Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (6): 1254-1267.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20240806.005
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Clinical efficacy and safety evaluation of Buzhongyiqi pills (补中益气丸) on appetite improvement in patients with colorectal cancer receiving chemotherapy: a pilot randomized cross-over clinical trial
QIAN Jianan1,2, XU Yan3, HU Hongyi4( ), ZHAO Aiguang3(
), ZHAO Aiguang3( )
)
- 1 Department of Gastroenterology, Longhua Hospital, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai, 200032, China
2 Institute of Digestive Diseases, Longhua Hospital, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200032, China
3 Department of Oncology, Longhua Hospital, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200032, China
4 Department of Gastroenterology, Longhua Hospital, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200032, China
-
Received:2023-05-02Accepted:2023-09-02Online:2024-12-15Published:2024-08-06 -
Contact:ZHAO Aiguang, Department of Oncology, Longhua Hospital, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200032, China. aiguangzhao@qq.com Telephone: +86-18918799919; +86-13661472241
HU Hongyi, Department of Gastroenterology, Longhua Hospital, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200032, China. hongyihu2003@shutcm.edu.cn -
Supported by:Shanghai Municipal Administrator of Traditional Chinese Medicine-funded Project: Ding’s Clinical Medicine Huang Wendong Base Li Dongyuan "Yin Fire" Theory Inheritance and Innovation Team(2021LPTD-009)
Cite this article
QIAN Jianan, XU Yan, HU Hongyi, ZHAO Aiguang. Clinical efficacy and safety evaluation of Buzhongyiqi pills (补中益气丸) on appetite improvement in patients with colorectal cancer receiving chemotherapy: a pilot randomized cross-over clinical trial[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(6): 1254-1267.
share this article
| Scales | Category | Number of items | Scoring range | Scoring formula |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Physical functioning | Multi-item functional scales | 5 | 3 | (Q1+Q2+Q3+Q4+Q5)/5 |
| Role functioning | 2 | 3 | (Q6+Q7)/2 | |
| Emotional functioning | 4 | 3 | (Q21+Q22+Q23+Q24)/4 | |
| Cognitive functioning | 2 | 3 | (Q20+Q25)/2 | |
| Social activity | 2 | 3 | (Q26+Q27)/2 | |
| Global health | A global health status sub-scale | 2 | 6 | (Q29+Q30)/2 |
| Fatigue | Multi-item symptom scales | 3 | 3 | (Q10+Q12+Q18)/3 |
| Nausea and vomiting | 2 | 3 | (Q14+Q15)/2 | |
| Pain | 2 | 3 | (Q9+Q19)/2 | |
| Dyspnea | Single items | 1 | 3 | Q8 |
| Insomnia | 1 | 3 | Q11 | |
| Appetite loss | 1 | 3 | Q13 | |
| Constipation | 1 | 3 | Q16 | |
| Diarrhea | 1 | 3 | Q17 | |
| Financial difficulties | 1 | 3 | Q28 |
Table 1 EORTC QLQ-C30 (V3.0) subscales and scoring methods
| Scales | Category | Number of items | Scoring range | Scoring formula |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Physical functioning | Multi-item functional scales | 5 | 3 | (Q1+Q2+Q3+Q4+Q5)/5 |
| Role functioning | 2 | 3 | (Q6+Q7)/2 | |
| Emotional functioning | 4 | 3 | (Q21+Q22+Q23+Q24)/4 | |
| Cognitive functioning | 2 | 3 | (Q20+Q25)/2 | |
| Social activity | 2 | 3 | (Q26+Q27)/2 | |
| Global health | A global health status sub-scale | 2 | 6 | (Q29+Q30)/2 |
| Fatigue | Multi-item symptom scales | 3 | 3 | (Q10+Q12+Q18)/3 |
| Nausea and vomiting | 2 | 3 | (Q14+Q15)/2 | |
| Pain | 2 | 3 | (Q9+Q19)/2 | |
| Dyspnea | Single items | 1 | 3 | Q8 |
| Insomnia | 1 | 3 | Q11 | |
| Appetite loss | 1 | 3 | Q13 | |
| Constipation | 1 | 3 | Q16 | |
| Diarrhea | 1 | 3 | Q17 | |
| Financial difficulties | 1 | 3 | Q28 |
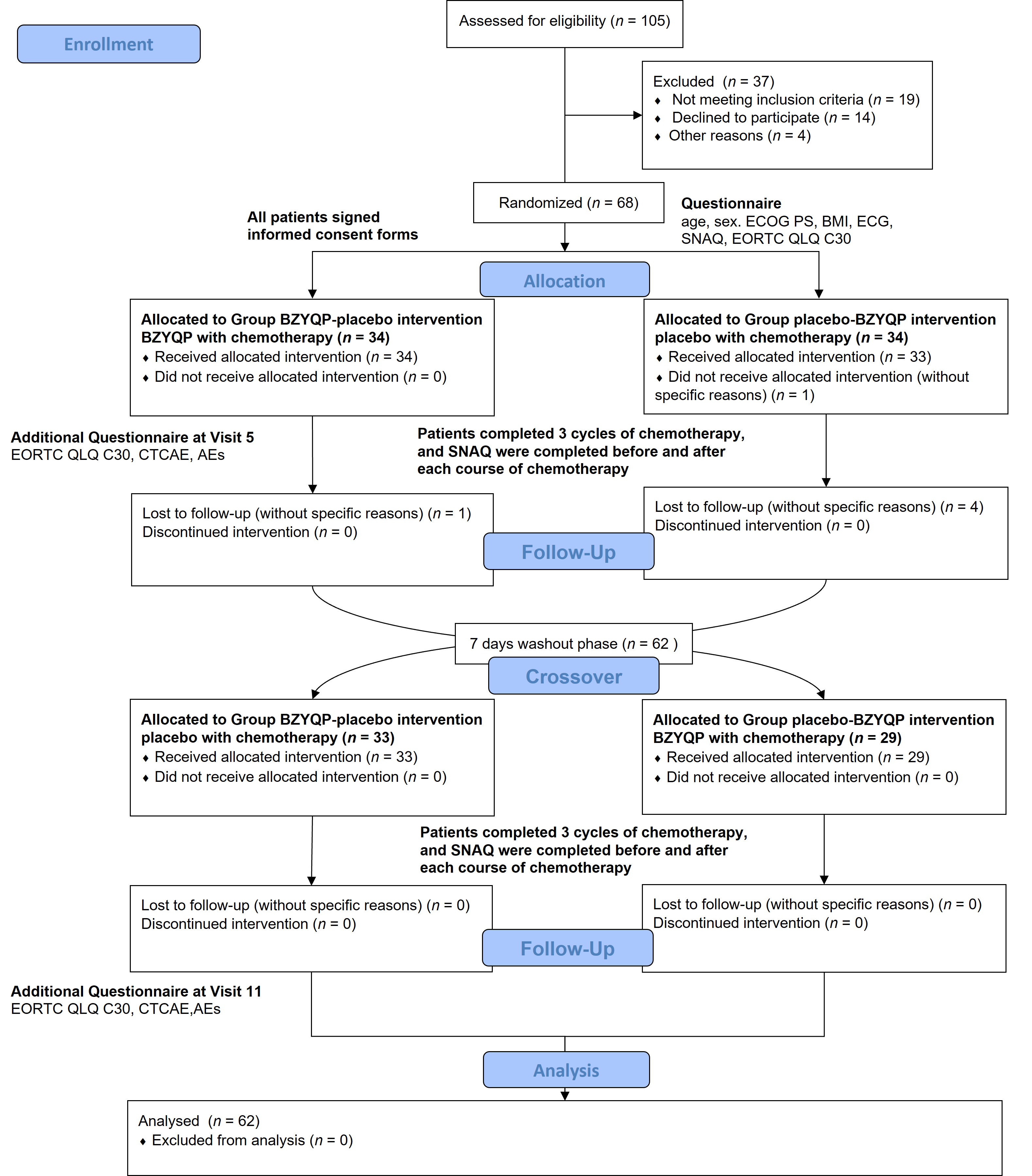
Figure 1 Flow chart of the study Note: placebo-BZYQP: treated with placebo during the first three cycles of chemotherapy and with Buzhongyiqi pills during the last three cycles of chemotherapy; BZYQP-placebo: treated with Buzhongyiqi pills during the first three cycles of chemotherapy and with placebo during the last three cycles of chemotherapy. BZYQP: Buzhongyiqi pills; ECOG PS: Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status; BMI: body mass index; SNAQ: simplified nutrition appetite questionnaire; EORTC QLQ-C30 (V3.0): the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Quality of Life Questionnaire (version 3.0); ECG: electrocardiogram; CTCAE: Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events; AEs: adverse events.
