Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (2): 430-436.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2025.02.021
• Original articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Efficacy and safety of Qingwei Zhitong pellets (清胃止痛微丸)-containing quadruple therapy for Helicobacter pylori eradication: a prospective, single-center, randomized trial
CHENG Jianping( ), FAN Chanjuan, ZHAI Lili, WANG Hui, XIE Dongling, CAI Yong, LI Zhen, HUANG Kun, BAI Qixuan
), FAN Chanjuan, ZHAI Lili, WANG Hui, XIE Dongling, CAI Yong, LI Zhen, HUANG Kun, BAI Qixuan
- Department of Gastroenterology and Oncology, Civil Aviation General Hospital, Beijing 100123, China
-
Received:2024-01-22Accepted:2024-06-12Online:2025-04-15Published:2025-03-10 -
Contact:CHENG Jianping, Department of Gastroenterology and Oncology, Civil Aviation General Hospital, Beijing 100123, China. cjpczy2004@163.com, Telephone: +86-15811282039 -
Supported by:China Zhongguancun Precision Medicine Science and Technology Foundation: Study on the Evaluation of Eradication Rate and Safety of Helicobacter Pylori in a Quadruple Therapy using Qingwei Zhitong Pellets as a Substitute for Bismuth Agent(320.6799.2022.09.24)
Cite this article
CHENG Jianping, FAN Chanjuan, ZHAI Lili, WANG Hui, XIE Dongling, CAI Yong, LI Zhen, HUANG Kun, BAI Qixuan. Efficacy and safety of Qingwei Zhitong pellets (清胃止痛微丸)-containing quadruple therapy for Helicobacter pylori eradication: a prospective, single-center, randomized trial[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(2): 430-436.
share this article
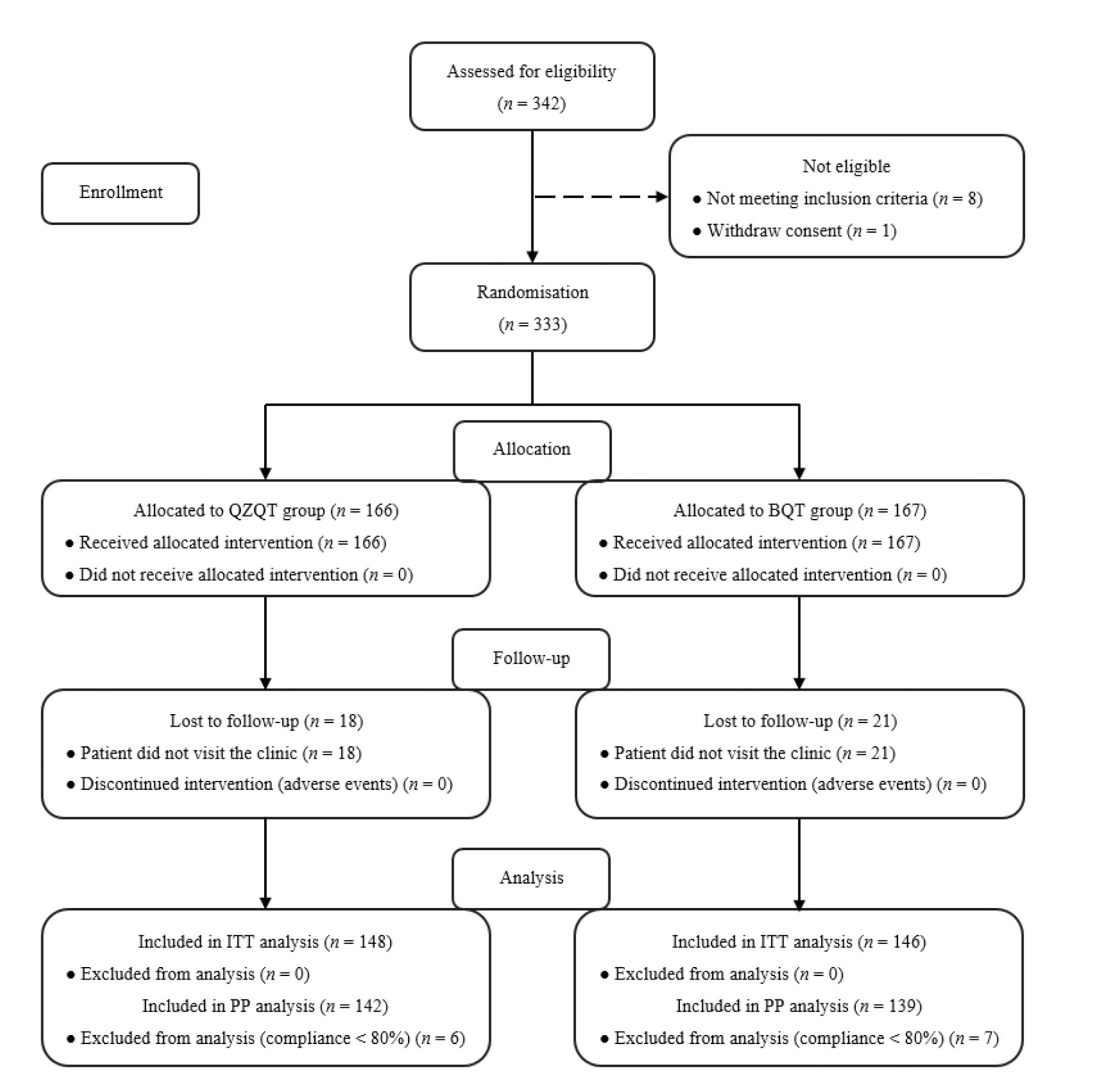
Figure 1 Flow chart of patient enrolment and study design ITT: intention-to-treat; PP: per-protocol; QZQT: Qingwei Zhitong pellets-containing quadruple therapy; BQT: bismuth-containing quadruple therapy.
| Variables | QZQT group (n = 166) | BQT group (n = 167) | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age [years, median (IQR)] | 37.5 (30.0-53.0) | 36.0 (29.0-46.0) | 0.134 | |
| Sex [n (%)] | Male | 76 (45.8) | 77 (46.1) | 0.953 |
| Female | 90 (54.2) | 90 (53.9) | ||
| BMI (kg/m2) | 23.69±3.76 | 23.18±3.53 | 0.208 | |
| Alcohol drinking [n (%)] | 17 (10.2) | 16 (9.6) | 0.840 | |
