Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (4): 722-733.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20231226.001
• Original articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect on serum metabolomics of rats with premature ovarian insufficiency by Zhibian (BL54) through Shuidao (ST28) acupuncture
YAN Jing1, FENG Huimin1, QIU Fang1, WANG Haijun1, YIN Luyun1, JIN Xiaofei1( ), ZHAO Jiyu2, WANG Hongyang1, YAN Xiaoqin3
), ZHAO Jiyu2, WANG Hongyang1, YAN Xiaoqin3
- 1 Second Clinical College of Shanxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinzhong 030619, China
2 Research Center of Experimental Acupuncture Science, Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin 301617, China
3 Department of Cervical and Lumbar Vertebral Diseases, Jinzhong Hospital Affiliated to Shanxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinzhong 030600, China
-
Received:2023-05-23Accepted:2023-09-12Online:2024-08-15Published:2023-12-26 -
Contact:JIN Xiaofei, Second Clinical College of Shanxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinzhong 030619, China.jinxiaofei@sxtcm.edu.cn Telephone: +86-13333419096 -
Supported by:Research Grant from the Natural Science Research Program of Shanxi Province: Based on Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry, the effect of "Zhibian (BL54) through Shuidao (ST28)" Needle Method on Ovarian Metabolism and Apoptosis Pathways in rats with Premature Ovarian Insufficiency was Discussed(2022030211216)
Cite this article
YAN Jing, FENG Huimin, QIU Fang, WANG Haijun, YIN Luyun, JIN Xiaofei, ZHAO Jiyu, WANG Hongyang, YAN Xiaoqin. Effect on serum metabolomics of rats with premature ovarian insufficiency by Zhibian (BL54) through Shuidao (ST28) acupuncture[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(4): 722-733.
share this article
| Group | n | Before modeling | After modeling | Post intervention |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 12 | 245±7 | 266±11 | 316±15 |
| POI | 12 | 244±10 | 253±11a | 286±13b |
| SA+POI | 12 | 244±7 | 255±12a | 288±13 |
| ZS+POI | 12 | 244±9 | 255±14a | 301±17c |
Table 1 Changes in body weight of rats (g, $\bar{x}±s$)
| Group | n | Before modeling | After modeling | Post intervention |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 12 | 245±7 | 266±11 | 316±15 |
| POI | 12 | 244±10 | 253±11a | 286±13b |
| SA+POI | 12 | 244±7 | 255±12a | 288±13 |
| ZS+POI | 12 | 244±9 | 255±14a | 301±17c |
| Group | n | After modeling | Post-intervention | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FSH (IU/L) | LH (mIU/mL) | E2 (pmol/L) | FSH (IU/L) | LH (mIU/mL) | E2 (pmol/L) | |||
| Control | 12 | 3.1±0.9 | 22.7±6.7 | 39.3±9.8 | 4.0±1.1 | 20.9±5.0 | 43.7±6.1 | |
| POI | 12 | 6.0±1.3a | 36.7±5.4a | 26.0±8.7a | 7.4±1.4a | 36.3±4.2a | 28.0±6.0a | |
| SA+POI | 12 | 5.8±0.9a | 38.8±5.1a | 29.6±6.5a | 7.3±0.9 | 35.2±4.4 | 30.6±6.1 | |
| ZS+POI | 12 | 6.3±0.9a | 36.8±6.2a | 27.1±8.6a | 6.1±0.9b | 30.3±4.4b | 38.0±7.0b | |
Table 2 Changes in serum hormone levels ($\bar{x}±s$)
| Group | n | After modeling | Post-intervention | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FSH (IU/L) | LH (mIU/mL) | E2 (pmol/L) | FSH (IU/L) | LH (mIU/mL) | E2 (pmol/L) | |||
| Control | 12 | 3.1±0.9 | 22.7±6.7 | 39.3±9.8 | 4.0±1.1 | 20.9±5.0 | 43.7±6.1 | |
| POI | 12 | 6.0±1.3a | 36.7±5.4a | 26.0±8.7a | 7.4±1.4a | 36.3±4.2a | 28.0±6.0a | |
| SA+POI | 12 | 5.8±0.9a | 38.8±5.1a | 29.6±6.5a | 7.3±0.9 | 35.2±4.4 | 30.6±6.1 | |
| ZS+POI | 12 | 6.3±0.9a | 36.8±6.2a | 27.1±8.6a | 6.1±0.9b | 30.3±4.4b | 38.0±7.0b | |

Figure 1 ovarian tissue morphology A: gross ovarian tissue specimen in control group; B: gross ovarian tissue specimen in POI group; C: gross ovarian tissue specimen in SA + POI group; D: gross ovarian tissue specimen in ZS + POI group; E: pathomorphological change ovarian tissue in control group; F: pathomorphological change ovarian tissue in POI group; G: pathomorphological change ovarian tissue in SA + POI group; H: pathomorphological change of ovarian tissue in ZS + POI group (HE, × 200). Control: normal feeding, without any treatment. POI: POI model was induced by intraperitoneal injection of CTX (2 mg/mL) for 15 d; SA+POI: sham acupuncture intervention in CTX-induced POI rats for 4 weeks; ZS + POI: Zhibian (BL54) through Shuidao (ST28) acupuncture intervention in CTX-induced POI rats for 4 weeks. PF: primary follicle; EA: early antral follicle; AF: atresia follicle; HE: hematoxylin-eosin staining; POI: premature ovarian insufficiency; CTX: cyclophosphamide; SA: sham acupuncture; ZS: Zhibian (BL54) through Shuidao (ST28) acupuncture.
