peking University 3rd Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
-
Received:2022-01-22Accepted:2022-03-17Online:2025-04-15Published:2022-04-19 -
Contact:Prof. ZHANG Li, Department of Acupuncture-Moxibustion and Tuina, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100029, China. zhangli1572@sina.com; HUO Zejun, Department of Chinese Medicine, Peking University 3rd Hospital, Beijing 100191, China. huozejun@163.com, Telephone: +86-10-64287525 -
Supported by:Natural Science Foundation-funded Project: Regulation of Autophagy by Electroacupuncture at Weizhong Point on the Proliferation of Multifidus Muscle Satellite Cells(81574052);Exosomes Arounding Acupoints Deliver miR-206 to Mediate Insulin - like Growth Factor 1/Phosphatidylinositol 3 - Kinase/Protein Kinase B Pathway and Regulate Muscle Satellite Cell Differentiation: Mechanism of Electroacupuncture in Promoting Rehabilization of Lumbar Multifidus Muscles Injury in Model Rats(82174482);Major Program of Foundation of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region: Study on the Eeffect of Pediatric Tuina Combined with Acupuncture on the Intestinal Microflora Structure in Children with Provisional Tic Disorder and its Therapeutic Mechanism(201802127)
Cite this article
TIAN Yuan, BU He, WANG Tieshan, YANG Dongliang, ZHANG Wei, LIU Tong, ZHANG Li, HUO Zejun. Efficacy of electro-acupuncture at “Weizhong” (BL40) on macrophage polarization in rats with injured lumbar multifidus[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(2): 335-347.
share this article

Figure 1 LM muscular H&E staining at different time points (1-, 2-, 3-, and 5-days) in each group BPVC injection induced the infiltration of local macrophages at the L4-L5 segment of lumbar multifidus. Original magnification: A × 100, B × 400, scale bar = 50 μm. A1-A2: control group, B1-B2: 1d Model group, B3-B4: 1d EA group, C1-C2: 2d Model group, C3-C4: 2 d EA group, D1-D2: 3 d Model group, D3-D4: 3 d EA group; E1-E2: 5 d Model group, E3-E4: 5 d EA group. The rats in the EA group received EA treatment [bilateral Weizhong (BL 40) acupoints, frequency of 2/10 Hz and an intensity of 2 mA for a total of 30 min] 24 h post-anesthesia recovery and model establishment, followed by daily sessions until euthanasia was performed. In the control group and model group, only grabbing and fixing were administered. LM: Lumbar multifidus; BPVC: Bupivacaine.

Figure 2 IHC showed electro-acupuncture reduced the positive expression of macrophages at the L4-L5 segment of lumbar multifidus A1-A2: control group; B1-B2: 2 d Model group; B3-B4: 2 d EA group; C1-C2: 2 d Model group; C3-C4: 2 d EA group; D1-D2: 5 d Model group; D3-D4: 5d EA group. Yellow brown-colored cells represent CD68+ macrophages. Black scale bar: 50 μm. Original magnification: A1, B1, C1, D1, B3, C3, D3 × 100, A2, B2, C2, D2, B4, C4, D4 × 400. E-F: The sum area and mean integrated optical density represents the expression level of CD68+ macrophages (n = 6). “a” indicates a significant difference (P < 0.001) when compared with the Control group; “b” indicates a difference (P < 0.001) when compared with the Model group; “c” indicates a difference (P < 0.05) when compared with the Control group; “d” indicates a difference (P < 0.05) when compared with the Model group. IHC: immunohistochemical staining.

