Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (4): 796-805.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2025.04.010
• Original Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Mechanism of electroacupuncture involve in lens-induced myopia guinea pigs by inhibiting wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
ZHAO Ping1, HE Xingbo1, HAN Xudong2, CHEN Xinyue1, LI Zhanglong1, SONG Jike1, XING Wenjia1, WU Jiangfeng1, GUO Bin1( ), BI Hongsheng1(
), BI Hongsheng1( )
)
- 1 Medical College of Optometry and Ophthalmology, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250000, China
2 College of Artificial Intelligence and Big Data for Medical Sciences, Shandong First Medical University, Shandong 250021, China
-
Received:2024-05-22Accepted:2024-11-25Online:2025-08-15Published:2025-07-25 -
Contact:GUO Bin,BI Hongsheng -
About author:BI Hongsheng, Medical College of Optometry and Ophthalmology, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250000, China, Hongshengbi@126.com,Telephone: + 86-531-58859697
GUO Bin, Medical College of Optometry and Ophthalmology, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250000, China, guobin@sdutcm.edu.cn;
-
Supported by:National Natural Youth Science Foundation: Research on the Mechanism of Acupuncture in Modulating the Inflammatory Microenvironment via the Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptor (mAChR1) Signaling Pathway for Myopia Intervention(82205198);China Postdoctoral Science Foundation Project: Research on the Mechanism of Acupuncture in Modulating the Inflammatory Microenvironment via the mAChR1 Signaling Pathway for Myopia Intervention(2022M711984);Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation General Program: to Investigate the Underlying Mechanism of Acupuncture in Treating Myopia Associated eith Kidney Yang Deficiency Syndrome through the Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptors (M-AChRs) Signaling Pathway(ZR2020MH393);Postdoctoral Innovation Project of Shandong Province: Research on the Mechanism of Electroacupuncture in Treating Myopia with "Kidney Yang Deficiency Syndrome" through the M-AChRs/Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid Signaling Pathway(202101012);China Postdoctoral Foundation General Program: to Investigate the Underlying Mechanism of Acupuncture in Treating Myopia Associated with Kidney Yang Deficiency Syndrome through the M-AChRs Signaling Pathway(2020M672127);National Natural Science Foundation: Research on the Influence of Acupuncture on the Accommodative Function and Visual Cortex Functional Network of Myopia and its Mechanism(82074498);National Key R & D Project: National Key Research and Development Program "Basic Research on High Myopia"(2019YFC1710200);National Natural Science Foundation of China: Research on the Relationship between Lens-Induced Myopia based on Omics Technology and Traditional Chinese Medicine Syndrome Types and its Molecular Mechanism(82474579)
Cite this article
ZHAO Ping, HE Xingbo, HAN Xudong, CHEN Xinyue, LI Zhanglong, SONG Jike, XING Wenjia, WU Jiangfeng, GUO Bin, BI Hongsheng. Mechanism of electroacupuncture involve in lens-induced myopia guinea pigs by inhibiting wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(4): 796-805.
share this article
