Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (2): 260-267.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20240203.003
Previous Articles Next Articles
Anti-inflammatory mechanism of the non-volatile ingredients originated from Guanghuoxiang (Pogostemonis Herba) based on high performance liquid chromatography-heated electron spray ionization-high resolution mass spectroscope and cell metabolomics
JING Wenguang1, LIN Xiaoyu2, LI Chu2, ZHAO Xiaoliang3, CHENG Xianlong1, WANG Penglong2, WEI Feng1( ), MA Shuangcheng1(
), MA Shuangcheng1( )
)
- 1 Institute of Control of Chinese Traditional Medicine and Ethnic Medicine, National Institutes for Food and Drug Control, Beijing 102629, China
2 School of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 102488, China
3 Beijing Key Laboratory of Traditional Chinese Medicine Basic Research on Prevention and Treatment of Major Diseases, Experimental Research Center, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100700, China
-
Received:2023-04-22Accepted:2023-09-05Online:2024-04-15Published:2024-02-03 -
Contact:MA Shuangcheng, Institute of Control of Chinese Traditional Medicine and Ethnic Medicine, National Institutes for Food and Drug Control, Beijing 102629, China.masc@nifdc.org.cn ; WEI Feng, Institute of Control of Chinese Traditional Medicine and Ethnic Medicine, National Institutes for Food and Drug Control, Beijing 102629, China.weifeng@nifdc.org.cn Telephone: +86-10-53852020 -