| Group | n | Left ovary | Right ovary | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight (mg) | Coefficient (mg/g) | Weight (mg) | Coefficient (mg/g) | |||
| Control | 12 | 73.333±6.513 | 0.233±0.023 | 71.667±12.673 | 0.227±0.037 | |
| POI | 12 | 44.167±12.401a | 0.153±0.039a | 45.000±7.977a | 0.157±0.026a | |
| SA+POI | 12 | 45.833±9.962 | 0.159±0.033 | 43.333±10.731 | 0.150±0.032 | |
| ZS+POI | 12 | 56.667±6.513b | 0.188±0.020b | 58.333±11.146b | 0.194±0.037b | |
Table 3 Changes in ovarian weight and coefficient ($\bar{x}±s$)
| Group | n | Left ovary | Right ovary | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight (mg) | Coefficient (mg/g) | Weight (mg) | Coefficient (mg/g) | |||
| Control | 12 | 73.333±6.513 | 0.233±0.023 | 71.667±12.673 | 0.227±0.037 | |
| POI | 12 | 44.167±12.401a | 0.153±0.039a | 45.000±7.977a | 0.157±0.026a | |
| SA+POI | 12 | 45.833±9.962 | 0.159±0.033 | 43.333±10.731 | 0.150±0.032 | |
| ZS+POI | 12 | 56.667±6.513b | 0.188±0.020b | 58.333±11.146b | 0.194±0.037b | |
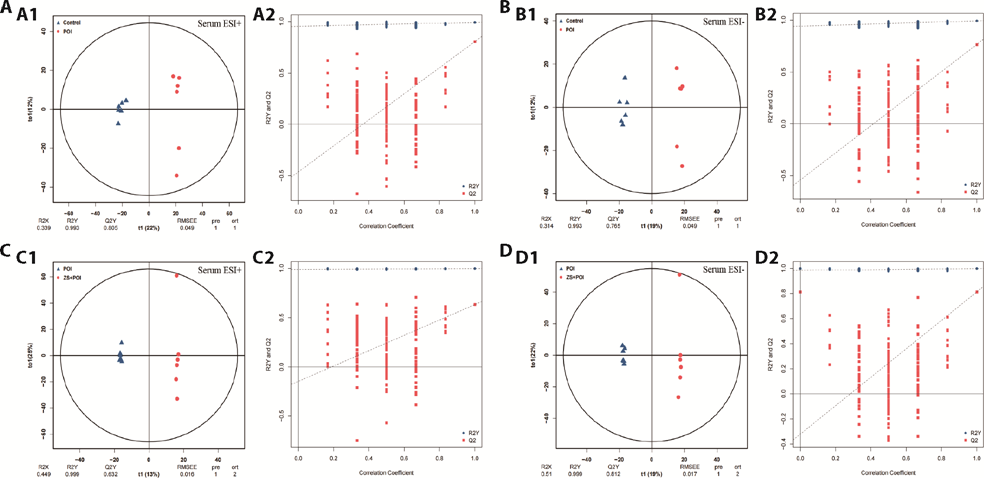
Figure 2 OPLS-DA score plots and model replacement test plots of rat serum samples A: OPLS-DA score plot and model replacement test plot of the control group vs the POI group in positive ion mode; B: OPLS-DA score plot and model replacement test plot of the control group vs the POI group in negative ion mode; C: OPLS-DA score plot and model replacement test plot of the POI group vs the ZS + POI group in positive ion mode; D: OPLS-DA score plot and model replacement test plot of the POI group vs the ZS+POI group in negative ion mode; A1, B1, C1, D1: OPLS-DA score plot; A2, B2, C2, D2: model replacement test plot. In the OPLS-DA score plots, the x-axis (t1) represents the prediction component (intergroup difference component), the y-axis (t2) represents the orthogonal component (intragroup difference component), and the percentage of the horizontal y-axis represents the proportion of this component in the total variance. In the model replacement test plots, the x-axis represents the correlation between the permutation group and the original model group, the y-axis represents the value of R2Y or Q2Y (where R2γ and Q2γ with 1 in the x-axis are the values of the original model), the blue point and the red point represent the R2γ and Q2γ of the replaced model, respectively, and the imaginary line is the fitted regression line. Control: normal feeding, without any treatment; POI: POI model was induced by intraperitoneal injection of CTX (2 mg/mL) for 15 d; ZS+POI: Zhibian (BL54) through Shuidao (ST28) acupuncture intervention in CTX-induced POI rats for 4 weeks. ESI: electron spray ionization; RMSEE: root mean square error, pre: number of predicted components, ort: number of orthogonal components; OPLS-DA: orthogonal partial least squares-discrimination analysis; POI: premature ovarian insufficiency; CTX: cyclophosphamide; ZS: Zhibian (BL54) through Shuidao (ST28) acupuncture.
