Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (5): 1106-1118.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20250107.001
• Original Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Hewei Jiangni recipe (和胃降逆方) improved the quality of life in patients with cold-heat mixed nonerosive reflux disease: a randomized, double-blinded study
ZHANG Xiaosi1, ZHANG Shuangyuan1, CHEN Hanqing1, LIN Zhengdao1, XIE Chune2, LI Junxiang1( ), LI Xiaohong1(
), LI Xiaohong1( )
)
- 1 Gastroenterology Department, Dongfang Hospital, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100078, China
2 Department of Spleen and Gastroenterology, Shenzhen Bao'an Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital Group, Shenzhen 518133, China
-
Received:2024-08-22Accepted:2024-12-30Online:2025-10-15Published:2025-03-18 -
Contact:Prof. LI Xiaohong, Gastroenterology Department, Dongfang Hospital, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100078, China. lxhktxz@163.com;
Prof. LI Junxiang, Gastroenterology Department, Dongfang Hospital, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100078, China. lijunxiang1226@126.com,Telephone: +86-10-67689751 -
Supported by:Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities: Research on the Mechanism of Hewei Jiangni Recipe on Nonerosive Gastroesophageal Reflux Based on the Correlation Analysis of Gut Microbiota and Metabolites(2020-JYB-ZDGG-128);National Natural Science Foundation of China: Exploring the Molecular Mechanism of "Hewei Jiangni Fang" Intervention in Non-erosive Reflux Disease Esophageal Hypersensitivity from the Perspective of Mas-related Gene X2/Stromal Interaction Molecule 1/Cell Adhesion Molecule 1 Pathway Regulation of Mast Cell/Dorsal Root Ganglion Communication Based on the "Xinkai-Kujiang" Method(82374401)
Cite this article
ZHANG Xiaosi, ZHANG Shuangyuan, CHEN Hanqing, LIN Zhengdao, XIE Chune, LI Junxiang, LI Xiaohong. Hewei Jiangni recipe (和胃降逆方) improved the quality of life in patients with cold-heat mixed nonerosive reflux disease: a randomized, double-blinded study[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(5): 1106-1118.
share this article
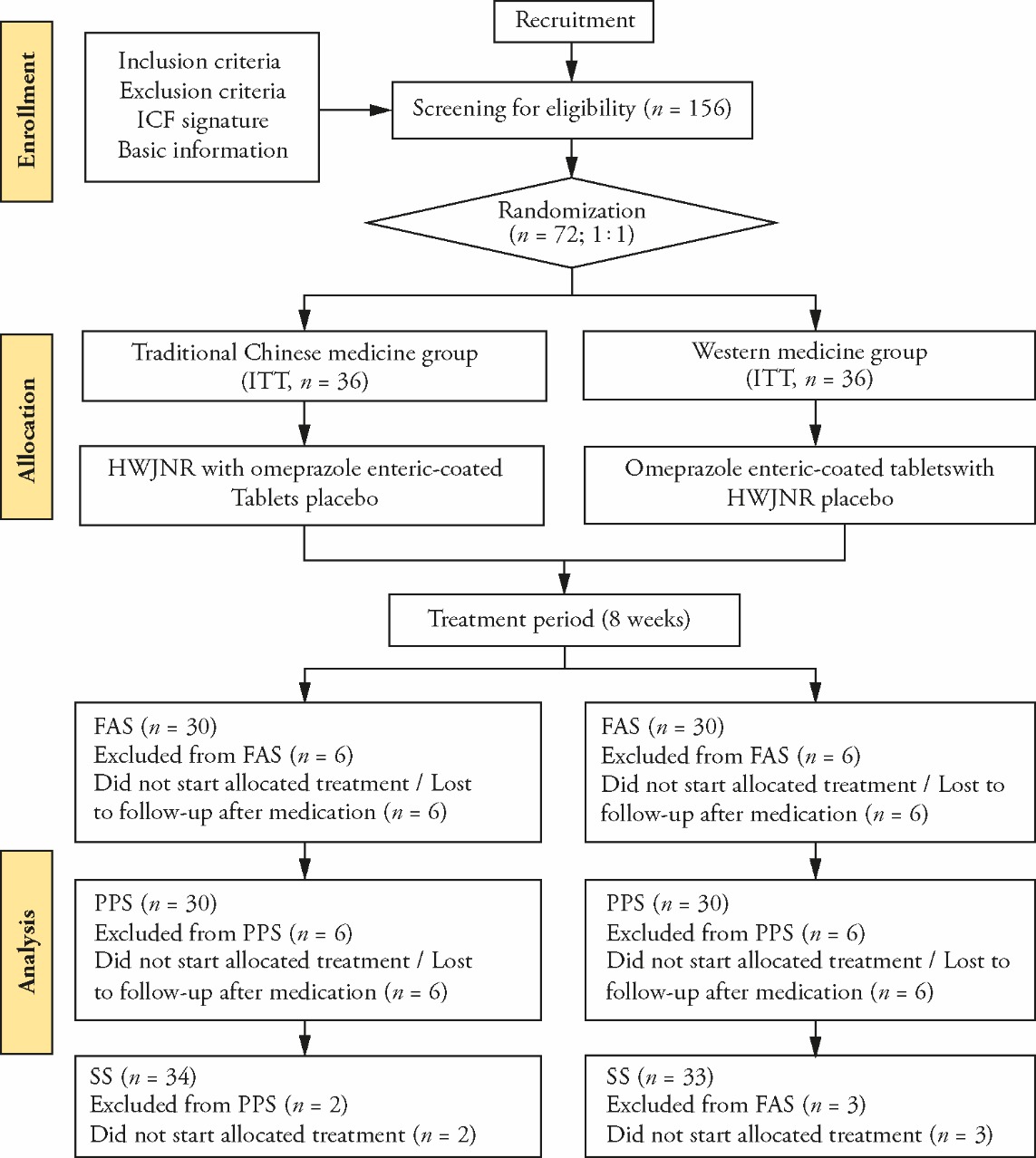
Figure 1 Flow chart of the study design according to the recommendations of the CONSORT ICF: informed consent form; HWJNNR: Hewei Jiangni recipe; ITT: intention-to-treat; FAS: full analysis set; PPS: per protocol set; SS: safety set; CONSORT: Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials.
