Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (6): 1236-1246.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20240626.004
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
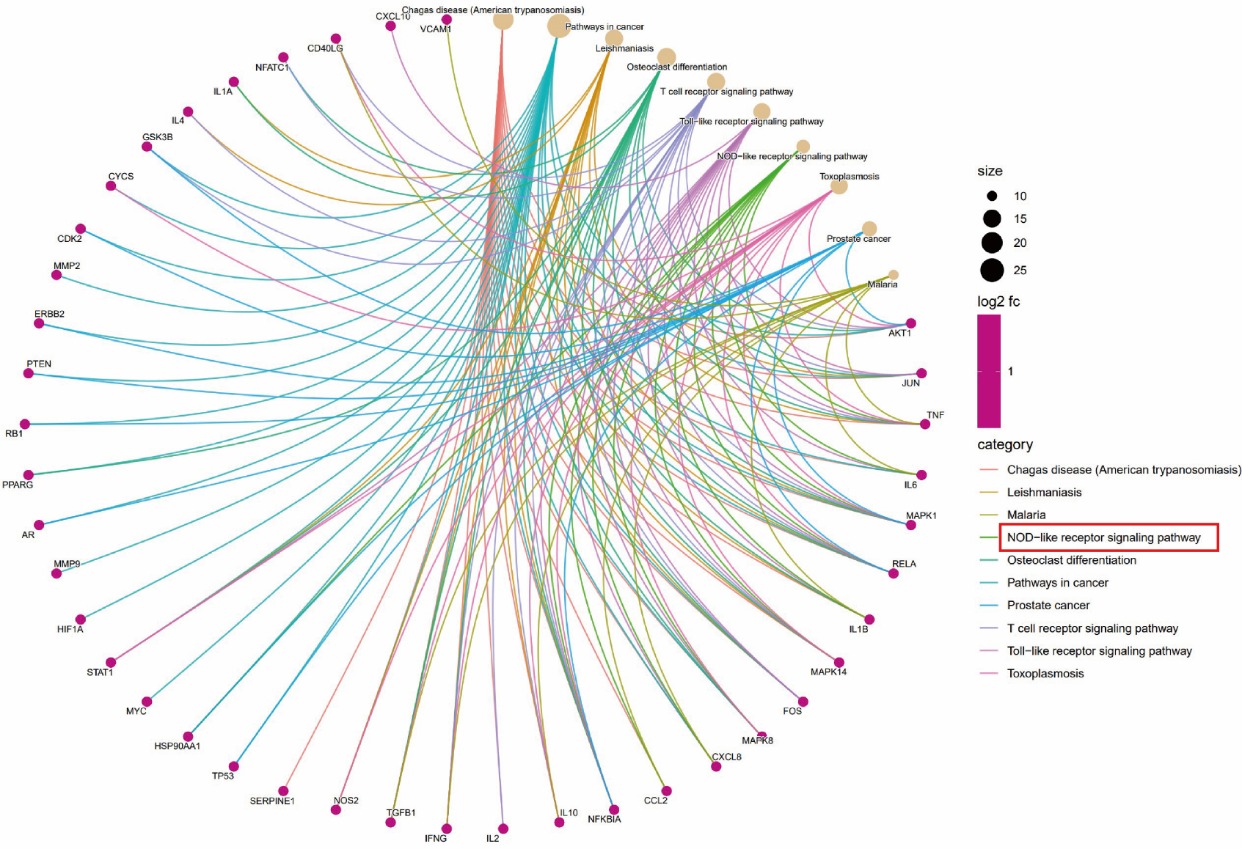
Bufei Huoxue capsule (补肺活血胶囊) alleviates silicosis by inhibiting the activation of nucleotide-like receptor containing pyrin domain 3 inflammasome and macrophages polarization based on network pharmacology
HANG Wenlu1, WANG Lin1, BO Yun2, ZUO Shurun1, WANG Songquan3, LI Haiquan1, BU Chunlu1, ZHAO Jie1( ), ZHOU Xianmei4(
), ZHOU Xianmei4( )
)
- 1 Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, Second Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou 221000, China
2 Medical College of Anhui University of Science and Technology, Anhui 232001, China
3 School of Mechatronic Engineering, Jiangsu Normal University, Xuzhou 221000, China
4 Department of Respiratory Medicine, Jiangsu Province Hospital of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210023, China
-
Received:2023-11-11Accepted:2024-03-08Online:2024-12-15Published:2024-06-26 -
Contact:Prof. ZHOU Xianmei, Department of Respiratory Medicine, Jiangsu Province Hospital of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210023, China. zhouxianmeijs@aliyun.com Telephone: +86-13813477830
Prof. ZHAO Jie, Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, Second Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou 221000, China.15005216612@163.com -
Supported by:Jiangsu Natural Science Foundation Youth Program: Regulation of Alveolar Macrophage Pyroptosis based on (Never in Mitosis Gene A)-Related Kinase 7 /Nucleotide-like Receptor Containing Pyrin Domain 3 Inflammasome to Explore the Mechanism of Bufei Huoxue Capsule on Pulmonary Fibrosis in Silicosis(BK20220236);Key Research and Development Project of Xuzhou City: Evaluation of Pyroptosis Induced by Nucleotide-like Receptor Containing Pyrin Domain 3 Inflammasome Activation in Pneumoconiosis Patients by Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid Ion Assay Combined with High-Resolution Computed Tomography Quantitative Analysis(KC22212);Youth Medical Science and Technology Innovation Project of Xuzhou Municipal Health Commission and Development Fund of Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University: Study on the Regulation of Various Cytokines and the Effect of c-Jun Activation Domain-Binding Protein 1 on Immune Response in Lung Cancer(XWKYHT20210565);Youth Medical Science and Technology Innovation Project of Xuzhou Municipal Health Commission and Development Fund of Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University: Study on the Regulation of Various Cytokines and the Effect of c-Jun Activation Domain-Binding Protein 1 on Immune Response in Lung Cancer(XYFY2020051)
