Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (1): 70-77.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20231204.001
• Original articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Caffeic acid 3,4-dihydroxyphenethyl ester prevents colorectal cancer through inhibition of multiple cancer-promoting signal pathways in 1,2-Dimethylhydrazine/dextran sodium sulphate mouse model
JIN Tao1( ), ZHOU Qian1, SHEN Jichen2, ZHANG Zhizhong3, LIAN Xiaoyuan4(
), ZHOU Qian1, SHEN Jichen2, ZHANG Zhizhong3, LIAN Xiaoyuan4( )
)
- 1 College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310058, China
2 Pharmaceutical Informatics Institute, College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310058, China
3 Ocean College, Zhoushan Campus of Zhejiang University, Zhoushan 316021, China
4 College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310058, China
-
Received:2022-07-22Accepted:2022-11-17Online:2024-02-15Published:2023-12-04 -
Contact:Prof. LIAN Xiaoyuan, College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310058, China. xylian@zju.edu.cn;JIN Tao, College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310058, China. jintaomark@zju.edu.cn. Telephone: +86-571-88208432;+86-17705814812 -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China Project: the Investigation of Anti-tumor Target System of Traditional Chinese Medicine(81274137, to Stimulate Research Targeted the Energy Metabolism Network of Tumor Cells)
Cite this article
JIN Tao, ZHOU Qian, SHEN Jichen, ZHANG Zhizhong, LIAN Xiaoyuan. Caffeic acid 3,4-dihydroxyphenethyl ester prevents colorectal cancer through inhibition of multiple cancer-promoting signal pathways in 1,2-Dimethylhydrazine/dextran sodium sulphate mouse model[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 70-77.
share this article

Figure 1 CADPE reduced production of inflammation and inhibited NF-κB activation in DMH/DSS induced CRC in vivo A: different images showed the CADPE treatment DMH/DSS induced male mice had fewer tumors in the colon than the model group male mice and without the effect of toxicity was found. A1, A2: na?ve group, only treated with water; A3, A4: model group, treated with DMH/DSS; A5, A6: 5-FU group, treated with 5-FU; A7, A8: CADPE group, treated with 15 mg/kg CADPE; A9, A10: CADPE group, treated with 25 mg/kg CADPE; A11, A12: CADPE group, treated with 35 mg/kg CADPE. B: HE staining images of three mouse groups na?ve (B1-B3), model (B4-B6) and CADPE (B7-B9). demonstrated the core incidence area of CRC in colons under ×4, ×40 and ×100 magnification. C: HE staining images of na?ve (C1-C3), model (C4-C6) and CADPE (C7-C9) at three time points (days 15, 18 and 25) showed the inflammation and crypt damage in colonic mucosa under ×40 magnification. CADPE: Caffeic acid 3,4-dihydroxyphenethyl ester; DMH/DSS: 1,2-Dimethylhydrazine/dextran sodium sulphate; HE: hematoxylin and eosin.
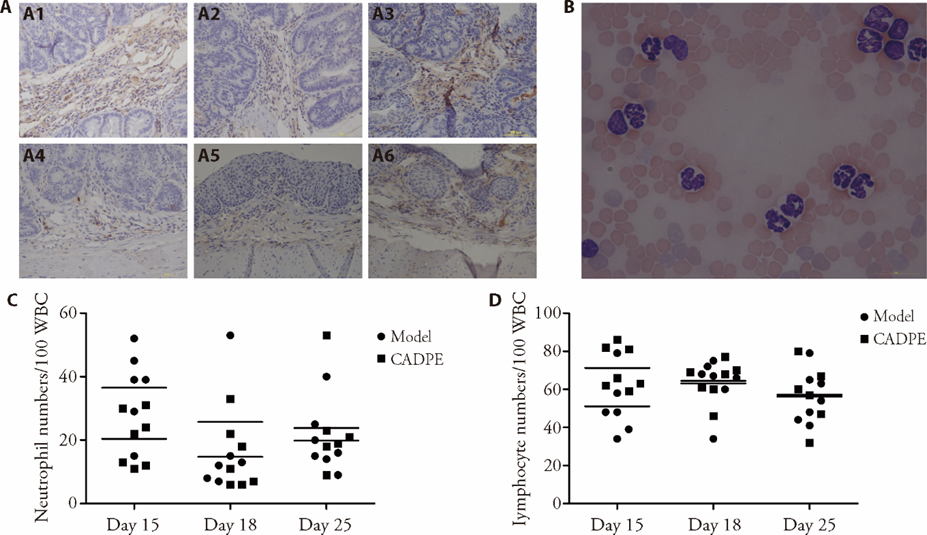
