Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (2): 359-367.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2025.02.020
• Original articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of acupuncture on serum levels of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis related hormones and immune factors in rats with allergic rhinitis
KANG Jiale1, DU Zhongming1, GUO Wei2, DU Shuo1, HAN Guanxiong3, CHEN Sheng1( )
)
- 1 Department of Acupuncture, Dongzhimen Hospital, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100700, China
2 Department of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai Ninth People's Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200011, China
3 Department of Traditional Chinese Medicine, China Aerospace Science & Industry Corporation 731 Hospital, Beijing 100074, China
-
Received:2024-07-08Accepted:2024-12-24Online:2025-04-15Published:2025-03-10 -
Contact:CHEN Sheng, Department of Acupuncture, Dongzhimen Hospital, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100700, China. qdchensheng@126.com, Telephone: +86-10-84013347 -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China: to Explore the Mechanism of Acupuncture Treatment on Rats with Allergic Rhinitis from the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal (HPA) Axis and Serum Immune Factor Levels(82004455)
Cite this article
KANG Jiale, DU Zhongming, GUO Wei, DU Shuo, HAN Guanxiong, CHEN Sheng. Effect of acupuncture on serum levels of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis related hormones and immune factors in rats with allergic rhinitis[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(2): 359-367.
share this article

Figure 1 Pathological manifestations of the nasal mucosa in rats by HE staining A1-A5 (×100); B7-B12 (×400). A1, B1: Blank control; A2, B2: Model control; A3, B3: ACU, acupuncture group; A4, B4: ACU + RU486, acupuncture + RU486 group; A5, B5: RU486 group. Blank control: were raised under routine conditions, with no interventions. Model control: after model construction, nasal drips of OVA saline solution (20 mg/mL, 50 μL/ side) were administered daily for 14 d, with no other interventions. ACU: acupuncture group, after model construction, nasal drips were administered as in the model control group, in addition, the rats were treated by acupuncture at the points of the Dazhui (GV14), bilateral Feishu (BL13) and bilateral Zusanli (ST36) every other day 30 min after the nasal drip, and the needles were retained for 20 min each time. ACU+RU486: acupuncture + RU486 group, after model construction, nasal drips were administered as in the model