Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (4): 759-769.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2025.04.006
• Original Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Mechanism analysis of Tongqiao Yizhi decoction (通窍益智颗粒) in treating vascular dementia rats by brain tissue untargeted metabonomics and fecal 16S rRNA gene sequencing
WANG Raoqiong1,2, HAO Linyao1,2, LU Ye1,2, WANG Lingxue1,2, LI Jianrong1,2, PENG Yan1,2, TANG Hongmei1,2, LI Shuangyang1,2( ), BAI Xue1,2(
), BAI Xue1,2( )
)
- 1 Department of Neurology, the Affiliated Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, China
2 Institute of Integrated Chinese and Western Medicine, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, China
-
Received:2024-02-22Accepted:2024-08-28Online:2025-08-15Published:2025-07-25 -
Contact:LI Shuangyang,BAI Xue -
About author:LI Shuangyang, Department of Neurology, The Affiliated Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, China. lisy@swmu.edu.cn,Telephone: +86-13909081756; +86-18208350086
Prof. BAI Xue, Department of Neurology, The Affiliated Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, China. baixue@swmu.edu.cn,
-
Supported by:Southwest Medical University Project: Exploring the Neuroprotective Mechanism of Tongqiao Yizhi Decoction on Vascular Dementia Rats Based on the Brain Gut Axis(southwest Medical University [2021] No. 1)
Cite this article
WANG Raoqiong, HAO Linyao, LU Ye, WANG Lingxue, LI Jianrong, PENG Yan, TANG Hongmei, LI Shuangyang, BAI Xue. Mechanism analysis of Tongqiao Yizhi decoction (通窍益智颗粒) in treating vascular dementia rats by brain tissue untargeted metabonomics and fecal 16S rRNA gene sequencing[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(4): 759-769.
