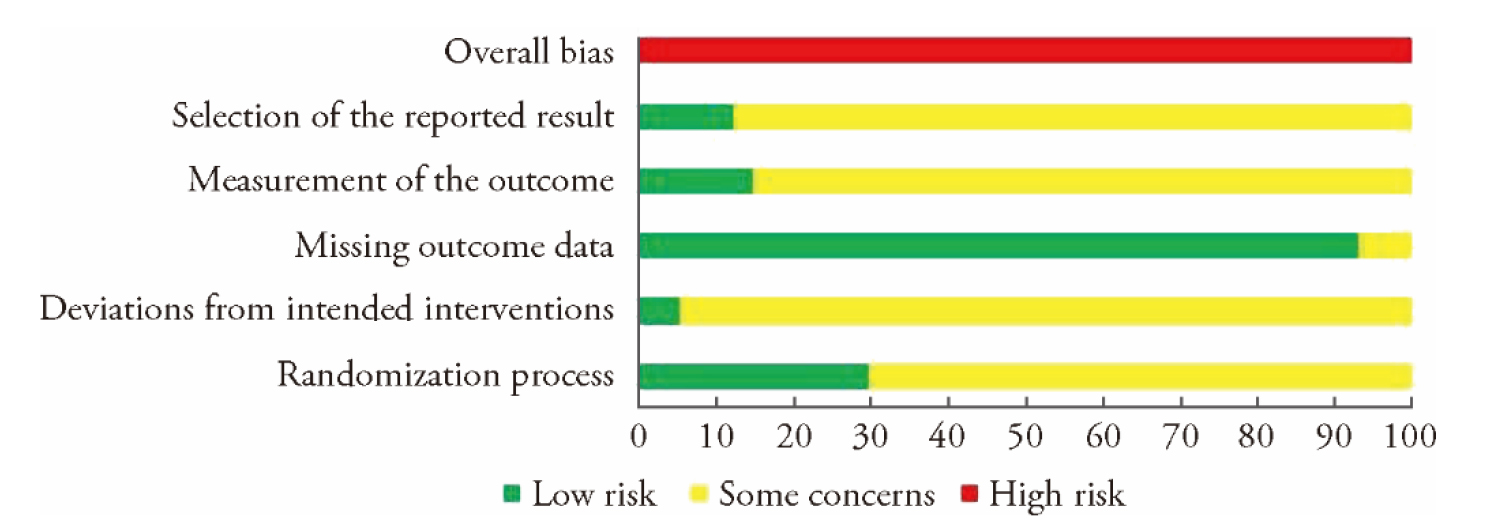
Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (2): 234-253.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2025.02.002
• Meta-Analyses • Previous Articles Next Articles
Update evidence of effectiveness on pain relieving of cupping therapy: a systematic review and Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
WANG Yiying, DONG Shuai, LI Bo, HAN Mei, CAO Huijuan( )
)
- Center for Evidence-Based Medicine, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100029, China
-
Received:2024-01-23Accepted:2024-05-15Online:2025-04-15Published:2025-03-10 -
Contact:Prof. CAO Huijuan, Center for Evidence-Based Medicine, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100029, China. huijuancao327@hotmail.com, Telephone: +86-13466615885 -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China Project: Research on the Correlation between Traditional Chinese Medicine Constitution, Cupping Marks Color, and Clinical Efficacy Based on Regression Models(81804000)
Cite this article
WANG Yiying, DONG Shuai, LI Bo, HAN Mei, CAO Huijuan. Update evidence of effectiveness on pain relieving of cupping therapy: a systematic review and Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(2): 234-253.
share this article
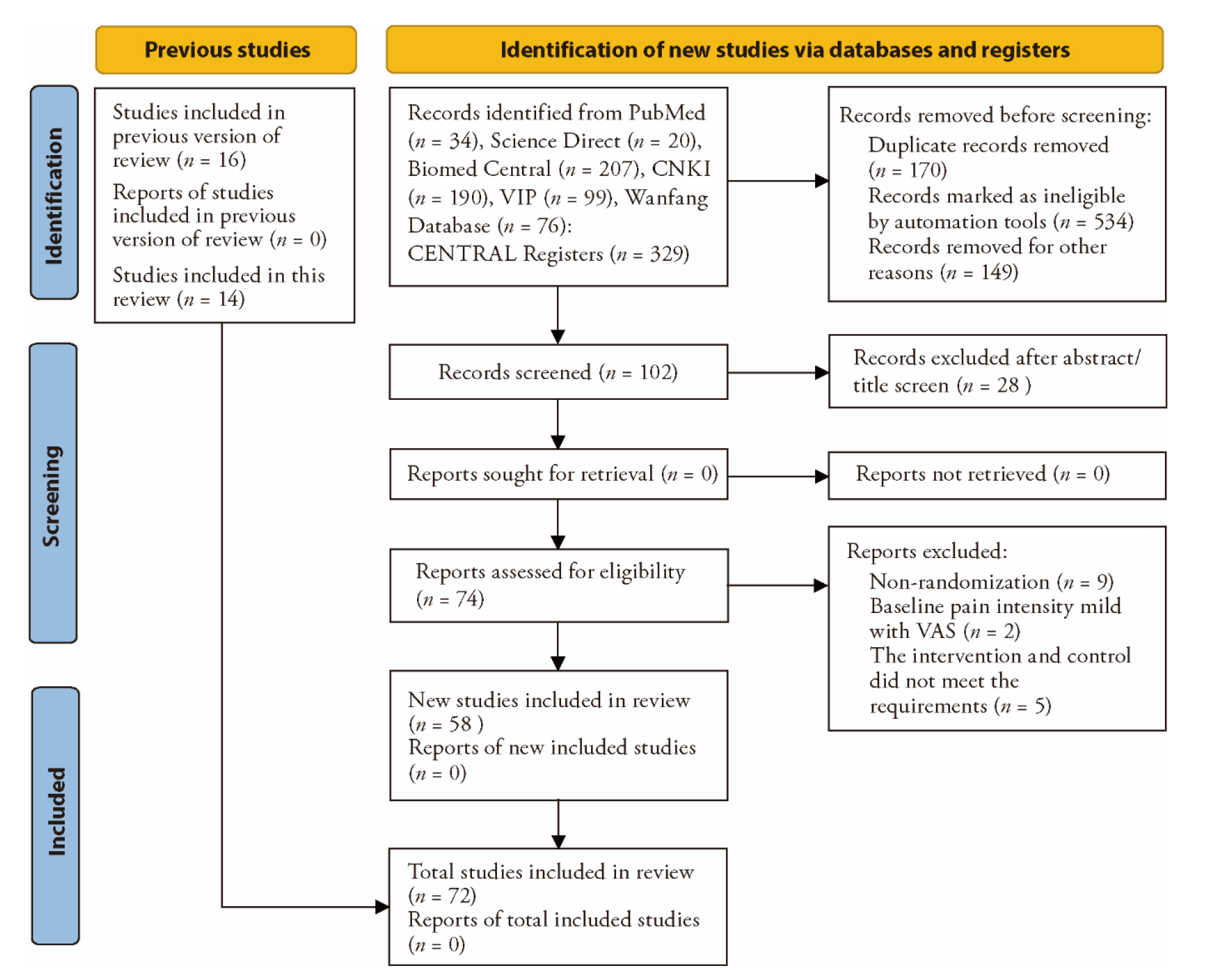
Figure 1 PRISMA 2020 flow diagram for updated systematic reviews PRISMA: preferred reporting items for systematic review and Meta-analyses; CNKI: Chinese national knowledge infrasturcture; VIP: China science and technology journal database; CENTRAL: Cochrane central registre of controlled trials; VAS: visual analog scale.
| Study ID | Disease type | Sample size (M/F) | Age (years, MD ± SD) or M (Q1,Q3) | Pain intensity at baseline | Outcome measurement | Intervention group operation | Control group operation | Treatment duration | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T | C | T | C | T | C | Type of cupping | Points of selection | Time of cupping retained (min) | Combination frequency | Combination on therapy | Control group | Usage | ||||||
| Cupping therapy vs waiting list/no treatment or usual care | ||||||||||||||||||
| Teut M et al 2012 | Osteoarthritis of theknee | 5/16 | 8/ 11 | 68.10±7.20 | 69.30± 6.80 | 2.90± 0.46 | 2.81± 0.55 | ①②③⑥ | a | The knee joint | 10 | Twice weekly | NA | Wait-list | NA | 2 | ||
| Kim JI et al 2011 | Non-specific low back pain | 5/16 | 3/8 | 44.20±9.40 | 48.00± 5.40 | 5.81± 1.12 | 5.27± 8.00 | ①②⑥ | b | Bilateral BL23, BL24, BL25 | 5 | Three times weekly | SAC | Wait-list | NA | 14 | ||
| Lauche R et al 2011 | Non-specific neck pain | 7/15 | 4/ 20 | 48.60±11.2 | 53.00± 11.40 | 4.55± 2.09 | 4.23± 1.08 | ①③⑥ | a | Tender points | 10-20 | Every 3-4 d | NA | Wait-list | NA | 14 | ||
| Wu ZS 2007 | Acute ankle sprain | 10/ 21 | 11/19 | NR | NR | 8.61± 1.06 | 8.74± 0.92 | ①④⑥ | b | Tender points | 10 | Once daily | NA | Wait-list | NA | 5 | ||
| Zhang QE, Lai Z 2017 | Low back pain | 50/ 52 | 52/54 | NR | NR | 4.03± 0.89 | 3.62± 0.91 | ①③④ | e | From DU14 to DU2 on the back midline | 10 | Once every 2 d | NA | Usual care 1k | 30 min, once every 2 d. | 14 | ||
| Dong G et al 2014 | Low back pain | 28/ 22 | 27/23 | 54.50 (39.00-70.00) | 54.00 (38.00-70.00) | 7.45± 1.48 | 7.38± 1.35 | ①④ | f | BL23, DU3, BL40 and Ashi (bilateral) | 5-15 | Once every 2 d | NA | Usual care 2 | 20-30 min, once daily. | 10 | ||
| Farhadi K et al 2009 | Non-specific low back pain | 30/ 18 | 37/13 | 44.90± 14.80 | 41.80± 13.90 | 2.70± 0.80 | 2.70± 0.90 | ①⑥ | b | Tender points | 3-5 | Once every 2 d | NA | Usual care 3 | See notes for details. | 6 | ||
| Lauche R et al 2013 | Chronic neck pain | 6/24 | 10/21 | 54.50± 12.30 | 53.70± 13.40 | 5.58± 1.97 | 5.63± 1.86 | ①②③⑥ | d | NA | 10-15 | Twice weekly | NA | Usual care 4 | 20 min, twice weekly. | 84 | ||
| Cramer H et al 2011 | Chronic neck pain | 4/20 | 6/ 18 | 44.50± 10.80 | 47.90± 13.50 | 4.12± 1.45 | 4.20± 1.57 | ①②③⑥ | ad | Ashi | 10-15 | Once every 3-4 d. | NA | Usual care 5 | See notes for details. | 14 | ||
| Kim TH et al 2012 | Neck pain | 7/13 | 11/9 | 25.50 (22.50-40.50) | 28.00 (25.00-31.50) | 5.93± 1.63 | 6.49± 1.49 | ①②③⑥ | b | Ashi | 5-10 | Three times weekly. | NA | Usual care 1l | 10 min, 3 times weekly. | 49 | ||
| Study ID | Disease type | Sample size (M/F) | Age (years, MD ± SD) or M (Q1,Q3) | Pain intensity at baseline | Outcome mea-surement | Intervention group operation | Control group operation | Treatment duration | ||||||||||
| T | C | T | C | T | C | Type of cupping | Points of selection | Time of cupping retained (min) | Combination frequency | Combination on therapy | Control group | Usage | ||||||
| MichalsenA et al 2009 | Carpal tunnel syndrome | 2/ 24 | 4/ 22 | 57.20±7.70 | 59.30±8.30 | 6.15± 2.49 | 5.86± 2.51 | ①②③⑥ | b | Tender points | 5-10 | Treatment once | NA | Usual care 1m | Once 15 min | 7 | ||
| Cupping therapy vs drugs | ||||||||||||||||||
| Xue M et al 2021 | Dysmenorrhea | 0/ 29 | 0/ 29 | 26.48±4.82 | 27.71±4.01 | NR | NR | ②④ | b | SP8 | 10 | Once a month | NA | Ibuprofen | 0.3-0.6 g, twice daily | 90 | ||
| Wang L et al 2020 | Postherpetic neuralgia | 16/19 | 17/ 18 | 58.60 | 57.80 | 9.15± 0.31 | 9.07± 0.27 | ①④⑤⑥ | b | Ashi | 15-20 | Once every 2 d | NA | Gabapentin capsule | 0.3 g, 3 times daily (once or twice on the first two days) | 16 | ||
| Li XJ et al 2019 | Postherpetic neuralgia | 16/16 | 14/ 18 | 46.90± 13.90 | 46.70± 14.30 | 6.90± 1.30 | 6.97± 1.40 | ①④⑥ | b | Zhuang medicine acupoints | 10-15 | Once every 3 d | NA | Gabapentin capsule | 300 mg,3 times daily | 60 | ||
| Liu MH, Wang GY 2017 | Postherpetic neuralgia | 18/17 | 19/ 14 | 52.00 | 49.00 | 7.91± 1.35 | 7.88± 1.47 | ①④⑤⑥ | b | NA | 5-10 | Once daily | NA | Flupentixol; Melitracen | 10.5 mg, twice daily; 0.5 mg, 3 times daily. | 28 | ||
| Luo CY et al 2017 | Postherpetic neuralgia (AIDS) | 8/ 14 | 10/ 12 | 48.00± 18.00 | 50.00± 18.00 | 8.30± 1.50 | 8.30± 1.40 | ①④ | b | Ashi | 20-30 | Once every 2 d | NA | Meco-balamin; Carba-mazepine | 10 mg, 3 times a day; 0.5 mg, 3 times a day; 0.1 g, 3 times a day. | 20 | ||
| Zhang XQ, Hu CL 2015 | Postherpetic neuralgia | 14/24 | 16/ 22 | 60.20±9.70 | 61.40± 10.20 | NR | NR | ②④ | b | The affected skin | NA | Once every 5 d | NA | Amitriptyline | 25 mg, once daily at bedtime. | 30 | ||
| Study ID | Disease type | Sample size (M/F) | Age (years, MD ± SD) or M (Q1,Q3) | Pain intensity at baseline | Outcome measurement | Intervention group operation | Control group operation | Treatment duration | ||||||||||
| T | C | T | C | T | C | Type of cupping | Points of selection | Time of cupping retained (min) | Combination frequency | Combination on therapy | Control group | Usage | ||||||
| Feng LF 2015 | Postherpetic neuralgia | 22/16 | 20/18 | 56.32±9.81 | 58.24±9.29 | 7.21± 1.16 | 7.18± 1.21 | ①④ | b | Ashi | 10 | Once every 3 d | NA | Mecobalamin; Indomethacin | 5 mg, twice daily; 5 mg, twice daily. | 30 | ||
| Xing YK et al 2017 | Herpes zoster | 14/14 | 15/13 | 40.02±19.62 | 42.50±18.32 | 7.80± 1.75 | 7.78± 1.70 | ①②④⑥ | b | NA | NA | Once daily | NA | sodium phosphonate (intravenous drip); Valaciclovir | 3 g, once daily; 0.15 g, twice daily | 14 | ||
| Li ZQ 2018 | Acute herpes zoster | 26/33 | 28/31 | 44.83±15.36 | 44.44±15.33 | NR | NR | ④ | b | Tender points | 1-2 | Once every 3 d | NA | Acyclovir; Mecobalamin; | 0.2 g, 3 times daily; 0.5 mg; 3 times daily. | 10 | ||