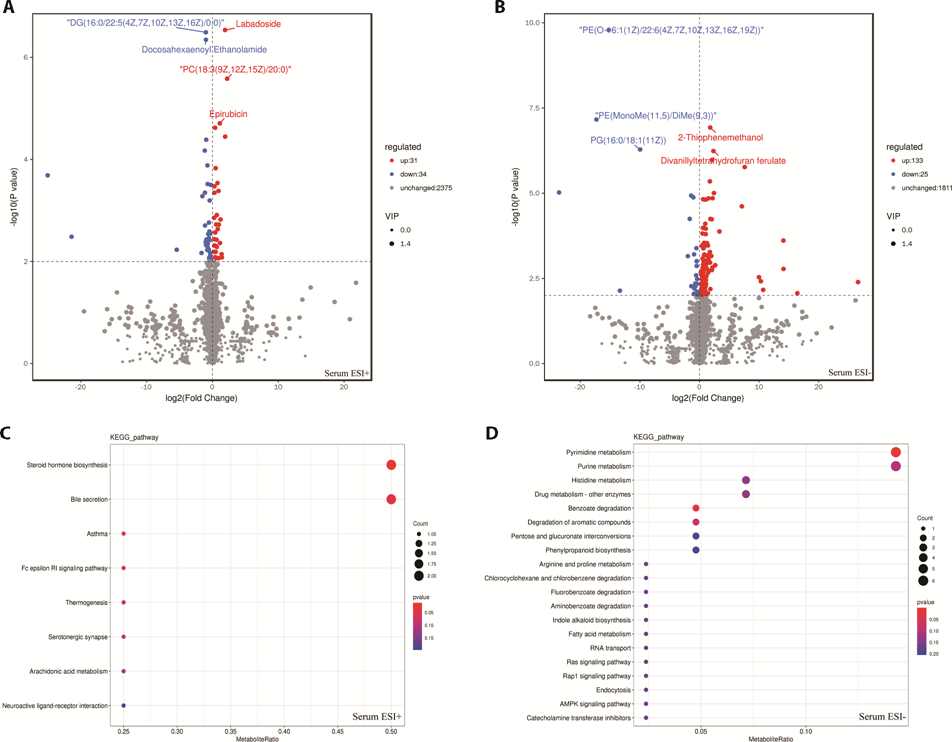
Figure 3 Screening of metabolic differentials and KEGG pathway enrichment maps in serum of POI model intervened by acupuncture intervention A: volcano map in positive ion mode, B: volcano map in negative ion mode, C: KEGG pathway enrichment map in positive ion mode, D: KEGG pathway enrichment map in negative ion mode. In the volcano map, the x-axis represents the difference multiple, the y-axis represents the P-value, and the scatter size represents the VIP value. Blue dots indicate down-regulation, red dots indicate up-regulation, and gray dots indicate no significant difference. In the KEGG pathway enrichment map, the x-axis is the ratio of the number of differential metabolites to the total number of metabolites, and the y-axis is the name of the pathway. The larger the point, the more the number of metabolites enriched, and the redder the color of the point, the more significant the enrichment pathway. KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes; POI: premature ovarian insufficiency.
