Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (1): 58-64.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2022.01.005
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of aqueous extract of Astragalus membranaceus on behavioral cognition of rats living at high altitude
Xing DU1, Tianlong LIU2, Wendi TAO2, Maoxing LI2( ), Xiaolin LI2, Lan YAN2
), Xiaolin LI2, Lan YAN2
- 1 Gansu Institute for Drug Control, Lanzhou 730050, China
2 Department of Clinical Pharmacy, 940th Hospital of Joint Logistic Support Force of PLA, Lanzhou 730050, China; Gansu Plateau Pharmaceutical Technology Center, Lanzhou 730050, China
-
Received:2021-02-25Accepted:2021-05-23Online:2022-02-15Published:2021-07-07 -
Contact:Maoxing LI -
About author:LI Maoxing, Department of Clinical Pharmacy, 940th Hospital of Joint Logistic Support Force of PLA, Lanzhou 730050, China; Gansu Plateau Pharmaceutical Technology Center, Lanzhou 730050, China. limaox2020@aliyun.com
-
Supported by:Top Medical Science and Technology Youth Cultivation Program(Study on the Mechanism of Cognitive Impairment at High Altitude and a Series of Target Compounds of Verbascoside Based on mTOR Signal Pathway)(16QNP055);Key Research and Development Program of Gansu Province(Preclinical Study on Rong-Zhi Granule, a New Drug to Improve the Efficiency of Working at High Altitude)(20YF3FA035);Emergency Medical Research Project of “Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia”(Study on the Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Effects of COVID-19 Based on Hypoxia Induced Cytokine Storm)(20yjky018);2020 Innovation Team Project of Central University(Innovation Team of Tibetan Medicine Modernization R & D)(31920200010)
Cite this article
Xing DU, Tianlong LIU, Wendi TAO, Maoxing LI, Xiaolin LI, Lan YAN. Effect of aqueous extract of Astragalus membranaceus on behavioral cognition of rats living at high altitude[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(1): 58-64.
share this article
| Primer name | Base sequence |
|---|---|
| GAPDH | Upstream: 5'-GGCACAGTCAAGGCTGAGAATG-3' |
| Downstream: 5'-ATGGTGGTGAAGACGCCAGTA-3' | |
| m-TOR | Upstream: 5'-CGTGCTGTTGGGTGAGAGAG-3' |
| Downstream: 5'-TTCGTGTCCATCTTCTTGTCG-3' | |
| P70S6K | Upstream: 5'-GCCTCCCTACCTCACACAAGA-3' |
| Downstream: 5'-CCACCTTCCGAGCCAAAA-3' | |
| 4E-BP1 | Upstream: 5'-GGAGAGCCACAGCAGTCAGG-3' |
| Downstream: 5'-TCAACAGAGGCACAAGGAGGTAT-3' |
Table 1 GAPDH, m-TOR, P70S6K and 4E-BP1 primer sequences
| Primer name | Base sequence |
|---|---|
| GAPDH | Upstream: 5'-GGCACAGTCAAGGCTGAGAATG-3' |
| Downstream: 5'-ATGGTGGTGAAGACGCCAGTA-3' | |
| m-TOR | Upstream: 5'-CGTGCTGTTGGGTGAGAGAG-3' |
| Downstream: 5'-TTCGTGTCCATCTTCTTGTCG-3' | |
