Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (5): 859-870.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20240828.008
Systematic review and Meta-analysis of brain plasticity associated with electroacupuncture in experimental ischemic stroke
XU Yingshan1, WU Chunxiao2, YU Wei3, GUO Hongji4, LU Liming4, XU Nenggui4( ), TANG Chunzhi4(
), TANG Chunzhi4( )
)
- 1 College of Acupuncture and Massage, Shaanxi University of Chinese Medicine, Middle Section of Century Avenue, Xianyang 712046, China
2 Department of Encephalopathy, Shenzhen Hospital of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Shenzhen 518000, China
3 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Shenzhen Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Shenzhen 518034, China
4 Medical College of Acu-Moxi and Rehabilitation, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510006, China
-
Received:2023-06-15Accepted:2023-11-27Online:2024-10-15Published:2024-09-11 -
Contact:Prof. TANG Chunzhi, Medical College of Acu-Moxi and Rehabilitation, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510006, China. jordan664@163.com; Prof. XU Nenggui, Medical College of Acu-Moxi and Rehabilitation, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510006, China. ngxu8018@gzucm.edu.cn Telephone: +86-13379180011 -
Supported by:Electroacupuncture Prevents Ferroptosis in Ischemic Stroke Through Regulating Ubiquitin Ligase NEDD4-like E3 and Inhibiting Ferritinophagy Pathway(82104978);Mechanism of Acupuncture on Microglia Activation in Mice with Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion(23JK0410)
Cite this article
XU Yingshan, WU Chunxiao, YU Wei, GUO Hongji, LU Liming, XU Nenggui, TANG Chunzhi. Systematic review and Meta-analysis of brain plasticity associated with electroacupuncture in experimental ischemic stroke[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(5): 859-870.
share this article
Figure 1 Study flow diagram: a PRISMA flow diagram of the study PRISMA: Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses; CNKI: China National Knowledge Infrastructure Database; CBM: Chinese Biomedical Literature Database; VIP: China Science and Technology Journal Database.
| Author | Year | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | Score | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bai MH | 2005 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Bao DP | 2007 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Cao XL et al | 2018 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Chen B et al | 2014 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Chen C et al | 2015 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Chen JJ | 2004 | √ | √ | 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Chen LR | 2008 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Chen WS | 2011 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Chen YH,Huang XF | 2000 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 5 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Cheng CY et al | 2014 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Ding J et al | 2017 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Ding J et al | 2018 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Ding L et al | 2012 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Du YX | 2008 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Duan XD et al | 2018 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Fan YS, Luo Y | 2008 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Fan YS | 2006 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Han XH et al | 2006 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Han YS | 2013 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Huang GX | 2009 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Huang LJ et al | 2013 | √ | √ | 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Huang XF,Chen YH | 2002 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Ji Z | 2005 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Jiang C | 2006 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Jiang HZ et al | 2006 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Kim Won-Seok et al | 2009 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Li HL | 2015 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Li J et al | 2014 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Li M et al | 2009 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Li QL et al | 2018 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Li QP et al | 2015 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Li T | 2016 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Li XJ et al | 2017 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Li XJ et al | 2015 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Lin R et al | 2017 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 5 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Lin T | 2009 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Lin XM et al | 2017 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Liu B | 2004 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Liu D et al | 2014 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Liu L, Zhang XQ | 2018 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Liu Y et al | 2014 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Liu YN et al | 2010 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Liu D et al | 2011 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Luo D et al | 2014 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Luo Y | 2009 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Luo ZD et al | 2002 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Luo ZD et al | 2004 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Lyu H | 2016 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Ma JX et al | 2013 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Ma JX | 2008 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Ma RR(1) et al [ | 2011 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Ma XM | 2009 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Ma Y et al | 2018 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Mao QJ, Chen BG | 2012 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Mi XJ | 2010 | √ | √ | 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Pan J | 2011 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Pan J et al | 2017 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Qin B et al | 2014 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Shen F | 2006 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Shen F et al | 2012 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Shen GY | 2009 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Song CM | 2018 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Song YS, Zhou MF | 2008 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Tan F et al | 2017 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Tan F et al | 2018 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 7 | ||||||||||||||||
| Tao J et al | 2016 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 6 | |||||||||||||||||
| Tao J | 2014 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 7 | ||||||||||||||||
| Wang GB et al [ | 2005 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Wang J et al | 2015 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Wang L | 2015 | √ | √ | 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Wang MP et al | 2018 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Wang Q et al | 2010 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Wang S et al | 2018 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Wang YC et al | 2012 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Wei XY | 2013 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Xiang F | 2015 | √ | √ | 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Xiao YC et al | 2013 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 5 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Xie CC | 2014 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Xu L et al | 2013 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Xu NG et al | 2004 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Yang MG et al | 2018 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Yao G et al | 2007 | √ | √ | 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Ye F et al | 2012 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Ye XQ et al | 2014 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Yi W et al | 2006 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Yin TR | 2005 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| You HL | 2012 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Yu JH et al | 2015 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Zhang HX et al | 2011 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Zhang SL | 2016 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Zhang XM | 2012 | √ | √ | 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Zhang YG et al | 2014 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Zhang YK, Tao LF | 2013 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Zhao HJ et al | 2018 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 6 | |||||||||||||||||