| Name | Formula | Mass-to-charge ratio (m/z) | RT (min) | Control vs POI | POI vs ZS+POI | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FC | P value | VIP | Trend | FC | P value | VIP | Trend | |||||
| Divanillyltetrahydrofuran ferulate | C30H32O8 | 1099.4293 | 11.4854 | 0.2409 | 0.0001 | 2.1464 | ↓a | 4.4102 | 0.0000 | 2.2110 | ↑c | |
| Rolitetracycline | C27H33N3O8 | 1099.4546 | 13.5905 | 0.1087 | 0.0011 | 2.0491 | ↓b | 6.5169 | 0.0000 | 2.1883 | ↑c | |
| Trans-ferulic acid | C10H10O4 | 239.0564 | 2.9167 | 0.6022 | 0.0006 | 1.9304 | ↓a | 1.5964 | 0.0027 | 1.8209 | ↑b | |
| Tryptamine | C10H12N2 | 159.0912 | 2.4098 | 0.7189 | 0.0023 | 1.8795 | ↓b | 4.2828 | 0.0000 | 2.2682 | ↑c | |
| Neuraminic acid | C9H17NO8 | 288.0653 | 2.0602 | 0.4761 | 0.0038 | 1.8148 | ↓b | 1.6599 | 0.0095 | 1.6740 | ↑b | |
| Eupatilin | C18H16O7 | 343.0840 | 4.2009 | 0.5563 | 0.0030 | 1.7867 | ↓b | 2.0420 | 0.0015 | 1.8760 | ↑b | |
Table 4 Effect of "Zhibian (BL54) through Shuidao (ST28)" acupuncture on potential biomarkers in the serum of rats with POI
| Name | Formula | Mass-to-charge ratio (m/z) | RT (min) | Control vs POI | POI vs ZS+POI | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FC | P value | VIP | Trend | FC | P value | VIP | Trend | |||||
| Divanillyltetrahydrofuran ferulate | C30H32O8 | 1099.4293 | 11.4854 | 0.2409 | 0.0001 | 2.1464 | ↓a | 4.4102 | 0.0000 | 2.2110 | ↑c | |
| Rolitetracycline | C27H33N3O8 | 1099.4546 | 13.5905 | 0.1087 | 0.0011 | 2.0491 | ↓b | 6.5169 | 0.0000 | 2.1883 | ↑c | |
| Trans-ferulic acid | C10H10O4 | 239.0564 | 2.9167 | 0.6022 | 0.0006 | 1.9304 | ↓a | 1.5964 | 0.0027 | 1.8209 | ↑b | |
| Tryptamine | C10H12N2 | 159.0912 | 2.4098 | 0.7189 | 0.0023 | 1.8795 | ↓b | 4.2828 | 0.0000 | 2.2682 | ↑c | |
| Neuraminic acid | C9H17NO8 | 288.0653 | 2.0602 | 0.4761 | 0.0038 | 1.8148 | ↓b | 1.6599 | 0.0095 | 1.6740 | ↑b | |
| Eupatilin | C18H16O7 | 343.0840 | 4.2009 | 0.5563 | 0.0030 | 1.7867 | ↓b | 2.0420 | 0.0015 | 1.8760 | ↑b | |
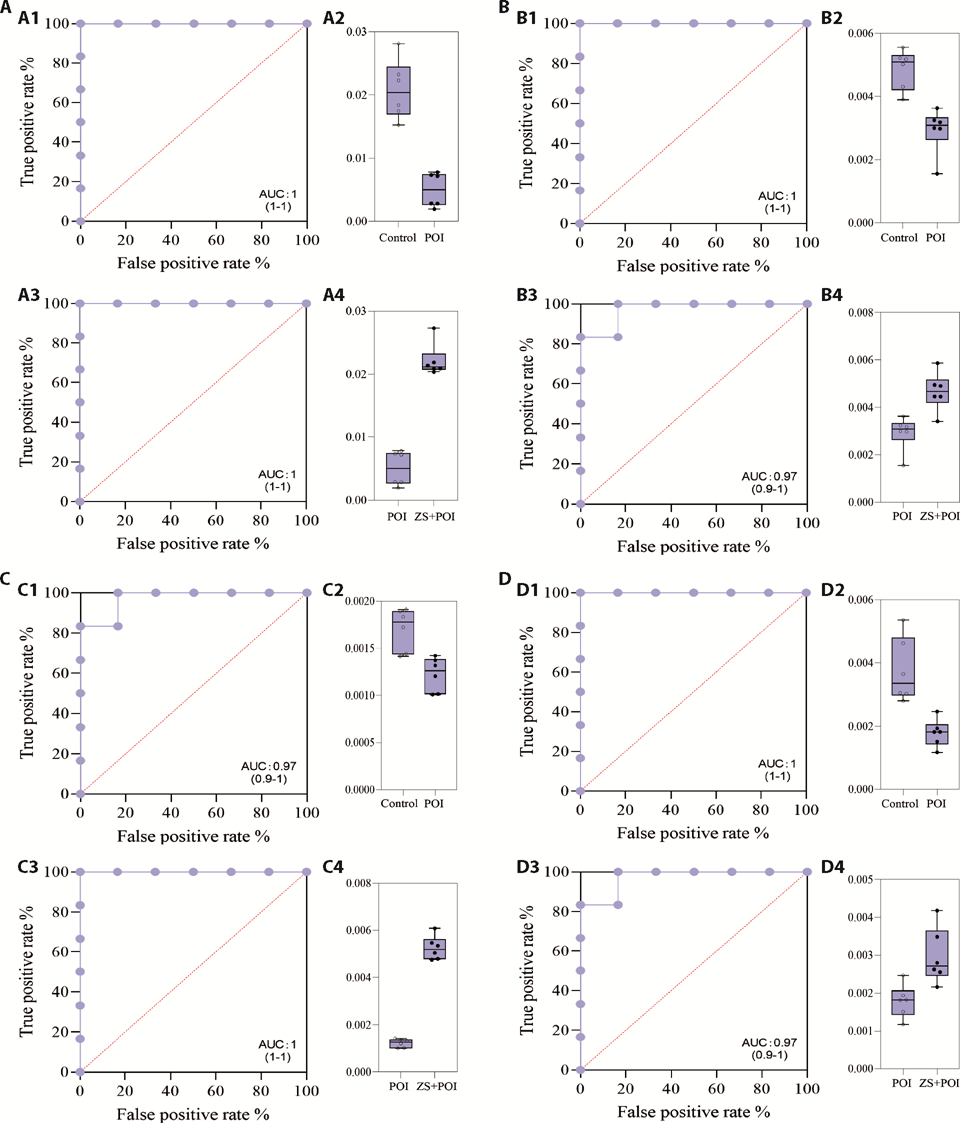
Figure 4 ROC curve and box plot of acupuncture on potential biomarkers in serum of rats with POI A: divanillyltetrahydrofuran ferulate; B: trans-ferulic acid; C: tryptamine; D: neuraminic acid. Each plot represents the ROC curve and metabolic box plot of the same metabolite in the Control vs POI group (above) and ZS + POI vs POI group (below). A1, B1, C1, D1: ROC curve plot in the Control vs POI group; A2, B2, C2, D2: box plot in the Control vs POI group; A3, B3, C3, D3: ROC curve plot