| P70S6K | Upstream: 5'-GCCTCCCTACCTCACACAAGA-3' |
| Downstream: 5'-CCACCTTCCGAGCCAAAA-3' | |
| 4E-BP1 | Upstream: 5'-GGAGAGCCACAGCAGTCAGG-3' |
| Downstream: 5'-TCAACAGAGGCACAAGGAGGTAT-3' |
| Group | Dose | n | WME (times) | RME (times) | TE (times) | TT (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCG | 0.1 mL/10 g | 10 | 0.5±0.4 | 0.5±0.5 | 1.0±0.6 | 112.1±31.0 |
| HCG | 0.1 mL/10 g | 10 | 1.8±1.0b | 3.2±1.2b | 5.0±1.3b | 224.2±42.9b |
| PG | 0.35 g/kg | 10 | 1.3±1.0a | 1.8±0.8bd | 3.1±1.9b | 154.5±57.6d |
| H-AMG | 0.35 g/kg | 10 | 1.4±0.6a | 1.9±0.8bc | 3.2±0.7bd | 133.3±47.5d |
| M-AMG | 0.15 g/kg | 10 | 1.2±0.7a | 1.9±0.8bc | 3.1±1.0bd | 152.1±49.0d |
| L-AMG | 0.05 g/kg | 10 | 1.3±0.9a | 2.2±0.9bc | 3.5±1.2bc | 174.3±50.9bc |
Table 2 Results of the eight-arm maze experimental ($\bar{x}$ ± s)
| Group | Dose | n | WME (times) | RME (times) | TE (times) | TT (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCG | 0.1 mL/10 g | 10 | 0.5±0.4 | 0.5±0.5 | 1.0±0.6 | 112.1±31.0 |
| HCG | 0.1 mL/10 g | 10 | 1.8±1.0b | 3.2±1.2b | 5.0±1.3b | 224.2±42.9b |
| PG | 0.35 g/kg | 10 | 1.3±1.0a | 1.8±0.8bd | 3.1±1.9b | 154.5±57.6d |
| H-AMG | 0.35 g/kg | 10 | 1.4±0.6a | 1.9±0.8bc | 3.2±0.7bd | 133.3±47.5d |
| M-AMG | 0.15 g/kg | 10 | 1.2±0.7a | 1.9±0.8bc | 3.1±1.0bd | 152.1±49.0d |
| L-AMG | 0.05 g/kg | 10 | 1.3±0.9a | 2.2±0.9bc | 3.5±1.2bc | 174.3±50.9bc |

Figure 1 Pathological damages in hippocampus of each group of rats (n = 8, ×100) A: NCG: normoxic control group; B: HCG: hypoxia control group; C: PG: positive group (1.35 g/kg L-leucine); D: H-AMG: high dose group (0.35 g/kg Astragalus membranaceus); E: M-AMG: middle dose group (0.15 g/kg Astragalus membranaceus); F: L-AMG: low dose group (0.05 g/kg Astragalus membranaceus). Rats were administered by gavage once a day for 7 d.
| Group | Dose | n | MDA (nmol/mgprot) | GSH (mg/gprot) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCG | 0.1 mL/10 g | 8 | 1.6±0.3 | 21.3±2.7 |
| HCG | 0.1 mL/10 g | 8 | 2.8±0.5a | 16.6±1.0a |
| PG | 0.35 g/kg | 8 | 1.7±0.5b | 19.4±2.5d |
| H-AMG | 0.35 g/kg | 8 | 1.8±0.6b | 19.1±2.6d |
| M-AMG | 0.15 g/kg | 8 | 1.9±0.4b | 19.0±2.3d |
| L-AMG | 0.05 g/kg | 8 | 2.0±0.4bc | 17.6±2.6cd |
Table 3 Contents of MDA and GSH in hippocampus of each group of rats ($\bar{x}$ ± s)
| Group | Dose | n | MDA (nmol/mgprot) | GSH (mg/gprot) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCG | 0.1 mL/10 g | 8 | 1.6±0.3 | 21.3±2.7 |
| HCG | 0.1 mL/10 g | 8 | 2.8±0.5a | 16.6±1.0a |
| PG | 0.35 g/kg | 8 | 1.7±0.5b | 19.4±2.5d |
| H-AMG | 0.35 g/kg | 8 | 1.8±0.6b | 19.1±2.6d |
| M-AMG | 0.15 g/kg | 8 | 1.9±0.4b | 19.0±2.3d |
| L-AMG | 0.05 g/kg | 8 | 2.0±0.4bc | 17.6±2.6cd |
