Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (1): 32-38.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20220425.001
Previous Articles Next Articles
Electroacupuncture alleviates zymosan-induced colorectal hypersensitivity
LI Siting1, WANG Shaojun1( ), YIN Yehui1, DE Gejing2, LI Caicai1, WANG Ziyan1, CAO Wenjie1
), YIN Yehui1, DE Gejing2, LI Caicai1, WANG Ziyan1, CAO Wenjie1
- 1 Institute of Acupuncture and Moxibustion, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100700, China
2 Institute of Chinese Materia Medica, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100700, China
-
Received:2022-01-16Accepted:2022-03-22Online:2025-02-15Published:2022-04-25 -
Contact:WANG Shaojun, Institute of Acupuncture and Moxibustion, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100700, China.ddwsj5@yeah.net , Telephone: +86-10-64089729 -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China(Transient Potential Vanilloid Receptor1 Participates In The Mechanism Of Acupuncture Alleviating Visceral Hypersensitivity)(81373724);The Joint Innovation Funds of China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences(Clinical observation of acupuncture in the treatment of chronic urticaria)(ZJYB2021-06)
Cite this article
LI Siting, WANG Shaojun, YIN Yehui, DE Gejing, LI Caicai, WANG Ziyan, CAO Wenjie. Electroacupuncture alleviates zymosan-induced colorectal hypersensitivity[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(1): 32-38.
share this article
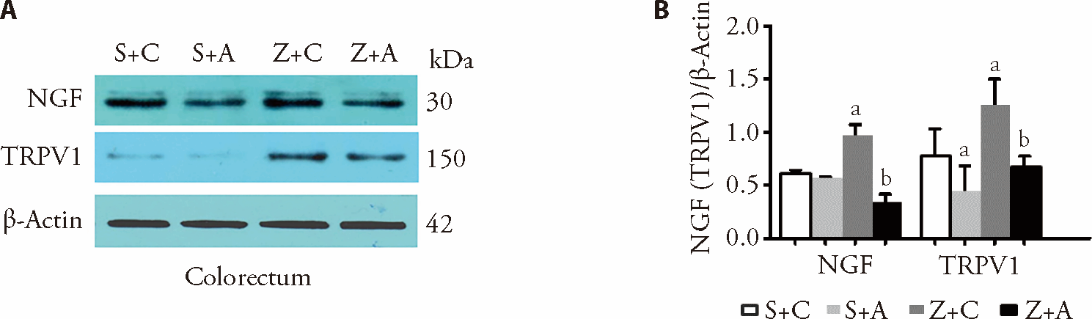
Figure 1 EA attenuates zymosan-induced expression of TRPV1 and NGF in the colorectum. Protein levels were evaluated by Western blotting. The representative western blot diagram was shown in A and the statistical analysis diagram was shown in B. Both proteins were upregulated by zymosan injection (P < 0.05, S + C vs Z + C), an effect that was abrogated by EA (P < 0.05, Z + A vs Z + C). Anti-TrpV1 (Alomone Labs, Jerusalem, Israel; #Acc-030, 150KD, delusion: 1 : 800), anti-NGF (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, #sc-548, 30 kDa, delusion: 1:800). aP < 0.05 (versus S + C). bP < 0.05 (versus Z + C).
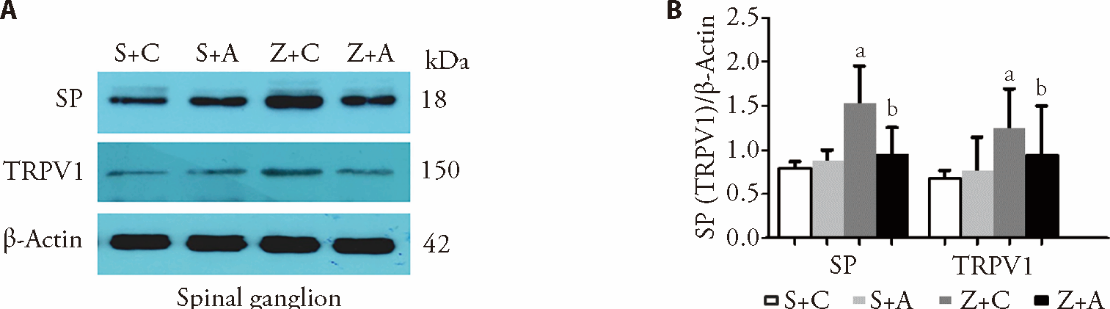
Figure 2 EA attenuates zymosan-induced expression of TRPV1 and SP in the spinal ganglion. Protein levels were evaluated by western blotting. Protein levels were evaluated by western blotting. The representative western blot diagram was shown in A and the statistical analysis diagram was shown in B. The expression of both proteins was upregulated by zymosan injection (P < 0.05, S + C vs Z + C), but this effect was reversed by EA (P < 0.05, Z + A vs Z + C). The blot is representative of at least 3 independent experiments. Anti-SP (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, 18 kDa, #sc-9758, delusion: 1 : 700). aP < 0.05 (versus S + C). bP < 0.05 (versus Z + C).