Cite this article
HANG Wenlu, WANG Lin, BO Yun, ZUO Shurun, WANG Songquan, LI Haiquan, BU Chunlu, ZHAO Jie, ZHOU Xianmei. Bufei Huoxue capsule (补肺活血胶囊) alleviates silicosis by inhibiting the activation of nucleotide-like receptor containing pyrin domain 3 inflammasome and macrophages polarization based on network pharmacology[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(6): 1236-1246.
share this article
| No. | Uniprot ID | Gene name | Protein target | Degree | Closeness centrality |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | P31749 | AKT1 | RAC-alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase | 98 | 0.514815 |
| 2 | P04637 | TP53 | Cellular tumor antigen p53 | 96 | 0.526515 |
| 3 | P05412 | JUN | Transcription factor Jun | 96 | 0.53668 |
| 4 | P01375 | TNF | Tumor necrosis factor | 86 | 0.5 |
| 5 | P07900 | HSP90AA1 | Heat shock protein HSP 90-alpha | 84 | 0.518657 |
| 6 | P05231 | IL6 | Interleukin-6 | 80 | 0.5 |
| 7 | P28482 | MAPK1 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 | 72 | 0.496429 |
| 8 | Q04206 | RELA | Transcription factor p65 | 70 | 0.477663 |
| 9 | P01106 | MYC | Myc proto-oncogene protein | 62 | 0.468013 |
| 10 | P03372 | ESR1 | Estrogen receptor | 60 | 0.466443 |
| 11 | P01584 | IL1B | Interleukin-1 beta | 60 | 0.458746 |
| 12 | Q16539 | MAPK14 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 14 | 58 | 0.464883 |
| 13 | P01100 | FOS | Protein c-Fos | 58 | 0.482639 |
| 14 | P42224 | STAT1 | Signal transducer and activator of transcription 1-alpha/beta | 52 | 0.468013 |
| 15 | Q16665 | HIF1A | Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha | 52 | 0.469595 |
| 16 | P14780 | MMP9 | Matrix metalloproteinase-9 | 50 | 0.457237 |
| 17 | P45983 | MAPK8 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 8 | 50 | 0.451299 |
| 18 | Q96EB6 | SIRT1 | NAD-dependent protein deacetylase sirtuin-1 | 48 | 0.448387 |
| 19 | P10145 | CXCL8 | Interleukin-8 | 48 | 0.444089 |
| 20 | P13500 | CCL2 | C-C motif chemokine 2 | 48 | 0.429012 |
| 21 | P10275 | AR | Androgen receptor | 44 | 0.448387 |
| 22 | P25963 | NFKBIA | NF-kappa-B inhibitor alpha | 44 | 0.448387 |
| 23 | P37231 | PPARG | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma | 44 | 0.454248 |
| 24 | P22301 | IL10 | Interleukin-10 | 44 | 0.394886 |
| 25 | P06400 | RB1 | Retinoblastoma-associated protein | 42 | 0.435737 |
| 26 | P60568 | IL2 | Interleukin-2 | 42 | 0.44127 |
