Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (2): 353-361.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20220602.001
Previous Articles Next Articles
Moxibustion of Zusanli (ST36) and Shenshu (BL23) alleviates the inflammation of rheumatoid arthritis in rats through regulating macrophage migration inhibitory factor/glucocorticoids signaling
ZHANG Linlin1, ZHONG Yumei2, LU Wenting5, SHANG Yanan1, GUO Yanding1, LUO Xiaochao3, CHEN Yang4, LUO Kun1, HU Danhui1, YU Huiling1, ZHOU Haiyan1( )
)
- 1 Acupuncture and Moxibustion College, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu 610075, China
2 Department of Painology, First People's Hospital of Chengdu, Chengdu 610095, China
3 Chinese Evidence-Based Medicine Centre, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610044, China
4 Traditional Chinese Medicine College, Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing 400016, China
5 External treatment center, First People's Hospital of Chengdu, Chengdu 610095, China
-
Received:2022-03-12Accepted:2022-05-22Online:2024-04-15Published:2022-06-02 -
Contact:ZHOU Haiyan, Acupuncture and Moxibustion College, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu 610075, China.zhouhaiyan@cdutcm.edu.cn Telephone: +86-13551039390 -
Supported by:National Key R&D Program of China: Research on the Functional Characteristics of "Special Effects" and "Common Effects" of Acupoints(2019YFC1709001);The National Natural Science Foundation of China: Study on the Immune Mechanisms of Macrophage M1/M2 Polarization in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis by Moxibustion "Strengthening Body Resistance and Eliminating Evil"(81973959);Research on "Immune-Inflammation" Molecular Signal Regulation of NLRP3 Inflammasomes in RA with Moxibustion Treatment(81774435);Foundation of Sichuan Provincial Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine: Research on the Mechanism of MIF-GC Rhythm in the Anti-inflammatory Effect of Moxibustion in Treating Rheumatoid Arthritis(2018JC007);Science and Technology Innovation Seedling Project of Sichuan Province, China: based on Macrophage M1 Polarization Signaling Pathway TLR4-MyD88-NF-κB and Its Regulatory Molecule TIM-3 Exploring the Effect Mechanism of Moxibustion on Experimental RA Model(2022037);Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine Foundation: Study on the Mechanism of "MIF-target Protein-GC-inflammation" in the Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Moxibustion in the Treatment of RA(QNXZ2018034)
Cite this article
ZHANG Linlin, ZHONG Yumei, LU Wenting, SHANG Yanan, GUO Yanding, LUO Xiaochao, CHEN Yang, LUO Kun, HU Danhui, YU Huiling, ZHOU Haiyan. Moxibustion of Zusanli (ST36) and Shenshu (BL23) alleviates the inflammation of rheumatoid arthritis in rats through regulating macrophage migration inhibitory factor/glucocorticoids signaling[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(2): 353-361.
share this article
| Pathological changes Score | Synovial tissue hyperplasia | Inflammatory cell infiltration | Macrophage proliferation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | None | None | None |
| 1 | Mild | Few | Few |
| 2 | Moderate | Dense | Dense |
| 3 | Massive | Numerous | Numerous |
Table 1 Rat synovial pathology scoring standard
| Pathological changes Score | Synovial tissue hyperplasia | Inflammatory cell infiltration | Macrophage proliferation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | None | None | None |
| 1 | Mild | Few | Few |
| 2 | Moderate | Dense | Dense |
| 3 | Massive | Numerous | Numerous |
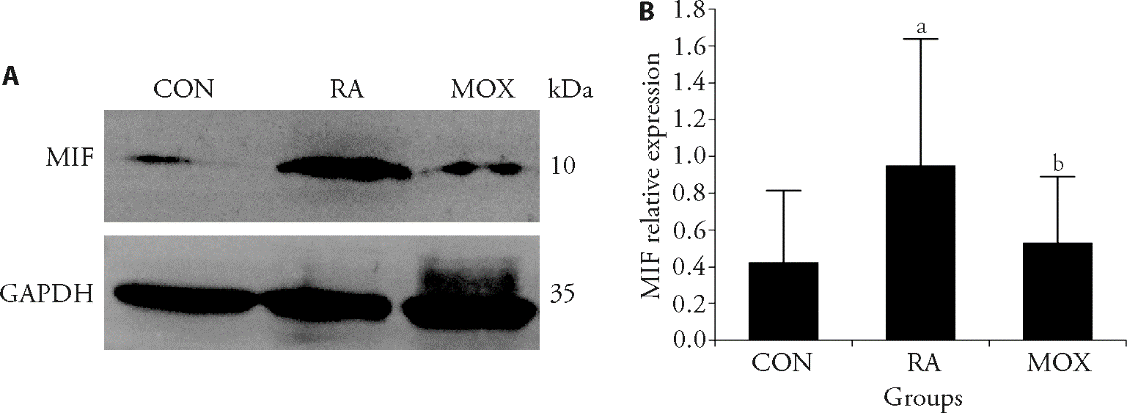
Figure 1 Measurement of MIF expression in synovium by Weston blot A: Western blot results showing expression level of MIF protein; B: Western blot analysis. CON: blank control group, rats did not undergo any treatment; RA: RA Model group, rats were injected with 0.1 mL FCA in rats' bilateral hind foot pads on the third day of the experiment, MOX: moxibustion group, Moxibustion was performed to rats on the 10th day of the experiment, a six-day course of treatment consists of three courses of treatment, with one day off between courses. MIF: macrophage migration inhibitory factor; GAPDH: glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; FCA: Freund's complete adjuvant. Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation (n = 10). aP < 0.05, compared with the CON group; bP < 0.05, compared with the RA group.