Figure 3 IFA showed EA regulated M1-macrophage polarization in injured LM A1-A4: control group; B1-B4: model 2 d group; C1-C4: EA 2 d group; D1-D4: model 3 d group; E1-E4: EA 3 d group; F: Counting and analysis were carried out in the same visual field (315.87 μm × 315.87 μm), and the cell counts of iNOs+ CD68+ M1-macrophagess at different time points (2- and 3 d) in each group (n = 6) were recorded. “a” indicates a significant difference (P < 0.001) when compared with the Control group; “b” indicates a difference (P < 0.001) when compared with the Model group; “c” indicates a difference (P < 0.05) when compared with the control group. Double immunofluorescence images of CD68 (green) and iNOS (red). Asterisks indicate co-expression. Arrowheads indicate myofibers. Arrows represents cells only expressing CD68 or iNOs, respectively. DAPI (blue) was used for nuclear staining. Scale bar: 50 μm. Original magnification: × 400. LM: Lumbar multifidus; IFA: Immunofluorescence Assay; EA: Electro-acupuncture.

Figure 4 IFA showed EA facilitated M2-macrophage polarization in injured LM A1-A4: control group; B1-B4: model 3 d group; C1-C4: EA 3 d group; D1-D4: model 5-days group; E1-E4: EA 5-d group; F: Counting and analysis were carried out in the same visual field (315.87 μm × 315.87 μm), and the positive percent of CD163+CD206+ M2-macrophages at different time points (3- and 5- d) in each group (n = 6) was recorded. “a” indicates a significant difference (P < 0.001) when compared with the Model group. Double immunofluorescence images of CD206 (green) and CD163 (red). Asterisks indicate co-expression. Arrowheads indicate myofibers. Arrows represents cells only expressing CD206 or CD163, respectively. DAPI (blue) was used for nuclear staining. Scale bar: 50 μm. Original magnification: × 400. LM: Lumbar multifidus; IFA: immunofluorescence assay; EA: Electro-acupuncture.
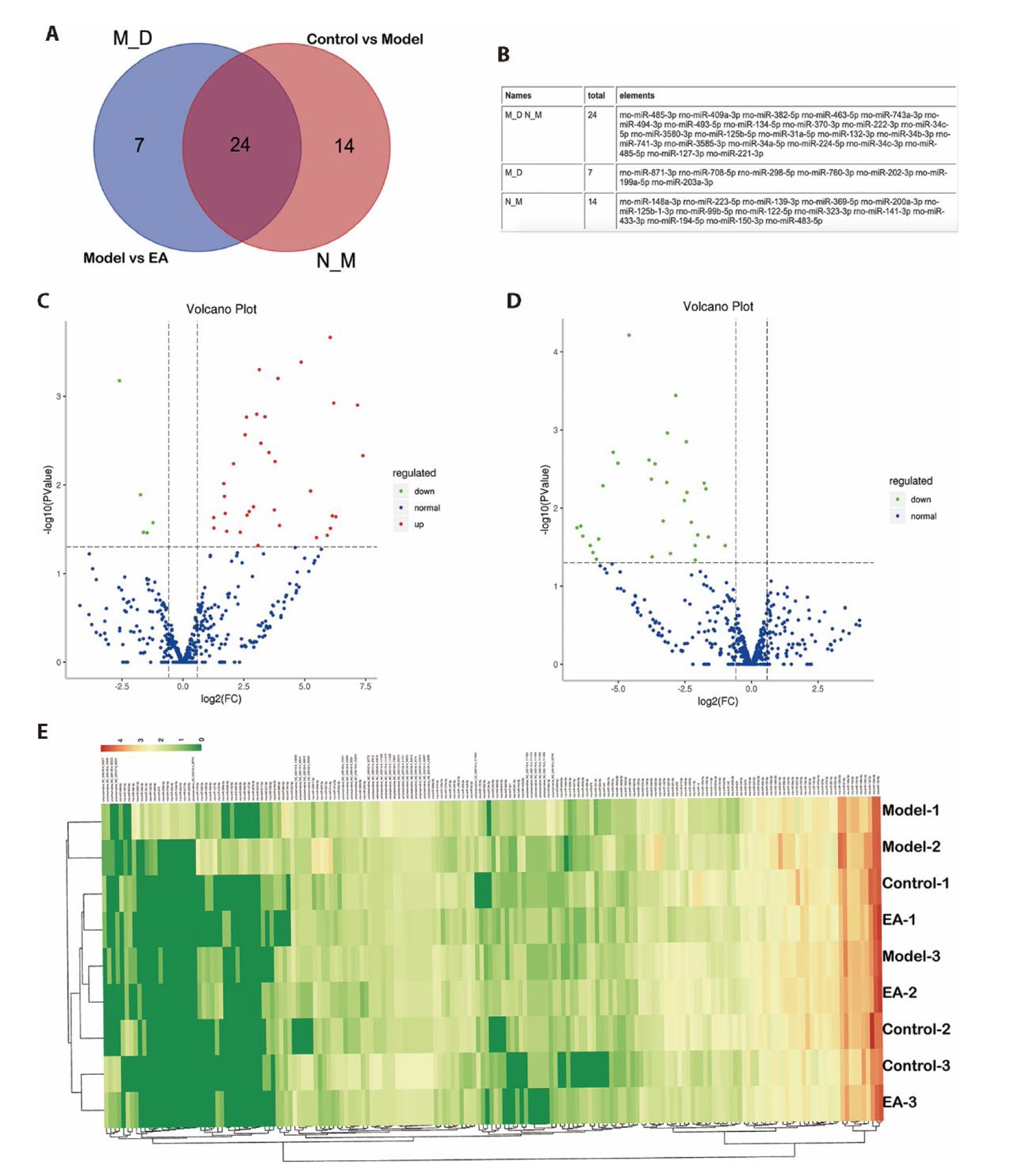
Figure 5 Exosomal miRNAs are involved in EA's regulation after LM muscular injury A: Venn diagram: N_M represents DEmiRs between the control group and model group; M_D represents DEmiRs between model group and electroacupuncture group. B: List of DEmiRs in each group. C: Volcano plots: DEmiRs between control and model groups. D: Volcano plots: DEmiRs between model and electroacupuncture groups. Each point in the volcano plot represents a miRNA. Blue dots represent non-differentially expressed miRNAs. Red dots represent the upregulated miRNAs while green dots represent the downregulated miRNAs. E: Clustering analysis of DEmiRs in the control, model, and EA groups. Blue indicates lower gene expression while red color indicates higher gene expression. LM: Lumbar multifidus; EA: Electro-acupuncture; DEmiRs: differentially expressed miRNAs.