share this article
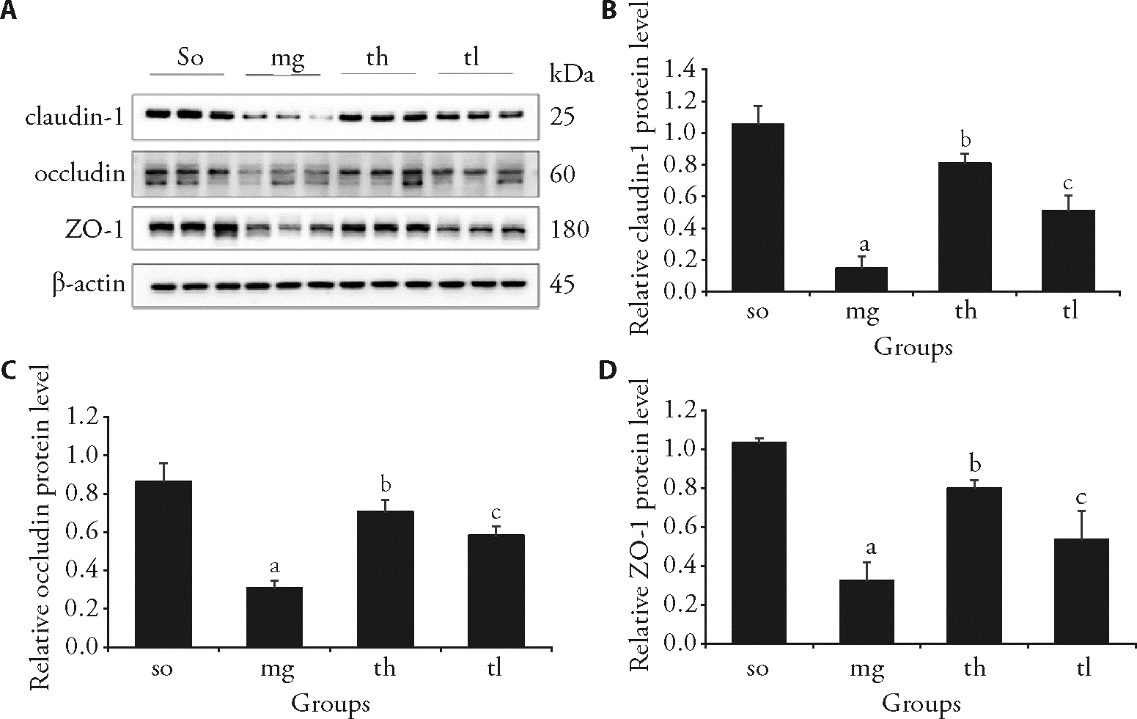
Figure 1 Results of Western blot analysis of claudin-1, occludin, and ZO-1 so: sham operation group; mg: model group; th: high-dose group (TQYZD 9.68 g·kg-1·d-1, 30 d); tl: low-dose group (TQYZD 2.42 g·kg-1·d-1, 30 d). TQYZD: Tongqiao Yizhi decoction; ZO-1: zonula occludens-1. The means of different groups were compared using the one-way analysis of variance test, and multiple comparisons were made after the incident using the least significant difference test. The data were presented as mean ± standard deviation (n = 3). Compared with the so group, aP < 0.05; compared with the mg group, bP < 0.05; compared with the th group, cP < 0.05.
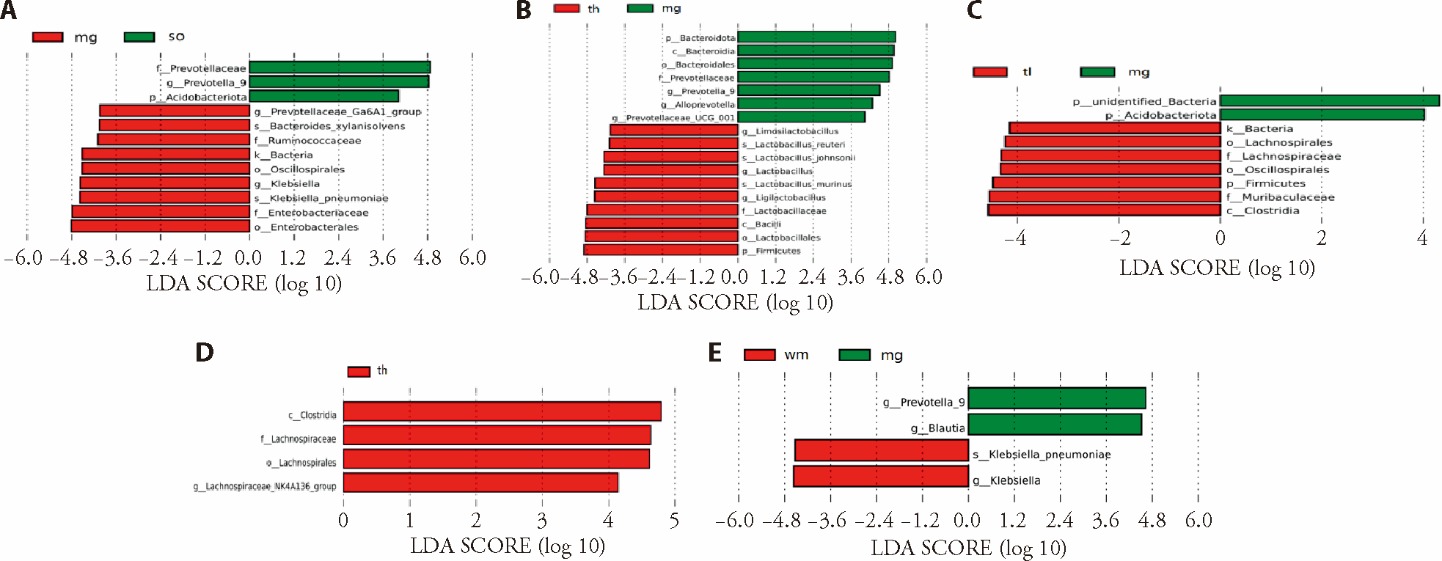
Figure 2 Effect of TQYZD on the gut microbiota of VaD rats (n = 3) A: results of LEfSe analysis of so group vs mg groups; B: results of LEfSe analysis of th group vs mg group; C: results of LEfSe analysis of tl group vs mg groups; D: results of LEfSe analysis of th group vs tl group. E: results of LEfSe analysis of wm group vs mg group. so: sham operation group; mg: model group; th: high-dose group (TQYZD 9.68 g·kg-1·d-1, 30 d); tm: middle-dose group (TQYZD 4.84 g·kg-1·d-1, 30 d); tl: low-dose group (TQYZD 2.42 g·kg-1·d-1, 30 d); wm: Western Medicine group (donepezil hydrochloride, 5 mg·kg-1·d-1, 30 d). The sham operation group and the model group were given 3 mL normal saline by gavage. Gavage once a day in the morning for 30 consecutive days. TQYZD: Tongqiao Yizhi decoction; VaD: vascular dementia; LEfSe: linear discriminant analysis effect size.