| Zhao JH et al | 2015 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 5 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Zhao JP et al | 2017 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Zhao JX et al | 2013 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Zheng CX | 2017 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Zhou CL et al | 2007 | √ | √ | 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Zhu YH et al | 2015 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Table 1 Quality assessment of studies included in the Meta-analysis using the CAMARADES risk of bias tool
| Author | Year | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | Score | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bai MH | 2005 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Bao DP | 2007 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Cao XL et al | 2018 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Chen B et al | 2014 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Chen C et al | 2015 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Chen JJ | 2004 | √ | √ | 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Chen LR | 2008 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Chen WS | 2011 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Chen YH,Huang XF | 2000 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 5 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Cheng CY et al | 2014 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Ding J et al | 2017 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Ding J et al | 2018 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Ding L et al | 2012 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Du YX | 2008 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Duan XD et al | 2018 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Fan YS, Luo Y | 2008 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Fan YS | 2006 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Han XH et al | 2006 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Han YS | 2013 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Huang GX | 2009 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Huang LJ et al | 2013 | √ | √ | 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Huang XF,Chen YH | 2002 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Ji Z | 2005 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Jiang C | 2006 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Jiang HZ et al | 2006 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Kim Won-Seok et al | 2009 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Li HL | 2015 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Li J et al | 2014 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Li M et al | 2009 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Li QL et al | 2018 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Li QP et al | 2015 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Li T | 2016 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Li XJ et al | 2017 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Li XJ et al | 2015 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Lin R et al | 2017 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 5 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Lin T | 2009 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Lin XM et al | 2017 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Liu B | 2004 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Liu D et al | 2014 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Liu L, Zhang XQ | 2018 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Liu Y et al | 2014 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Liu YN et al | 2010 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Liu D et al | 2011 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Luo D et al | 2014 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Luo Y | 2009 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Luo ZD et al | 2002 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Luo ZD et al | 2004 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Lyu H | 2016 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Ma JX et al | 2013 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Ma JX | 2008 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Ma RR(1) et al [ | 2011 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Ma XM | 2009 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Ma Y et al | 2018 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Mao QJ, Chen BG | 2012 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Mi XJ | 2010 | √ | √ | 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Pan J | 2011 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Pan J et al | 2017 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Qin B et al | 2014 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Shen F | 2006 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Shen F et al | 2012 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Shen GY | 2009 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Song CM | 2018 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Song YS, Zhou MF | 2008 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Tan F et al | 2017 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Tan F et al | 2018 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 7 | ||||||||||||||||
| Tao J et al | 2016 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 6 | |||||||||||||||||
| Tao J | 2014 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 7 | ||||||||||||||||
| Wang GB et al [ | 2005 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Wang J et al | 2015 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Wang L | 2015 | √ | √ | 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Wang MP et al | 2018 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Wang Q et al | 2010 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Wang S et al | 2018 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Wang YC et al | 2012 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Wei XY | 2013 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Xiang F | 2015 | √ | √ | 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Xiao YC et al | 2013 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 5 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Xie CC | 2014 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Xu L et al | 2013 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Xu NG et al | 2004 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Yang MG et al | 2018 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Yao G et al | 2007 | √ | √ | 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Ye F et al | 2012 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Ye XQ et al | 2014 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Yi W et al | 2006 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Yin TR | 2005 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| You HL | 2012 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Yu JH et al | 2015 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Zhang HX et al | 2011 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Zhang SL | 2016 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Zhang XM | 2012 | √ | √ | 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Zhang YG et al | 2014 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Zhang YK, Tao LF | 2013 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Zhao HJ et al | 2018 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 6 | |||||||||||||||||
| Zhao JH et al | 2015 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 5 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Zhao JP et al | 2017 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Zhao JX et al | 2013 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Zheng CX | 2017 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Zhou CL et al | 2007 | √ | √ | 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Zhu YH et al | 2015 | √ | √ | √ | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
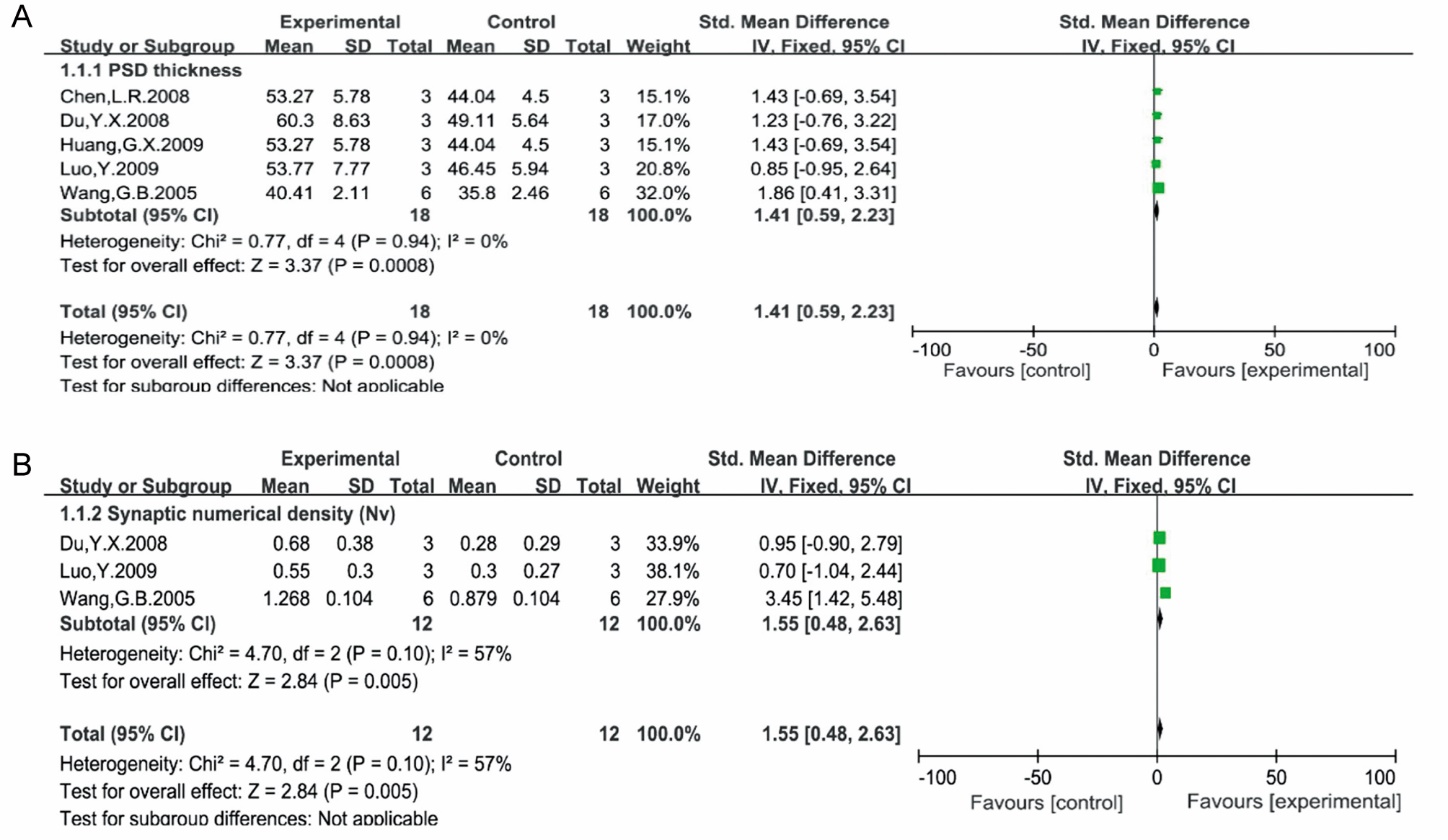
Figure 2 Forest polot of the effects of EA on synaptic structure A: forest plot of the effects of EA on PSD thickness; B: forest plot of the effects of EA on Nv; PSD: postsynaptic density; Nv: synaptic numerical density; EA: electroacupuncture; CI: confidence interval; IV: inverse variance; SD: standard deviation.