in the ZS+POI vs POI group; A4, B4, C4, D4: box plot in the ZS + POI vs POI group. In the ROC curve plot, the area surrounded by the blue dot solid line and the straight line (x = 1, y = 0) is AUC, the closer the AUC value is to 1, the higher the accuracy of the prediction. In the box plot, the content distribution of metabolites in each group was shown. Control: normal feeding, without any treatment; POI: POI model was induced by intraperitoneal injection of CTX (2 mg/mL) for 15 d; SA + POI: sham acupuncture intervention in CTX-induced POI rats for 4 weeks; ZS + POI: Zhibian (BL54) through Shuidao (ST28) acupuncture intervention in CTX-induced POI rats for 4 weeks. ROC: receiver operating characteristic curve; POI: premature ovarian insufficiency; ZS: Zhibian (BL54) through Shuidao (ST28) acupuncture; AUC: area under roc; CTX: cyclophosphamide.
| 1. | Wesevich V, Kellen AN, Pal L. Recent advances in understanding primary ovarian insufficiency. F1000Res 2020; 9: F1000 Faculty Rev-1101. |
| 2. |
Meirow D, Biederman H, Anderson RA, Wallace WH. Toxicity of chemotherapy and radiation on female reproduction. Clin Obstet Gynecol 2010; 53: 727-39.
DOI PMID |
| 3. |
Oktem O, Oktay K. Quantitative assessment of the impact of chemotherapy on ovarian follicle reserve and stromal function. Cancer 2007; 110: 2222-9.
DOI PMID |
| 4. |
Spears N, Lopes F, Stefansdottir A, et al. Ovarian damage from chemotherapy and current approaches to its protection. Hum Reprod Update 2019; 25: 673-93.
DOI PMID |
| 5. | Xu H, Bao X, Kong H, Yang J, Li Y, Sun Z. Melatonin protects against cyclophosphamide-induced premature ovarian failure in rats. Hum Exp Toxicol 2022; 41: 9603271221127430. |
| 6. |
Emadi A, Jones RJ, Brodsky RA. Cyclophosphamide and cancer: golden anniversary. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2009; 6: 638-47.
DOI PMID |
| 7. | Chen SL, Zhou XY. Clinical research advances on premature ovarian insufficiency. Shandong Da Xue Xue Bao (Yi Xue Ban) 2018; 56: 1-7. |
| 8. |
Torrealday S, Kodaman P, Pal L. Premature ovarian insufficiency-an update on recent advances in understanding and management. F1000Res 2017; 6: 2069.
DOI PMID |
| 9. | Nicholson JK, Lindon JC. Systems biology: metabonomics. Nature 2008; 455: 1054-6. |
| 10. |
Nicholson JK, Lindon JC, Holmes E. 'Metabonomics': understanding the metabolic responses of living systems to patho-physiological stimuli via multivariate statistical analysis of biolo-gical NMR spectroscopic data. Xenobiotica 1999; 29: 1181-9.