Figure 2 CADPE prevented the inflammation and colorectal cancer progression by inhibiting the infiltration of immune cells from the peripheral blood. A: three samples from Model mouse group (A1-A3): treated only with DMH (20 mg/kg) and DSS (2%) for two weeks; three samples from CADPE treatment mouse group (A4-A6): treated with DMH/DSS for two weeks and CADPE (25 mg/kg) for twelve weeks. The immunohistochemistry images of mouse groups model (A1-A3) and CADPE (A4-A6) marked by CD3 under × 40 magnification domostrated that tumor tissues were surrounding by more brown colored positive cells from the peripheral blood in the model mouse group samples than the CADPE treatment group samples. B: image of the polymorphic immune cells from the mouse peripheral blood was observed under microscope at ×100 magnification. C: expression level of neutrophils and its tendency between the CADPE treatment (25 mg/kg) and model mouse groups were compared at the 15th, 18th and 25th day. D: expression level of lymphocytes and its tendency between the CADPE treatment (25 mg/kg) and model mouse groups were compared at the 15th, 18th and 25th day. Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation; n = 7 for each group; one-way analysis of variance followed by Dunnett's multiple comparison (C, D); aP < 0.05 compared with the model group. CADPE: Caffeic acid 3, 4-dihydroxyphenethyl ester; DMH: the 1, 2-Dimethylhydrazine; DSS: dextran sodium sulphate.

Figure 3 CADPE reduced tumor growth of CRC via blocking three potential targets and two cancer related pathways A: the molecular simulation data indicated that the small CADPE molecule was tighly binding the surface of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) active site; B: the molecular simulation data showed that the small CADPE molecule was tighly binding the surface of the mTOR active site; C: the molecular simulation data demonstrated that the small CADPE molecule was tighly binding the surface of the ERK active site. The arrows indicated the amplified locations. CADPE: Caffeic acid 3,4-dihydroxyphenethyl ester; EGFR: epidermal growth factor receptor; CRC: colorectal cancer; mTOR: the mechanistic target of rapamycin.
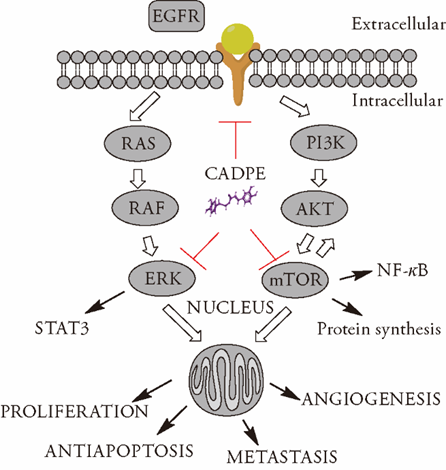
Figure 4 Summary chart of CADPE mechanism in the MAPK/ERK and PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathways EGFR: epidermal growth factor receptor; RAS: ras protein kinase; RAF: Raf protein kinase; CADPE: Caffeic acid 3,4-dihydroxyphenethyl ester; MAPK/ERK: mitogen-activated protein kinases/extracellular signal-regulated kinase; NF-κB: nuclear factor-kappa B; PI3K-AKT-mTOR: phosphatidylinositol three kinase AK strain transforming-mammalian target of rapamycin.
| 1. |
Marmol I, Sanchez-de-Diego C, Pradilla Dieste A, Cerrada E, Rodriguez Yoldi MJ. Colorectal carcinoma: a general overview and future perspectives in colorectal cancer. Int J Mol Sci 2017; 18: 197.
DOI URL |
| 2. |
Binefa G, Rodríguez-Moranta F, Teule à, Medina-Hayas M. Colorectal cancer: from prevention to personalized medicine. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20: 6786.
DOI URL |
| 3. |
Roshan MHK, Tambo A, Pace NP. The role of testosterone in colorectal carcinoma: pathomechanisms and open questions. EPMA J 2016; 7: 22.
PMID |
| 4. |
Zhang MJ, Su H, Yan JY, et al. Chemopreventive effect of Myricetin, a natural occurring compound, on colonic chronic inflammation and inflammation-driven tumorigenesis in male mice. Biomed Pharmacother 2017; 97: 1131-37.
DOI URL |
| 5. |
Ferrero-Miliani L, Nielsen OH, Andersen PS, Girardin SE. Chronic inflammation: importance of NOD2 and NALP3 in interleukin-1β generation. Clin Exp Immunol 2007; 147: 227.