| Group | n | 0 w | 1 w | 2 w | 3 w | 4 w | 5 w | 6 w | 7 w | 8 w |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NC | 20 | 4.89±0.63 | 1.72±0.47 | 0.97±1.27 | 0.17±1.39 | -0.88±0.94 | -0.39±0.47 | 0.33±0.70 | -0.31±2.36 | 0.00±0.35 |
| LIM | 20 | 3.44±2.34 | -1.53±3.31a | -3.06±1.60a | -4.84±1.45a | -5.56±1.54a | -6.72±1.38a | -6.50±1.37a | -8.13±2.32a | -7.57±1.43a |
| LIM + EA | 20 | 3.10±2.73 | -3.90±3.10 | -2.47±1.55 | -3.10±1.87b | -3.00±3.32b | -4.03±1.71b | -4.25±1.84b | -4.50±1.63b | -4.92±2.94b |
Table 1 Ocular refraction difference before and after modeling in each group of guinea pigs (D, $\bar{x} \pm s$)
| Group | n | 0 w | 1 w | 2 w | 3 w | 4 w | 5 w | 6 w | 7 w | 8 w |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NC | 20 | 4.89±0.63 | 1.72±0.47 | 0.97±1.27 | 0.17±1.39 | -0.88±0.94 | -0.39±0.47 | 0.33±0.70 | -0.31±2.36 | 0.00±0.35 |
| LIM | 20 | 3.44±2.34 | -1.53±3.31a | -3.06±1.60a | -4.84±1.45a | -5.56±1.54a | -6.72±1.38a | -6.50±1.37a | -8.13±2.32a | -7.57±1.43a |
| LIM + EA | 20 | 3.10±2.73 | -3.90±3.10 | -2.47±1.55 | -3.10±1.87b | -3.00±3.32b | -4.03±1.71b | -4.25±1.84b | -4.50±1.63b | -4.92±2.94b |
| Group | n | 0 w | 1 w | 2 w | 3 w | 4 w | 5 w | 6 w | 7 w | 8 w |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NC | 10 | 7.93±0.18 | 8.22±0.14 | 8.29±0.18 | 8.41±0.16 | 8.49±0.13 | 8.54±0.15 | 8.62±0.16 | 8.66±0.14 | 8.69±0.14 |
| LIM | 10 | 7.98±0.14 | 8.25±0.13 | 8.40±0.14a | 8.55±0.21a | 8.61±0.12a | 8.70±0.11a | 8.77±0.12a | 8.79±0.08a | 8.84±0.08a |
| LIM + EA | 10 | 7.97±0.12 | 8.20±0.13 | 8.34±0.10b | 8.44±0.12b | 8.54±0.09b | 8.60±0.08b | 8.69±0.09b | 8.71±0.06b | 8.75±0.07b |
Table 2 Axial Length difference before and after modelling in each group of guinea pigs (mm, $\bar{x} \pm s$)
| Group | n | 0 w | 1 w | 2 w | 3 w | 4 w | 5 w | 6 w | 7 w | 8 w |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NC | 10 | 7.93±0.18 | 8.22±0.14 | 8.29±0.18 | 8.41±0.16 | 8.49±0.13 | 8.54±0.15 | 8.62±0.16 | 8.66±0.14 | 8.69±0.14 |
| LIM | 10 | 7.98±0.14 | 8.25±0.13 | 8.40±0.14a | 8.55±0.21a | 8.61±0.12a | 8.70±0.11a | 8.77±0.12a | 8.79±0.08a | 8.84±0.08a |
| LIM + EA | 10 | 7.97±0.12 | 8.20±0.13 | 8.34±0.10b | 8.44±0.12b | 8.54±0.09b | 8.60±0.08b | 8.69±0.09b | 8.71±0.06b | 8.75±0.07b |

Figure 1 At the 4-week time point, qPCR and ELISA were employed to assess the mRNA and protein levels of MMP-2, TIMP-2, MMP-3, and TIMP-3 in the retina, choroid, sclera and serum A: mRNA expression level of factors in the retina; B: mRNA expression level of factors in the choroid; C: mRNA expression level of factors in the sclera; D: protein expression level in the serum. A1, B1, C1, D1: MMP-2. A2, B2, C2, D2: MMP-3. A3, B3, C3, D3: TIMP-2. A4, B4, C4, D4: TIMP-3. NC: normal control group, both eyes were not intervened for 4 weeks; LIM: lens-induced myopia group, only the right eye wore the -6.00D lens for 4 weeks; LIM + EA: lens-induced myopia + electroacupuncture group, only the right eye wore the -6.00D lens and perform electroacupuncture treatment at bilateral Taiyang (EX-HN5) and Hegu (LI4) for 4 weeks.; qPCR: quantitative polymerase chain reaction; ELISA: enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; MMP: matrix metallopeptidase. TIMP: tissue inhibitor of metalloprotease. Statistical analyses were measured using an independent sample t-test was performed for each group. Data are provided as mean ± standard deviation, qPCR (n = 8), ELISA (n = 3). Compared with the NC group, aP < 0.05; compared with the LIM group, bP < 0.05.

