Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (4): 734-744.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20240610.004
• Original articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Electroacupuncture ameliorates blood-brain barrier disruption after ischemic stroke through histone acetylation regulation at the matrix metalloproteinase 9 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 2 genes
CHEN Yonglin, OUYANG Ling, MENG Lingling, WU Bufan, PENG Rou, LIU Sitong, HOU Dan, WANG Yaling, JING Xinyue, LU Shengfeng( ), FU Shuping(
), FU Shuping( )
)
- Key Laboratory of Acupuncture and Medicine Research of Ministry of Education, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210023, China
-
Received:2023-02-22Accepted:2023-07-20Online:2024-08-15Published:2024-06-10 -
Contact:Prof. FU Shuping, Key Laboratory of Acupuncture and Medicine Research of Ministry of Education, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing, 210023, China.shupingfu@njucm.edu.cn ; Prof. LU Shengfeng, Key Laboratory of Acupuncture and Medicine Research of Ministry of Education, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing, 210023, China.lushengfeng@njucm.edu.cn Telephone: +86-18761894980 -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China: the Role of Intestinal Flora-Treg/γδT Cell-IL-17 Signaling in the Neuroprotective Effect of Electroacupuncture on Ischemic Brain Injury(81774403);Natural Science Foundation of the Jiangsu Province of China: Study on the Mechanism of Acupuncture Anti-stroke Immune Inflammatory Response Based on Intestinal Treg/γδT Cell-IL-17 Signaling Pathway(BK20171492);Postgraduate Scientific Research Innovation Practice Project of the Jiangsu Province of China: a Study based on the Butyric Acid-HDAC-Foxp3 Pathway to Explore the Regulatory Effect of Acupuncture on Intestinal Treg in Rats with Stroke(KYCX21_1715);a Study on the Anti-brain Injury of Electroacupuncture Based on Intestinal Microbiota-Treg/γδT Cell-IL-17 Pathway(KYCX21_1716);Key University Science Research Project of Jiangsu Province: the Role of Preactivation of the Treg Immune Response in the Mechanism of Anti-stroke Neuroinflammatory Response in Acupuncture Pretreatment(22KJA360003)
Cite this article
CHEN Yonglin, OUYANG Ling, MENG Lingling, WU Bufan, PENG Rou, LIU Sitong, HOU Dan, WANG Yaling, JING Xinyue, LU Shengfeng, FU Shuping. Electroacupuncture ameliorates blood-brain barrier disruption after ischemic stroke through histone acetylation regulation at the matrix metalloproteinase 9 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 2 genes[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(4): 734-744.
