Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (5): 981-990.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2024.05.005
Previous Articles Next Articles
Regulatory role of electroacupuncture on satellite glial cell activity in the colon and dorsal root ganglion of rats with irritable bowel syndrome
ZHANG Fang1,2, YAN Cuina3, WENG Zhijun1,2, WU Luyi3,4, QI Li3, ZHAO Min3, XIN Yuhu5, WU Huangan1,2, LIU Huirong1,2( )
)
- 1 Key Laboratory of Acupuncture and Immunological Effects, Yueyang Hospital of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200437, China
2 Shanghai Research Institute of Acupuncture and Meridian, Shanghai 200030, China
3 Key Laboratory of Acupuncture and Immunological Effects, Yueyang Hospital of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200437, China
4 Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 201203, China
5 Cancer Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai 200032, China
-
Received:2023-06-11Accepted:2023-11-27Online:2024-10-15Published:2024-09-11 -
Contact:Prof. LIU Huirong, Shanghai Research Institute of Acupuncture and Meridian, Shanghai 200030, China; lhr_tcm@139.com Telephone: +86-21-64644238 -
Supported by:Research on the Initiation Mechanism of Moxibustion Effect and Its Endogenous Regulation Mechanism (973 program, No. 2015CB554501);Interaction Mechanism of the Information between Electroacupuncture Stimulation to Zusanli and Visceral Pain in Dorsal Root Ganglion of Rats with Irritable Bowel Syndrome(81873367);Study on the Mechanism of Periaqueductal gray Purinergic Ion Channel Receptor 3 Mediated in Electro-acupuncture Relieving Visceral Hypersensitivity in Mice with Irritable Bowel Syndrome(81904301);based on Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid 1 Mediated Calcium/Calmodulin-dependent Protein Kinase Ⅱ Signaling Pathway Involved in Electroacupuncture to Relieve Irritable Bowel Syndrome Mice Visceral Pain Mechanism Study(22ZR1458600);Shanghai Clinical Research Center for Acupuncture and Moxibustion(20MC1920500)
