Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (6): 1190-1199.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20230802.005
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Moxibustion enables protective effects on rheumatoid arthritis-induced myocardial injury via transforming growth factor beta1 signaling and metabolic reprogramming
WANG Miao1, ZHU Yan2( ), ZHAO Hui1, ZHAO Hongfang1
), ZHAO Hui1, ZHAO Hongfang1
- 1 the Geriatrics, Anhui University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Hefei 230031, China
2 the Geriatrics, the Second Hospital Affiliated of Anhui University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Hefei 230061, China
-
Received:2022-09-12Accepted:2022-12-18Online:2023-10-25Published:2023-08-02 -
Contact:ZHU Yan, the Geriatrics, the Second Hospital Affiliated of Anhui University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Hefei 230061, China. zydzf2008@163.com. Telephone: +86-551-62668514 -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China: a Metabolomic Study of the Effects of Moxibustion on Cardiac Function and Its Intervention in RA Model Rats Based on the TGF-β1/Smads Signaling Pathway(81403484);Exploring the Mechanism of Action of Moxibustion in AA Rats Based on Intestinal Flora and TLR4/NF-KB Signaling Pathway(KJ2019A0448);Exploring the Mechanism of Action of Moxibustion in AA Rats Based on Intestinal Flora and TLR4/NF-KB Signaling Pathway(2019py01);Anhui Province Clinical Medical Research Center [Anhui Provincial Science and Technology Department Anhui Social Science((2020) 41);2021 Domestic Visiting Training Program for Outstanding Young Key Teachers in Colleges and Universities(gxgnfx2021122)
Cite this article
WANG Miao, ZHU Yan, ZHAO Hui, ZHAO Hongfang. Moxibustion enables protective effects on rheumatoid arthritis-induced myocardial injury via transforming growth factor beta1 signaling and metabolic reprogramming[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1190-1199.
share this article
| Group | n | Joint swelling scores (%) | AI (points) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before modeling | Before therapy | After therapy | Before modeling | Before therapy | After therapy | |||
| NC | 20 | 1.75±0.23 | 1.83±0.11 | 1.85±0.24 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Model | 20 | 1.76±0.17 | 2.95±0.14a | 2.68±0.11a | 0 | 9.34±0.67a | 7.02±1.08a | |
| MOX | 20 | 1.79±0.10 | 2.93±0.17 | 2.35±0.09b | 0 | 9.33±0.09 | 3.62±0.91b | |
| APT | 20 | 1.77±0.13 | 2.93±0.14 | 2.36±0.12b | 0 | 9.29±1.05 | 3.68±1.02b | |
| TPT | 20 | 1.78±0.11 | 2.91±0.15 | 2.41±0.09b | 0 | 9.31±0.15 | 4.11±0.97bc | |