| Characteristic | TCM group (n = 30) | Western Medicine group (n = 30) | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender [n (%)] | Male | 7 (23.33) | 23 (76.67) | 0.390 |
| Female | 10 (33.33) | 20 (66.67) | ||
| Age (years) | 18-44 | 10 | 10 | 0.700 |
| 45-59 | 9 | 12 | ||
| 60-65 | 11 | 8 |
Table 1 Patient demographics and baseline clinical characteristic
| Characteristic | TCM group (n = 30) | Western Medicine group (n = 30) | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender [n (%)] | Male | 7 (23.33) | 23 (76.67) | 0.390 |
| Female | 10 (33.33) | 20 (66.67) | ||
| Age (years) | 18-44 | 10 | 10 | 0.700 |
| 45-59 | 9 | 12 | ||
| 60-65 | 11 | 8 |
| Group | n | Before treatment | After treatment | t value | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TCM | 30 | 9.6±1.8 | 6.2±1.9 | 9.029 | <0.001 |
| Western Medicine | 30 | 9.6±1.6 | 6.1±1.6 | 12.209 | <0.001 |
Table 2 The total score of GERD-Q scale before and after treatment between the two groups
| Group | n | Before treatment | After treatment | t value | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TCM | 30 | 9.6±1.8 | 6.2±1.9 | 9.029 | <0.001 |
| Western Medicine | 30 | 9.6±1.6 | 6.1±1.6 | 12.209 | <0.001 |
| Outcome | Group | n | Before treatment | After treatment | Z/t value | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SF-36 | TCM | 30 | 121.55 (108.4, 132.4) | 124 (112.55, 135) | -3.271 | 0.001 |
| Western Medicine | 30 | 122.3 (112.1, 130.25) | 122.4 (112.4, 132.35) | -1.477 | 0.140 | |
| PRO | TCM | 30 | 50±20 | 27±17 | 8.381 | <0.001 |
| Western Medicine | 30 | 44±13 | 28±13 | 7.807 | <0.001 | |
| TCM symptom points | TCM | 30 | 13±5 | 4±3 | 9.298 | <0.001 |
| Western Medicine | 30 | 14±5 | 6±4 | 9.888 | <0.001 |
Table 3 Second outcomes before and after treatment
| Outcome | Group | n | Before treatment | After treatment | Z/t value | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SF-36 | TCM | 30 | 121.55 (108.4, 132.4) | 124 (112.55, 135) | -3.271 | 0.001 |
| Western Medicine | 30 | 122.3 (112.1, 130.25) | 122.4 (112.4, 132.35) | -1.477 | 0.140 | |
| PRO | TCM | 30 | 50±20 | 27±17 | 8.381 | <0.001 |
| Western Medicine | 30 | 44±13 | 28±13 | 7.807 | <0.001 | |
| TCM symptom points | TCM | 30 | 13±5 | 4±3 | 9.298 | <0.001 |
| Western Medicine | 30 | 14±5 | 6±4 | 9.888 | <0.001 |
| Symptoms | Group | n | Before treatment | After treatment | Z value | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heartburn | TCM Western Medicine | 30 30 | 2 (2, 4.5) 4 (2, 6) | 0 (0, 0) 0 (0, 0) | -4.218 -4.815 | <0.001 <0.001 |
| Reflux | TCM Western Medicine | 30 30 | 2 (2, 6) 2 (2, 4) | 0 (0, 0) 0 (0, 0.5) | -4.477 -4.303 | <0.001 <0.001 |
| Latent pain in the upper abdominal | TCM Western Medicine | 30 30 | 2 (0, 4) 2 (0, 4) | 0 (0, 2) 0 (0, 2) | -3.535 -3.213 | <0.001 0.001 |