share this article
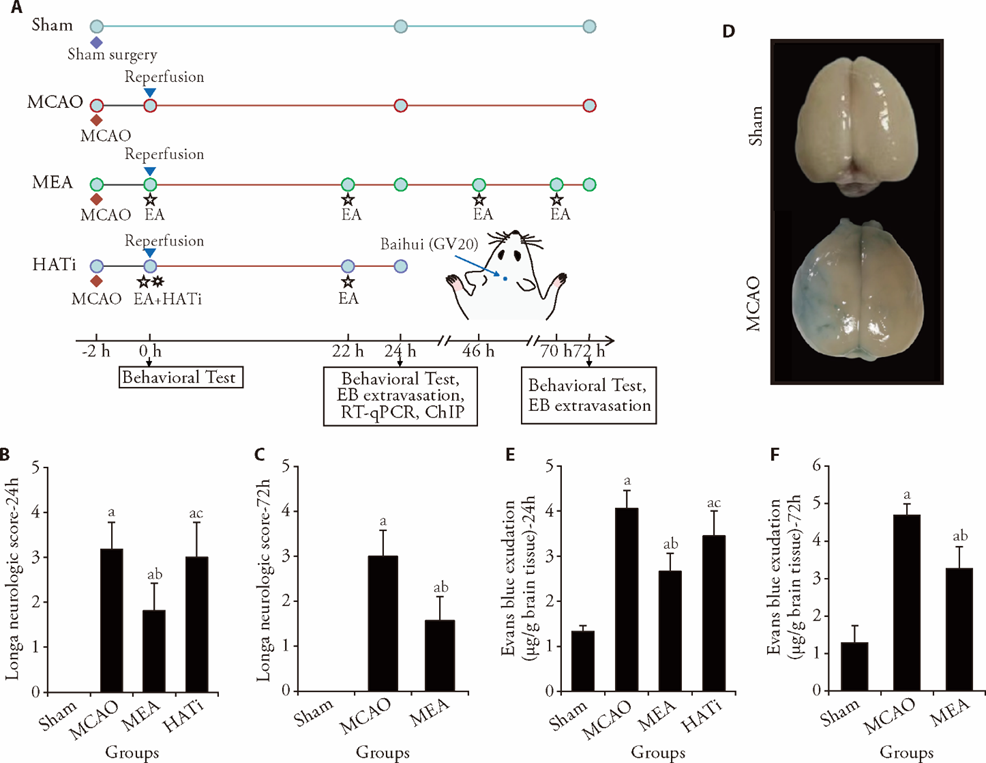
Figure 1 EA treatment reduced cerebral damage after I/R injury in rats A: the experimental timeline; B: Longa neurologic score 1 d after ischemia, n = 11; C: Longa neurologic score 3 d after ischemia, n = 7; D: representative photograph of Evans blue extravasation in the brains of rats 24 h after I/R injury. The blue area shows penetrating Evans blue, signifying BBB destruction; E: quantitative analysis of Evans blue penetration in each group 1 d after ischemic stroke, n = 7; F: Evans blue exudation 3 d after ischemia, n = 4. Sham group: sham operated; MCAO group: MCAO operated; MEA group: MCAO rats received 3 d of EA treatment; HATi group: MCAO rats received 3 d of EA treatment and a single 4 mg/kg intraperitoneal injection of HATi. I/R: ischemia/reperfusion; MCAO: middle cerebral artery occlusion; EA: electroacupuncture; HATi: histone acetyltransferase inhibitor; EB: Evans blue; RT-qPCR: real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction; ChIP: chromatin immunoprecipitation; BBB: blood-brain barrier. Data were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance and are represented as the mean ± standard deviation. aP < 0.05 vs the sham group, bP < 0.05 the MCAO group vs the MEA group, cP < 0.05 the MEA group vs the HATi group.
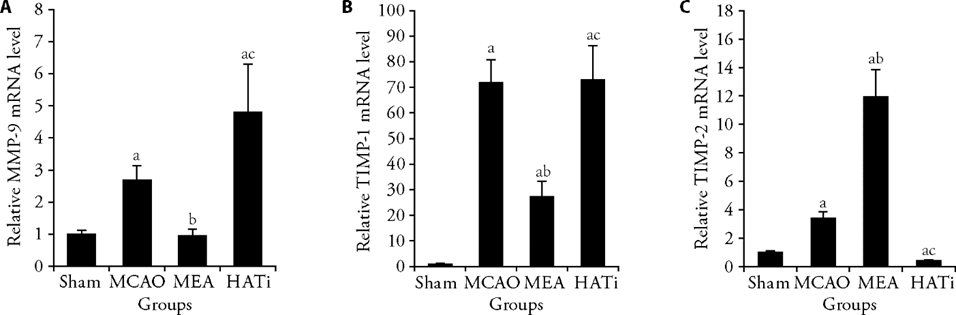
Figure 2 EA treatment regulated the expression of MMP-9 and TIMP-1/2 after MCAO A: RT-qPCR shows the relative mRNA levels of MMP-9 in ischemic brain tissues 24 h after I/R injury, n = 4; B: RT-qPCR shows the relative mRNA levels of TIMP-1 in ischemic brain tissues 24 h after ischemia/reperfusion injury, n = 4; C: RT-qPCR shows the relative mRNA levels of TIMP-2 in ischemic brain tissues 24 h after I/R injury, n = 4. Sham group: sham operated; MCAO group: MCAO operated; MEA group: MCAO rats received 3 d of EA treatment; HATi group: MCAO rats received 3 d of EA treatment and a single 4 mg/kg intraperitoneal injection of HATi. MMP-9: matrix metalloproteinase 9; TIMP-1/2: tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 1/2; MCAO: middle cerebral artery occlusion; EA: electroacupuncture; HATi: histone acetyltransferase inhibitor; RT-qPCR: real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction. Data were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance and are represented as the mean ± standard deviation. aP < 0.05, vs the sham group; bP < 0.05, the MCAO group vs the MEA group; cP < 0.05, the MEA group vs the HATi group.