Supported by:Institute of Chinese Medicine Discipline Construction Project of National Institutes for Food and Drug Control: Disciplinary Construction Program of Chinese Medicine Institute of NIFDC(1020050090116);Training Fund for Academic Leaders of NIFDC(2023X10);Program of State Drug Administraion-Key Laboratory of Quality Control of Chinese Medicinal Materials and Decoction Pieces(2022GSMPA-KL02)
Cite this article
JING Wenguang, LIN Xiaoyu, LI Chu, ZHAO Xiaoliang, CHENG Xianlong, WANG Penglong, WEI Feng, MA Shuangcheng. Anti-inflammatory mechanism of the non-volatile ingredients originated from Guanghuoxiang (Pogostemonis Herba) based on high performance liquid chromatography-heated electron spray ionization-high resolution mass spectroscope and cell metabolomics[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(2): 260-267.
share this article
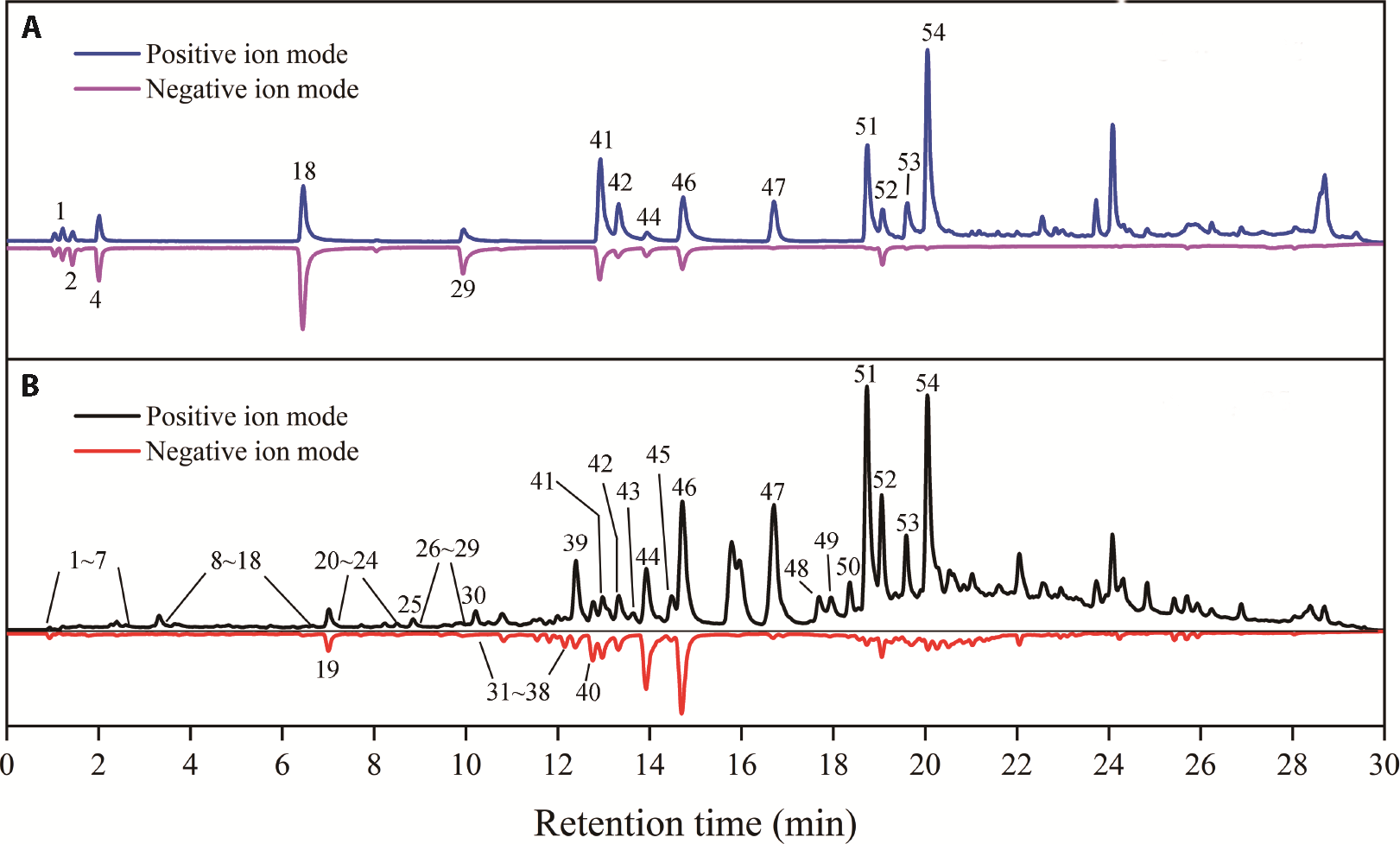
Figure 1 Total ion flow diagram of standard substances and the non-volatile ingredients of patchouli A: total ion flow diagram of the standard; B: total ion flow diagram of the sample.
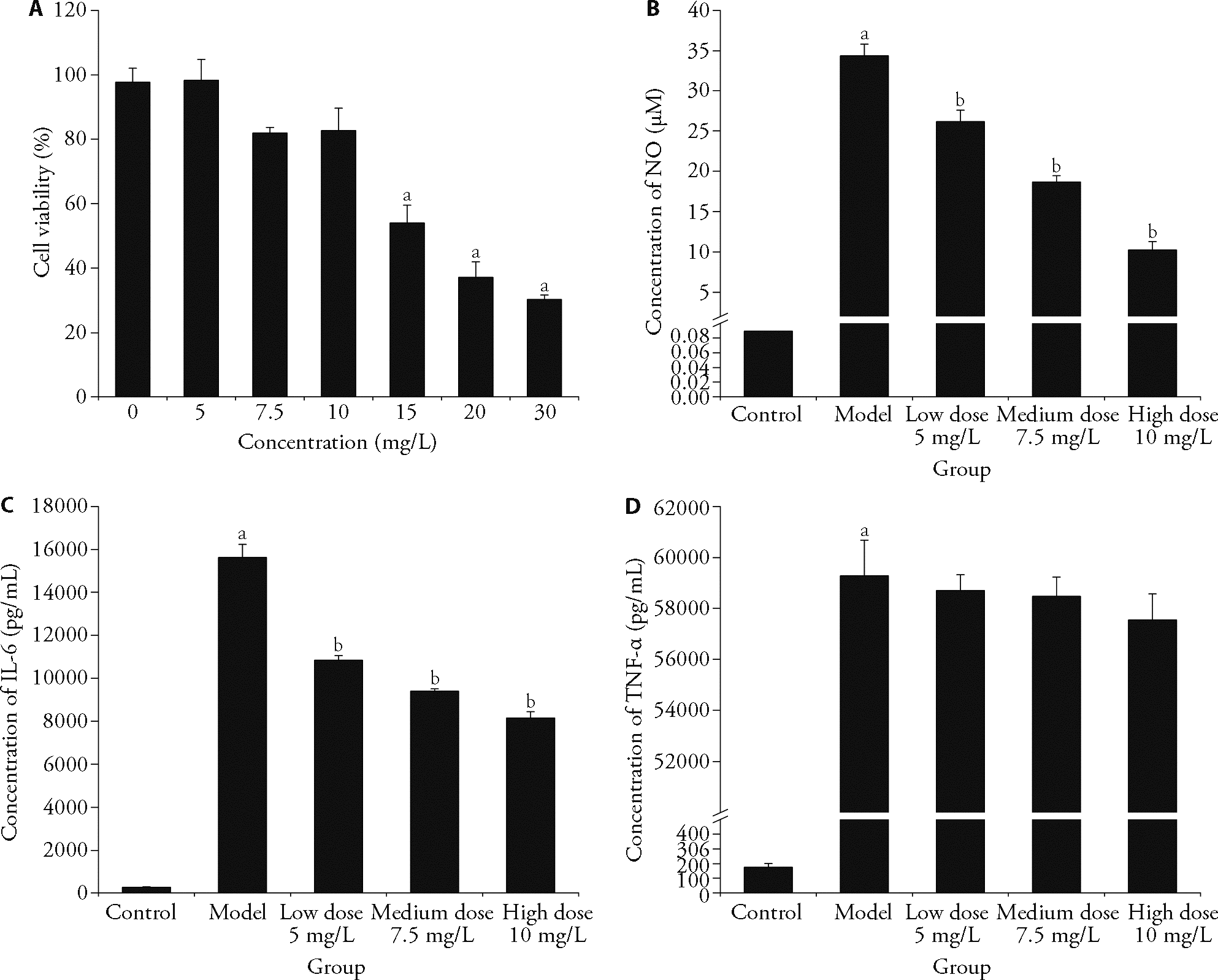
Figure 2 LPS induced cell inflammatory model A: toxicity of the samples to RAW264.7; B: NO content of each sample; C: IL-6 content of each sample; D: TNF-α content of each sample. LPS: lipid polysaccharide. Control group: without treatment; Model group: treated with lipopolysaccharide; Sample group: treated with lipopolysaccharide