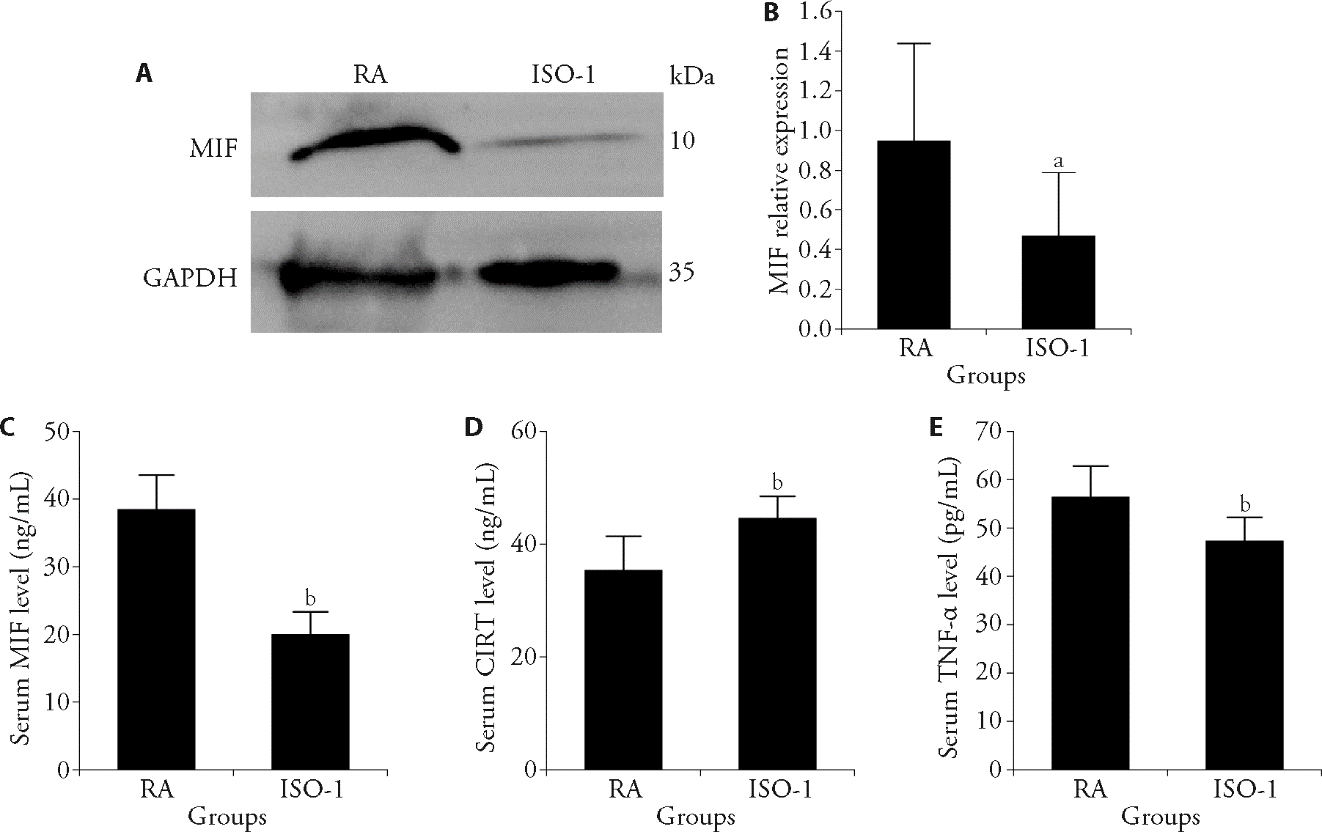
Figure 2 ISO-1 can inhibit the expression of MIF in RA rats A: Weston blot was used to detect the expression of MIF in the synovium of rats ankle joint; B: Western blot analysis; C: ELISA was used to detect the levels of MIF in rats serum; D: ELISA was used to detect the levels of CORT in rats serum; E: ELISA was used to detect the levels of TNF-α in rats serum. RA: RA Model group, rats were injected with 0.1 mL FCA in rats' bilateral hind foot pads on the third day of the experiment, ISO-1: MIF inhibitor ISO-1 group, rats were intraperitoneally injected ISO-1 every other day on the first day of the experiment with 15 injections in total, and be injected with 0.1 mL FCA in rats' bilateral hind foot pads on the third day of the experiment. MIF: Macrophage migration inhibitory factor; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; ISO-1: (S,R)-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4,5-dihydro-5-isoxazole acetic acid methyl ester; CORT: corticosterone; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor-α; FCA: Freund's complete adjuvant; ELISA: Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Data are mean ± standard deviation (n = 10). aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, compared with the RA group.

Figure 3 Moxibustion alleviate inflammation and hyperplasia of ankle synovium in RA rats A: photo of footpads of rats in the CON group; B: HE stained image of ankle synovial tissue of CON groups, magnification:× 25 and scale bars represent 200 μm; C: HE staining magnified image of ankle