Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (4): 753-761.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20240610.003
• Original articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Study on the anti-inflammatory mechanism of moxibustion in rheumatoid arthritis in rats based on phospholipaseA2 signaling inhibition by Annexin 1
GUO Yanding1, LUO Kun1, ZHANG Linlin1, LU Wenting3, SHANG Yanan1, ZHONG Yumei2, HU Danhui1, YANG Xin4, ZHOU Haiyan1( )
)
- 1 Department of Acupuncture-Moxibustion and Tuina, the Third Affiliated Hospital, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu 610075, China
2 Department of Chengdu Integrated Traditional Chinese Medicine and Western Medicine Hospital, Chengdu 610075, China
3 External Treatment Center, First People's Hospital of Chengdu, Chengdu 610095, China
4 Department of Health Rehabilitation School, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu 610075, China
-
Received:2023-02-12Accepted:2023-07-20Online:2024-08-15Published:2024-06-10 -
Contact:ZHOU Haiyan, Acupuncture and Moxibustion College, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu 610075, China.zhouhaiyan@cdutcm.edu.cn Telephone: +86-13551039390 -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China: Study on the Immune Mechanism of Macrophages 1/Macrophages 2 Polarization of Macrophages Treated with Moxibustion "Strengthening the Body and Expelling Pathogenic Qi" for "Struggle Between Healthy Qi and Pathogenic Qi" in Rheumatoid Arthritis(81973959);National Key R&D Program of China: a Comparative Study of Moxibustion at Zusanli (ST36) on the Polarization of Knee Synovial Macrophage in Kneeosteoar-thritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis Rat Models(2019YFC1709001);National Natural Science Foundation of China: Study on the Regulatory Mechanism of the "Immune-Inflammation" Molecular Signal of the Nucleotide—Binding Oligomerization Domain, Leucine rich Repeat and Pyrin domain containing Proteins 3 Inflammasome Treated by Moxibustion for Rheumatoid Arthritis(81774435);Foundation of Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine: Study on the Mechanism of " Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor -Target Protein-Glucocorticoid-Inflammation" in Moxibustion Treatment and Anti-inflammatory Effect of Rheumatoid Arthritis(QNXZ2018034);Science and Technology Innovation Seedling Project of Sichuan Province: Exploring the Effector Mechanism of Moxibustion Treatment in the Experimental Rheumatoid Arthritis Model based on the Macrophage Macrophages 1 Polarization Signaling Pathway Toll-like Receptors 4-Maximum Tolerated Dose 88- Nuclear Factor-Kappa B and its Regulatory Molecule T Cell Immunoglobulin and Mucin Domain-containing Protein 3(2022037)
Cite this article
GUO Yanding, LUO Kun, ZHANG Linlin, LU Wenting, SHANG Yanan, ZHONG Yumei, HU Danhui, YANG Xin, ZHOU Haiyan. Study on the anti-inflammatory mechanism of moxibustion in rheumatoid arthritis in rats based on phospholipaseA2 signaling inhibition by Annexin 1[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(4): 753-761.
share this article
| Pathological changes score | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synovial tissue hyperplasia | None (-) | Mild (+) | Moderate (++) | Massive (+++) |
| Inflammatory cell infitration | None (-) | Few (+) | Dense (++) | Numerous (+++) |
| Macrophage proliferation | None (-) | Few (+) | Dense (++) | Numerous (+++) |
Table 1 Classification criteria of synovial tissue lesions
| Pathological changes score | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synovial tissue hyperplasia | None (-) | Mild (+) | Moderate (++) | Massive (+++) |
| Inflammatory cell infitration | None (-) | Few (+) | Dense (++) | Numerous (+++) |
| Macrophage proliferation | None (-) | Few (+) | Dense (++) | Numerous (+++) |

Figure 1 Effect of moxibustion on reducing the swelling of the foot A: photos of the control group. A1: photo of the rat foot pad; A2: HE stained image of ankle synovial tissue (× 20); A3: HE staining magnified image of ankle joint synovial tissue (× 200); B: photos of the rheumatoid arthritis group. B1: photo of the rat foot pad; B2: HE stained image of ankle synovial tissue (× 20); B3: HE staining magnified image of ankle joint synovial tissue (× 200); C: photos of the moxibustion group. C1: photo of the rat foot pad; C2: HE stained image of ankle synovial tissue (× 20); C3: HE staining magnified image of ankle joint synovial tissue (× 200); D: line diagram of the thickness change of the left foot pad in each group after three cycles of moxibustion treatment. E: line diagram of the thickness change of the right foot pad in each group after three cycles of moxibustion treatment. The control group received 0.1 mL of saline with bilateral foot pads; the rheumatoid arthritis group received 0.1 mL of FCA with bilateral foot pads; the moxibustion group received 0.1 mL of FCA with bilateral foot pads for three cycles of moxibustion treatment. HE: hematoxylin-eosin staining; FCA: Freund's Adjuvant Complete. The Data represent the mean ± standard deviation using one-way analysis of variance (n = 6). aP < 0.01 versus the control group; bP < 0.01 versus the rheumatoid arthritis group.