control group, followed by IP of RU486 (45 mg/mL) in DMSO every other day and acupuncture 30 min after the injection. Acupuncture was administered as in the acupuncture group. RU486: after model construction, nasal drips were administered as in the model control group, followed by IP of RU486 (45 mg/mL) in DMSO every other day, without acupuncture interventions. HE: hematoxylin and eosin; ACU: acupuncture; RU486: mifepristone; IP: intraperitoneal injection; OVA: ovalbumin; DMSO: dimethyl sulfoxide.
| Group | n | IL-4 (pg/mL) | IL-5 (pg/mL) | IL-13 (pg/mL) | IFN-γ (ng/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank control | 12 | 47.3±1.1 | 13.4±1.7 | 3.6±1.2 | 51.0±2.1 |
| Model control | 12 | 75.2±7.0ab | 54.3±2.3ab | 14.4±1.3ab | 14.7±1.8a |
| Acupuncture | 12 | 60.9±4.6a | 20.2±2.1a | 7.5±0.7a | 37.4±3.4a |
| Acupuncture+RU486 | 12 | 70.7±4.1ab | 25.8±1.2ab | 12.2±1.9ab | 27.9±2.3a |
| RU486 | 12 | 74.1±5.3ab | 46.6±5.0ab | 11.8±1.8ab | 20.4±3.4a |
Table 1 Serum IL-4, IL-5, IL-13, and IFN-γ levels in rats by group ($\bar{x}±s$)
| Group | n | IL-4 (pg/mL) | IL-5 (pg/mL) | IL-13 (pg/mL) | IFN-γ (ng/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank control | 12 | 47.3±1.1 | 13.4±1.7 | 3.6±1.2 | 51.0±2.1 |
| Model control | 12 | 75.2±7.0ab | 54.3±2.3ab | 14.4±1.3ab | 14.7±1.8a |
| Acupuncture | 12 | 60.9±4.6a | 20.2±2.1a | 7.5±0.7a | 37.4±3.4a |
| Acupuncture+RU486 | 12 | 70.7±4.1ab | 25.8±1.2ab | 12.2±1.9ab | 27.9±2.3a |
| RU486 | 12 | 74.1±5.3ab | 46.6±5.0ab | 11.8±1.8ab | 20.4±3.4a |
| Group | n | CORT (ng/mL) | CRH (pg/mL) | ACTH (pg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank control | 12 | 62.1±3.9 | 9.6±1.0 | 7.7±1.8 |
| Model control | 12 | 86.0±2.8ab | 21.8±1.2ab | 16.5±0.8ab |
| Acupuncture | 12 | 69.1±1.9a | 11.0±1.3a | 11.5±0.8a |
| Acupuncture+RU486 | 12 | 82.7±2.9ab | 11.7±0.8a | 15.5±1.3ab |
| RU486 | 12 | 78.6±6.2ab | 14.2±0.5ab | 14.7±2.2ab |
Table 2 Serum CORT, CRH, and ACTH levels in rats by group ($\bar{x}±s$)
| Group | n | CORT (ng/mL) | CRH (pg/mL) | ACTH (pg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank control | 12 | 62.1±3.9 | 9.6±1.0 | 7.7±1.8 |
| Model control | 12 | 86.0±2.8ab | 21.8±1.2ab | 16.5±0.8ab |
| Acupuncture | 12 | 69.1±1.9a | 11.0±1.3a | 11.5±0.8a |
| Acupuncture+RU486 | 12 | 82.7±2.9ab | 11.7±0.8a | 15.5±1.3ab |
| RU486 | 12 | 78.6±6.2ab | 14.2±0.5ab | 14.7±2.2ab |
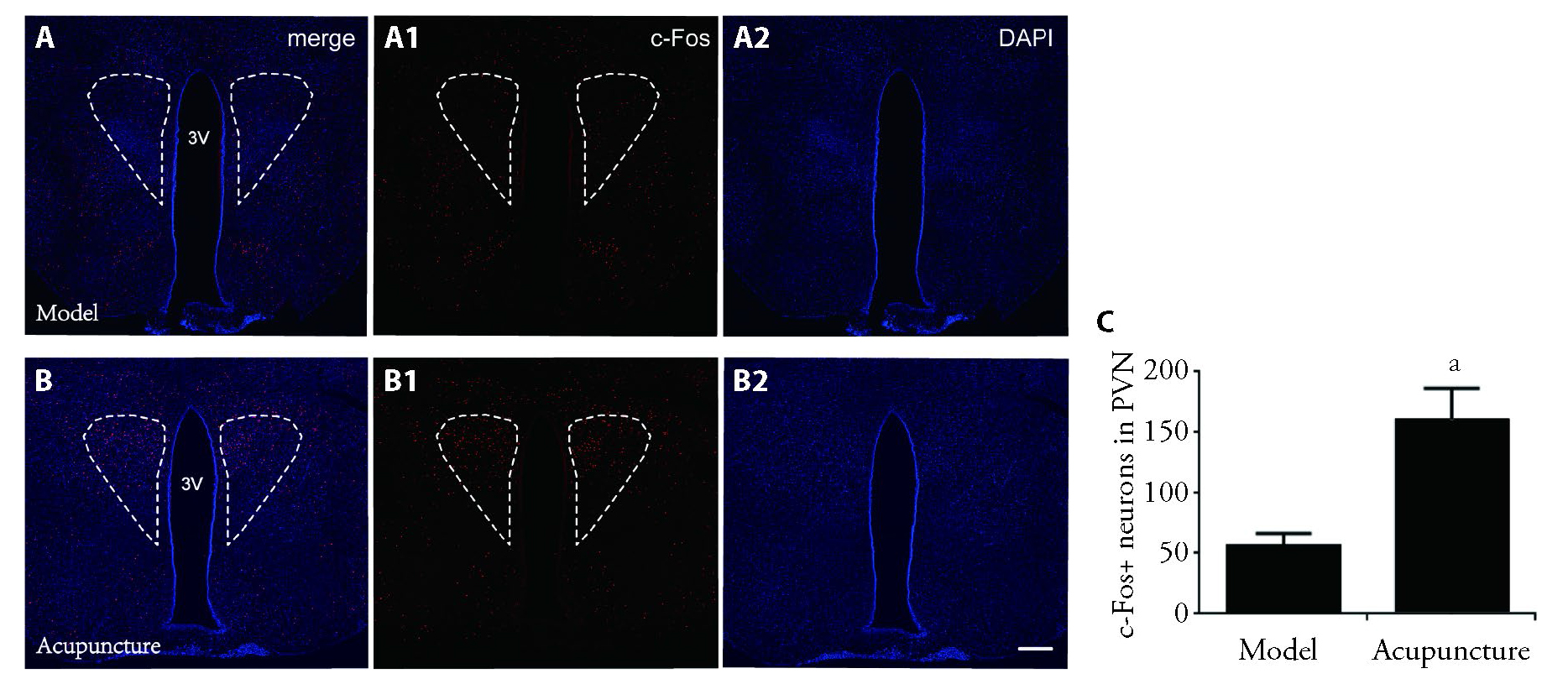