Cite this article
ZHANG Fang, YAN Cuina, WENG Zhijun, WU Luyi, QI Li, ZHAO Min, XIN Yuhu, WU Huangan, LIU Huirong. Regulatory role of electroacupuncture on satellite glial cell activity in the colon and dorsal root ganglion of rats with irritable bowel syndrome[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(5): 981-990.
share this article
| Group | n | 20 mm Hg | 40 mm Hg | 60 mm Hg | 80 mm Hg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NG | 8 | 0.33 (0, 0.33) | 1.33 (1.33, 1.33) | 2.67 (2.67, 2.67) | 3.84 (3.33, 4) |
| MG | 24 | 0.67 (0.33, 1.00)a | 2.33 (2, 2.67)a | 3.33 (3, 3.33)a | 4 (3.67, 4) |
Table 1 AWR scores before EA and drug intervention [M (Q25, Q75)]
| Group | n | 20 mm Hg | 40 mm Hg | 60 mm Hg | 80 mm Hg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NG | 8 | 0.33 (0, 0.33) | 1.33 (1.33, 1.33) | 2.67 (2.67, 2.67) | 3.84 (3.33, 4) |
| MG | 24 | 0.67 (0.33, 1.00)a | 2.33 (2, 2.67)a | 3.33 (3, 3.33)a | 4 (3.67, 4) |
| Group | n | 20 mm Hg | 40 mm Hg | 60 mm Hg | 80 mm Hg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NG | 8 | 0.33 (0, 0.33) | 1.5 (1.33, 1.67) | 2.33 (2.08, 2.59) | 3.33 (3.08, 3.67) |
| MG | 8 | 0.67 (0.67, 0.92)a | 2 (2, 2.33)a | 3 (2.75, 3.25)a | 4 (3.67, 4)a |
| EA | 8 | 0.33 (0.08, 0.67)b | 2 (1.67, 2)b | 2.67 (2.67, 2.92)b | 3.5 (3.08, 3.92)b |
| FCA | 8 | 0.17 (0, 0.33)c | 2 (1.67, 2)b | 2.67 (2.42, 2.92)b | 3.33 (3.33, 3.59)b |
Table 2 AWR scores after EA and drug intervention [M (Q25, Q75)]
| Group | n | 20 mm Hg | 40 mm Hg | 60 mm Hg | 80 mm Hg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NG | 8 | 0.33 (0, 0.33) | 1.5 (1.33, 1.67) | 2.33 (2.08, 2.59) | 3.33 (3.08, 3.67) |
| MG | 8 | 0.67 (0.67, 0.92)a | 2 (2, 2.33)a | 3 (2.75, 3.25)a | 4 (3.67, 4)a |
| EA | 8 | 0.33 (0.08, 0.67)b | 2 (1.67, 2)b | 2.67 (2.67, 2.92)b | 3.5 (3.08, 3.92)b |
| FCA | 8 | 0.17 (0, 0.33)c | 2 (1.67, 2)b | 2.67 (2.42, 2.92)b | 3.33 (3.33, 3.59)b |