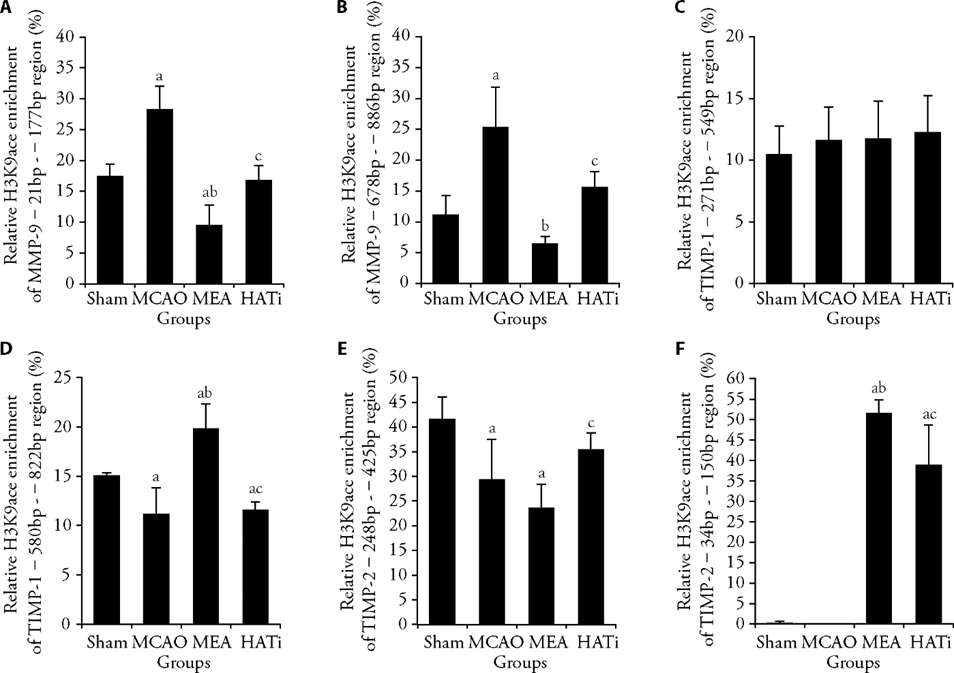
Figure 3 EA treatment regulated H3K9ace occupancy at target gene promoters A: ChIP analysis of the enrichment of acetylated H3K9 on promoters of MMP-9 -21 bp - -177 bp region, n = 3 or 4; B: ChIP analysis of the enrichment of acetylated H3K9 on promoters of MMP-9 -678 bp - -886 bp region, n = 3 or 4; C: ChIP analysis of the enrichment of acetylated H3K9 on promoters of TIMP-1 -271 bp - -549 bp region, n = 3 or 4; D: ChIP analysis of the enrichment of acetylated H3K9 on promoters of TIMP-1 -580 bp - -822 bp region, n = 3 or 4. E: ChIP analysis of the enrichment of acetylated H3K9 on promoters of TIMP-2 -248 bp - -425 bp region, n = 3 or 4. F: ChIP analysis of the enrichment of acetylated H3K9 on promoters of TIMP-2 -34 bp - -150 bp region, n = 3 or 4. Sham group: sham operated; MCAO group: MCAO operated; MEA group: MCAO rats received 3 d of EA treatment; HATi group: MCAO rats received 3 d of EA treatment and a single 4 mg/kg intraperitoneal injection of HATi. MCAO: middle cerebral artery occlusion; EA: electroacupuncture; HATi: histone acetyltransferase inhibitor; H3K9ace: histone H3 lysine 9 acetylation; MMP-9: matrix metalloproteinase 9; TIMP-1: tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 1; TIMP-2: tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 2; ChIP: chromatin immunoprecipitation. Data were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance and are represented as the mean ± standard deviation. aP < 0.05 vs the sham group, bP < 0.05 the MCAO group vs the MEA group, cP < 0.05 the MEA group vs the HATi group.

Figure 4 EA treatment regulated H3K27ace occupancy at target gene promoters A: ChIP analysis of the enrichment of acetylated H3K27 on promoters of MMP-9 -21 bp - -177 bp region, n = 3 or 4; B: ChIP analysis of the enrichment of acetylated H3K27 on promoters of MMP-9 -678 bp - -886 bp region, n = 3 or 4; C: ChIP analysis of the enrichment of acetylated H3K27 on promoters of TIMP-1 -271 bp - -549 bp region, n = 3 or 4; D: ChIP analysis of the enrichment of acetylated H3K27 on promoters of TIMP-1 -580 bp - -822 bp region, n = 3 or 4; E: ChIP analysis of the enrichment of acetylated H3K27 on promoters of TIMP-2 -248 bp - -425 bp region, n = 3 or 4. F: ChIP analysis of the enrichment of acetylated H3K27 on promoters of TIMP-2 -34 bp - -150 bp region, n = 3 or 4. Sham group: sham operated; MCAO group: MCAO operated; MEA group: MCAO rats received 3 d of EA treatment; HATi group: MCAO rats received 3 d of EA treatment and a single 4 mg/kg intraperitoneal injection of HATi. MCAO: middle cerebral artery occlusion; EA: electroacupuncture; HATi: histone acetyltransferase inhibitor; H3K27ace: histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation; MMP-9: matrix metalloproteinase 9; TIMP-1: tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 1; TIMP-2: tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 2; ChIP: chromatin immunoprecipitation. Data were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance and are represented as the mean ± standard deviation. aP < 0.05 vs the sham group, bP < 0.05 the MCAO group vs the MEA group, cP < 0.05 the MEA group vs the HATi group.
| 1. |
Collaborators GBDS. Global, regional, and national burden of stroke, 1990-2016: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2016. Lancet Neurol 2019; 18: 439-58.