and non-volatile ingredients of patchouli of 5, 7.5, 10 mg/L. IL-6: interleukin-6; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor-α. Student’s-test was used for statistical significance (P < 0.05); data are presented as mean ± standard deviation (n = 3). Significant differences compared with control group were designated as aP < 0.001 and with model group as bP < 0.001.
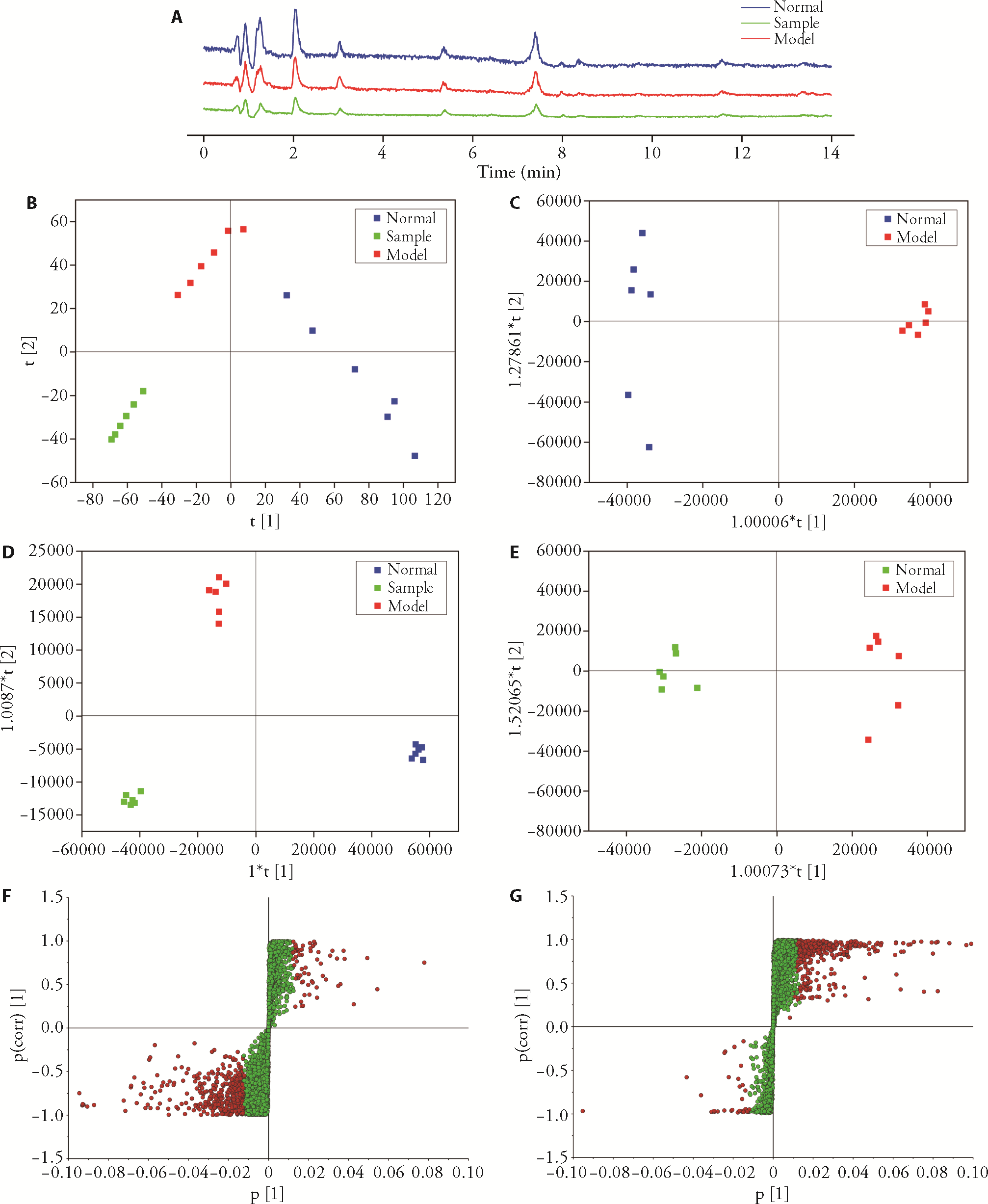
Figure 3 Metabolomic difference analysis A: total ion flow diagram of each group; B: PCA scores; C: OPLS-DA scores of normal group, model group and treated group; D: OPLS-DA scores of normal group and model group; E: OPLS-DA scores of the treated group and model group; F: S-plot of normal group and model group; G: S-plot of the treated group and model group; Control group: without treatment; Model group: treated with lipopolysaccharide; Sample group: treated with lipopolysaccharide and non-volatile ingredients of patchouli of 10 mg/L. PCA: principal component analysis; OPLS-DA: orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis. Student’s t-test was used for statistical significance (P < 0.05); Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation (n = 3).

Figure 4 Metabolomics pathway analysis A: clustering heat map of differential metabolites in the normal group and the model group; B: clustering heat map of differential metabolites in the treated group and the model group; C: arginine levels in cell samples; D: