Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (6): 1366-1375.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20250508.001
• Original Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Exploration of the mechanism of the Mongolian medicine Tonglaga-5 (通拉嘎-5) for the treatment of n-methyl-n′-nitro-n-nitrosoguanidine-induced chronic atrophic gastritis based on network pharmacology and metabolomics
CHENG Ziqi1, DONG Xin1, Temuribagen 2, XU Caimeng1, HU Shaonan1, CHEN Qianwen1, WANG Yuewu1, WANG Haibo1, HE Xiaoyu1, XUE Dan1, XUE Peifeng1( )
)
- 1 Department of Pharmacy, Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010110, China
2 Department of Orthopedic, Hohhot city Mongolian medicine Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Hohhot 010110, China
-
Received:2024-12-14Accepted:2025-03-25Online:2025-12-15Published:2025-05-08 -
Contact:Prof. XUE Peifeng, Department of Pharmacy, Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010110, China. xpfdc153@163.com, Telephone: +86-471-6653132 -
About author:CHENG Ziqi and DONG Xin are co-first authors and contributed equally to this work -
Supported by:New Quality Control Model of Mongolian Medicine Tonglaga-5 “Qingzhuo Shenghua” Based on “Stomach Blood Bone Correlation Tracking”(82160745);Grassland Talent Rolling Support Program([2023]3);Research on the Mechanism of Mongolian Prescription Tonglaga-5 in Treating Chronic Atrophic Gastritis based on Multiomics Integration(YKD2024ZD001);Preparation and Pharmacological Study of Mongolian Medicine Tonglaga-5 Transdermal Patch(MYYXTPY202313)
Cite this article
CHENG Ziqi, DONG Xin, Temuribagen , XU Caimeng, HU Shaonan, CHEN Qianwen, WANG Yuewu, WANG Haibo, HE Xiaoyu, XUE Dan, XUE Peifeng. Exploration of the mechanism of the Mongolian medicine Tonglaga-5 (通拉嘎-5) for the treatment of n-methyl-n′-nitro-n-nitrosoguanidine-induced chronic atrophic gastritis based on network pharmacology and metabolomics[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(6): 1366-1375.
share this article

Figure 1 Effect of TLG-5 on CAG rats A: HE staining of the gastric tissues at × 20 magnification, scaler bar = 100 μm; A1: control group; A2: model group; A3: teprenone group (15.75 mg·kg?1·d?1); A4: TLG-5 L (0.315 g·kg?1·d?1) group; A5: TLG-5 M (0.63 g·kg?1·d?1) group; A6: TLG-5 H (1.26 g·kg?1·d?1) group. Purple arrow: loss of gastric epithelial cells, green arrow: infiltration of inflammatory cells. B: levels of B1: G-17; B2: PG Ⅰ; B3: PG Ⅱ and B4: PGR in serum. Control group: drink and eat freely; other groups, were given 170 μg/mL of MNNG solution freely while MNNG and 2% sodium salicylate solution were administered by gavage alternately while the hunger and satiety disorders for 12 weeks. Each dosing group received the corresponding drug treatment separately for 8 weeks. Control and model groups received intragastric administration of an equivalent volume of saline. TLG-5: tonglaga-5; TLG-5 L: TLG-5 low-dose; TLG-5 M: TLG-5 middle-dose; TLG-5 H: TLG-5 high-dose; CAG: chronic atrophic gastritis; HE: hematoxylin-eosin. PG Ⅰ: pepsinogen Ⅰ; PG Ⅱ: pepsinogen Ⅱ; PGR (PG Ⅰ/PG Ⅱ); G-17: gastrin-17. Data between multiple groups were processed using one-way analysis of variance, and data was expressed using mean ± standard deviation (n = 8). aP < 0.001, eP < 0.01, when compared with the control group; bP < 0.01, cP < 0.05, dP < 0.001, when compared with the model group.