DOI PMID |
| 2. | Yang C, Hawkins KE, Dore S, Candelario-Jalil E. Neuroinflammatory mechanisms of blood-brain barrier damage in ischemic stroke. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 2019; 316: 135-53. |
| 3. |
Keaney J, Campbell M. The dynamic blood-brain barrier. FEBS J 2015; 282: 4067-79.
DOI PMID |
| 4. |
Zhong C, Yang J, Xu T, et al. Serum matrix metalloproteinase-9 levels and prognosis of acute ischemic stroke. Neurology 2017; 89: 805-12.
DOI PMID |
| 5. |
Rosell A, Ortega-Aznar A, Alvarez-Sabin J, et al. Increased brain expression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 after ischemic and hemorrhagic human stroke. Stroke 2006; 37: 1399-406.
DOI PMID |
| 6. |
Rosell A, Cuadrado E, Ortega-Aznar A, Hernandez-Guillamon M, Lo EH, Montaner J. MMP-9-positive neutrophil infiltration is associated to blood-brain barrier breakdown and basal lamina type IV collagen degradation during hemorrhagic transformation after human ischemic stroke. Stroke 2008; 39: 1121-6.
DOI PMID |
| 7. | Rosenberg GA, Yang Y. Vasogenic edema due to tight junction disruption by matrix metalloproteinases in cerebral ischemia. Neurosurg Focus 2007; 22: 1-9. |
| 8. | Yang Y, Estrada EY, Thompson JF, Liu W, Rosenberg GA. Matrix metalloproteinase-mediated disruption of tight junction proteins in cerebral vessels is reversed by synthetic matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor in focal ischemia in rat. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2007; 27: 697-709. |
| 9. |
Asahi M, Wang X, Mori T, et al. Effects of matrix metalloproteinase-9 gene knock-out on the proteolysis of blood-brain barrier and white matter components after cerebral ischemia. J Neurosci 2001; 21: 7724-32.
PMID |
| 10. | Bauer AT, Burgers HF, Rabie T, Marti HH. Matrix metalloproteinase-9 mediates hypoxia-induced vascular leakage in the brain via tight junction rearrangement. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2010; 30: 837-48. |
| 11. | Yang Y, Thompson JF, Taheri S, et al. Early inhibition of MMP activity in ischemic rat brain promotes expression of tight junction proteins and angiogenesis during recovery. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2013; 33: 1104-14. |
| 12. | Cui J, Chen S, Zhang C, et al. Inhibition of MMP-9 by a selective gelatinase inhibitor protects neurovasculature from embolic focal cerebral ischemia. Mol Neurodegener 2012; 7: 1-21. |
| 13. | Krizanac-Bengez L, Hossain M, Fazio V, Mayberg M, Janigro D. Loss of flow induces leukocyte-mediated MMP/TIMP imbalance in dynamic in vitro blood-brain barrier model: role of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 2006; 291: 740-9. |
| 14. |
Guo T, Hao H, Zhou L, Zhou F, Yu D. Association of SNPs in the TIMP-2 gene and large artery atherosclerotic stroke in southern Chinese Han population. Oncotarget 2018; 9: 4698-706.
DOI PMID |
| 15. |
Wei H, Wang S, Zhen L, et al. Resveratrol attenuates the blood-brain barrier dysfunction by regulation of the MMP-9/TIMP-1 balance after cerebral ischemia reperfusion in rats. J Mol Neurosci 2015; 55: 872-9.
DOI PMID |
| 16. |
Rivera S, Ogier C, Jourquin J, et al. Gelatinase B and TIMP-1 are regulated in a cell- and time-dependent manner in association with neuronal death and glial reactivity after global forebrain ischemia. Eur J Neurosci 2002; 15: 19-32.
DOI PMID |
| 17. | Fujimoto M, Takagi Y, Aoki T, et al. Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases protect blood-brain barrier disruption in focal cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2008; 28: 1674-85. |
| 18. |
Huang YG, Tao W, Yang SB, Wang JF, Mei ZG, Feng ZT. Autophagy: novel insights into therapeutic target of electroacupuncture against cerebral ischemia/ reperfusion injury. Neural Regen Res 2019; 14: 954-61.