Table 1 Evaluation of rat joint swelling scores and AI in each group ($\bar{x}$ ± s)
| Group | n | Joint swelling scores (%) | AI (points) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before modeling | Before therapy | After therapy | Before modeling | Before therapy | After therapy | |||
| NC | 20 | 1.75±0.23 | 1.83±0.11 | 1.85±0.24 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Model | 20 | 1.76±0.17 | 2.95±0.14a | 2.68±0.11a | 0 | 9.34±0.67a | 7.02±1.08a | |
| MOX | 20 | 1.79±0.10 | 2.93±0.17 | 2.35±0.09b | 0 | 9.33±0.09 | 3.62±0.91b | |
| APT | 20 | 1.77±0.13 | 2.93±0.14 | 2.36±0.12b | 0 | 9.29±1.05 | 3.68±1.02b | |
| TPT | 20 | 1.78±0.11 | 2.91±0.15 | 2.41±0.09b | 0 | 9.31±0.15 | 4.11±0.97bc | |
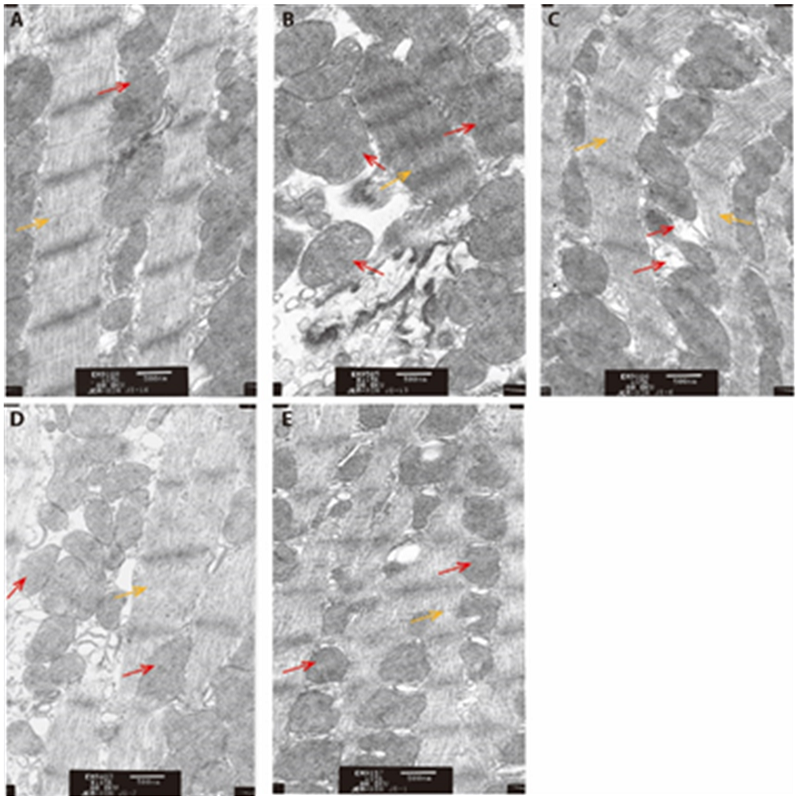
Figure 1 Protecting effects on the myocardial ultrastructure with or without therapy (×15000) A-E: electron microscopic ultrastructural basis of rat heart muscles (n = 7). A: NC group treated only with normal saline; B: model group treated with CFA and normal saline; C: TPT group treated with CFA with TPT solution by gavage (dose 8 mg·kg-1·d-1); D: APT group treated with CFA and acupuncture; E: MOX group treated with CFA and suspension moxibustion. In the figures, red arrows indicate mitochondria and yellow arrows indicate transverse striations. NC: normal control; TPT: tripterygium wilfordii polyglycoside tablets; CFA: complete Freund’s adjuvant; MOX: moxibustion; APT: acupuncture.
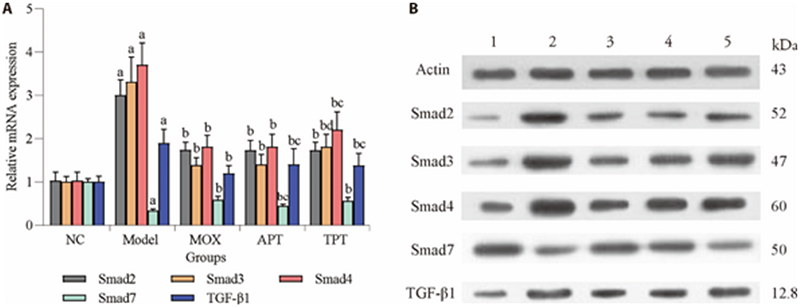
Figure 2 Expression of TGF-β signaling molecules upon therapy A: the heart mRNA expression of TGF-β1, Smad2, Smad3, Smad4, and Smad7 in rats receiving indicated treatment. Approximately 100 mg were used for Total RNA of heart tissues were extracted, reverse-transcribed and subjected to real-time PCR using indicated primers. All PCR reactions were done in triplicates. Showed is data from 3 independent experiments. B: total proteins were isolated, quantified, and separated by SDS-PAGE, followed by Western blotting analysis using indicated antibodies. 1: NC group treated only with normal saline; 2: model group treated with CFA and normal saline; 3: TPT group treated with CFA with TPT solution by gavage (dose 8 mg·kg-1·d-1); 4: APT group treated with CFA and acupuncture; 5: MOX group treated with CFA and suspension moxibustion. NC: normal control; TPT: tripterygium wilfordii polyglycoside tablets; CFA: complete Freund’s adjuvant; MOX: moxibustion; APT: acupuncture; TGF-β1: transforming growth factor beta1. Data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (n = 7). aP < 0.01, compared with NC group; bP < 0.01, compared with model group; cP < 0.05, dP < 0.01, compared with MOX group.