| Chen W et al 2014 | Acute herpes zoster | 12/18 | 10/20 | Range 40.00-76.00 | Range 46.00-80.00 | 7.63± 1.19 | 7.40± 1.11 | ①④⑥ | b | Tender points | 10-15 | Once every 2 d | NA | Valaciclovir hydrochloride (Fasting before meals). | 0.3 g, twice daily. | 10 | ||
| Liu Y, et al 2016 | Migraine | 10/20 | 12/18 | 41.47±13.51 | 42.47 ±13.60 | 5.73± 2.01 | 6.07± 1.61 | ①②④ | b | EX-HN5 (bilateral) and its nearby | NA | NA | NA | Diclofenac sodium | 75 mg, once daily. | 90 | ||
| Jiang HW et al 2015 | Migraine | 7/23 | 9/21 | 20.00-65.00 | 18.00-57.00 | NR | NR | ④⑥ | b | BL17 | 20 | Twice weekly | NA | Ceftriaxone hydrochloride | 10 mg every night. | 28 | ||
| Song N et al 2013 | Migraine | 16/29 | 18/27 | 35.40±3.10 | 36.10 ±2.30 | 6.76± 1.48 | 6.44± 1.78 | ①②④ | b | G20, GV14 | 15 | Twice weekly | NA | Flunarizine | 10 mg, once daily at bedtime. | 56 | ||
| Zhou YC 2016 | Neck myofascial pain syndrome | 7/23 | 9/21 | 38.33±8.63 | 36.90 ±9.03 | 6.03± 1.32 | 5.93± 1.36 | ①② | b | Ashi | 10 | Once every 3 d | NA | Lidocaine | 2 mL at each point, once every 3 d. | 15 | ||
| Wu K 2013 | Osteoarthritis | 8/22 | 7/23 | 56.70±6.60 | 57.40±5.80 | 6.97± 0.85 | 7.00± 0.87 | ①⑥ | b | Ex-LE4, Ex-LE5, ST34, SP10, SP9, Ashi | 3-4 | Once every 2 d | NA | Diclofenac | 50 mg, twice daily. | 14 | ||
| Study ID | Disease type | Sample size (M/F) | Age (years, MD ± SD) or M (Q1,Q3) | Pain intensity at baseline | Outcome measure-ment | Intervention group operation | Control group operation | Treat-ment duration | ||||||||||
| T | C | T | C | T | C | Type of cupping | Points of selection | Time of cupping retained (min) | Com-bination frequency | Combin-ation on therapy | Control group | Usage | ||||||
| Cupping therapy plus drugs vs drugs | ||||||||||||||||||
| Hou YW et al 2022 | Postherpetic neuralgia | 13/17 | 14/16 | 49.79±3.46 | 55.34±1.78 | 8 (8,9) | 8 (7,9) | ①②④ | j | Ashi | 10 | Once every 2 d | SAC | Dihydrocodeine Tartrate Tablets | 60 mg, 3 times daily | 20 | ||
| Luo TW, Wu XY 2022 | Haemorr-hoids | 15/12 | 15/18 | 38±16 | 39±14 | 6.18± 1.85 | 6.27± 1.89 | ①④ | b | BL57 | 5 | Once every 4 d | SAC | Diosmin tablets; Yinglong Ma musk hemorrhoid Cream; Potassium permanganate solution | 1 g, twice daily; (applied externally), 20 min, twice daily; (sitting bath) twice daily | 14 | ||
| Xia ZY et al 2022 | Pain after fracture | 25/19 | 23/21 | 67.72±0.68 | 67.32±1.11 | NR | NR | ①② | b | GB34, GB39, BL57, Ashi, BL-25, BL54, GB30, etc | 8 | Once daily | SAC | Self controlledanalgesics (intravenous injection) | 5 mL (first), 15 min, 2 mL/h (sustained dose), a single dose of 0.5 mL | 7 | ||
| Zhang CF 2022 | Herpes zoster | 22/18 | 24/16 | 45.26±3.74 | 45.48±3.62 | 6.94± 0.54 | 7.05± 0.57 | ①②④ | b | Ashi | 10 | Once daily | SAC | Valacyclovir hydrochloride tablets, Mecobalamin tablets | 0.3 g, twice daily 0.5 mg, 3 times daily | 10 | ||
| Li H 2022 | Acute herpes zoster | 14/18 | 15/17 | Range27-78 | Range20-76 | 7.21± 1.21 | 7.15± 1.14 | ①④ | b | Ashi | 3-5 | Once daily | SAC | Acyclovir sodium needle, Me-cobalamin | 0.5 g, 3 times daily; 0.5 mg, 3 times daily | 7 | ||
| Zhang LQ et al 2021 | Postherpetic neuralgia | 16/15 | 17/13 | 61.69±8.43 | 61.42±7.96 | 7.09± 1.33 | 7.05± 1.30 | ①②④⑥ | b | Ashi | 15-20 | Once every 2 d | SAC | Pregabalin | 150 mg, twice daily. | 30 | ||
| Yang C et al 2019 | Postherpetic neuralgia | 33/32 | 34/31 | 39.78±5.24 | 40.15±4.92 | 39.78±5.24 | 40.15± 4.92 | ①③④ | b | The herpes area | NA | Once every 2 d | SAC | Rat nerve growth factor (Injected intra-muscularly) | 30 μg, once daily. | 14 | ||
| Study ID | Disease type | Sample size (M/F) | Age (years, MD ± SD) or M (Q1,Q3) | Pain intensity at baseline | Outcome measure-ment | Intervention group operation | Control group operation | Treatment duration | ||||||||||
| T | C | T | C | T | C | Type of cup-ing | Points of selection | Time of cupping retained (min) | Combina-tion frequency | Combina-tion on therapy | Control group | Usage | ||||||
| Su ZY et al 2020 | Acute gouty arthritis | 18/ 12 | 11/ 19 | 38.10±5.30 | 39.20±5.60 | 8.43± 1.17 | 8.46± 1.12 | ①②④⑥ | b | NA | 3-5 | Once every 2 days | SAC | Fibulinastat | 40 mg, once daily. | 5 | ||
| Wang D, Huang CZ 2020 | Acute gouty arthritis | 31/ 19 | 30/ 20 | 65.13±14.24 | 15.55±4.49 | 8.35± 1.50 | 8.23± 1.45 | ①④⑥ | b | ST44, BL66, GB43 | 10-15 | Once every 2 d | SAC | Diclofenac sodium | 75 mg, once daily. | 16 | ||
| Jiang GL et al 2019 | Acute herpes zoster pain | 18/ 12 | 16/ 14 | 47.30±13.20 | 44.20±15.30 | 7.26± 1.34 | 7.18± 1.47 | ①⑥ | b | The herpes area | 10-15 | NA | SAC | Valaciclovir hydrochlorideMecobalamin | 0.3 g, twice daily; 0.5 mg, 3 times daily; 10 mg, 3 times daily. | 15 | ||
| Liu Z 2019 | Herpes zoster acute blister | 22/ 20 | 20/ 21 | 44.80±13.70 | 44.30±15.80 | 6.60± 1.31 | 6.46± 1.55 | ①④⑥ | a | The herpes area | 10 | Once every 4 d | SAC | Valaciclovir hydrochloride | 300 mg, twice a day; 10 mg, 3 times a day. | 12 | ||
| Tong LS 2016 | Herpes zoster | 24/ 18 | 22/ 18 | 45.00±8.40 | 44.50±5.30 | NR | NR | ④⑥ | b | Ashi | 15 | Once 2 d | SAC | Acyclovir ointment; Acyclovir tablets | 3 times daily; 0.4 g, 5 times daily. | 10 | ||
| Feng L, Huang SY 2018 | Cervicalspondylotic radiculo-pathy | 10/ 10 | 8/ 12 | 53.00±14.00 | 46.00±14.00 | 6.40± 1.54 | 6.30± 1.95 | ①②④ | c | DU14, GB21, SI11, SI15, SI14, SI13, Ashi | 5-10 | Once daily | SAC | Loxoprofen sodium | 60 mg, 3 times a day. | 30 | ||
| Zhang HY 2014 | Lumbodor-sal myofasciitis | 22/ 38 | 24/ 36 | 39.20±3.40 | 40.10±3.60 | 6.81± 2.26 | 6.77± 2.34 | ①④ | de | Bladder meridians | 10 | Once 2 d | SAC | Votalin emulsion | 3-4 times daily. | 10 | ||
| Li BJ 2022 | Cervical spondyosis | 23/17 | 22/ 18 | 47±6 | 46±7 | 7.48± 0.51 | 7.42± 0.55 | ①④⑥ | b | GV14, SI11 | 8 | Once every 5 d | SAC | Electro-acupuncture | 20 min, once daily | 20 | ||
| Cupping therapy plus acupuncture vs acupuncture | ||||||||||||||||||
| Xu J, yANG LL 2022 | Lumbago | 18/17 | 19/ 16 | 56.47±3.18 | 56.42±3.16 | 8.16± 1.05 | 8.09± 1.02 | ①②④ | b | BL40, BL17, Ashi, BL23 | 5 | Once every 2 d | SAC | Warm needling (acupuncture) | 30 min, once daily | 30 | ||
| Study ID | Disease type | Sample size (M/F) | Age (years, MD ± SD) or M (Q1,Q3) | Pain intensity at baseline | Outcome measure-ment | Intervention group operation | Control group operation | Treatment duration | ||||||||||
| T | C | T | C | T | C | Type of cup-ing | Points of selection | Time of cupping retained (min) | Combination frequency | Combination on therapy | Control group | Usage | ||||||
| Wu XY et al 2022 | Scapulo-humeral periarthritis | 14/19 | 11/20 | 52.36±4.99 | 51.35±5.10 | 5.70± 2.08 | 5.71± 2.20 | ①④ | d | Ashi | NA | Once every week | SAC | Acupuncture | 30 min, Once every 2 d | 14 | ||
| Huang HP et al 2022 | Scapulo-humeral periarthritis | 20/16 | 19/17 | 50.78±2.98 | 51.21±3.23 | 7.43± 1.04 | 7.45± 1.11 | ①②④ | b | TE14, LI15, SI11, Ashi | 3-7 | Once daily | SAC | Warm needling (acupuncture) | 30 min, Once every other day | 10 | ||
| Dong JP et al 2021 | Dysmenorr-hea | 0/26 | 0/26 | 18.00-35.00 | 20.00-33.00 | 9.56± 1.71 | 9.75± 1.81 | ④⑥ | ad | Bilateral of spine | NA | Once every 3 d | SAC | Acupuncture | 40 min, once daily | 90 | ||
| Zhang QH 2020 | Postherpetic neuralgia | 19/16 | 20/15 | 56.90±3.30 | 57.30±3.10 | 8.20± 0.50 | 8.10± 0.70 | ①④⑤⑥ | b | Ashi | 10 | Once every 2 d | SAC | Fire-acupuncture | NA, Once every 2 d | 20 | ||
| Zhao XX 2018 | Postherpetic neuralgia | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | ①④⑤⑥ | b | Ashi | 10 | Once every 2 d | SAC | Fire-acupuncture | NA, Once every other day | 10 | ||