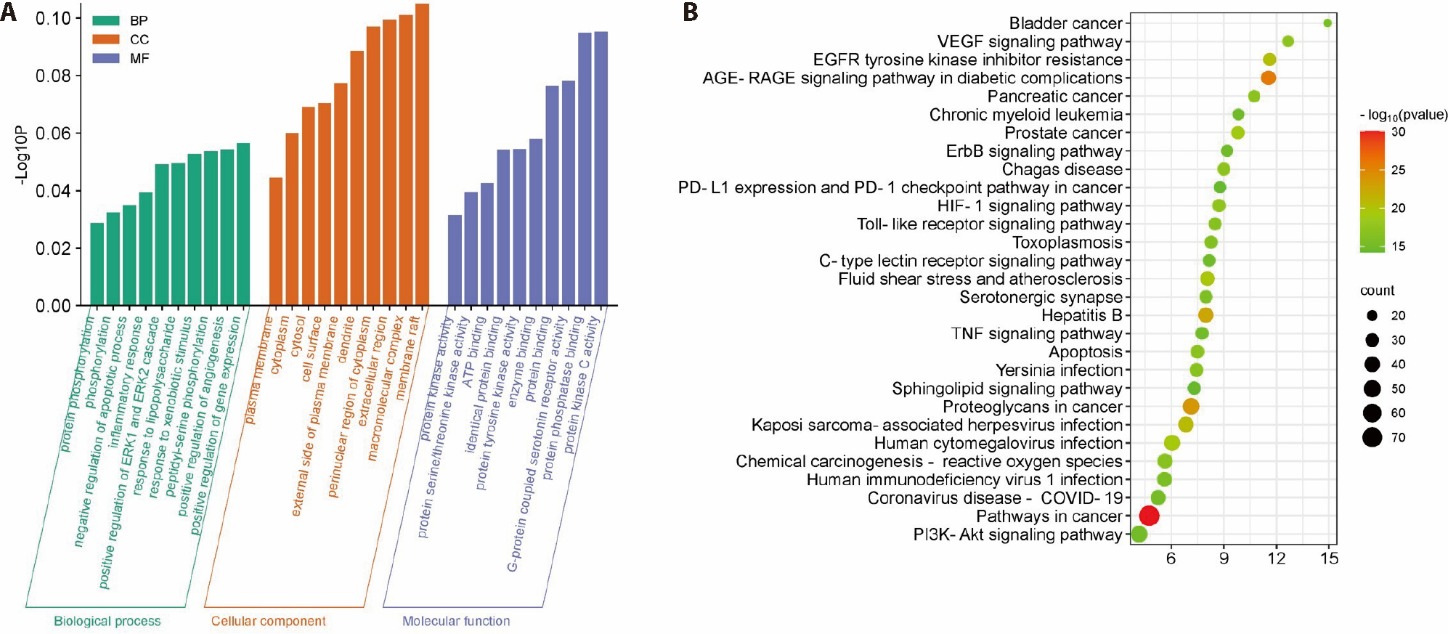
Figure 2 Network pharmacology analysis A: GO enrichment analysis of the potential targets; B: KEGG pathway enrichment of the potential targets. GO: gene ontology; KEGG: kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes.
| Group | Positive mode | Negative mode | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2X | R2Y | Q | R2X | R2Y | Q | ||
| Model vs Control | 0.382 | 0.996 | 0.671 | 0.457 | 0.997 | 0.887 | |
| TLG-5 H vs Model | 0.287 | 0.992 | 0.868 | 0.394 | 0.998 | 0.961 | |
Table 1 Parameters of OPLS-DA model
| Group | Positive mode | Negative mode | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2X | R2Y | Q | R2X | R2Y | Q | ||
| Model vs Control | 0.382 | 0.996 | 0.671 | 0.457 | 0.997 | 0.887 | |
| TLG-5 H vs Model | 0.287 | 0.992 | 0.868 | 0.394 | 0.998 | 0.961 | |
| Metabolite name | Formula | Adduct | m/z | Error (ppm) | RT (min) | Log2FC (Model/Control) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measured value | Theoretical value | ||||||
| 3-methylhistidine | C7H11N3O2 | [M+H]+ | 170.0931 | 170.0924 | 4.115 | 0.477 | -0.704 |
| Anhydroretinol | C20H28 | [M+H]+ | 269.2268 | 269.2264 | 1.486 | 17.990 | -0.742 |
| Cytidine | C9H13N3O5 | [M+Na]+ | 266.0755 | 266.0747 | 3.007 | 0.454 | 0.618 |
| Anthranilic acid | C7H7NO2 | [M+H]+ | 138.0562 | 138.0550 | 8.692 | 2.831 | 2.348 |
| Vernolic acids | C18H32O3 | [M+H]+ | 297.2430 | 297.2424 | 2.019 | 19.695 | 0.624 |
| Sphingosine | C18H37NO2 | [M+H]+ | 300.2900 | 300.2897 | 0.999 | 15.334 | -1.982 |
| Sphinganine | C18H39NO2 | [M+H]+ | 302.3056 | 302.3054 | 0.662 | 15.965 | -1.373 |
| 2'-deoxycytidine | C9H13N3O4 | [M+H]+ | 228.0981 | 228.0979 | 0.877 | 0.449 | 0.237 |
| 8-oxohexadecanoic acid | C16H30O3 | [M+H]+ | 271.2276 | 271.2268 | 2.950 | 0.270 | 0.839 |
| L-Tyrosin | C9H11NO3 | [M+H]+ | 182.0821 | 182.0812 | 4.943 | 0.099 | -0.117 |
| 3,4-dihydroxy-phenylacetic acid | C8H8O4 | [M+H]+ | 169.0503 | 169.0495 | 4.732 | 6.567 | 0.854 |
| Homovanillic acid | C9H10O4 | [M+ACN+H]+ | 224.0916 | 224.0917 | -0.446 | 4.853 | 0.876 |
| Trichloroacetic acid | C2HCl3O2 | [M-H]- | 160.8964 | 160.8969 | -3.516 | 1.072 | -0.669 |
| Pidolic acid | C5H7NO3 | [M-H]- | 128.0346 | 128.0353 | -5.752 | 0.520 | 0.459 |
| Thymidine | C10H14N2O5 | [M-H]- | 241.0844 | 241.0830 | 5.621 | 0.704 | 2.415 |
| 5-aminolevulinate | C5H9NO3 | [M-H]- | 130.0500 | 130.0510 | -7.585 | 0.497 | -0.721 |
Table 2 Differential metabolites of model vs control group
| Metabolite name | Formula | Adduct | m/z | Error (ppm) | RT (min) | Log2FC (Model/Control) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measured value | Theoretical value | ||||||