| 27 | P60484 | PTEN | Phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate 3-phosphatase and dual-specificity protein phosphatase PTEN | 40 | 0.434375 |
| 28 | P05112 | IL4 | Interleukin-4 | 40 | 0.41369 |
| 29 | P17612 | PRKACA | cAMP-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha | 40 | 0.431677 |
| 30 | P01579 | IFNG | Interferon gamma | 40 | 0.418675 |
| 31 | P04626 | ERBB2 | Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-2 | 38 | 0.455738 |
| 32 | Q03135 | CAV1 | Caveolin-1 | 38 | 0.445513 |
| 33 | P08253 | MMP2 | 72 kDa type IV collagenase | 36 | 0.435737 |
| 34 | Q13950 | RUNX2 | Runt-related transcription factor 2 | 36 | 0.434375 |
| 35 | P01137 | TGFB1 | Transforming growth factor beta-1 proprotein | 34 | 0.439873 |
| 36 | P02741 | CRP | C-reactive protein | 34 | 0.380822 |
| 37 | P24941 | CDK2 | Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 | 32 | 0.417417 |
| 38 | P09601 | HMOX1 | Heme oxygenase 1 | 30 | 0.42638 |
| 39 | P99999 | CYCS | Cytochrome c | 30 | 0.430341 |
| 40 | P35228 | NOS2 | Nitric oxide synthase, inducible | 30 | 0.430341 |
| 41 | P05121 | SERPINE1 | Plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 | 30 | 0.374663 |
| 42 | P19320 | VCAM1 | Vascular cell adhesion protein 1 | 30 | 0.379781 |
| 43 | P02778 | CXCL10 | C-X-C motif chemokine 10 | 30 | 0.3687 |
| 44 | P29474 | NOS3 | Nitric oxide synthase, endothelial | 28 | 0.431677 |
| 45 | P49841 | GSK3B | Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta | 28 | 0.422492 |
| 46 | P01583 | IL1A | Interleukin-1 alpha | 28 | 0.394886 |
| 47 | Q07869 | PPARA | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha | 28 | 0.457237 |
| 48 | P31751 | AKT2 | RAC-beta serine/threonine-protein kinase | 26 | 0.394886 |
| 49 | P01375 | TNF | Tumor necrosis factor | 26 | 0.414925 |
| 50 | Q14568 | HSP90AA2 | Heat shock protein HSP 90-alpha A2 | 24 | 0.410029 |
| 51 | P13232 | IL7 | Interleukin-7 | 24 | 0.361039 |
| 52 | P49137 | MAPK2 | MAP kinase-activated protein kinase 2 | 24 | 0.381868 |
| 53 | Q04206 | RELA | Transcription factor p65 | 24 | 0.402899 |
Table 1 Core gene targets for silicosis treatment with Bufei Huoxue capsule
| No. | Uniprot ID | Gene name | Protein target | Degree | Closeness centrality |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | P31749 | AKT1 | RAC-alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase | 98 | 0.514815 |
| 2 | P04637 | TP53 | Cellular tumor antigen p53 | 96 | 0.526515 |
| 3 | P05412 | JUN | Transcription factor Jun | 96 | 0.53668 |
| 4 | P01375 | TNF | Tumor necrosis factor | 86 | 0.5 |