DOI PMID |
| 11. |
Zhang Y, Zhang A, Yan G, et al. High-throughput metabolomic approach revealed the acupuncture exerting intervention effects by perturbed signatures and pathways. Mol Biosyst 2014; 10: 65-73.
DOI PMID |
| 12. | Zhang HL, Si YM. Significance and practice exploration of Traditional Chinese Medicine syndrome research based on metabolomics. Zhong Hua Zhong Yi Yao Xue Kan 2021; 39: 21-4. |
| 13. | Fu XF, He YL. Establishment of ratmodel of chemotherapy-induced premature ovarian failure. Guangdong Yi Xue 2008: 1952-4. |
| 14. | China Association for Acupuncture and Moxibustion. Name and location of commonly used acupoints in experimental animals part 2: rats. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu 2021; 46: 351-2. |
| 15. | Burke AW, Broadhurst PL. Behavioural correlates of the oestrous cycle in the rat. Nature 1966; 209: 223-4. |
| 16. |
Scandroglio R. Sugli aspetti dell'epitelio della bagina del ratto nel corso del ciclo estrale. Ricerche istologiche ed istochimiche [On aspects of the epithelium of the rat vagina during the estrus cycle. Histological and histochemical studies]. Atti Accad Fisiocrit Siena Med Fis 1967; 16: 629-47.
PMID |
| 17. | Tian DH, Liu GS. Ling Shu Jing. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House, 2021: 1-4+22. |
| 18. | Hao CY, Zhang TS, Jin XF, Ji LX. Clinical application and expansion of 'Zhibian (BL54) through Shuidao (ST28)' acupuncture needling system. Zhong Guo Zhong Yi Ji Chu Yi Xue Za Zhi 2015; 21: 1433-4. |
| 19. | Rice-Evans CA, Miller NJ, Paganga G. Structure-antioxidant activity relationships of flavonoids and phenolic acids. Free Radic Biol Med 1996; 20: 933-56. |
| 20. |
Gupta A, Singh AK, Loka M, Pandey AK, Bishayee A. Ferulic acid-mediated modulation of apoptotic signaling pathways in cancer. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol 2021; 125: 215-57.
DOI PMID |
| 21. |
Haddad JJ. Redox and oxidant-mediated regulation of apoptosis signaling pathways: immuno-pharmaco-redox conception of oxidative siege versus cell death commitment. Int Immunopharmacol 2004; 4: 475-93.
DOI PMID |
| 22. | Roy S, Metya SK, Rahaman N, Sannigrahi S, Ahmed F. Ferulic scid in the treatment of post-diabetes testicular damage: relevance to the down regulation of apoptosis correlates with antioxidant status via modulation of TGF-β1, IL-1β and Akt signalling. Cell Biochem Funct 2014; 32: 115-24. |
| 23. | Li D, Rui YX, Guo SD, Luan F, Liu R, Zeng N. Ferulic acid: a review of its pharmacology, pharmacokinetics and derivatives. Life Sci 2021; 284: 119921. |
| 24. |
Cione E, Tucci P, Senatore V, et al. Synthesized esters of ferulic acid induce release of cytochrome c from rat testes mitochondria. J Bioenerg Biomembr 2008; 40: 19-26.
PMID |
| 25. | Lin QL, Wen QB, Ou SY, Wu LY, Lai FR. Scavenging of in vitro hydroxyl free radical using feruloyl-arabinose. Hua Nan Li Gong Da Xue Xue Bao (Zi Ran Ke Xue Ban) 2010; 38: 110-4. |
| 26. | Zhang X, Gao ZP. Research progress in ferulic acid. Zhong Guo Xian Dai Zhong Yao 2020; 22: 138-47. |
| 27. |
Ayala ME. Brain serotonin, psychoactive drugs, and effects on reproduction. Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem 2009; 9: 258-76.
PMID |
| 28. | Li SQ, Yang B, Xu CT. The research status for neurotransmitter 5-hydroxytryptamine. Lin Chuang Yi Xue Gong Cheng 2010; 17: 145-7. |
| 29. |
Nikishin DA, Alyoshina NM, Shmukler YB. Synthesis and membrane transport of serotonin in the developing ovarian follicle of mouse. Dokl Biochem Biophys 2018; 478: 4-7.
DOI PMID |
| 30. |
Tanaka E, Baba N, Toshida K, Suzuki K. Serotonin stimulates steroidogenesis in rat preovulatory follicles: involvement of 5-HT2 receptor. Life Sci 1993; 53: 563-70.