| 3-methylhistidine | C7H11N3O2 | [M+H]+ | 170.0931 | 170.0924 | 4.115 | 0.477 | -0.704 |
| Anhydroretinol | C20H28 | [M+H]+ | 269.2268 | 269.2264 | 1.486 | 17.990 | -0.742 |
| Cytidine | C9H13N3O5 | [M+Na]+ | 266.0755 | 266.0747 | 3.007 | 0.454 | 0.618 |
| Anthranilic acid | C7H7NO2 | [M+H]+ | 138.0562 | 138.0550 | 8.692 | 2.831 | 2.348 |
| Vernolic acids | C18H32O3 | [M+H]+ | 297.2430 | 297.2424 | 2.019 | 19.695 | 0.624 |
| Sphingosine | C18H37NO2 | [M+H]+ | 300.2900 | 300.2897 | 0.999 | 15.334 | -1.982 |
| Sphinganine | C18H39NO2 | [M+H]+ | 302.3056 | 302.3054 | 0.662 | 15.965 | -1.373 |
| 2'-deoxycytidine | C9H13N3O4 | [M+H]+ | 228.0981 | 228.0979 | 0.877 | 0.449 | 0.237 |
| 8-oxohexadecanoic acid | C16H30O3 | [M+H]+ | 271.2276 | 271.2268 | 2.950 | 0.270 | 0.839 |
| L-Tyrosin | C9H11NO3 | [M+H]+ | 182.0821 | 182.0812 | 4.943 | 0.099 | -0.117 |
| 3,4-dihydroxy-phenylacetic acid | C8H8O4 | [M+H]+ | 169.0503 | 169.0495 | 4.732 | 6.567 | 0.854 |
| Homovanillic acid | C9H10O4 | [M+ACN+H]+ | 224.0916 | 224.0917 | -0.446 | 4.853 | 0.876 |
| Trichloroacetic acid | C2HCl3O2 | [M-H]- | 160.8964 | 160.8969 | -3.516 | 1.072 | -0.669 |
| Pidolic acid | C5H7NO3 | [M-H]- | 128.0346 | 128.0353 | -5.752 | 0.520 | 0.459 |
| Thymidine | C10H14N2O5 | [M-H]- | 241.0844 | 241.0830 | 5.621 | 0.704 | 2.415 |
| 5-aminolevulinate | C5H9NO3 | [M-H]- | 130.0500 | 130.0510 | -7.585 | 0.497 | -0.721 |
| Metabolite Name | Formula | Adduct | m/z | Error (ppm) | RT (min) | Log2FC (TLG-5 H/Model) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measured value | Theoretical value | ||||||
| Histidine | C6H9N3O2 | [M+H]+ | 156.0775 | 156.0768 | 4.657 | 0.475 | -0.947 |
| Anthranilic acid | C7H7NO2 | [M+H]+ | 138.0562 | 138.0550 | 8.656 | 2.831 | 1.432 |
| Sphingosine | C18H37NO2 | [M+H]+ | 300.2900 | 300.2897 | 0.879 | 15.334 | 1.466 |
| 3,4-dihydroxyglutamic acid | C5H9NO6 | [2M+K]+ | 397.0475 | 397.0491 | -4.060 | 5.249 | -0.831 |
| 2'-deoxycytidine | C9H13N3O4 | [M+H]+ | 228.0981 | 228.0979 | 1.129 | 0.449 | -0.626 |
| Hydroxyrepaglinide | C27H36N2O5 | [M+H]+ | 469.2693 | 469.2697 | -0.914 | 0.304 | -1.034 |
| Spermine | C10H26N4 | [M+H]+ | 203.2234 | 203.2230 | 1.656 | 0.362 | -1.126 |
| Retinal | C20H28O | [M+H]+ | 285.2217 | 285.2213 | 1.570 | 18.005 | -0.436 |
| Homovanillic acid | C9H10O4 | [M+ACN+H]+ | 224.0916 | 224.0917 | -0.555 | 4.853 | -1.353 |
| Naphthalene epoxide | C10H8O | [M+H]+ | 145.0653 | 145.0648 | 3.574 | 9.652 | -1.137 |
| Acetylcarnitine | C9H17NO4 | [M+H]+ | 204.1232 | 204.1230 | 0.566 | 3.390 | -1.242 |