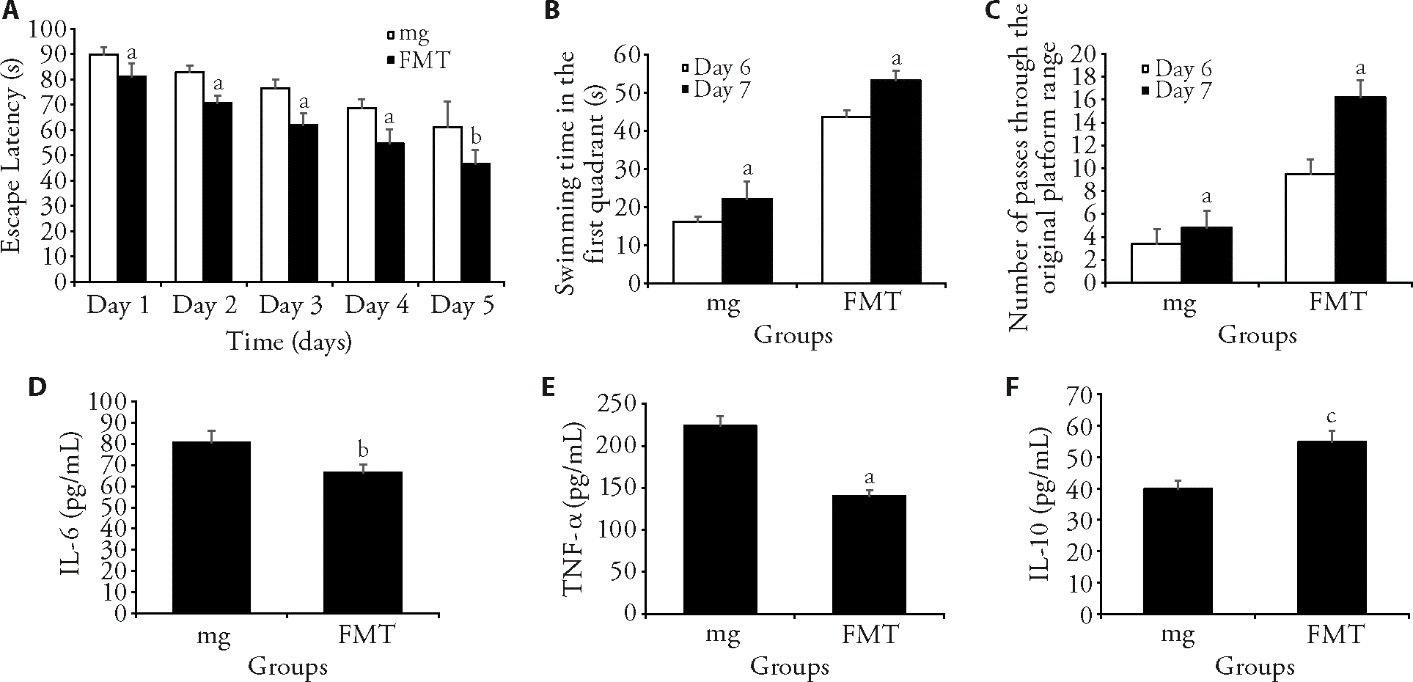
Figure 3 Results of FMT experimental results A: results of positioning navigation experiment; B: swimming time in the quadrant 1; C: number of crossing the original platform range; D: results of ELISA detection of inflammatory factors IL-6; E: results of ELISA detection of inflammatory factors TNF-α; F: results of ELISA detection of anti-inflammatory factors IL-10. TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor-α; IL-6: interleukin-6; IL-10: interleukin-10; mg: model group; FMT: Fecal Microbiota Transplantation group; ELISA: enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The model group were given 3 mL normal saline by gavage for 30 consecutive days; The FMT group were given 200 μL supernatant by tube feeding method for 30 consecutive days. The information was presented as mean ± standard deviation (n = 3). The means of different groups were compared using the one-way analysis of variance test, and multiple comparisons were made after the incident using the least significant difference test. The difference between the groups was deemed significant when the test result was P < 0.05. Compared with the mg group, aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001.
| 1. |
O'Brien JT, Thomas A. Vascular dementia. Lancet 2015; 386: 1698-706.
DOI PMID |
| 2. |
Smith EE. Clinical presentations and epidemiology of vascular dementia. Clin Sci (Lond) 2017; 131: 1059-68.
DOI PMID |
| 3. |
Korczyn AD, Vakhapova V, Grinberg LT. Vascular dementia. J Neurol Sci 2012; 322: 2-10.
DOI PMID |
| 4. |
Schneider E, O'Riordan KJ, Clarke G, Cryan JF. Feeding gut microbes to nourish the brain: unravelling the diet-microbiota-gut-brain axis. Nat Metab 2024; 6: 1454-78.
DOI PMID |
| 5. | Ma Q, Xing C, Long W, Wang HY, Liu Q, Wang RF. Impact of microbiota on central nervous system and neurological diseases: the gut-brain axis. J Neuroinflammation 2019; 16: 53. |
| 6. | Yang YF, Xu GY, Wang Q, et al. The effect of mangiferin on the structure and abundance of intestinal microbiota in mice. Xi Nan Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 2023; 46: 344-9. |
| 7. |
Antushevich H. Fecal microbiota transplantation in disease high-doseerapy. Clin Chim Acta 2020; 503: 90-8.