| Cigarette smoking [n (%)] | 37 (22.3) | 27 (16.2) | 0.156 | |
| Disease duration [n (%)] | ≤1 month | 117 (70.5) | 119 (71.3) | 0.876 |
| >1 month | 49 (29.5) | 48 (28.7) | ||
| Marital status [n (%)] | Married | 114 (68.7) | 100 (59.9) | 0.094 |
| Single or divorced or widowed | 52 (31.3) | 67 (40.1) | ||
| Clinical condition [n (%)] | Epigastric pain | 87 (52.4) | 81 (48.5) | 0.476 |
| Acid reflux | 81 (48.8) | 83 (49.7) | 0.869 | |
| Heartburn | 62 (37.3) | 69 (41.3) | 0.459 | |
| Epigastric distention | 104 (62.7) | 119 (71.3) | 0.095 | |
| Nausea | 50 (30.1) | 69 (41.3) | 0.033 | |
| Dry stool | 50 (30.1) | 36 (21.6) | 0.074 | |
| Dry mouth | 82 (49.4) | 82 (49.1) | 0.957 | |
| Bitter taste of mouth | 56 (33.7) | 56 (33.5) | 0.969 | |
| Oral malodour | 87 (52.4) | 86 (51.5) | 0.868 | |
| Irritability | 58 (34.9) | 50 (29.9) | 0.330 | |
| Diarrhea | 56 (33.7) | 50 (29.9) | 0.457 | |
| Constipation | 70 (42.2) | 58 (34.7) | 0.476 | |
| Comorbidity | Diabetes | 8 (4.8) | 6 (3.6) | 0.577 |
| Hypertension | 15 (9.0) | 22 (13.2) | 0.230 | |
| Baseline GSRS [scores, median (IQR)] | 7.00 (3.75-11.00) | 7.00 (4.00-11.00) | 0.419 | |
| DOB of 13C-UBT [median (IQR)] | 13.65 (6.95-25.43) | 16.10 (9.28-26.85) | 0.306 | |
Table 1 Baseline characteristics of the study patients
| Variables | QZQT group (n = 166) | BQT group (n = 167) | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age [years, median (IQR)] | 37.5 (30.0-53.0) | 36.0 (29.0-46.0) | 0.134 | |
| Sex [n (%)] | Male | 76 (45.8) | 77 (46.1) | 0.953 |
| Female | 90 (54.2) | 90 (53.9) | ||
| BMI (kg/m2) | 23.69±3.76 | 23.18±3.53 | 0.208 | |
| Alcohol drinking [n (%)] | 17 (10.2) | 16 (9.6) | 0.840 | |
| Cigarette smoking [n (%)] | 37 (22.3) | 27 (16.2) | 0.156 | |
| Disease duration [n (%)] | ≤1 month | 117 (70.5) | 119 (71.3) | 0.876 |
| >1 month | 49 (29.5) | 48 (28.7) | ||
| Marital status [n (%)] | Married | 114 (68.7) | 100 (59.9) | 0.094 |
| Single or divorced or widowed | 52 (31.3) | 67 (40.1) | ||
| Clinical condition [n (%)] | Epigastric pain | 87 (52.4) | 81 (48.5) | 0.476 |
| Acid reflux | 81 (48.8) | 83 (49.7) | 0.869 | |
| Heartburn | 62 (37.3) | 69 (41.3) | 0.459 | |