| Variable | Placebo-BZYQP (n = 29) [n (%)] | BZYQP-Placebo (n = 33) [n (%)] | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | <50 | 7 (11.3) | 9 (14.5) | 0.165 |
| ≥50 | 22 (35.5) | 24 (38.7) | ||
| 61.79±8.99 | 59.55±8.98 | 0.330 | ||
| Sex | Male | 17 (27.4) | 23 (37.1) | 0.363 |
| Female | 12 (19.4) | 10 (16.1) | ||
| Diagnosis | Colon cancer (right) | 7 (11.3) | 6 (9.7) | 0.225 |
| Colon cancer (left) | 15 (24.2) | 12 (19.4) | ||
| Rectal cancer | 7 (11.3) | 15 (24.2) | ||
| Stage | Ⅱa | 2 (3.2) | 5 (8.1) | 0.577 |
| Ⅲ | 22 (35.5) | 21 (33.9) | ||
| Ⅳ | 5 (8.1) | 7 (11.3) | ||
| Surgical situation | postoperative | 24 (82.8) | 26 (78.8) | 0.693 |
| non-operative | 5 (17.2) | 7 (21.2) | ||
| ECOG PS | 0 | 5 (17.2) | 8 (24.2) | 0.713 |
| 1 | 20 (69.0) | 22 (66.7) | ||
| 2 | 4 (13.8) | 3 (9.0) | ||
| Height (cm) | 162.12±8.31 | 162.54±7.92 | 0.631 | |
| Weight (kg) | 63.13±10.76 | 63.91±10.12 | 0.991 | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 24.02±3.71 | 24.19±3.93 | 0.773 | |
| SNAQ | SNAQ score | 14.00±0.96 | 14.15±0.91 | 0.526 |
| SNAQ item 1 | 3.34±0.61 | 3.27±0.45 | 0.598 | |
| SNAQ item 2 | 3.55±0.51 | 3.76±0.44 | 0.090 | |
| SNAQ item 3 | 3.00±0.38 | 3.18±0.47 | 0.099 | |
| SNAQ item 4 | 4.10±0.41 | 3.94±0.24 | 0.056 | |
| EORTC QLQ C30 (V3.0) | PF | 2 (1.4) | 1.6 (1.6) | 0.092 |
| RF | 3.5 (1.5) | 2.0 (1.5) | 0.195 | |
| EF | 2.0 (0.5) | 1.75 (0.75) | 0.057 | |
| CF | 2.5 (1.0) | 2.0 (0.5) | 0.916 | |
| SA | 3.0 (0) | 3.0 (0) | 0.578 | |
| GH | 4.5 (0.8) | 5.0 (0.5) | 0.070 | |
| FA | 2.67 (0.67) | 2.67 (0.0) | 0.475 | |
| NV | 2.5 (1.5) | 1.5 (1.5) | 0.173 | |
| PA | 3.0 (1.5) | 2.0 (2.0) | 0.059 | |
| DY | 1.0 (1.0) | 2.0 (1.0) | 0.091 | |
| SL | 1.0 (2.0) | 3.0 (2.0) | 0.198 | |
| AL | 1.0 (1.0) | 1.0 (1.0) | 0.070 | |
| CO | 1.0 (1.0) | 1. 0 (0.0) | 0.164 | |
| DI | 1.0 (1.0) | 1.0 (0.0) | 0.128 | |
| FD | 2.0 (0.0) | 2.0 (1.0) | 0.200 |
Table 2 Baseline characteristics of all patients
| Variable | Placebo-BZYQP (n = 29) [n (%)] | BZYQP-Placebo (n = 33) [n (%)] | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | <50 | 7 (11.3) | 9 (14.5) | 0.165 |
| ≥50 | 22 (35.5) | 24 (38.7) | ||
| 61.79±8.99 | 59.55±8.98 | 0.330 | ||
| Sex | Male | 17 (27.4) | 23 (37.1) | 0.363 |
| Female | 12 (19.4) | 10 (16.1) | ||
| Diagnosis | Colon cancer (right) | 7 (11.3) | 6 (9.7) | 0.225 |
| Colon cancer (left) | 15 (24.2) | 12 (19.4) | ||
| Rectal cancer | 7 (11.3) | 15 (24.2) | ||
| Stage | Ⅱa | 2 (3.2) | 5 (8.1) | 0.577 |
| Ⅲ | 22 (35.5) | 21 (33.9) | ||
| Ⅳ | 5 (8.1) | 7 (11.3) | ||
| Surgical situation | postoperative | 24 (82.8) | 26 (78.8) | 0.693 |
| non-operative | 5 (17.2) | 7 (21.2) | ||
| ECOG PS | 0 | 5 (17.2) | 8 (24.2) | 0.713 |
| 1 | 20 (69.0) | 22 (66.7) | ||
| 2 | 4 (13.8) | 3 (9.0) | ||
| Height (cm) | 162.12±8.31 | 162.54±7.92 | 0.631 | |
| Weight (kg) | 63.13±10.76 | 63.91±10.12 | 0.991 | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 24.02±3.71 | 24.19±3.93 | 0.773 | |
| SNAQ | SNAQ score | 14.00±0.96 | 14.15±0.91 | 0.526 |
| SNAQ item 1 | 3.34±0.61 | 3.27±0.45 | 0.598 | |
| SNAQ item 2 | 3.55±0.51 | 3.76±0.44 | 0.090 | |
| SNAQ item 3 | 3.00±0.38 | 3.18±0.47 | 0.099 | |
| SNAQ item 4 | 4.10±0.41 | 3.94±0.24 | 0.056 | |
| EORTC QLQ C30 (V3.0) | PF | 2 (1.4) | 1.6 (1.6) | 0.092 |
| RF | 3.5 (1.5) | 2.0 (1.5) | 0.195 | |
| EF | 2.0 (0.5) | 1.75 (0.75) | 0.057 | |
| CF | 2.5 (1.0) | 2.0 (0.5) | 0.916 | |
| SA | 3.0 (0) | 3.0 (0) | 0.578 | |
| GH | 4.5 (0.8) | 5.0 (0.5) | 0.070 | |
| FA | 2.67 (0.67) | 2.67 (0.0) | 0.475 | |
| NV | 2.5 (1.5) | 1.5 (1.5) | 0.173 | |
| PA | 3.0 (1.5) | 2.0 (2.0) | 0.059 | |
| DY | 1.0 (1.0) | 2.0 (1.0) | 0.091 | |
| SL | 1.0 (2.0) | 3.0 (2.0) | 0.198 | |
| AL | 1.0 (1.0) | 1.0 (1.0) | 0.070 | |
| CO | 1.0 (1.0) | 1. 0 (0.0) | 0.164 | |
| DI | 1.0 (1.0) | 1.0 (0.0) | 0.128 | |
| FD | 2.0 (0.0) | 2.0 (1.0) | 0.200 |
| Source | Sum of squares | df | Mean squares | F value | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Visit point | 75.840 | 1.000 | 75.840 | 14.952 | < 0.001 |
| Visit point * group | 682.722 | 1.000 | 682.722 | 134.595 | < 0.001 |
| Error (visit point) | 304.345 | 60.000 | 5.072 |
Table 3 Tests of within-subjects effects at Visit 0 to Visit 5
| Source | Sum of squares | df | Mean squares | F value | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Visit point | 75.840 | 1.000 | 75.840 | 14.952 | < 0.001 |
| Visit point * group | 682.722 | 1.000 | 682.722 | 134.595 | < 0.001 |
| Error (visit point) | 304.345 | 60.000 | 5.072 |
| Variable | Visit point | Placebo-BZYQP (n = 29) | BZYQP-Placebo (n = 33) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNAQ score (V0) | baseline, Pre cycle 1 | 14.0±1.0 | 14.1±0.9 | 0.526 |
| SNAQ score (V01) | Post cycle 1 | 11.9±1.8 | 15.2±1.4 | < 0.001a |