PMID |
| 31. |
Cruz MH, Leal CL, da Cruz JF, Tan DX, Reiter RJ. Role of melatonin on production and preservation of gametes and embryos: a brief review. Anim Reprod Sci 2014; 145: 150-60.
DOI PMID |
| 32. | Ezzati M, Velaei K, Kheirjou R. Melatonin and its mechanism of action in the female reproductive system and related malignancies. Mol Cell Biochem 2021; 476: 3177-90. |
| 33. |
Tamura H, Takasaki A, Taketani T, et al. The role of melatonin as an antioxidant in the follicle. J Ovarian Res 2012; 5: 5.
DOI PMID |
| 34. |
Keshavarzi S, Salehi M, Farifteh-Nobijari F, et al. Melatonin modifies histone acetylation during in vitro maturation of mouse oocytes. Cell J 2018; 20: 244-9.
DOI PMID |
| 35. |
Kilic U, Kilic E, Reiter RJ, Bassetti CL, Hermann DM. Signal transduction pathways involved in melatonin-induced neuroprotection after focal cerebral ischemia in mice. J Pineal Res 2005; 38: 67-71.
PMID |
| 36. | Barberino RS, Lins TLBG, Monte APO, et al. Melatonin attenuates cyclophosphamide-induced primordial follicle loss by interaction with MT1 receptor and modulation of PTEN/Akt/FOXO3a proteins in the mouse ovary. Reprod Sci 2022; 29: 2505-14. |
| 37. |
Tang J, Chen R, Wang L, et al. Melatonin attenuates thrombin-induced inflammation in BV2 cells and then protects HT22 cells from apoptosis. Inflammation 2020; 43: 1959-70.
DOI PMID |
| 38. |
Varki A. Sialic acids in human health and disease. Trends Mol Med 2008; 14: 351-60.
DOI PMID |
| 39. | Lewis AL, Chen X, Schnaar RL, Varki A. Sialic acids and other nonulosonic acids. In: Varki A, Cummings RD, Esko JD, et al., eds. Essentials of glycobiology. 4th ed. New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, 2022: 185-204. |
| 40. |
Bhide GP, Colley KJ. Sialylation of N-glycans: mechanism, cellular compartmentalization and function. Histochem Cell Biol 2017; 147: 149-74.
DOI PMID |
| 41. | Zhou X, Yang G, Guan F. Biological functions and analytical strategies of sialic acids in tumor. Cells 2020; 9: 273. |
| 42. | Wang X, Chen ZJ. A decade of discovery: the stunning progress of premature ovarian insufficiency research in China. Biol Reprod 2022; 107: 27-39. |
| 43. |
Shoham Z, Schachter M. Estrogen biosynthesis-regulation, action, remote effects, and value of monitoring in ovarian stimulation cycles. Fertil Steril 1996; 65: 687-701.
PMID |
| 44. | Liu DE. Gynecological sex hormone regulation mechanism. Zhong Guo Shi Yong Fu Ke Yu Chan Ke Za Zhi 2000: 18-20. |
| 45. | Monniaux D, Huet C, Pisselet C, Mandon-Pépin B, Monget P. Mechanism, regulation, and manipulations of follicular atresia. Contracept Fertil Sex 1998; 26: 528-35. |
| 46. |
Waetzig V, Herdegen T. Context-specific inhibition of JNKs: overcoming the dilemma of protection and damage. Trends Pharmacol Sci 2005; 26: 455-61.
PMID |
| 47. | Bode AM, Dong ZG. The functional contrariety of JNK. Mol Carcinog 2007; 46: 591-8. |
| 48. | Jin XF, Yan J, Zhao JY, Yin LY, Ma MN, Wang HY. Effect of penetrative needling of "Zhibian" (BL54) through "Shuidao" (ST28) on expression of TRAIL and its receptors in rats with premature ovrian insufficiency. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu 2023; 48: 259-66+80. |
| 49. |
Malamitsi-puchner A, Sarandakou A, Tziotis J, Stavreus-Evers A, Tzonou A, Landgren BM. Circulating angiogenic factors during periovulation and the luteal phase of normal menstrual cycles. Fertil Steril 2004; 81: 1322-7.