| 5 | P07900 | HSP90AA1 | Heat shock protein HSP 90-alpha | 84 | 0.518657 |
| 6 | P05231 | IL6 | Interleukin-6 | 80 | 0.5 |
| 7 | P28482 | MAPK1 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 | 72 | 0.496429 |
| 8 | Q04206 | RELA | Transcription factor p65 | 70 | 0.477663 |
| 9 | P01106 | MYC | Myc proto-oncogene protein | 62 | 0.468013 |
| 10 | P03372 | ESR1 | Estrogen receptor | 60 | 0.466443 |
| 11 | P01584 | IL1B | Interleukin-1 beta | 60 | 0.458746 |
| 12 | Q16539 | MAPK14 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 14 | 58 | 0.464883 |
| 13 | P01100 | FOS | Protein c-Fos | 58 | 0.482639 |
| 14 | P42224 | STAT1 | Signal transducer and activator of transcription 1-alpha/beta | 52 | 0.468013 |
| 15 | Q16665 | HIF1A | Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha | 52 | 0.469595 |
| 16 | P14780 | MMP9 | Matrix metalloproteinase-9 | 50 | 0.457237 |
| 17 | P45983 | MAPK8 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 8 | 50 | 0.451299 |
| 18 | Q96EB6 | SIRT1 | NAD-dependent protein deacetylase sirtuin-1 | 48 | 0.448387 |
| 19 | P10145 | CXCL8 | Interleukin-8 | 48 | 0.444089 |
| 20 | P13500 | CCL2 | C-C motif chemokine 2 | 48 | 0.429012 |
| 21 | P10275 | AR | Androgen receptor | 44 | 0.448387 |
| 22 | P25963 | NFKBIA | NF-kappa-B inhibitor alpha | 44 | 0.448387 |
| 23 | P37231 | PPARG | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma | 44 | 0.454248 |
| 24 | P22301 | IL10 | Interleukin-10 | 44 | 0.394886 |
| 25 | P06400 | RB1 | Retinoblastoma-associated protein | 42 | 0.435737 |
| 26 | P60568 | IL2 | Interleukin-2 | 42 | 0.44127 |
| 27 | P60484 | PTEN | Phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate 3-phosphatase and dual-specificity protein phosphatase PTEN | 40 | 0.434375 |
| 28 | P05112 | IL4 | Interleukin-4 | 40 | 0.41369 |
| 29 | P17612 | PRKACA | cAMP-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha | 40 | 0.431677 |
| 30 | P01579 | IFNG | Interferon gamma | 40 | 0.418675 |
| 31 | P04626 | ERBB2 | Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-2 | 38 | 0.455738 |
| 32 | Q03135 | CAV1 | Caveolin-1 | 38 | 0.445513 |
| 33 | P08253 | MMP2 | 72 kDa type IV collagenase | 36 | 0.435737 |
| 34 | Q13950 | RUNX2 | Runt-related transcription factor 2 | 36 | 0.434375 |
| 35 | P01137 | TGFB1 | Transforming growth factor beta-1 proprotein | 34 | 0.439873 |
| 36 | P02741 | CRP | C-reactive protein | 34 | 0.380822 |
| 37 | P24941 | CDK2 | Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 | 32 | 0.417417 |
| 38 | P09601 | HMOX1 | Heme oxygenase 1 | 30 | 0.42638 |
| 39 | P99999 | CYCS | Cytochrome c | 30 | 0.430341 |