| Epigastric distention | 104 (62.7) | 119 (71.3) | 0.095 | |
| Nausea | 50 (30.1) | 69 (41.3) | 0.033 | |
| Dry stool | 50 (30.1) | 36 (21.6) | 0.074 | |
| Dry mouth | 82 (49.4) | 82 (49.1) | 0.957 | |
| Bitter taste of mouth | 56 (33.7) | 56 (33.5) | 0.969 | |
| Oral malodour | 87 (52.4) | 86 (51.5) | 0.868 | |
| Irritability | 58 (34.9) | 50 (29.9) | 0.330 | |
| Diarrhea | 56 (33.7) | 50 (29.9) | 0.457 | |
| Constipation | 70 (42.2) | 58 (34.7) | 0.476 | |
| Comorbidity | Diabetes | 8 (4.8) | 6 (3.6) | 0.577 |
| Hypertension | 15 (9.0) | 22 (13.2) | 0.230 | |
| Baseline GSRS [scores, median (IQR)] | 7.00 (3.75-11.00) | 7.00 (4.00-11.00) | 0.419 | |
| DOB of 13C-UBT [median (IQR)] | 13.65 (6.95-25.43) | 16.10 (9.28-26.85) | 0.306 | |
| Variable | QZQT grou (n = 166) | BQT group (n = 167) | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total patients | 96 (57.8) | 151 (90.4) | < 0.001 | |
| Adverse events | Dizziness | 9 (5.4) | 13 (7.8) | 0.385 |
| Skin rash | 6 (3.6) | 10 (6.0) | 0.311 | |
| Black stools | 46 (27.7) | 140 (83.8) | < 0.001 | |
| Diarrhea with black stools | 4 (2.4) | 29 (17.4) | < 0.001 | |
| Diarrhea | 15 (9.0) | 30 (18.0) | 0.017 | |
| Bitter taste of mouth | 40 (24.1) | 92 (55.1) | < 0.001 | |
| Nausea | 9 (5.4) | 16 (9.6) | 0.150 | |
| Abdominal pain | 17 (10.2) | 16 (9.6) | 0.840 | |
| Abdominal distension | 18 (10.8) | 11 (6.6) | 0.168 | |
| Constipation | 13 (7.8) | 15 (9.0) | 0.705 | |
| Dysgeusia (taste change) | 4 (2.4) | 10 (6.0) | 0.104 | |
| Treatment compliance | 161 (96.9) | 161 (96.4) | 0.612 | |
Table 2 Overview of drug-induced adverse events of each therapy group [n (%)]
| Variable | QZQT grou (n = 166) | BQT group (n = 167) | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total patients | 96 (57.8) | 151 (90.4) | < 0.001 | |
| Adverse events | Dizziness | 9 (5.4) | 13 (7.8) | 0.385 |
| Skin rash | 6 (3.6) | 10 (6.0) | 0.311 | |
| Black stools | 46 (27.7) | 140 (83.8) | < 0.001 | |
| Diarrhea with black stools | 4 (2.4) | 29 (17.4) | < 0.001 | |
| Diarrhea | 15 (9.0) | 30 (18.0) | 0.017 | |
| Bitter taste of mouth | 40 (24.1) | 92 (55.1) | < 0.001 | |
| Nausea | 9 (5.4) | 16 (9.6) | 0.150 | |
| Abdominal pain | 17 (10.2) | 16 (9.6) | 0.840 | |