joint synovial tissue in the CON group, magnification: × 100 and scale bars represent 50 μm; D: photo of footpads of rats in the RA group; E: HE stained image of ankle synovial tissue of RA groups, magnification: × 25 and scale bars represent 200 μm; F: HE staining magnified image of ankle joint synovial tissue in the RA group, magnification: × 100 and scale bars represent 50 μm. G: photo of footpads of rats in the MOX group; H: HE stained image of ankle synovial tissue of MOX groups, magnification: × 25 and scale bars represent 200 μm; I: HE staining magnified image of ankle joint synovial tissue in the MOX group, magnification: × 100 and scale bars represent 50 μm. J: rat synovial pathology scores of different groups. K: expression of CORT in serum in in different groups. L: expression of TNF-α in serum in in different groups. CON: Blank Control group, rats did not undergo any treatment; RA: RA Model group, rats were injected with 0.1 mL FCA in rats' bilateral hind foot pads on the third day of the experiment, MOX: Moxibustion group, rats were injected with 0.1 mL FCA in rats' bilateral hind foot pads on the third day of the experiment, and moxibustion was performed to rats on the 10th day of the experiment, a six-day course of treatment consists of three courses of treatment, with one day off between courses. CORT: corticosterone; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor-α; HE: hematoxylin and eosin; FCA: Freund's complete adjuvant. Data are mean ± standard deviation (n = 10). aP < 0.01, compared with the CON group; bP < 0.01, compared with the RA group.