DOI PMID |
| 8. | Tian Z, Liu J, Liao M, et al. Beneficial effects of fecal microbiota transplantation on ulcerative colitis in mice. Dig Dis Sci 2016; 61: 2262-71. |
| 9. | Meng S, Li S, Chen H, Deng C, Meng Z, Wang Y. Metabolomics deciphering high-dosee potential biomarkers of Hengqing I prescription against vascular dementia. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2022; 2022: 1636145. |
| 10. | Fleszar MG, Wiśniewski J, Zboch M, Diakowska D, Gamian A, Krzystek-Korpacka M. Targeted metabolomic analysis of nitric oxide/L-arginine pahigh-doseway metabolites in dementia: association wihigh-dose pahigh-doseology, severity, and structural brain changes. Sci Rep 2019; 9: 13764. |
| 11. | Jian WX, Zhang Z, Zhan JH. Donepezil attenuates vascular dementia in rats through increasing BDNF induced by reducing HDAC6 nuclear translocation. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2020; 41: 588-98. |
| 12. | Xu P, Liang L, Bai X. Clinical observation on the effect of modified Qufeng Tongqiao recipe on cognitive dysfunction after stroke. Shi Jie Zui Xin Yi Xue Xin Xi Wen Zhai 2019; 19: 16-7. |
| 13. | Ye LS, Bai X, Zhang DC. Observation on the effect of Qufeng Tongqiao recipe in the treatment of post circulatory transient ischemic attack. Zhong Guo Yi Liao Ji Qiu 2022; 31: 1415-8. |
| 14. | Ren JH, Xu P, Li SY, et al. The effect and mechanism of Tongqiao Yizhi granules on blood-brain barrier function and angiogenesis in vascular dementia rats. Xian Dai Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Ji 2022; 31: 3238-3245. |
| 15. | Li SY, Wang LX, Pu YT, Wang RQ, Tang HM, Bai X. Study on the effect of Tongqiao Yizhi Granule on apoptosis of hippocampal neurons in rats with vascular dementia through cAMP/PKA-CREB signal pathway. Zhong Yao Yao Li Yu Lin Chuang 2020; 36: 190-5. |
| 16. | Wang G, Zhao G, Chao X, Xie L, Wang H. The characteristic of virulence, biofilm and antibiotic resistance of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2020; 17: 6278. |
| 17. | Yang Q, Wu SM, Wang CM, et al. Effects of decabromodiphenyl ether exposure on learning and memory and hippocampal NMDA receptors in rats. Xi Nan Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 2022; 45: 211-6. |