| 40 | P35228 | NOS2 | Nitric oxide synthase, inducible | 30 | 0.430341 |
| 41 | P05121 | SERPINE1 | Plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 | 30 | 0.374663 |
| 42 | P19320 | VCAM1 | Vascular cell adhesion protein 1 | 30 | 0.379781 |
| 43 | P02778 | CXCL10 | C-X-C motif chemokine 10 | 30 | 0.3687 |
| 44 | P29474 | NOS3 | Nitric oxide synthase, endothelial | 28 | 0.431677 |
| 45 | P49841 | GSK3B | Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta | 28 | 0.422492 |
| 46 | P01583 | IL1A | Interleukin-1 alpha | 28 | 0.394886 |
| 47 | Q07869 | PPARA | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha | 28 | 0.457237 |
| 48 | P31751 | AKT2 | RAC-beta serine/threonine-protein kinase | 26 | 0.394886 |
| 49 | P01375 | TNF | Tumor necrosis factor | 26 | 0.414925 |
| 50 | Q14568 | HSP90AA2 | Heat shock protein HSP 90-alpha A2 | 24 | 0.410029 |
| 51 | P13232 | IL7 | Interleukin-7 | 24 | 0.361039 |
| 52 | P49137 | MAPK2 | MAP kinase-activated protein kinase 2 | 24 | 0.381868 |
| 53 | Q04206 | RELA | Transcription factor p65 | 24 | 0.402899 |
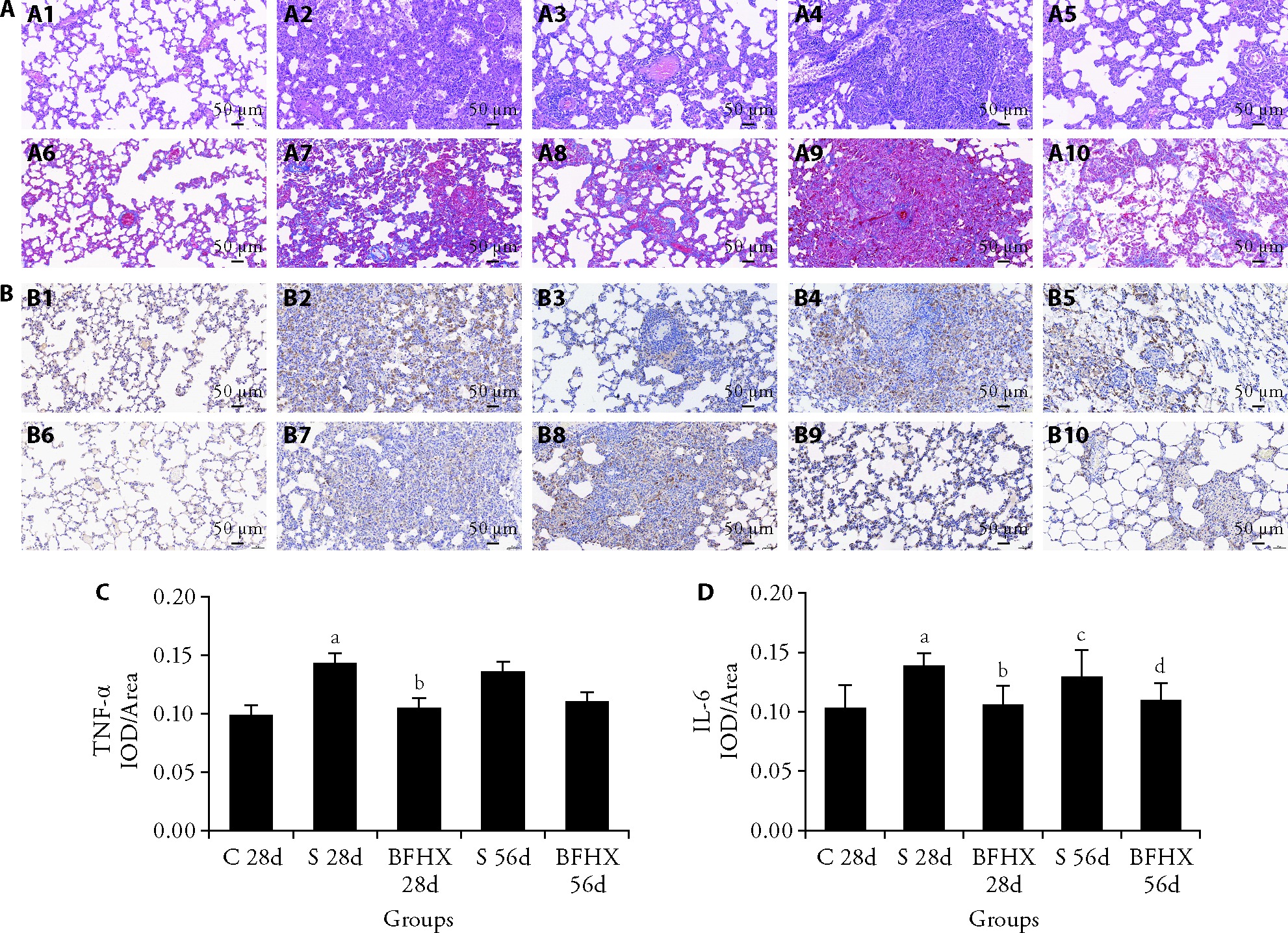
Figure 3 BFHX treatment reduced silicotic lung inflammation and fibrosis A: HE and Masson staining of lung tissues (× 20); A1-A5: HE staining; A1: control group; A2: model 28 d group; A3: BFHX 28 d group; A4: model 56 d group; A5: BFHX 56 d group; A6-10: Masson staining; A6: control group; A7: model 28 d group; A8: BFHX 28 d group; A9: model 56 d group; A10: BFHX 56 d group; B: immunohistochemical staining of TNF-α, IL-6 (× 20); B1-5: TNF-α staining; B1: control group; B2: model 28 d group; B3: BFHX 28 d group; B4: model 56 d group; B5: BFHX 56 d group; B6-10: IL-6 staining; B6: control group; B7: model 28 d group; B8: BFHX 28 d group; B9: model 56 d group; B10: BFHX 56 d group; C: analysis of TNF-α expression; D: analysis of IL-6 expression. Model group: modeling by SiO2 suspension of 50 mg/mL; BFHX group: modeling followed by drug treatment intragastrically at a daily dose of 0.82 g/kg. BFHX: Bufei Huoxue capsule; C: control; S: SiO2 exposure model group; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor-alpha; IL-6: interleukin-6; IOD: integrated optical density; HE: hematoxylin and eosin. One?way analysis of variance was used to analyze the significance of differences between groups. The data were presented as the mean ± standard deviation (n = 6). aP < 0.01, compared with control group; bP < 0.01, compared with the SiO2 exposure group at the same time point; cP < 0.05, compared with control group; dP < 0.05, compared with the SiO2 exposure group at the same time point.