| Zhang HX et al 2009 | Herpes zoster | 10/15 | 12/13 | 18.00-66.00 | 19.00-67.00 | NR | NR | ①④ | b | Ashi | 5-10 | Once daily | SAC | Electro-acupuncture | 30 min, NA. | 10 | ||
| Xie FL et al 2019 | Lumbar disc herniation | 86/64 | 80/70 | 48.70±4.60 | 46.20 ±4.10 | 5.24± 0.54 | 5.35± 0.61 | ①③④⑥ | b | Ashi | 10 | Once in 2-3 d | SAC | Acupuncture | 30 min, 3 times weekly | 14-21 | ||
| Wang ZJ et al 2018 | Lumbar disc herniation | 43/37 | 46/34 | 48.15±4.43 | 47.88 ±4.43 | 4.61± 0.79 | 4.53± 0.76 | ①⑥ | c | Wrist and ankle | 10 | Once daily | SAC | Acupuncture (Wrist ankle acupuncture therapy) | 30 min, once daily. | 7 | ||
| Cupping therapy plus acupuncture vs acupuncture | ||||||||||||||||||
| Lu P et al 2016 | Lumbar disc herniation | 17/14 | 15/16 | 47.48±7.05 | 45.70±8.37 | 6.452±0.624 | 6.355±0.733 | ①⑥ | eg | EX-B2, BL17 BL23, BL25 and EX-B6 (bilateral) | 5 | Once daily | SAC | Acupuncture | 30 min, once daily | 28 | ||
| Study ID | Disease type | Sample size (M/F) | Age (years, MD ± SD) or M (Q1,Q3) | Pain intensity at baseline | Outcome measure-ment | Intervention group operation | Control group operation | Treatment duration | ||||||||||
| T | C | T | C | T | C | Type of cupping | Points of selection | Time of cupping retained (min) | Combination frequency | Combina-tion on therapy | Control group | Usage | ||||||
| Chen WJ et al 2019 | Chronic low back pain | 17/20 | 16/21 | 58.00±6.20 | 58.00±7.80 | 8.11±1.22 | 8.05±0.97 | ①⑥ | i | Ashi | NA | Once daily | SAC | Acupuncture | 30 min, once daily | 10 | ||
| Liu HY 2020 | Low back pain | 20/20 | 21/19 | 42.48±2.59 | 41.22±1.96 | NR | NR | ①④ | a | Dai meridian | ≤15 | Every 2 d | SAC | Acupuncture | 15 min, once daily | NR | ||
| Ma LY, Bi Y 2020 | Knee osteoarthritis | 16/14 | 15/15 | 53.36±5.15 | 55.73±5.66 | 6.48±1.52 | 6.60±1.40 | ①④⑥ | c | Ashi, EX-LE2, EX-LE4, EX-LE5, SP10, ST35, ST36, GB34, GB33, SP9Y | 5-10 | Once daily | SAC | Acupuncture | 30 min, once daily | 10 | ||
| Zhu WJ et al 2017 | Dorsal myofasciitis | 15/20 | 16/19 | 36.20±6.70 | 35.80±7.30 | 6.31±1.62 | 6.42±2.05 | ①④⑥ | h | Ashi | 10 | Once every 2 d | SAC | Electro-acupuncture | 30 min, once daily | 16 | ||
| Chen JJ 2009 | Scapulohumeral periarthritis | 16/14 | 15/13 | 52.00±1.56 | 53.00±1.25 | 4.63±1.42 | 4.63±1.42 | ①④⑥ | b | Ashi | 10 | Once every 2 d | SAC | Electro-acupuncture | 30 min, once daily | 60 | ||
| Cupping therapy plus other therapy vs other therapy | ||||||||||||||||||
| Malik S et al 2022 | Chronic plantar fasciitis | 0/15 | 0/15 | 22.2±1.85 | 22.8±2.18 | 7.67±0.90 | 7.07±0.96 | ① | a | Affected side | 10 | Thrice a week | SAC | Excercise | 25-30 min, 3 times/ week | 28 | ||
| Han LL et al 2022 | Breast carbuncle | 0/32 | 0/32 | 36.75±4.87 | 36.91±4.49 | 7.00 (5.25,8.00) | 6.50 (6.00,8.00) | ①②④ | b | Ashi | NA | Once every 5 days | SAC | Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) formula | twice daily | 14 | ||
| Jiang Q, Chen Y 2022 | Acute lumbago | 27/20 | 25/22 | 42.09±6.35 | 42.18±6.44 | 6.10±0.72 | 6.03±0.68 | ①③④⑥ | j | Du Meridian and Bladder Meridians | 5-10 | Once every 3 days | SAC | Celecoxib capsules; Yulong powder (External Applied) | 100 mg, twice daily; once daily | 21 | ||
| Sun ZZ et al 2022 | Cervical spondyosis | 20/25 | 21/23 | 45.91±5.47 | 46.35±5.41 | 5.82±0.81 | 5.74±0.77 | ①⑥ | d | Shoulder dorsal to lumbar | 45 | Once every 3 days | SAC | Massage | 30 min | 21 | ||
| Study ID | Disease type | Sample size (M/F) | Age (years, MD ± SD) or M (Q1,Q3) | Pain intensity at baseline | Out-come measure-ment | Intervention group operation | Control group operation | Treatment duration | ||||||||||
| T | C | T | C | T | C | Type of cup-ping | Points of selection | Time of cupping retained (min) | Combination frequency | Combination on therapy | Control group | Usage | ||||||
| Liang NJ 2022 | Cervical spondyosis | 17/27 | 19/25 | 52.84±3.91 | 53.02±3.12 | 6.74±0.55 | 6.88±0.51 | ①④⑥ | c | Cervical Jiaji | 5-8 | Once daily | SAC | Massage | 20 min | 12 | ||
| Dong PP, Li FF 2022 | Acute lumbar posterior joint disorder | 46/49 | 43/52 | 42.6±5.9 | 42.3±5.7 | 5.94±0.55 | 5.87±0.58 | ①④⑥ | f | Ashi | 10-15 | Once daily | SAC | Massage | Once daily | 14 | ||
| Wan FD et al 2022 | Cervical spondyosis | 17/13 | 16/14 | 46.87±5.34 | 46.43±5.74 | 5.67±1.56 | 5.61±1.63 | ①④⑥ | c | Acupoints were selected based on meridian flow | 8-10 | Once daily | SAC | Massage | Once daily | 14 | ||
| Moura CC et al 2021 | Chronic back pain | 15/73 | 15/79 | 48.20±11.62 | 47.87±13.18 | NR | NR | ①⑥ | a | Selection according to the region of pain | 10 | Once a week | SAC | Ear acupuncture | Once a week | 42 | ||
| Xiao BE et al 2021 | Chronic non-specific low back pain | 36/32 | 38/30 | 57.65±5.37 | 57.27±5.62 | 7.18±1.05 | 7.10±1.08 | ①⑥ | j | Du Meridian and Bladder Meridians | 5-10 | Once every 3 d | SAC | Exercise | Core muscle group training (NA) | 28 | ||
| Chen JX et al 2021 | Chronic non-specific lower back pain | 27/21 | 26/22 | 63.50±3.40 | 64.20±3.40 | 6.33±1.72 | 6.29±1.66 | ①③⑥ | b | Ashi | 10 | Once every 2 d | SAC | Exercise | McKenzie therapy once a day | 10 | ||
| Feng WH, Shao P 2017 | Low back and leg pain | NR | NR | NR | NR | 8.73±0.51 | 8.80±0.47 | ①⑥ | c | DU3, EX-B2, BL25 point, and Ashi | 8 | Twice weekly | SAC | Exercise | Physical therapy (NA) | 14 | ||
| Chen JX et al 2020 | Low back pain | 22/26 | 25/23 | 46.10±3.20 | 42.30±3.50 | 7.73±1.21 | 7.78±1.23 | ①⑥ | b | Ashi | 10 | Once daily | SAC | Exercise | McKenzie therapy, once a day | 10 | ||
| He YM et al 2020 | Breast pain | 0/40 | 0/40 | 35.60±3.40 | 35.80±3.20 | 6.17±1.08 | 5.96±1.15P | ③④⑥ | bj | LA14 | 5 | Twice weekly | SAC | Xiaopi oral liquid | 15-30 mL, 3 times daily | 60 | ||
| Wang J et al 2019 | Shoulder pain | 14/9 | 13/10 | 56.71±5.49 | 56.31±5.63 | NR | NR | ① | a | GB21, Ashi | 8-10 | Treatment only once | SAC | Massage | NA | 2 | ||
| Study ID | Disease type | Sample size (M/F) | Age (years, MD ± SD) or M (Q1,Q3) | Pain intensity at baseline | Outcome measure-ment | Intervention group operation | Control group operation | Treatment duration | ||||||||||
| T | C | T | C | T | C | Type of cupping | Points of selection | Time of cupping retained (min) | Combination frequency | Combination on therapy | Control group | Usage | ||||||
| Chen X et al 2017 | Scapulohumeral periarthritis | 17/23 | 18/22 | 52.72±10.35 | 51.34±11.37 | 5.82± 0.71 | 6.13± 0.74 | ①④⑥ | a | Ashi, SI11, SI9, and LI15 of the affected side | 10 | Once a week | SAC | Gua-sha therapy | 10 min, once weekly | 28 | ||
| Ouyang Q et al 2001 | Hemiplegic shoulder pain | 18/8 | 22/8 | 58.20 (27.00-75.00) | 56.80 (29.00-71.00) | 6.37± 3.22 | 6.25± 3.01 | ①⑥ | b | Ashi | 10 | Once every 2 d | SAC | Exercise | 30 min once daily | 30 | ||
Table 1 Characteristics of 72 included trials
| Study ID | Disease type | Sample size (M/F) | Age (years, MD ± SD) or M (Q1,Q3) | Pain intensity at baseline | Outcome measurement | Intervention group operation | Control group operation | Treatment duration | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T | C | T | C | T | C | Type of cupping | Points of selection | Time of cupping retained (min) | Combination frequency | Combination on therapy | Control group | Usage | ||||||
| Cupping therapy vs waiting list/no treatment or usual care | ||||||||||||||||||