Figure 1 HE staining of colon tissues A-D: HE staining of colon tissues, scale bar: 100 μm. A: NG; B: MG; C: EA; D: FCA. NG: normal group, the same fixation as the EA group; MG: model group, the same fixation as the EA group; EA: electroacupuncture group, EA at bilateral Tianshu (ST25) and Shangjuxu (ST37) (2/100 Hz, 1 mA, 30 min, 7 d); FCA: DL-fluorocitric acid barium salt group, intrathecal injection of FCA (10 μL, 1 nmol/μL) every three days. HE: hematoxylin and eosin.
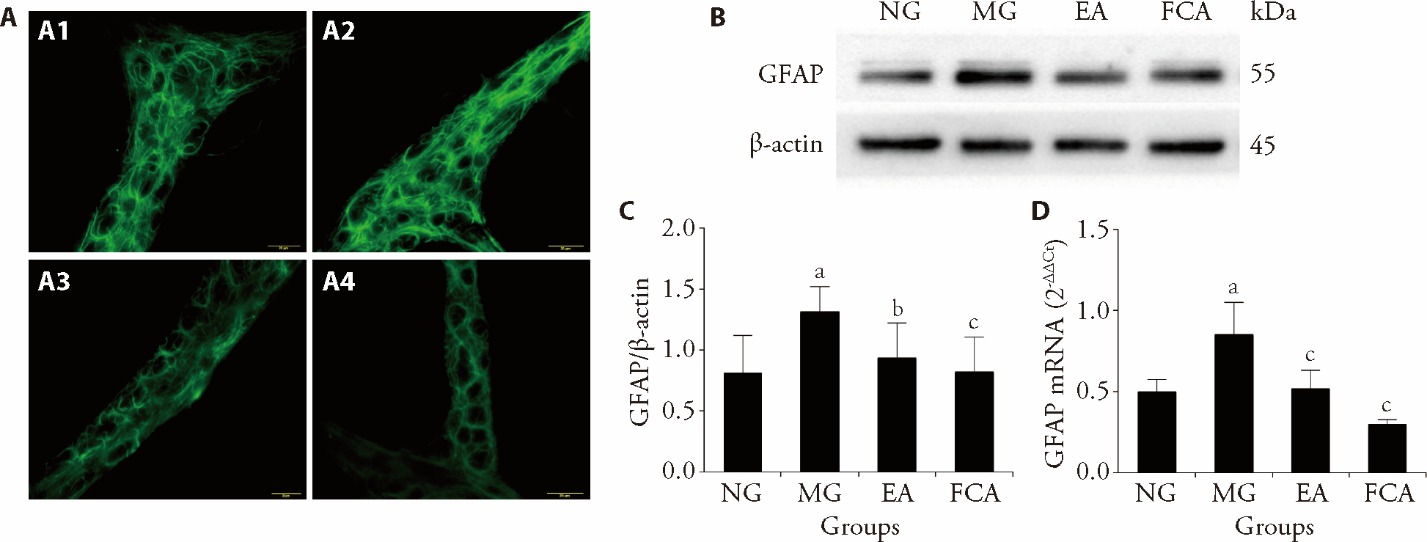
Figure 2 GFAP expression in the colonic myenteric plexus and colon A: immunofluorescence was used to detect the distribution of GFAP in the colonic myenteric plexus, scale bar: 20 μm; A1: NG; A2: MG; A3: EA; A4: FCA. B: representative gel images show the protein level of GFAP in the colon, β-Actin was used as a loading control; Western blotting was used to detect the expression of GFAP protein in the colon. C: quantitative analysis of GFAP protein expression in the colon. D: relative expression of GFAP mRNA in the colon, real-time polymerase chain reaction was used to detect the expression of GFAP mRNA in the colon. NG (n = 8): normal group, the same fixation as the EA group; MG (n = 8): model group, the same fixation as the EA group; EA (n = 8): electroacupuncture group, EA stimulation at bilateral Tianshu (ST25) and Shangjuxu (ST37) (2/100 Hz, 1 mA, 30 min, 7 d); FCA (n = 8): DL-fluorocitric acid barium salt group, intrathecal injection of FCA (10 μL, 1 nmol/μL) every three days. GFAP: glial fibrillary acidic protein; mRNA: messenger ribonucleic acid. All data was easured by one-way analysis, and least significance difference test was performed for inter-group comparisons. All data was presented as mean ± standard deviation. Compared with the normal group, aP<0.01; compared with the model group, bP<0.05, cP<0.01.
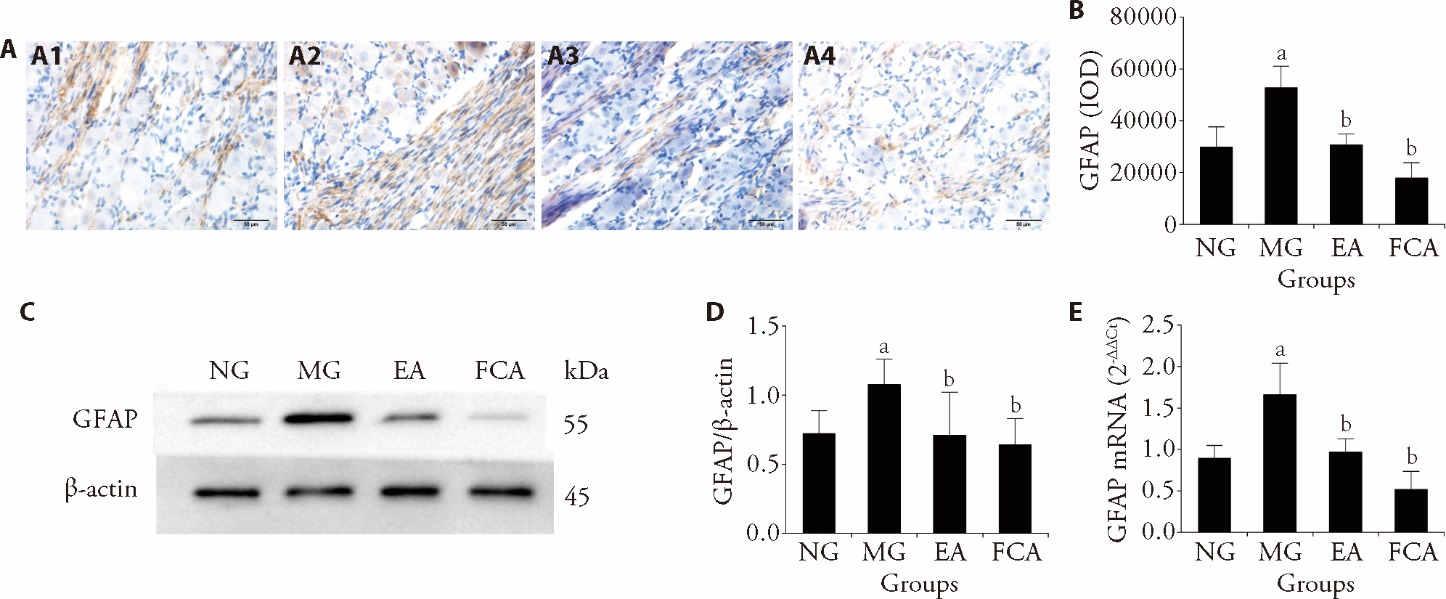