Figure 2 mRNA expression levels of WNT7B, WNT2B, WNT3A, CTNNB1, and DKK1 in the retina, choroid, and sclera were detected by qPCR at four weeks A: mRNA expression level of factors in the retina; B: mRNA expression level of factors in the choroid; C: mRNA expression level of factors in the sclera; A1, B1, C1: WNT2B. A2, B2, C2: WNT3A. A3, B3, C3: WNT7B. A4, B4, C4: CTNNB1. A5, B5, C5, D5: DKK1. NC: normal control group, both eyes were not intervened for 4 weeks; LIM: lens-induced myopia group, only the right eye wore the -6.00D lens for 4 weeks; LIM + EA: lens-induced myopia + electroacupuncture group, only the right eye wore the -6.00D lens and perform electroacupuncture treatment at bilateral Taiyang (EX-HN5) and Hegu (LI4), parameters for 4 weeks; qPCR: quantitative polymerase chain reaction; WNT: wingless-related integration site; CTNNB1: beta-catenin 1; DKK1: dickkopf wnt signaling pathway inhibitor 1. Statistical analyses were measured using aan independent sample t-test was performed for each group. Data are provided as mean ± standard deviation (n = 8). Compared with the NC group, aP < 0.05; compared with the LIM group, bP < 0.05.

Figure 3 Protein levels of WNT7B, WNT2B, WNT3A, CTNNB1, DKK1 in the retina, choroid, and sclera were measured using WB at the 4-week after the LIM + EA group used the DKK1 inhibitor A1: protein levels of WNT7B/2B/3A, β-catenin and DKK1 in the retina; A2: protein levels of WNT7B/2B/3A, β-catenin and DKK1 in the choroid; A3: protein levels of WNT7B/2B/3A, β-catenin and DKK1 in the sclera; B: band intensity in the retina; C: band intensity in the choroid; D: band intensity in the sclera; B1, C1, D1: WNT2B. B2, C2, D2: WNT3A. B3, C3, D3: WNT7B. B4, C4, D4: β-catenin. B5, C5, D5: DKK1. NC: normal control group, both eyes were not intervened for 4 weeks; LIM: lens-induced myopia group, only the right eye wore the -6.00D lens for 4 weeks; LIM + EA: lens-induced myopia + electroacupuncture group, only the right eye wore the -6.00D lens and perform electroacupuncture treatment at bilateral Taiyang (EX-HN5) and Hegu (LI4) for 4 weeks; EA + DKK1 inhibitor: electroacupuncture+dickkopf wnt signaling pathway inhibitor injection group, lens-induced myopia + electroacupuncture group, only the right eye wore the -6.00D lens and perform electroacupuncture treatment at bilateral Taiyang (EX-HN5) and Hegu (LI4), 5 μL DKK1 inhibitor