| SNAQ score (V02) | Pre cycle 2 | 12.0±1.6 | 15.2±0.9 | < 0.001a |
| SNAQ score (V03) | Post cycle 2 | 10.7±1.5 | 14.9±0.6 | < 0.001a |
| SNAQ score (V04) | Pre cycle 3 | 10.6±2.1 | 17.6±0.8 | < 0.001a |
| SNAQ score (V05) | Post cycle 3 | 9.1±1.8 | 17.6±1.7 | < 0.001a |
Table 4 Change in SNAQ score between treatment groups at Visit 0 to Visit 5
| Variable | Visit point | Placebo-BZYQP (n = 29) | BZYQP-Placebo (n = 33) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNAQ score (V0) | baseline, Pre cycle 1 | 14.0±1.0 | 14.1±0.9 | 0.526 |
| SNAQ score (V01) | Post cycle 1 | 11.9±1.8 | 15.2±1.4 | < 0.001a |
| SNAQ score (V02) | Pre cycle 2 | 12.0±1.6 | 15.2±0.9 | < 0.001a |
| SNAQ score (V03) | Post cycle 2 | 10.7±1.5 | 14.9±0.6 | < 0.001a |
| SNAQ score (V04) | Pre cycle 3 | 10.6±2.1 | 17.6±0.8 | < 0.001a |
| SNAQ score (V05) | Post cycle 3 | 9.1±1.8 | 17.6±1.7 | < 0.001a |
| Source | Sum of squares | df | Mean squares | F value | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Visit point | 90.727 | 1.000 | 90.727 | 22.951 | < 0.001 |
| Visit point * group | 967.845 | 1.000 | 967.845 | 244.828 | < 0.001 |
| Error (visit point) | 237.189 | 60.000 | 3.953 |
Table 5 Tests of within-subjects effects at Visit 6 to Visit 11
| Source | Sum of squares | df | Mean squares | F value | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Visit point | 90.727 | 1.000 | 90.727 | 22.951 | < 0.001 |
| Visit point * group | 967.845 | 1.000 | 967.845 | 244.828 | < 0.001 |
| Error (visit point) | 237.189 | 60.000 | 3.953 |
| Variables | Visit point | Placebo-BZYQP (n = 29) | BZYQP-Placebo (n = 33) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNAQ score (V06) | after Washout Period, Pre cycle 4 | 11.0±1.9 | 17.3±2.0 | < 0.001a |
| SNAQ score (V07) | Post cycle 4 | 11.5±1.8 | 14.6±1.3 | < 0.001a |
| SNAQ score (V08) | Pre cycle 5 | 14.0±1.6 | 14.6±1.4 | 0.148 |
| SNAQ score (V09) | Post cycle 5 | 13.4±1.6 | 13.2±1.5 | 0.667 |
| SNAQ score (V10) | Pre cycle 6 | 14.4±2.1 | 12.8±1.1 | < 0.001a |
| SNAQ score (V11) | Post cycle 6 | 14.8±1.8 | 11.2±1.3 | < 0.001a |
Table 6 Change in SNAQ score between treatment groups at Visit 6 to Visit 11
| Variables | Visit point | Placebo-BZYQP (n = 29) | BZYQP-Placebo (n = 33) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNAQ score (V06) | after Washout Period, Pre cycle 4 | 11.0±1.9 | 17.3±2.0 | < 0.001a |
| SNAQ score (V07) | Post cycle 4 | 11.5±1.8 | 14.6±1.3 | < 0.001a |
| SNAQ score (V08) | Pre cycle 5 | 14.0±1.6 | 14.6±1.4 | 0.148 |
| SNAQ score (V09) | Post cycle 5 | 13.4±1.6 | 13.2±1.5 | 0.667 |
| SNAQ score (V10) | Pre cycle 6 | 14.4±2.1 | 12.8±1.1 | < 0.001a |
| SNAQ score (V11) | Post cycle 6 | 14.8±1.8 | 11.2±1.3 | < 0.001a |
| Variable | Visit point | Placebo-BZYQP (n = 29) | BZYQP-Placebo (n = 33) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PF | V0, Pre | 2 (1.4, 3.8) | 1.6 (1.0, 3.0) | 0.092 |
| V05, Post | 3.0 (1.4, 4.0) | 1.6 (1.4, 3.0) | 0.000a | |
| RF | Pre | 3.5 (1.0, 4.0) | 2.0 (1.0, 3.5) | 0.195 |
| Post | 4.0 (1.5, 4.0) | 2.0 (1.0, 3.0) | < 0.001a | |
| EF | Pre | 2.0 (1.0, 2.75) | 1.75 (1.0, 2.75) | 0.057 |
| Post | 3.0 (1.3, 3.8) | 1.3 (1.0, 3.0) | < 0.001a | |
| CF | Pre | 2.5 (1.0, 4.0) | 2.0 (1.0, 2.5) | 0.916 |
| Post | 3.5 (1.0, 4.0) | 1.0 (1.0, 3.0) | < 0.001a | |
| SA | Pre | 3.0 (1.0, 4.5) | 3.0 (1.0, 4.0) | 0.578 |
| Post | 3.0 (1.0, 4.0) | 2.0 (1.0, 3.0) | < 0.001a | |
| GH | Pre | 4.5 (2.5, 5.5) | 5.0 (3.0, 6.0) | 0.070 |
| Post | 4.0 (1.0, 6.0) | 4.0 (2.0, 6.0) | 0.971 | |
| FA | Pre | 2.67 (1.0, 3.67) | 2.67 (1.0, 3.3) | 0.475 |
| Post | 4.0 (1.7, 4.0) | 1.7 (1.7, 3.0) | < 0.001a | |
| NV | Pre | 2.5 (1.0, 2.5) | 1.5 (1.0, 2.5) | 0.173 |
| Post | 2.5 (1.0, 3.0) | 1.0 (1.0, 2.5) | < 0.001a | |
| PA | Pre | 3.0 (1.0, 3.0) | 2.0 (1.0, 3.0) | 0.059 |
| Post | 3.5 (1.0, 3.5) | 3.0 (1.0, 3.0) | 0.169 | |
| DY | Pre | 1.0 (1.0, 4.0) | 2.0 (1.0, 2.0) | 0.091 |
| Post | 2.0 (1.0, 4.0) | 1.0 (1.0, 3.0) | < 0.001a | |
| SL | Pre | 1.0 (1.0, 4.0) | 3.0 (1.0, 4.0) | 0.198 |
| Post | 1.0 (1.0, 4.0) | 2.0 (1.0, 3.0) | 0.014a | |
| AL | Pre | 1.0 (1.0, 3.0) | 1.0 (1.0, 3.0) | 0.070 |
| Post | 3.0 (1.0, 4.0) | 1.0 (1.0, 3.0) | < 0.001a | |
| CO | Pre | 1.0 (1.0, 4.0) | 1.0 (1.0, 4.0) | 0.164 |
| Post | 1.0 (1.0, 4.0) | 1.0 (1.0, 3.0) | 0.164 | |
| DI | Pre | 1.0 (1.0, 4.0) | 1.0 (1.0, 3.0) | 0.128 |
| Post | 2.0 (1.0, 4.0) | 1.0 (1.0, 2.0) | < 0.001a | |
| FD | Pre | 2.0 (1.0, 5.0) | 2.0 (1.0, 3.0) | 0.200 |
| Post | 3.0 (1.0, 5.0) | 3.0 (1.0, 3.0) | 0.971 |
Table 7 EORTC score (Visit 0 to Visit 5)
| Variable | Visit point | Placebo-BZYQP (n = 29) | BZYQP-Placebo (n = 33) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PF | V0, Pre | 2 (1.4, 3.8) | 1.6 (1.0, 3.0) | 0.092 |