| Succinic acid | C4H6O4 | [M-H]- | 117.0188 | 117.0193 | -4.289 | 0.579 | 4.186 |
| Taurine | C2H7NO3S | [M-H]- | 124.0068 | 124.0074 | -5.138 | 0.462 | 5.901 |
| Thymidine | C10H14N2O5 | [M-H]- | 241.0844 | 241.0830 | 5.621 | 0.704 | 0.705 |
| 5-Aminolevulinate | C5H9NO3 | [M-H]- | 130.0500 | 130.0510 | -7.585 | 0.497 | 0.512 |
Table 3 Differential metabolites of TLG-5 H vs model group
| Metabolite Name | Formula | Adduct | m/z | Error (ppm) | RT (min) | Log2FC (TLG-5 H/Model) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measured value | Theoretical value | ||||||
| Histidine | C6H9N3O2 | [M+H]+ | 156.0775 | 156.0768 | 4.657 | 0.475 | -0.947 |
| Anthranilic acid | C7H7NO2 | [M+H]+ | 138.0562 | 138.0550 | 8.656 | 2.831 | 1.432 |
| Sphingosine | C18H37NO2 | [M+H]+ | 300.2900 | 300.2897 | 0.879 | 15.334 | 1.466 |
| 3,4-dihydroxyglutamic acid | C5H9NO6 | [2M+K]+ | 397.0475 | 397.0491 | -4.060 | 5.249 | -0.831 |
| 2'-deoxycytidine | C9H13N3O4 | [M+H]+ | 228.0981 | 228.0979 | 1.129 | 0.449 | -0.626 |
| Hydroxyrepaglinide | C27H36N2O5 | [M+H]+ | 469.2693 | 469.2697 | -0.914 | 0.304 | -1.034 |
| Spermine | C10H26N4 | [M+H]+ | 203.2234 | 203.2230 | 1.656 | 0.362 | -1.126 |
| Retinal | C20H28O | [M+H]+ | 285.2217 | 285.2213 | 1.570 | 18.005 | -0.436 |
| Homovanillic acid | C9H10O4 | [M+ACN+H]+ | 224.0916 | 224.0917 | -0.555 | 4.853 | -1.353 |
| Naphthalene epoxide | C10H8O | [M+H]+ | 145.0653 | 145.0648 | 3.574 | 9.652 | -1.137 |
| Acetylcarnitine | C9H17NO4 | [M+H]+ | 204.1232 | 204.1230 | 0.566 | 3.390 | -1.242 |
| Succinic acid | C4H6O4 | [M-H]- | 117.0188 | 117.0193 | -4.289 | 0.579 | 4.186 |
| Taurine | C2H7NO3S | [M-H]- | 124.0068 | 124.0074 | -5.138 | 0.462 | 5.901 |
| Thymidine | C10H14N2O5 | [M-H]- | 241.0844 | 241.0830 | 5.621 | 0.704 | 0.705 |
| 5-Aminolevulinate | C5H9NO3 | [M-H]- | 130.0500 | 130.0510 | -7.585 | 0.497 | 0.512 |
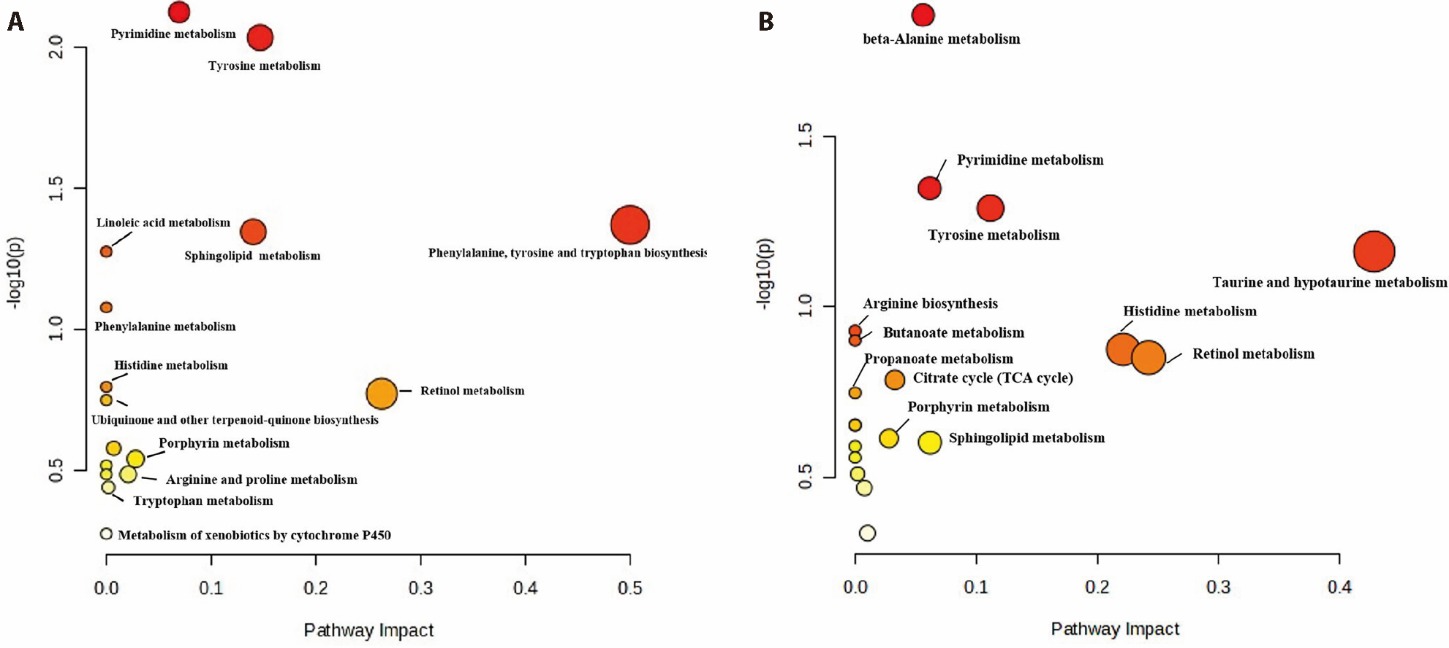
Figure 3 Metabolomics analysis A: metabolic pathway in pathogenicity of CAG rats; B: metabolic pathways in TLG-5 H (1.26 g·kg?1·d?1) against MNNG-induced CAG rats. Control group: drink and eat freely; Other groups, were given 170 μg/mL of MNNG solution freely while MNNG and 2% sodium salicylate solution were administered by gavage alternately while the hunger and satiety disorders for 12 weeks. Each dosing group received the corresponding drug treatment separately for 8 weeks. Control and model groups received intragastric administration of an equivalent volume of saline. TLG-5 H: TLG-5 high-dose; TLG-5: tonglaga-5; CAG: chronic atrophic gastritis; MNNG: n-methyl-n’-nitro-n-nitrosoguanidine.