was injected into the vitreous cavity of the right eye for 4 weeks; WB: western blot; WNT: wingless-related integration site; CTNNB1: beta-catenin 1; DKK1: dickkopf wnt signaling pathway inhibitor 1. Data are provided as mean ± standard deviation (n = 3). Statistical analyses were measured using an independent sample t-test was performed for each group. Compared with the NC group, aP < 0.05; compared with the LIM group, bP < 0.05.
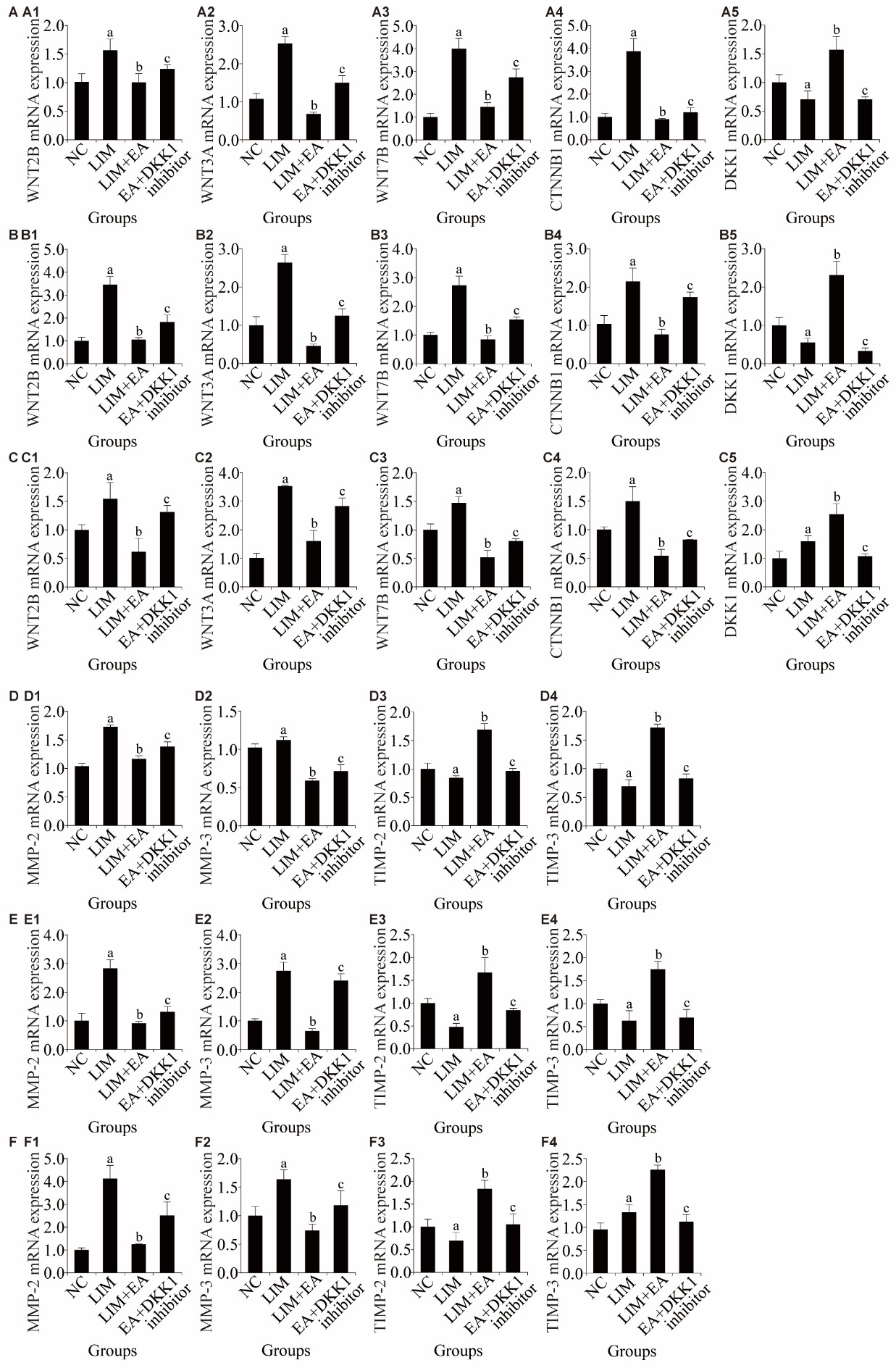
Figure 4 At the 4-week mark following the administration of the DKK1 inhibitor in the LIM + EA group, we utilized qPCR to quantify the mRNA levels of WNT7B, WNT2B, WNT3A, CTNNB1, DKK1 and MMP-2, MMP-3, TIMP-2, TIMP-3 within the retina, choroid, and sclera tissues A, D: mRNA expression level in the retina. B, E: mRNA expression level in the choroid. C, F: mRNA expression level in the sclera. A1, B1, C1: WNT2B. A2, B2, C2: WNT3A. A3, B3, C3: WNT7B. A4, B4, C4: CTNNB1.A5, B5, C5: DKK1. D1, E1, F1: MMP-2. D2, E2, F2: MMP-3. D3, E3, F3: TIMP-2. D4, E4, F4: TIMP-3. NC: normal control group, both eyes were not intervened for 4 weeks; LIM: lens-induced myopia group, only the right eye wore the -6.00D lens for 4 weeks; LIM + EA: lens-induced myopia + electroacupuncture group, only the right eye wore the -6.00D lens and perform electroacupuncture treatment at bilateral Taiyang (EX-HN5) and Hegu (LI4) for 4 weeks; EA + DKK1 inhibitor: electroacupuncture + dickkopf wnt signaling pathway inhibitor injection group, lens-induced myopia + electroacupuncture group, only the right eye wore the -6.00D lens and perform electroacupuncture treatment at bilateral Taiyang (EX-HN5) and Hegu (LI4), 5 μL DKK1 inhibitor was injected into the vitreous cavity of the right eye for 4 weeks; qPCR: quantitative polymerase chain reaction; WNT: wingless-related integration site; CTNNB1: beta-catenin 1; DKK1: dickkopf wnt signaling pathway inhibitor 1; MMP: matrix metallopeptidase; TIMP: tissue inhibitor of metalloprotease. Statistical analyses were measured using an independent sample t-test was performed for each group. Data are provided as mean ± standard deviation (n = 8). Compared with the NC group, aP < 0.05; compared with the LIM group, bP < 0.05; compared with the LIM + EA group, cP < 0.05.
| 1. |
Baird PN, Saw SM, Lanca C, et al. Myopia. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2020; 6: 99.