| V05, Post | 3.0 (1.4, 4.0) | 1.6 (1.4, 3.0) | 0.000a | |
| RF | Pre | 3.5 (1.0, 4.0) | 2.0 (1.0, 3.5) | 0.195 |
| Post | 4.0 (1.5, 4.0) | 2.0 (1.0, 3.0) | < 0.001a | |
| EF | Pre | 2.0 (1.0, 2.75) | 1.75 (1.0, 2.75) | 0.057 |
| Post | 3.0 (1.3, 3.8) | 1.3 (1.0, 3.0) | < 0.001a | |
| CF | Pre | 2.5 (1.0, 4.0) | 2.0 (1.0, 2.5) | 0.916 |
| Post | 3.5 (1.0, 4.0) | 1.0 (1.0, 3.0) | < 0.001a | |
| SA | Pre | 3.0 (1.0, 4.5) | 3.0 (1.0, 4.0) | 0.578 |
| Post | 3.0 (1.0, 4.0) | 2.0 (1.0, 3.0) | < 0.001a | |
| GH | Pre | 4.5 (2.5, 5.5) | 5.0 (3.0, 6.0) | 0.070 |
| Post | 4.0 (1.0, 6.0) | 4.0 (2.0, 6.0) | 0.971 | |
| FA | Pre | 2.67 (1.0, 3.67) | 2.67 (1.0, 3.3) | 0.475 |
| Post | 4.0 (1.7, 4.0) | 1.7 (1.7, 3.0) | < 0.001a | |
| NV | Pre | 2.5 (1.0, 2.5) | 1.5 (1.0, 2.5) | 0.173 |
| Post | 2.5 (1.0, 3.0) | 1.0 (1.0, 2.5) | < 0.001a | |
| PA | Pre | 3.0 (1.0, 3.0) | 2.0 (1.0, 3.0) | 0.059 |
| Post | 3.5 (1.0, 3.5) | 3.0 (1.0, 3.0) | 0.169 | |
| DY | Pre | 1.0 (1.0, 4.0) | 2.0 (1.0, 2.0) | 0.091 |
| Post | 2.0 (1.0, 4.0) | 1.0 (1.0, 3.0) | < 0.001a | |
| SL | Pre | 1.0 (1.0, 4.0) | 3.0 (1.0, 4.0) | 0.198 |
| Post | 1.0 (1.0, 4.0) | 2.0 (1.0, 3.0) | 0.014a | |
| AL | Pre | 1.0 (1.0, 3.0) | 1.0 (1.0, 3.0) | 0.070 |
| Post | 3.0 (1.0, 4.0) | 1.0 (1.0, 3.0) | < 0.001a | |
| CO | Pre | 1.0 (1.0, 4.0) | 1.0 (1.0, 4.0) | 0.164 |
| Post | 1.0 (1.0, 4.0) | 1.0 (1.0, 3.0) | 0.164 | |
| DI | Pre | 1.0 (1.0, 4.0) | 1.0 (1.0, 3.0) | 0.128 |
| Post | 2.0 (1.0, 4.0) | 1.0 (1.0, 2.0) | < 0.001a | |
| FD | Pre | 2.0 (1.0, 5.0) | 2.0 (1.0, 3.0) | 0.200 |
| Post | 3.0 (1.0, 5.0) | 3.0 (1.0, 3.0) | 0.971 |
| Variable | After washout period | Placebo-BZYQP (n = 29) | BZYQP-Placebo (n = 33) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PF | V06, Pre | 3.5 (1.5, 4.0) | 1.6 (1.4, 3.0) | < 0.001a |
| V11, Post | 2.0 (1.4, 3.4) | 1.8 (1.0, 4.0) | 0.018a | |
| RF | Pre | 3.5 (1.5, 4.0) | 2.0 (1.5, 3.0) | < 0.001a |
| Post | 2.0 (1.0, 4.0) | 2.5 (1.5, 4.0) | < 0.001a | |
| EF | Pre | 2.3 (1.0, 3.8) | 1.0 (1.0, 3.0) | < 0.001a |
| Post | 1.5 (1.0, 3.0) | 1.8 (1.0, 4.0) | 0.040a | |
| CF | Pre | 2.0 (1.0, 4.0) | 1.0 (1.0, 3.0) | < 0.001a |
| Post | 1.0 (1.0, 3.5) | 2.0 (1.0, 4.0) | < 0.001a | |
| SA | Pre | 2.5 (1.0, 4.0) | 2.0 (1.0, 3.0) | < 0.001a |
| Post | 2.0 (1.0, 4.5) | 3.0 (1.0, 4.0) | 0.001a | |
| GH | Pre | 4.5 (1.0, 6.0) | 4.0 (3.0, 6.0) | < 0.001a |
| Post | 5.0 (3.0, 6.0) | 4.0 (1.0, 6.0) | < 0.001a | |
| FA | Pre | 3.3 (1.7, 3.7) | 1.7 (1.7, 3.0) | < 0.001a |
| Post | 1.7 (1.3, 3.7) | 3.0 (1.0, 3.7) | < 0.001a | |
| NV | Pre | 1.0 (1.0, 3.0) | 1.0 (1.0, 2.5) | 0.243 |
| Post | 1.0 (1.0, 3.0) | 1.0 (1.0, 2.5) | 0.594 | |
| PA | Pre | 3.0 (1.0, 3.0) | 2.0 (1.0, 3.0) | 0.059 |
| Post | 1.5 (1.0, 3.0) | 1.5 (1.0, 4.0) | 0.729 | |
| DY | Pre | 2.0 (1.0, 4.0) | 1.0 (1.0, 3.0) | < 0.001a |
| Post | 1.0 (1.0, 4.0) | 2.0 (1.0, 4.0) | < 0.001a | |
| SL | Pre | 1.0 (1.0, 4.0) | 2.0 (1.0, 3.0) | 0.054 |
| Post | 3.5 (1.0, 3.5) | 3.0 (1.0, 3.0) | 0.169 | |
| AL | Pre | 3.0 (1.0, 4.0) | 1.0 (1.0, 3.0) | < 0.001a |
| Post | 1.0 (1.0, 3.0) | 3.0 (1.0, 4.0) | < 0.001a | |
| CO | Pre | 1.0 (1.0, 4.0) | 1.0 (1.0, 3.0) | 0.064 |
| Post | 1.5 (1.0, 3.0) | 1.5 (1.0, 4.0) | 0.729 | |
| DI | Pre | 2.0 (1.0, 4.0) | 1.0 (1.0, 3.0) | < 0.001a |
| Post | 2.0 (1.0, 4.0) | 1.0 (1.0, 4.0) | < 0.001a | |
| FD | Pre | 3.0 (1.0, 3.0) | 2.0 (1.0, 2.5) | 0.060 |
| Post | 3.0 (1.0, 5.0) | 3.0 (1.0, 3.0) | 0.607 |
Table 8 EORTC scores (Visit 6-Visit 11)
| Variable | After washout period | Placebo-BZYQP (n = 29) | BZYQP-Placebo (n = 33) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PF | V06, Pre | 3.5 (1.5, 4.0) | 1.6 (1.4, 3.0) | < 0.001a |
| V11, Post | 2.0 (1.4, 3.4) | 1.8 (1.0, 4.0) | 0.018a | |
| RF | Pre | 3.5 (1.5, 4.0) | 2.0 (1.5, 3.0) | < 0.001a |
| Post | 2.0 (1.0, 4.0) | 2.5 (1.5, 4.0) | < 0.001a | |
| EF | Pre | 2.3 (1.0, 3.8) | 1.0 (1.0, 3.0) | < 0.001a |
| Post | 1.5 (1.0, 3.0) | 1.8 (1.0, 4.0) | 0.040a | |
| CF | Pre | 2.0 (1.0, 4.0) | 1.0 (1.0, 3.0) | < 0.001a |
| Post | 1.0 (1.0, 3.5) | 2.0 (1.0, 4.0) | < 0.001a | |
| SA | Pre | 2.5 (1.0, 4.0) | 2.0 (1.0, 3.0) | < 0.001a |
| Post | 2.0 (1.0, 4.5) | 3.0 (1.0, 4.0) | 0.001a | |
| GH | Pre | 4.5 (1.0, 6.0) | 4.0 (3.0, 6.0) | < 0.001a |
| Post | 5.0 (3.0, 6.0) | 4.0 (1.0, 6.0) | < 0.001a | |
| FA | Pre | 3.3 (1.7, 3.7) | 1.7 (1.7, 3.0) | < 0.001a |
| Post | 1.7 (1.3, 3.7) | 3.0 (1.0, 3.7) | < 0.001a | |
| NV | Pre | 1.0 (1.0, 3.0) | 1.0 (1.0, 2.5) | 0.243 |
| Post | 1.0 (1.0, 3.0) | 1.0 (1.0, 2.5) | 0.594 | |
| PA | Pre | 3.0 (1.0, 3.0) | 2.0 (1.0, 3.0) | 0.059 |
| Post | 1.5 (1.0, 3.0) | 1.5 (1.0, 4.0) | 0.729 | |
| DY | Pre | 2.0 (1.0, 4.0) | 1.0 (1.0, 3.0) | < 0.001a |
| Post | 1.0 (1.0, 4.0) | 2.0 (1.0, 4.0) | < 0.001a | |
| SL | Pre | 1.0 (1.0, 4.0) | 2.0 (1.0, 3.0) | 0.054 |