DOI PMID |
| 19. | Jung YS, Lee SW, Park JH, Seo HB, Choi BT, Shin HK. Electroacupuncture preconditioning reduces ROS generation with NOX4 down-regulation and ameliorates blood-brain barrier disruption after ischemic stroke. J Biomed Sci 2016; 23: 1-32. |
| 20. | Xu H, Zhang Y, Sun H, Chen S, Wang F. Effects of acupuncture at GV20 and ST36 on the expression of matrix metalloproteinase 2, aquaporin 4, and aquaporin 9 in rats subjected to cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. PLoS One 2014; 9: e97488. |
| 21. |
Ma R, Yuan B, Du J, et al. Electroacupuncture alleviates nerve injury after cerebra ischemia in rats through inhibiting cell apoptosis and changing the balance of MMP-9/TIMP-1 expression. Neurosci Lett 2016; 633: 158-64.
DOI PMID |
| 22. |
Lin R, Yu K, Li X, et al. Electroacupuncture ameliorates post-stroke learning and memory through minimizing ultrastructural brain damage and inhibiting the expression of MMP-2 and MMP-9 in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injured rats. Mol Med Rep 2016; 14: 225-33.
DOI PMID |
| 23. | Zhang XC, Gu YH, Xu WT, et al. Early electroacupuncture extends the rtpa time window to 6 h in a male rat model of embolic stroke via the ERK1/2-MMP9 pathway. Neural Plasticity 2020; 2020: 1-15. |
| 24. |
Jiang X, Tian Y, Xu L, et al. Inhibition of triple-negative breast cancer tumor growth by electroacupuncture with encircled needling and its mechanisms in a mice xenograft model. Int J Med Sci 2019; 16: 1642-51.
DOI PMID |
| 25. | Bao F, Sun H, Wu ZH, Wang DH, Zhang YX. Effect of acupuncture on expression of matrix metalloproteinase and tissue inhibitor in cartilage of rats with knee osteoarthritis. Zhong Guo Zhen Jiu 2011; 31: 241-6. |
| 26. |
Ren L, Wang YK, Fang YN, Zhang AW, Li XL. Effect of electroacupuncture therapy on the expression of Na(v)1.1 and Na(v)1.6 in rat after acute cerebral ischemia. Neurol Res 2010; 32: 1110-6.
DOI PMID |
| 27. | Zhang JJ, Du YH, Li J, Yang LH, Chen LL, Zha QP. Effect of electroacupuncture on neurological function and Wnt signaling pathway in ischemic brain tissue of cerebral infarction rats. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu 2020; 45: 202-8. |
| 28. | Li MX, Fu ZT, Liu Q, Song ZS, Zhang H, Tang W. Effect of electroacupuncture of different acupoint groups on cerebral cortical neurovascular unit and PI3K/Akt signaling in rats with ischemic stroke. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu 2021; 46: 921-8. |
| 29. | Yang LH, Du YH, Li J. Effect of electroacupuncture on expression of apelin-APJ system of cerebral vascular endothelial cell in rats with cerebral infarction. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu 2017; 42: 9-13. |
| 30. | Zhang YM, Xu H, Sun H, Chen SH, Wang FM. Electroacupuncture treatment improves neurological function associated with regulation of tight junction proteins in rats with cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2014; 2014: 989340. |
| 31. | Wang C, Yang F, Liu X, Liu M, Zheng Y, Guo J. Neurotrophic signaling factors in brain ischemia/reperfusion rats: differential modulation pattern between single-time and multiple electroacupuncture stimulation. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2014; 2014: 625050. |
| 32. |
Tang J, Zhuang S. Histone acetylation and DNA methylation in ischemia/reperfusion injury. Clin Sci (Lond) 2019; 133: 597-609.
DOI PMID |
| 33. | Demyanenko S, Uzdensky A. Epigenetic alterations induced by photothrombotic stroke in the rat cerebral cortex: deacetylation of histone h3, upregulation of histone deacetylases and histone acetyltransferases. Int J Mol Sci 2019; 20: 2882. |
| 34. | Gao Y, Ya B, Li X, Guo Y, Yin H. Myricitrin ameliorates cognitive deficits in MCAO cerebral stroke rats via histone acetylation-induced alterations of brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Mol Cell Biochem 2021; 476: 609-17. |
| 35. | Cao W, Feng Z, Zhu D, et al. The role of PGK1 in promoting ischemia/reperfusion injury-induced microglial M1 polarization and inflammation by regulating glycolysis. Neuromolecular Med 2023; 25: 301-11. |
| 36. |
Wang Z, Tsai LK, Munasinghe J, et al. Chronic valproate treatment enhances postischemic angiogenesis and promotes functional recovery in a rat model of ischemic stroke. Stroke 2012; 43: 2430-6.