| 1. | Srivastava A, Srivastava P, Verma R. Role of bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs) in neurovascular interactions during stroke. Neurochem Int 2019; 129: 104480. |
| 2. | Datta A, Sarmah D, Mounica L, et al. Cell death pathways in ischemic stroke and targeted pharmacotherapy. Transl Stroke Res 2020; 11: 1185-202. |
| 3. | Wang S, Lin B, Lin G, et al. Automated label-free detection of injured neuron with deep learning by two-photon microscopy. J Biophotonics 2020; 13: e201960062. |
| 4. | Yuan L, Sun S, Pan X, et al. Pseudoginsenoside-F11 improves long-term neurological function and promotes neurogenesis after transient cerebral ischemia in mice. Neurochem Int 2020; 133: 104586. |
| 5. | Surugiu R, Olaru A, Hermann DM, Glavan D, Catalin B, Popa-Wagner A. Recent advances in mono-and combined stem cell therapies of stroke in animal models and humans. Int J Mol Sci 2019; 20: 6029. |
| 6. |
Gulyaeva NV. Molecular mechanisms of neuroplasticity: an expanding universe. Biochemistry (Mosc) 2017; 82: 237-42.
DOI PMID |
| 7. | Lai HC, Chang QY, Hsieh CL. Signal transduction pathways of acupuncture for treating some nervous system diseases. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2019; 2019: 1-37. |
| 8. | Chavez LM, Huang SS, MacDonald I, Lin JG, Lee YC, Chen YH. Mechanisms of acupuncture therapy in ischemic stroke rehabilitation: a literature review of basic studies. Int J Mol Sci 2017; 18: 2270. |
| 9. | Lu L, Zhang XG, Zhong LL, et al. Acupuncture for neurogenesis in experimental ischemic stroke: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. Sci Rep 2016; 6: 1-16. |
| 10. |
Macleod MR, O'Collins T, Howells DW, Donnan GA. Pooling of animal experimental data reveals influence of study design and publication bias. Stroke 2004; 35: 1203-8.
DOI PMID |
| 11. | Chen LR. Effects of acupuncture on communication junction among nerve cells in rats with ischemia. Guangzhou: Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, 2008: 25-64. |
| 12. | Du YX. Study on the relativity between astrocyte and synaptic reconstruction after ischemia as the influence of acupuncture in rat. Guangzhou: Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, 2008: 45-97. |
| 13. | Huang GX. The mechanism of PKA signaling pathway in synaptic plasticity after cerebral ischemia and intervention studies of acupuncture. Guangzhou: Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, 2009: 42-90. |
| 14. | Luo Y. The improvement effects of acupuncture on synaptic reorganization in rats with cerebral ischemia. Guangzhou: Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, 2009: 39-113. |
| 15. | Wang GB, Xu NG, She SF, Yi W, Huang ZY, Lai XS. Effect of electroacupuncture on the synaptic structure in the ischemic areas of rats with focal cerebral ischemia. Zhong Guo Lin Chuang Kang Fu 2005; 9: 115-7. |
| 16. | Cao XL, Wu XG, Zhang JC, et al. Effects of electroacupuncture on motor function and expression of GAP-43 and MAP-2 in the contralateral cerebral cortex of MCAO rats. Hua Zhong Ke Ji Da Xue Xue Bao 2018; 47: 274-9. |
| 17. | Han YS, Xu Y, Han YZ, et al. Effects of electroacupuncture on motor function and neural plasticity at focal cerebral infarction and reperfusion in rats. Liaoning Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue Xue Bao 2013; 15: 92-7. |
| 18. | Huang XF, Chen YH. Effect of electroacupuncture on GAP-43 and synaptophysin expression of ischemic Brain in the MCAO Rats. Zhong Guo Zhen Jiu 2002; 22: 54-7. |
| 19. | Ma RR, Li GQ, Wang JP, et al. Effect of electroacupuncture of different acupointson GAP-43 expression after focal cerebral in farction in rat. Chongqing Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 2011; 36: 38-41. |
| 20. | Mi XJ. The mechanism of electroacupuncture on the neural regeneration in cerebral ischemia rats. Chongqing: Chongqing Medical University, 2010: 20-46. |
| 21. | Qin B, Duan XD, Yu Q. Effect of electro-acupuncture on GAP-43 and c-fos of hippocampal neurons in ischemia side and relationship between effects and learning and memory in cerebral infarction rats. Chengdu Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue Xue Bao 2014; 37: 33-7. |
| 22. | Xu Lei, Yan XZ, Jiang Y, et al. Effect of electro-acupuncture on expressions of GAP-43 and VEGF in ischemic stroke rats. Qiqihaer Yi Xue Yuan Xue Bao 2013; 34: 1100-2. |
| 23. | Yao G, Chen YH, Cheng J, et al. The effect of electroacupuncture on GAP-43 expression of ischemic brain and infarct volume in MCAO rat. Zhong Guo Yi Shi Za Zhi 2007; 9: 1308-10. |
| 24. | Chen JJ. Mechanism of cerebral plasticity and acupuncture’s efficacy after cerebral infarction. Changchun: Jilin University, 2004: 41-115. |