| Teut M et al 2012 | Osteoarthritis of theknee | 5/16 | 8/ 11 | 68.10±7.20 | 69.30± 6.80 | 2.90± 0.46 | 2.81± 0.55 | ①②③⑥ | a | The knee joint | 10 | Twice weekly | NA | Wait-list | NA | 2 | ||
| Kim JI et al 2011 | Non-specific low back pain | 5/16 | 3/8 | 44.20±9.40 | 48.00± 5.40 | 5.81± 1.12 | 5.27± 8.00 | ①②⑥ | b | Bilateral BL23, BL24, BL25 | 5 | Three times weekly | SAC | Wait-list | NA | 14 | ||
| Lauche R et al 2011 | Non-specific neck pain | 7/15 | 4/ 20 | 48.60±11.2 | 53.00± 11.40 | 4.55± 2.09 | 4.23± 1.08 | ①③⑥ | a | Tender points | 10-20 | Every 3-4 d | NA | Wait-list | NA | 14 | ||
| Wu ZS 2007 | Acute ankle sprain | 10/ 21 | 11/19 | NR | NR | 8.61± 1.06 | 8.74± 0.92 | ①④⑥ | b | Tender points | 10 | Once daily | NA | Wait-list | NA | 5 | ||
| Zhang QE, Lai Z 2017 | Low back pain | 50/ 52 | 52/54 | NR | NR | 4.03± 0.89 | 3.62± 0.91 | ①③④ | e | From DU14 to DU2 on the back midline | 10 | Once every 2 d | NA | Usual care 1k | 30 min, once every 2 d. | 14 | ||
| Dong G et al 2014 | Low back pain | 28/ 22 | 27/23 | 54.50 (39.00-70.00) | 54.00 (38.00-70.00) | 7.45± 1.48 | 7.38± 1.35 | ①④ | f | BL23, DU3, BL40 and Ashi (bilateral) | 5-15 | Once every 2 d | NA | Usual care 2 | 20-30 min, once daily. | 10 | ||
| Farhadi K et al 2009 | Non-specific low back pain | 30/ 18 | 37/13 | 44.90± 14.80 | 41.80± 13.90 | 2.70± 0.80 | 2.70± 0.90 | ①⑥ | b | Tender points | 3-5 | Once every 2 d | NA | Usual care 3 | See notes for details. | 6 | ||
| Lauche R et al 2013 | Chronic neck pain | 6/24 | 10/21 | 54.50± 12.30 | 53.70± 13.40 | 5.58± 1.97 | 5.63± 1.86 | ①②③⑥ | d | NA | 10-15 | Twice weekly | NA | Usual care 4 | 20 min, twice weekly. | 84 | ||
| Cramer H et al 2011 | Chronic neck pain | 4/20 | 6/ 18 | 44.50± 10.80 | 47.90± 13.50 | 4.12± 1.45 | 4.20± 1.57 | ①②③⑥ | ad | Ashi | 10-15 | Once every 3-4 d. | NA | Usual care 5 | See notes for details. | 14 | ||
| Kim TH et al 2012 | Neck pain | 7/13 | 11/9 | 25.50 (22.50-40.50) | 28.00 (25.00-31.50) | 5.93± 1.63 | 6.49± 1.49 | ①②③⑥ | b | Ashi | 5-10 | Three times weekly. | NA | Usual care 1l | 10 min, 3 times weekly. | 49 | ||
| Study ID | Disease type | Sample size (M/F) | Age (years, MD ± SD) or M (Q1,Q3) | Pain intensity at baseline | Outcome mea-surement | Intervention group operation | Control group operation | Treatment duration | ||||||||||
| T | C | T | C | T | C | Type of cupping | Points of selection | Time of cupping retained (min) | Combination frequency | Combination on therapy | Control group | Usage | ||||||
| MichalsenA et al 2009 | Carpal tunnel syndrome | 2/ 24 | 4/ 22 | 57.20±7.70 | 59.30±8.30 | 6.15± 2.49 | 5.86± 2.51 | ①②③⑥ | b | Tender points | 5-10 | Treatment once | NA | Usual care 1m | Once 15 min | 7 | ||
| Cupping therapy vs drugs | ||||||||||||||||||
| Xue M et al 2021 | Dysmenorrhea | 0/ 29 | 0/ 29 | 26.48±4.82 | 27.71±4.01 | NR | NR | ②④ | b | SP8 | 10 | Once a month | NA | Ibuprofen | 0.3-0.6 g, twice daily | 90 | ||
| Wang L et al 2020 | Postherpetic neuralgia | 16/19 | 17/ 18 | 58.60 | 57.80 | 9.15± 0.31 | 9.07± 0.27 | ①④⑤⑥ | b | Ashi | 15-20 | Once every 2 d | NA | Gabapentin capsule | 0.3 g, 3 times daily (once or twice on the first two days) | 16 | ||
| Li XJ et al 2019 | Postherpetic neuralgia | 16/16 | 14/ 18 | 46.90± 13.90 | 46.70± 14.30 | 6.90± 1.30 | 6.97± 1.40 | ①④⑥ | b | Zhuang medicine acupoints | 10-15 | Once every 3 d | NA | Gabapentin capsule | 300 mg,3 times daily | 60 | ||
| Liu MH, Wang GY 2017 | Postherpetic neuralgia | 18/17 | 19/ 14 | 52.00 | 49.00 | 7.91± 1.35 | 7.88± 1.47 | ①④⑤⑥ | b | NA | 5-10 | Once daily | NA | Flupentixol; Melitracen | 10.5 mg, twice daily; 0.5 mg, 3 times daily. | 28 | ||
| Luo CY et al 2017 | Postherpetic neuralgia (AIDS) | 8/ 14 | 10/ 12 | 48.00± 18.00 | 50.00± 18.00 | 8.30± 1.50 | 8.30± 1.40 | ①④ | b | Ashi | 20-30 | Once every 2 d | NA | Meco-balamin; Carba-mazepine | 10 mg, 3 times a day; 0.5 mg, 3 times a day; 0.1 g, 3 times a day. | 20 | ||
| Zhang XQ, Hu CL 2015 | Postherpetic neuralgia | 14/24 | 16/ 22 | 60.20±9.70 | 61.40± 10.20 | NR | NR | ②④ | b | The affected skin | NA | Once every 5 d | NA | Amitriptyline | 25 mg, once daily at bedtime. | 30 | ||
| Study ID | Disease type | Sample size (M/F) | Age (years, MD ± SD) or M (Q1,Q3) | Pain intensity at baseline | Outcome measurement | Intervention group operation | Control group operation | Treatment duration | ||||||||||
| T | C | T | C | T | C | Type of cupping | Points of selection | Time of cupping retained (min) | Combination frequency | Combination on therapy | Control group | Usage | ||||||
| Feng LF 2015 | Postherpetic neuralgia | 22/16 | 20/18 | 56.32±9.81 | 58.24±9.29 | 7.21± 1.16 | 7.18± 1.21 | ①④ | b | Ashi | 10 | Once every 3 d | NA | Mecobalamin; Indomethacin | 5 mg, twice daily; 5 mg, twice daily. | 30 | ||
| Xing YK et al 2017 | Herpes zoster | 14/14 | 15/13 | 40.02±19.62 | 42.50±18.32 | 7.80± 1.75 | 7.78± 1.70 | ①②④⑥ | b | NA | NA | Once daily | NA | sodium phosphonate (intravenous drip); Valaciclovir | 3 g, once daily; 0.15 g, twice daily | 14 | ||
| Li ZQ 2018 | Acute herpes zoster | 26/33 | 28/31 | 44.83±15.36 | 44.44±15.33 | NR | NR | ④ | b | Tender points | 1-2 | Once every 3 d | NA | Acyclovir; Mecobalamin; | 0.2 g, 3 times daily; 0.5 mg; 3 times daily. | 10 | ||
| Chen W et al 2014 | Acute herpes zoster | 12/18 | 10/20 | Range 40.00-76.00 | Range 46.00-80.00 | 7.63± 1.19 | 7.40± 1.11 | ①④⑥ | b | Tender points | 10-15 | Once every 2 d | NA | Valaciclovir hydrochloride (Fasting before meals). | 0.3 g, twice daily. | 10 | ||
| Liu Y, et al 2016 | Migraine | 10/20 | 12/18 | 41.47±13.51 | 42.47 ±13.60 | 5.73± 2.01 | 6.07± 1.61 | ①②④ | b | EX-HN5 (bilateral) and its nearby | NA | NA | NA | Diclofenac sodium | 75 mg, once daily. | 90 | ||
| Jiang HW et al 2015 | Migraine | 7/23 | 9/21 | 20.00-65.00 | 18.00-57.00 | NR | NR | ④⑥ | b | BL17 | 20 | Twice weekly | NA | Ceftriaxone hydrochloride | 10 mg every night. | 28 | ||
| Song N et al 2013 | Migraine | 16/29 | 18/27 | 35.40±3.10 | 36.10 ±2.30 | 6.76± 1.48 | 6.44± 1.78 | ①②④ | b | G20, GV14 | 15 | Twice weekly | NA | Flunarizine | 10 mg, once daily at bedtime. | 56 | ||
| Zhou YC 2016 | Neck myofascial pain syndrome | 7/23 | 9/21 | 38.33±8.63 | 36.90 ±9.03 | 6.03± 1.32 | 5.93± 1.36 | ①② | b | Ashi | 10 | Once every 3 d | NA | Lidocaine | 2 mL at each point, once every 3 d. | 15 | ||
| Wu K 2013 | Osteoarthritis | 8/22 | 7/23 | 56.70±6.60 | 57.40±5.80 | 6.97± 0.85 | 7.00± 0.87 | ①⑥ | b | Ex-LE4, Ex-LE5, ST34, SP10, SP9, Ashi | 3-4 | Once every 2 d | NA | Diclofenac | 50 mg, twice daily. | 14 | ||
| Study ID | Disease type | Sample size (M/F) | Age (years, MD ± SD) or M (Q1,Q3) | Pain intensity at baseline | Outcome measure-ment | Intervention group operation | Control group operation | Treat-ment duration | ||||||||||
| T | C | T | C | T | C | Type of cupping | Points of selection | Time of cupping retained (min) | Com-bination frequency | Combin-ation on therapy | Control group | Usage | ||||||
| Cupping therapy plus drugs vs drugs | ||||||||||||||||||
| Hou YW et al 2022 | Postherpetic neuralgia | 13/17 | 14/16 | 49.79±3.46 | 55.34±1.78 | 8 (8,9) | 8 (7,9) | ①②④ | j | Ashi | 10 | Once every 2 d | SAC | Dihydrocodeine Tartrate Tablets | 60 mg, 3 times daily | 20 | ||
| Luo TW, Wu XY 2022 | Haemorr-hoids | 15/12 | 15/18 | 38±16 | 39±14 | 6.18± 1.85 | 6.27± 1.89 | ①④ | b | BL57 | 5 | Once every 4 d | SAC | Diosmin tablets; Yinglong Ma musk hemorrhoid Cream; Potassium permanganate solution | 1 g, twice daily; (applied externally), 20 min, twice daily; (sitting bath) twice daily | 14 | ||