Figure 6 GO-BP and KEGG enrichment analyses of target genes corresponding to 24 DEmiRs A: the bar chart of the KEGG pathway enrichment comparing the control group and the model group; B: the bar chart of the KEGG pathway enrichment comparing the model group and the electro-acupuncture group; C: the bubble plot of biological processes comparing the control group and the model group; D: the bubble plot of biological processes comparing the model group and the electro-acupuncture group. GO-BP: Gene Ontology - Biological Process; KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes.
| 1. | Kritikaki E, Asterling R, Ward L, et al. Exercise training-induced extracellular matrix protein adaptation in locomotor muscles: a systematic review. Cells 2021; 10: 1022. |
| 2. | Wang-Price S, Zafereo J, Couch Z, et al. Short-term effects of two deep dry needling techniques on pressure pain thresholds and electromyographic amplitude of the lumbosacral multifidus in patients with low back pain - a randomized clinical trial. J Man Manip Ther 2020; 28: 254-65. |
| 3. | Zhang SS, Wu W, Han XL, et al. Time- frequency analysis of EMG signals of the deep lumbar multifidus in patients with chronic low back pain. Zhong Guo Kang Fu Yi Xue Za Zhi 2019; 34: 642-7. |
| 4. | Merinero D, Rodriguez-Aragon M, Alvarez-Gonzalez J, et al. Acute effects of global postural re-education on non-specific low back pain. does time-of-day play a role? Int J Environ Res Public Health 2021; 18: 713. |
| 5. | Hoy D, Bain C, Williams G, et al. A systematic review of the global prevalence of low back pain. Arthritis Rheum 2012; 64: 2028-37. |
| 6. | Manchikanti L, Singh V, Falco F J, et al. Epidemiology of low back pain in adults. Neuromodulation 2014; 17 Suppl 2: 3-10. |
| 7. | L'Honore A, Commere P H, Negroni E, et al. The role of Pitx2 and Pitx3 in muscle stem cells gives new insights into P38alpha MAP kinase and redox regulation of muscle regeneration. Elife 2018; 7: e32991. |
| 8. |
Le GF, Rudnicki MA. Skeletal muscle satellite cells and adult myogenesis. Curr Opin Cell Biol 2007; 19: 628-33.