| 25. | Li QP, Wang W, Han YS, et al. Effect of experimental study of Xingnao Kaiqiao acupuncture therapy on the recovery of motor function and the expression of SYN on cerebral ischemia reperfusion rat model at early stage. Zhong Guo Zhong Yi Ji Zheng 2015; 24: 19-23. |
| 26. | Lin XM, Huang J, You XF, et al. Effects of electroacupuncture at Baihui and Shenting acupoints on learning and memory and synaptic plasticity in rats with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Kang Fu Xue Bao 2017; 27: 29-35. |
| 27. | Liu B. The experimental study of the effect of electroacupuncture to the nervous plasticity in rats after acute cerebral infarction. Ha'erbin: Heilongjiang university of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2004: 11-35. |
| 28. | Song CM. Electroacupuncture at DU20 and DU24 regulates hippocampal synaptic plasticity via purinoceptor P2X7 in cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injured rats. Fuzhou: Fujian university of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2018: 24-61. |
| 29. | Yang MG, Huang J, Song CM, et al. Effects of EA at Baihui (DU20) and Shenting (DU24) on learning-memory function and the expression of synaptophysin in hippocampal CA1 in a cerebral ischemia-reperfusion rat model. Zhong Guo Zhong Yi Ji Zheng 2018; 27: 1886-90. |
| 30. | Zhao JP, Huang DX, Huang SE, et al. Effect of electroacupuncture at Quchi and Zusanli acupoint on the expressions of cortical synaptophysin and brain-derived neurotrophic factor in cerebral ischemia rats. Zhong Guo Dong Mai Ying Hua Za Zhi 2017; 25: 1099-106. |
| 31. | Li HL. The effects of electricity on the synaptic remodeling related factors in the ephrinB2/EphB2 signaling pathway of MCAO rats. Changsha: Hunan university of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2015: 18-66. |
| 32. | Li T. Different frequency electrical research on cerebral ischemia synaptic structural plasticity effects. Ha'erbin: Heilongjiang university of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2016: 15-49. |
| 33. | Lin R, Li X, Liu W, et al. Electro-acupuncture ameliorates cognitive impairment via improvement of brain-derived neurotropic factor-mediated hippocampal synaptic plasticity in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injured rats. Exp Ther Med 2017; 14: 2373-9. |
| 34. | Song YS, Zhou MF. The effects of acupuncture on astrocyte proliferation after cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Zhong Hua Wu Li Yi Xue Yu Kang Fu Za Zhi 2008; 244-7. |
| 35. | Tan F, Wang J, Chen J, et al. Effect of electroacupuncture on the expression of hippocampal eNSCs in MCAO model rats. Zhong Guo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi 2017; 37: 198-203. |
| 36. | Tao J, Zheng Y, Liu W, et al. Electro-acupuncture at LI11 and ST36 acupoints exerts neuroprotective effects via reactive astrocyte proliferation after ischemia and reperfusion injury in rats. Brain Res Bull 2016; 120: 14-24. |
| 37. |
Xiao Y, Wu X, Deng X, Huang L, Zhou Y, Yang X. Optimal electroacupuncture frequency for maintaining astrocyte structural integrity in cerebral ischemia. Neural Regen Res 2013; 8: 1122-31.
DOI PMID |
| 38. | Zhang YG, Gong X, Li HB. Effects of electroacupuncture on the expressions of nestin and glial fibrilliary acidic protein in dentate gyrus of focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion rats. Zhong Guo Zu Zhi Hua Xue Yu Xi Bao Hua Xue Za Zhi 2014; 23: 148-53. |
| 39. | Zhao H, Lu Y, Wang Y, et al. Electroacupunture contributes to recovery of neurological deficits in experimental stroke by activating astrocytes. Restor Neurol Neurosci 2018; 36: 301-12. |
| 40. | Zhao J, Sui M, Lu X, Jin D, Zhuang Z, Yan T. Electroacupuncture promotes neural stem cell proliferation and neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus of rats following stroke via upregulation of Notch1 expression. Mol Med Rep 2015; 12: 6911-7. |
| 41. | Chen B, Tao J, Huang J, et al. The possible mechanism of electroacupuncture promoting hippocampal neural stem cells proliferation in rats with focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion via activation of Notch signaling pathway. Zhong Guo Kang Fu Yi Xue Za Zhi 2014; 29: 399-404. |
| 42. | Luo D, Fan X, Ma C, et al. A study on the effect of neurogenesis and regulation of GSK 3 beta/PP2A expression in acupuncture treatment of neural functional damage caused by focal ischemia in MCAO rats. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2014; 2014: 962343. |
| 43. | Lyu H. The impact of electroacupuncture to middle cerebral artery occlusion rats in neurogenesis. Guangzhou: Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, 2016: 11-39. |
| 44. |
Tan F, Wang J, Liu JX, et al. Electroacupuncture stimulates the proliferation and differentiation of endogenous neural stem cells in a rat model of ischemic stroke. Exp Ther Med 2018; 16: 4943-50.