| 18. |
Borody TJ, Paramsothy S, Agrawal G. Fecal microbiota transplantation: indications, methods, evidence, and future directions. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 2013; 15: 337.
DOI PMID |
| 19. | Djoumbou FY, Eisner R, Knox C. Classyfire: automated chemical classification with a comprehensive, computable taxonomy. J Cheminform 2016; 8: 61. |
| 20. | Lazarov O, Hollands C. Hippocampal neurogenesis: learning to remember. Prog Neurobiol 2016; 138-40: 1-18. |
| 21. | Georgy GS, Nassar NN, Mansour HA, Abdallah DM. Cerebrolysin ameloriates cognitive deficits in type Ⅲ diabetic rats. PLoS One 2013; 8: e64847. |
| 22. |
Rosenberg GA. Extracellular matrix inflammation in vascular cognitive impairment and dementia. Clin Sci (Lond) 2017; 131: 425-37.
DOI PMID |
| 23. |
Skoog I, Korczyn AD, Guekht A. Neuroprotection in vascular dementia: a future path. J Neurol Sci 2012; 322: 232-6.
DOI PMID |
| 24. | Wang HX, Wang YP. Gut microbiota-brain axis. Chin Med J (Engl) 2016; 129: 2373-80. |
| 25. |
McDonald AJ, Mott DD. Functional neuroanatomy of amygdalohippocampal interconnections and their role in learning and memory. J Neurosci Res 2017; 95: 797-820.
DOI PMID |
| 26. | Qiao L, Li B, Li Q. Effects of polygonum multiflorum on vascular dementia and IL-6, IL-8 and TNF- α Horizontal influence. Shangxi Zhong Yi 2018; 39: 1177-80. |
| 27. |
Ohland CL, Kish L, Bell H. Effects of Lactobacillus helveticus on murine behavior are dependent on diet and genotype and correlate with alterations in the gut microbiome. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2013; 38: 1738-47.
DOI PMID |
| 28. | Huang HM, Wu XX, Wang Y, et al. Effects of excessive intake of free sugars on colitis mice and gut microbiota. Xi Nan Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 2021; 44: 619-27. |
| 29. | Wang L, Yang JW, Lin LT. Acupuncture attenuates inflammation in microglia of vascular dementia rats by inhibiting miR-93-mediated low-doseR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2020; 2020: 8253904. |
| 30. |
Toombs-Ruane LJ, Benschop J, Burgess S, Priest P, Murdoch DR, French NP. Multidrug resistant enterobacteriaceae in New Zealand: a current perspective. N Z Vet J 2017; 65: 62-70.