| Xia ZY et al 2022 | Pain after fracture | 25/19 | 23/21 | 67.72±0.68 | 67.32±1.11 | NR | NR | ①② | b | GB34, GB39, BL57, Ashi, BL-25, BL54, GB30, etc | 8 | Once daily | SAC | Self controlledanalgesics (intravenous injection) | 5 mL (first), 15 min, 2 mL/h (sustained dose), a single dose of 0.5 mL | 7 | ||
| Zhang CF 2022 | Herpes zoster | 22/18 | 24/16 | 45.26±3.74 | 45.48±3.62 | 6.94± 0.54 | 7.05± 0.57 | ①②④ | b | Ashi | 10 | Once daily | SAC | Valacyclovir hydrochloride tablets, Mecobalamin tablets | 0.3 g, twice daily 0.5 mg, 3 times daily | 10 | ||
| Li H 2022 | Acute herpes zoster | 14/18 | 15/17 | Range27-78 | Range20-76 | 7.21± 1.21 | 7.15± 1.14 | ①④ | b | Ashi | 3-5 | Once daily | SAC | Acyclovir sodium needle, Me-cobalamin | 0.5 g, 3 times daily; 0.5 mg, 3 times daily | 7 | ||
| Zhang LQ et al 2021 | Postherpetic neuralgia | 16/15 | 17/13 | 61.69±8.43 | 61.42±7.96 | 7.09± 1.33 | 7.05± 1.30 | ①②④⑥ | b | Ashi | 15-20 | Once every 2 d | SAC | Pregabalin | 150 mg, twice daily. | 30 | ||
| Yang C et al 2019 | Postherpetic neuralgia | 33/32 | 34/31 | 39.78±5.24 | 40.15±4.92 | 39.78±5.24 | 40.15± 4.92 | ①③④ | b | The herpes area | NA | Once every 2 d | SAC | Rat nerve growth factor (Injected intra-muscularly) | 30 μg, once daily. | 14 | ||
| Study ID | Disease type | Sample size (M/F) | Age (years, MD ± SD) or M (Q1,Q3) | Pain intensity at baseline | Outcome measure-ment | Intervention group operation | Control group operation | Treatment duration | ||||||||||
| T | C | T | C | T | C | Type of cup-ing | Points of selection | Time of cupping retained (min) | Combina-tion frequency | Combina-tion on therapy | Control group | Usage | ||||||
| Su ZY et al 2020 | Acute gouty arthritis | 18/ 12 | 11/ 19 | 38.10±5.30 | 39.20±5.60 | 8.43± 1.17 | 8.46± 1.12 | ①②④⑥ | b | NA | 3-5 | Once every 2 days | SAC | Fibulinastat | 40 mg, once daily. | 5 | ||
| Wang D, Huang CZ 2020 | Acute gouty arthritis | 31/ 19 | 30/ 20 | 65.13±14.24 | 15.55±4.49 | 8.35± 1.50 | 8.23± 1.45 | ①④⑥ | b | ST44, BL66, GB43 | 10-15 | Once every 2 d | SAC | Diclofenac sodium | 75 mg, once daily. | 16 | ||
| Jiang GL et al 2019 | Acute herpes zoster pain | 18/ 12 | 16/ 14 | 47.30±13.20 | 44.20±15.30 | 7.26± 1.34 | 7.18± 1.47 | ①⑥ | b | The herpes area | 10-15 | NA | SAC | Valaciclovir hydrochlorideMecobalamin | 0.3 g, twice daily; 0.5 mg, 3 times daily; 10 mg, 3 times daily. | 15 | ||
| Liu Z 2019 | Herpes zoster acute blister | 22/ 20 | 20/ 21 | 44.80±13.70 | 44.30±15.80 | 6.60± 1.31 | 6.46± 1.55 | ①④⑥ | a | The herpes area | 10 | Once every 4 d | SAC | Valaciclovir hydrochloride | 300 mg, twice a day; 10 mg, 3 times a day. | 12 | ||
| Tong LS 2016 | Herpes zoster | 24/ 18 | 22/ 18 | 45.00±8.40 | 44.50±5.30 | NR | NR | ④⑥ | b | Ashi | 15 | Once 2 d | SAC | Acyclovir ointment; Acyclovir tablets | 3 times daily; 0.4 g, 5 times daily. | 10 | ||
| Feng L, Huang SY 2018 | Cervicalspondylotic radiculo-pathy | 10/ 10 | 8/ 12 | 53.00±14.00 | 46.00±14.00 | 6.40± 1.54 | 6.30± 1.95 | ①②④ | c | DU14, GB21, SI11, SI15, SI14, SI13, Ashi | 5-10 | Once daily | SAC | Loxoprofen sodium | 60 mg, 3 times a day. | 30 | ||
| Zhang HY 2014 | Lumbodor-sal myofasciitis | 22/ 38 | 24/ 36 | 39.20±3.40 | 40.10±3.60 | 6.81± 2.26 | 6.77± 2.34 | ①④ | de | Bladder meridians | 10 | Once 2 d | SAC | Votalin emulsion | 3-4 times daily. | 10 | ||
| Li BJ 2022 | Cervical spondyosis | 23/17 | 22/ 18 | 47±6 | 46±7 | 7.48± 0.51 | 7.42± 0.55 | ①④⑥ | b | GV14, SI11 | 8 | Once every 5 d | SAC | Electro-acupuncture | 20 min, once daily | 20 | ||
| Cupping therapy plus acupuncture vs acupuncture | ||||||||||||||||||
| Xu J, yANG LL 2022 | Lumbago | 18/17 | 19/ 16 | 56.47±3.18 | 56.42±3.16 | 8.16± 1.05 | 8.09± 1.02 | ①②④ | b | BL40, BL17, Ashi, BL23 | 5 | Once every 2 d | SAC | Warm needling (acupuncture) | 30 min, once daily | 30 | ||
| Study ID | Disease type | Sample size (M/F) | Age (years, MD ± SD) or M (Q1,Q3) | Pain intensity at baseline | Outcome measure-ment | Intervention group operation | Control group operation | Treatment duration | ||||||||||
| T | C | T | C | T | C | Type of cup-ing | Points of selection | Time of cupping retained (min) | Combination frequency | Combination on therapy | Control group | Usage | ||||||
| Wu XY et al 2022 | Scapulo-humeral periarthritis | 14/19 | 11/20 | 52.36±4.99 | 51.35±5.10 | 5.70± 2.08 | 5.71± 2.20 | ①④ | d | Ashi | NA | Once every week | SAC | Acupuncture | 30 min, Once every 2 d | 14 | ||
| Huang HP et al 2022 | Scapulo-humeral periarthritis | 20/16 | 19/17 | 50.78±2.98 | 51.21±3.23 | 7.43± 1.04 | 7.45± 1.11 | ①②④ | b | TE14, LI15, SI11, Ashi | 3-7 | Once daily | SAC | Warm needling (acupuncture) | 30 min, Once every other day | 10 | ||
| Dong JP et al 2021 | Dysmenorr-hea | 0/26 | 0/26 | 18.00-35.00 | 20.00-33.00 | 9.56± 1.71 | 9.75± 1.81 | ④⑥ | ad | Bilateral of spine | NA | Once every 3 d | SAC | Acupuncture | 40 min, once daily | 90 | ||
| Zhang QH 2020 | Postherpetic neuralgia | 19/16 | 20/15 | 56.90±3.30 | 57.30±3.10 | 8.20± 0.50 | 8.10± 0.70 | ①④⑤⑥ | b | Ashi | 10 | Once every 2 d | SAC | Fire-acupuncture | NA, Once every 2 d | 20 | ||
| Zhao XX 2018 | Postherpetic neuralgia | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | ①④⑤⑥ | b | Ashi | 10 | Once every 2 d | SAC | Fire-acupuncture | NA, Once every other day | 10 | ||
| Zhang HX et al 2009 | Herpes zoster | 10/15 | 12/13 | 18.00-66.00 | 19.00-67.00 | NR | NR | ①④ | b | Ashi | 5-10 | Once daily | SAC | Electro-acupuncture | 30 min, NA. | 10 | ||
| Xie FL et al 2019 | Lumbar disc herniation | 86/64 | 80/70 | 48.70±4.60 | 46.20 ±4.10 | 5.24± 0.54 | 5.35± 0.61 | ①③④⑥ | b | Ashi | 10 | Once in 2-3 d | SAC | Acupuncture | 30 min, 3 times weekly | 14-21 | ||
| Wang ZJ et al 2018 | Lumbar disc herniation | 43/37 | 46/34 | 48.15±4.43 | 47.88 ±4.43 | 4.61± 0.79 | 4.53± 0.76 | ①⑥ | c | Wrist and ankle | 10 | Once daily | SAC | Acupuncture (Wrist ankle acupuncture therapy) | 30 min, once daily. | 7 | ||
| Cupping therapy plus acupuncture vs acupuncture | ||||||||||||||||||
| Lu P et al 2016 | Lumbar disc herniation | 17/14 | 15/16 | 47.48±7.05 | 45.70±8.37 | 6.452±0.624 | 6.355±0.733 | ①⑥ | eg | EX-B2, BL17 BL23, BL25 and EX-B6 (bilateral) | 5 | Once daily | SAC | Acupuncture | 30 min, once daily | 28 | ||
| Study ID | Disease type | Sample size (M/F) | Age (years, MD ± SD) or M (Q1,Q3) | Pain intensity at baseline | Outcome measure-ment | Intervention group operation | Control group operation | Treatment duration | ||||||||||
| T | C | T | C | T | C | Type of cupping | Points of selection | Time of cupping retained (min) | Combination frequency | Combina-tion on therapy | Control group | Usage | ||||||
| Chen WJ et al 2019 | Chronic low back pain | 17/20 | 16/21 | 58.00±6.20 | 58.00±7.80 | 8.11±1.22 | 8.05±0.97 | ①⑥ | i | Ashi | NA | Once daily | SAC | Acupuncture | 30 min, once daily | 10 | ||
| Liu HY 2020 | Low back pain | 20/20 | 21/19 | 42.48±2.59 | 41.22±1.96 | NR | NR | ①④ | a | Dai meridian | ≤15 | Every 2 d | SAC | Acupuncture | 15 min, once daily | NR | ||
| Ma LY, Bi Y 2020 | Knee osteoarthritis | 16/14 | 15/15 | 53.36±5.15 | 55.73±5.66 | 6.48±1.52 | 6.60±1.40 | ①④⑥ | c | Ashi, EX-LE2, EX-LE4, EX-LE5, SP10, ST35, ST36, GB34, GB33, SP9Y | 5-10 | Once daily | SAC | Acupuncture | 30 min, once daily | 10 | ||
| Zhu WJ et al 2017 | Dorsal myofasciitis | 15/20 | 16/19 | 36.20±6.70 | 35.80±7.30 | 6.31±1.62 | 6.42±2.05 | ①④⑥ | h | Ashi | 10 | Once every 2 d | SAC | Electro-acupuncture | 30 min, once daily | 16 | ||