| Group | Dose | n | T-SOD (U/mgprot) | ROS (FU/mgprot) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCG | 0.1 mL/10 g | 8 | 303.2±34.7 | 1.4±0.3 (107) |
| HCG | 0.1 mL/10 g | 8 | 244.3±39.1a | 2.0±0.3a (107) |
| PG | 0.35 g/kg | 8 | 286.0±34.0b | 1.4±0.2c (107) |
| H-AMG | 0.35 g/kg | 8 | 285.0±25.0b | 1.5±0.2c (107) |
| M-AMG | 0.15 g/kg | 8 | 280.4±26.6b | 1.6±0.3c (107) |
| L-AMG | 0.05 g/kg | 8 | 249.6 ±19.2a | 1.8±0.3d (107) |
Table 4 T-SOD activity and ROS content in hippocampus of each group of rats ($\bar{x}$ ± s)
| Group | Dose | n | T-SOD (U/mgprot) | ROS (FU/mgprot) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCG | 0.1 mL/10 g | 8 | 303.2±34.7 | 1.4±0.3 (107) |
| HCG | 0.1 mL/10 g | 8 | 244.3±39.1a | 2.0±0.3a (107) |
| PG | 0.35 g/kg | 8 | 286.0±34.0b | 1.4±0.2c (107) |
| H-AMG | 0.35 g/kg | 8 | 285.0±25.0b | 1.5±0.2c (107) |
| M-AMG | 0.15 g/kg | 8 | 280.4±26.6b | 1.6±0.3c (107) |
| L-AMG | 0.05 g/kg | 8 | 249.6 ±19.2a | 1.8±0.3d (107) |
| Group | Dose | n | mTOR mRNA | P70S6K mRNA | 4E-BP1 mRNA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCG | 0.1 mL/10 g | 8 | 1.0±0.1 | 1.0±0.1 | 1.0±0.0 |
| HCG | 0.1 mL/10 g | 8 | 0.5±0.1a | 0.7±0.1a | 1.5±0.2d |
| PG | 0.35 g/kg | 8 | 0.9±0.1b | 1.0±0.1b | 0.8±0.1c |
| H-AMG | 0.35 g/kg | 8 | 0.9±0.2b | 0.9±0.2c | 0.8±0.1c |
| M-AMG | 0.15 g/kg | 8 | 0.9±0.1b | 0.8±0.1 | 0.9±0.1c |
| L-AMG | 0.05 g/kg | 8 | 0.7±0.1c | 0.8±0.1 | 1.26± 0.3 |
Table 5 Effect of aqueous extract of Astragalus membranaceus on target gene expression ($\bar{x}$ ± s)
| Group | Dose | n | mTOR mRNA | P70S6K mRNA | 4E-BP1 mRNA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCG | 0.1 mL/10 g | 8 | 1.0±0.1 | 1.0±0.1 | 1.0±0.0 |
| HCG | 0.1 mL/10 g | 8 | 0.5±0.1a | 0.7±0.1a | 1.5±0.2d |
| PG | 0.35 g/kg | 8 | 0.9±0.1b | 1.0±0.1b | 0.8±0.1c |
| H-AMG | 0.35 g/kg | 8 | 0.9±0.2b | 0.9±0.2c | 0.8±0.1c |
| M-AMG | 0.15 g/kg | 8 | 0.9±0.1b | 0.8±0.1 | 0.9±0.1c |
| L-AMG | 0.05 g/kg | 8 | 0.7±0.1c | 0.8±0.1 | 1.26± 0.3 |
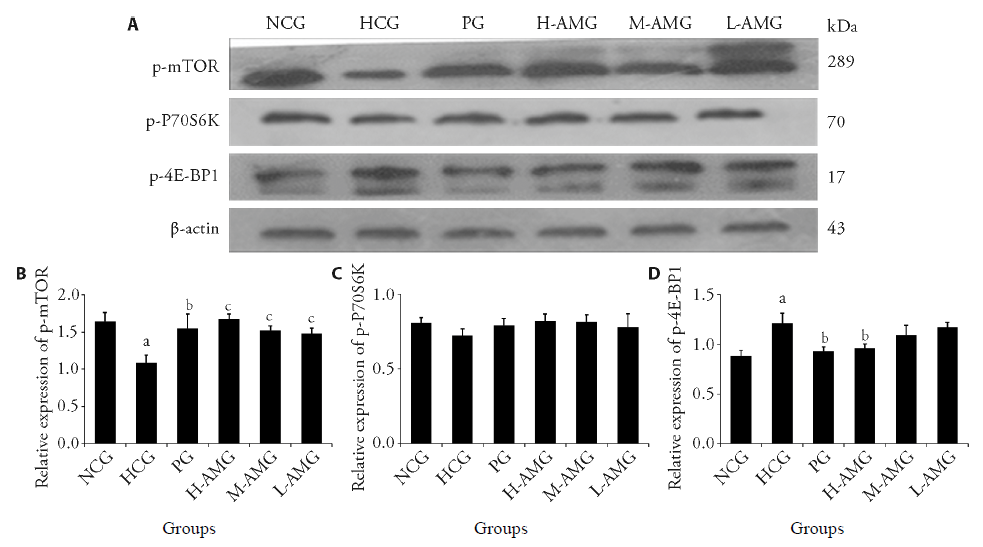
Figure 2 Effect of aqueous extract of Astragalus membranaceus on target gene expression ($\bar{x}$± s, n = 3) A: Western blot banding of protein expression; B: quantitative analysis of p-mTOR; C: quantitative analysis of p-P70S6K; D: quantitative analysis of p-4E-BP1. NCG: normoxic control group; HCG: hypoxia control group; PG: positive group (1.35 g/kg L-leucine); H-AMG: high dose group (0.35 g/kg Astragalus membranaceus); M-AMG: middle dose group (0.15 g/kg Astragalus membranaceus); L-AMG: low dose group (0.05 g/kg Astragalus membranaceus). Rats were administered by gavage once a day for 7 d. mTOR: mammalian target of rapamycin; 4E-BP1: 4E-binding protein 1. Compared with NCG, aP < 0.01; compared with HCG group, bP < 0.05, cP < 0.01.