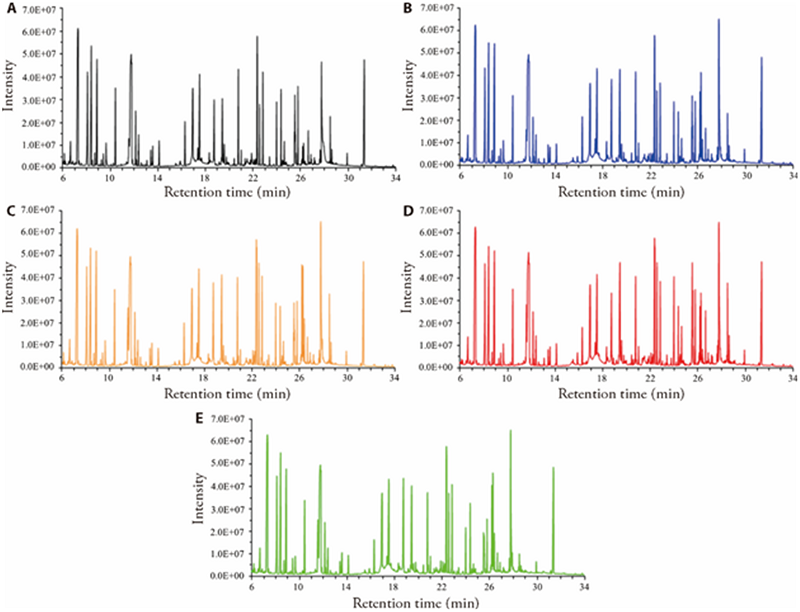
Figure 3 TIC of myocardial samples Representative TIC diagrams for each group are shown above (n = 5). A: NC group treated only with normal saline; B: MOX group treated with CFA and suspension moxibustion; C: model group treated with CFA and normal saline; D: TPT group treated with CFA with TPT solution by gavage (dose 8 mg·kg-1·d-1); E: APT group treated with CFA and acupuncture. Visual inspection of the TIC chromatograms of all samples revealed that the instrumental analysis of all samples had a strong signal, high peak capacity, and good retention time reproducibility. TIC: total ion flow chromatogram; NC: normal control; CFA: complete Freund’s adjuvant; MOX: moxibustion; TPT: tripterygium wilfordii polyglycoside tablets; APT: acupuncture; GC/MS: Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometer. GC/MS detected a large number of peaks from each sample, such as the raw instrumental data files of the samples were analyzed by deconvolution using the default parameters of the AMDIS software (National Institute of Standards and Technology). Software algorithms were used to pre-process and analyze the acquired mass spectrometry data to convert the complex mass spectrometry signals into useful qualitative and quantitative data.
| 1. |
Semb AG, Ikdahl E, Wibetoe G, Crowson C, Rollefstad S. Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease prevention in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol 2020; 16: 361-79.
DOI PMID |
| 2. |
Gouze H, Aegerter P, Said-Nahal R, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis, as a clinical disease, but not rheumatoid arthritis-associated autoimmunity, is linked to cardiovascular events. Arthritis Res Ther 2022; 24: 1-8.
DOI |
| 3. |
Ikdahl E, Wibetoe G, Rollefstad S, et al. Guideline recommended treatment to targets of cardiovascular risk is inadequate in patients with inflammatory joint diseases. Int J Cardiol 2019; 274: 311-8.