DOI PMID |
| 45. | Ye F, Yu JJ, Deng XL, et al. Electroacupuncture for promoting endogenous neural stem cell proliferation and neurological rehabilitation early after cerebral infarction. Zhong Hua Wu Li Yi Xue Yu Kang Fu 2012; 34: 801-5. |
| 46. | You HL. Effects of electroacupuncture on hypertension induced cerebral infarction in rats proliferation of neural precursor cells in brain and nerve regeneration in rats. Taiyuan: Shanxi medical university, 2012: 9-35. |
| 47. | Zhang HX, Wang Q, Yue W, et al. Stalp-acupuncture on the content of BrdU/nestin in acute cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury rats. Hubei Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue Xue Bao 2011; 13: 3-6. |
| 48. | Zhang YK, Tao LF. Effect of electroacupuncture on learning and memory ability and expression of VEGF in rats after middle cerebral artery occlusion/reperfusion. Hua Zhong Ke Ji Da Xue Xue Bao 2013; 42: 70-3. |
| 49. | Bao DP. The mechanism study on the effect of electroacupuncture on inherent neural stem cells after cerebral ischemic injury in rats. Ha'erbin: Heilongjiang university of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2007: 46-103. |
| 50. | Jiang C. From BDNF, NGF and Nestin angle to study the protection and repair mechanism of electro acupuncture on the neural damage of brain ischemia. Ha'erbin: Heilongjiang university of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2006: 21-34. |
| 51. | Ma JX, Luo Y, Cai M. Effect of electroacupuncture on expression of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 mRNA and brain-derived neuro-trophic factor protein in brain tissue of rats with focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion. Zhong Guo Kang Fu Li Lun Yu Shi Jian 2013; 19: 114-8. |
| 52. | Shen GY. Effects of electroacupuncture on expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and angiopoietin-1 after focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Wuhan: Hubei university of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2009: 18-53. |
| 53. | Zhang SL. Brain tissue of rats injured by cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by opposing needling Effects of VEGF and ang-1 expression. Changsha: Hunan university of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2016: 17-51. |
| 54. | Zhang XM. Electroacupuncture promotes angiogenesis and attenuates neuron injury in rat with focal cerebral ischemia. Changsha: Hunan university of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2012: 32-80. |
| 55. | Huang LJ, Chen BG, Hong YQ. Research of electro-acupuncture on the expressions of survivin and VEGF in ischemic brain tissue and their associativity. Shanxi Zhong Yi 2013; 29: 41-3. |
| 56. | Li QL, Jiang J, Ma HM, et al. Effects of electroacupuncture on angiogenesis via AKT/ mTOR/ P70S6K pathway in rats ischemic cerebral cortex after focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion. Zhong Guo Kang Fu Yi Xue Za Zhi 2018; 33: 397-404. |
| 57. | Lin T. Experimental study of electroacupuncture promoting the improvement of limb function and expression of PCNA and VEGF in rats with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Beijing: Beijing university of Chinese medicine, 2007: 26-69. |
| 58. | Pan J. The effect of VEGF gene expression in the cerebral tissue of MCAO rats by electro-acupuncture point of hand Jueyin pericardial channel. Changsha: Hunan university of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2011: 21-50. |
| 59. | Wang J, Wei D, Xie YC. Effects of electroacupuncture on angiogenesis after ischemia and reperfusion. Zhong Hua Wu Li Yi Xue Yu Kang Fu 2015; 37: 503-7. |
| 60. | Wang L. The protective mechanism of acupuncture on neurons in rats with acute cerebral ischemia reperfusion model. Shenyang: Liaoning university of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2015: 21-53. |
| 61. | Xiang F. The effects of electroacupuncture on expressions of angiogenesis related factors in ephrinB2/EphB2 signaling pathway in MCAO model rats. Changsha: Hunan university of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2015: 11-51. |
| 62. | Zhou CL, Chen BG, Mao QJ, et al. Effects of electroacupuncture on endovascular growth factor and endostatin in rats with focal cerebral ischemia and reperfusion. Hubei Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue Xue Bao 2007; 29: 8-10. |
| 63. | Jiang HZ, Huang GY, Zhang MM. Effect of acupuncture on the VEGF expression and regional blood blow in the rats with cerebral ischemia. Wei Xun Huan Xue Za Zhi 2006; 16: 9-11. |
| 64. | Li J, Ma Y, He JJ, et al. Effects of electroacupuncture on expression of VEGF/Flt-1 mRNA and protein in rats with acute cerebral infarction. Tianjin Zhong Yi Yao 2014; 31: 425-9. |
| 65. |
Ma JX, Luo Y. Effects of electroacupuncture on expressions of angiogenesis factors and anti-angiogenesis factors in brain of experimental cerebral ischemic rats after reperfusion. J Tradit Chin Med 2008; 28: 217-22.