Figure 3 GFAP protein and mRNA expression in the colon-related DRG A: immunohistochemical assay was used to detect the expression of GFAP protein in the colon-related DRG, scale bar: 50 μm; A1: NG; A2: MG; A3: EA; A4: FCA; dyeing method of all pictures are the immunohistochemical DAB method. B: semiquantitative analysis of GFAP protein expression in the colon-related DRG. C: representative gel images show the protein level of GFAP in the colon-related DRG, β-Actin was used as a loading control; Western blotting was used to detect the expression of GFAP protein in the colon-related DRG. D: quantitative analysis of GFAP protein expression in the colon-related DRG. E: relative expression of GFAP mRNA in the colon-related DRG, Real-time Polymerase Chain Reaction was used to detect the expression of GFAP mRNA in the colon. NG (n = 8): normal group, the same fixation as the EA group; MG (n = 8): model group, the same fixation as the EA group; EA (n = 8): electroacupuncture group, EA stimulation at bilateral Tianshu (ST25) and Shangjuxu (ST37) (2/100 Hz, 1 mA, 30 min, 7 d); FCA (n = 8): DL-fluorocitric acid barium salt group, intrathecal injection of FCA (10 μL, 1 nmol/μL) every three days. GFAP: glial fibrillary acidic protein; DAB: diaminobenzidine; IOD: immunohistochemical optical density. mRNA: messenger ribonucleic acid; DRG: dorsal root ganglion. All data was measured by one-way analysis, and least significance difference test was performed for inter-group comparisons. All data was presented as mean ± standard deviation. Compared with the normal group, aP<0.01; compared with the model group, bP<0.01.
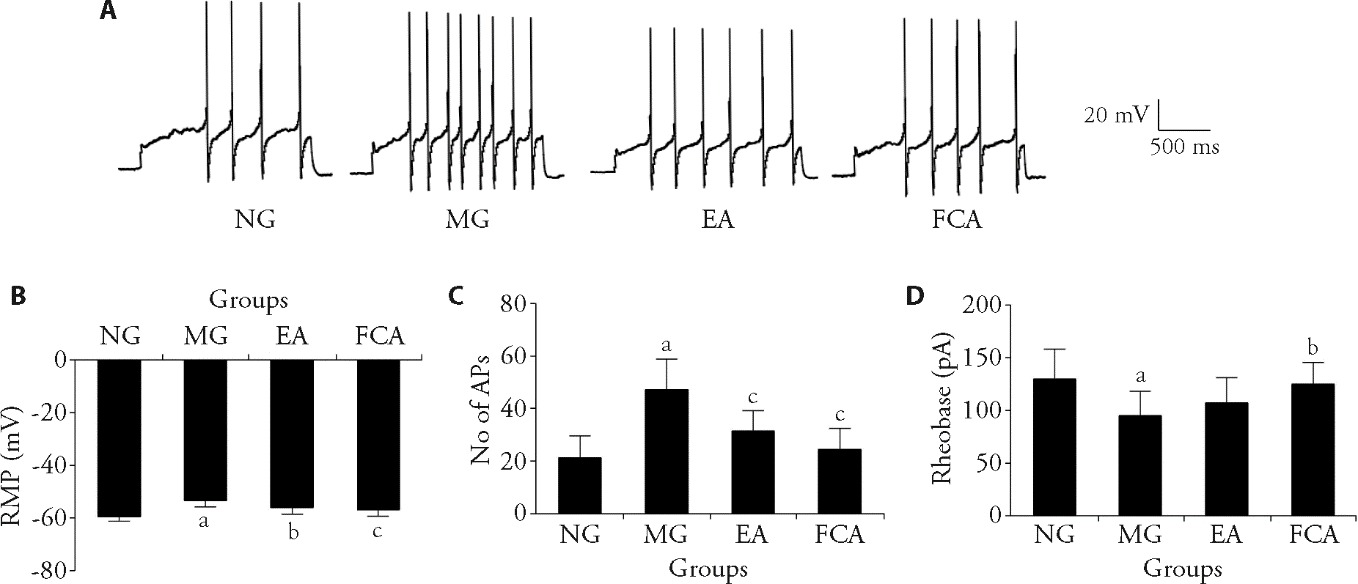
Figure 4 Changes in the electrical properties of membrane of the colon-related DRG neurons A: representative traces of APs after a 200 pA depolarization current injection into colon-related DRG neurons of the NG, MG, and the EA, and FCA groups; single cell patch clamp recording was used to detect the RMP, rheobase and AP frequency of the colon-related DRG neurons. B: changes in the cell RMP in colon-related DRG neurons; C: number of APs of neuronal cells in colon-related DRG; D: changes in the rheobase in colon-related DRG neurons. NG (n = 8): normal group, the same fixation as the EA group; MG (n = 8): model group, the