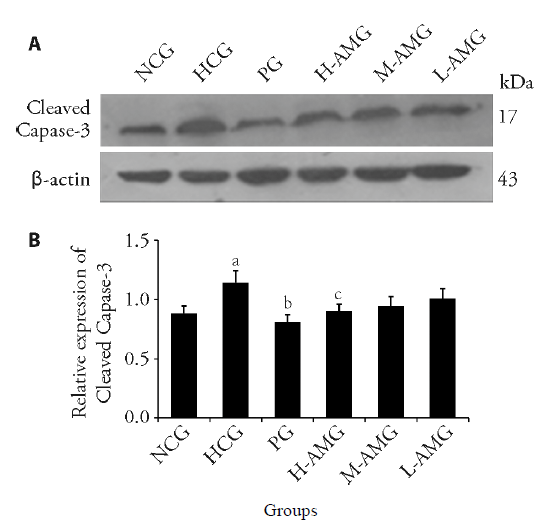
Figure 3 Effect of aqueous extract of Astragalus membranaceus on cleaved capase-3 protein expression ($\bar{x}$ ± s, n = 3) A: Western blot banding of protein expression; B: quantitative analysis of cleaved capase-3. NCG: normoxic control group; HCG: hypoxia control group; PG: positive group (1.35 g/kg L-leucine); H-AMG: high dose group (0.35 g/kg Astragalus membranaceus); M-AMG: middle dose group (0.15 g/kg Astragalus membranaceus); L-AMG: low dose group (0.05 g/kg Astragalus membranaceus). Rats were administered by gavage once a day for 7 d. Compared with NCG, aP < 0.05; compared with HCG group, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.05.
| [1] | Zhao J, Zhang R, Yu Q, et al. Characteristics of EEG activity during high altitude hypoxia and lowland reoxygenation. Brain Res 2016;1648:243-9. |
| [2] | Wei D, Wei L, Li X, et al. Effect of hypoxia on Ldh-c expression in somatic cells of plateau pika. Int J Env Res Pub He 2016;13:773. |
| [3] | Vargas M, Becerril-Ángeles M, Medina-Reyes I, et al. Altitude above 1500 m is a major determinant of asthma incidence. An ecological study. Resp Med 2018;135:1-7. |
| [4] | Luks A, Auerbach P, Freer L, et al. Wilderness medical society clinical practice guidelines for the prevention and treatment of acute altitude illness: 2019 update. Wild Environ Med 2019;30:S3-S18. |
| [5] | Bärtsch P, Swenson E. Acute high-altitude illnesses. NEJM 2013;368:2294-302. |
| [6] | Asmaro D, Mayall J, Ferguson S. Cognition at altitude: impairment in executive and memory processes under hypoxic conditions. Aviat Space Environ Med 2013;84:1159-65. |
| [7] | Yan X. Cognitive impairments at high altitudes and adaptation. High Alt Med Biol 2014;15:141-5. |
| [8] | Wilson M, Newman S, Imray C. The cerebral effects of ascent to high altitudes. Lancet Neurol 2009;8:175-91. |
| [9] | Movafeghi A, Djozan D, Razeghi J, et al. Identification of volatile organic compounds in leaves, roots and gum of Astragalus compactus Lam. using solid phase microextraction followed by GC-MS analysis. Nat Prod Res 2010;24:703-9. |
| [10] | Auyeung KK, Han Q, Ko JK. Astragalus membranaceus: a review of its protection against inflammation and gastrointestinal cancers. Am J Chin Med 2016;44:1-22. |
| [11] | Li X, Qu L, Dong Y, et al. A review of recent research progress on the astragalus genus. Molecules 2014;19:18850-80. |
| [12] | Wang Y, Liu L, Ma Y, et al. Chemical discrimination of astragalus mongholicus and astragalus membranaceus based on metabolomics using UHPLC-ESI-Q-TOF-MS/MS approach. molecules 2019;24:4064. |
| [13] | Liu M, Wu K, Mao X, et al. Astragalus polysaccharide improves insulin sensitivity in KKAy mice: regulation of PKB/GLUT4 signaling in skeletal muscle. J Ethnopharmacol 2010;127:32-37. |
| [14] | Du X, Chen X, Zhao B, et al. Astragalus polysaccharides enhance the humoral and cellular immune responses of hepatitis B surface antigen vaccination through inhibiting the expression of transforming growth factor β and the frequency of regulatory T cells. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 2011;63:228-35. |
| [15] | Nalbantsoy A, Nesil T, Erden S, et al. Adjuvant effects of Astragalus saponins macrophyllosaponin B and astragaloside VII. J Ethnopharmacol 2011;134:897-903. |
| [16] | Linnek J, Mitaine-Offer A, Miyamoto T, et al. Cycloartane-type glycosides from two species of Astragalus (Fabaceae). Nat Prod Commun 2009;4:477-78. |