DOI PMID |
| 2. |
Morgan IG, French AN, Ashby RS, et al. The epidemics of myopia: aetiology and prevention. Prog Retin Eye Res 2018; 62: 134-49.
DOI PMID |
| 3. |
Torii H, Kurihara T, Seko Y, et al. Violet light exposure can be a preventive strategy against myopia progression. EBioMedicine 2017; 15: 210-9.
DOI PMID |
| 4. |
Nakamura Y, Hieda O, Yokota I, Teramukai S, Sotozono C, Kinoshita S. Comparison of myopia progression between children wearing three types of orthokeratology lenses and children wearing single-vision spectacles. Jpn J Ophthalmol 2021; 65: 632-43.
DOI PMID |
| 5. | Wang WY, Chen C, Chang J, et al. Pharmacotherapeutic candidates for myopia: a review. Biomed Pharmacother 2021; 133: 111092. |
| 6. | Shinojima A, Negishi K, Tsubota K, Kurihara T. Multiple factors causing myopia and the possible treatments: a mini review. Front Public Health 2022; 10: 897600. |
| 7. |
Du R, Xie S, Igarashi-Yokoi T, et al. Continued increase of axial length and its risk factors in adults with high myopia. JAMA Ophthalmol 2021; 139: 1096-103.
DOI PMID |
| 8. |
Han X, Ong JS, An J, et al. Association of myopia and intraocular pressure with retinal detachment in european descent participants of the UK biobank cohort: a mendelian randomization study. JAMA Ophthalmol 2020; 138: 671-8.
DOI PMID |
| 9. | Ha A, Kim CY, Shim SR, Chang IB, Kim YK. Degree of myopia and glaucoma risk: a dose-response Meta-analysis. Am J Ophthalmol 2022; 236: 107-19. |
| 10. | Haarman AEG, Enthoven CA, Tideman JWL, Tedja MS, Verhoeven VJM, Klaver CCW. The complications of myopia: a review and Meta-analysis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2020; 61: 49. |
| 11. | Boote C, Sigal IA, Grytz R, Hua Y, Nguyen TD, Girard MJA. Scleral structure and biomechanics. Prog Retin Eye Res 2020; 74: 100773. |
| 12. |
Wallman J, Winawer J. Homeostasis of eye growth and the question of myopia. Neuron 2004; 43: 447-68.
DOI PMID |
| 13. | Wu H, Chen W, Zhao F, et al. Scleral hypoxia is a target for myopia control. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2018; 115: e7091-100. |
| 14. | Cabral-Pacheco GA, Garza-Veloz I, Castruita-De la Rosa C, et al. The roles of matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in human diseases. Int J Mol Sci 2020; 21: 9739. |
| 15. | Jia Y, Hu DN, Zhu D, et al. MMP-2, MMP-3, TIMP-1, TIMP-2, and TIMP-3 protein levels in human aqueous humor: relationship with axial length. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2014; 55: 3922-8. |
| 16. | Mao JJ, Liou KT, Baser RE, et al. Effectiveness of electroacupuncture or auricular acupuncture vs usual care for chronic musculoskeletal pain among cancer survivors: the PEACE randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol 2021; 7: 720-7. |
| 17. | Ulloa L. Electroacupuncture activates neurons to switch off inflammation. Nature 2021; 598: 573-4. |
| 18. |
Liu Z, Liu Y, Xu H, et al. Effect of electroacupuncture on urinary leakage among women with stress urinary incontinence: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2017; 317: 2493-501.
DOI PMID |
| 19. | Liu B, Wu J, Yan S, et al. Electroacupuncture vs prucalopride for severe chronic constipation: a multicenter, randomized, controlled, noninferiority trial. Am J Gastroenterol 2021; 116: 1024-35. |
| 20. | Jin ZR, Fang D, Liu BH, et al. Roles of catsper channels in the pathogenesis of asthenozoospermia and the therapeutic effects of acupuncture-like treatment on asthenozoospermia. Theranostics 2021; 11: 2822-44. |
| 21. | Yu T, Xie X, Wei H, et al. Electroacupuncture improves choroidal blood flow to inhibit the development of lens-induced myopia in guinea pigs. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2022; 2022: 3286583. |
| 22. | Yemanyi F, Bora K, Blomfield AK, Wang Z, Chen J. Wnt signaling in inner blood-retinal barrier maintenance. Int J Mol Sci 2021; 22: 11877. |
| 23. |
Wang Z, Liu CH, Huang S, Chen J. Wnt Signaling in vascular eye diseases. Prog Retin Eye Res 2019; 70: 110-33.