DOI PMID |
| 4. | Mo M. Clinical analysis of 117 cases of rheumatoid arthritis combined with cardiovascular diseases. Guangxi: Guangxi Medical University, 2015: 1-61. |
| 5. | Hu J, Yang HY. The transduction pathway and function of physical signals stimulated by moxibustion. Zhong Guo Zhen Jiu 2021; 41: 577-81. |
| 6. | Yu HW, Zhu Y, Pan YZ, et al. Clinical efficacy of moxibustion as supplement on rheumatoid arthritis and the exploration on its mechanism. Zhong Guo Zhen Jiu 2016; 36: 17-20. |
| 7. | Zhu Y, Zhang M, Zhao C. Effect of moxibustion "Zusanli" and "Shenshu" on intestinal microflora in rats with adjuvant arthritis. Zhong Guo Zhen Jiu 2021; 41: 1119-25. |
| 8. | Tao S, Wang X, Liao C, et al. The efficacy of moxibustion on the serum levels of CXCL1 and β-EP in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Pain Res Manag 2021; 2021: 1-10. |
| 9. | Goumans MJ, Ten DP. TGF-beta signaling in control of cardiovascular function. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2018; 10: 1-39. |
| 10. |
Frangogiannis NG. Transforming growth factor-β in myocardial disease. Nat Rev Cardiol 2022; 19: 435-55.
DOI PMID |
| 11. |
Kodo K, Ong S, Jahanbani F, et al. iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes reveal abnormal TGF-β signalling in left ventricular non-compaction cardiomyopathy. Nat Cell Biol 2016; 18: 1031-42.
DOI PMID |
| 12. |
Hanna A, Humeres C, Frangogiannis NG. The role of Smad signaling cascades in cardiac fibrosis. Cell Signal 2021; 77: 109826.
DOI URL |
| 13. | Lü SC, Zhang JP. Advances in the role of transforming growth factor-β1/Smads pathway in cardiovascular diseases. Zhong Guo Lao Nian Xue Za Zhi 2016; 36: 5208-10. |
| 14. |
Rinschen MM, Ivanisevic J, Giera M, Siuzdak G. Identification of bioactive metabolites using activity metabolomics. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2019; 20: 353-67.
DOI |
| 15. | Hu L, Lars D, Song X, et al. Effect of moxibustion on IL-1β and IL-2 in rat models of rheumatoid arthritis. J Acupunct Tuina Sci 2010; 8: 149-53. |
| 16. | Ma YC, Duan F, Meng M, et al. Preparation of a rat rheumatoid arthritis model with modified Freund's complete adjuvant. Xian Dai Yu Fang Yi Xue 2008; 35: 1989-91. |
| 17. |
Corrao S, Messina S, Pistone G, Calvo L, Scaglione R, Licata G. Heart involvement in rheumatoid arthritis: systematic review and Meta-analysis. Int J Cardiol 2013; 167: 2031-8.
DOI PMID |
| 18. |
Lei W, Jian L, Chuanbing H, Yuan W, Li Z. Effect of Xinfeng capsule on pulmonary function in a adjuvant arthritis rat model. J Tradit Chin Med 2014; 34: 76-85.
PMID |
| 19. |
Szymanska E, Saccenti E, Smilde AK, Westerhuis JA. Double-check: validation of diagnostic statistics for PLS-DA models in metabolomics studies. Metabolomics 2012; 8: 3-16.
PMID |
| 20. |
Deng M, Zhang M, Huang X, et al. A gas chromatography-mass spectrometry based study on serum metabolomics in rats chronically poisoned with hydrogen sulfide. J Forensic Leg Med 2015; 32: 59-63.
DOI PMID |
| 21. | Gao X, Pujos-Guillot E, Sébédio J. Development of a quantitative metabolomic approach to study clinical human fecal water metabolome based on trimethylsilylation derivatization and GC/MS analysis. Anal Chem 2010; 82: 6447-56. |
| 22. | Sun Y, Liu J, Wan L, Wang F, Qi YJ. Mechanism of Xinfeng capsule in improving cardiac function in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi 2015; 31: 93-6. |
| 23. | Xiao Y, Ding L, Chen H, et al. Effect of wheat grain moxibustion on the anti-oxidative stress effect in rats with adriamycin-induced cardiomyopathy. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu 2016; 41: 502-8. |
| 24. | Liu NN, Jia XZ, Wang J, et al. Effect of moxibustion on autophagic function of cardiomyocytes in rats with chronic heart failure. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu 2019; 44: 25-30. |
| 25. |
Ranjbarvaziri S, Kooiker KB, Ellenberger M, et al. Altered cardiac energetics and mitochondrial dysfunction in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Circulation 2021; 144: 1714-31.