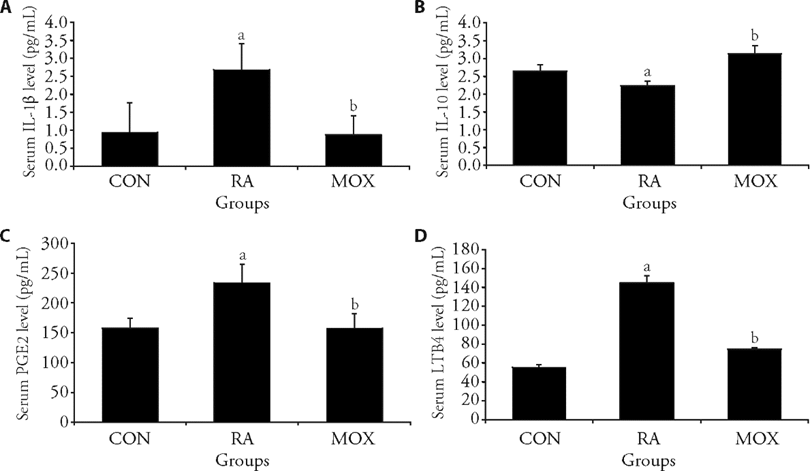
Figure 2 Moxibustion regulated the expression of inflammatory factors in the serum A: serum IL-1β level in rats from each group; B: serum IL-10 level in rats from each group; C: serum PGE2 levels in rats from each group; D: serum LTB4 level in rats from each group. The rheumatoid arthritis and moxibustion groups injected 0.1 mL of FCA, the control group received an equal amount of normal saline, and three cycles of moxibustion operation for the moxibustion group. IL-1β: interleukin-1beta; IL-10: interleukin-10; PGE2: pmstaglandi E2; LTB4: leukotrine4; FCA: Freund's Adjuvant Complete. The Data represent the mean ± standard deviation using one-way analysis of variance (n = 6). aP < 0.01, compared with the control group; bP < 0.01, compared with the rheumatoid arthritis group.

Figure 3 Measurement of Annexin 1, cPLA2α and p-cPLA2α expression in synovium by Weston blot A: Weston blot was used to detect the expression of Annexin 1, cPLA2α and p-cPLA2α in the synovium of rats ankle joint. B: Western blot analysis of Annexin 1; C: Western blot analysis of cPLA2α; D: Western blot analysis of p-cPLA2α. The rheumatoid arthritis, moxibustion, Annexin 1 lentiviral intervention and Annexin 1 lentiviral intervention + moxibustion intervention groups injected 0.1 mL of FCA, the control group received an equal amount of normal saline, and three cycles of moxibustion operation for the moxibustion and Annexin 1 lentiviral intervention + moxibustion intervention groups. Lentiviral vector-mediated RNAi-Anxa 1 was injected at a dose of 10 μL / rat into the rat foot pads of the Annexin 1 lentiviral intervention and Annexin 1 lentiviral intervention + moxibustion intervention groups. cPLA2α: phospholipaseA2; p-cPLA2α: phosphor-phospholipaseA2; FCA: Freund's Adjuvant Complete. The Data represent the mean ± standard deviation using one-way analysis of variance (n = 6). aP < 0.01, compared with the control group; bP < 0.01, compared with the rheumatoid arthritis group, cP < 0.01, compared with the moxibustion group.