| Pain relief after eating | TCM Western Medicine | 30 30 | 0 (0, 2) 0 (0, 2) | 0 (0, 0) 0 (0, 2) | -2.000 -2.333 | 0.046 0.020 |
| Loss of appetite | TCM Western Medicine | 30 30 | 1 (0, 1.25) 1 (0, 1) | 0 (0, 0.25) 0 (0, 1) | -3.346 -0.577 | 0.001 0.564 |
| Fatigue | TCM Western Medicine | 30 30 | 1 (1, 2) 1 (1, 2) | 1 (0, 1) 1 (1, 1.25) | -3.448 -1.342 | 0.001 0.180 |
| Bowel sounds | TCM Western Medicine | 30 30 | 1 (0, 2) 1 (0, 2) | 0 (0, 1) 1 (0, 2) | -3.640 -1.081 | <0.001 0.279 |
| Coldness in the hands and feet | TCM group Western Medicine | 30 30 | 1 (0.75, 2) 1 (1, 1.25) | 1 (0, 1) 1 (1, 1) | -3.520 -1.000 | <0.001 0.317 |
Table 4 TCM single-symptom scores between the two groups before and after drug treatment [M (P25, P75)]
| Symptoms | Group | n | Before treatment | After treatment | Z value | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heartburn | TCM Western Medicine | 30 30 | 2 (2, 4.5) 4 (2, 6) | 0 (0, 0) 0 (0, 0) | -4.218 -4.815 | <0.001 <0.001 |
| Reflux | TCM Western Medicine | 30 30 | 2 (2, 6) 2 (2, 4) | 0 (0, 0) 0 (0, 0.5) | -4.477 -4.303 | <0.001 <0.001 |
| Latent pain in the upper abdominal | TCM Western Medicine | 30 30 | 2 (0, 4) 2 (0, 4) | 0 (0, 2) 0 (0, 2) | -3.535 -3.213 | <0.001 0.001 |
| Pain relief after eating | TCM Western Medicine | 30 30 | 0 (0, 2) 0 (0, 2) | 0 (0, 0) 0 (0, 2) | -2.000 -2.333 | 0.046 0.020 |
| Loss of appetite | TCM Western Medicine | 30 30 | 1 (0, 1.25) 1 (0, 1) | 0 (0, 0.25) 0 (0, 1) | -3.346 -0.577 | 0.001 0.564 |
| Fatigue | TCM Western Medicine | 30 30 | 1 (1, 2) 1 (1, 2) | 1 (0, 1) 1 (1, 1.25) | -3.448 -1.342 | 0.001 0.180 |
| Bowel sounds | TCM Western Medicine | 30 30 | 1 (0, 2) 1 (0, 2) | 0 (0, 1) 1 (0, 2) | -3.640 -1.081 | <0.001 0.279 |
| Coldness in the hands and feet | TCM group Western Medicine | 30 30 | 1 (0.75, 2) 1 (1, 1.25) | 1 (0, 1) 1 (1, 1) | -3.520 -1.000 | <0.001 0.317 |
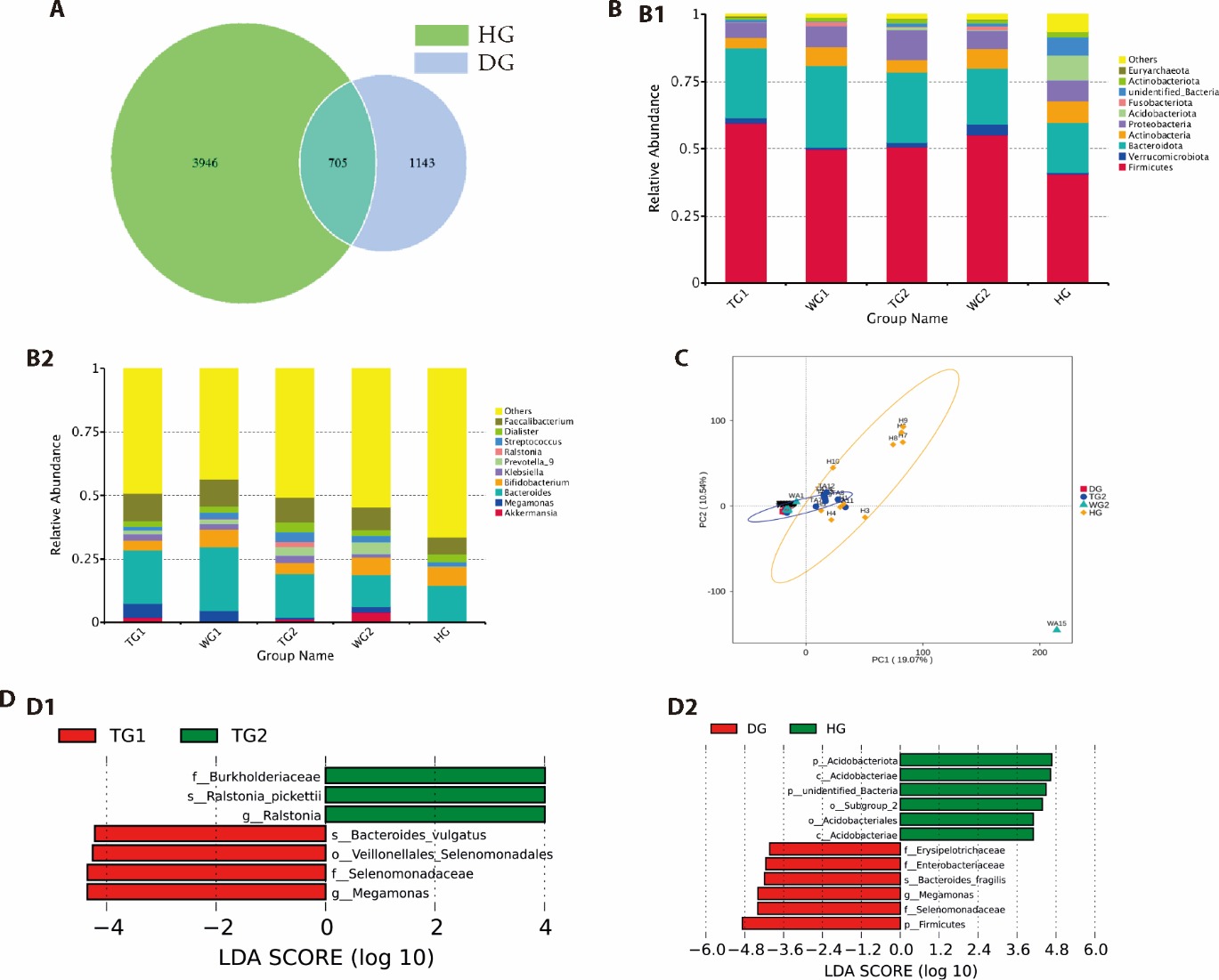
Figure 2 Changes in flora between patients with NERD and normal subjects, and changes before and after drug treatment A: OUT clustering machine species annotation; B: distribution of gut microbiota in each group at the phylum and genus levels. B1: phylum level; B2: genus level; C: β-diversity analysis of intergroup flora differences across multiple groups by PCA; D: LEfSe analysis for identifying differential bacteria between the diseased and treated groups. D1: LDA thresholds of nonerosive gastroesophageal reflux patients compared with healthy subjects; D2: LDA thresholds of nonerosive gastroesophageal reflux patients before and after treatment with Hewei Jiangni recipe. HG: healthy group; TG1: before treatment of Hewei Jiangni recipe; WG1: before treatment of omeprazole; TG2: after treatment of Hewei Jiangni recipe; WG2: after treatment of omeprazole; DG: diseased group of nonerosive gastroesophageal reflux (TG1 + WG1).