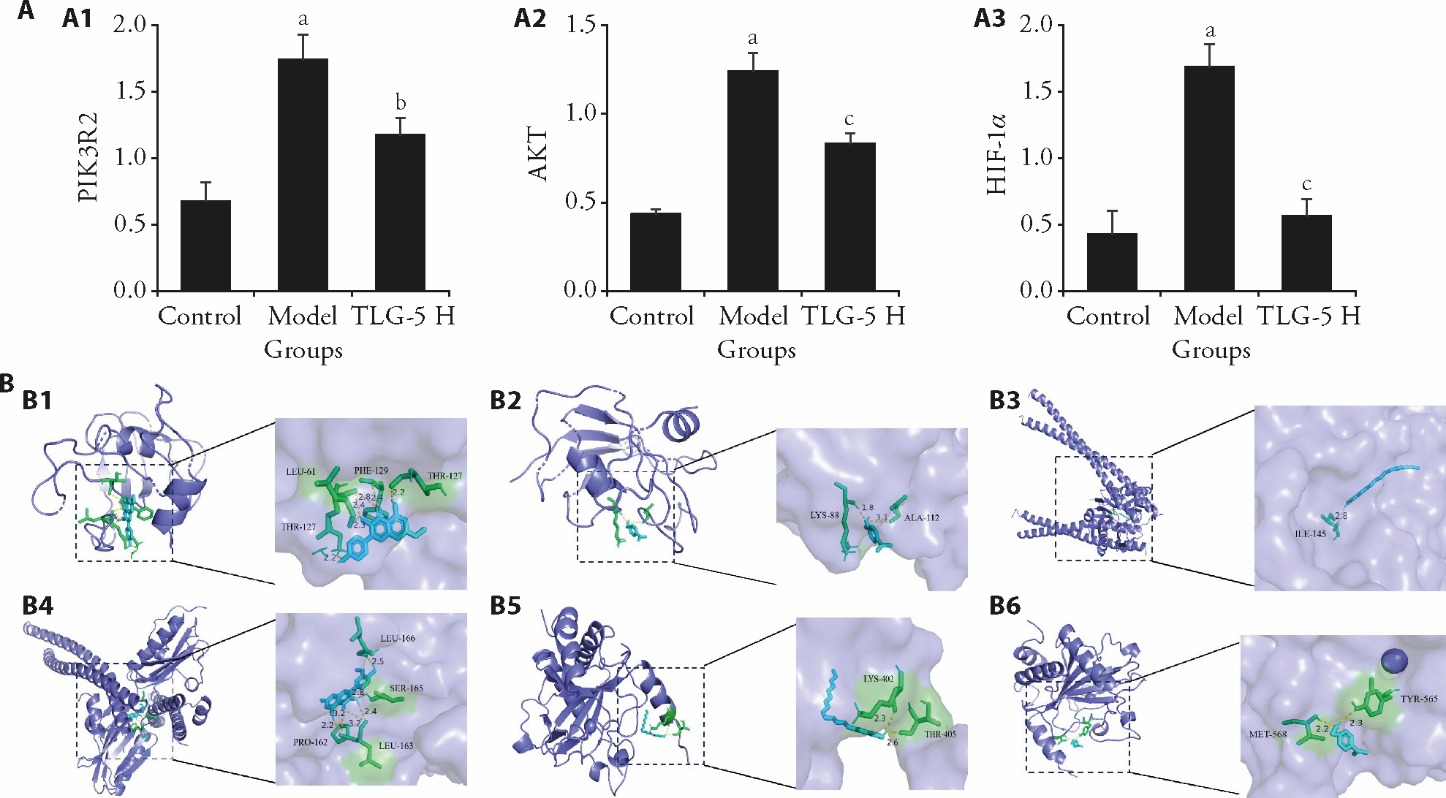
Figure 4 Simple verification of experimental results A: relative mRNA expression of A1: PIK3R2, A2: AKT, A3: HIF-1α in the gastric tissue. B: molecular docking results. B1: rhamnocitrin-AKT1; B2: terpineol-AKT1; B3: linoleic acid-PIK3R2; B4: isorhamnetin-PIK3R2; B5: linoleic acid-HIF-1α; B6: terpineol-HIF-1α. Control group: drink and eat freely; other groups, were given 170 μg/mL of MNNG solution freely while MNNG and 2% sodium salicylate solution were administered by gavage alternately while the hunger and satiety disorders for 12 weeks. Each dosing group received the corresponding drug treatment separately for 8 weeks. Control and model groups received intragastric administration of an equivalent volume of saline. TLG-5: tonglaga-5; CAG: chronic atrophic gastritis; TLG-5 H: TLG-5 high-dose, 1.26 g·kg?1·d?1; PIK3R2: phosphoinositide-3-kinase regulatory subunit 2; AKT1: AKT serine/threonine kinase 1; HIF-1α: hypoxia inducible factor 1 subunit alpha. Data between multiple groups were processed using one-way analysis of variance, and data was expressed using mean ± standard deviation (n = 8). aP < 0.001, when compared with the control group; bP < 0.05, cP < 0.001, when compared with the model group.