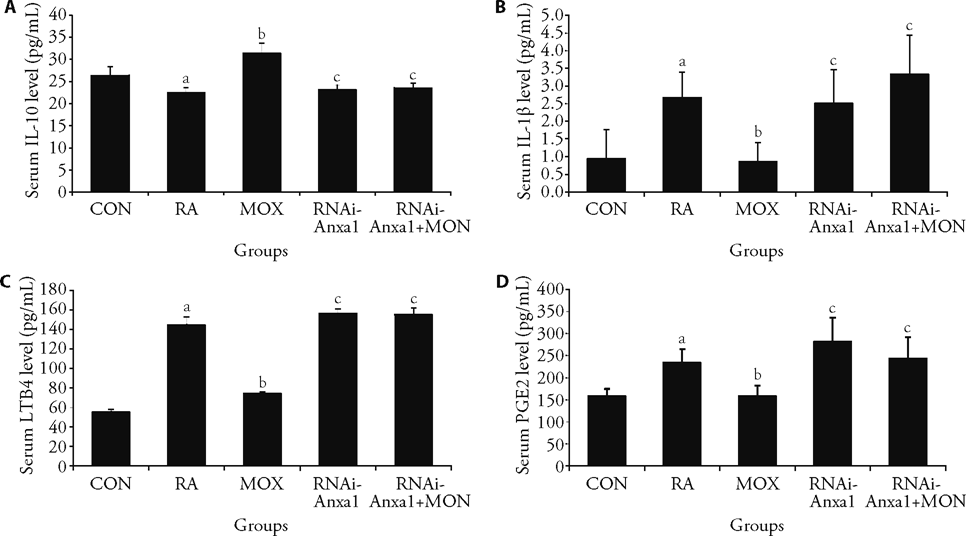
Figure 4 Moxibustion treatment in RA rats can regulate downstream inflammatory cytokines and exert anti-inflammatory effects via Annexin 1/cPLA2α A: serum IL-10 level in rats from each group; B: serum IL-1β level in rats from each group; C: serum LTB4 level in rats from each group; D: serum PGE2 level in rats from each group. The rheumatoid arthritis, moxibustion, Annexin 1 lentiviral intervention and Annexin 1 lentiviral intervention + moxibustion intervention groups injected 0.1 mL of FCA, the control group received an equal amount of normal saline, and three cycles of moxibustion operation for the moxibustion and Annexin 1 lentiviral intervention + moxibustion intervention groups. Lentiviral vector-mediated RNAi-Anxa 1 was injected at a dose of 10 μL/rat into the rat foot pads of the Annexin 1 lentiviral intervention and Annexin 1 lentiviral intervention + moxibustion intervention groups. IL-10: interleukin- 10; IL-1β: interleukin- 1beta; PGE2: pmstaglandi E2; LTB4: leukotrine4; FCA: Freund's adjuvant complete. The Data represent the mean ± standard deviation using one-way analysis of variance (n = 6). aP < 0.01, compared with the control group; bP < 0.01, compared with the rheumatoid arthritis group, cP < 0.01, compared with the moxibustion group.
| 1. |
Jing W, Yuan Q, Yu PZ, Jia XD, Q HY. Rhamm induces progression of rheumatoid arthritis by enhancing the functions of fibroblast-like synoviocytes. BMC musculoskeletal disorders 2018; 19: 455.
DOI PMID |
| 2. |
Moudgil KD. Advances in the pathogenesis and treatment of autoimmunity. Cell Immunol 2019; 339: 1-3.
DOI PMID |
| 3. | The Rheumatology Branch of the Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Chin J Rheumatol 2010; 14: 265-70. |
| 4. |
Perretti M, D’Acquisto F. AnnexinA1 and glucocoeticoids as effectors of the resolution of inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol 2009; 9: 62-70.