| Group | SS | df | Fs | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DG-HG | 0.690482 (4.68263) | 1 (38) | 5.60333 | < 0.001a |
| TG1-WG1 | 0.236027 (4.29291) | 1 (28) | 1.53946 | 0.169b |
Table 5 AMOVA between-group analysis
| Group | SS | df | Fs | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DG-HG | 0.690482 (4.68263) | 1 (38) | 5.60333 | < 0.001a |
| TG1-WG1 | 0.236027 (4.29291) | 1 (28) | 1.53946 | 0.169b |
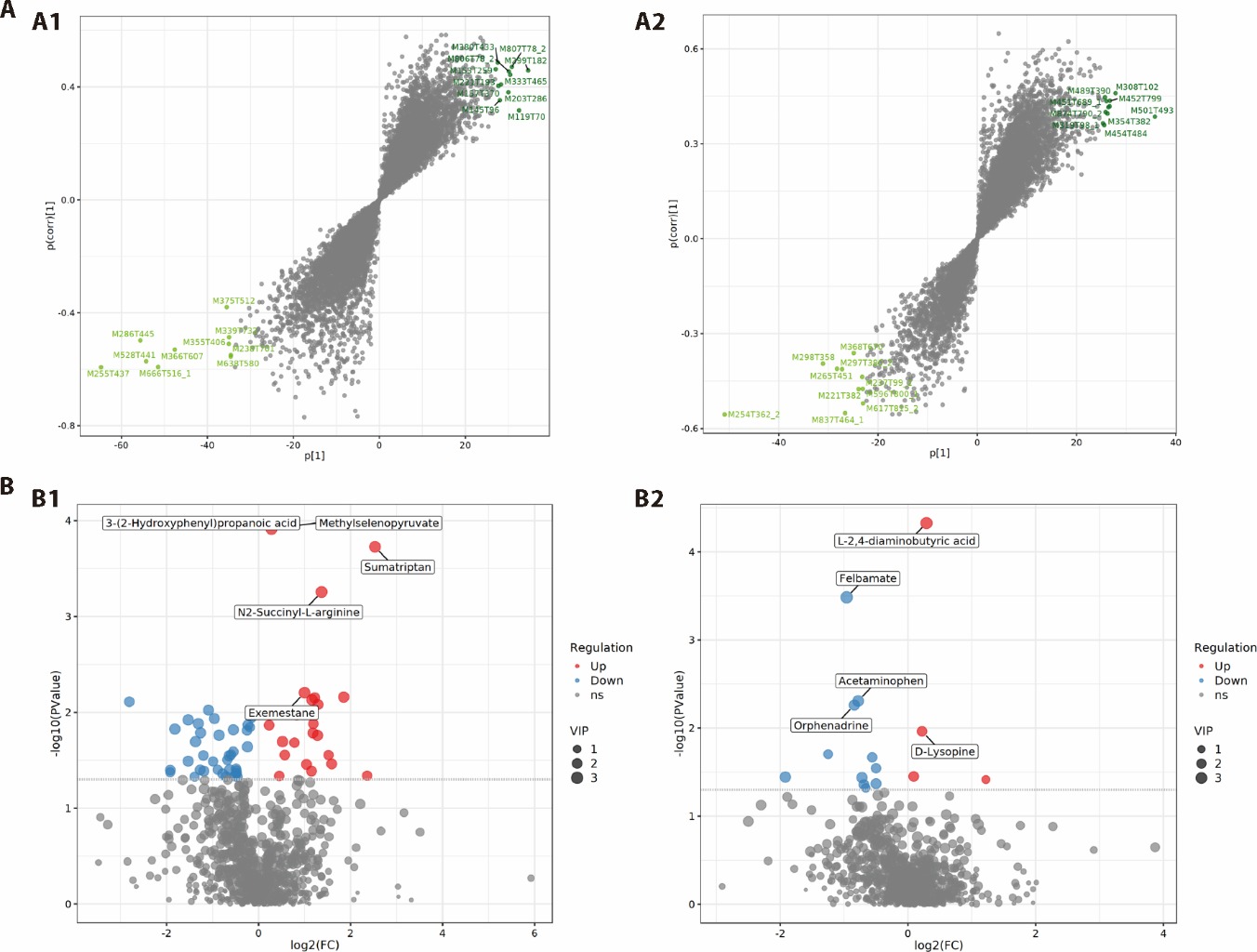
Figure 3 Differences in metabolites and metabolic pathways between patients and normal subjects, and before and after Hewei Jiangni recipe treatment A: OPLS-DA splot showing the clustering of samples between patients, normal subjects, and before and after the treatment of Hewei Jiangni recipe. A1: OPLS-DA splot under positive ion mode; A2: OPLS-DA under negative ion mode. B: differential metabolite volcano plots and z-score. B1: the volcano plot of differential metabolite between nonerosive gastroesophageal reflux patients before Hewei Jiangni recipe treatment and normal subjects; B2: the volcano plot of differential metabolite after and before treatment of Hewei Jiangni recipe. OPLS-DA: orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis; HG: healthy group; TG1: before treatment of Hewei Jiangni recipe; TG2: after treatment of Hewei Jiangni recipe.