| No. | Compound | Binding energy (kcal/mol) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AKT1 | PIK3R2 | HIF-1α | ||
| 1 | α-Linolenic acid | -6.66 | -5.96 | -5.57 |
| 2 | Linoleic acid | -7.51 | -7.69 | -6.49 |
| 3 | Apigenin | -7.18 | -6.08 | -6.19 |
| 4 | Isorhamnetin | -6.71 | -5.5 | -5.6 |
| 5 | Luteolin | -7.32 | -6.66 | -5.84 |
| 6 | Rhamnocitrin | -7.64 | -6.5 | -5.78 |
| 7 | Terpineol | -6.65 | -5.82 | -5.2 |
| 8 | 5-hydroxy-3',4',7-trime-thoxyflavone | -6.97 | -5.79 | -6.35 |
Table 4 Summary of compounds and targets molecular docking binding energy
| No. | Compound | Binding energy (kcal/mol) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AKT1 | PIK3R2 | HIF-1α | ||
| 1 | α-Linolenic acid | -6.66 | -5.96 | -5.57 |
| 2 | Linoleic acid | -7.51 | -7.69 | -6.49 |
| 3 | Apigenin | -7.18 | -6.08 | -6.19 |
| 4 | Isorhamnetin | -6.71 | -5.5 | -5.6 |
| 5 | Luteolin | -7.32 | -6.66 | -5.84 |
| 6 | Rhamnocitrin | -7.64 | -6.5 | -5.78 |
| 7 | Terpineol | -6.65 | -5.82 | -5.2 |
| 8 | 5-hydroxy-3',4',7-trime-thoxyflavone | -6.97 | -5.79 | -6.35 |
| 1. |
Fang JY, Du YQ, Liu WZ, et al. Chinese consensus on chronic gastritis (2017, shanghai). J Dig Dis 2018; 19: 182-203.
DOI URL |
| 2. | Bai Y, Li ZS, Zou DW, et al. Alarm features and age for predicting upper gastrointestinal malignancy in chinese patients with dyspepsia with high background prevalence of helicobacter pylori infection and upper gastrointestinal malignancy:an endoscopic database review of 102 665 patients from 1996 to 2006. Gut 2010; 59: 722-8. |
| 3. | Zheng R, Zhang S, Zeng H, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality in China, 2016. J Natl Cancer Cent 2022; 2: 1-9. |
| 4. | Zhou ZH, Liang K, Cui B, You LS, An R, Wang XH. Traditional Chinese Medicine intervenes in signaling pathways associated with hp-negative chronic atrophic gastritis: a review. Zhong Hua Zhong Yi Yao Xue Kan 2024; 42: 82-8+279-80. |
| 5. |
Pollard JW. Tumour-educated macrophages promote tumour progression and metastasis. Nat Rev Cancer 2004; 4: 71-8.
DOI PMID |
| 6. |
Zhang LY, Zhang J, Li D, et al. Bile reflux is an independent risk factor for precancerous gastric lesions and gastric cancer: an observational cross-sectional study. J Dig Dis 2021; 22: 282-90.
DOI URL |
| 7. | Yue P, Zhong J, Huang J, Lan Z, Zhong S. The efficacy and safety of Xiangsha Liujunzi decoction in the treatment of chronic non-atrophic gastritis: a protocol for a systematic review and Meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore) 2021; 100: e24504. |
| 8. |
Kim GH. Proton pump inhibitor-related gastric mucosal changes. Gut Liver 2021; 15: 646-52.
DOI URL |
| 9. | Su DN, Ce LMG, Hou YH, Tu Y, Nie B. Research progress of the compound five-flavour clearing powder of Mongolian medicine. Xian Dai Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi 2017; 26: 1479-82. |
| 10. | Committee NP. Pharmacopoeia of the people's republic of China:Part I. Beijing: China Medical Science Press, 2020; 648. |
| 11. | Committee CHME. Chinese herbal medicine: Mongolian medicine volume. Shanghai: Shanghai Scientific and Technical Publishers, 1998: 162-4. |
| 12. | Kang MH. Clinical study on the treatment of hp-associated chronic gastritis (cold hila-type gastric failure disease) with traditional Mongolian medicine. Inner Mongolia: Inner Mongolia University for the Nationalities, 2023: 17-8. |
| 13. |
Čolić M, Mihajlović D, Bekić M, et al. Immunomodulatory activity of punicalagin, punicalin, and ellagic acid differs from the effect of pomegranate peel extract. Molecules 2022; 27: 7871.
DOI URL |
| 14. | Song L, Zhu Y, Jin M, Zang B. Hydroxysafflor yellow a inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory signal transduction in human alveolar epithelial a549 cells. Fitoterapia 2013; 84: 107-14. |
| 15. |
Hoch CC, Petry J, Griesbaum L, et al. 1,8-cineole (eucalyptol): a versatile phytochemical with therapeutic applications across multiple diseases. Biomed Pharmacother 2023; 167: 115467.
DOI URL |
| 16. |
Zhu L, Andersen-Civil AIS, Myhill LJ, et al. The phytonutrient cinnamaldehyde limits intestinal inflammation and enteric parasite infection. J Nutr Biochem 2022; 100: 108887.