DOI PMID |
| 24. |
Fujimura N. Wnt/β-catenin signaling in vertebrate eye development. Front Cell Dev Biol 2016; 4: 138.
PMID |
| 25. |
Hu S, Ouyang S, Liu H, Zhang D, Deng Z. The effect of Wnt/β-catenin pathway on the scleral remolding in the mouse during form deprivation. Int Ophthalmol 2021; 41: 3099-107.
DOI PMID |
| 26. | Liu Z, Xiu Y, Qiu F, et al. Canonical Wnt signaling drives myopia development and can be pharmacologically modulated. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2021; 62: 21. |
| 27. | Ma M, Zhang Z, Du E, et al. Wnt signaling in form deprivation myopia of the mice retina. PLoS One 2014; 9: e91086. |
| 28. | Shi S, Wang M, Liu X, Han S, Zhu P. Scalp electroacupuncture promotes angiogenesis after stroke in rats by activation of Wnt/β-catenin signal pathway. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2022; 2022: 1649605. |
| 29. |
Jing Q, Ren L, Deng X, et al. Electroacupuncture promotes neural proliferation in hippocampus of perimenopausal depression rats via Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. J Acupunct Meridian Stud 2020; 13: 94-103.
DOI PMID |
| 30. |
Sha F, Ye X, Zhao W, et al. Effects of electroacupuncture on the levels of retinal gamma-aminobutyric acid and its receptors in a guinea pig model of lens-induced myopia. Neuroscience 2015; 287: 164-74.
DOI PMID |
| 31. | Zhang T, Jiang Q, Xu F, et al. Alternation of resting-state functional connectivity between visual cortex and hypothalamus in guinea pigs with experimental glucocorticoid enhanced myopia after the treatment of electroacupuncture. Front Neuroinform 2020; 14: 579769. |
| 32. | Suo NC, Lei CL, Zhang YC, Li XZ, Li FZ, Gong K. Effects of latanoprost on the expression of TGF-β1 and Wnt / β-catenin signaling pathway in the choroid of form-deprivation myopia rats. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand) 2020; 66: 71-5. |
| 33. | Liu HH, Kenning MS, Jobling AI, McBrien NA, Gentle A. Reduced scleral TIMP-2 expression is associated with myopia development: TIMP-2 supplementation stabilizes scleral biomarkers of myopia and limits myopia development. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2017; 58: 1971-81. |
| 34. | Liu YX, Sun Y. MMP-2 participates in the sclera of guinea pig with form-deprivation myopia via IGF-1/STAT3 pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2018; 22: 2541-8. |
| 35. | Wu W, Su Y, Hu C, et al. Hypoxia-induced scleral HIF-2α upregulation contributes to rises in MMP-2 expression and myopia development in mice. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2022; 63: 2. |
| 36. |
Peng M, Wei Y, Zhang Z, et al. Increased levels of DKK1 in vitreous fluid of patients with pathological myopia and the correlation between DKK1 levels and axial length. Curr Eye Res 2020; 45: 104-10.
DOI PMID |
| 37. |
Fang Q, Liu T, Yu C, et al. LncRNA TUG1 alleviates cardiac hypertrophy by targeting miR-34a/DKK1/Wnt-β-catenin signalling. J Cell Mol Med 2020; 24: 3678-91.