| No. | Name | mz | Formula | VIP | TG2 vs TG1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | L-2,4-diaminobutyric acid | 119.0897 | C4H10N2O2 | 3.343279 | ↓a |
| 2 | Acetaminophen | 151.0619 | C8H9NO2 | 2.988399 | ↑b |
| 3 | Tryptamine | 161.1076 | C10H12N2 | 2.117216 | ↑c |
| 4 | L-Alanyl-D-glutamate | 201.0871 | C8H14N2O5 | 2.324239 | ↓c |
| 5 | D-Lysopine | 219.1344 | C9H18N2O4 | 2.236051 | ↓c |
| 6 | Felbamate | 239.1031 | C11H14N2O4 | 3.525943 | ↑a |
| 7 | Orphenadrine | 270.1861 | C18H23NO | 2.649173 | ↑b |
| 8 | Propafenone | 342.2057 | C21H27NO3 | 2.805302 | ↑a |
| 9 | Norsolorinic acid | 371.1453 | C20H18O7 | 1.769136 | ↑a |
| 10 | 24,25-Dihydrolanosterol | 428.3764 | C30H52O | 1.340831 | ↓a |
| 11 | Thioguanine | 166.0185 | C5H5N5S | 1.70374 | ↑a |
| 12 | Beta-Glycerophosphoric acid | 171.007 | C3H9O6P | 2.367763 | ↑a |
| 13 | L-Theanine | 173.0938 | C7H14N2O3 | 2.505759 | ↑a |
| 14 | Carglumic acid | 190.0553 | C6H10N2O5 | 2.145167 | ↑a |
| 15 | 20-HETE | 320.2314 | C20H32O3 | 2.747996 | ↑a |
Table 6 Differential metabolites identified after HWJNR treatment compared to pre-treatment
| No. | Name | mz | Formula | VIP | TG2 vs TG1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | L-2,4-diaminobutyric acid | 119.0897 | C4H10N2O2 | 3.343279 | ↓a |
| 2 | Acetaminophen | 151.0619 | C8H9NO2 | 2.988399 | ↑b |
| 3 | Tryptamine | 161.1076 | C10H12N2 | 2.117216 | ↑c |
| 4 | L-Alanyl-D-glutamate | 201.0871 | C8H14N2O5 | 2.324239 | ↓c |
| 5 | D-Lysopine | 219.1344 | C9H18N2O4 | 2.236051 | ↓c |
| 6 | Felbamate | 239.1031 | C11H14N2O4 | 3.525943 | ↑a |
| 7 | Orphenadrine | 270.1861 | C18H23NO | 2.649173 | ↑b |
| 8 | Propafenone | 342.2057 | C21H27NO3 | 2.805302 | ↑a |
| 9 | Norsolorinic acid | 371.1453 | C20H18O7 | 1.769136 | ↑a |
| 10 | 24,25-Dihydrolanosterol | 428.3764 | C30H52O | 1.340831 | ↓a |
| 11 | Thioguanine | 166.0185 | C5H5N5S | 1.70374 | ↑a |
| 12 | Beta-Glycerophosphoric acid | 171.007 | C3H9O6P | 2.367763 | ↑a |
| 13 | L-Theanine | 173.0938 | C7H14N2O3 | 2.505759 | ↑a |
| 14 | Carglumic acid | 190.0553 | C6H10N2O5 | 2.145167 | ↑a |
| 15 | 20-HETE | 320.2314 | C20H32O3 | 2.747996 | ↑a |
| No. | Name | mz | Formula | VIP | TG1 vs HG | TG2 vs TG1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | L-2,4-diaminobutyric acid | 119.0897 | C4H10N2O2 | 3.343279 | ↑a | ↓b |
| 2 | Felbamate | 239.1031 | C11H14N2O4 | 2.988399 | ↓a | ↑b |
| 3 | Orphenadrine | 270.1861 | C18H23NO | 2.747996 | ↓a | ↑c |
Table 7 Reversal of 3 differential metabolites in NERD patients after HWJNR
| No. | Name | mz | Formula | VIP | TG1 vs HG | TG2 vs TG1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | L-2,4-diaminobutyric acid | 119.0897 | C4H10N2O2 | 3.343279 | ↑a | ↓b |
| 2 | Felbamate | 239.1031 | C11H14N2O4 | 2.988399 | ↓a | ↑b |
| 3 | Orphenadrine | 270.1861 | C18H23NO | 2.747996 | ↓a | ↑c |
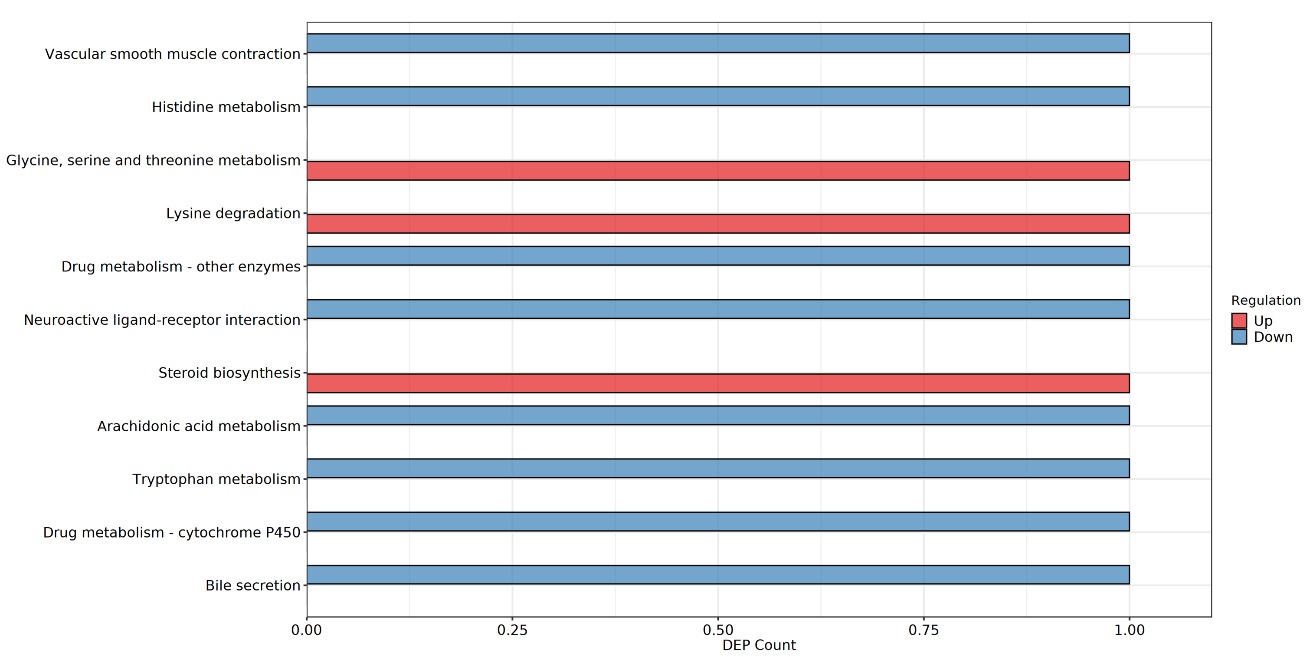
Figure 4 Differential metabolic pathways between patients and normal subjects, and before and after HWJNR treatment A: histogram of metabolic pathway differences between nonerosive gastroesophageal reflux patients before HWJNR treatment and normal subjects; B: bubble chart of metabolic pathway differences between nonerosive gastroesophageal reflux patients before HWJNR treatment and normal subjects; C: histogram of metabolic pathway differences after and before treatment of HWJNR; D: bubble chart of metabolic pathway differences after and before treatment of HWJNR. HWJNR: Hewei Jiangni recipe.
| 1. |
Richter JE, Rubenstein JH. Presentation and epidemiology of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Gastroenterology 2018; 154: 267-76.