Figure 3 EA attenuates zymosan-induced expression of TRPV1 and PKCγ the in spinal cord. Protein levels were evaluated by western blotting The representative western blot diagram was shown in A and the statistical analysis diagram was shown in B. Both proteins were upregulated by zymosan injection (P < 0.05, S + C vs Z + C), but the increase was abolished by EA. The blot is representative of at least 3 independent experiments. PKCγ (Millipore; 75kD, #05983, delusion: 1 : 800). aP < 0.05 (versus S + C). bP < 0.05 (versus Z + C).

Figure 4 TRPV1/IB4 double immunofluorescence labeling of neurons in the spinal ganglion Coexpression of TRPV1 (red) and IB4 (green) in neurons can be seen in the merged images (yellow). Representative neurons are shown enlarged in the inset in the upper-left corner of each panel. Arrowheads indicate immunopositive neurons. Scale bar, 100 μm. Anti-IB4 (Sigma-Aldrich; #L2895, delusion: 1 : 500).
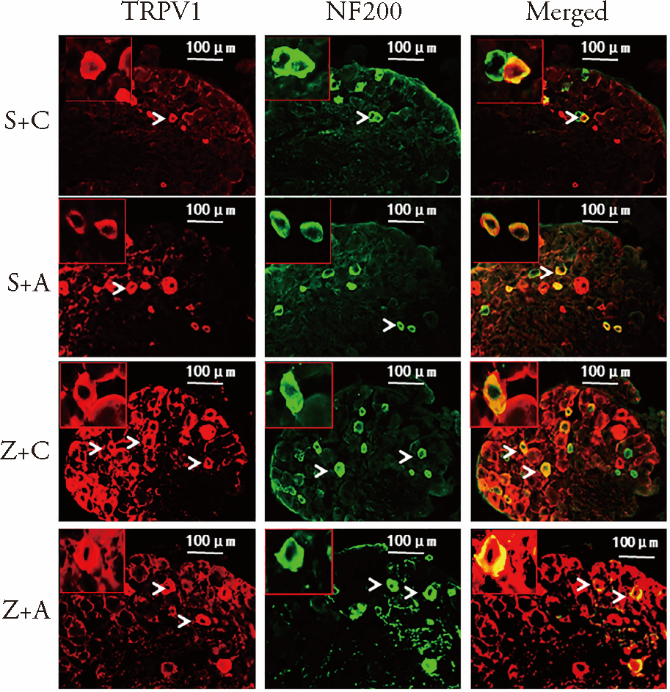
Figure 5 TRPV1/CGRP double immunofluorescence labeling of neurons in the spinal ganglion Coexpression of TRPV1 (red) and CGRP (green) in neurons can be seen in the merged images (yellow). Representative neurons are shown enlarged in the inset in the upper-left corner of each panel. Arrowheads indicate immunopositive neurons. Scale bar, 100 μm. Goat anti-mouse CGRP (Pierce, Rockford, IL, USA; #PA1-85250, delusion: 1∶400).

Figure 6 TRPV1/NF200 double immunofluorescence labeling of neurons in the spinal ganglion. Coexpression of TRPV1 (red) and NF200 (green) in neurons can be seen in the merged images (yellow). Representative neurons are shown enlarged in the inset in the upper-left corner of each panel. Arrowheads indicate immunopositive neurons. Scale bar, 100 μm. NF200 (Abcam; #ab4680, delusion: 1∶500).
| 1. | Wang SJ, Yang HY, Xu GS. Acupuncture alleviates colorectal hypersensitivity and correlates with the regulatory mechanism of TrpV1 and p-ERK. ECAM 2012: 483123. |
| 2. |
Shinoda M, Feng B, Gebhart GF. Peripheral and central P2X receptor contributions to colon mechanosensitivity and hypersensitivity in the mouse. Gastroenterology 2009; 137: 2096-104.
DOI PMID |
| 3. | Wang SJ, Yang HY, Wang F, et al. Acupoint specificity on colorectal hypersensitivity alleviated by acupuncture and the correlation with the brain-gut axis. Neurochemical Res 2015; 40: 1274-82. |
| 4. | Zhao M, Wang Z, Weng Z, et al. Electroacupuncture improves ibs visceral hypersensitivity by inhibiting the activation of astrocytes in the medial thalamus and anterior cingulate cortex. ECAM 2020: 2562979. |
| 5. | Jin D, Liu Y, Lyu S, et al. Electroacupuncture and moxibustion modulate the bdnf and trkb expression in the colon and dorsal root ganglia of ibs rats with visceral hypersensitivity. ECAM 2021: 8137244. |
| 6. |
Chen Y, Cheng J, Zhang Y, et al. Electroacupuncture at ST36 relieves visceral hypersensitivity via the NGF/TrkA/TRPV1 peripheral afferent pathway in a rodent model of post-inflammation rectal hypersensitivity. J Inflamm Res 2021; 14: 325-39.