| Chen JJ 2009 | Scapulohumeral periarthritis | 16/14 | 15/13 | 52.00±1.56 | 53.00±1.25 | 4.63±1.42 | 4.63±1.42 | ①④⑥ | b | Ashi | 10 | Once every 2 d | SAC | Electro-acupuncture | 30 min, once daily | 60 | ||
| Cupping therapy plus other therapy vs other therapy | ||||||||||||||||||
| Malik S et al 2022 | Chronic plantar fasciitis | 0/15 | 0/15 | 22.2±1.85 | 22.8±2.18 | 7.67±0.90 | 7.07±0.96 | ① | a | Affected side | 10 | Thrice a week | SAC | Excercise | 25-30 min, 3 times/ week | 28 | ||
| Han LL et al 2022 | Breast carbuncle | 0/32 | 0/32 | 36.75±4.87 | 36.91±4.49 | 7.00 (5.25,8.00) | 6.50 (6.00,8.00) | ①②④ | b | Ashi | NA | Once every 5 days | SAC | Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) formula | twice daily | 14 | ||
| Jiang Q, Chen Y 2022 | Acute lumbago | 27/20 | 25/22 | 42.09±6.35 | 42.18±6.44 | 6.10±0.72 | 6.03±0.68 | ①③④⑥ | j | Du Meridian and Bladder Meridians | 5-10 | Once every 3 days | SAC | Celecoxib capsules; Yulong powder (External Applied) | 100 mg, twice daily; once daily | 21 | ||
| Sun ZZ et al 2022 | Cervical spondyosis | 20/25 | 21/23 | 45.91±5.47 | 46.35±5.41 | 5.82±0.81 | 5.74±0.77 | ①⑥ | d | Shoulder dorsal to lumbar | 45 | Once every 3 days | SAC | Massage | 30 min | 21 | ||
| Study ID | Disease type | Sample size (M/F) | Age (years, MD ± SD) or M (Q1,Q3) | Pain intensity at baseline | Out-come measure-ment | Intervention group operation | Control group operation | Treatment duration | ||||||||||
| T | C | T | C | T | C | Type of cup-ping | Points of selection | Time of cupping retained (min) | Combination frequency | Combination on therapy | Control group | Usage | ||||||
| Liang NJ 2022 | Cervical spondyosis | 17/27 | 19/25 | 52.84±3.91 | 53.02±3.12 | 6.74±0.55 | 6.88±0.51 | ①④⑥ | c | Cervical Jiaji | 5-8 | Once daily | SAC | Massage | 20 min | 12 | ||
| Dong PP, Li FF 2022 | Acute lumbar posterior joint disorder | 46/49 | 43/52 | 42.6±5.9 | 42.3±5.7 | 5.94±0.55 | 5.87±0.58 | ①④⑥ | f | Ashi | 10-15 | Once daily | SAC | Massage | Once daily | 14 | ||
| Wan FD et al 2022 | Cervical spondyosis | 17/13 | 16/14 | 46.87±5.34 | 46.43±5.74 | 5.67±1.56 | 5.61±1.63 | ①④⑥ | c | Acupoints were selected based on meridian flow | 8-10 | Once daily | SAC | Massage | Once daily | 14 | ||
| Moura CC et al 2021 | Chronic back pain | 15/73 | 15/79 | 48.20±11.62 | 47.87±13.18 | NR | NR | ①⑥ | a | Selection according to the region of pain | 10 | Once a week | SAC | Ear acupuncture | Once a week | 42 | ||
| Xiao BE et al 2021 | Chronic non-specific low back pain | 36/32 | 38/30 | 57.65±5.37 | 57.27±5.62 | 7.18±1.05 | 7.10±1.08 | ①⑥ | j | Du Meridian and Bladder Meridians | 5-10 | Once every 3 d | SAC | Exercise | Core muscle group training (NA) | 28 | ||
| Chen JX et al 2021 | Chronic non-specific lower back pain | 27/21 | 26/22 | 63.50±3.40 | 64.20±3.40 | 6.33±1.72 | 6.29±1.66 | ①③⑥ | b | Ashi | 10 | Once every 2 d | SAC | Exercise | McKenzie therapy once a day | 10 | ||
| Feng WH, Shao P 2017 | Low back and leg pain | NR | NR | NR | NR | 8.73±0.51 | 8.80±0.47 | ①⑥ | c | DU3, EX-B2, BL25 point, and Ashi | 8 | Twice weekly | SAC | Exercise | Physical therapy (NA) | 14 | ||
| Chen JX et al 2020 | Low back pain | 22/26 | 25/23 | 46.10±3.20 | 42.30±3.50 | 7.73±1.21 | 7.78±1.23 | ①⑥ | b | Ashi | 10 | Once daily | SAC | Exercise | McKenzie therapy, once a day | 10 | ||
| He YM et al 2020 | Breast pain | 0/40 | 0/40 | 35.60±3.40 | 35.80±3.20 | 6.17±1.08 | 5.96±1.15P | ③④⑥ | bj | LA14 | 5 | Twice weekly | SAC | Xiaopi oral liquid | 15-30 mL, 3 times daily | 60 | ||
| Wang J et al 2019 | Shoulder pain | 14/9 | 13/10 | 56.71±5.49 | 56.31±5.63 | NR | NR | ① | a | GB21, Ashi | 8-10 | Treatment only once | SAC | Massage | NA | 2 | ||
| Study ID | Disease type | Sample size (M/F) | Age (years, MD ± SD) or M (Q1,Q3) | Pain intensity at baseline | Outcome measure-ment | Intervention group operation | Control group operation | Treatment duration | ||||||||||
| T | C | T | C | T | C | Type of cupping | Points of selection | Time of cupping retained (min) | Combination frequency | Combination on therapy | Control group | Usage | ||||||
| Chen X et al 2017 | Scapulohumeral periarthritis | 17/23 | 18/22 | 52.72±10.35 | 51.34±11.37 | 5.82± 0.71 | 6.13± 0.74 | ①④⑥ | a | Ashi, SI11, SI9, and LI15 of the affected side | 10 | Once a week | SAC | Gua-sha therapy | 10 min, once weekly | 28 | ||
| Ouyang Q et al 2001 | Hemiplegic shoulder pain | 18/8 | 22/8 | 58.20 (27.00-75.00) | 56.80 (29.00-71.00) | 6.37± 3.22 | 6.25± 3.01 | ①⑥ | b | Ashi | 10 | Once every 2 d | SAC | Exercise | 30 min once daily | 30 | ||
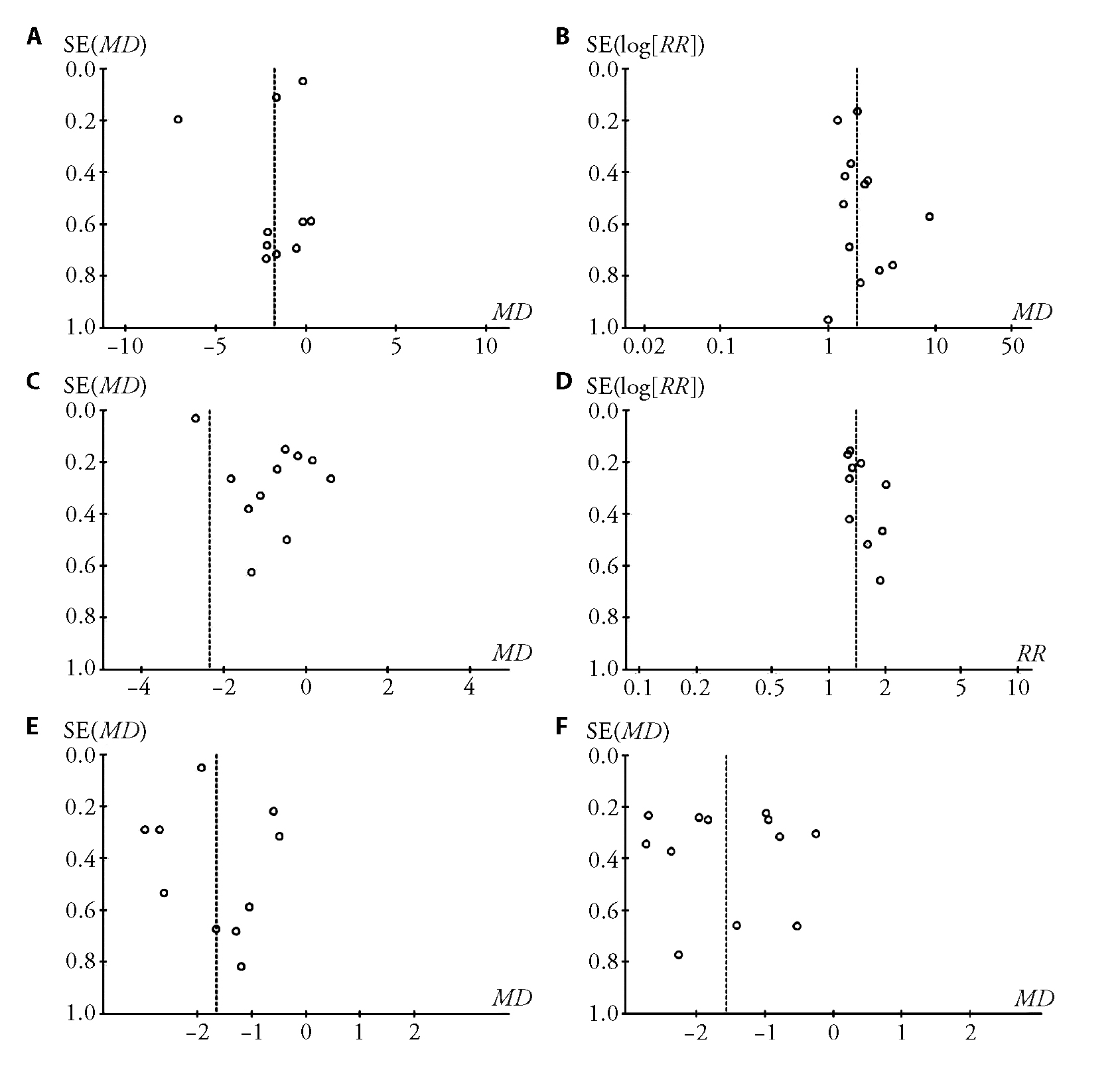
Figure 3 Funnel plot of 6 types comparisons A: cupping vs no treatment about VAS; B: cupping vs drugs about cure rate; C: cupping vs drugs about VAS; D: cupping plus acupuncture vs acupuncture about cure rate; E: cupping plus acupuncture vs acupuncture about VAS; F: cupping plus other therapy vs other therapy about VAS; VAS: visual analog scale; RR: risk ratio; MD: mean difference.
| 1. | Winsett F, Gleghorn K, Croley J, Wagner RF Jr. Managing pain associated with dermatologic procedures. Int J Dermatol 2021; 60: e480-5. |
| 2. |
Blakeslee W. Managing pain. Sci Am 2018; 319: 6.
DOI |
| 3. | Franklin AE, Lovell MR. Pain and pain management in palliative care. In: MacLeod RD, Vanden Block L, editors. Textbook of palliative care. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2020: 1-27. |
| 4. |
Groenewald CB, Essner BS, Wright D, Fesinmeyer MD, Palermo TM. The economic costs of chronic pain among a cohort of treatment-seeking adolescents in the United States. J Pain 2014; 15: 925-33.
DOI PMID |
| 5. |
Williams ACC, Craig KD. Updating the definition of pain. Pain 2016; 157: 2420-3.
DOI PMID |
| 6. | Chou R, Fu R, Dana T, Pappas M, Hart E, Mauer KM. Interventional treatments for acute and chronic pain: systematic review. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US) online, 2021-09, cited 2023-03-28; Compara Eff Rev, No. 247. Available from URL: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK573963/. |
| 7. | Treede RD, Rief W, Barke A, et al. Chronic pain as a symptom or a disease: the IASP classification of chronic pain for the international classification of diseases (ICD-11). Pain 2019; 160: 19-27. |
| 8. | Gaskin DJ, Richard P. The economic costs of pain in the United States. Pain 2012; 13: 715-24. |
| 9. | Dahlhamer J, Lucas J, Zelaya C. Prevalence of chronic pain and high-Impact chronic pain among adults-United States, 2016. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2018; 67: 1001-6. |
| 10. | Healthcare Improvement Scotland, issuing body, and issuing body Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network. Management of chronic pain: a national clinical guideline. Edinburgh, Scotland: Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network SIGN, 2013. Print. |
| 11. | Mauer K. Systematic Review on Treatments for Acute Pain: Surveillance Report 2: Literature Update Period: November 1, 2021, through January 22, 2022. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US), 2022-03, cited 2023-3-28. Available from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36940277/. |
| 12. |
Motov S, Strayer R, Hayes BD, et al. The treatment of acute pain in the emergency department: a white paper position statement prepared for the American Academy of Emergency Medicine. J Emerg Med 2018; 54: 731-6.