DOI PMID |
| 37. |
Patnala R, Arumugam TV, Gupta N, Dheen ST. HDAC inhibitor sodium butyrate-mediated epigenetic regulation enhances neuroprotective function of microglia during ischemic stroke. Mol Neurobiol 2017; 54: 6391-411.
DOI PMID |
| 38. | Demyanenko S, Dzreyan V, Sharifulina S. Histone deacetylases and their isoform-specific inhibitors in ischemic stroke. Biomedicines 2021; 9: 1445. |
| 39. | Fu SP, He SY, Xu B, et al. Acupuncture promotes angiogenesis after myocardial ischemia through H3K 9 acetylation regulation at VEGF gene. PLoS One 2014; 9: e94604. |
| 40. | Fu SP, Gong L, Li XX, Wang YL, Yuan J, Lu SF. Effects of acupuncture at “baihui” (GV20) on histone deacetylases expression in ischemia-reperfusion injury model rats. J Tradit Chin Med 2020; 61: 146-51. |
| 41. | Xu SY, Lv HQ, Li WQ, Hong H, Peng YJ, Zhu BM. Electroacupuncture alleviates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats by histone H4 lysine 16 acetylation-mediated autophagy. Front Psychiatry 2020; 11: 576539. |
| 42. | Fu S, Gu Y, Jiang JQ, et al. Calycosin-7-O-beta-D-glucoside regulates nitric oxide /caveolin-1/matrix metalloproteinases pathway and protects blood-brain barrier integrity in experimental cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Ethnopharmacol 2014; 155: 692-701. |
| 43. | Fu S, Yu M, Xu H, et al. Genome-wide transcription analysis of electroacupuncture precondition-induced ischemic tolerance on SD rat with ischemia-reperfusion injury. Front Genet 2021; 12: 719201. |
| 44. | Bernardo-Castro S, Sousa JA, Bras A, et al. Pathophysiology of blood-brain barrier permeability throughout the different stages of ischemic stroke and its implication on hemorrhagic transformation and recovery. Front Neurol 2020; 11: 594672. |
| 45. |
Thompson JW, Narayanan SV, Koronowski KB, Morris-Blanco K, Dave KR, Perez-Pinzon MA. Signaling pathways leading to ischemic mitochondrial neuroprotection. J Bioenerg Biomembr 2015; 47: 101-10.
DOI PMID |
| 46. |
Sahota P, Savitz SI. Investigational therapies for ischemic stroke: neuroprotection and neurorecovery. Neurotherapeutics 2011; 8: 434-51.
DOI PMID |
| 47. |
Liu P, Zhang R, Liu D, et al. Time-course investigation of blood-brain barrier permeability and tight junction protein changes in a rat model of permanent focal ischemia. J Physiol Sci 2018; 68: 121-7.
DOI PMID |
| 48. | Pillai DR, Dittmar MS, Baldaranov D, et al. Cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats--a 3 T MRI study on biphasic blood-brain barrier opening and the dynamics of edema formation. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2009; 29: 1846-55. |
| 49. | Huang Y, Chen S, Luo Y, Han Z. Crosstalk between inflammation and the BBB in stroke. Curr Neuropharmacol 2020; 18: 1227-1236. |
| 50. | Chavez L, Huang SS, MacDonald I, Lin JG, Lee YC, Chen YH. Mechanisms of acupuncture therapy in ischemic stroke rehabilitation: a literature review of basic studies. Int J Mol Sci 2017; 18: 2270. |
| 51. |
Young-Wook P, Gi Yoon H, Min Jae K, Seo-Yeon L, Byung Tae C, Hwa Kyoung S. Subacute electroacupuncture at Baihui (GV 20) and Dazhui (GV 14) promotes post-stroke functional recovery via neurogenesis and astrogliosis in a photothrombotic stroke mouse model. J Tradit Chin Med 2019; 39: 833-41.
PMID |
| 52. | Li SS, Hua XY, Zheng MX, et al. Electroacupuncture treatment improves motor function and neurological outcomes after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. Neural Regen Res 2022; 17: 1545-55. |
| 53. |
Chen B, Lin WQ, Li ZF, et al. Electroacupuncture attenuates ischemic brain injury and cellular apoptosis via mitochondrial translocation of cofilin. Chin J Integr Med 2021; 27: 705-12.