DOI PMID |
| 9. |
Schultz E, Mccormick K M. Skeletal muscle satellite cells J. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol 1994; 123: 213-57.
PMID |
| 10. |
Robinson MM, Turner SM, Hellerstein MK, et al. Long-term synthesis rates of skeletal muscle DNA and protein are higher during aerobic training in older humans than in sedentary young subjects but are not altered by protein supplementation. FASEB J 2011; 25: 3240-9.
DOI PMID |
| 11. |
Dumont NA, Bentzinger CF, Sincennes MC, et al. Satellite cells and skeletal muscle regeneration. Compr Physiol 2015; 5: 1027-59.
DOI PMID |
| 12. |
Snow MH. The effects of aging on satellite cells in skeletal muscles of mice and rats. Cell Tissue Res 1977; 185: 399-408.
PMID |
| 13. | Li H, Chen Q, Li C, et al. Muscle-secreted granulocyte colony-stimulating factor functions as metabolic niche factor ameliorating loss of muscle stem cells in aged mice. EMBO J 2019; 38: e102154. |
| 14. |
Salminen A, Kaarniranta K, Kauppinen A. Beclin 1 interactome controls the crosstalk between apoptosis, autophagy and inflammasome activation: impact on the aging process. Ageing Res Rev 2013; 12: 520-34.
DOI PMID |
| 15. | Padwal J, Berry DB, Hubbard JC, et al. Regional differences between superficial and deep lumbar multifidus in patients with chronic lumbar spine pathology. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 2020; 21: 764. |
| 16. | Shahidi B, Parra CL, Berry DB, et al. Contribution of lumbar spine pathology and age to paraspinal muscle size and fatty infiltration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2017; 42: 616-23. |
| 17. | Yang X, Li S, Zhao Y, et al. GRK2 Mediated abnormal transduction of PGE2-EP4-cAMP-CREB signaling induces the imbalance of macrophages polarization in collagen-induced arthritis mice. Cells 2019; 8: 1596. |
| 18. | Lekkerkerker AN, Aarbiou J, van Es T, et al. Cellular players in lung fibrosis. Curr Pharm Des 2012; 18: 4093-102. |
| 19. | Arnold L, Henry A, Poron F, et al. Inflammatory monocytes recruited after skeletal muscle injury switch into anti-inflammatory macrophages to support myogenesis. J Exp Med 2007; 204: 1057-69. |
| 20. | Peng MF, Li K, Wang C, et al. Therapeutic effect and mechanism of electroacupuncture at Zusanli on plasticity of interstitial cells of Cajal: a study of rat ileum. BMC Complement Altern Med 2014; 14: 186. |
| 21. |
Zhuang Y, Xing JJ, Li J, et al. History of acupuncture research. Int Rev Neurobiol 2013; 111: 1-23.
DOI PMID |
| 22. | Gong M, Wang X, Mao Z, et al. Effect of electroacupuncture on leptin resistance in rats with diet-induced obesity. Am J Chin Med 2012; 40: 511-20. |
| 23. |
Choi DC, Lee JY, Moon YJ, et al. Acupuncture-mediated inhibition of inflammation facilitates significant functional recovery after spinal cord injury. Neurobiol Dis 2010; 39: 272-82.