| Group | n | Foot pad thickness (mm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3rd | 10th 31st | ||||
| Control | 10 | 3.85±0.13 | 3.80±0.13 | 3.76±0.21 | |
| Model | 10 | 3.87±0.34 | 6.68±0.89a | 7.34±0.60b | |
| Moxibustion | 10 | 3.72±0.20 | 6.64±0.64a | 5.72±0.43c | |
Table 2 Thickness of foot pad in the experiment ($\bar{x}±s$)
| Group | n | Foot pad thickness (mm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3rd | 10th 31st | ||||
| Control | 10 | 3.85±0.13 | 3.80±0.13 | 3.76±0.21 | |
| Model | 10 | 3.87±0.34 | 6.68±0.89a | 7.34±0.60b | |
| Moxibustion | 10 | 3.72±0.20 | 6.64±0.64a | 5.72±0.43c | |

Figure 4 Moxibustion treatment of RA rats may exert anti-inflammatory effects through MIF/CORT. A: levels of MIF in serum of different groups; B: levels of CORT in serum of different groups; C: levels of TNF-α in serum of different groups; D: photo of footpads of rats in the RA group; E: HE stained image of ankle synovial tissue of RA groups, magnification: × 25 and scale bars represent 200 μm; F: HE staining magnified image of ankle joint synovial tissue in the RA group, magnification: × 100 and scale bars represent 50 μm; G: photo of footpads of rats in the MOX + ISO-1 group; H: HE stained image of ankle synovial tissue of MOX + ISO-1 groups, magnification: × 25 and scale bars represent 200 μm; I: HE staining magnified image of ankle joint synovial tissue in the MOX + ISO-1 group, magnification: × 100 and scale bars represent 50 μm. CON: Blank Control group, rats did not undergo any treatment; RA: RA Model group,rats were injected with 0.1 mL FCA in rats' bilateral hind foot pads on the third day of the experiment; ISO-1: MIF inhibitor ISO-1 group, rats were intraperitoneally injected ISO-1 every other day on the first day of the experiment with 15 injections in total and be injected with 0.1mL FCA in rats' bilateral hind foot pads on the third day of the experiment; MOX + ISO-1: Moxibustion + MIF inhibitor ISO-1 group, rats were intraperitoneally injected ISO-1 every other day on the first day of the experiment, be injected with 0.1 mL FCA in rats' bilateral hind foot pads on the third day of the experiment, and moxibustion was performed to rats on the 10th day of the experiment. MIF: macrophage migration inhibitory factor; CORT: corticosterone; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor - α; HE: hematoxylin and eosin; ISO-1: (S,R)-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4,5-dihydro-5-isoxazole acetic acid methyl ester; FCA: Freund's complete adjuvant. Data are mean ± standard deviation (n = 10). aP < 0.01, compared with the RA group; bP < 0.05, compared with the ISO-1 group.
| 1. |
Smolen JS, Aletaha D, McInnes IB. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 2016; 388: 2023-38.
DOI PMID |
| 2. |
McInnes IB, Schett G. Pathogenetic insights from the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 2017; 389: 2328-37.
DOI PMID |
| 3. |
Gunther S, Fagone P, Jalce G, Atanasov AG, Guignabert C, Nicoletti F. Role of MIF and D-DT in immune-inflammatory, autoimmune, and chronic respiratory diseases: from pathogenic factors to therapeutic targets. Drug Discov Today 2019; 24: 428-39.
DOI PMID |
| 4. |
Kim KW, Kim HR. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor: a potential therapeutic target for rheumatoid arthritis. Korean J Intern Med 2016; 31: 634-42.
DOI URL |
| 5. |
Bilsborrow JB, Doherty E, Tilstam PV, Bucala R. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) as a therapeutic target for rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Expert Opin Ther Targets 2019; 23: 733-44.
DOI URL |
| 6. | Calandra T, Bucala R. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF): a glucocorticoid counter-regulator within the immune system. Crit Rev Immunol 2017; 37: 381-91. |
| 7. | Yang ZX, Li ZB. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor and rheumatoid arthritis. Zhong Guo Zu Zhi Gong Cheng Yan Jiu 2007; 36: 7252-6. |
| 8. |
Morand EF, Leech M. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor in rheumatoid arthritis. Front Biosci Landmark 2005; 10: 12-22.
DOI URL |
| 9. |
Shirin M, Navid N, Manica N, Younes G. A new approach for cancer immunotherapy based on the cancer stem cell antigens properties. Curr Mol Med 2019; 19: 2-11.
DOI PMID |
| 10. |
Radstake TRDJ, Sweep FCGJ, Welsing P, et al. Correlation of rheumatoid arthritis severity with the genetic functional variants and circulating levels of macrophage migration inhibitory factor. Arthritis Rheumatol 2005; 52: 3020-9.
DOI URL |
| 11. |
Yilmaz D, Gönüllü E, Gürsoy M, Könönen E, Gürsoy UK. Salivary and serum concentrations of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, macrophage inhibitory factor, and fractalkine in relation to rheumatoid arthritis and periodontitis. J Periodontol 2021; 92: 1295-305.
DOI PMID |
| 12. | Liu X, Bi QJ. Role of macrophage migration inhibitory factor in resistance mechanism of glucocorticoid in inflammatory diseases. Yao Wu Ping Jia Yan Jiu 2019; 42: 1670-5. |
| 13. |
Hartmann K, Koenen M, Schauer S, et al. Molecular actions of glucocorticoids in cartilage and bone during health, disease, and steroid therapy. Physiol Rev 2016; 96: 409-47.