DOI PMID |
| 38. | Henderson J, Pryzborski S, Stratton R, O'Reilly S. Wnt antagonist DKK-1 levels in systemic sclerosis are lower in skin but not in blood and are regulated by microRNA33a-3p. Exp Dermatol 2021; 30: 162-8. |
| 39. |
Sujitha S, Dinesh P, Rasool M. Berberine encapsulated PEG-coated liposomes attenuate Wnt1/β-catenin signaling in rheumatoid arthritis via miR-23a activation. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 2020; 149: 170-91.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | XU Jiawei, LU Haisong, SHI Yushi, LEI Yu, LI Xueping, CHENG Weimin. Dujieqing decoction (毒结清复方) suppresses multiple myeloma growth by inhibiting the Wnt/β-catenin pathway [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(4): 720-729. |
| [2] | ZHENG Ruwen, DONG Xu, WANG Tianyi, FENG Liyuan, ZHANG Hongyan, HUO Hong, ZHANG Ying, ZHANG Qianshi, ZHU Xingyan, WANG Dongyan. Electroacupuncture versus conventional acupuncture of scalp motor area for post-stroke wrist dyskinesia and its effect on muscle function: a randomized, controlled clinical trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(4): 852-859. |
| [3] | SUN Jiao, WANG Yueming, LYU Jian, LIU Xin, YUE Bingnan, LI Yinyin, LIU Jipeng, SUN Yize, LIU Qingguo, YAN Liu. Effect of electroacupuncture on hypertensive and sympathetic excitability mechanism mediated by the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus in spontaneous hypertensive rats [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(3): 586-596. |
| [4] | FENG Guiling, ZHOU Xiaolin, SHEN Chengwan, LI Panxiao, ABULIZI ·Abudula. Effects of Huluan decotion (护卵汤) on cyclophosphamide-induced autoimmune premature ovarian failure in murine models [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(2): 266-271. |
| [5] | LI Yongfeng, CHEN Xinyi, REN Wei, QIAO Haifa. Electroacupuncture stimulation of auricular concha region improves loss of control over stress induced depression-like behavior by modulating 5-hydroxytryptamine 1A receptor [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(2): 326-334. |
| [6] | HU Junwei, FENG Jiwei, LI Wen, LIU Lumin, LI Xu, XU Ge, LIU Jiandang, CHEN Yuelai. Electroacupuncture improves cyclophosphamide-induced bladder overactivity by reducing mechanotransduction in the rat urothelium [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(2): 348-358. |
| [7] | LI Siting, WANG Shaojun, YIN Yehui, DE Gejing, LI Caicai, WANG Ziyan, CAO Wenjie. Electroacupuncture alleviates zymosan-induced colorectal hypersensitivity [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(1): 32-38. |
| [8] | Emre Bulut, Didem Özkal Eminoğlu, Yasemin Çayır. Effect of electroacupuncture on pain after periodontal flap surgery: a randomized controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(1): 184-191. |
| [9] | ZHANG Boyang, ZHOU Yang, FENG Liyuan, SUI Dan, HE Lei, TONG Dan, WANG Ruoyu, SUI Xue, SONG Jing, WANG Dongyan. A neural regulation mechanism of head electroacupuncture on brain network of patients with stroke related sleep disorders [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(6): 1268-1276. |
| [10] | XU Yingshan, WU Chunxiao, YU Wei, GUO Hongji, LU Liming, XU Nenggui, TANG Chunzhi. Systematic review and Meta-analysis of brain plasticity associated with electroacupuncture in experimental ischemic stroke [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(5): 859-870. |
| [11] | ZHANG Fang, YAN Cuina, WENG Zhijun, WU Luyi, QI Li, ZHAO Min, XIN Yuhu, WU Huangan, LIU Huirong. Regulatory role of electroacupuncture on satellite glial cell activity in the colon and dorsal root ganglion of rats with irritable bowel syndrome [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(5): 981-990. |
| [12] | ZHU Xuan, LOU An, ZHU Keke, RUAN Mingyu. Effect of Jiedu Huayu decoction (解毒化瘀汤) on oral mucosal Axin and β-catenin expression in oral submucosal fibrosis model rats [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(4): 688-693. |
| [13] | CHEN Yonglin, OUYANG Ling, MENG Lingling, WU Bufan, PENG Rou, LIU Sitong, HOU Dan, WANG Yaling, JING Xinyue, LU Shengfeng, FU Shuping. Electroacupuncture ameliorates blood-brain barrier disruption after ischemic stroke through histone acetylation regulation at the matrix metalloproteinase 9 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 2 genes [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(4): 734-744. |
| [14] | WANG Shaosong, SUN Jingqing, FENG Qingyin, LI Bin, WANG Xin, YUAN Fan, CUI Yingxue. Effectivenss of electroacupuncture for skeletal muscle pain in Parkinson's disease: a Clinical randomized controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(2): 388-395. |
| [15] | QIN Xiaoyu, WANG Chunai, XUE Jianjun, ZHANG Jie, LU Xiaoting, DING Shengshuang, GE Long, WANG Minzhen. Efficacy of electroacupuncture on myocardial protection and postoperative rehabilitation in patients undergoing cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 1-15. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