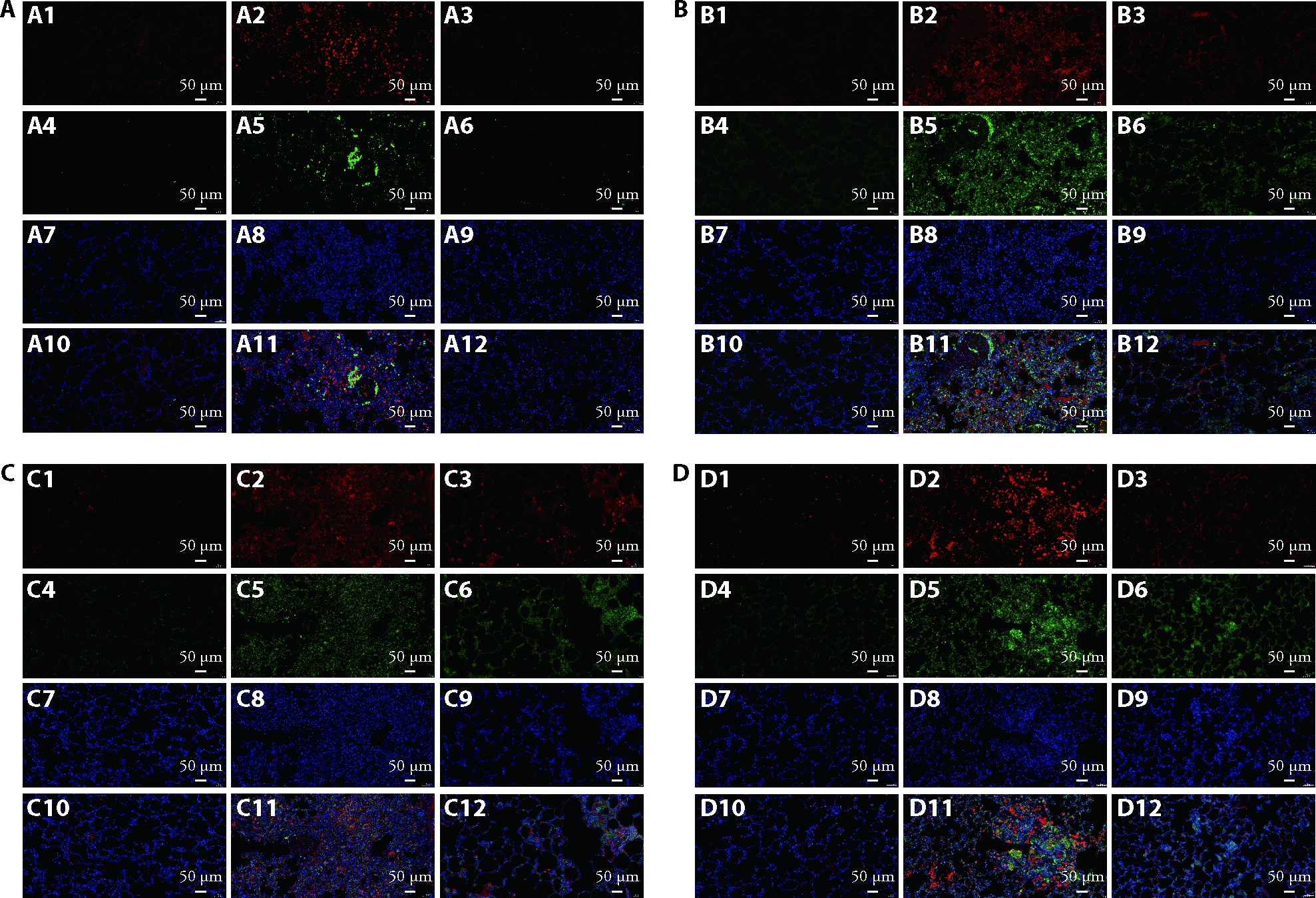
Figure 4 Immunofluorescence staining of NLRP3 signaling pathway in PMs A: double immunofluorescence staining for CD68+ and NLRP3 in lung tissues (× 20); A1, A2, A3: CD68+ staining; A4, A5, A6: NLRP3 staining; A7, A8, A9: DAPI staining; A10, A11, A12: merge of CD68+ and NLRP3 staining; A1, A4, A7, A10: control group; A2, A5, A8, A11: model group; A3, A6, A9, A12: BFHX group; B: double immunofluorescence staining for CD68+ and caspase-1 in lung tissues (× 20); B1, B2, B3: CD68+ staining; B4, B5, B6: caspase-1 staining; B7, B8, B9: DAPI staining; B10, B11, B12: merge of CD68+ and caspase-1 staining; B1, B4, B7, B10: control group; B2, B5, B8, B11: model group; B3, B6, B9, B12: BFHX group; C: double immunofluorescence staining for CD68+ and IL-1β in lung tissues (× 20); C1, C2, C3: CD68+ staining; C4, C5, C6: IL-1β staining; C7, C8, C9: DAPI staining; C10, C11, C12: merge of CD68+ and IL-1β staining; C1, C4, C7, C10: control group; C2, C5, C8, C11: model group; C3, C6, C9, C12: BFHX group; D: double immunofluorescence staining for CD68+ and IL-18 in lung tissues (× 20); D1, D2, D3: CD68+ staining; D4, D5, D6: IL-18 staining; D7, D8, D9: DAPI staining; D10, D11, D12: merge of CD68+ and IL-18 staining; D1, D4, D7, D10: control group; D2, D5, D8, D11: model group; D3, D6, D9, D12: BFHX group. Model group: 56 d of modeling by SiO2 suspension of 50 mg/mL (n = 3); BFHX group: 56 d of modeling followed by drug treatment intragastrically at a daily dose of 0.82 g/kg (n = 3). NLRP3: nucleotide-like receptor containing pyrin domain 3; PM: pulmonary macrophage; BFHX: Bufei Huoxue capsule; DAPI: 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; IL-1β: interleukin-1β; IL-18: interleukin-18.