DOI PMID |
| 14. |
Yao J, Leng L, Fu W, Li J, Bronner C, Bucala R. ICBP90 regulates MIF expression, glucocorticoid sensitivity, and apoptosis at the MIf immune susceptibility locus. Arthritis Rheumatol 2021; 73: 1931-42.
DOI URL |
| 15. |
Leech M, Metz C, Hall P, et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor in rheumatoid arthritis-evidence of proinflammatory function and regulation by glucocorticoids. Arthritis Rheumatol 1999; 42: 1601-8.
DOI URL |
| 16. |
Zeng C, Bai XJ, Qin HP, Wang H, Rong XF, Yan J. Effect of adjuvant therapy with electroacupuncture on bone turnover markers and interleukin 17 in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Tradit Chin Med 2019; 39: 582-6.
PMID |
| 17. |
Hughes JG. "When I first started going I was going in on my knees, but I came out and I was skipping": exploring rheumatoid arthritis patients' perceptions of receiving treatment with acupuncture. Complement Ther Med 2009; 17: 269-73.
DOI PMID |
| 18. | Kim TH, Kim KH, Kang JW, et al. Moxibustion treatment for knee osteoarthritis: a multi-centre, non-blinded, randomised controlled trial on the effectiveness and safety of the moxibustion treatment versus usual care in knee osteoarthritis patients. PLoS One 2014; 9: 8. |
| 19. | Lu WT, Luo XC, Shang YN, et al. Effects of moxibustion on serum cytokines in experimental animals with rheumatoid arthritis : a systematic review and Meta-analysis. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu 2020; 45: 751-61. |
| 20. | Zhong YM, Wu F, Luo XC, et al. Mechanism on moxibustion for rheumatoid arthritis based on PD-1/PD-L1 signaling pathway. Zhong Guo Zhen Jiu 2020; 40: 976-82. |
| 21. | Zhong YM, Wu F, Luo XC, Zhou HY. Research progress on mechanism of moxibustion in treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Zhong Guo Zhong Yi Yao Xin Xi Za Zhi 2021; 28: 133-7. |
| 22. | Zhong YM, Cheng B, Zhang LL, Lu WT, Shang YN, Zhou HY. Effect of moxibustion on inflammatory cytokines in animals with rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2020; 2020: 6108619. |
| 23. |
Shalev M. APHIS, FDA, and NIH issue memorandum of understanding on laboratory animal welfare. Lab Animal 2006; 35: 13.
PMID |
| 24. |
Leech M, Metz C, Santos L, et al. Involvement of macrophage migration inhibitory factor in the evolution of rat adjuvant arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 1998; 41: 910-7.
DOI URL |
| 25. | Wu X, Liu XG, Jing ZK, Chen Y, Liu HH, Ma WB. Moxibustion benignantly regulates circadian rhythm of REV-ERB alpha in RA rats. Am J Transl Res 2020; 12: 1459-68. |
| 26. | You YD, Zhao L, Mei FC, Hong YP, Wang WX. Effects of macrophage migration inhibitory factor inhibitor ISO-1 on intestinal injury induced by acute necrotic pancreatitis in pregnant rat model. Zhong Guo Pu Wai Ji Chu Yu Lin Chuang 2018; 25: 1308-12. |
| 27. | Yang B, Zhang X, Li JC, Zhu QB, Guo RX, Chen L. Impact of ISO-1 intervention on expression of macrophage migration inhibitory factor in the myocardium of diabetic rats. Lin Chuang Xin Xue Guan Za Zhi 2012; 28: 111-4. |
| 28. |
Liu Y, Liu Y, Wang Q, et al. MIF inhibitor ISO-1 alleviates severe acute pancreatitis-associated acute kidney injury by suppressing the NLRP 3 inflammasome signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol 2021; 96: 107555.
DOI URL |
| 29. | Gao XH, Liu XG, Jin S, et al. Effect of moxibustion therapy on the balance of Th17 /Treg in rabbits with rheumatoid arthritis. Zhong Guo Zhong Yi Ji Chu Yi Xue Za Zhi 2019; 25: 1404-6+19. |
| 30. |
Smolen JS, Aletaha D, Barton A, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2018; 4: 18001.