DOI PMID |
| 26. |
Xu YB, Wang NZ, Yang LL, Cui HD, Xue HX, Zhang N. Expression of peptidylarginine deiminase 4 and protein tyrosine phosphatase nonreceptor type 22 in the synovium of collagen-induced arthritis rats. Chin Med Sci J 2014; 29: 85-90.
PMID |
| 27. | Chen Y, Li H, Luo X, et al. Moxibustion of Zusanli (ST36) and Shenshu (BL23) alleviates cartilage degradation through RANKL/OPG signaling in a rabbit model of rheumatoid arthritis. Evid-Based Compl Alt 2019; 2019: 1-8. |
| 28. |
Park KC, Gaze DC, Collinson PO, et al. Cardiac troponins: from myocardial infarction to chronic disease. Cardiovasc Res 2017; 113: 1708-18.
DOI PMID |
| 29. | Muñoz-Valle JF, Torres-Carrillo NM, Guzmán-Guzmán IP, et al. The functional class evaluated in rheumatoid arthritis is associated with soluble TGF-β1 serum levels but not with G915C (Arg25Pro) TGF-β1 polymorphism. Rheumatol Int 2012; 32: 367-72. |
| 30. |
Sun J, Zhu J, Chen L, et al. Forsythiaside B inhibits myocardial fibrosis via down regulating TGF-beta1/Smad signaling pathway. Eur J Pharmacol 2021; 908: 174354.
DOI URL |
| 31. |
Miyazawa K, Miyazono K. Regulation of TGF-beta family signaling by inhibitory Smads. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2017; 9: a022095.
DOI URL |
| 32. | Li MT, Deng J, Yang DL, Gao Y. Interactive regulation between TGF-β and MAPK signaling pathways in myocardial hypertrophy. Zhong Guo Xin Yao Yu Lin Chuang Za Zhi 2022; 41: 257-63. |
| 33. | Luo WZ, Qiao XF, Ye ZH, Sheng YL, Wang JJ. Effects of chuanxiongzine on TGF-β1/Smads in rats with rheumatoid arthritis lung function impairment. Zhong Guo Lao Nian Xue Za Zhi 2017; 37: 42-4. |
| 34. |
Yan A, Xie G, Ding X, et al. Effects of lipid overload on heart in metabolic diseases. Horm Metab Res 2021; 53: 771-8.
DOI PMID |
| 35. |
Wang Y, Li C, Liu Z, et al. Danqi pill protects against heart failure through the arachidonic acid metabolism pathway by attenuating different cyclooxygenases and leukotrienes B4. BMC Complement Altern Med 2014; 14: 67.
DOI URL |
| 36. | Mu F, Lin R, Zhang HY, et al. A metabolomics-based approach to study the interventional effect of the Chinese herbal medicine Suhe Xiang on coronary heart disease in rats with evidence of cardiac blood stasis. Zhong Guo Xin Yao Za Zhi 2019; 28: 620-7. |
| 37. |
Palomer X, Barroso E, Zarei M, Botteri G, Vazquez-Carrera M. PPARbeta/delta and lipid metabolism in the heart. Biochim Biophys Acta 2016; 1861: 1569-78.
DOI PMID |
| 38. |
Amorim JA, Coppotelli G, Rolo AP, et al. Mitochondrial and metabolic dysfunction in ageing and age-related diseases. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2022; 18: 243-58.
DOI PMID |
| 39. |
Bhatti JS, Bhatti GK, Reddy PH. Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in metabolic disorders-A step towards mitochondria based therapeutic strategies. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis 2017; 1863: 1066-77.
DOI URL |
| 40. | Li CY, Zhang N, Xie LS, Wu QF, Yu SG. Effect of moxibustion on mitochondrial crest structure protein Mic10 and Mic60 in hippocampus and prefrontal cortex of App/Ps1 mice. Zhong Hua Zhong Yi Yao Za Zhi 2022; 37: 140-5. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