same fixation as the EA group; EA (n = 8): electroacupuncture group, EA stimulation at bilateral Tianshu (ST25) and Shangjuxu (ST37) (2/100 Hz, 1 mA, 30 min, 7 d); FCA (n = 8): DL-fluorocitric acid barium salt group, intrathecal injection of FCA (10 μL, 1 nmol/μL) every three days. RMP: resting membrane potential; No: number; AP: action potential; DRG: dorsal root ganglion. All data was measured by one-way analysis, and least significance difference test was performed for inter-group comparisons. All data was presented as mean ± standard deviation. Compared with the normal group, aP<0.01; Compared with the model group, bP<0.05, cP<0.01.
| 1. | Sinagra E, Morreale GC, Mohammadian G, et al. New therapeutic perspectives in irritable bowel syndrome: targeting low-grade inflammation, immuno-neuroendocrine axis, motility, secretion and beyond. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23: 6593-627. |
| 2. | Császár-Nagy N, Bókkon I. Hypnotherapy and IBS: implicit, long-term stress memory in the ENS? Heliyon 2023; 9: e12751. |
| 3. | Grundy D. What activates visceral afferents? Gut 2004; 53: ii5-8. |
| 4. |
Chao G, Wang Z, Zhang S. Research on correlation between psychological factors, mast cells, and PAR-2 signal pathway in irritable bowel syndrome. J Inflamm Res 2021; 14: 1427-36.
DOI PMID |
| 5. | Zhang F, Weng ZJ, Wu LY, et al. Etiology related irritable bowel syndrome animal models. Shi Jie Hua Ren Xiao Hua Za Zhi 2018; 26: 1772-77. |
| 6. |
Barbara G, Cremon C, De Giorgio R, et al. Mechanisms underlying visceral hypersensitivity in irritable bowel syndrome. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 2011; 13: 308-15.
DOI PMID |
| 7. | Tian S, Zhang H, Chen S, Wu P, Chen M. Global research progress of visceral hypersensitivity and irritable bowel syndrome: bibliometrics and visualized analysis. Front Pharmacol 2023; 14: 1175057. |
| 8. |
Morales-Soto W, Gulbransen BD. Enteric glia: a new player in abdominal pain. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol 2019; 7: 433-45.
