Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (6): 1103-1109.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2023.06.001
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Electroacupuncture stimulating Zusanli (ST36), Sanyinjiao (SP6) in mice with collagen-induced arthritis leads to adenosine A2A receptor-mediated alteration of p38α mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling and inhibition of osteoclastogenesis
DU Zhongheng1, CONG Wenjie1, TANG Kejing1, ZHENG Qiqi1, SONG Zhiwei1, CHEN Yong1, YANG Su3, ZHANG Chunwu2, YE Tianshen1
- 1 Department of Acupuncture, the First Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou 325000, China
2 Department of Traditional Chinese Orthopedics & Traumatology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou 325000, China
3 Zhejiang Provincial Key Laboratory of Aging and Neurological Disorder Research, the First Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou 325000, China
-
Received:2022-06-22Accepted:2022-09-21Online:2023-10-25Published:2023-11-01 -
Contact:ZHANG Chunwu, Department of Traditional Chinese Orthopedics and Traumatology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou 325000, China. zcw6681@126.com; YE Tianshen, Department of Acupuncture, the First Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou 325000, China. yetianshen@wmu.edu.cn. Telephone: +86-13706660570 -
Supported by:Mechanism of Adenosine A2A Receptor Modulate Electroacupuncture Inhibiting Osteoclast Formation in Mice with Collagen-Induced Arthritis(81674053);Role of P38 MAPK Pathway in the Inhibition of CIA Osteoclast Differentiation by Electroacupuncture via Adenosine Pathway(LY20H270015);Electroacupuncture of Mice with CIA Mitigate Joint Damage by the p38MAPK Pathway(Y20190198);Electroacupuncture of Mice with CIA Mitigate Joint Damage by the p38MAPK Pathway(FHY2019021)
Cite this article
DU Zhongheng, CONG Wenjie, TANG Kejing, ZHENG Qiqi, SONG Zhiwei, CHEN Yong, YANG Su, ZHANG Chunwu, YE Tianshen. Electroacupuncture stimulating Zusanli (ST36), Sanyinjiao (SP6) in mice with collagen-induced arthritis leads to adenosine A2A receptor-mediated alteration of p38α mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling and inhibition of osteoclastogenesis[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1103-1109.
share this article

Figure 1 Expression of p38α, NF-κB, NFATc1 in the ankle joints of mice in the different treatment groups A: expression of p38α in Blank group (× 100); B: expression of p38α in CIA-control group (× 100); C: expression of p38α in CIA-EA group (× 100); D: expression of p38α in CIA-EA-SCH58261 group (× 100); E: quantitation of p38α in all mice; F: expression of NF-κB in Blank group (× 100); G: expression of NF-κB in CIA-control group (× 100); H: expression of NF-κB in CIA-EA group (× 100); I: expression of NF-κB in CIA-EA-SCH58261 group (× 100); J: quantitation of NF-κB in all mice; K: expression of NFATc1 in Blank group (× 100); L: expression of NFATc1 in CIA-control group (× 100); M: expression of NFATc1 in CIA-EA group (× 100); N: expression of NFATc1 in CIA-EA-SCH58261 group (× 100); O: quantitation of NFATc1 in all mice. NF-κB: nuclear transcription factor-κB; NFATc1: nuclear factor of activated T cells C1; CIA: collagen induced arthritis; EA: electroacupuncture. Dyeing method of all pictures are the immunohistochemical SP method, PBS was used as negative control. Blank group: not have CIA and daily headgear fixation 30 min for 14 d (n =10); CIA-control group: become a CIA model and daily headgear fixation 30 min for 14 d (n = 10); CIA-EA group: become a CIA model, electroacupuncture stimulating Zusanli (ST36), Sanyinjiao (SP6) and daily headgear fixation 30 min at the same time for 14 d (n = 10); CIA-EA-SCH58261 group: received intraperitoneal injections of SCH58261 (adenosine A2A receptor antagonist, 5 mg/kg), and then headgear fixation, EA as in the CIA-EA group (n = 10). aP < 0.05, compared with the Blank group. bP < 0.05, compared with the CIA-control group. cP < 0.05, compared with the CIA-EA group. Data were compared using a one-way analysis of variance.
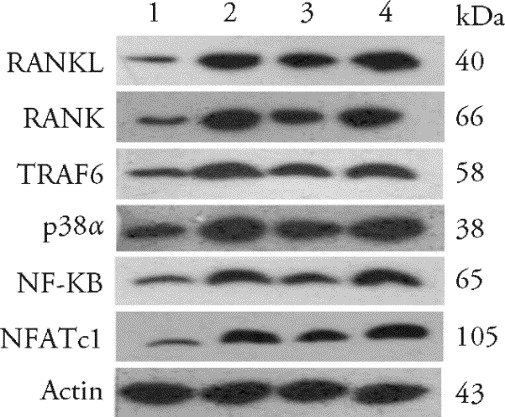
Figure 2 Western blotting of proteins in the p38α-MAPK signaling pathway in the different treatment groups 1: Blank group, not have CIA and daily headgear fixation 30 min for 14 d; 2: CIA-control group, become a CIA model and daily headgear fixation 30 min for 14 d; 3: CIA-EA group, become a CIA model, electroacupuncture stimulating Zusanli (ST36), Sanyinjiao (SP6) and daily headgear fixation 30 min at the same time for 14 d; 4: CIA-EA-SCH58261 group, received intraperitoneal injections of SCH58261 (Adenosine A2A receptor antagonist, 5 mg/kg), and then headgear fixation, EA as in the CIA-EA group. RANKL: receptor activator of nuclear transcription factor-κB ligand; RANK: receptor activator of NF-κB; TRAF6: tumor necrosis factor receptor associated factor 6; NF-κB: nuclear transcription factor-κB; NFATc1: nuclear factor of activated T cells C1; MAPK: mitogen-activated protein kinase; CIA: collagen induced arthritis; EA: electroacupuncture.