DOI URL |
| 17. |
Chen WS, An J, Li JJ, Hong L, Xing ZB, Li CQ. Piperine attenuates lipopolysaccharide (lps)-induced inflammatory responses in bv2 microglia. Int Immunopharmacol 2017; 42: 44-8.
DOI URL |
| 18. | Yang HX, Dang XJ. Experimental study on the effect of five-flavour clearing powder of mongolian medicine on gastric function. Zhong Guo Min Zu Yi Yao Za Zhi 2000; 6: 43. |
| 19. |
Zhao M, Che Y, Gao Y, Zhang X. Application of multi-omics in the study of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Front Pharmacol 2024; 15: 1431862.
DOI URL |
| 20. |
Wang X, Che X, Yu Y, et al. Hypoxia-autophagy axis induces vegfa by peritoneal mesothelial cells to promote gastric cancer peritoneal metastasis through an integrin α5-fibronectin pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 2020; 39: 221.
DOI PMID |
| 21. |
Wang Z, Li S. Network pharmacology in quality control of Traditional Chinese Medicines. Chin Herb Med 2022; 14: 477-8.
DOI PMID |
| 22. | Du L, Xiao Y, Xu Y, et al. The potential bioactive components of nine tcm prescriptions against COVID-19 in lung cancer were explored based on network pharmacology and molecular docking. Front Med (Lausanne) 2021; 8: 813119. |
| 23. |
Nicholson JK, Lindon JC, Holmes E. 'Metabonomics': understanding the metabolic responses of living systems to pathophysiological stimuli via multivariate statistical analysis of biological nmr spectroscopic data. Xenobiotica 1999; 29: 1181-9.
DOI PMID |
| 24. |
Zheng S, Zhou B, Yang L, et al. System pharmacology analysis to decipher the effect and mechanism of active ingredients combination from Duhuo Jisheng decoction on osteoarthritis in rats. J Ethnopharmacol 2023; 315: 116679.
DOI URL |
| 25. |
Cao H, Zhang A, Zhang H, Sun H, Wang X. The application of metabolomics in Traditional Chinese Medicine opens up a dialogue between chinese and western medicine. Phytother Res 2015; 29: 159-66.
DOI PMID |
| 26. |
Wang P, Wang Q, Yang B, Zhao S, Kuang H. The progress of metabolomics study in Traditional Chinese Medicine research. Am J Chin Med 2015; 43: 1281-310.
DOI URL |
| 27. |
Tsukamoto H, Mizoshita T, Katano T, et al. Preventive effect of rebamipide on n-methyl-n'-nitro-n-nitrosoguanidine-induced gastric carcinogenesis in rats. Exp Toxicol Pathol 2015; 67: 271-7.
DOI PMID |
| 28. | Yu CY, Li YC, Su ZQ, et al. Research progress on mnng-induced multi-factor disease and TCM syndrome integrated model of chronic atrophic gastritis in rats. Zhong Hua Zhong Yi Yao Za Zhi 2020; 35: 292-6. |
| 29. |
Guo K, Wang L, Mahe J, et al. Effect of aqueous extract of seed of broccoli on inflammatory cytokines and helicobacter pylori infection: a randomized, double-blind, controlled trial in patients without atrophic gastritis. Inflammopharmacology 2022; 30: 1659-68.
DOI PMID |
| 30. |
Alikhani M, Saberi S, Esmaeili M, et al. Mitochondrial DNA copy number variations and serum pepsinogen levels for risk assessment in gastric cancer. Iran Biomed J 2021; 25: 323-33.
DOI PMID |
| 31. |
Zhao J, Tian W, Zhang X, et al. The diagnostic value of serum trefoil factor 3 and pepsinogen combination in chronic atrophic gastritis: a retrospective study based on a gastric cancer screening cohort in the community population. Biomarkers 2024; 29: 384-92.
DOI URL |
| 32. |
Tu H, Sun L, Dong X, et al. Temporal changes in serum biomarkers and risk for progression of gastric precancerous lesions: a longitudinal study. Int J Cancer 2015; 136: 425-34.
DOI PMID |
| 33. |
Watson SA, Grabowska AM, El-Zaatari M, Takhar A. Gastrin-active participant or bystander in gastric carcinogenesis? Nat Rev Cancer 2006; 6: 936-46.
DOI PMID |
| 34. | Sun QQ. Metabolomics study on the mechanism of action of Hanxia Laxingxin Tang in intervening chronic atrophic gastritis. Shandong: Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2019: 61-5. |
| 35. |
Jafari M, Ghadami E, Dadkhah T, Akhavan-Niaki H. Pi3k/akt signaling pathway: erythropoiesis and beyond. J Cell Physiol 2019; 234: 2373-85.