DOI PMID |
| 31. | Iljazovic A, Roy U, Gálvez EJC. Perturbation of the gut microbiome by Prevotella spp. enhances host susceptibility to mucosal inflammation. Mucosal Immunol 2021; 14: 113-24. |
| 32. | Zafar H, Saier MH. Gut Bacteroides species in health and disease. Gut Microbes 2021; 13: 1-20. |
| 33. |
O'Callaghan J, O'Toole PW. Lactobacillus: host-microbe relationships. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 2013; 358: 119-54.
DOI PMID |
| 34. | Rocha-Ramírez LM, Pérez-solano RA, Castañón-Alonso SL, et al. Probiotic Lactobacillus strains stimulate the Inflammatory response and activate human macrophages. J Immunol Res 2017; 2017: 4607491. |
| 35. |
Wu H, Xie S, Miao J. Lactobacillus reuteri maintains intestinal epithelial regeneration and repairs damaged intestinal mucosa. Gut Microbes 2020; 11: 997-1014.
DOI PMID |
| 36. |
Rudolphi KA, Schubert P. Modulation of neuronal and glial cell function by adenosine and neuroprotection in vascular dementia. Behav Brain Res 1997; 83: 123-8.
PMID |
| 37. | Du B, Zhang Y, Liang M. N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification and its clinical relevance in cognitive dysfunctions. Aging (Albany NY) 2021; 13: 20716-37. |
| 38. |
Rudman D, Mattson DE, Feller AG. Serum fatty acid profile of elderly tube-fed men in a nursing home. J Am Geriatr Soc 1989; 37: 229-34.
PMID |
| 39. |
Rönnemaa E, Zethelius B, Vessby B, Lannfelt L, Byberg L, Kilander L. Fatty-acid composition and the risk of Alzheimer's disease: a longitudinal population-based study. Eur J Clin Nutr 2012; 66: 885-90.
DOI PMID |
| 40. | Li CY, Zhang L, Li J. Effect of endogenous arginine-vasopressin arising from the paraventricular nucleus on learning and memory functions in vascular dementia model rats. Biomed Res Int 2017; 2017: 3214918. |
| [1] | ZHANG Lina, LIN Xiu, ZHAO Xin, LI Wenjuan, ZHAO Ye. Study on the mechanism of Fuzi Lizhong decoction (附子理中汤) in the treatment of colorectal cancer of spleen kidney Yang deficiency from the perspective of intestinal flora and hypoxia inducible factor-1α signalling pathway [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(4): 845-851. |
| [2] | LIU Qian, XIAO Liuchen, YUAN Yue, DANG Xiaopeng, WEN Jie, TAN Moye, LIU Yuxin, GU Hongfeng, XIE Xuejiao. Xiong's Shiwei Wendan decoction (熊氏十味温胆汤) attenuates plaque lesions and balances gut microbiota dysbiosis in ApoE-/- mice with high-fat diet [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(3): 508-517. |
| [3] | WU Jiaman, NING Yan, TAN Liya, MA Fei, LIN Yanting, ZHUO Yuanyuan. Difference of the gut microbiota of premature ovarian insufficiency in two traditional Chinese syndromes [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(1): 132-139. |
| [4] | WANG Yiying, LIU Jianjun, XIONG Yongjian, ZHANG Yongli, WEN Yuqi, XUE Mengli, GUO Huishu, QIU Juanjuan. Analysis of composition of gut microbial community in a rat model of functional dyspepsia treated with Simo Tang (四磨汤) [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(6): 1168-1176. |
| [5] | LIAO Mengting, LI Tao, CHU Fuhao, CHEN Yan, LOU Ni, ZHUANG Yuan, BO Rongqiang, DING Xia. Weichang’ an pill (胃肠安丸) alleviates functional dyspepsia through modulating brain-gut peptides and gut microbiota [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(6): 1177-1186. |