DOI PMID |
| 2. | Arguero J, Sifrim D. Pathophysiology of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease: implications for diagnosis and management. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2024; 21: 282-93. |
| 3. |
Fass R, Boeckxstaens GE, El-Serag H, Rosen R, Sifrim D, Vaezi MF. Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2021; 7: 55.
DOI PMID |
| 4. |
Markar RS, Staller K, Chan AT. Review of gastroesophageal reflux disease. JAMA 2021; 325: 1472.
DOI PMID |
| 5. | Lee SW, Lee TY, Lien HC, Peng YC, Yeh HJ, Chang CS. Correlation between symptom severity and health-related life quality of a population with gastroesophageal reflux disease. Gastroenterology Res 2017; 10: 78-83. |
| 6. |
Lippmann QK, Crockett SD, Dellon ES, Shaheen NJ. Quality of life in GERD and Barrett's esophagus is related to gender and manifestation of disease. Am J Gastroenterol 2009; 104: 2695-703.
DOI PMID |
| 7. |
Miwa H, Igarashi A, Teng L, Uda A, Deguchi H, Tango T. Systematic review with network Meta-analysis: indirect comparison of the efficacy of vonoprazan and proton-pump inhibitors for maintenance treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease. J Gastroenterol 2019; 54: 718-29.
DOI PMID |
| 8. |
Richter JE, Kumar A, Lipka S, Miladinovic B, Velanovich V. Efficacy of laparoscopic nissen fundoplication vs transoral incisionless fundoplication or proton pump inhibitors in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease: a systematic review and network Meta-analysis. Gastroenterology 2018; 154: 1298-308.
DOI PMID |
| 9. | Grishechkina IA, Trukhan DI. The role of psycho-autonomic status and the serotonergic system in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease. Eksp Klin Gastroenterol 2014; 7: 48-51. |
| 10. | Gupta SK, Hassall E, Chiu YL, Amer F, Heyman MB. Presenting symptoms of nonerosive and erosive esophagitis in pediatric patients. Dig Dis Sci 2006; 51: 858-63. |
| 11. |
Kindt S, Imschoot J, Tack J. Prevalence of and impact of pantoprazole on nocturnal heartburn and associated sleep complaints in patients with erosive esophagitis. Dis Esophagus 2011; 24: 531-7.
DOI PMID |
| 12. | Chen Y, Sun XH, Fan WJ, et al. Differences in dietary and lifestyle triggers between non-erosive reflux disease and reflux esophagitis-a multicenter cross-sectional survey in China. Nutrients 2023; 15: 3400. |
| 13. |
El-Salhy M, Gilja OH, Hatlebakk JG. Overlapping of irritable bowel syndrome with erosive esophagitis and the performance of Rome criteria in diagnosing IBS in a clinical setting. Mol Med Rep 2019; 20: 787-94.
DOI PMID |
| 14. | Xiao J, Yang YF, Zhu YR, et al. Efficacy and safety of Traditional Chinese Medicine on nonerosive reflux disease: a Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2018; 2018: 1505394. |
| 15. | Yang Q, Li JX, Li XH. Observation on the therapeutic efficacy of the modified Banxia Xiexin decoction in the treatment of nonerosive reflux disease with cold-heat complex syndrome. Jilin Zhong Yi Yao 2012; 32: 907-10. |
| 16. |
Zhang XS, Cheng Y, Li XH, et al. Efficacy and safety of the Chinese herbal formula Hewei Jiangni recipe for NERD with cold-heat complex syndrome: study protocol for a double-blinded randomized controlled trial. Trials 2021; 22: 545.
DOI PMID |
| 17. | Li JX, Chen J, Li Y. Consensus opinion on integrated Chinese and Western Medicine diagnosis and treatment of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (2017). Zhong Guo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xiao Hua Za Zhi 2018; 26: 221-6+32. |
| 18. | Chen MH, Hou XH, Xiao YL, et al. Expert consensus opinion on gastro-oesophageal reflux disease in China 2014. Wei Chang Bing Xue 2015; 20: 155-68. |
| 19. | Katz PO, Dunbar KB, Schnoll-Sussman FH, Greer KB, Yadlapati R, Spechler SJ. ACG clinical guideline for the diagnosis and management of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Am J Gastroenterol 2022; 117: 27-56. |
| 20. | Savarino V, Marabotto E, Zentilin P, Demarzo MG, de Bortoli N, Savarino E. Pharmacological management of gastro-esophageal reflux disease: an update of the state-of-the-art. Drug Des Devel Ther 2021; 15: 1609-21. |
| 21. | Rossetti G, Limongelli P, Cimmino M, et al. Outcome of medical and surgical therapy of GERD: predictive role of quality of life scores and instrumental evaluation. Int J Surg 2014; 12 Suppl 1: S112-6. |
| 22. |
Makunts T, Cohen IV, Awdishu L, Abagyan R. Analysis of postmarketing safety data for proton-pump inhibitors reveals increased propensity for renal injury, electrolyte abnormalities, and nephrolithiasis. Sci Rep 2019; 9: 2282.
DOI PMID |
| 23. | Zhu JY, Sun CQ, Li M, Hu GR, Zhao XM, Chen WH. Compared to histamine-2 receptor antagonist, proton pump inhibitor induces stronger oral-to-gut microbial transmission and gut microbiome alterations: a randomised controlled trial. Gut 2024; 73: 1087-97. |
| 24. |
Northuis CA, Bell EJ, Lutsey PL, et al. Cumulative use of proton pump inhibitors and risk of dementia: the atherosclerosis risk in communities study. Neurology 2023; 101: e1771-8.
DOI PMID |
| 25. | Dalal J, Dutta AL, Hiremath J, et al. Cardiovascular compatibility of proton pump inhibitors: practice recommendations. Cardiol Ther 2023; 12: 557-70. |
| 26. | Nagao S, Yabuuchi Y, Tanaka K, et al. Multiple gastric neuroendocrine tumors associated with long-term use of a proton pump inhibitor and a potassium-competitive acid blocker. Intern Med 2024; 63: 2001-10. |
| 27. |
Najah H, Edelmuth RCL, Riascos MC, et al. Long-term potassium-competitive acid blockers administration causes microbiota changes in rats. Surg Endosc 2023; 37: 7980-90.