DOI PMID |
| 54. | Liu R, Xu NG, Yi W, Ji C. Electroacupuncture attenuates inflammation after ischemic stroke by inhibiting NF-kappaB-mediated activation of microglia. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2020; 2020: 8163052. |
| 55. | Wang WW, Xie CL, Lu L, Zheng GQ. A systematic review and Meta-analysis of Baihui (GV20)-based scalp acupuncture in experimental ischemic stroke. Sci Rep 2014; 4: 3981. |
| 56. |
Hu Q, Chen C, Khatibi NH, et al. Lentivirus-mediated transfer of MMP-9 shRNA provides neuroprotection following focal ischemic brain injury in rats. Brain Res 2011; 1367: 347-59.
DOI PMID |
| 57. |
Cunningham LA, Wetzel M, Rosenberg GA. Multiple roles for MMPs and TIMPs in cerebral ischemia. Glia 2005; 50: 329-39.
DOI PMID |
| 58. | Kaczorowska A, Miekus N, Stefanowicz J, Adamkiewicz-Drozynska E. Selected matrix metalloproteinases (MMP-2, MMP-7) and their inhibitor (TIMP-2) in adult and pediatric cancer. Diagnostics (Basel) 2020; 10: 547. |
| 59. | Adibhatla RM, Hatcher JF. Tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) and matrix metalloproteinases in the pathogenesis of stroke: therapeutic strategies. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 2008; 7: 243-53. |
| 60. |
Lee JE, Yoon YJ, Moseley ME, Yenari MA. Reduction in levels of matrix metalloproteinases and increased expression of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2 in response to mild hypothermia therapy in experimental stroke. J Neurosurg 2005; 103: 289-97.
PMID |
| 61. |
Palm F, Pussinen PJ, Safer A, et al. Serum matrix metalloproteinase-8, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase and myeloperoxidase in ischemic stroke. Atherosclerosis 2018; 271: 9-14.
DOI PMID |
| 62. |
Cuadrado E, Rosell A, Penalba A, et al. Vascular MMP-9/TIMP-2 and neuronal MMP-10 up-regulation in human brain after stroke: a combined laser microdissection and protein array study. J Proteome Res 2009; 8: 3191-7.
DOI PMID |
| 63. | Voss AK, Thomas T. Histone lysine and genomic targets of histone acetyltransferases in mammals. Bioessays 2018; 40: e1800078. |
| 64. | Wang Z, Leng Y, Tsai LK, Leeds P, Chuang DM. Valproic acid attenuates blood-brain barrier disruption in a rat model of transient focal cerebral ischemia: the roles of HDAC and MMP-9 inhibition. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2011; 31: 52-7. |
| 65. | Yang L, Yu Y, Tian G, Deng H, Yu B. H3K9ac modification was involved in doxorubicin induced apoptosis by regulating Pik3ca transcription in H9C2 cells. Life Sci 2021; 284: 119107. |
| 66. | Creyghton MP, Cheng AW, Welstead GG, et al. Histone H3K27ac separates active from poised enhancers and predicts developmental state. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2010; 107: 21931-6. |
| 67. |
Zhang W, Sun W, Qin Y, et al. Knockdown of KDM1A suppresses tumour migration and invasion by epigenetically regulating the TIMP1/MMP9 pathway in papillary thyroid cancer. J Cell Mol Med 2019; 23: 4933-44.
DOI PMID |
| 68. |
Wang J, Gao Y, Ma M, et al. Effect of miR-21 on renal fibrosis by regulating MMP-9 and TIMP1 in kk-ay diabetic nephropathy mice. Cell Biochem Biophys 2013; 67: 537-46.