| [6] | HUANG Xiaona, LI Yuzhen, ZHU Chenyang, ZHU Hengzhou, JIANG Chenyu, ZHU Xiaodan, ZHANG Chencen, JIN Chunhui. Weitiao No. 3 (微调3号方) enhances the efficacy of anti-programmed cell death protein-1 immunotherapy by modulating the intestinal microbiota in an orthotopic model of gastric cancer mice [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(5): 906-915. |
| [7] | SUN Chuanbo, XU Guangpei, JIANG Ping, HUANG Shipping, CHEN Cunwu, HE Yanfei. Protective effect of Zhizi Huangqi Shanzha formula (栀子黄芪山楂方) on aflatoxin poisoning in mice and its effect on intestinal flora [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(5): 926-933. |
| [8] | GAO Jiaming, ZHANG Yehao, Chen Yuanyuan, JIN Long, ZHAO Jianfeng, GUO Hao, FU Jianhua. Qingfei Zhisou oral liquid (清肺止嗽口服液) alleviates fever-induced inflammation by regulating arachidonic acid and lysophospholipids metabolism and inhibiting hypothalamus transient receptor potential ion channels expression [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(5): 954-962. |
| [9] | SONG Zhenguang, YANG Bin, WANG Fei, YAN Dongmei, ZHOU Xiaoqing, HUANG Liping, GAO Xuemei, LI Bin, HUANG Luqi. Study on the four Qi of Pfaffia glomerata based on the metabolomics technology and comparison of Dangshen (Radix Codonopsis) in the equivalent substitution prescription [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(4): 713-721. |
| [10] | YAN Jing, FENG Huimin, QIU Fang, WANG Haijun, YIN Luyun, JIN Xiaofei, ZHAO Jiyu, WANG Hongyang, YAN Xiaoqin. Effect on serum metabolomics of rats with premature ovarian insufficiency by Zhibian (BL54) through Shuidao (ST28) acupuncture [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(4): 722-733. |
| [11] | WANG Xiang, HUANG Jianping, WANG Yupeng, WANG Qilong, JING Yajiang, ZHANG Gang, PENG Liang, GAO Jing, WANG Hongyan, YAN Yonggang. Differential metabolite analysis of the pharmacodynamic differences between different ratios of Dahuang (Radix Et Rhizoma Rhei Palmati)-Taoren (Semen Persicae) herb pair [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(3): 515-523. |
| [12] | REN Li, HAI Yang, YANG Xue, LUO Xianqin. Yemazhui (Herba Eupatorii Lindleyani) ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via modulation of the toll-like receptor 4/nuclear factor kappa-B/nod-like receptor family pyrin domain-containing 3 protein signaling pathway and intestinal flora in rats [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(2): 303-314. |
| [13] | JING Wenguang, LIN Xiaoyu, LI Chu, ZHAO Xiaoliang, CHENG Xianlong, WANG Penglong, WEI Feng, MA Shuangcheng. Anti-inflammatory mechanism of the non-volatile ingredients originated from Guanghuoxiang (Pogostemonis Herba) based on high performance liquid chromatography-heated electron spray ionization-high resolution mass spectroscope and cell metabolomics [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(2): 260-267. |
| [14] | LI Chaoran, YANG Yan, FENG Chuwen, LI Heng, QU Yuanyuan, WANG Yulin, WANG Delong, WANG Qingyong, GUO Jing, SHI Tianyu, SUN Xiaowei, WANG Xue, HOU Yunlong, SUN Zhongren, YANG Tiansong. Integrated 'omics analysis for the gut microbiota response to moxibustion in a rat model of chronic fatigue syndrome [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1176-1189. |
| [15] | WANG Miao, ZHU Yan, ZHAO Hui, ZHAO Hongfang. Moxibustion enables protective effects on rheumatoid arthritis-induced myocardial injury via transforming growth factor beta1 signaling and metabolic reprogramming [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1190-1199. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||