Figure 2 The expression levels of c-Fos in the PVN region Representative images of c-Fos-expressed neurons in the PVN region of rats in Model (A) and Acupuncture (B) groups. A: model group, B: Acupuncture group: the merge view; A1: Model group, B1: Acupuncture group: red particles in the dotted box represent c-Fos+ neurons in the PVN region; A2: Model group, B2: Acupuncture group: DAPI colored view. The PVN region is defined by dotted line. Scale bar, 500 um. C: Total number of c-Fos-expressed neurons of PVN in the two groups (n = 12 for each group, aP < 0.01 vs Model).
| 1. |
Dykewicz MS, Wallace DV, Amrol DJ, et al. Rhinitis 2020: a practice parameter update. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2020; 146: 721-67.
DOI PMID |
| 2. |
Singh K, Axelrod S, Bielory L. The epidemiology of ocular and nasal allergy in the United States, 1988-1994. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2010; 126: 778-83.
DOI PMID |
| 3. | The Inner Canon of the Yellow Emperor:Plain Conversation. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House, 2012: 184. |
| 4. | Yin Z, Geng G, Xu G, et al. Acupuncture methods for allergic rhinitis: a systematic review and bayesian Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Chin Med 2020; 15: 109. |
| 5. | Wise SK, Damask C, Roland LT, et al. International consensus statement on allergy and rhinology: allergic rhinitis-2023. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol 2023; 13: 293-859. |
| 6. | Liu S, Wang Z, Su Y, et al. A neuroanatomical basis for electroacupuncture to drive the vagal-adrenal axis. Nature 2021; 598: 641-5. |
| 7. | Min S. Study on common brain nuclei of two-way neural pathways in rat Feishu and lower respiratory tract based on the technique of neurotropic virus labeling. Shanghai: Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2019: 83-4. |
| 8. | Wang SJ, Zhang JJ, Yang HY, et al. Acupoint specificity on acupuncture regulation of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal cortex axis function. BMC Complement Altern Med 2015; 15: 87. |
| 9. |
Trikojat K, Luksch H, Rosen-Wolff A, et al. "Allergic mood" - Depressive and anxiety symptoms in patients with seasonal allergic rhinitis (SAR) and their association to inflammatory, endocrine, and allergic markers. Brain Behav Immun 2017; 65: 202-9.
DOI PMID |
| 10. | Chen S, Wang J, Bai P, et al. Moderate and severe persistent allergic rhinitis treated with acupuncture:a randomized controlled trial. Zhong Guo Zhen Jiu 2015, 35: 1209-13. |
| 11. | Chen S, Qu S, Zhang Y, et al. Impact of acupuncture for allergic rhinitis on the activity of the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials 2019; 20: 1-7. |
| 12. |
Kar M, Muluk BN, Bafaqeeh AS, et al. Consensus on the methodology for experimental studies in allergic rhinitis. Int J Pediatr Otorhi 2019; 121: 68-71.