| [17] | Li M, Zhu Y, Li J, et al. Effect and mechanism of verbascoside on hypoxic memory injury in plateau. Phytother Res 2019;33:2692-701. |
| [18] | Xu H, Baracskay P, O'Neill J, et al. Assembly responses of hippocampal CA1 place cells predict learned behavior in goal-directed spatial tasks on the radial eight-arm maze. Neuron 2019;101:119-32. |
| [19] | Sharma V, Das S, Dhar P, et al. Domain specific changes in cognition at high altitude and its correlation with hyperhomocysteinemia. Plos One 2014;9:e101448. |
| [20] | Rimoldi S, Rexhaj E, Duplain H, et al. Acute and chronic altitude-induced cognitive dysfunction in children and adolescents. J Pediatr 2016;169:238-43. |
| [21] | Zhou B, Li M, Cao X, et al. Phenylethanoid glycosides of Pedicularis muscicola Maxim ameliorate high altitude-induced memory impairment. Physiol Behav 2016;157:39-46. |
| [22] | Zhang G, Zhou S, Yuan C, et al. The effects of short-term and long-term exposure to a high altitude hypoxic environment on neurobehavioral function. High Alt Med Biol 2013;14:338-41. |
| [23] | Joyce K, Lucas S, Imray C, et al. Advances in the available non-biological pharmacotherapy prevention and treatment of acute mountain sickness and high altitude cerebral and pulmonary oedema. Expert Opin Pharmaco 2018;19:1891-902. |
| [24] | Davranche K, Casini L, Arnal P, et al. Cognitive functions and cerebral oxygenation changes during acute and prolonged hypoxic exposure. Physiol Behav 2016;164:189-97. |
| [25] | Ma H, Li X, Liu M, et al. Mental Rotation Effect on Adult Immigrants with Long-term Exposure to High Altitude in Tibet: An ERP Study. Neuroscience 2018;386:339-50. |
| [26] | Fuhrmann D, Brüne B. Mitochondrial composition and function under the control of hypoxia. Redox Biol 2017;12:208-15. |
| [27] | Zeng H. mTOR signaling in immune cells and its implications for cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Lett 2017;408:182-89. |
| [28] | Woillard J, Kamar N, Rousseau A, et al. Association of sirolimus adverse effects with mTOR, p70S6K or Raptor polymorphisms in kidney transplant recipients. Pharmacogenet Genomics 2012;22:725-32. |
| [29] | Fu S, Imai K, Sawasaki T, et al. ScreenCap3: Improving prediction of caspase-3 cleavage sites using experimentally verified noncleavage sites. Proteomics 2014;14:2042-6. |
| [1] | HUANG Hongmei, YANG Maojun, LI Ting, WANG Dandan, LI Ying, TANG Xiaochi, YUAN Lu, GU Shi, XU Yong. Neferine inhibits the progression of diabetic nephropathy by modulating the miR-17-5p/nuclear factor E2-related factor 2 axis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 44-53. |
| [2] | YANG Xirui, ZHAO Hui, SHAN Muhammad, DONG Feixue, ZHANG Dandan, WANG Jixue, YUAN Xingxing. Efficacy of bioactive compounds of Chaihu (Radix Bupleuri Chinensis) on glaucomatous optic atrophy through interleukin-6/hypoxia inducible factor-1α signal pathway [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1219-1226. |
| [3] | ZHANG Xiaoying, WANG Ruixuan, WANG Yiqing, XU Fanxing, YAN Tingxu, WU Bo, ZHANG Ming, JIA Ying. Spinosin protects Neuro-2a/APP695 cells from oxidative stress damage by inactivating p38 [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 868-875. |
| [4] | YANG Xiaohui, WANG Jian, CHENG Li, ZHANG Yuxi, HUANG Jianlin, LIU Minghua. Active compounds of Caodoukou (Semen Alpinia Katsumadai) inhibit the migration, invasion and metastasis of human pancreatic cancer cells by targeting phosphoinosmde-3-kinase/ protein kinase B/mammalian target of rapamycin pathway [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 876-886. |