sorbitol levels in cell samples; E: KEGG enrichment pathway map of differential metabolic pathway between the normal group and the model group; F: KEGG enrichment pathway map of differential metabolic pathway between the treated group and the model group. Control group: without treatment; Model group: treated with lipopolysaccharide; Sample group: treated with lipopolysaccharide and non-volatile ingredients of patchouli of 10 mg/L. Student’s t-test was used for statistical significance (P < 0.05); Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation (n = 6). Significant differences compared with control group were designated as aP < 0.001 and with model group as bP < 0.001.
| 1. | Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China. Beijing: China Medical Science and Technology Press, 2020: 46. |
| 2. |
Yarovaya O, Salakhutdinov N. Mono- and sesquiterpenes as a starting platform for the development of antiviral drugs. Russ Chem Rev 2021; 90: 488-510.
DOI URL |
| 3. |
Da S, Figueried P, Byler G, et al. Essential oils as antiviral agents, potential of essential oils to treat SARS-CoV-2 infection: an in-silico investigation. Int J Mol Sci 2020; 21: 1-35.
DOI URL |
| 4. |
Zrieq R, Ahmad I, Snoussi M, et al. Tomatidine and patchouli alcohol as inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 enzymes (3CLpro, PLpro and NSP15) by molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulations. Int J Mol Sci 2021; 22: 10693.