DOI PMID |
| 13. | China Association of Acupuncture and Moxibustion. Nomenclature and location of acupuncture points for laboratory animals — Part 2: Rat. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu 2021; 46: 351-2. |
| 14. | Zhang LF. Experimental acupuncture. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2018: 219-21. |
| 15. | Tu W, Chen X, Wu Q, et al. Acupoint application inhibits nerve growth factor and attenuates allergic inflammation in allergic rhinitis model rats. J Inflamm (Lond) 2020; 17: 4. |
| 16. | Yang S, Wu J, Zhang Q, et al. Catgut implantation at acupoint reduces immune reaction in a rat model of allergic rhinitis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2018; 2018: 7629239. |
| 17. | Liu JH, Gu JW, Hu Q, et al. Effect of catgut implantation at "Yingxiang" (LI20) on lower airway remodeling in allergic rhinitis rats. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu 2020; 45: 461-7. |
| 18. | Zhang Q, Wang Y, Zhou YL, et al. Synergistic effect of acupoint injection and moxibustion or catgut embedding or acupuncture on symptoms and expression of Th1/Th2 related cytokines in nasal mucosa of rats with allergic rhinitis. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu 2022; 47: 409-14. |
| 19. | Zheng XL, Tian YP, Luo HY, et al. Effect of warm acupuncture on the levels of serum immunoglobulin E, interleukin-1 beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in rats with allergic rhinitis. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu 2018; 43: 35-8. |
| 20. |
Jung D, Lee S, Hong S. Effects of acupuncture and moxibustion in a mouse model of allergic rhinitis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2012; 146: 19-25.
DOI PMID |
| 21. |
Zhang Y, Lan F, Zhang L. Update on pathomechanisms and treatments in allergic rhinitis. Allergy 2022; 77: 3309-19.
DOI PMID |
| 22. | Huang Z, Chu M, Chen X, et al. Th2A cells: The pathogenic players in allergic diseases. Front Immunol 2022; 13: 916778. |
| 23. | Kato A. Group2 innate lymphoid cells in airway diseases. Chest 2019; 156: 141-9. |
| 24. | Zhao Y, Huang Y, Huang J, et al. The effect of acupuncture on the levels of IL-4 and IFN-γ in rats with allergic rhinitis. Fujian Zhong Yi Yao 2010; 41: 52-3. |
| 25. | Xu N, Shao S, Hua J, et al. Effect of acupuncture and moxibustion of BL13, GV14 and BL12 on the expressions of STAT6 in lung tissue and IL-13 in serum of asthmatic rats. Zhong Yi Yao Xin Xi 2021; 38: 42-5. |
| 26. |
Wei Y, Dong M, Zhong L, et al. Regulation of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis activity and immunologic function contributed to the anti-inflammatory effect of acupuncture in the OVA-induced murine asthma model. Neurosci Lett 2017; 636: 177-83.