PMID |
| 66. | Mao QJ, Chen BG. Effects of electroacupuncture on microvascular ultrastructure and VEGF expression of the right cerebral cortex in focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury rats. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu 2012; 37: 476-81. |
| 67. | Wang MP, Zhan ZT, Zhu M. Regulation of CREB signal transduction pathway in rats with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury and the effect of electroacupuncture at Zusanli. Lin Chuang Wu Zhen Wu Zhi 2018; 31: 94-8. |
| 68. | Xie CC. Electroacupuncture mobilizes bone marrow endothelial progenitor cells homing and promoting angiogenesis in ischemic brain after focal cerebral. Chongqing: Chongqing Medical University, 2014: 29-81. |
| 69. | Zhu YH, Luo Y, Xu HB, et al. Electroacupuncture promotes revascularization via eNOS mobilizing EPCs in the middle cerebral artery occlusion/reperfusion rat. Zhong Guo Shi Yan Dong Wu Xue Bao 2015; 23: 291-6. |
| 70. | Chen C, Zhang W, Lou BD, et al. Effect of electroacupuncture stimulation of acupoints of the pericardium meridian on serum NGF and Nogo-A Contents and Cerebral NGF and Nogo-A expression in cerebral ischemia rats. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu 2015; 40: 94-8. |
| 71. | Chen WS. The effects of electroacupuncture Du Meridian on the expression of NGF in serum and brain in MCAO rats models. Changsha: Hunan university of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2011: 17-51. |
| 72. | Chen YH, Huang XF. The effect of electroacupuncture on neurotrophins expression of ischemic cortex in MCAO rat. Zhong Feng Yu Shen Jing Ji Bing Za Zhi 2000; 17: 12-14. |
| 73. | Ding J, Wu F, Liao HC, et al. Effect of electroacupuncture intervention on expressions of nerve growth factor and growth arrest-specific protein 7 in ventral posterolateral thalamic nucleus in cerebral ischemia rats. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu 2017; 42: 125-30. |
| 74. | Ding J, Wu F, Liao HC, et al. Effect of electroacupuncture intervention on NGF and Gas7 expression in hippocampal CA3 region in cerebral ischemia rats. Wan Nan Yi Xue Yuan Xue Bao 2018; 37: 210-3. |
| 75. | Duan XD, Zhang L, Yu J, et al. The effect of different frequencies of electroacupuncture on BDNF and NGF expression in the hippocampal CA3 area of the ischemic hemisphere in cerebral ischemic rats. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 2018; 14: 2689-96. |
| 76. | Fan YS, Luo Y. Effect of superficial acupuncture on the expression of NGF in ischemic penumbra in rats with cerebral infarction. Zhen Jiu Lin Chuang Za Zhi 2008; 24: 36-8. |
| 77. | Ji Z. Effect of electroacupuncture at Baihui point on nerve growth factor in ischemic brain tissue of rats. Zhejiang Zhong Yi Xue Yuan Xue Bao 2005; 67-92. |
| 78. | Liu L, Zhang XQ. Effect of Electroacupuncture on expression of NGF and p75NTR in brain tissue of cerebral ischemia reperfusion rats and its related mechanisms. Ya Tai Chuan Tong Zhong Yao 2018; 14: 18-20. |
| 79. | Luo ZD, Luo ZK, Xu NG, et al. Influence of electroacupuncure on apoptosis and nerve growth factor of focal cerebral ischemia of rats. Zhong Guo Lin Chuang Kang Fu 2004; 8: 1382-3. |
| 80. | Ma XM. Effects of electro acupuncturing Ren Meridian on growth factor expression after focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion in rats. Guangzhou: Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, 2009: 30-98. |
| 81. | Ma Y, Yang CZ, Lei L, et al. The effect of electroacupuncture motor areas on the expression of NGF and VEGF in the cerebral cortex and serum of MCAO rats. Zhong Guo Zhong Yi Yao Xian Dai Yuan Cheng Jiao Yu 2018; 16: 94-6. |
| 82. | Pan J, Chen WS, Chen C, et al. Effects of electric-acupuncture at Du Meridian on MCAO rats infarct volume and NGF in brain tissue. Zhong Hua Zhong Yi Yao Za Zhi 2017; 35: 541-3. |
| 83. | Shen F. The study of electroacupuncture on the apoptosis of nerve cells and related nutrient factors in rats after cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury. Wuhan: Hubei university of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2006: 10-41. |
| 84. | Wang Q, Zhang HX, Zhou L, et al. Scalp-acupuncture on content of NGF in acute cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury rats. Zhong Feng Yu Shen Jing Ji Bing Za Zhi 2010; 27: 924-7. |
| 85. | Yi W, Xu NG, Wang GB, et al. Effect of electroacupuncture on nerve growth factor expression in ischemic cortex of rats with focal cerebral ischemia. Guangzhou Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue Xue Bao 2006; 23: 35-8. |
| 86. | Yin TR. Study on the expression of nerve growth factor and its receptor in rats with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Wuhan: Hubei university of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2005: 9-36 |
| 87. | Bai MH. Effects of electroacupuncture on neurotrophic factors in rats with cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury. Wuhan: Hubei university of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2005: 10-40. |
| 88. | Liu D, Sun ST, Fan S, et al. Effect of acupuncture at different time on expression of GDNF and bFGF protein in rats with focal cerebral ischemia and reperfusion. Xian Dai Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi 2011; 20: 1588-9. |
| 89. | Shen F, Kong LH, Ren J, et al. Effects of electroacupuncture on the expression of GDNF in the hippocampus of rats after cerebral ischemia reperfusion. Hubei Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue Xue Bao 2012; 34: 25-6. |
| 90. | Ding Li, Chen BG, Zhang Xi, et al. Effects of electro-acupuncture on expression of basic fibroblast growth factor and endostatin in the brain tissue of the rat after focal cerebral ischemia reperfusion. Zhong Guo Quan Ke Yi Xue Yu She Qu Yi Xue Za Zhi 2012; 27: 879-81. |
| 91. | Fan YS. The research of the protective mechanisms of subcutaneous superficial needling to cerebral ischemic penumbra neuron. Changsha: Hunan university of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2006: 25-81. |
| 92. | Han XH, Huang XL, Guo TC, et al. Effect of electroacupuncture on bFGF, Ang-2 and Tie-2 expression in rats with cerebral ischemia. Zhong Hua Wu Li Yi Xue Yu Kang Fu 2006; 28: 581-3. |