| Post | 3.5 (1.0, 3.5) | 3.0 (1.0, 3.0) | 0.169 | |
| AL | Pre | 3.0 (1.0, 4.0) | 1.0 (1.0, 3.0) | < 0.001a |
| Post | 1.0 (1.0, 3.0) | 3.0 (1.0, 4.0) | < 0.001a | |
| CO | Pre | 1.0 (1.0, 4.0) | 1.0 (1.0, 3.0) | 0.064 |
| Post | 1.5 (1.0, 3.0) | 1.5 (1.0, 4.0) | 0.729 | |
| DI | Pre | 2.0 (1.0, 4.0) | 1.0 (1.0, 3.0) | < 0.001a |
| Post | 2.0 (1.0, 4.0) | 1.0 (1.0, 4.0) | < 0.001a | |
| FD | Pre | 3.0 (1.0, 3.0) | 2.0 (1.0, 2.5) | 0.060 |
| Post | 3.0 (1.0, 5.0) | 3.0 (1.0, 3.0) | 0.607 |
| Variable | Grade 1-4 | Grade 3/4 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Placebo-BZYQP (n = 29) | BZYQP-Placebo (n = 33) | P value | Placebo-BZYQP (n = 29) | BZYQP-Placebo (n = 33) | P value | |||||||
| n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | |||||
| Leukopenia | 15 | 51.7 | 5 | 15.2 | 0.002a | 2 | 6.9 | 1 | 3.0 | 0.479 | ||
| Neutropenia | 10 | 34.5 | 3 | 9.1 | 0.014a | 2 | 6.9 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.125 | ||
| Thrombocytopenia | 5 | 17.2 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.013a | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 | - | ||
| Anemia | 12 | 41.4 | 5 | 15.2 | 0.021a | 3 | 10.3 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.058 | ||
| Elevated alkaline phosphatase | 3 | 10.3 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.058 | 1 | 3.4 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.282 | ||
| Hyperbilirubinemia | 5 | 17.2 | 2 | 6.1 | 0.165 | 2 | 6.9 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.125 | ||
| Gastrointestinal bleeding | 1 | 3.4 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.282 | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 | - | ||
| Diarrhea | 13 | 44.8 | 4 | 12.1 | 0.004a | 6 | 20.7 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.006a | ||
| Nausea and vomiting | 18 | 62.1 | 3 | 9.1 | 0.000a | 7 | 24.1 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.003a | ||
| Neurotoxicity | 1 | 3.4 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.282 | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 | - | ||
| Allergic reaction | 2 | 6.9 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.125 | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 | - | ||
| Fever | 1 | 3.4 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.282 | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 | - | ||
| Rash | 1 | 3.4 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.282 | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 | - | ||
| Alopecia | 4 | 13.8 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.027a | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 | - | ||
| Pain | 4 | 13.8 | 1 | 3.0 | 0.120 | 2 | 6.9 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.125 | ||
| Hand-foot syndrome | 7 | 24.1 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.003a | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 | - | ||
Table 9 Frequency of Chemotherapy-induced AEs
| Variable | Grade 1-4 | Grade 3/4 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Placebo-BZYQP (n = 29) | BZYQP-Placebo (n = 33) | P value | Placebo-BZYQP (n = 29) | BZYQP-Placebo (n = 33) | P value | |||||||
| n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | |||||
| Leukopenia | 15 | 51.7 | 5 | 15.2 | 0.002a | 2 | 6.9 | 1 | 3.0 | 0.479 | ||
| Neutropenia | 10 | 34.5 | 3 | 9.1 | 0.014a | 2 | 6.9 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.125 | ||
| Thrombocytopenia | 5 | 17.2 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.013a | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 | - | ||
| Anemia | 12 | 41.4 | 5 | 15.2 | 0.021a | 3 | 10.3 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.058 | ||
| Elevated alkaline phosphatase | 3 | 10.3 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.058 | 1 | 3.4 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.282 | ||
| Hyperbilirubinemia | 5 | 17.2 | 2 | 6.1 | 0.165 | 2 | 6.9 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.125 | ||
| Gastrointestinal bleeding | 1 | 3.4 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.282 | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 | - | ||
| Diarrhea | 13 | 44.8 | 4 | 12.1 | 0.004a | 6 | 20.7 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.006a | ||
| Nausea and vomiting | 18 | 62.1 | 3 | 9.1 | 0.000a | 7 | 24.1 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.003a | ||
| Neurotoxicity | 1 | 3.4 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.282 | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 | - | ||
| Allergic reaction | 2 | 6.9 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.125 | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 | - | ||