DOI PMID |
| 6. |
Hanai J, Doro N, Sasaki AT, et al. Inhibition of lung cancer growth: ATP citrate lyase knockdown and statin treatment leads to dual blockade of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K)/AKT pathways. J Cell Physiol 2012; 227: 1709-20.
DOI URL |
| 7. |
Liu L, Li YH, Niu YB, et al. An apple oligogalactan prevents against inflammation and carcinogenesis by targeting LPS/TLR4/NF-kappa B pathway in a mouse model of colitis-associated colon cancer. Carcinogenesis 2010; 31: 1822-32.
DOI PMID |
| 8. |
Schwitalla S, Fingerle AA, Cammareri P, et al. Intestinal tumorigenesis initiated by dedifferentiation and acquisition of stem-cell-like properties. Cell 2013; 152: 25-38.
DOI PMID |
| 9. | Sun Y, Zhao Y, Wang X, et al. Wogonoside prevents colitis-associated colorectal carcinogenesis and colon cancer progression in inflammation-related microenvironment via inhibiting NF-kappaB activation through PI3K/Akt pathway. Oncotarget 2016; 7: 34300-15. |
| 10. |
Srivastava JK, Pillai GG, Bhat HR, Verma A, Singh UP. Design and discovery of novel monastrol-1,3,5-triazines as potent anti-breast cancer agent via attenuating epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase. Sci Rep 2017; 7: 5851.
DOI PMID |
| 11. |
Gkouveris I, Nikitakis N, Karanikou M, Rassidakis G, Sklavounou A. Erk1/2 activation and modulation of STAT3 signaling in oral cancer. Oncol Rep 2014; 32: 2175-82.
DOI PMID |
| 12. |
Moschetta M, Reale A, Marasco C, Vacca A, Carratu MR. Therapeutic targeting of the mTOR-signalling pathway in cancer: benefits and limitations. Br J Pharmacol 2014; 171: 3801-13.
DOI URL |
| 13. |
De P, Miskimins K, Dey N, Leyland-Jones B. Promise of rapalogues versus mTOR kinase inhibitors in subset specific breast cancer: old targets new hope. Cancer Treat Rev 2013; 39: 403-12.
DOI PMID |
| 14. |
Wullschleger S, Loewith R, Hall MN. TOR rignaling in growth and metabolism. Cell 2006; 124: 471.
DOI PMID |
| 15. | Tsai YC, Chen SH, Lin LC, Fu SL. Anti-infalmmatory principles from sarcandra glabra. J Agric Food Chem 2017; 65: 6497-505. |
| 16. |
Guo X, Shen L, Tong Y, et al. Antitumor activity of caffeic acid 3,4-dihydroxyphenethyl ester and its pharmacokinetic and metabolic properties. Phytomedicine 2013; 20: 904-12.
DOI PMID |
| 17. |
Jung JE, Kim HS, Lee CS, et al. Caffeic acid and its synthetic derivative CADPE suppress tumor angiogenesis by blocking STAT3-mediated VEGF expression in human renal carcinoma cells. Carcinogenesis 2007; 28: 1780-7.
PMID |
| 18. | Won C, Lee CS, Lee JK, et al. CADPE suppresses cyclin D 1 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma by blocking IL-6-induced STAT3 activation. Anticancer Res 2010 ; 30(2): 481-8. |
| 19. |
Han H, Du B, Pan X, et al. CADPE inhibits PMA-stimulated gastric carcinoma cell invasion and matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression by FAK/MEK/ERK-mediated AP-1 activation. Mol Cancer Res 2010; 8: 1477.
DOI PMID |
| 20. |
Jia J, Yang M, Chen Y, et al. Inducing apoptosis effect of caffeic acid 3,4-dihydroxy-phenethyl ester on the breast cancer cells. Tumour Biol 2014; 35: 11781-9.
DOI URL |
| 21. |
Zheng GW, Tang MM, Shu CY, et al. A small natural molecule CADPE kills residual colorectal cancer cells by inhibiting key transcription factors and translation initiation factors. Cell Death Dis 2020; 11: 982.
DOI |
| 22. |
Tang M, Xie X, Shi M, et al. Antileukemic effect of caffeic acid 3,4-dihydroxyphenetyl ester. Evidences for its mechanisms of action. Phytomedicine 2021; 80: 153383.
DOI URL |
| 23. |
Prabhu PN, Ashokkumar P, Sudhandiran G. Antioxidative and antiproliferative effects of astaxanthin during the initiation stages of 1,2-dimethyl hydrazine-induced experimental colon carcinogenesis. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 2009; 23: 225-34.