| [5] | LIU Bingbing, LI Jieru, SI Jianchao, CHEN Qi, YANG Shengchang, JI Ensheng. Ginsenoside Rb1 alleviates chronic intermittent hypoxia-induced diabetic cardiomyopathy in db/db mice by regulating the adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase/Nrf2/heme oxygenase-1 signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 906-914. |
| [6] | ZHOU Hua, LI Hui, WANG Haihua. Potential protective effects of the water-soluble Chinese propolis on experimental ulcerative colitis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 925-933. |
| [7] | GUO Ziliang, QIAN Qingyuan, LI Xiaolin, ZHU Yuting, REN Jun, LI Maoxing. Efficacy of verbascoside, echinacoside, crenatoside on altitude-induced fatigue in rats and possible mechanism [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 934-943. |
| [8] | XIN Zhixiong, LI Jiyuan, XU Yanni, LING Jing, JIANG Min, YU Yutian. Acupuncture on intrauterine growth restriction associated brain injury: case study including use of magnetic resonance imaging [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(3): 602-605. |
| [9] | ZHENG Wei, WANG Mingxing, LIU Shanxue, LUAN Chao, ZHANG Yanqiu, XU Duoduo, WANG Jian. Buyang Huanwu Tang (补阳还五汤) protects H2O2-induced RGC-5 cell against oxidative stress and apoptosis via reactive oxygen species-mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(6): 885-891. |
| [10] | HENG Xianpei, LI Liang, YANG Liuqin, WANG Zhita. Efficacy of Dangua Fang (丹瓜方) on endothelial cells damaged by oxidative stress [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(6): 900-907. |
| [11] | HUANG Qiuyue, YE Hui, SHI Zongming, JIA Xiaofen, LIN Miaomiao, CHU Yingming, YU Jing, ZHANG Xuezhi. Efficacy of Qingre Huashi decoction (清热化湿方) on infection of Helicobacter pylori: inhibiting adhesion, antioxidant, and anti-inflammation [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(6): 915-921. |
| [12] | YANG Mengzhe, ZHANG Beibei, LIANG Zhenqiang, CHENG Nannan, Lü Anqiao, YANG Jianyu, GUO Xingzhe, BAI Xianyu, HUANG Yuanjiao, JIAO Aijun, XU Ning. Sanguinarine suppresses cell proliferation, migration and invasion in nasopharyngeal carcinoma via inhibiting mTOR signaling [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(5): 687-692. |
| [13] | ZHAO Lixia, SUN Wei, BAI Decheng. Protective effect of resveratrol on rat cardiomyocyte H9C2 cells injured by hypoxia/reoxygenation by regulating mitochondrial autophagy via PTEN-induced putative kinase protein 1/Parkinson disease protein 2 signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(2): 176-186. |
| [14] | ZHONG Jian, FANG Guiyu, WANG Zixia, CHEN Ping, LU Dengyong, SHI Xiaodong. Yishen Huoxue decoction(益肾活血方) attenuates unilateral ureteric obstruction-induced renal fibrosis and hypoxia-induced reactive oxygen species generation via adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase/peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor coa [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(6): 875-882. |
| [15] | ZHANG Yongcang, LIU Tonghua, LIU Lan, ZONG Yonghua, LI Yu, XIONG Hai, WU Lili. Efficacy of Shouzhangshen (Rhizoma Gymnadeniae Crassinervidis) extract against acute high altitude hypoxia-induced brain injury in mice [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(4): 546-555. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