DOI PMID |
| 13. | Feldman DE, Nahin RL. National estimates of chronic musculoskeletal pain and its treatment in children, adolescents, and young adults in the United States: Data from the 2007-2015 National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey. J Pediatr 2021; 233: 212-9. |
| 14. | Cox F. Basic principles of pain management: assessment and intervention. Nurs Stand 2010; 25: 36-9. |
| 15. | Chou R, Selph S, Wagner J, et al. Systematic review on opioid treatments for chronic pain: surveillance report 3. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US), 2019-08,cited 2023-03-28. Available from URL: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK589631/. |
| 16. | Stephens SL, DeJong Lempke AF, Hertel J, Saliba S. Clinical usage, application procedures, and perceived effectiveness of cupping therapy among healthcare professionals in the United States: a cross-sectional survey. Complement Ther Clin Pract 2022; 48: 101610. |
| 17. | Mohamed AA, Zhang X, Jan YK. Evidence-based and adverse-effects analyses of cupping therapy in musculoskeletal and sports rehabilitation: a systematic and evidence-based review. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil 2023; 36: 3-19. |
| 18. | Cao HJ, Li X, Yan X, Wang NS, Bensoussan A, Liu JP. Cupping therapy for acute and chronic pain management: a systematic review of randomized clinical trials. J Tradit Chin Med Sci 2014; 1: 49-61. |
| 19. | Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021; 372: n71. |
| 20. | Sterne JAC, Savović J, Page MJ, et al. RoB 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2019; 366: l4898. |
| 21. |
Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Akl EA, et al. GRADE guidelines: 1. Introduction-GRADE evidence profiles and summary of findings tables. J Clin Epidemiol 2011; 64: 383-94.
DOI PMID |
| 22. | Teut M, Kaiser S, Ortiz M, et al. Pulsatile dry cupping in patients with osteoarthritis of the knee-a randomized controlled exploratory trial. BMC Complement Altern Med 2012; 12: 184. |
| 23. | Kim JI, Kim TH, Lee MS, et al. Evaluation of wet-cupping therapy for persistent non-specific low back pain: a randomized, waiting-list controlled, open-label, parallel-group pilot trial. Trials 2011; 12: 146. |
| 24. | Lauche R, Cramer H, Choi KE, et al. The influence of a series of five dry cupping treatments on pain and mechanical thresholds in patients with chronic non-specific neck pain--a randomised controlled pilot study. BMC Complement Altern Med 2011; 11: 63. |
| 25. | Wu ZS. Clinical study and efficacy evaluation of pricking collaterals and bloodletting in the treatment of acute ankle sprain. Beijing: Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, 2007: 24-42. |
| 26. | Zhang QE, Lai Z. Comparative study of cupping and hot compress in the treatment of low back pain in orthopedic bedridden patients. Zhong Guo Xian Dai Yi Sheng 2017; 55: 130-3. |
| 27. | Dong G, Tian LQ, Zhu SF, He AM, Wei YT. Observation on 50 cases of wind-induced low back pain treated by bladder needling cupping. Shi Jie Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi 2014; 9: 1312-4. |
| 28. |
Farhadi K, Schwebel DC, Saeb M, Choubsaz M, Mohammadi R, Ahmadi A. The effectiveness of wet-cupping for nonspecific low back pain in Iran: a randomized controlled trial. Complement Ther Med 2009; 17: 9-15.
DOI PMID |
| 29. | Lauche R, Materdey S, Cramer H, et al. Effectiveness of home-based cupping massage compared to progressive muscle relaxation in patients with chronic neck pain--a randomized controlled trial. PLoS One 2013; 8: e65378. |
| 30. |
Cramer H, Lauche R, Hohmann C, et al. Randomized controlled trial of pulsating cupping (pneumatic pulsation therapy) for chronic neck pain. Forsch Komplementmed 2011; 18: 327-34.
DOI PMID |
| 31. | Kim TH, Kang JW, Kim KH, et al. Cupping for treating neck pain in video display terminal (VDT) users: a randomized controlled pilot trial. J Occup Health 2012; 54: 416-26. |
| 32. |
Michalsen A, Bock S, Lüdtke R, et al. Effects of traditional cupping therapy in patients with carpal tunnel syndrome: a randomized controlled trial. J Pain 2009; 10: 601-8.
DOI PMID |
| 33. | Xue M, Bao YY, Jiang WY. Clinical observation on the treatment of dysmenorrhea of cold coagulation and blood stasis type by wet cupping at Xi points. Zhong Wai Nv Xing Jian Kang Yan Jiu 2021; 1: 58-9. |
| 34. | Wang L, Fang YF, Li QJ, Li JW, Li WL. Effect of pricking collaterals and cupping on serum substance P and IL-6 in patients with postherpetic neuralgia. Zhong Guo Zhong Yi Yao Xian Dai Yuan Cheng Jiao Yu 2020; 18: 92-4. |
| 35. | Li XJ, Han HT, Li J, et al. The effect of Zhuang medicine lotus needle cupping and removing blood stasis therapy on postherpetic neuralgia and its effect on the expression of neurotransmitter substance P and neurokinin-1. Guangxi Yi Xue 2019; 41: 545-8. |
| 36. | Liu MH, Wang GY. Clinical observation on treatment of postherpetic neuralgia with wet cupping. Xin Zhong Yi 2017; 49: 136-9. |
| 37. | Luo CY, Jiang ZC, Liu ZW. 22 cases of AIDS complicated with postherpetic neuralgia were treated by peripheral needling and cupping. Zhong Yi Wai Ke Za Zhi 2017; 26: 9-10. |
| 38. | Zhang XQ, Hu CL. Observation on the curative effect of wet cupping combined with moving cupping in the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia. An Mo Yu Kang Fu Yi Xue 2015; 6: 28-9. |
| 39. | Feng LF. Clinical observation of plum blossom needle percussion and cupping in the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia. Guang Ming Zhong Yi 2015; 30: 1114-5. |
| 40. | Xing YK, Pan JJ, Liu JW. Clinical observation on 56 cases of herpes zoster treated by wet cupping. Shou Du Shi Pin Yu Yi Yao 2017; 24: 112-3. |
| 41. | Li ZQ. A randomized parallel control study of plum blossom needle percussion, bloodletting and cupping in the treatment of acute herpes zoster. Shi Yong Zhong Yi Nei Ke Za Zhi 2018; 32: 69-70. |
| 42. | Chen W, Liu GZ, Yao QH. Clinical observation of wet cupping in the treatment of acute herpes zoster. Shanghai Zhen Jiu Za Zhi 2014; 33: 1132-4. |
| 43. | Liu Y, Li PF. Treatment of 30 cases of migraine attack by pricking collaterals, bloodletting and cupping Clinical. Zhen Jiu Lin Chuang Za Zhi 2016; 32: 37-9. |
| 44. | Jiang HW, Liu C, Jing K. Treatment of migraine with Geshu pricking collaterals and cupping. Changchun Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue Xue Bao 2015; 31: 579-81. |
| 45. | Song N, Qin ZJ, Liang W, Huang X, Huang JM, Su QZ. Observation on the curative effect of Zhuang medicine lotus needle cupping and removing blood stasis in the treatment of blood stasis type migraine. Zhong Hua Zhong Yi Yao Za Zhi 2013; 28: 1904-6. |
| 46. | Zhou YC. Clinical observation of bloodletting and cupping in the treatment of neck myofascial pain syndrome. Guangzhou: Guangzhou TCM University, 2016: 9-20. |
| 47. | Wu K. Clinical study of collateral pricking therapy in the treatment of pain symptoms of knee osteoarthritis. Fujian: Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2013: 7-15. |
| 48. | Hou YW, Li X, Liu R, Yang J. Balanced hotpot therapy intervention for postherpetic neuralgia: a clinical observation. Zhong Guo Min Jian Liao Fa 2022; 30: 48-50. |
| 49. | Luo TW, Wu XY. Chengshan acupoint (BL 57) puncture and cupping cooperate with drugs for the treatment of early embedded hemorrhoids. Shanghai Zhen Jiu Za Zhi 2022; 41: 569-72. |
| 50. | Xia ZY, Xu JD, Wei K. Effect of Acanthopanax senticosus cupping on postoperative pain and levels of stress hormones and proinflammatory factors in elderly patients. Shi Yong Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Lin Chuang 2022; 22: 29-31+56. |
| 51. | Zhang CF, Zhou P, Hu FM. Prune belly with cupping for herpes zoster: a review. Ji Ceng Yi Xue Lun Tan 2022; 26: 87-9. |
| 52. | Li H. A clinical study of periacanthopanax complex cupping for the treatment of acute phase herpes zoster. Guang Ming Zhong Yi 2022; 37: 2003-5. |
| 53. | Zhang LQ, Ding F, Jiao Y. Clinical effect of Guishao granule, wet cupping combined with pregabalin on patients with postherpetic neuralgia. Zhong Cheng Yao 2021; 43: 560-2. |
| 54. | Yang C, Lin JX, Wang W, Wang YZ, Han PP, Wang B. Therapeutic effect of wet cupping combined with mouse nerve growth factor on postherpetic neuralgia. Zhong Guo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Pi Fu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi 2019; 18: 460-2. |
| 55. | Su ZY, Cai DM, Huang G, Xu WD, Zhang ZN, Su YX. Effects of BL40 wet cupping combined with febuvastatin on knee function and serum CRP and SUA levels in patients with acute gouty arthritis. Zhong Wai Yi Xue Yan Jiu 2020; 18: 21-3. |
| 56. | Wang D, Huang CZ. Clinical value of blood pricking and cupping therapy in the treatment of acute gouty arthritis of damp heat internal node type. She Hui Yi Xue Za Zhi 2020; 18: 445-9. |
| 57. | Jiang GL, Zhu XX, Wu CZ. Effect of wet cupping on pain and anxiety of acute herpes zoster. Zhong Yi Yao Lin Chuang Za Zhi 2019; 31: 1574-6. |
| 58. | Liu Z. Comparative study on the efficacy of blister cupping and fire acupuncture in the acute stage of herpes zoster. Guangzhou: Guangzhou TCM University, 2019: 11-9. |
| 59. | Tong LS. Clinical observation on 62 cases of herpes zoster treated by Mongolian medicine cupping and bloodletting combined with acyclovir. Zhong Guo Min Zu Yi Yao Za Zhi 2016; 22: 11-2. |
| 60. | Feng L, Huang SY. Observation on the therapeutic effect of wrist-ankle acupuncture combined with medicine pot in the treatment of cervical spondylotic radiculopathy. Shanghai Zhen Jiu Za Zhi 2018; 37: 70-3. |
| 61. | Zhang HY. The therapeutic effect of moving cupping combined with Votalin emulsion on low back myofasciitis. Shanxi Zhong Yi 2014; 35: 1071-2. |
| 62. | Li BJ. Effect of Baowen stinging cupping combined with electroacupuncture on pain in patients with cervical radiculopathy. Henan Zhong Yi 2022; 42: 620-3. |
| 63. | Xu J, Yang LL. Effect of Acanthopanax cupping method combined with acupuncture in patients with stasis blocking collaterals type of low back pain. Zhong Guo Min Kang Yi Xue 2022; 34: 120-2. |
| 64. | Wu XY, Chen Z, Liang YY. Clinical observation of shoulder girdle acupuncture combined with walking cupping for periarthritis. Shanxi Zhong Yi 2022; 38: 38-9. |
| 65. | Huang HP, Gao QQ, Hong Q, Fu JJ, Shen Z. Effect of warm acupuncture combined with bloodletting cupping on shoulder mobility and pain in patients with painful shoulder periodontitis. Yi Xue Xin Xi 2022; 35: 168-70. |
| 66. | Dong JP, Yang WT, Wang DD, Tan JH. Observation on 52 cases of dysmenorrhea of Qi stagnation and blood stasis type treated by acupuncture combined with moving cupping. Heilongjiang Zhong Yi Yao 2021; 50: 67-8. |
| 67. | Zhang QH. Clinical observation on the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia with fire acupuncture combined with wet cupping. Zhong Guo Min Jian Liao Fa 2020; 28: 36-7. |
| 68. | Zhao XX. linical effect of fire acupuncture combined with wet cupping in the treatment of patients with postherpetic neuralgia. Lin Chuang Yi Xue Yan Jiu Yu Shi Jian 2018; 3: 106-7. |