DOI PMID |
| 69. | Zhao BQ, Wang S, Kim HY, et al. Role of matrix metalloproteinases in delayed cortical responses after stroke. Nat Med 2006; 12: 441-5. |
| 70. |
Rosenberg GA, Estrada EY, Dencoff JE. Matrix metalloproteinases and TIMPs are associated with blood-brain barrier opening after reperfusion in rat brain. Stroke 1998; 29: 2189-95.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | LUO Shan, YANG Fan, CHEN Yuanchun, ZHAO Ruoxi, LIU Haiye, GAO Fei, MA Wencan, GAO Weijuan, YU Wentao. Sanhua Tang (三化汤) protects against ischemic stroke by preventing blood-brain barrier injury: a network pharmacology and in vivo experiments [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(4): 794-803. |
| [2] | WANG Shaosong, SUN Jingqing, FENG Qingyin, LI Bin, WANG Xin, YUAN Fan, CUI Yingxue. Effectivenss of electroacupuncture for skeletal muscle pain in Parkinson's disease: a Clinical randomized controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(2): 388-395. |
| [3] | QIN Xiaoyu, WANG Chunai, XUE Jianjun, ZHANG Jie, LU Xiaoting, DING Shengshuang, GE Long, WANG Minzhen. Efficacy of electroacupuncture on myocardial protection and postoperative rehabilitation in patients undergoing cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 1-15. |
| [4] | SUN Qianhui, CHENG Kai, DAI Xingye, YANG Zhiwen, WU Xiaoling, XU Chang, QIU Xinghua, GAO Xiaofeng, LIU Daonan, YANG Qirui. Effect of electroacupuncture at Neiguan (PC6) at different time points on myocardial ischemia reperfusion arrhythmia in rats [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 113-121. |
| [5] | DU Zhongheng, CONG Wenjie, TANG Kejing, ZHENG Qiqi, SONG Zhiwei, CHEN Yong, YANG Su, ZHANG Chunwu, YE Tianshen. Electroacupuncture stimulating Zusanli (ST36), Sanyinjiao (SP6) in mice with collagen-induced arthritis leads to adenosine A2A receptor-mediated alteration of p38α mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling and inhibition of osteoclastogenesis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1103-1109. |
| [6] | JIANG Jianzhen, ZHANG Xin, LUO Zhenguo, SU Chengguo, ZHOU Haiyan, JIANG Yuqing, XIAO Xianjun, CHEN Yunfei, ZHU Jun. Efficacy of electroacupuncture stimulating Zusanli (ST36) and Xuanzhong (GB39) on synovial angiogenesis in rats with adjuvant arthritis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 955-962. |
| [7] | LI Zhihao, HAN Wenjun, SONG Xiuling, LI Yan, CHEN Yuelai. Electroacupuncture stimulating Zhongji (CV3), Guanyuan (CV4), and bilateral Dahe (KI12) attenuates inflammation in rats with chronic nonbacterial prostatitis induced by estradiol through inhibiting toll-like receptor 4 pathway [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 963-972. |
| [8] | DING Luobin, WANG Huajun, LI Yao, LI Jia, LI Ling, GAO Yangping, GUAN Jian, GENG Weiqiang. Electroacupuncture stimulating Neixiyan (EX-LE5) and Dubi (ST35) alleviates osteoarthritis in rats induced by anterior cruciate ligament transaction via affecting DNA methylation regulated transcription of miR-146a and miR-140-5p [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 983-990. |
| [9] | SUN Mengzhu, ZHANG Yujie, SONG Yafang, GUO Jing, WANG Yuhang, XIN Chen, GU Dongmei, SUN Jianhua, PEI Lixia. Electroacupuncture alleviates water avoidance stress-induced irritable bowel syndrome in mice by improving intestinal barrier functions and suppressing the expression of inflammatory cytokines [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(3): 494-500. |
| [10] | HAN Rui, CHANG Junzhao, LIU Qianqian, LIU Haitao, LI Junwei. Efficacy of electroacupunture at Zusanli (ST36) on jumping-injured muscle based on transcriptome sequencing and genes analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(2): 322-328. |
| [11] | Minh Duc Nguyen, Thanh Van Tran, Quoc Vinh Nguyen, Ninh Khac Nguyen, Son Truong Vu, Luu Trong Nguyen, Linh Vu Phuong Dang. Effectiveness on post-stroke hemiplegia in patients: electroacupuncture plus cycling vs electroacupuncture alone [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(2): 352-358. |
| [12] | XU Chang, LI Na, WU Xiaoling, DAI Xingye, YANG Zhiwen, SUN Qianhui, SHI Tianyu, CHAI Yemao, PANG Dandan, CHENG Kai. Effect of electroacupuncture on inflammatory signal expression in local tissues of rats with chronic pelvic pain syndrome based on purinergic 2X7 receptor/NOD-like receptor pyrin domain-containing 3 signal pathway [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(6): 965-971. |
| [13] | SUN Mengzhu, ZHANG Yujie, SONG Yafang, GUO Jing, ZHAO Tingting, WANG Yuhang, PEI Lixia, SUN Jianhua. Electroacupuncture at Tianshu (ST25) and Zusanli (ST36) alleviates stress-induced irritable bowel syndrome in mice by modulating gut microbiota and corticotropin-releasing factor [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(5): 732-740. |
| [14] | HU Xijiao, CHENG Yinglong, KANG Huanan, LI Shuoxi, WANG Yawen, LIU Jinzhe, SUN Yiming, LIU Li. Electroacupuncture attenuates chronic salpingitis via transforming growth factor-β1/p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(5): 781-787. |
| [15] | HUANG Yusi, YANG Jiju, LI Xinyi, HAO Huifeng, LI Chong, ZHANG Fan, LIN Haiming, XIE Xianfei, HE Ke, TIAN Guihua. Effectiveness and safety of electroacupuncture for the treatment of pain after laparoscopic surgery: a systematic review [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(4): 505-512. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