DOI PMID |
| 28. |
Li X, Wu HM, Zhang BH, et al. Traditional Chinese Medicine based on Tongjiang methodology combined with proton pump inhibitor (PPI) step-down in treating non-erosive reflux disease: a study protocol for a multicentered, randomized controlled clinical trial. Trials 2022; 23: 879.
DOI PMID |
| 29. | Zhang JQ, Che H, Zhang BH, et al. JianpiQinghua granule reduced PPI dosage in patients with nonerosive reflux disease: a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, double-dummy, noninferiority study. Phytomedicine 2021; 88: 153584. |
| 30. |
Kiecka A, Szczepanik M. Proton pump inhibitor-induced gut dysbiosis and immunomodulation: current knowledge and potential restoration by probiotics. Pharmacol Rep 2023; 75: 791-804.
DOI PMID |
| 31. | Yang Y, Liu Y, Zhang F, et al. Correlation of spleen deficiency and viscera diseases based on the research of mitochondria. J Tradit Chin Med 2018; 59: 1742-6. |
| 32. | Alsudayri A, Perelman S, Brewer M, et al. Gut microbiota regulate maturation and mitochondrial function of the nutrient-sensing enteroendocrine cell. Development 2024; 151: dev202544. |
| 33. |
Chak A, Falk G, Grady WM, et al. Assessment of familiality, obesity, and other risk factors for early age of cancer diagnosis in adenocarcinomas of the esophagus and gastroesophageal junction. Am J Gastroenterol 2009; 104: 1913-21.
DOI PMID |
| 34. |
Lagergren J. Influence of obesity on the risk of esophageal disorders. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2011; 8: 340-7.
DOI PMID |
| 35. |
Neto AG, Whitaker A, Pei Z. Microbiome and potential targets for chemoprevention of esophageal adenocarcinoma. Semin Oncol 2016; 43: 86-96.
DOI PMID |
| 36. | Yang F, Xie XH, Li X, Liao HN, Zou B. Analysis of psychological and gut microbiome characteristics in patients with non-erosive reflux disease. Front Psychiatry 2021; 12: 741049. |
| 37. | Lin YT, Wang YC, Xue YM, et al. Decoding the influence of low temperature on biofilm development: The hidden roles of c-di-GMP. Sci Total Environ 2024; 927: 172376. |
| 38. | Xi L, Song YM, Han JC, Qin XX. Microbiome analysis reveals the significant changes in gut microbiota of diarrheic Baer's Pochards (Aythya baeri). Microb Pathog 2021; 157: 105015. |
| 39. | Rivera-Zuluaga K, Hiles R, Barua P, Caldwell D, Iyer-Pascuzzi AS. Getting to the root of Ralstonia invasion. Semin Cell Dev Biol 2023; 148-9: 3-12. |
| 40. | Yang XP, Che TT, Tian SS, et al. A Living Microecological hydrogel with microbiota remodelling and immune reinstatement for diabetic wound healing. Adv Healthc Mater 2024; 13: e2400856. |
| 41. | Cheng Y, Kou FS, Zhang XS, et al. Network pharmacology analysis of Hewei Jiangni granule for gastroesophageal reflux disease and experimental verification of its anti-neurogenic inflammation mechanism. Drug Des Devel Ther 2022; 16: 1349-63. |
| 42. | Soheilian Khorzoghi M, Rostami-Nejad M, Yadegar A, Dabiri H, Hadadi A, Rodrigo L. Impact of probiotics on gut microbiota composition and clinical symptoms of coeliac disease patients following gluten-free diet. Contemp Clin Trials Commun 2023; 35: 101201. |
| 43. | Wang JH, Choi Y, Lee JS, Hwang SJ, Gu J, Son CG. Clinical evidence of the link between gut microbiome and myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome: a retrospective review. Eur J Med Res 2024; 29: 148. |
| 44. | Giridhar P, Pradhan S, Dokania S, Venkatesulu B, Sarode R, Welsh JS. Microbiome and abdominopelvic radiotherapy related chronic enteritis: a microbiome-based mechanistic role of probiotics and antibiotics. Am J Clin Oncol 2024; 47: 246-52. |
| 45. |
Cheung SG, Goldenthal AR, Uhlemann AC, Mann JJ, Miller JM, Sublette ME. Systematic review of gut microbiota and major depression. Front Psychiatry 2019; 10: 34.
DOI PMID |
| 46. | Pan LY, Zhou YY, Zhang X, Jiang HY. Gut microbiota is associated with weight gain in children treated with atypical antipsychotic: a pilot longitudinal study. Psychiatry Res 2022; 316: 114784. |
| 47. | Xie ZJ, Xing LM, Zhao MQ, et al. Versatile, vigilance, and gut microbiome support the priority of high-ranking hens. Front Vet Sci 2023; 10: 1324937. |
| 48. | Gaël T, Marie-José B, Jean-Christophe R, et al. Association between gut microbiota at 3.5 years of age and body mass index at 5 years: results from two French nationwide birth cohorts. Int J Obes (Lond) 2024; 48: 503-11. |
| 49. |
Zhao FY, Feng J, Li J, et al. Alterations of the gut microbiota in hashimoto's thyroiditis patients. Thyroid 2018; 28: 175-86.
DOI PMID |
| 50. |
Oland LA, Gibson NJ, Tolbert LP. Localization of a GABA transporter to glial cells in the developing and adult olfactory pathway of the moth Manduca sexta. J Comp Neurol 2010; 518: 815-38.
DOI PMID |
| 51. | Gao YN, Liu YT, Zhao SH, et al. MRS study on the correlation between frontal GABA + /Glx ratio and abnormal cognitive function in medication-naive patients with narcolepsy. Sleep Med 2024; 119: 1-8. |
| 52. |
Smith MD, Woodhead JH, Handy LJ, et al. Preclinical comparison of mechanistically different antiseizure, antinociceptive, and/or antidepressant drugs in a battery of rodent models of nociceptive and neuropathic pain. Neurochem Res 2017; 42: 1995-2010.