Figure 3 TRAP-staining of osteoclasts in representative mice from the different treatment groups A: expression of osteoclasts in Blank group (× 200); B: expression of osteoclasts in CIA-control group (× 200); C: expression of osteoclasts in CIA-EA group (× 200); D: expression of osteoclasts in CIA-EA-SCH58261 group (× 200). E: quantitation of osteoclasts in all mice. TRAP: tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase; CIA: collagen induced arthritis; EA: electroacupuncture. Dyeing method of all pictures are the TRAP staining method. Blank group: not have CIA and daily headgear fixation 30 min for 14 d (n = 10); CIA-control group: become a CIA model and daily headgear fixation 30 min for 14 d (n = 10); CIA-EA group: become a CIA model, electroacupuncture stimulating Zusanli (ST36), Sanyinjiao (SP6) and daily headgear fixation 30 min at the same time for 14 d (n = 10); CIA-EA-SCH58261 group: received intraperitoneal injections of SCH58261 (Adenosine A2A receptor antagonist, 5 mg/kg), and then headgear fixation, EA as in the CIA-EA group (n = 10). Data were compared using a one-way analysis of variance. aP < 0.05, compared with the Blank group; bP < 0.05, compared with the CIA-control group. cP < 0.05, compared with the CIA-EA group.
| 1. |
Myasoedova E, Davis J, Matteson EL, Crowson CS. Is the epidemiology of rheumatoid arthritis changing? Results from a population-based incidence study, 1985-2014. Ann Rheum Dis, 2020; 79: 440-4.
DOI PMID |
| 2. | Zhang W, Jiang G, Zhou X, et al. α-Mangostin inhibits LPS-induced bone resorption by restricting osteoclastogenesis via NF-κB and MAPK signaling. Chin Med 2022; 17: 34. |
| 3. |
Yasuda H. Discovery of the RANKL/RANK/OPG system. J Bone Miner Metab 2021; 39: 2-11.
DOI PMID |
| 4. |
Wanachewin O, Boonmaleerat K, Pothacharoen P, Reutrakul V, Kongtawelert P. Sesamin stimulates osteoblast differentiation through p38 and ERK1/2 MAPK signaling pathways. BMC Complement Altern Med 2012; 12: 71.
DOI |
| 5. |
Boyle WJ, Simonet WS, Lacey DL. Osteoclast differentiation and activation. Nature 2003; 423: 337-42.
DOI URL |
| 6. |
Koul HK, Pal M, Koul S. Role of p38 MAP kinase signal transduction in solid tumors. Genes Cancer 2013; 4: 342-59.
DOI URL |
| 7. |
Kim BH, Oh JH, Lee NK. The inactivation of ERK1/2, p38 and NF-kB is involved in the down-regulation of osteoclastogenesis and function by A2B adenosine receptor stimulation. Mol Cells 2017; 40: 752-60.
DOI PMID |
| 8. |
Asagiri M, Takayanagi H. The molecular understanding of osteoclast differentiation. Bone 2007; 40: 251-64.
DOI PMID |
| 9. | Hong G, Zhou L, Shi X, et al. Bajijiasu abrogates osteoclast differentiation via the suppression of RANKL signaling pathways through NF-κB and NFAT. Int J Mol Sci 2017; 18. |
| 10. |
Hajizadeh F, Masjedi A, Heydarzedeh Asl S, et al. Adenosine and adenosine receptors in colorectal cancer. Int Immunopharmacol 2020; 87: 106853.
DOI URL |
| 11. |
Goldman N, Chen M, Fujita T, et al. Adenosine A1 receptors mediate local anti-nociceptive effects of acupuncture. Nat Neurosci 2010; 13: 883-8.
DOI PMID |
| 12. | Ye TS, Du ZH, Li ZH, et al. Repeated electroacupuncture persistently elevates adenosine and ameliorates collagen-induced arthritis in rats. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2016; 2016: 3632168. |
| 13. | Jiang Y, He X, Yin X, Shen Y, Fang J. Anti-inflammatory and synovial-opioid system effects of electroacupuncture intervention on chronic pain in arthritic rats. Zhong Guo Zhen Jiu 2015; 35: 917-21. |
| 14. |
Seca S, Patrício M, Kirch S, Franconi G, Cabrita AS, Greten HJ. Effectiveness of acupuncture on pain, functional disability, and quality of life in rheumatoid arthritis of the hand: results of a double-blind randomized clinical trial. J Altern Complement Med 2019; 25: 86-97.