| 1. | Leso V, Fontana L, Romano R, Gervetti P, Iavicoli I. Artificial stone associated silicosis: a systematic review. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2019; 16: 568. |
| 2. |
Harris DA, Willis J, Tomann M. A new era of coal workers' pneumoconiosis: decades in mines may not be required. Lancet 2020; 395: e82.
DOI PMID |
| 3. | Fubini B, Hubbard A. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS) generation by silica in inflammation and fibrosis. Free Radic Biol Med 2003; 34: 1507-16. |
| 4. |
Liu S, Chen D, Li X, et al. Fullerene nanoparticles: a promising candidate for the alleviation of silicosis-associated pulmonary inflammation. Nanoscale 2020; 12: 17470-9.
DOI PMID |
| 5. |
Huang Y, Xu W, Zhou R. NLRP3 inflammasome activation and cell death. Cell Mol Immunol 2021; 18: 2114-27.
DOI PMID |
| 6. |
Campden RI, Zhang Y. The role of lysosomal cysteine cathepsins in NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Arch Biochem Biophys 2019; 670: 32-42.
DOI PMID |
| 7. |
Luna-Gomes T, Santana PT, Coutinho-Silva R. Silica-induced inflammasome activation in macrophages: role of ATP and P2X7 receptor. Immunobiology 2015; 220: 1101-6.
DOI PMID |
| 8. |
Li X, Yan X, Wang Y, et al. NLRP3 inflammasome inhibition attenuates silica-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) in human bronchial epithelial cells. Exp Cell Res 2018; 362: 489-97.
DOI PMID |
| 9. | Tan S, Chen S. The mechanism and effect of autophagy, apoptosis, and pyroptosis on the Progression of Silicosis. Int J Mol Sci 2021; 22: 8110. |
| 10. | Jing Y, Zhang H, Cai Z, et al. Bufei Huoxue capsule attenuates PM2.5-induced pulmonary inflammation in mice. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2017; 2017: 1575793. |
| 11. | Hang WL, Li WJ, Shao Q, et al. Exploring the therapeutic effect of Bufei Huoxue capsule on patients with pneumoconiosis of Qi deficiency and blood stasis syndrome based on network pharmacology and clinical research. Zhong Cao Yao 2023; 45: 3819-25. |
| 12. | Gong XW, Cui KW, Huang YM, et al. Effects of Bufei Huoxue capsule on quality of life, respiratory function and oxidative stress in patients with stageⅡ pneumoconiosis. Jian Yan Yi Xue Yu Lin Chuang 2022; 19: 2628-31. |
| 13. | Hang WL, Zhao J, Li YJ, Wang L, Li HQ. Experimental study on the effect of Si and P ion content in SiO2 exposure environment on the degree of pulmonary fibrosis. Indian J Pathol Microbiol 2021; 64: 644-50. |
| 14. |
Schniering J, Guo L, Brunner M, et al. Evaluation of (99m)Tc-rhAnnexin V-128 SPECT/CT as a diagnostic tool for early stages of interstitial lung disease associated with systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Res Ther 2018; 20: 183.
DOI PMID |
| 15. | Wang L, Hauenstein AV. The NLRP3 inflammasome: Mechanism of action, role in disease and therapies. Mol Aspects Med 2020; 76: 100889. |
| 16. | Li T, Yang X, Xu H, Liu H. Early identification, accurate diagnosis, and treatment of Silicosis. Can Respir J 2022; 2022: 3769134. |
| 17. |
Almberg KS, Friedman LS, Rose CS, Go LHT, Cohen RA. Progression of coal workers' pneumoconiosis absent further exposure. Occup Environ Med 2020; 77: 748-51.