DOI PMID |
| 31. | Nissen SE. Cardiovascular safety of celecoxib, naproxen, or ibuprofen for arthritis reply. NEJM 2017; 376: 2519-29. |
| 32. |
Strehl C, Bijlsma JWJ, de Wit M, et al. Defining conditions where long-term glucocorticoid treatment has an acceptably low level of harm to facilitate implementation of existing recommendations: viewpoints from an EULAR task force. Ann Rheum Dis 2016; 75: 952-7.
DOI PMID |
| 33. |
Burmester GR, Landew R, Genovese MC, et al. Adalimumab long-term safety: infections, vaccination response and pregnancy outcomes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 2017; 76: 414-7.
DOI PMID |
| 34. |
Feldmann M, Steinman L. Design of effective immunotherapy for human autoimmunity. Nature 2005; 435: 612-9.
DOI |
| 35. | Zhu Y, Yu HW, Pan YZ, et al. Moxibustion therapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and influences on peripheral blood NLR, PLR and RDW. Liaoning Zhong Yi Za Zhi 2019; 46: 385-7. |
| 36. |
Feng H, Qiang W, Lei L, et al. Effect of moxibustion on autophagy and the inflammatory response of synovial cells in rheumatoid arthritis model rats. J Tradit Chin Med 2022; 42: 73-82.
DOI |
| 37. | Tao S, Wang X, Liao C, et al. The efficacy of moxibustion on the serum Levels of CXCL1 and beta-EP in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Pain Res Manag 2021; 2021: 7466313. |
| 38. | Yu Z, Wang Y, Li Y, et al. Effect of moxibustion on the serum Levels of MMP-1, MMP-3, and VEGF in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2020; 2020: 7150605. |
| 39. |
Zhong YM, Zhang LL, Lu WTT, Shang YN, Zhou HY. Moxibustion regulates the polarization of macrophages through the IL-4/STAT6 pathway in rheumatoid arthritis. Cytokine 2022; 152: 155835.
DOI URL |
| 40. |
Calandra T, Roger T. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor: a regulator of innate immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 2003; 3: 791-800.
DOI PMID |
| 41. |
Leech M, Metz C, Bucala R, Morand EF. Regulation of macrophage migration inhibitory factor by endogenous glucocorticoids in rat adjuvant-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol 2000; 43: 827-33.
DOI URL |
| 42. |
Morand EF. New therapeutic target in inflammatory disease: macrophage migration inhibitory factor. Intern Med J 2005; 35: 419-26.
PMID |
| 43. |
Fu X, Niu N, Li G, et al. Blockage of macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) suppressed uric acid-induced vascular inflammation, smooth muscle cell de-differentiation, and remodeling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2019; 508: 440-4.
DOI URL |
| 44. | Ma WB, Liu XG, Zhou HY. Effects of chronological moxibustion on circadian rhythm activities of hypothalamus-pituitary-axis in rheumatoid arthritis rats. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu 2016; 41: 100-7. |
| 45. | Zhou HY, Liu XG, Huang DJ, et al. Study of moxibustion regulating RA rats' HPAA functional glucocorticoid receptor mechanism. Zhong Hua Zhong Yi Yao Xue Kan 2010; 28: 1167-9. |
| 46. | Zhou HY, Liu XG, Gao J. Research of moxibustion influence on GR and MEL1B expressions in hippocampus of experimental RA rats. Liaoning Zhong Yi Za Zhi 2012; 39: 2313-5. |
| [1] | LI Chaoran, YANG Yan, FENG Chuwen, LI Heng, QU Yuanyuan, WANG Yulin, WANG Delong, WANG Qingyong, GUO Jing, SHI Tianyu, SUN Xiaowei, WANG Xue, HOU Yunlong, SUN Zhongren, YANG Tiansong. Integrated 'omics analysis for the gut microbiota response to moxibustion in a rat model of chronic fatigue syndrome [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1176-1189. |
| [2] | WANG Miao, ZHU Yan, ZHAO Hui, ZHAO Hongfang. Moxibustion enables protective effects on rheumatoid arthritis-induced myocardial injury via transforming growth factor beta1 signaling and metabolic reprogramming [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1190-1199. |