DOI PMID |
| 7. | Galoyan SM, Petruska JC, Mendell LM. Mechanisms of sensitization of the response of single dorsal root ganglion cells from adult rat to noxious heat. Eur J Neurosci 2015; 18: 535-41. |
| 8. |
McDowell TS, Wang ZY, Singh R, et al. CB1 cannabinoid receptor agonist prevents NGF-induced sensitization of TRPV1 in sensory neurons. Neurosci Lett 2013; 551: 34-8.
DOI PMID |
| 9. |
Becker A, Grecksch G, Schwegler H, et al. Expression of mRNA of neurotrophic factors and their receptors are significantly altered after subchronic ketamine treatment. Med Chem 2008; 4: 256-63.
PMID |
| 10. | Tu WZ, Lou XF, Jiang SH, et al. Effect of electroacupuncture of local plus distal acupoints in the same segments of spinal cord on spinal substance P expression in rats with chronic radicular pain. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu 2008; 33: 7-12. |
| 11. | Polgár E, Fowler JH, McGill MM, et al. The types of neuron which contain protein kinase C gamma in rat spinal cord. Brain Res 1999; 933: 71-80. |
| 12. | Kim MJ, Namgung U, Hong KE. Regenerative effects of moxibustion on skeletal muscle in collagen-induced arthritic mice. J Acupunct Meridian Stud 2012; 5: 126-35. |
| 13. | Han JS. Acupuncture: neuropeptide release produced by electrical stimulation of different frequencies. Trends Neurosci 2003; 26: 17-22. |
| 14. |
Li F, Omori N, Sato K, et al. Coordinate expression of survival p-ERK and proapoptotic cytochrome c signals in rat brain neurons after transient MCAO. Brain Res 2002; 958: 83-8.
DOI PMID |
| 15. | Xian PF, Chen Y, Yang L, et al. Effect of bee venom injection on TrkA and TRPV1 expression in the dorsal root ganglion of rats with collagen-induced arthritis. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 2016; 36: 838-41. |
| 16. | Bao Y, Gao Y, Yang L, et al. The mechanism of μ-opioid receptor (MOR)-TRPV1 crosstalk in TRPV1 activation involves morphine anti-nociception, tolerance and dependence. Channels (Austin) 2015; 9: 235-43. |
| 17. |
Khan AA, Diogenes A, Jeske NA, et al. Tumor necrosis factor alpha enhances the sensitivity of rat trigeminal neurons to capsaicin. Neuroscience 2008; 155: 503-9.
DOI PMID |
| 18. |
Aguilera M, Cerdà-Cuéllar M, Martínez V. Antibiotic-induced dysbiosis alters host-bacterial interactions and leads to colonic sensory and motor changes in mice. Gut Microbes 2015; 6: 10-23.
DOI PMID |
| 19. |
Watkins LR, Milligan ED, Maier SF. Spinal cord glia: New players in pain. Pain 2001; 93: 201-5.
DOI PMID |
| 20. |
Ciccarelli R, Ballerini P, Sabatino G, et al. Involvement of astrocytes in purine-mediated reparative processes in the brain. Int J Dev Neurosci 2001; 19: 395-414.
PMID |
| 21. |
Shumilla JA, Liron T, Mochly-Rosen D, et al. Ethanol withdrawal-associated allodynia and hyperalgesia: Age-dependent regulation by protein kinase C epsilon and gamma isoenzymes. J Pain 2005; 6: 535-49.
PMID |
| 22. | Wang LD, Zhao JM, Huang RJ, et al. Study on the mechanism underlying the regulation of the NMDA receptor pathway in spinal dorsal horns of visceral hypersensitivity rats by moxibustion. ECAM 2016: 3174608. |
| 23. | Blivis D, Haspel G, Mannes PZ, et al. Identification of a novel spinal nociceptive-motor gate control for Aδ pain stimuli in rats. Elife 2017: 24: 6-10. |
| 24. | Kashiba H, Ueda Y. Acupuncture to the skin induces release of substance P and calcitonin gene-related peptide from peripheral terminals of primary sensory neurons in the rat. Am J Chinese Med 2012; 19: 189-97. |
| 25. |
Millan MJ. The induction of pain: An integrative review. Prog Neurobiol 1999; 57: 1-164.
DOI PMID |
| 26. |
Liang L, Wang Z, Lü N, et al. Involvement of nerve injury and activation of peripheral glial cells in tetanic sciatic stimulation-induced persistent pain in rats. J Neurosci Res 2010; 88: 2899-910.
DOI PMID |
| 27. |
Zheng Q, Fang D, Cai J, et al. Enhanced excitability of small dorsal root ganglion neurons in rats with bone cancer pain. Mol Pain 2012; 8: 24.
DOI PMID |
| 28. |
Yu L, Yang F, Luo H, et al. The role of TRPV1 in different subtypes of dorsal root ganglion neurons in rat chronic inflammatory nociception induced by complete Freund’s adjuvant. Mol Pain 2008; 4: 61.
DOI PMID |
| 29. | Ye Y, Bae SS, Viet CT, et al. , IB4 (+) and TRPV1 (+) sensory neurons mediate pain but not proliferation in a mouse model of squamous cell carcinoma. Behav Brain Funct 2014; 10. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