DOI URL |
| 5. |
Chen JR, Xie XF, Li MT, et al. Pharmacological activities and mechanisms of action of Pogostemon cablin Benth: a review. Chin Med 2021; 16: 1-20.
DOI |
| 6. |
Swamy MK, Sinniah UR. A Comprehensive review on the phytochemical constituents and pharmacological activities of Pogostemon cablin Benth: an aromatic medicinal plant of industrial importance. Molecules 2015; 20: 8521-47.
DOI PMID |
| 7. |
Verma R, Padalia R, Chauhan A, et al. Chemical composition of leaves, inflorescence, whole aerial-parts and root essential oils of patchouli {Pogostemon cablin (Blanco) Benth.}. J Essent Oil Res 2019; 31: 319-25.
DOI URL |
| 8. | Srivastava S, Lal R, Singh V, et al. Chemical investigation and biological activities of Patchouli [Pogostemon cablin (Blanco) Benth] essential oil. Ind Crop Prod 2022; 26: 328-37. |
| 9. |
Pandey S, Bhandari S, Sarma N, et al. Essential oil compositions, pharmacological importance and agro technological practices of Patchouli (Pogostemon cablin Benth.): a review. J Essent Oil Bear Pl 2021; 24: 1212-26.
DOI URL |
| 10. |
Jain P, Patel S, Desai M. Patchouli oil: an overview on extraction method, composition and biological activities. J Essent Oil Res 2022; 34: 1-11.
DOI URL |
| 11. |
Lee H, Lee J, Smolensky D, et al. Potential benefits of patchouli alcohol in prevention of human diseases: a mechanistic review. Int Immunopharmacol 2020; 89: 107056.
DOI URL |
| 12. |
Xu LQ, Huang QH, Tan XC, et al. Patchouli alcohol ameliorates acute liver injury via inhibiting oxidative stress and gut-origin LPS leakage in rats. Int Immunopharmacol 2021; 98: 107897.
DOI URL |
| 13. |
Ye QY, Ling QH, Shen J, et al. Protective effect of pogostone on murine norovirus infected-RAW264.7 macrophages through inhibition of NF-kappa B/NLRP3-dependent pyroptosis. J Ethnopharmacol 2021; 278: 114250.
DOI URL |
| 14. |
Peng F, Wan F, Xiong L, et al. In vitro and in vivo antibacterial activity of Pogostone. Chin Med J 2014, 127: 4001-5.
DOI URL |
| 15. |
Chen GR, Xie XF, Peng F, et al. Protective effect of the combination of essential oil from patchouli and tangerine peel against gastric ulcer in rats. J Ethnopharmacol 2022; 282: 114645.
DOI URL |
| 16. |
Xie L, Guo YL, Chen Y R, et al. A potential drug combination of omeprazole and patchouli alcohol significantly normalizes oxidative stress and inflammatory responses against gastric ulcer in ethanol-induced rat model. Int Immunopharmacol 2020; 85: 106660.
DOI URL |
| 17. |
Wu ZN, Zeng HR, Zhang LL, et al. Patchouli alcohol: a natural sesquiterpene against both inflammation and intestinal barrier damage of ulcerative colitis. Inflammation 2020; 43: 1423-35.
DOI PMID |
| 18. |
Lian DW, Xu YF, Ren WK, et al. Unraveling the novel protective effect of patchouli alcohol against helicobacter pylori-induced gastritis: insights into the molecular mechanism in vitro and in vivo. Front Pharmacol 2018; 9: 1347.
DOI URL |
| 19. | Galovicova L, Bortova P, Valkova V, et al. Biological activity of pogostemon cablin essential oil and its potential use for food preservation. Agronomy-Basel 2022; 12: 387. |
| 20. |
Zhong YZ, Tang LY, Deng QH, et al. Unraveling the novel effect of patchouli alcohol against the antibiotic resistance of helicobacter pylori. Front Microbiol 2021; 12: 674560.
DOI URL |
| 21. |
Xu YF, Deng QH, Zhong YZ, et al. Clinical strains of helicobacter pylori with strong cell invasiveness and the protective effect of patchouli alcohol by improving miR-30b/C nediated xenophagy. Front Pharmacol 2021; 12: 666903.