| Fever | 1 | 3.4 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.282 | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 | - | ||
| Rash | 1 | 3.4 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.282 | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 | - | ||
| Alopecia | 4 | 13.8 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.027a | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 | - | ||
| Pain | 4 | 13.8 | 1 | 3.0 | 0.120 | 2 | 6.9 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.125 | ||
| Hand-foot syndrome | 7 | 24.1 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.003a | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 | - | ||
| Variable | Grade 1-4 | Grade 3/4 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Placebo-BZYQ pills (n = 29) | BZYQ pills-Placebo (n = 33) | P value | Placebo-BZYQ pills (n = 29) | BZYQ pills-Placebo (n = 33) | P value | |||||
| n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | |||
| Hepatic dysfunction events* | 10 | 34.5 | 2 | 6.1 | 0.005a | 1 | 3.4 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.282 |
| Acute kidney injury | 4 | 13.8 | 2 | 6.1 | 0.304 | 1 | 3.4 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.282 |
Table 10 Assessment of AEs: drug safety
| Variable | Grade 1-4 | Grade 3/4 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Placebo-BZYQ pills (n = 29) | BZYQ pills-Placebo (n = 33) | P value | Placebo-BZYQ pills (n = 29) | BZYQ pills-Placebo (n = 33) | P value | |||||
| n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | |||
| Hepatic dysfunction events* | 10 | 34.5 | 2 | 6.1 | 0.005a | 1 | 3.4 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.282 |
| Acute kidney injury | 4 | 13.8 | 2 | 6.1 | 0.304 | 1 | 3.4 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.282 |
| 1. | Siegel RL, Wagle NS, Cercek A, Smith RA, Jemal A. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin 2023; 73: 233-54. |
| 2. | Qian JN, Bao CQ, Hu HY. Research progress of Traditional Chinese Medicine in treatment of gastrointestinal adverse effects of colon cancers caused by chemotherapy. Zhong Guo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xiao Hua Za Zhi 2022; 30: 456-60. |
| 3. |
Davis MP, Dreicer R, Walsh D, Lagman R, LeGrand SB. Appetite and cancer-associated anorexia: a review. J Clin Oncol 2004; 22: 1510-7.
PMID |
| 4. | Hariyanto TI, Kurniawan A. Appetite problem in cancer patients: pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Cancer Treat Res Commun 2021; 27: 100336. |
| 5. |
Shinsyu A, Bamba S, Kurihara M, et al. Inflammatory cytokines, appetite‑regulating hormones, and energy metabolism in patients with gastrointestinal cancer. Oncol Lett 2020; 20: 1469-79.
DOI PMID |
| 6. |
Meng QY, Tan SJ, Jiang Y, et al. Post-discharge oral nutritional supplements with dietary advice in patients at nutritional risk after surgery for gastric cancer: a randomized clinical trial. Clin Nutr 2021; 40: 40-6.
DOI PMID |
| 7. | Schlumberger M, Tahara M, Wirth LJ, et al. Lenvatinib versus placebo in radioiodine-refractory thyroid cancer. N Engl J Med 2015; 372: 621-30. |
| 8. | Gupta A, Nshuti L, Grewal US, et al. Limited benefit and high financial burden of drugs used to manage cancer-associated anorexia/cachexia syndrome (CACS). J Clin Oncol 2021; 39: 55. |
| 9. | Arora N, Ramesh V, Virnig BA, Blaes AH, Gupta A. Medications to manage cancer-associated anorexia/cachexia syndrome (CACS) in patients with advanced gastrointestinal (GI) cancer. J Clin Oncol 2022; 40: 658. |
| 10. |
Naito T, Uchino J, Kojima T, et al. A multicenter, open-label, single-arm study of anamorelin (ONO-7643) in patients with cancer cachexia and low body mass index. Cancer 2022; 128: 2025-35.
DOI PMID |
| 11. |
Zarifi SH, Bagherniya M, Banach M, Johnston TP, Sahebkar A. Phytochemicals: a potential therapeutic intervention for the prevention and treatment of cachexia. Clin Nutr 2022; 41: 2843-57.
DOI PMID |
| 12. |
Ruiz-García V, López-Briz E, Carbonell-Sanchis R, Bort-Martí S, Gonzálvez-Perales JL. Megestrol acetate for cachexia-anorexia syndrome. A systematic review. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2018; 9: 444-52.
DOI PMID |
| 13. | Li J, Yang HY. Clinical observation of Buzhong Yiqi pill in the treatment of breast-cancer-related fatigue. Liaoning Yi Xue Yuan Xue Bao 2015; 36: 12-4. |
| 14. | Ke W. A study of Buzhong Yiqi decoction combined with CapeOX chemotherapy for the treatment of advanced gastric cancer. Ji Ceng Yi Xue Lun Tan 2022; 26: 67-9. |
| 15. |
Costa RGF, Caro PL, De Matos-Neto EM, et al. Cancer cachexia induces morphological and inflammatory changes in the intestinal mucosa. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2019; 10: 1116-27.