DOI PMID |
| 24. | He TF, Yang WJ, Zhang SH, et al. Electroacupuncture inhibits inflammation reaction by upregulating vasoactive intestinal Peptide in rats with adjuvant-induced arthritis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2011; 2011: 290489. |
| 25. | Peng YY, Liu T, Chen YP, et al. Effects of electroacupuncture at “Weizhong” (BL 40) on regeneration and morphology in rats with bupivacaine-induced multifidus muscle injury. Zhong Guo Zhen Jiu 2016; 36: 287-94. |
| 26. | Zou DH, Chen YP, Liu T, et al. Effects of electroacupuncture at “Weizhong” (BL 40) on morphology and expression of CK and IL-17 in rats with bupivacaine-induced multifidus muscle injury. Zhong Guo Zhen Jiu 2017; 37: 971-6. |
| 27. |
Wang K, Wu H, Wang G, et al. The effects of electroacupuncture on TH1/TH2 cytokine mRNA expression and mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways in the splenic T cells of traumatized rats. Anesth Analg 2009; 109: 1666-73.
DOI PMID |
| 28. | Shen MH, Zhang CB, Zhang JH, et al. Electroacupuncture attenuates cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury in middle cerebral artery occlusion of rat via modulation of apoptosis, inflammation, oxidative stress, and excitotoxicity. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2016; 2016: 9438650. |
| 29. | Shi GX, Tu JF, Wang TQ, et al. Effect of electro-acupuncture (EA) and manual acupuncture (MA) on markers of inflammation in knee osteoarthritis. J Pain Res 2020; 13: 2171-9. |
| 30. | Chen YP, Liu T, Zou DH, et al. Histomorphological assessment of a rat model of skeletal muscle injury induced by local injection of bupivacaine. Zhong Guo Zu Zhi Gong Cheng Yan Jiu 2016; 20: 2615-21. |
| 31. |
Taguchi T, Hoheisel U, Mense S. Dorsal horn neurons having input from low back structures in rats. Pain 2008; 138: 119-29.
DOI PMID |
| 32. | Cherng CH, Wong CS, Wu CT, et al. Intramuscular bupivacaine injection dose-dependently increases glutamate release and muscle injury in rats. Acta Anaesthesiol Taiwan 2010; 48: 8-14. |
| 33. | Li ZR. Experimental acupuncture Science. Beijing: China Press of Traditional Chinese medicine, 2007: 121-5. |
| 34. | Thery C, Amigorena S, Raposo G, et al. Isolation and characterization of exosomes from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids. Curr Protoc Cell Biol 2006; Chapter 3: 3-22. |
| 35. | Boing AN, van der Pol E, Grootemaat AE, et al. Single-step isolation of extracellular vesicles by size-exclusion chromatography. J Extracell Vesicles 2014: 3. |
| 36. |
Betel D, Wilson M, Gabow A, et al. The microRNA.org resource: targets and expression. Nucleic Acids Res 2008; 36: D149-53.
DOI PMID |
| 37. |
Kruger J, Rehmsmeier M. RNAhybrid: microRNA target prediction easy, fast and flexible. Nucleic Acids Res 2006; 34: W451-4.
DOI PMID |
| 38. |
Givant-Horwitz V, Davidson B, Reich R. Laminin-induced signaling in tumor cells. Cancer Lett 2005; 223: 1-10.
PMID |
| 39. |
Zhao X, Qu J, Liu X, et al. Baicalein suppress EMT of breast cancer by mediating tumor-associated macrophages polarization. Am J Cancer Res 2018; 8: 1528-40.
PMID |
| 40. | Novak ML, Weinheimer-Haus EM, Koh TJ. Macrophage activation and skeletal muscle healing following traumatic injury. J Pathol 2014; 232: 344-55. |
| 41. | Chen YP, Liu T, Zou DH, et al. Histomorphological assessment of a rat model of skeletal muscle injury induced by local injection of bupivacaine. Chin J Tissue Eng Res 2016; 20: 2615-21. |
| 42. |
Hoheisel U, Reuter R, de Freitas MF, et al. Injection of nerve growth factor into a low back muscle induces long-lasting latent hypersensitivity in rat dorsal horn neurons. Pain 2013; 154: 1953-60.