DOI URL |
| 22. |
Li D, Xing ZW, Yu TT, et al. Pogostone attenuates adipose tissue inflammation by regulating the adipocyte-macrophage crosstalk via activating SIRT1. Food Funct 2022; 13: 11853-64.
DOI URL |
| 23. |
Zhao YG, Yang YT, Zhang JX, et al. Lactoferrin-mediated macrophage targeting delivery and patchouli alcohol-based therapeutic strategy for inflammatory bowel diseases. Acta Pharmacol Sin B 2020; 10: 1966-76.
DOI URL |
| 24. |
Leong W, Huang GX, Liao WL, et al. Traditional Patchouli essential oil modulates the host's immune responses and gut microbiota and exhibits potent anti-cancer effects in Apc (Min /+) mice. Pharmacol Res 2022; 176: 106082.
DOI URL |
| 25. |
Song YR, Chang L, Wang XY, et al. Regulatory mechanism and experimental verification of patchouli alcohol on gastric cancer cell based on network pharmacology. Front Oncol 2021; 11: 711984.
DOI URL |
| 26. | Santos L, Brandao L, Martins R L, et al. Evaluation of the larvicidal potential of the essential oil pogostemon cablin (Blanco) Benth in the control of aedes aegypti. Pharmaceuticals-Base 2019; 12: 53. |
| 27. |
Xu FF, Cai WN, Ma T, et al. Traditional uses, phytochemistry, pharmacology, quality control, industrial application, pharmacokinetics and network pharmacology of pogostemon cablin: a comprehensive review. Am J Chinese Med 2022; 50: 691-721.
DOI URL |
| 28. |
Kim E, Kim J, Jeong S, et al. Pachypodol, a methoxyflavonoid isolated from pogostemon cablin bentham exerts antioxidant and cytoprotective effects in HepG2 cells: possible role of ERK-dependent Nrf2 activation. Int J Mol Sci 2019; 20: 4082.
DOI URL |
| 29. |
Chen M, Wang PL, Li T, et al. Comprehensive analysis of Huanglian Jiedu decoction: revealing the presence of a self-assembled phytochemical complex in its naturally-occurring precipitate. J Pharmaceut Biomed 2021; 195: 113820.
DOI URL |
| 30. | Hu Q, Chen M, Yan MM, et al. Comprehensive analysis of Sini decoction and investigation of acid-base self-assembled complexes using cold spray ionization mass spectrometry. Microchem J 2022; 173: 117008. |
| 31. |
Yang WH, Liu YH, Liang JL, et al. Beta-patchoulene, isolated from patchouli oil, suppresses inflammatory mediators in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages. Eur J Inflamm 2017; 15: 136-41.
DOI URL |
| 32. |
Jeong J, Shin Y, Lee SH. Anti-inflammatory activity of patchouli alcohol in RAW264.7 and HT-29 cells. Food Chem Toxicol 2013; 55: 229-33.
DOI PMID |
| 33. |
Xian YF, Li YC, Ip SP, et al. Anti-inflammatory effect of patchouli alcohol isolated from Pogostemonis herba in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages. Exp Ther Med 2011; 2: 545-50.
DOI URL |
| 34. |
Lindez A, Reith W. Arginine-dependent immune responses. Cell Mol Life Sci 2021; 78: 5303-24.
DOI |
| 35. |
Ulrich E, Donkt W. Cameo appearances of aminoacyl-tRNA in natural product biosynthesis. Curr Opin Chem Biol 2016; 35: 29-36.
DOI PMID |
| 36. |
Ramana K, Srivastava S. Aldose reductase: a novel therapeutic target for inflammatory pathologies. Int J Biochem Cell B 2010; 42: 17-20.
DOI URL |
| 37. |
Lanaspa M, Ishimoto T, Cicerchi C, et al. Endogenous fructose production and fructokinase activation mediate renal injury in diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 2014; 25: 2526-38.
DOI PMID |
| 38. |
Curley S, Gall J, Byrne R, et al. Metabolic inflammation in obesity-at the crossroads between fatty acid and cholesterol metabolism. Mol Nutr Food Res 2021; 65: 1900482.