DOI PMID |
| 16. | Wilson M-MG, Thomas DR, Rubenstein LZ, et al. Appetite assessment: Simple appetite questionnaire predicts weight loss in community-dwelling adults and nursing home residents. Am J Clin Nutr 2005; 82: 1074-81. |
| 17. |
Sun LY, Mao JJ, Liu Q, Yang YF, He B. Effects of auricular acupuncture on appetite in patients with advanced cancer: a pilot randomized controlled trial. Ann Palliat Med 2020; 9: 1804-11.
DOI PMID |
| 18. | Koh SJ, Oh SY, Baek JY, et al. Validity and reliability of Korean version of simplified nutritional appetite questionnaire in patients with advanced cancer: a multicenter, longitudinal study. J Clin Oncol 2017; 35: 211. |
| 19. | El Alami Y, Essangri H, Majbar MA, et al. Psychometric validation of the Moroccan version of the EORTC QLQ-C 30 in colorectal cancer patients: cross-sectional study and systematic literature review. BMC Cancer 2021; 21: 99. |
| 20. | Wan CH, Chen MQ, Zhang CZ, Tang XL, Meng Q, Zhang XQ. The Chinese version of EORTC QLQ-C3 form in evaluation of quality of life for patients with cancer. Shi Yong Zhong Liu Za Zhi 2005; 20: 353-5. |
| 21. | Kruizenga HM, Seidell JA, De Vet HCW, Van Bokhorst MAE. Development of a short nutritional assessment questionnaire (SNAQ). Clin Nutr 2003; 22: S96. |
| 22. | Ouyang MZ, Liu YY, Tan W, et al. Bu-Zhong-Yi-Qi pill alleviate the chemotherapy-related fatigue in 4 T 1 murine breast cancer model. BMC Complement Altern Med 2014; 14: 497. |
| 23. | Inoue M, Hoshino E. Symptoms of cancer patients and kampo formulas effective for them. Gan Kagaku Ryoho 2015; 42: 2418-22. |
| 24. | He M, Chen WW, Wang MM, et al. Simultaneous determination of multiple bioactive components of Bu-Zhong-Yi-Qi-Tang in rat tissues by LC-MS/MS: application to a tissue distribution study. J Chromatogr B 2017; 1044-1045: 177-84. |
| 25. | Liu K, Wang BJ, Ma H, Song XL, Bian RQ. Influences of Buzhong Yiqi tang on gastrointestinal function and nutriture status of gastric carcinoma after operation. Zhong Guo Shi Yan Fang Ji Xue Za Zhi 2015; 21: 152-6. |
| 26. | Liu XL, Wang RJ, Fu QS. Effect of Buzhongyiqi decoction on MEK/ERKmRNA expression in gastric mucosa of rats with spleen deficiency. Zhong Yao Yao Li Yu Lin Chuang 2013; 29: 5-8. |
| 27. |
Xiong Y, Shang BZ, Xu SY, Zhao R, Gou H, Wang C. Protective effect of Bu-zhong-yi-qi decoction, the water extract of Chinese traditional herbal medicine, on 5-fluorouracil-induced renal injury in mice. Ren Fail 2016; 38: 1240-8.
DOI PMID |
| 28. |
Kim J, Kim H, Kim KH. Effects of Bu-Zhong-Yi-Qi-Tang for the treatment of functional dyspepsia: a feasibility study protocol. Integr Med Res 2017; 6: 317-24.
DOI PMID |
| 29. | Hu LF, Yao ZH, Qin ZF, et al. In vivo metabolic profiles of Bu-Zhong-Yi-Qi-Tang, a famous Traditional Chinese Medicine prescription, in rats by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry. J Pharm Biomed Anal 2019; 171: 81-98. |
| 30. | Cai MD, Yang EJ. Hochu-Ekki-To improves motor function in an amyotrophic lateral sclerosis animal model. Nutrients 2019; 11: 2644. |
| 31. | Yakabe M, Hosoi T, Sasakawa H, Akishita M, Ogawa S. Kampo formula Hochu-Ekki-To (Bu-Zhong-Yi-Qi-Tang, TJ-41) ameliorates muscle atrophy by modulating atrogenes and AMPK in vivo and in vitro. BMC Complement Med Ther 2022; 22: 341. |
| 32. | Ahmadimoghaddam D, Zarei M, Mohammadi S, Izadidastenaei Z, Salehi I. Bupleurum falcatum L. alleviates nociceptive and neuropathic pain: potential mechanisms of action. J Ethnopharmacol 2021; 273: 113990. |
| 33. | Kim SM, Kim SC, Chung IK, Cheon WH, Ku SK. Antioxidant and protective effects of Bupleurum Falcatum on the L-thyroxine-induced hyperthyroidism in rats. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2012; 2012: 578497. |
| 34. | Lee MY, Shin IS, Jeon WY, et al. Protective effect of Bojungikki-tang, a traditional herbal formula, against alcohol-induced gastric injury in rats. J Ethnopharmacol 2012; 142: 346-53. |
| 35. | Li XM, Wang XL, Han CY, et al. Astragaloside IV suppresses collagen production of activated hepatic stellate cells via oxidative stress-mediated p38 MAPK pathway. Free Radic Biol Med 2013; 60: 168-76. |
| 36. | Grabiec K, Burchert M, Milewska M, Błaszczyk M, Grzelkowska-Kowalczyk K. Systemic and local mechanisms leading to cachexia in cancer. Adv Hyg Exp Med 2013; 67: 1397-409. |
| 37. | Shu G, Xu D, Ran CL, et al. Protective effect of dietary supplementation of Bupleurum falcatum L Saikosaponins on ammonia exposure-induced ileum injury in broilers. Poult Sci 2021; 100: 100803. |
| 38. |
Li XJY, Li XY, Huang NN, Liu RP, Sun R. A comprehensive review and perspectives on pharmacology and toxicology of Saikosaponins. Phytomedicine 2018; 50: 73-87.
DOI PMID |
| 39. |
Han H, Yi B, Zhong RQ, et al. From gut microbiota to host appetite: gut microbiota-derived metabolites as key regulators. Microbiome 2021; 9: 162.
DOI PMID |
| 40. |
Utsuyama M, Seidlar H, Kitagawa M, Hirokawa K. Immunological restoration and anti-tumor effect by Japanese herbal medicine in aged mice. Mech Ageing Dev 2001; 122: 341-52.
PMID |
| 41. |
Ishimitsu R, Nishimura H, Kawauchi H, Kawakita T, Yoshikai Y. Dichotomous effect of a traditional Japanese medicine, Bu-Zhong-Yi-Qi-Tang on allergic asthma in mice. Int Immunopharmacol 2001; 1: 857-65.
DOI PMID |
| 42. |
Yamaoka Y, Kawakita T, Nomoto K. Protective effect of a traditional Japanese medicine Hochu-Ekki-To (Chinese name: Bu-Zhong-Yi-Qi-Tang), on the susceptibility against Listeria monocytogenes in infant mice. Int Immunopharmacol 2001; 1: 1669-77.