DOI PMID |
| 9. | Zhao M, Wang Z, Weng Z, et al. Electroacupuncture improves IBS visceral hypersensitivity by inhibiting the activation of astrocytes in the medial thalamus and anterior cingulate cortex. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2020; 2020: 2562979. |
| 10. | Donnelly CR, Andriessen AS, Chen G, et al. Central nervous system targets: glial cell mechanisms in chronic pain. Neurotherapeutics 2020; 17: 846-60. |
| 11. |
Seguella L, Gulbransen BD. Enteric glial biology, intercellular signalling and roles in gastrointestinal disease. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2021; 18: 571-87.
DOI PMID |
| 12. | Soto F, Garcia-Guzman M, Stühmer W. Cloned ligand-gated channels activated by extracellular ATP (P2X receptors). J Membr Biol 1997; 160: 91-100. |
| 13. |
Fields RD, Burnstock G. Purinergic signalling in neuron-glia interactions. Nat Rev Neurosci 2006; 7: 423-36.
DOI PMID |
| 14. |
Ciccarelli R, Di Iorio P, Ballerini P, et al. Effects of exogenous ATP and related analogues on the proliferat ionrate of dissociated primary cultures of rat astrocytes. J Neurosci Res 1994; 39: 556-66.
PMID |
| 15. | Huang LZ, Ma JL, Wang YL, Xu X, Qin R, Wang J. The relation between krebs cycle of astrocytes and central sensitization in rats induced by formalin. Shen Jing Jie Pou Xue Za Zhi 2015; 3: 315-21. |
| 16. | Wu HG, Jiang B, Zhou EH, et al. Regulatory mechanism of electroacupuncture in irritable bowel syndrome: preventing MC activation and decreasing SP VIP secretion. Dig Dis Sci 2008; 53: 1644-51. |
| 17. | Shi Y, Chen YH, Yin XJ, et al. Electroacupuncture versus moxibustion for irritable bowel syndrome: a randomized, parallel-controlled trial. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2015; 2015: 361786. |
| 18. | Weng ZJ, Wu LY, Zhou CL, et al. Effect of electroacupuncture on P2X3 receptor regulation in the peripheral and central nervous systems of rats with visceral pain caused by irritable bowel syndrome. Purinergic Signal 2015; 11: 321-9. |
| 19. | Zhang F, Ma Z, Weng ZJ, et al. P2X3 receptor in primary afferent neurons mediates the relief of visceral hypersensitivity by electroacupuncture in an irritable bowel syndrome rat model. Gastroenterol Res Pract 2020; 2020: 8186106. |
| 20. | Kilkenny C, Browne W, Cuthill IC, Emerson M, Altman DG. NC3Rs reporting guidelines working group. Animal research: reporting in vivo experiments: the ARRIVE guidelines. Br J Pharmacol 2010; 160: 1577-9. |
| 21. |
Al-Chaer ED, Kawasaki M, Pasricha PJ. A new model of chronic uisceral hypersensitivity in adult rats induced by colon irritation during postnatal development. Gastroenterology 2000; 119: 1276-85.
DOI PMID |
| 22. |
Weng ZJ, Wu LY, Lu Y, et al. Electroacupuncture diminishes P2X2 and P2X3 purinergic receptor expression in dorsal root ganglia of rats with visceral hypersensitivity. Neural Regen Res 2013; 8: 802-8.