DOI URL |
| [1] | CHENG Huanbo, HU Hui, SUN Daihua, WANG Guangzhong. Anti-inflammatory, anti-tussive effects and toxicity evaluation of Qingfei Dayuan granules (清肺达原颗粒) [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1110-1117. |
| [2] | LIU Yue, ZHANG Fan, HAN Xiaomeng, XU Ningyang, ZHAO Yu, WANG Qige, WANG Jianan, LU Bingjiu, Zhang Yan. Jianpi Qutan Fang (健脾祛痰方) induces anti-atherosclerosis and ameliorates endothelial cell injury in high-fat diet rats via an anti-inflammatory and inhibiting Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1168-1175. |
| [3] | LI Zhihao, HAN Wenjun, SONG Xiuling, LI Yan, CHEN Yuelai. Electroacupuncture stimulating Zhongji (CV3), Guanyuan (CV4), and bilateral Dahe (KI12) attenuates inflammation in rats with chronic nonbacterial prostatitis induced by estradiol through inhibiting toll-like receptor 4 pathway [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 963-972. |
| [4] | Naser Mirazi, Sheida Hesami, Alireza Nourian, Abdolkarim Hosseini. Protective efficacy of dark chocolate in letrozole-induced ovary toxicity model rats: hormonal, biochemical, and histopathological investigation [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(5): 741-748. |
| [5] | FENG Junfang, CHEN Ou, WANG Yibiao. Anti-inflammatory mechanism of rhein in treating asthma based on network pharmacology [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(2): 296-303. |
| [6] | Kamal Dawood, Roohullah, Rabbi Fazle, Naz Attiqa, Bilal Muhammad. In-vitro and in-vivo pharmacological screening of Iris albicans [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(1): 9-16. |
| [7] | ZHANG Qiongzhi, FU Tingting, DAI Jianing, ZHOU Zhinan, SHEN Cuizhen. Sodium Danshensu promotes the healing of stage 2 pressure injury wounds in ischemia/reperfusion injury rat models: possible regulation of apoptosis and inflammatory response [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(4): 571-580. |
| [8] | Chien Yi Koay;Anna Pick Kiong Ling;Ying Pei Wong;Rhun Yian Koh;Sobri Hussein;. Anti-neuroinflammatory responses in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated BV2 microglial cells upon treatment with methanol extract of Panax ginseng root [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(2): 185-193. |
| [9] | ZHANG Jiayan, KANG Xiuhong, SUN Mengyun, ZHANG Shengsheng. Qingre Jianpi decoction(清热健脾汤) attenuates inflammatory responses by suppressing NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain-containing 3 inflammasome activation in dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis mice [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(1): 68-78. |
| [10] | Emel Akta?, Hilal Yildiran. Antioxidant and ntiinflammatory efficacy of curcumin on lung tissue in rats with sepsis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020, 40(5): 820-826. |
| [11] | Anto Suganya Regisa, Jeya Jothi Gabriel. Enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and anticancer activities of Floscopa scandens Lour [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020, 40(3): 473-483. |
| [12] | Dong Jianxia, Chen Xiaoshuang, Song Yi, Fei Xiaofan. Chaiqin Chengqi decoction inhibits inflammatory mediators and attenuates acute pancreatitis through deactivation of janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2019, 39(02): 166-173. |
| [13] | Xia Xichao, Ma Yuhong, Wang Fuan, Zheng Xinhua, Liu Yang, Zhang Junfeng, Cui Juan, Shi Bingqin, Li Hongwen, Liu Rongzhi, Zhang Yaping, Cheng Zhaofei, Han Xiaolong. Effects of extracts from Chuanwu(Aconitum Carmichaelii) and Banxia(Rhizoma Pinelliae) on excisional wound healing in a rat's model [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2019, 39(01): 65-73. |
| [14] | Alamgeer, Ambreen Malik Uttra, Haseeb Ahsan, Umme Habiba Hasan, Mueen Ahmad Chaudhary. Traditional medicines of plant origin used for the treatment of inflammatory disorders in Pakistan:A review [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2018, 38(04): 636-656. |
| [15] | Eunjeong Choi, Heesook Park, Jehyuk Lee, Gunhee Kim. Anticancer,antiobesity,and anti-inflammatory activity of Artemisia species invitro [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2013, 33(01): 92-97. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