| 93. | Wei XY. Effects of electroacupuncture on the expression of bFGF and CD34 and the function of EPCs in rats with cerebral ischemia and reperfusion. Beijing: Beijing university of Chinese medicine, 2013: 47-129. |
| 94. | Cheng CY, Lin JG, Su SY, Tang NY, Kao ST, Hsieh CL. Electroacupuncture-like stimulation at Baihui and Dazhui acupoints exerts neuroprotective effects through activation of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor-mediated MEK1/2/ERK1/2/ p90RSK/bad signaling pathway in mild transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats. BMC Complement Altern Med 2014; 14: 92. |
| 95. | Chen YH, Huang XF. Effect of electroacupuncture on BDNF expression at ischemia cortex and infarct volume after middle cerebral artery occlusion in rat. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu 2000; 17: 165-9. |
| 96. | Tao J, Chen B, Gao Y, et al. Electroacupuncture enhances hippocampal NSCs proliferation in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injured rats via activation of notch signaling pathway. Int J Neurosci 2014; 124: 204-12. |
| 97. | Kim WS, Kim IS, Kim SJ, Wei P, Hyung Choi D, Han TR. Effect of electroacupuncture on motor recovery in a rat stroke model during the early recovery stage. Brain Res 2009; 1248: 176-83. |
| 98. | Li XJ, Lin RH, Tao J, et al. Effects of electroacupuncture on learning and memory and expression of brain-derived neuro-trophic factor and p75 neurotrophin receptor in rats with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion. Zhong Guo Kang Fu Li Lun Yu Shi Jian 2015; 21: 1020-4. |
| 99. | Li XJ, Yu KQ, Zhao CK, et al. The effects and mechanisms of electroacupuncture at Shenting and Baihui acupoints on learning and memory in MCAO rats. Zhong Guo Lin Chuang Kang Fu 2017; 32: 869-73. |
| 100. | Liu D, Zhang ZF, Shan FY. Early intervention of electroacupuncture on the brain of rats with chronic cerebral ischemia Expression of p53 and BDNF in cortex. Zhong Yi Yao Xue Bao 2014; 42: 107-8. |
| 101. | Liu Y, Zhao J, Wang H, et al. Effect of acupuncture intervention time on energy metabolism and BDNF, TrKB in rats with cerebral infarction. Zhong Guo Lin Chuang Bao Jian Za Zhi 2014; 17: 376-80. |
| 102. | Liu YN, Zhang HX, Huang GF, et al. Experimental study of scalp-acupuncture on BDNF expression in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion rats. Zhong Guo Zhong Yi Ji Zheng 2010; 19: 810-3. |
| 103. | Luo ZD, Luo ZK, Xu NG, et al. Effect of electroacupuncture on brain-derived neurotrophic factor in rats with focal brain ischemia. Zhen CI Yan Jiu 2002; 27: 105-7. |
| 104. | Wang S, Zhang XQ, Meng Y, et al. The effect of electroacupuncture on the expression of BDNF and TrkB in brain tissue of rats with cerebral ischemia/reperfusion model and its mechanism. Ya Tai Chuan Tong Yi Yao 2018; 14: 17-9. |
| 105. | Wang YC, Liang SR, Ma J, et al. Influence of electroacupuncture on the expressions of BDNF and TrkB in ischemic cortex of rats with local cerebral ischemia. Zhong Hua Zhong Yi Yao Za Zhi 2012; 30: 469-71. |
| 106. | Xu NG, Wang GB, Yu SF, et al. The effect of electroacupuncture on the expression of BDNF in the ischemic cortex of rats with focal cerebral ischemia at different time periods. Zhong Yi Yao Tong Bao 2004; 3: 3-5. |
| 107. | Ye XQ, You YM, Jiang YJ, et al. The effect of electroacupuncture the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury model rats. Zhong Guo Lin Chuang Kang Fu 2014; 29: 204-7. |
| 108. | Zheng CX. The Mechanisms of the PKA/CREB signaling pathway in effects of electroacupuncture on learning and memory in rats with cerebral hypoperfusion. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2017: 41-129. |
| 109. | Li M, Wang MD, Mei YW, et al. Effect of electro-acupuncture in different time windows on the expression of Bcl-2 and brain derived neurotrophic factor in rats with cerebral infarction. Zhong Feng Yu Shen Jing Ji Bing Za Zhi 2009; 26: 603-5. |
| 110. | Yu JH, Xiao N, Xiang H, et al. Effects of early electroacupuncture on the expression of brain derived neurotrophic factor-mRNA in the bilateral cerebral cortex after local cerebral ischemia in rats. Zhong Guo Lin Chuang Kang Fu 2015; 30: 122-6. |
| 111. | Zhao J, Xu H, Tian Y, Hu M, Xiao H. Effect of electroacupuncture on brain-derived neurotrophic factor mRNA expression in mouse hippocampus following cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Zhong Yi Yao Tong Bao 2013; 33: 253-7. |
| 112. |
Guggisberg AG, Koch PJ, Hummel FC, Buetefisch CM. Brain networks and their relevance for stroke rehabilitation. Clin Neurophysiol 2019; 130: 1098-124.
DOI PMID |
| 113. | Xiao LY, Wang XR, Yang Y, et al. Applications of acupuncture therapy in modulating plasticity of central nervous system. Neuromodulation 2018; 21: 762-76. |
| 114. | Yi W, Xu NG, Wang GB. Experimental study on effects of electro-acupuncture in improving synaptic plasticity in focal cerebral ischemia rats. Zhong Guo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi 2006; 26: 710-4. |
| 115. | Xia WG, Zheng CJ, Zhang X, Wang J. Effects of "nourishing liver and kidney" acupuncture therapy on expression of brain derived neurotrophic factor and synaptophysin after cerebral ischemia reperfusion in rats. Hua Zhong Ke Ji Da Xue Xue Bao 2017; 37: 271-8. |
| 116. | Xie G, Song C, Lin X, et al. Electroacupuncture regulates hippo-campal synaptic plasticity via inhibiting janus-activated kinase 2/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 signaling in cerebral ischemic rats. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 2019; 28: 792-9. |
| 117. | Xu L, Yan XZ, Li ZY, Cao XF, Wang M. Effect of "Xingnao Kaiqiao Zhenfa" (acupuncture technique for restoring consciousness) combined with rehabilitation training on nerve repair and expression of growth-associated protein-43 of peri-ischemic cortex in ischemic stroke rats. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu 2017; 42: 223-8. |
| 118. | Alia C, Cangi D, Massa V, et al. Cell-to-cell interactions mediating functional recovery after stroke. Cells 2021; 10: 3050. |
| 119. |
Wilhelmsson U, Lebkuechner I, Leke R, et al. Nestin regulates neurogenesis in mice through notch signaling from astrocytes to neural stem cells. Cereb Cortex 2019; 29: 4050-66.
DOI PMID |
| 120. |
Apte RS, Chen DS, Ferrara N. VEGF in signaling and disease: beyond discovery and development. Cell 2019; 176: 1248-64.