DOI PMID |
| 23. | Fan F, Chen Y, Chen Z, et al. Blockade of BK channels attenuates chronic visceral hypersensitivity in an IBS-like rat model. Mol Pain 2021; 17: 17448069211040364. |
| 24. | Huang LY, Sun RR, Sun N, Zhou YF, Zeng F, Liang FR. Research progress of central-peripheral mechanism of acupuncture regulating visceral pain. Shi Jie Ke Xue Ji Shu-Zhong Yi Yao Xian Dai Hua 2021; 23: 232-8. |
| 25. | Sadeghi R, Heidarnia MA, Zagheri Tafreshi M, Rassouli M, Soori H. The reasons for using acupuncture for pain relief. Iran Red Crescent Med J 2014; 16: e15435. |
| 26. | He YX, Chu HR, Tong L, Li N, Sun PY, Wu LB. Effect of mild moxibustion on “Shangjuxu” and “Tianshu” points on the expression of orexin-A and its receptor in rats with irritable bowel syndrome. Liaoning Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue Xue Bao 2020; 22: 88-91. |
| 27. | Luo J, Ran N, Zhou JW, Hou XM. Analysis of acupoint selection rules for acupuncture treatment of diarrhea type irritable bowel syndrome based on data mining technology. Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xin Xue Guan Bing Dian Zi Za Zhi 2020; 8: 156-7+160. |
| 28. | Weng ZJ, Hu SX, Zhang F, et al. Spinal cord astrocyte P2X7Rs mediate the inhibitory effect of electroacupuncture on visceral hypersensitivity of rat with irritable bowel syndrome. Purinergic Signal 2023; 19: 43-53. |
| 29. | Ji RR, Xu ZZ, Gao YJ. Emerging targets in neuroinflammation-driven chronic pain. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2014; 13: 533-48. |
| 30. | Greenwald JD, Shafritz KM. An Integrative neuroscience framework for the treatment of chronic pain: from cellular alterations to behavior. Front Integr Neurosci 2018; 12: 18. |
| 31. | Sun YN, Luo JY, Rao ZR, Lan L, Duan L. GFAP and Fos immunoreactivity in lumbo-sacral cord and medulla oblongata after chronic colonic inflammation in rats. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11: 4827-32. |
| 32. | Zhou Y, Zhang F, Weng ZJ, et al. Regulation of GFAP and P2X3 receptors in the spinal cord of IBS rats with visceral pain. Shi Jie Ke Xue Ji Shu-Zhong Yi Yao Xian Dai Hua 2021; 23: 2919-27. |
| 33. | Allen NJ, Barres BA. Neuroscience: Glia - more than just brain glue. Nature 2009; 457: 675-7. |
| 34. |
Chen Y, Zhang X, Wang C, Li G, Gu Y, Huang LY. Activation of P2X7 receptors in glial satellite cells reduces pain through downregulation of P2X3 receptors in nociceptive neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008; 105: 16773-8.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | ZHANG Boyang, ZHOU Yang, FENG Liyuan, SUI Dan, HE Lei, TONG Dan, WANG Ruoyu, SUI Xue, SONG Jing, WANG Dongyan. A neural regulation mechanism of head electroacupuncture on brain network of patients with stroke related sleep disorders [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(6): 1268-1276. |
| [2] | XU Yingshan, WU Chunxiao, YU Wei, GUO Hongji, LU Liming, XU Nenggui, TANG Chunzhi. Systematic review and Meta-analysis of brain plasticity associated with electroacupuncture in experimental ischemic stroke [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(5): 859-870. |
| [3] | CHEN Yonglin, OUYANG Ling, MENG Lingling, WU Bufan, PENG Rou, LIU Sitong, HOU Dan, WANG Yaling, JING Xinyue, LU Shengfeng, FU Shuping. Electroacupuncture ameliorates blood-brain barrier disruption after ischemic stroke through histone acetylation regulation at the matrix metalloproteinase 9 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 2 genes [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(4): 734-744. |
| [4] | WANG Shaosong, SUN Jingqing, FENG Qingyin, LI Bin, WANG Xin, YUAN Fan, CUI Yingxue. Effectivenss of electroacupuncture for skeletal muscle pain in Parkinson's disease: a Clinical randomized controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(2): 388-395. |