PMID |
| 50. | Yan J, Zhao JY, Yin LY, Yan XQ, Jin XF. Effect of acupuncture at "Zhibian" (BL54) through "Shuidao" (ST28) on the expression of apoptosis-related factors in rats with premature ovarian insufficieney based on oxidative stress. Zhong Guo Zhen Jiu 2023; 43: 454-60. |
| [1] | LI Zhongzheng, ZHAO Yadan, Ma Weigang, Zhang Yonglong, XU Zhifang, XI Qiang, LI Yanqi, QIN Siru, ZHANG Zichen, WANG Songtao, ZHAO Xue, LIU Yangyang, GUO Yi, GUO Yongming. Adenosine triphosphate mediates the pain tolerance effect of manual acupuncture at Zusanli (ST36) in mice [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(4): 660-669. |
| [2] | SONG Zhenguang, YANG Bin, WANG Fei, YAN Dongmei, ZHOU Xiaoqing, HUANG Liping, GAO Xuemei, LI Bin, HUANG Luqi. Study on the four Qi of Pfaffia glomerata based on the metabolomics technology and comparison of Dangshen (Radix Codonopsis) in the equivalent substitution prescription [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(4): 713-721. |
| [3] | CHEN Yonglin, OUYANG Ling, MENG Lingling, WU Bufan, PENG Rou, LIU Sitong, HOU Dan, WANG Yaling, JING Xinyue, LU Shengfeng, FU Shuping. Electroacupuncture ameliorates blood-brain barrier disruption after ischemic stroke through histone acetylation regulation at the matrix metalloproteinase 9 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 2 genes [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(4): 734-744. |
| [4] | SUN Junjian, XIE Henghui, LI Huanhuan, TIAN Xiangming, FANG Yigong, ZHOU Wenhui. Acupuncture improves the live birth of patients with repeated implantation failure: a retrospective cohort study [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(4): 830-838. |
| [5] | ZHU Wenting, GUO Changqing, DU Mei, MA Yunxuan, CUI Yongqi, CHEN Xilin, GUO Changqing. Acupotomy alleviates knee osteoarthritis in rabbit by regulating chondrocyte mitophagy via Pink1-Parkin pathway [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(3): 468-477. |
| [6] | WANG Xiang, HUANG Jianping, WANG Yupeng, WANG Qilong, JING Yajiang, ZHANG Gang, PENG Liang, GAO Jing, WANG Hongyan, YAN Yonggang. Differential metabolite analysis of the pharmacodynamic differences between different ratios of Dahuang (Radix Et Rhizoma Rhei Palmati)-Taoren (Semen Persicae) herb pair [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(3): 515-523. |
| [7] | YU Wenxi, TANG Lina, LI Hongtao, WANG Yonggang, SHEN Zan. Neiguan (PC6) acupoint stimulation for preventing chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting: a cost-effective supplement in guideline-inconsistent chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting prophylaxis subgroup [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(3): 581-585. |
| [8] | WANG Dingyue, YU Yana, WANG Yiyuan, ZHANG Zhen. Musculoskeletal ultrasound to evaluate the efficacy of acupuncture: a review [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(3): 629-632. |
| [9] | WANG Shaosong, SUN Jingqing, FENG Qingyin, LI Bin, WANG Xin, YUAN Fan, CUI Yingxue. Effectivenss of electroacupuncture for skeletal muscle pain in Parkinson's disease: a Clinical randomized controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(2): 388-395. |
| [10] | ZHANG Xinchang, HUANG Zheng, HUANG Peiyan, YANG Mengning, ZHANG Zhihui, NI Guangxia. Mechanism of acupuncture in attenuating cerebral ischaemia-reperfusion injury based on nuclear receptor coactivator 4 mediated ferritinophagy [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(2): 345-352. |
| [11] | JING Wenguang, LIN Xiaoyu, LI Chu, ZHAO Xiaoliang, CHENG Xianlong, WANG Penglong, WEI Feng, MA Shuangcheng. Anti-inflammatory mechanism of the non-volatile ingredients originated from Guanghuoxiang (Pogostemonis Herba) based on high performance liquid chromatography-heated electron spray ionization-high resolution mass spectroscope and cell metabolomics [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(2): 260-267. |
| [12] | QIN Xiaoyu, WANG Chunai, XUE Jianjun, ZHANG Jie, LU Xiaoting, DING Shengshuang, GE Long, WANG Minzhen. Efficacy of electroacupuncture on myocardial protection and postoperative rehabilitation in patients undergoing cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 1-15. |
| [13] | SUN Qianhui, CHENG Kai, DAI Xingye, YANG Zhiwen, WU Xiaoling, XU Chang, QIU Xinghua, GAO Xiaofeng, LIU Daonan, YANG Qirui. Effect of electroacupuncture at Neiguan (PC6) at different time points on myocardial ischemia reperfusion arrhythmia in rats [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 113-121. |
| [14] | LIU Tingting, LIU Tongou, LIU Mingfu. Effectiveness and safety of acupuncture in treatment of pregnancy-related symptoms: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 16-26. |
| [15] | YANG Yi, YE Huijun, ZHENG Huiling, JIN Lihua. Clinical observation on 90 cases of primary dysmenorrhea treated by buccal acupuncture therapy: a randomized controlled study [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 172-181. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