DOI PMID |
| 43. |
Miyagi M, Ishikawa T, Kamoda H, et al. Assessment of gait in a rat model of myofascial inflammation using the CatWalk system. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2011; 36: 1760-4.
DOI PMID |
| 44. | Zou DH, Lu ZX, Yan J, et al. Effects of electroacupuncture“Weizhong” (BL40) on the expression of LIF and IL-17 in rats withmultifidus muscle injury. Huan Qiu Zhong Yi Yao 2017; 10: 436-42. |
| 45. |
Oz GO, Bayram A, Gergin IS, et al. Comparison of myotoxic effects of levobupivacaine, bupivacaine and ropivacaine: apoptotic activity and acute effect on pro-inflammatory cytokines. Biotech Histochem 2019; 94: 252-60.
DOI PMID |
| 46. |
Oz GO, Yildiz K, Bayram A, et al. Comparison of the myotoxic effects of levobupivacaine, bupivacaine, and ropivacaine: an electron microscopic study. Ultrastruct Pathol 2015; 39: 169-76.
DOI PMID |
| 47. |
Politi PK, Havaki S, Manta P, et al. Bupivacaine-induced regeneration of rat soleus muscle: ultrastructural and immunohistochemical aspects. Ultrastruct Pathol 2006; 30: 461-9.
PMID |
| 48. | Du ZF, Chi HJ, Li AH, et al. Study on changes of multifidus in patients with lumber disc herniation. Lin Chuang He Shi Yan Yi Xue Za Zhi 2012; 11: 608-10. |
| 49. | Zhao H, Liu ZS, Xie LM, et al. Interpretation of clinical practice guideline for low Ba Pain treated with acupuncture and moxibustion. Zhong Guo Zhen Jiu 2015; 35: 1065-8. |
| 50. | Cui JJ, Ha LJ, Zhu XL, et al. Specificity of sensory and motor neurons associated with BL40 and GB 30 in the rat: a dual fluorescent labeling study. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2013; 2013: 643403. |
| 51. | Wang LL, Zhang WB, Xie HH, et al. Experimental verification of “treating lumbar-back problems by puncturing Weizhong (BL 40) with blood perfusion imaging technique. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu 2007; 32: 247-51. |
| 52. |
Ardura JA, Rackov G, Izquierdo E, et al. Targeting macrophages: friends or foes in disease? Front Pharmacol 2019; 10: 1255.
DOI PMID |
| 53. | Ochoa O, Sun D, Reyes-Reyna SM, et al. Delayed angiogenesis and VEGF production in CCR2-/- mice during impaired skeletal muscle regeneration. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 2007; 293: R651-61. |
| 54. | St PB, Tidball JG. Differential response of macrophage subpopulations to soleus muscle reloading after rat hindlimb suspension. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1994; 77: 290-7. |
| 55. |
Wang X, He X, Zhang CF, et al. Anti-arthritic effect of berberine on adjuvant-induced rheumatoid arthritis in rats. Biomed Pharmacother 2017; 89: 887-93.
DOI PMID |
| 56. |
Wang Y, Han CC, Cui D, et al. Is macrophage polarization important in rheumatoid arthritis? Int Immunopharmacol 2017; 50: 345-52.
DOI PMID |
| 57. | Li R, Liu W, Yin J, et al. TSG-6 attenuates inflammation-induced brain injury via modulation of microglial polarization in SAH rats through the SOCS3/STAT3 pathway. J Neuroinflammation 2018; 15: 231. |
| 58. |
Zhou Y, Yoshida S, Kubo Y, et al. Different distributions of M1 and M2 macrophages in a mouse model of laser-induced choroidal neovascularization. Mol Med Rep 2017; 15: 3949-56.