DOI PMID |
| 5. | Daniel A, Yuan Y, Ashley M, Lanie S, Michelle L, Eric FM. Endogenous macrophage migration inhibitory factor modulates glucocorticoid sensitivity in macrophages via effects on MAP kinase phosphatase-1 and p38 MAP kinase. FEBS Lett 2006; 580: 974-81. |
| 6. | Daun JM, Cannon JG. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor antagonizes hydrocortisone induced increases in cytosolic ikappa balpha. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 2000; 279: R1043-9. |
| 7. | Li CZ, Li SY, Wang JJ. The anti-inflammatory effects of MIF against glucocorticoids and its mechanisms. Zhong Guo Mian Yi Xue 2013; 11:1146-50. |
| 8. | Sun Y, Han S, Wang JJ. the effect of siRNA silencing genes on glucocorticoid hormones to inhibit the release of lipid inflammatory mediators and its mechanism. Chin J Pathophysiol 2023; 10: 1803-6. |
| 9. | Qin C, Yang YH, May L. Cardio protective epoten-tial of annexin-A1 mimetic sinmyo cardial in farction. Pharmacol Ther 2015; 148: 47-65. |
| 10. | Horlacher T, Noti C, Paz DJL, et al. Characterization of annexin Al glycan binding reveals binding to highly sulfated glycans with preference for highly sulfated heparan sulfate and heparin. Biochemistry 2015; 2650-9. |
| 11. | Bizzarro V, Fontanella B, Franceschelli S, et al. Role of Annexin Al in mouse myoblast cell differentiation. J Cell Physiol 2010; 224: 757-65. |
| 12. | Mauro P, Fulvio D'A. Annexin A1 and glucocorticoids as effectors of the resolution of Inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol 2009; 9: 92-70. |
| 13. | Gao J, Liu XG, Zhou HY, Yang LC, Hou JY, Yu XX. Explore the HPAA circadian basis of moxibustion anti-inflammatory effect from the nighttime ACTH and CS levels of RA rats. Zhong Hua Zhong Yi Ji Chu Yi Xue 2010; 16: 515-16+23. |
| 14. | Gao J, Liu XG, Huang JJ, et al. HPAA in moxibustion in regulating NF-kB signaling in the synovial tissue of rats with rheumatoid arthritis. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu 2010; 35: 198-203. |
| 15. | Gao J, Zhou HY, Liu XG, Tang Y. Experimental study on the effects of moxibustion on plasma th1/th2 cytokines balance in experimental RA rats. Chengdu Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue Xue Bao 2008; 31: 21-3. |
| 16. | Ren JG, Liu XG, Lei X. Moxibustion therapy Study on the anti-inflammatory effect and its effect on MPD-1 expression in experimental rats. Shi Zhen Guo Yi Guo Yao 2017; 28: 3048-50. |
| 17. | Zhong YM, Zhang LL, Lu WT, Shang YN, Zhou HY. Moxibustion regulates the polarization of macrophages through the IL-4/STAT6 pathway in rheumatoid arthritis. Cytokine 2022; 152: 155835. |
| 18. | Zhou HY, Liu XG, Gao J. Research of moxibustion influence on GR and MEL1B expressions in hippocampus of experimental RA rats. Liaoning Zhong Yi Za Zhi 2012; 39: 2313-5. |
| 19. | Zhou HY, Liu XG, Huang DJ, et al. Study of moxibustion regulating RA rats' HPAA functional glucocorticoid receptor mechanism. Zhong Hua Zhong Yi Yao Xue Kan 2010; 28: 1167-9. |
| 20. |
Shalev M. APHIS, FDA, and NIH issue memorandum of understanding on laboratory animal welfare. Lab animal 2006; 35: 13.