DOI PMID |
| 43. |
Liu LY, Hu LF, Yao ZH, et al. Mucosal immunomodulatory evaluation and chemical profile elucidation of a classical traditional Chinese formula, Bu-Zhong-Yi-Qi-Tang. J Ethnopharmacol 2019; 228: 188-99.
DOI PMID |
| 44. | Gemta LF, Siska PJ, Nelson ME, et al. Impaired enolase 1 glycolytic activity restrains effector functions of tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells. Sci Immunol 2019; 4: eaap9520. |
| 45. | Tsuge A, Chiba SSK, Yagura Y, et al. Hochuekkito exerts the anti-allergic effects via activating regulatory T cells in a murine model of contact hypersensitivity. J Nat Med 2023; 77: 352-62. |
| 46. |
Kuroiwa A, Liou S, Yan H, Eshita A, Naitoh S, Nagayama A. Effect of a traditional Japanese herbal medicine, Hochu-ekki-to (Bu-Zhong-Yi-Qi Tang), on immunity in elderly persons. Int Immunopharmacol 2004; 4: 317-24.
DOI PMID |
| 47. | Minagawa T, Domen T, Suzuki T, et al. Effectiveness of hochuekkito (Japanese herbal medicine) for general fatigue after introduction of enzalutamide in three cases of castration-resistant prostate cancer. Jpn J Urol 2019; 110: 86-91. |
| 48. | Okabe H, Kinjo Y, Obama KZTK, et al. A randomized phaseⅡ study of S-1 adjuvant chemotherapy with or without Hochu-Ekki-To, a Japanese herbal medicine, for stage Ⅱ/Ⅲ gastric cancer: The KUGC07 (SHOT) trial. Front Oncol 2019; 9: 294. |
| 49. | Nagata N. Current status of Japanese traditional medicine “Kampo” in chemotherapy. Gan Kagaku Ryoho 2015; 42: 2423-9. |
| [1] | WU Qiaomin, GUAN Xuanke, LIU Jinfeng, WANG Yanli, CHANG Xing, LIU Zhiming, LIU Ruxiu. Compound Tongyang Fumai decoction (通阳复脉方) improves quality of life in sick sinus syndrome: a randomized controlled study [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(6): 1247-1253. |
| [2] | WANG Ming, ZHENG Yun. Clinical value of modified Shenling Baizhu powder (加味参苓白术散) in treating targeted therapy-induced diarrhea in non-small cell lung cancer [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(5): 1000-1005. |
| [3] | GU Xiangchen, QIU Meisi, XIE Lin, CHEN Min, DENG Yueyi, ZHANG Changming, JIAN Guihua, WANG Chen, WANG Yi. Individualized Traditional Chinese Medicine treatment vs antibiotics for recurrent urinary tract infections: a multicenter, randomized controlled study [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(3): 524-529. |
| [4] | JIN Tao, ZHOU Qian, SHEN Jichen, ZHANG Zhizhong, LIAN Xiaoyuan. Caffeic acid 3,4-dihydroxyphenethyl ester prevents colorectal cancer through inhibition of multiple cancer-promoting signal pathways in 1,2-Dimethylhydrazine/dextran sodium sulphate mouse model [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 70-77. |
| [5] | LI Xiaohua, DUAN Zhihang, YUE Jianjun, ZHANG Yongyu, LI Yihang, LIU Shifang, NIE Qu, YANG Depo, ZHANG Lixia. Bornyl acetate extracted from Sharen (Fructus Amomi) inhibits proliferation, invasion and induces apoptosis by suppressing phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase/protein kinase B signaling in colorectal cancer [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1081-1091. |
| [6] | JIANG Yiqian, ZHOU Xibin, PU Wenyuan, ZHOU Chunxiang. Sanwu Baisan decoction (三物白散) inhibits colorectal cancer progression in mice by remodeling gut microbiota and tumorigenesis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(3): 466-473. |
| [7] | ZHU Xuewei, LIU Minghui, ZONG Minru, CHEN Qianqian, WANG Jianfeng. Effect of three tongue needles acupoints Lianquan (CV23) and Hegu (LI4) combined with swallowing training on the quality of life of laryngeal cancer patients with dysphagia after surgery [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(4): 617-621. |
| [8] | Lakkana Rerksuppaphol, Sanguansak Rerksuppaphol. Efficacy of short duration versus conventional electroacupuncture in the treatment of obesity: a randomized crossover study [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(2): 256-263. |
| [9] | BI Yingfei, WANG Xianliang, ZHANG Xuan, HOU Yazhu, ZHAO Zhiqiang, REN Xiaoyu, YANG Zhihua, MAO Jingyuan. Protocol to study the effects of Traditional Chinese Medicine on patients with coronary heart disease showing phlegm-heat-stasis symptom pattern [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(5): 826-832. |
| [10] | Zhao Yueyang, Wang Sumei, Li Jinhua, Zhou Yushu, Wu Wanyin, Swei Sunny Hann. Effectiveness and safety of traditional Chinese medical therapy for cancer-related fatigue: a systematic review and Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020, 40(5): 738-748. |
| [11] | Zhang Jinchao, Hu Jing, He Xiujuan, Meng Yujiao, Chen Guangkun, Chen Zhaoxia, Lü Jingjing, Li Ping. Effectiveness of Chinese herbal medicine for primary Raynaud's phenomenon: a systematic review and Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020, 40(4): 509-517. |
| [12] | Pang Lijian, Zhang Haoyang, Lü Xiaodong, Liu Jianping, Liu Chuang, Lü Ling. Preventive and therapeutic effectiveness of Sanfu acupoint herbal patching for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease at stable stages: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020, 40(4): 530-549. |
| [13] | Liu Jian, Wang Yuan, Sun Yue, Huang Chuanbing, Chen Xi, Zhang Wandong, He Liyun, James Cheng-Chung Wei. Efficacy and safety of Xinfeng capsule in the treatment of osteoarthritis:a multicenter, randomized, double-blinded, controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020, 40(2): 284-295. |
| [14] | Li Yifan, Li Juan, Fan Bifa, Wang Yitong, Jiang Juling, Zhang Zhenhua, Wang Xinxing, Lu Wenping. Efficacy and safety of Yiqi Huoxue Jiedu decoction for the treatment of advanced epithelial ovarian cancer patients: a double-blind randomized controlled clinical trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020, 40(1): 103-111. |
| [15] | Li Tiantian, Zhou Dongmei, Xu Xuying, Qu Jianhua, Jiang Chunyan, Lan Haibing, Lou Weihai, Chen Weiwen, Jin Li, Liu Rongqi, Liu Zhiyong, Zhang Cang, Duan Lanhua, Bohua Li, Xu Jingna, Zhou Tao, Jiang Xi, Cao Wei, Zhang Guangzhong, Liu Jianping, Sun Liyun, Wang Ping. Effect of Traditional Chinese Medicine plus narrow-band medium-wave ultraviolet B radiation on moderate-to-severe psoriasis vulgaris in a case series [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2019, 39(05): 692-699. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