DOI PMID |
| 27. | Wang J, Lu S, Yang F, et al. The role of macrophage polarization and associated mechanisms in regulating the anti-inflammatory action of acupuncture: a literature review and perspectives. Chin Med 2021; 16: 56. |
| [1] | LI Yongfeng, CHEN Xinyi, REN Wei, QIAO Haifa. Electroacupuncture stimulation of auricular concha region improves loss of control over stress induced depression-like behavior by modulating 5-hydroxytryptamine 1A receptor [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(2): 326-334. |
| [2] | TIAN Yuan, BU He, WANG Tieshan, YANG Dongliang, ZHANG Wei, LIU Tong, ZHANG Li, HUO Zejun. Efficacy of electro-acupuncture at “Weizhong” (BL40) on macrophage polarization in rats with injured lumbar multifidus [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(2): 335-347. |
| [3] | HU Junwei, FENG Jiwei, LI Wen, LIU Lumin, LI Xu, XU Ge, LIU Jiandang, CHEN Yuelai. Electroacupuncture improves cyclophosphamide-induced bladder overactivity by reducing mechanotransduction in the rat urothelium [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(2): 348-358. |
| [4] | BAI Tianyu, YANG Jiaen, YIN Liang, LI Jinling, LIU Jianxian, LI Zongchang, SUN Zeming, JIA Ning, XU Chengchao. Effect of acupuncture on brain activity in patients with decreasing ovarian reserve: a resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging study [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(2): 450-457. |
| [5] | WU Jiaman, TANG Meng, LUO Yu, ZHU Haimin, ZHAO Tianqi, MA Fei, NING Yan. Electroacupuncture enhances the mitophagy of granulosa cells in premature ovarian insufficiency model mice by inactivating the hippo-yes-associated protein/transcriptional co-activator with postsynaptic density protein, drosophila disc large tumor suppressor, and zonula occludens-1 protein binding motif pathway [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(1): 13-21. |
| [6] | LI Siting, WANG Shaojun, YIN Yehui, DE Gejing, LI Caicai, WANG Ziyan, CAO Wenjie. Electroacupuncture alleviates zymosan-induced colorectal hypersensitivity [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(1): 32-38. |
| [7] | LANG Jiawang, JIN Lingqing, LUO Jianchang, LANG Boxu. Effects of acupuncture combined with bone-setting therapy to treat tourette syndrome: a three-arm randomized controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(1): 176-183. |
| [8] | Emre Bulut, Didem Özkal Eminoğlu, Yasemin Çayır. Effect of electroacupuncture on pain after periodontal flap surgery: a randomized controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(1): 184-191. |
| [9] | HE Ling, YANG Hui, LI Kang, WANG Junwen, SUN Zhibo, YANG Jinsheng, ZHANG Jing. Research on acupuncture robots based on the OptiTrack motion capture system and a robotic arm [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(1): 201-212. |
| [10] | WANG Bingyu, JIN Fangfang, GAO Jiawei, YANG Liuxin, ZHANG Yali, YUAN Xingxing, ZHANG Yang. Acupuncture reduces sedative and anaesthetic consumption and improves pain tolerance in patients undergoing colonoscopy: a Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(6): 1091-1103. |
| [11] | ZHANG Boyang, ZHOU Yang, FENG Liyuan, SUI Dan, HE Lei, TONG Dan, WANG Ruoyu, SUI Xue, SONG Jing, WANG Dongyan. A neural regulation mechanism of head electroacupuncture on brain network of patients with stroke related sleep disorders [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(6): 1268-1276. |
| [12] | XI Hanqing, LI Xia, ZHANG Ziyi, CUI Xiang, JING Xianghong, ZHU Bing, GAO Xinyan. Neuro- and immuno-modulation mediated by the cardiac sympathetic nerve: a novel insight into the anti-ischemic efficacy of acupuncture [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(5): 1058-1066. |
| [13] | XU Yingshan, WU Chunxiao, YU Wei, GUO Hongji, LU Liming, XU Nenggui, TANG Chunzhi. Systematic review and Meta-analysis of brain plasticity associated with electroacupuncture in experimental ischemic stroke [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(5): 859-870. |
| [14] | ZHENG Peng, MENG Ying, LIU Meijun, YU Di, LIU Huiying, WANG Fuchun, XU Xiaohong. Electroacupuncture inhibits hippocampal oxidative stress and autophagy in sleep-deprived rats through the protein kinase B and mechanistic target of rapamycin signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(5): 974-980. |
| [15] | ZHANG Fang, YAN Cuina, WENG Zhijun, WU Luyi, QI Li, ZHAO Min, XIN Yuhu, WU Huangan, LIU Huirong. Regulatory role of electroacupuncture on satellite glial cell activity in the colon and dorsal root ganglion of rats with irritable bowel syndrome [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(5): 981-990. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