DOI URL |
| 24. |
Onose J, Imai T, Hasumura M, Ueda M, Hirose M. Rapid induction of colorectal tumors in rats initiated with 1,2-dimethylhydrazine followed by dextran sodium sulfate treatment. Cancer Lett 2003; 198: 145-52.
DOI URL |
| 25. |
Li H, Wu WK, Li ZJ, et al. 2,3',4,4',5'-Pentamethoxy-trans-stilbene, a resveratrol derivative, inhibits colitis-associated colorectal carcinogenesis in male mice. Br J Pharmacol 2010; 160: 1352-61.
DOI URL |
| 26. | Verma S, Das P, Kumar VL. Chemoprevention by artesunate in a preclinical model of colorectal cancer involves down regulation of β-catenin, suppression of angiogenesis, cellular proliferation and induction of apoptosis. Chem Biol Interact 2017; 278: 84-91. |
| 27. |
Warhurst DC, Williams JE. ACP Broadsheet no 148. July 1996. Laboratory diagnosis of malaria. J Clin Pathol 1996; 49: 533-8.
DOI PMID |
| 28. | Zhao H, Zhang H, Wu H, et al. Protective role of 1,25(OH)2 vitamin D3 in the mucosal injury and epithelial barrier disruption in DSS-induced acute colitis in male mice. BMC Gastroenterol 2012; 12: 57. |
| 29. |
Egger B, Procaccino F, Lakshmanan J, et al. Male mice lacking transforming growth factor alpha have an increased susceptibility to dextran sulfate-induced colitis. Gastroenterology 1997; 113: 825-32.
PMID |
| 30. |
Murthy SN, Cooper HS, Shim H, Shah RS, Ibrahim SA, Sedergran DJ. Treatment of dextran sulfate sodium-induced murine colitis by intracolonic cyclosporin. Dig Dis Sci 1993; 38: 1722-34.
DOI URL |
| 31. |
Zhang Z, Xiao B, Chen Q, Lian XY. Synthesis and biological evaluation of caffeic acid 3,4-dihydroxyphenethyl ester. J Nat Prod 2010; 73: 252-4.
DOI PMID |
| 32. |
Pikarsky E, Porat RM, Stein I, et al. NF-kappaB functions as a tumour promoter in inflammation-associated cancer. Nature 2004; 431: 461-66.
DOI |
| 33. | Thompson PA, Khatami M, Baglole CJ, et al. Environmental immune disruptors, inflammation and cancer risk. Carcinogenesis 2015; 36 Suppl 1: S232-53. |
| 34. |
Ferrero-Miliani L, Nielsen OH, Andersen PS, Girardin SE. Chronic inflammation: importance of NOD2 and NALP3 in interleukin-1beta generation. Clin Exp Immunol 2007; 147: 227-35.
DOI PMID |
| 35. |
Mitrasinovic PM. Inhibitory activity against epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) based on single point mutations of active site residues. J Med Chem 2014; 10: 252-70.
DOI URL |
| 36. |
Yang H, Rudge DG, Koos JD, Vaidialingam B, Yang HJ, Pavletich NP. mTOR kinase structure, mechanism and regulation. Nature 2013; 497: 217-23.
DOI |
| 37. |
Lee SY, Lee H, Lee HK, et al. Proximity-directed labeling reveals a new rapamycin-induced heterodimer of FKBP25 and FRB in live cells. ACS Cent Sci 2016; 2: 506-16.
DOI URL |
| 38. | Ahmad A, Biersack B, Li YW, et al. Targeted regulation of PI3K/Akt/mTOR/NF-κB signaling by indole compounds and their derivatives: mechanistic details and biological implications for cancer therapy. Anticancer Agents Med Chem 2013; 13: 1002-13. |
| 39. |
Tkach M, Rosemblit C, Rivas MA, et al. p42/p 44 MAPK-mediated Stat3Ser727. phosphorylation is required for progestin-induced full activation of Stat3 and breast cancer growth. Endocr relat cancer 2013; 20: 197.
DOI URL |
| 40. |
Hare SH, Harvey AJ. mTOR function and therapeutic targeting in breast cancer. Am J Cancer Res 2017; 7: 383-404.
PMID |
| 41. |
Yuan ZL, Guan YJ, Wang L, Wei W, Kane AB, Chin YE. Central role of the threonine residue within the p+1 loop of receptor tyrosine kinase in STAT3 constitutive phosphorylation in metastatic cancer cells. Mol Cell Biol 2004; 24: 9390-400.
DOI URL |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