DOI PMID |
| 59. |
Genin M, Clement F, Fattaccioli A, et al. M1 and M2 macrophages derived from THP-1 cells differentially modulate the response of cancer cells to etoposide. BMC Cancer 2015; 15: 577.
DOI PMID |
| 60. | Meng XM, Tang PM, Li J, et al. Macrophage phenotype in kidney injury and repair. Kidney Dis (Basel) 2015; 1: 138-46. |
| 61. | Peng B, Zhang L, Chen H, et al. Effects of electroacupuncture at BL40 on CK, VEGF and MVD in rabbits with psoas muscle damage. Zhong Guo Kang Fu 2014; 29: 3-7. |
| 62. | Fang YS, Chen SQ, Lian XY, et al. Effects of electroacupuncture at “Weizhong” point on TNF-α and IGF-1 expression in skeletal muscle of rats with blunt lumbar muscle contusion. Zhong Guo Kang Fu Yi Xue Za Zhi 2016; 31: 201-4. |
| 63. | Anand S, Coussens LM. Manipulating microRNAs to regulate macrophage polarization in gliomas. J Natl Cancer Inst 2014; 106: dju230. |
| 64. |
Ebert M, Sharp PA. Roles for microRNAs in conferring robustness to biological processes. Cell 2012; 149: 515-24.
DOI PMID |
| 65. | Cheng L, Sharples RA, Scicluna BJ, et al. Exosomes provide a protective and enriched source of miRNA for biomarker profiling compared to intracellular and cell-free blood. J Extracell Vesicles 2014: 3. |
| 66. | Weng YS, Tseng HY, Chen YA, et al. MCT-1/miR-34a/IL-6/IL-6R signaling axis promotes EMT progression, cancer stemness and M2 macrophage polarization in triple-negative breast cancer. Mol Cancer 2019; 18: 42. |
| 67. | Yang L, Sun J, Liu Q, et al. Synergetic functional nanocomposites enhance immunotherapy in solid tumors by remodeling the immunoenvironment. Adv Sci (Weinh) 2019; 6: 1802012. |
| 68. | Khan MJ, Singh P, Dohare R, et al. Inhibition of miRNA-34a promotes M2 macrophage polarization and improves LPS-induced lung injury by targeting Klf4. Genes (Basel) 2020; 11: 966. |
| 69. |
Pan Y, Hui X, Hoo R, et al. Adipocyte-secreted exosomal microRNA-34a inhibits M2 macrophage polarization to promote obesity-induced adipose inflammation. J Clin Invest 2019; 129: 834-49.
DOI PMID |
| 70. | Zhang T, Yang WX, Wang Y L, et al. Electroacupuncture preconditioning attenuates acute myocardial ischemia injury through inhibiting NLRP 3 inflammasome activation in mice. Life Sci 2020; 248: 117451. |
| 71. | Feng Y, Zheng C, Zhang Y, et al. Triptolide inhibits preformed fibril-induced microglial activation by targeting the MicroRNA155-5p/SHIP1 pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2019; 2019: 6527638. |
| 72. |
Vergadi E, Ieronymaki E, Lyroni K, et al. Akt signaling pathway in macrophage activation and M1/M2 polarization. J Immunol 2017; 198: 1006-14.
DOI PMID |
| 73. | Yin L, Fan Z, Liu P, et al. Anemoside A3 activates TLR4-dependent M1-phenotype macrophage polarization to represses breast tumor growth and angiogenesis. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 2021; 432: 115755. |
| 74. |
Kang CH, Shin MJ, Kim SM, et al. MRI of paraspinal muscles in lumbar degenerative kyphosis patients and control patients with chronic low back pain. Clin Radiol 2007; 62: 479-86.
DOI PMID |
| 75. |
Abe H, Takei K, Uematsu T, et al. Significance of sarcopenia as a prognostic factor for metastatic urothelial carcinoma patients treated with systemic chemotherapy. Int J Clin Oncol 2018; 23: 338-46.
DOI PMID |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