PMID |
| 21. | Shi XP, Zong AN, Tao J, Wang ZL. Study of instructive notions with respect to caring for laboratory animals. Zhong Guo Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 2007; 36: 493. |
| 22. | Li ZR. Experimental Acupuncture Science. 2nd ed. Beijing: Zhong Guo Zhong Yi Yao Chu Ban She, 2007: 255-7. |
| 23. | Chen Q. Methodology of Chinese Medicine. 2nd ed. Beijing: People's Health Publishing House, 2006; 1-3. |
| 24. | Zhou B. Effects of lentivirus-mediated RNAi silencing of IL-1 type I receptors on the MAPKs pathway in rat knee arthritis. Shanghai: Shanghai Fudan University 2009; 1-56. |
| 25. | Li Y, Liu R, Chu YK, et al. The effect of shRNA silencing of the ANXA1 gene on FPR1 and F-actin expression. Ningxia Med J 2020; 390-3. |
| 26. | Hu JG. Chen XJ. Professor Chen Xiangjun discusses on the experience analysis of treating rheumatoid arthritis. Zhong Guo Dang Dai Yi Yao 2020; 12: 157-9, 63. |
| 27. | Choi TY, Kim TH, Kang JW, Lee MS, Ernst E. Moxibustion for rheumatic conditions: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. Clin Rheumatol 2011; 30: 937-45. |
| 28. | Shang YN. Study on the mechanism of IKKβ/I κ B- α in exploring the anti-inflammatory effect of moxibustion in rheumatoid arthritis rats based on the NF- κB signaling pathway. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021: 1-67. |
| 29. | Zhang LL, Zhong YM, Lu WT, et al. Moxibustion of Zusanli (ST36) and Shenshu (BL23) alleviates the inflammation of rheumatoid arthritis in rats through regulating macrophage migration inhibitory factor/ glucocorticoids signaling. J Tradit Chin Med 2024; 44: 353-61. |
| 30. | Lee MS, Shin BC, Ernst E. Acupuncture for rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review. Rheumatology 2008; 47: 1747-53. |
| 31. | Ibfelt EH, Jacobsen RK, Kopp TI, Cordtz RL, Jakobsen AS, Seersholm N. Methotrexate and risk of interstitial lung diseaseand respiratory failure in rheumatoid arthritis: an ationwide population-based study. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2021; 60: 346-52. |
| 32. |
Tu J, Hong W, Zhang P, Wang X, Körner H, Wei W. Ontology and function of fibroblast-like and macrophage-like synoviocytes: how do they talk to each other and can they be targeted for rheumatoid arthritis therapy? Front Immunol 2018; 9: 1467.
DOI PMID |
| 33. | Ma WK, Yao H, Huang Y. The combination of activator protein-1 nuclear factor-kB regulates synovial cell proliferation and apoptosis mechanisms in rheumatoid arthritis. Chin J Rheumatol 2014; 18: 345-7. |
| 34. | Elshabrawy HA, Chen Z, Volin MV, Ravella S, Virupannavar S, Shahrara S. The path-ogenie role of an giogenesis in rheumatoid arthrit. Angio-genesis 2015; 18: 433-48. |
| 35. |
Solito E, Coupa de CD, Parente L, Flower RJ, Russo-Marie F. IL-6 stimulates Annexin 1 expression and translocation and suggests a new biological role as class Ⅱ acutephase protein. Cytokine 1998; 10: 514-21.
PMID |
| 36. | Mizuno H, Uemura K, Moriyama A, et al. Glucocorticoid induced the expression of mRNA and the secretion of lipocortin1 in rat astrocytoma cells. Brain 1997; 746: 256-64. |
| 37. |
Antonicelli F, De Coupade C, Russo-Marie F, Le Garrec Y. CREB is involved in mouse annexin A1 regulation by cAMP and glucocorticoids. Eur J Biochem 2001; 268: 62-9.
PMID |
| 38. |
Kim SW, Rhee HJ, Ko J, et al. Inhibition of cytosolic phospholipase A2 by annexin I. Specific interaction model and mapping of the interaction site. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 15712-9.
DOI PMID |
| 39. |
Ford-Hutchinson AW. Leukotriene B4 in inflammation. . Crit Rev Immunol 1990; 10: 1-12.
PMID |
| 40. |
Woodward DF, Jones RL, Narumiya S. International union of basic and clinical pharmacology. LXXXⅢ: classification of prostanoid receptors, updating 15 years of progress. Pharmacol Rev 2011; 63: 471-538.
DOI PMID |
| 41. | Dong ZF. Progress in bone destruction of rheumatoid arthritis. Shi Jie Zui Xin Yi Xue Xin Xi Wen Zhai 2018; 18: 43-4. |
| 42. | Wu LM, Ye JF, Xie WH. Role of leukotriene B4 in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Zhong Guo Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi 2014; 30: 689-93. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