DOI URL |
| 15. |
Seca S, Miranda D, Cardoso D, et al. Effectiveness of acupuncture on pain, physical function and health-related quality of life in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review of quantitative evidence. Chin J Integr Med 2019; 25: 704-9.
DOI PMID |
| 16. | Li QH, Xie WX, Li XP, et al. Adenosine A2A receptors mediate anti-inflammatory effects of electroacupuncture on synovitis in mice with collagen-induced arthritis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2015; 2015: 809560. |
| 17. |
Mediero A, Kara FM, Wilder T, Cronstein BN. Adenosine A (2A) receptor ligation inhibits osteoclast formation. Am J Pathol 2012; 180: 775-86.
DOI URL |
| 18. |
Mediero A, Wilder T, Perez-Aso M, Cronstein BN. Direct or indirect stimulation of adenosine A2A receptors enhances bone regeneration as well as bone morphogenetic protein-2. Faseb j 2015; 29: 1577-90.
DOI PMID |
| 19. | Du ZH, Zhang CW, Xie WX, et al. Adenosine A2A receptor mediates inhibition of synovitis and osteoclastogenesis after electroacupuncture in rats with collagen-induced arthritis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2019; 2019: 4617464. |
| 20. |
Xu M, Liu S, Wan R, Chen Y. Combined treatment with sinomenine and acupuncture on collagen-induced arthritis through the NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathway. Oncol Lett 2018; 15: 8770-6.
DOI PMID |
| 21. | Tan LH, Shi YN, Sun SY, Qiao LN, Yan QQ, Yang YS. Effect of electroacupuncture on articular morphological changes and serum inflammatory factors and synovial MMPs in collagen-induced arthritis rats. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu 2021; 46: 649-55. |
| 22. | Fang JQ, Shao XM, Ma GZ. Effect of electroacupuncture at "Zusanli" (ST36) and "Sanyinjiao" (SP6) on collagen-induced arthritis and secretory function of knee-joint synoviocytes in rats. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu 2009; 34: 93-6. |
| 23. |
Yim YK, Lee H, Hong KE, et al. Electro-acupuncture at acupoint ST36 reduces inflammation and regulates immune activity in collagen-induced arthritic mice. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2007; 4: 51-7.
DOI URL |
| 24. | Chen XH, Yao WM, Zou CP, Xu HB. Observation on therapeutic effect of muscular needling combined with scarring moxibustion on active stage of rheumatoid arthritis. Zhong Guo Zhen Jiu 2009; 29: 884-6. |
| 25. |
Nagy V, Penninger JM. The RANKL-RANK story. The RANKL-RANK story. Gerontology 2015; 61: 534-42.
DOI PMID |
| 26. | Yu T, Dou C, Lu Y, et al. Klotho upregulates the interaction between RANK and TRAF 6 to facilitate RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis via the NF-κB signaling pathway. Ann Transl Med 2021; 9: 1499. |
| 27. | Zhi X, Wang L, Chen H, et al. l-tetrahydropalmatine suppresses osteoclastogenesis in vivo and in vitro via blocking RANK-TRAF 6 interactions and inhibiting NF-κB and MAPK pathways. J Cell Mol Med 2020; 24:785-98. |
| 28. | Han B, Lu Y, Zhao H, Wang Y, Li L, Wang T. Electroacupuncture modulated the inflammatory reaction in MCAO rats via inhibiting the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway in microglia. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015; 8: 11199-205. |
| 29. |
Arthur JS, Ley SC. Mitogen-activated protein kinases in innate immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 2013; 13: 679-92.
DOI PMID |
| 30. |
Matsumoto M, Sudo T, Saito T, Osada H, Tsujimoto M. Involvement of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway in osteoclastogenesis mediated by receptor activator of NF-kappa B ligand (RANKL). J Biol Chem 2000; 275: 31155-61.
DOI PMID |
| 31. |
Liu J, Wang Q, Yang S, et al. Electroacupuncture inhibits apoptosis of peri-ischemic regions via modulating p38, extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK1/2), and c-jun N terminal kinases (JNK) in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion-injured rats. Med Sci Monit 2018; 24: 4395-404.
DOI URL |
| 32. |
Takayanagi H. The role of NFAT in osteoclast formation. Ann NY Acad Sci 2007; 1116: 227-37.
PMID |
| 33. |
Chaweewannakorn W, Ariyoshi W, Okinaga T, Fujita Y, Maki K, Nishihara T. Ameloblastin attenuates RANKL-mediated osteoclastogenesis by suppressing activation of nuclear factor of activated T-cell cytoplasmic 1 (NFATc1). J Cell Physiol 2019; 234: 1745-57.
DOI URL |
| 34. |
Takatsuna H, Asagiri M, Kubota T, et al. Inhibition of RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis by (-)-DHMEQ, a novel NF-kappaB inhibitor, through downregulation of NFATc1. J Bone Miner Res 2005; 20: 653-62.
PMID |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