DOI PMID |
| 53. |
Rumore MM, Schlichting DA. Analgesic effects of antihistaminics. Life Sci 1985; 36: 403-16.
PMID |
| 54. | Maltese M, Martella G, Madeo G, et al. Anticholinergic drugs rescue synaptic plasticity in DYT1 dystonia: role of M1 muscarinic receptors. Mov Disord 2014; 29: 1655-65. |
| 55. | Xue C, Li G, Zheng Q, et al. Tryptophan metabolism in health and disease. Cell Metab 2023; 35: 1304-26. |
| 56. |
Gao K, Mu CL, Farzi A, Zhu WY. Tryptophan metabolism: a link between the gut microbiota and brain. Adv Nutr 2020; 11: 709-23.
DOI PMID |
| 57. |
Palecek J, Paleckova V, Willis WD. The effect of phorbol esters on spinal cord amino acid concentrations and responsiveness of rats to mechanical and thermal stimuli. Pain 1999; 80: 597-605.
DOI PMID |
| 58. | Liu T, Wu ML, Deng GY, et al. Linderae Radix water extract treats diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome in rats: a serum metabolomics study. Zhong Guo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2023; 48: 5356-64. |
| [1] | HAO Shulan, NAN Peng, LIU Likun, LI Xiaoli, ZHONG Qiming, GAO Yu, WANG Xixing, NIE Yingfang. Effectiveness of Yiqi Chupi powder (益气除疲散) for alleviating cancer-related fatigue in patients following colorectal cancer surgery: a randomized controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(5): 1119-1126. |
| [2] | GUO Jixing, JI Changchun, XIE Chaoju, RAO Xiang, SUN Zhangyin, XING Yu, ZHANG Rongni, QU Qiangqiang, DONG Youpeng, YANG Jinsheng. Various acupuncture therapies for managing nonspecific low back pain: a network Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(5): 954-962. |
| [3] | CHEN Ziying, ZHAO Xiaoping, FAN Xiaoxuan, TANG Didi, SUN Wen, LYU Jing, HUANG Lan, QI Fan. Seven Traditional Chinese Medicine external treatments combined with rehabilitation training on the functional recovery of limbs in patients with cerebral hemorrhage: a network Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(4): 711-719. |
| [4] | ZHAO Weibo, WANG Yaqi, KONG Lingyao, WANG Tianyi, ZHAO Haihong, ZHANG Ying, LUO Bin, WANG Ji, WANG Qi. Efficacy and safety of Tuomin Zhiti decoction (脱敏止嚏汤) on patients with seasonal allergic rhinitis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(4): 829-835. |
| [5] | LI Yuxuan, LI Yan, WANG Wujiao, CUI Xiaoyun, WAN Jie, ZHOU Kun, LU Jinjin, LIU Jing, LIN Qian, LI Dong. Clinical study of Yiqi Liangxue Shengji prescription (益气凉血生肌方) for improving cardiac function after myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury in patients with acute myocardial infarction: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(4): 836-844. |
| [6] | ZHENG Ruwen, DONG Xu, WANG Tianyi, FENG Liyuan, ZHANG Hongyan, HUO Hong, ZHANG Ying, ZHANG Qianshi, ZHU Xingyan, WANG Dongyan. Electroacupuncture versus conventional acupuncture of scalp motor area for post-stroke wrist dyskinesia and its effect on muscle function: a randomized, controlled clinical trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(4): 852-859. |
| [7] | XIAO Jing, SONG Danlei, LIANG Caiming, HE Yinuo, ZHENG Weifang, WU Xiaqiu. Efficacy of Jianpi formulas (健脾剂) in reducing the recurrence of colorectal adenoma after polypectomy: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(2): 225-233. |
| [8] | LAI Xiaolei, SHANG Juju, LIU Hongxu, HU Jing, LI Xiang, ZHANG Zhenmin, XING Wenlong. Clinical efficacy of Angong Jiangya pill (安宫降压丸) for grade 2 hypertension with liver-fire hyperactivity syndrome: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(2): 422-429. |
| [9] | CHENG Jianping, FAN Chanjuan, ZHAI Lili, WANG Hui, XIE Dongling, CAI Yong, LI Zhen, HUANG Kun, BAI Qixuan. Efficacy and safety of Qingwei Zhitong pellets (清胃止痛微丸)-containing quadruple therapy for Helicobacter pylori eradication: a prospective, single-center, randomized trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(2): 430-436. |
| [10] | YE Wujie, YANG Yawei, ZHANG Da, TANG Ling, CUI Minying, FU Bin, ZHANG Meng, HU Xingang, ZHAO Yan. Effectiveness of combining Qingyanyin formulated granules (轻燕饮配方颗粒) with press needles in treating abdominal obesity: a multicenter randomized controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(1): 107-114. |
| [11] | LANG Jiawang, JIN Lingqing, LUO Jianchang, LANG Boxu. Effects of acupuncture combined with bone-setting therapy to treat tourette syndrome: a three-arm randomized controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(1): 176-183. |
| [12] | Emre Bulut, Didem Özkal Eminoğlu, Yasemin Çayır. Effect of electroacupuncture on pain after periodontal flap surgery: a randomized controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(1): 184-191. |
| [13] | WU Qiaomin, GUAN Xuanke, LIU Jinfeng, WANG Yanli, CHANG Xing, LIU Zhiming, LIU Ruxiu. Compound Tongyang Fumai decoction (通阳复脉方) improves quality of life in sick sinus syndrome: a randomized controlled study [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(6): 1247-1253. |
| [14] | QIAN Jianan, XU Yan, HU Hongyi, ZHAO Aiguang. Clinical efficacy and safety evaluation of Buzhongyiqi pills (补中益气丸) on appetite improvement in patients with colorectal cancer receiving chemotherapy: a pilot randomized cross-over clinical trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(6): 1254-1267. |
| [15] | DENG Yasheng, HAN Siyin, XI Lanhua, HUANG Hui, LIANG Tianwei, ZHENG Yiqing, FAN Yanping, LIN Jiang. Traditional Chinese Medicine in the treatment of recurrent respiratory tract infections in children: an overview of systematic reviews and Meta-analyses [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(5): 871-884. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