| [5] | QIN Xiaoyu, WANG Chunai, XUE Jianjun, ZHANG Jie, LU Xiaoting, DING Shengshuang, GE Long, WANG Minzhen. Efficacy of electroacupuncture on myocardial protection and postoperative rehabilitation in patients undergoing cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 1-15. |
| [6] | SUN Qianhui, CHENG Kai, DAI Xingye, YANG Zhiwen, WU Xiaoling, XU Chang, QIU Xinghua, GAO Xiaofeng, LIU Daonan, YANG Qirui. Effect of electroacupuncture at Neiguan (PC6) at different time points on myocardial ischemia reperfusion arrhythmia in rats [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 113-121. |
| [7] | DU Zhongheng, CONG Wenjie, TANG Kejing, ZHENG Qiqi, SONG Zhiwei, CHEN Yong, YANG Su, ZHANG Chunwu, YE Tianshen. Electroacupuncture stimulating Zusanli (ST36), Sanyinjiao (SP6) in mice with collagen-induced arthritis leads to adenosine A2A receptor-mediated alteration of p38α mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling and inhibition of osteoclastogenesis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1103-1109. |
| [8] | JIANG Jianzhen, ZHANG Xin, LUO Zhenguo, SU Chengguo, ZHOU Haiyan, JIANG Yuqing, XIAO Xianjun, CHEN Yunfei, ZHU Jun. Efficacy of electroacupuncture stimulating Zusanli (ST36) and Xuanzhong (GB39) on synovial angiogenesis in rats with adjuvant arthritis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 955-962. |
| [9] | LI Zhihao, HAN Wenjun, SONG Xiuling, LI Yan, CHEN Yuelai. Electroacupuncture stimulating Zhongji (CV3), Guanyuan (CV4), and bilateral Dahe (KI12) attenuates inflammation in rats with chronic nonbacterial prostatitis induced by estradiol through inhibiting toll-like receptor 4 pathway [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 963-972. |
| [10] | DING Luobin, WANG Huajun, LI Yao, LI Jia, LI Ling, GAO Yangping, GUAN Jian, GENG Weiqiang. Electroacupuncture stimulating Neixiyan (EX-LE5) and Dubi (ST35) alleviates osteoarthritis in rats induced by anterior cruciate ligament transaction via affecting DNA methylation regulated transcription of miR-146a and miR-140-5p [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 983-990. |
| [11] | SUN Mengzhu, ZHANG Yujie, SONG Yafang, GUO Jing, WANG Yuhang, XIN Chen, GU Dongmei, SUN Jianhua, PEI Lixia. Electroacupuncture alleviates water avoidance stress-induced irritable bowel syndrome in mice by improving intestinal barrier functions and suppressing the expression of inflammatory cytokines [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(3): 494-500. |
| [12] | HAN Rui, CHANG Junzhao, LIU Qianqian, LIU Haitao, LI Junwei. Efficacy of electroacupunture at Zusanli (ST36) on jumping-injured muscle based on transcriptome sequencing and genes analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(2): 322-328. |
| [13] | Minh Duc Nguyen, Thanh Van Tran, Quoc Vinh Nguyen, Ninh Khac Nguyen, Son Truong Vu, Luu Trong Nguyen, Linh Vu Phuong Dang. Effectiveness on post-stroke hemiplegia in patients: electroacupuncture plus cycling vs electroacupuncture alone [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(2): 352-358. |
| [14] | XU Chang, LI Na, WU Xiaoling, DAI Xingye, YANG Zhiwen, SUN Qianhui, SHI Tianyu, CHAI Yemao, PANG Dandan, CHENG Kai. Effect of electroacupuncture on inflammatory signal expression in local tissues of rats with chronic pelvic pain syndrome based on purinergic 2X7 receptor/NOD-like receptor pyrin domain-containing 3 signal pathway [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(6): 965-971. |
| [15] | SUN Mengzhu, ZHANG Yujie, SONG Yafang, GUO Jing, ZHAO Tingting, WANG Yuhang, PEI Lixia, SUN Jianhua. Electroacupuncture at Tianshu (ST25) and Zusanli (ST36) alleviates stress-induced irritable bowel syndrome in mice by modulating gut microbiota and corticotropin-releasing factor [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(5): 732-740. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