DOI PMID |
| 18. | Wang M, Zhang Z, Liu J, et al. Gefitinib and fostamatinib target EGFR and SYK to attenuate silicosis: a multi-omics study with drug exploration. Signal Transduct Target Ther 2022; 7: 157. |
| 19. | Hang WL, Wu Q, Li W, Bo Y, Zhou XM. Effect of silicon dioxide exposure on airway surface microenvironment and NEK7/NLPR3 inflammasome in rats. Yu Fang Yi Xue 2023; 35: 180-4. |
| 20. | Lam M, Mansell A, Tate MD. Another one fights the dust: targeting the NLRP3 inflammasome for the treatment of silicosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2022; 66: 601-11. |
| 21. | Peng Z, Duan M, Zhao K, Tang Y, Liang F. RAB20 deficiency promotes the development of silicosis via NLRP3 inflammasome. Front Immunol 2022; 13: 967299. |
| 22. |
Dostert C, Pétrilli V, Van Bruggen R, Steele C, Mossman BT, Tschopp J. Innate immune activation through Nalp3 inflammasome sensing of asbestos and silica. Science 2008; 320: 674-7.
DOI PMID |
| 23. | Song MY, Wang JX, Sun YL, et al. Tetrandrine alleviates silicosis by inhibiting canonical and non-canonical NLRP3 inflammasome activation in lung macrophages. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2022; 43: 1274-84. |
| 24. |
Phan THG, Paliogiannis P, Nasrallah GK, et al. Emerging cellular and molecular determinants of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Cell Mol Life Sci 2021; 78: 2031-57.
DOI PMID |
| 25. | Bing P, Zhou W, Tan S. Study on the mechanism of astragalus polysaccharide in treating pulmonary fibrosis based on "Drug-Target-Pathway" network. Front Pharmacol 2022; 13: 865065. |
| 26. | Li Y, Qin W, Liang Q, et al. Bufei Huoxue capsule alleviates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice via TGF-β1/Smad2/3 signaling. J Ethnopharmacol 2023; 316: 116733. |
| 27. | Tian LY, Cao GQ, Liu GT. Efficacy of Bufei Huoxue capsules in the treatment of silicosis. Guangdong Yi Xue 2014; 35:1778-9. |
| 28. |
Wei X, Xie F, Zhou X, et al. Role of pyroptosis in inflammation and cancer. Cell Mol Immunol 2022; 19: 971-92.
DOI PMID |
| 29. | Zhao Y, Hao C, Bao L, et al. Silica particles disorganize the polarization of pulmonary macrophages in mice. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 2020; 193: 110364. |
| 30. |
Wynn TA, Vannella KM. Macrophages in tissue repair, regeneration, and fibrosis. Immunity 2016; 44: 450-62.
DOI PMID |
| 31. |
Jorgensen I, Miao EA. Pyroptotic cell death defends against intracellular pathogens. Immunol Rev 2015; 265: 130-42.
DOI PMID |
| 32. | Nawaz A, Bilal M, Fujisaka S, et al. Depletion of CD206(+) M2-like macrophages induces fibro-adipogenic progenitors activation and muscle regeneration. Nat Commun 2022; 13: 7058. |
| 33. |
Wang J, Xu L, Xiang Z, et al. Microcystin-LR ameliorates pulmonary fibrosis via modulating CD206(+) M2-like macrophage polarization. Cell Death Dis 2020; 11: 136.
DOI PMID |
| 34. | Fan M, Xiao H, Song D, et al. A novel N-Arylpyridone compound alleviates the inflammatory and fibrotic reaction of silicosis by inhibiting the ASK1-p 38 pathway and regulating macrophage polarization. Front Pharmacol 2022; 13: 848435. |
| 35. |
Hussell T, Bell TJ. Alveolar macrophages: plasticity in a tissue-specific context. Nat Rev Immunol 2014; 14: 81-93.
DOI PMID |
| 36. |
Barbieri PG, Somigliana A, Carradori G. Severe silicosis due to diatomaceous earth in dental alginate: a necropsy study. Med Lav 2020; 111: 222-31.
DOI PMID |
| 37. |
Drinkall S, Lawrence CB, Ossola B, et al. The two pore potassium channel THIK-1 regulates NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Glia 2022; 70: 1301-16.
DOI PMID |
| 38. | Duan WX, Ye LS, Du H, Liu C, Duan Y, Mao LC. Analysis of the detection of metals and metalloids in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid for the etiological diagnosis value of pneumoconiosis. Zhong Hua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi 2021; 39: 844-8. |
| 39. | Kelley N, Jeltema D, Duan Y, He Y. The NLRP3 Inflammasome: an overview of mechanisms of activation and regulation. Int J Mol Sci 2019; 20: 3328. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 95
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 58
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||