| [3] | LI Xingjie, LIU Qiqi, XIA Rui, LIU Jun, WANG Dan, SHI Jiao, KUANG Yuxing, DAI Yalan, HUANG Haoyu, TANG Wei, CHEN Shangjie. Moxibustion modulates working memory in patients with amnestic mild cognitive impairment: a functional magnetic resonance imaging study [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(4): 801-808. |
| [4] | MA Fangfang, ZHANG Hewei, LI Bingxue, CHENG Peiyu, YU Mingwei, WANG Xiaomin. Acupuncture and moxibustion for malignant tumor patients with psychological symptoms of insomnia, anxiety and depression: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(3): 441-456. |
| [5] | MIN Youjiang, YAO Haihua, WANG Zhiqin, LUO Kaitao, SUN Jie, YUAN Zheng, WU Huiqi, CHENG Lihong. Efficacy of suspended moxibustion stimulating Shenshu (BL23) and Guanyuan (CV4) on the amygdala-HPA axis in rats with kidney-Yang deficiency symptom pattern induced by hydrocortisone [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(1): 113-123. |
| [6] | YAO Yao, ZHAO Zhenni, CHEN Fengqin, LENG Yufei, PANG Xiangtian, XU Xiao, SUN Zhiling. Effectiveness of moxibustion alone on lumbar disc herniation: a Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(1): 14-26. |
| [7] | YANG Jun, XIONG Jun, XU Shaozhong, XIE Hongwu, XIANG Jie. Effect and cerebral mechanism of moxibustion at heat-sensitized Yaoyangguan (GV3) in patients with lumbar disc herniation and myofascial pain syndrome by resting-state functionality magnetic resonance imaging: protocol for an observational study [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(1): 175-180. |
| [8] | FANG Jing, PAN Wen, WANG Xiangyun, LI Fengxing, ZHAO Ling, HUANG Zouqin, SHEN Xueyong. Efficacy of stimulating Mingmen (GV4) and Guanyuan (CV4) on kidney Yang deficiency in rat model: laser irradiation vs traditional moxibustion [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(6): 972-979. |
| [9] | ZHOU Haiyan, ZHONG Yumei, GAO Xiuhua, WU Fei, JIA Min, YANG Xin. Efficacy of Moxa-burning heat stimulating Zusanli (ST36) and Shenshu (BL23) on expressions of macrophage migration inhibitory factor and macrophage apoptosis in rabbits with adjuvant-induced arthritis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(6): 980-987. |
| [10] | WANG Wei, LI Qingling, MA Qiang, XIA Ran, GAO Bing, WANG Yi, WANG Jing. Effects of moxibustion at bilateral Feishu (BL13) and Xinshu (BL15) combined with benazepril on myocardial cells apoptosis index and apoptosis-related proteins cytochrome c and apoptosis-inducing factor in rats with chronic heart failure [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(2): 227-233. |
| [11] | MA Tingting, WU Jie, YANG Lijie, FENG Fen, YANG Huilin, ZHANG Jinhua, ZHONG Yanjin, NING Qing, HUANG Lirong, LIN Youbing, YAN Jue, CHEN Guiquan, HOU Tianshu, WANG Li, REN Yuanfang, TAN Jing. Ginger-indirect moxibustion plus acupuncture versus acupuncture alone for chronic fatigue syndrome: a randomized controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(2): 242-249. |
| [12] | Jing ZHANG, Jingjing ZHU, Siqi HE, Jianxun WANG. Efficacy of glucocorticoids, chloroquine and vitamin A on cytokine release syndrome: a network pharmacology study [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(1): 116-121. |
| [13] | Feng HAO, Qiang WANG, Lei LIU, Libin WU, Ronglin CAI, Jiajia SANG, Jun HU, Jie WANG, Qing YU, Lu HE, Yingchao SHEN, Yiming MIAO, Ling HU, Zijian WU. Effect of moxibustion on autophagy and the inflammatory response of synovial cells in rheumatoid arthritis model rats [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(1): 73-82. |
| [14] | PAN Lijia, MA Shuya, WEN Jing, ZHANG Xiaoqi, XING Haijiao, JIA Chunsheng. Direct contact moxibustion promotes apoptosis of gastric cancer cells in rats by regulating intestinal flora [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(6): 943-952. |
| [15] | LIU Di, WU Yongli, LI Chun, WANG Minglei, MA Xiaoxiu, LIU Junwei, ZHANG Yanling, YANG Lei. Warming moxibustion attenuates inflammation and cartilage degradation in experimental rabbit knee osteoarthritis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(6): 959-967. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