DOI PMID |
| 121. | Gudasheva TA, Povarnina PY, Volkova AA, Kruglov SV, Antipova TA, Seredenin SB. A nerve growth factor dipeptide mimetic stimulates neurogenesis and synaptogenesis in the hippocampus and striatum of adult rats with focal cerebral ischemia. Acta Natura 2019; 11: 31-7. |
| 122. | Cai W, Shen WD. Anti-apoptotic mechanisms of acupuncture in neurological diseases: a review. Am J Chin Med 2018; 46: 515-35. |
| 123. | Wlodarczyk L, Szelenberger R, Cichon N, Saluk-Bijak J, Bijak M, Miller E. Biomarkers of angiogenesis and neuroplasticity as promising clinical tools for stroke recovery evaluation. Int J Mol Sci 2021; 22: 3949. |
| 124. | Zhu W, Ye Y, Liu Y, Wang XR, Shi GX, Zhang S, Liu CZ. Mechanisms of acupuncture therapy for cerebral ischemia: an evidence-based review of clinical and animal studies on cerebral ischemia. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 2017; 12: 575-92. |
| 125. |
Xing Y, Bai Y. A review of exercise-induced neuroplasticity in ischemic stroke: pathology and mechanisms. Mol Neurobiol 2020; 57: 4218-31.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | GAN Chang, TAO Qingwen, YI Haoying, BIAN Yuting, WANG Jianming. Network Meta-analysis of the clinical efficacy and safety of kidney-tonifying and bone-strengthening therapies for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with kidney deficiency type [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(6): 1067-1081. |
| [2] | XU Jian, LIU Yuntao, LUO Zhihao, ZHAO Zhen, WANG Dawei, LIU Qing. Chinese patent medicine for atherosclerosis: a systematic review and Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(6): 1082-1090. |
| [3] | WANG Bingyu, JIN Fangfang, GAO Jiawei, YANG Liuxin, ZHANG Yali, YUAN Xingxing, ZHANG Yang. Acupuncture reduces sedative and anaesthetic consumption and improves pain tolerance in patients undergoing colonoscopy: a Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(6): 1091-1103. |
| [4] | ZHANG Boyang, ZHOU Yang, FENG Liyuan, SUI Dan, HE Lei, TONG Dan, WANG Ruoyu, SUI Xue, SONG Jing, WANG Dongyan. A neural regulation mechanism of head electroacupuncture on brain network of patients with stroke related sleep disorders [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(6): 1268-1276. |
| [5] | DENG Yasheng, HAN Siyin, XI Lanhua, HUANG Hui, LIANG Tianwei, ZHENG Yiqing, FAN Yanping, LIN Jiang. Traditional Chinese Medicine in the treatment of recurrent respiratory tract infections in children: an overview of systematic reviews and Meta-analyses [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(5): 871-884. |
| [6] | ZHANG Fang, YAN Cuina, WENG Zhijun, WU Luyi, QI Li, ZHAO Min, XIN Yuhu, WU Huangan, LIU Huirong. Regulatory role of electroacupuncture on satellite glial cell activity in the colon and dorsal root ganglion of rats with irritable bowel syndrome [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(5): 981-990. |
| [7] | CHEN Dandan, JIN Qianhong, SHEN Yuanjuan, WANG Qing, DAI Zhengxiang. Scraping therapy for knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(4): 633-641. |
| [8] | CHEN Yonglin, OUYANG Ling, MENG Lingling, WU Bufan, PENG Rou, LIU Sitong, HOU Dan, WANG Yaling, JING Xinyue, LU Shengfeng, FU Shuping. Electroacupuncture ameliorates blood-brain barrier disruption after ischemic stroke through histone acetylation regulation at the matrix metalloproteinase 9 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 2 genes [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(4): 734-744. |
| [9] | ZHU Ruifang, ZHANG Jun, LYU Yaru, CHEN Yulu, HAN Shifan, WANG Hongwei. Efficacy of substances containing 3 types of active ingredients-saponins, flavones, and alkaloids in regulation of cytokines in autoimmune diseases a systematic review and Meta-analysis based on animal studies [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(3): 417-426. |
| [10] | WANG Yuhuang, ZHANG Le, ZHANG Zhengshan, YAO Zhi, LI Xiyao, SUN Luying, LIAO Xing. Characteristics and quality of clinical practice guidelines for diabetic kidney disease: a systematic review [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(3): 609-619. |
| [11] | WANG Shaosong, SUN Jingqing, FENG Qingyin, LI Bin, WANG Xin, YUAN Fan, CUI Yingxue. Effectivenss of electroacupuncture for skeletal muscle pain in Parkinson's disease: a Clinical randomized controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(2): 388-395. |
| [12] | PING Jing, HAO Hongzheng, WU Zhenqi, ZOU Meijuan, LI Zuojing, CHENG Gang. Long-term efficacy and safety of Huangqi (Radix Astragali Mongolici)-based Traditional Chinese Medicine in diabetic peripheral neuropathy: a Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(2): 229-242. |
| [13] | ZHOU Mingwang, DONG Zhuanli, WEI Changhao, FENG Lufang, WANG Xiaoping, LIU Haiping, JI Xing, YANG Kehu, LI Shenghua. Efficacy and safety of extracorporeal shock wave therapy combined with sodium hyaluronate in treatment of knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(2): 243-250. |
| [14] | QIN Xiaoyu, WANG Chunai, XUE Jianjun, ZHANG Jie, LU Xiaoting, DING Shengshuang, GE Long, WANG Minzhen. Efficacy of electroacupuncture on myocardial protection and postoperative rehabilitation in patients undergoing cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 1-15. |
| [15] | SUN Qianhui, CHENG Kai, DAI Xingye, YANG Zhiwen, WU Xiaoling, XU Chang, QIU Xinghua, GAO Xiaofeng, LIU Daonan, YANG Qirui. Effect of electroacupuncture at Neiguan (PC6) at different time points on myocardial ischemia reperfusion arrhythmia in rats [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 113-121. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