| 69. | Zhang HX, Liu YN, Hung GF, Zou R, Wei W. Observation on analgesic effect of different acupuncture methods on herpes zoster. Zhong Guo Zhong Yi Ji Zheng 2009; 18: 1979-80+96. |
| 70. | Xie FL, Zhang XQ, Zhong XW. Clinical evaluation of blood pricking and cupping combined with acupuncture in the treatment of lumbar disc herniation. Heilongjiang Zhong Yi Yao 2019; 48 286-7. |
| 71. | Wang ZJ, Cui HQ, Xie XJ. The therapeutic effect of wrist-ankle acupuncture combined with Traditional Chinese Medicine cupping on lumbar disc herniation of blood stasis type. Xin Zhong Yi 2018; 50: 162-5. |
| 72. | Lu P, Liu M, Liu XY, et al. Clinical randomized controlled trial of Kaixuan Chongluo cupping in the treatment of lumbar disc herniation. Zhen Jiu Lin Chuang Za Zhi 2016; 32: 5-8. |
| 73. | Chen WJ, Zeng YF, Liu MY, Huang WF, Wu YF. Clinical observation on 37 cases of chronic low back pain treated by Yi cupping therapy combined with acupuncture. Guangdong Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 2019; 37: 717-9. |
| 74. | Liu HY. Clinical effect analysis of Dai Channel cupping combined with acupuncture and moxibustion in the treatment of low back pain. Xin Li Yue Kan 2020; 15: 188. |
| 75. | Ma LY, Bi Y. Clinical observation on 30 cases of knee osteoarthritis treated with medicinal cupping combined with UVA light irradiation. Zhong Guo Ji Ceng Yi Yao 2020; 27: 2269-71. |
| 76. | Zhu WJ, Zhang YY, Luo J. Therapeutic effect of electroacupuncture combined with bioceramic cupping on dorsal myofasciitis. Zhong Guo Zhong Yi Ji Zheng 2017; 26: 1638-40. |
| 77. | Chen JJ. Observation on the therapeutic effect of Electroacupuncture plus wet cupping on scapulohumeral periarthritis. Zhen Jiu Lin Chuang Za Zhi 2009; 25: 27-8. |
| 78. | Malik S, Anand P, Bhati P, Hussain ME. Effects of dry cupping therapy on pain, dynamic balance and functional performance in young female with recreational runners’ chronic plantar fasciitis. Sports Orthop Traumatol 2022; 38: 159-70. |
| 79. | Han LL, Zhu YJ, Feng GA, Sun ZM. Clinical evaluation of Acanthopanax senticosus cupping exsanguination therapy combined with Wenyang invigorating blood formula for the mass stage of comedo lactis. Zhong Guo Min Jian Liao Fa 2022; 30: 72-5. |
| 80. | Jiang Q, Chen Y. Effect of balanced tank therapy for acute phase discogenic low back pain on improving the patient's lumbar mobility function and pain relief. Xian Dai Yi Yao Wei Sheng 2022; 38: 126-9. |
| 81. | Sun ZZ, Zhang XY, Wang Z. To explore the effects of Fuyang tank therapy of traditional Chinese medicine on pain relief in patients with cervical radiculopathy. Zhong Guo Liao Yang Yi Xue 2022; 31: 394-7. |
| 82. | Liang NJ. Clinical observation on 44 cases of cervical spondylosis of Qi stagnation and blood stasis type treated by medicine cupping therapy and manipulation massage. Zhong Guo Min Jian Yi Yao 2022; 31: 104-6. |
| 83. | Dong PP, Li FF. Clinical observation of acute posterior lumbar arthrogryposis treated by needle cupping combined with manual reduction. Shi Yong Zhong Yi Yao Za Zhi 2022; 38: 661-2. |
| 84. | Wan FD, Zhou Q, Xu X. A review of the clinical effects of meridional flow infusion of a bamboo drug tank combined with manual manipulation in the treatment of cervical radiculopathy. Dang Dai Hu Li 2022; 29: 5-7. |
| 85. | Moura CC, Chaves ECL, Nogueira DA, et al. Effects of ear acupuncture combined with cupping therapy on severity and threshold of chronic back pain and physical disability: a randomized clinical trial. J Tradit Complement Med 2021; 12: 152-61. |
| 86. | Xiao BE, Chen YY, Fan WF, et al. Application of core muscle group training combined with balance cupping therapy in patients with chronic nonspecific low back pain. Zhong Hua Xian Dai Hu Li Za Zhi 2021; 27: 1060-4. |
| 87. | Chen JX, An Y, Duan YF. Clinical observation of wet cupping combined with Mackenzie therapy in the treatment of senile chronic nonspecific lower back pain. Xian Dai Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi 2021; 30: 1442-6. |
| 88. | Feng WH, Shao P. Therapeutic effect of cupping on low back and leg pain. Zhong Guo Ji Xu Yi Xue Jiao Yu 2017; 9: 108-9. |
| 89. | Chen JX, An Y, Duan YF, Hu YX. Effect of McKenzie therapy combined with wet cupping on lower back pain. Hebei Zhong Yi Yao Xue Bao 2020; 35: 47-50. |
| 90. | He YM, Zhang LL, Chen YY, Li HQ, Lian XL. Effects of balanced cupping combined with blood pricking and cupping on clinical symptoms and quality of life of patients with breast pain. Quan Ke Hu Li 2020; 18: 1234-6. |
| 91. | Wang J, Zhu JY, Shen XF, Gu XM. The effect of two Traditional Chinese Medicine therapies on patients with shoulder pain after laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Dang Dai Yi Yao Lun Cong 2019; 17: 178-9. |
| 92. | Chen X, Ju XT, Chen XZ, Zhang Y. Gua-sha combined with cupping in the treatment of scapulohumeral periarthritis. Jilin Zhong Yi Yao 2017; 37: 832-4. |
| 93. | Ouyang Q, He Y, Zhao D, Huang JL. Comparative observation of wet cupping combined with rehabilitation training in the treatment of 26 cases of hemiplegic shoulder pain. Zhong Guo Kang Fu Yi Xue Za Zhi 2001; 6: 38-40. |
| 94. | Wu X, Hu H, Guo L, Wang H. Clinical observation on the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia with medicinal cupping. Zhong Guo Zhen Jiu 2013; 33: 141-4. |
| 95. | Fu L, Liu WA, Wu QM, et al. Treatment of shoulder hand syndrome after stroke by acupuncture combined with acupoint cupping. Shanghai Zhen Jiu Za Zhi 2009; 28: 132-4. |
| 96. | Li L, Wang HM, Shen Y. Development of the Chinese version of the SF-36 health survey scale and its performance testing. Zhong Hua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi 2002; 36: 109-13. |
| 97. | Cramer H, Klose P, Teut M, et al. Cupping for patients with chronic pain: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. J Pain 2020; 21: 943-56. |
| 98. | Moura CC, Chaves ÉCL, Cardoso ACLR, Nogueira DA, Corrêa HP, Chianca TCM. Cupping therapy and chronic back pain: systematic review and Meta-analysis. Rev Lat Am Enfermagem 2018; 26: e3094. |
| 99. | Kim JI, Lee MS, Lee DH, Boddy K, Ernst E. Cupping for treating pain: a systematic review. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2011; 2011: 467014. |
| 100. | Fei YT, Cao HJ, Xia RY, et al. Methodological challenges in design and conduct of randomized controlled trials in acupuncture. Br Med J 2022; 376: e064345. |
| 101. | Zhang X, Tian R, Lam WC, et al. Standards for reporting interventions in clinical trials of cupping (STRICTOC): extending the CONSORT statement. Chin Med 2020; 15: 10. |
| [1] | XIAO Jing, SONG Danlei, LIANG Caiming, HE Yinuo, ZHENG Weifang, WU Xiaqiu. Efficacy of Jianpi formulas (健脾剂) in reducing the recurrence of colorectal adenoma after polypectomy: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(2): 225-233. |
| [2] | Emre Bulut, Didem Özkal Eminoğlu, Yasemin Çayır. Effect of electroacupuncture on pain after periodontal flap surgery: a randomized controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(1): 184-191. |
| [3] | GAN Chang, TAO Qingwen, YI Haoying, BIAN Yuting, WANG Jianming. Network Meta-analysis of the clinical efficacy and safety of kidney-tonifying and bone-strengthening therapies for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with kidney deficiency type [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(6): 1067-1081. |
| [4] | XU Jian, LIU Yuntao, LUO Zhihao, ZHAO Zhen, WANG Dawei, LIU Qing. Chinese patent medicine for atherosclerosis: a systematic review and Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(6): 1082-1090. |
| [5] | WANG Bingyu, JIN Fangfang, GAO Jiawei, YANG Liuxin, ZHANG Yali, YUAN Xingxing, ZHANG Yang. Acupuncture reduces sedative and anaesthetic consumption and improves pain tolerance in patients undergoing colonoscopy: a Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(6): 1091-1103. |
| [6] | WU Ruixin, FANG Qingliang, GUAN Sisi, WEI Xianglong, SHAN Mengjun, MAO Zhujun, GONG Yabin, XU Ling, ZHOU Di, DONG Changsheng. A pilot study of precision treatment for patients with lung cancer pain by Longteng Tongluo recipe (龙藤通络方) using serum genomics [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(5): 1006-1016. |
| [7] | XU Yingshan, WU Chunxiao, YU Wei, GUO Hongji, LU Liming, XU Nenggui, TANG Chunzhi. Systematic review and Meta-analysis of brain plasticity associated with electroacupuncture in experimental ischemic stroke [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(5): 859-870. |
| [8] | DENG Yasheng, HAN Siyin, XI Lanhua, HUANG Hui, LIANG Tianwei, ZHENG Yiqing, FAN Yanping, LIN Jiang. Traditional Chinese Medicine in the treatment of recurrent respiratory tract infections in children: an overview of systematic reviews and Meta-analyses [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(5): 871-884. |
| [9] | YU Siyun, ZHANG Shiwen, XIA Yu, LIU Xiaoqing, LIU Yajie, FU Jinrong. Network-based pharmacology and experimental validation to explore the mechanism of action of the Jiawei Pentongling formula (加味盆痛灵方) for the treatment of endometriosis-related pain [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(5): 991-999. |
| [10] | CHEN Dandan, JIN Qianhong, SHEN Yuanjuan, WANG Qing, DAI Zhengxiang. Scraping therapy for knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(4): 633-641. |
| [11] | ZHU Ruifang, ZHANG Jun, LYU Yaru, CHEN Yulu, HAN Shifan, WANG Hongwei. Efficacy of substances containing 3 types of active ingredients-saponins, flavones, and alkaloids in regulation of cytokines in autoimmune diseases a systematic review and Meta-analysis based on animal studies [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(3): 417-426. |
| [12] | MO Xiaoqiang, CHEN Yating, YIN Qian, CHEN Haibo, BAN Qiang, LI Jun, CHEN Su, YAO Jinguang. Transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 involved in the analgesic effects of total flavonoids extracted from Longxuejie (Resina Dracaenae Cochinchinensis) [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(3): 437-447. |
| [13] | WANG Yuhuang, ZHANG Le, ZHANG Zhengshan, YAO Zhi, LI Xiyao, SUN Luying, LIAO Xing. Characteristics and quality of clinical practice guidelines for diabetic kidney disease: a systematic review [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(3): 609-619. |
| [14] | WANG Shaosong, SUN Jingqing, FENG Qingyin, LI Bin, WANG Xin, YUAN Fan, CUI Yingxue. Effectivenss of electroacupuncture for skeletal muscle pain in Parkinson's disease: a Clinical randomized controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(2): 388-395. |
| [15] | PING Jing, HAO Hongzheng, WU Zhenqi, ZOU Meijuan, LI Zuojing, CHENG Gang. Long-term efficacy and safety of Huangqi (Radix Astragali Mongolici)-based Traditional Chinese Medicine in diabetic peripheral neuropathy: a Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(2): 229-242. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||