DOI PMID |
| 36. | Wu D, Wu P, Huang Q, Liu Y, Ye J, Huang J. Interleukin-17: a promoter in colorectal cancer progression. Clin Dev Immunol 2013; 2013: 436307. |
| [1] | ZHANG Yuan, CHENG Shizan, HUA Yue, SHI Ji, SU Guoming, ZHANG Chao, LIAN Jing, LIU Pengpeng, JIA Tianzhu. Mechanisms of Suanzaoren (Ziziphi Spinosae Semen) and its processed products in treating insomnia: an integrated study based on network pharmacology and metabolomics [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(6): 1307-1316. |
| [2] | PAN Tingyu, YAO Jing, GE Yue, YANG Shuang, SUN Zikai, WEI Yu, WU Jieyu, XU Yong, ZHOU Xianmei, HE Hailang. Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry-based metabolomics study of the protective mechanism of Shenji Guben decoction (参吉固本方) on chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(5): 1009-1018. |
| [3] | WANG Yue, LIU Xingxing, GUO Yi, GUO Yongming, YUAN Gongming, ZHANG Yu, ZHENG Zhiyu, XU Yuan, LI Yuan. Characterization of acupuncture on central amino acid metabolism based on targeted neurotransmitter analysis in mice with inflammatory pain [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(5): 1019-1027. |
| [4] | WANG Raoqiong, HAO Linyao, LU Ye, WANG Lingxue, LI Jianrong, PENG Yan, TANG Hongmei, LI Shuangyang, BAI Xue. Mechanism analysis of Tongqiao Yizhi decoction (通窍益智颗粒) in treating vascular dementia rats by brain tissue untargeted metabonomics and fecal 16S rRNA gene sequencing [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(4): 759-769. |
| [5] | GAO Jiaming, ZHANG Yehao, Chen Yuanyuan, JIN Long, ZHAO Jianfeng, GUO Hao, FU Jianhua. Qingfei Zhisou oral liquid (清肺止嗽口服液) alleviates fever-induced inflammation by regulating arachidonic acid and lysophospholipids metabolism and inhibiting hypothalamus transient receptor potential ion channels expression [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(5): 954-962. |
| [6] | SONG Zhenguang, YANG Bin, WANG Fei, YAN Dongmei, ZHOU Xiaoqing, HUANG Liping, GAO Xuemei, LI Bin, HUANG Luqi. Study on the four Qi of Pfaffia glomerata based on the metabolomics technology and comparison of Dangshen (Radix Codonopsis) in the equivalent substitution prescription [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(4): 713-721. |
| [7] | YAN Jing, FENG Huimin, QIU Fang, WANG Haijun, YIN Luyun, JIN Xiaofei, ZHAO Jiyu, WANG Hongyang, YAN Xiaoqin. Effect on serum metabolomics of rats with premature ovarian insufficiency by Zhibian (BL54) through Shuidao (ST28) acupuncture [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(4): 722-733. |
| [8] | WANG Xiang, HUANG Jianping, WANG Yupeng, WANG Qilong, JING Yajiang, ZHANG Gang, PENG Liang, GAO Jing, WANG Hongyan, YAN Yonggang. Differential metabolite analysis of the pharmacodynamic differences between different ratios of Dahuang (Radix Et Rhizoma Rhei Palmati)-Taoren (Semen Persicae) herb pair [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(3): 515-523. |
| [9] | JING Wenguang, LIN Xiaoyu, LI Chu, ZHAO Xiaoliang, CHENG Xianlong, WANG Penglong, WEI Feng, MA Shuangcheng. Anti-inflammatory mechanism of the non-volatile ingredients originated from Guanghuoxiang (Pogostemonis Herba) based on high performance liquid chromatography-heated electron spray ionization-high resolution mass spectroscope and cell metabolomics [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(2): 260-267. |
| [10] | LI Chaoran, YANG Yan, FENG Chuwen, LI Heng, QU Yuanyuan, WANG Yulin, WANG Delong, WANG Qingyong, GUO Jing, SHI Tianyu, SUN Xiaowei, WANG Xue, HOU Yunlong, SUN Zhongren, YANG Tiansong. Integrated 'omics analysis for the gut microbiota response to moxibustion in a rat model of chronic fatigue syndrome [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1176-1189. |
| [11] | WANG Miao, ZHU Yan, ZHAO Hui, ZHAO Hongfang. Moxibustion enables protective effects on rheumatoid arthritis-induced myocardial injury via transforming growth factor beta1 signaling and metabolic reprogramming [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1190-1199. |
| [12] | JIANG Wenjing, JIANG Huaying, YUAN Lihua, SA Yuanhong, XIAO Jimei, SUN Hongqi, SONG Jingyan, SUN Zhengao. Xiaoyi Yusi decoction (消异育嗣汤) improves in vitro fertilization and embryo transfer outcomes in patients with endometriosis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 1026-1033. |
| [13] | LIU Di, ZHANG Yingqi, YU Tianyuan, LIU Zhifeng, JIAO Yi, WANG Hourong, XU Yajing, GUAN Qian, CHEN Lulu, HU Hui. Protective mechanisms of Tuina therapy against lipopolysaccharide-induced fever in young rabbits based on untargeted metabolomics analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(4): 725-733. |
| [14] | HONG Zongchao, CAI Quan, DUAN Xueyun, YANG Yanfang, WU Hezhen, JIANG Nan, FAN Heng. Effect of compound Sophorae decoction in the treatment of ulcerative colitis by tissue extract metabolomics approach [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(3): 414-423. |
| [15] | Liu Mi, Shen Jiacheng, Liu Caichun, Zhong Huan, Yang Qing, Shu Wenna, Ma Mingzhu, Dong Jiyang, Yang Zongbao, Chang Xiaorong, She Chang, Yu Shu. Effects of moxibustion and acupuncture at Zusanli(ST 36) and Zhongwan(CV 12) on chronic atrophic gastritis in rats [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020, 40(5): 827-835. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