| Abdominal distension | 18 (10.8) | 11 (6.6) | 0.168 | |
| Constipation | 13 (7.8) | 15 (9.0) | 0.705 | |
| Dysgeusia (taste change) | 4 (2.4) | 10 (6.0) | 0.104 | |
| Treatment compliance | 161 (96.9) | 161 (96.4) | 0.612 | |
| 1. |
Suzuki S, Gotoda T, Kusano C, et al. Seven-day vonoprazan and low-dose amoxicillin dual therapy as first-line Helicobacter pylori treatment: a multicentre randomised trial in Japan. Gut 2020; 69: 1019-26.
DOI PMID |
| 2. |
Codolo G, Toffoletto M, Chemello F, et al. Helicobacter pylori dampens HLA-Ⅱ expression on macrophages via the up-regulation of miRNAs targeting CIITA. Front Immunol 2019; 10: 2923.
DOI PMID |
| 3. | Gunawardhana N, Jang S, Choi YH, et al. Helicobacter pylori-induced HB-EGF upregulates gastrin expression via the EGF receptor, C-Raf, Mek1, and Erk2 in the MAPK pathway. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2017; 7: 541. |
| 4. | Sun L, Talarico S, Yao L, et al. Droplet digital PCR-based detection of clarithromycin resistance in Helicobacter pylori isolates reveals frequent heteroresistance. J Clin Microbiol 2018; 56: 274. |
| 5. | Ye H, Shi ZM, Chen Y, et al. Innovative perspectives of integrated Chinese medicine on H. pylori. Chin J Integr Med 2018; 24: 873-80. |
| 6. | Ye H, Liu Y, Li N, et al. Anti-Helicobacter pylori activities of Chenopodium ambrosioides L. in vitro and in vivo. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21: 4178-83. |
| 7. | Wu JY, Liou JM, Graham DY. Evidence-based recommendations for successful Helicobacter pylori treatment. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2014; 8: 21-8. |
| 8. | Song Z, Li B, Zhang Y, et al. Outer membrane vesicles of Helicobacter pylori 7.13 as adjuvants promote protective efficacy against Helicobacter pylori infection. Front Microbiol 2020; 11: 1340. |
| 9. | Zhao M, Jiang Y, Chen Z, et al. Traditional Chinese Medicine for Helicobacter pylori infection: a protocol for a systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore) 2021; 100: e24282. |
| 10. | Lin J, Huang WW. A systematic review of treating Helicobacter pylori infection with traditional Chinese medicine. World J Gastroenterol 2009; 15: 4715-19. |
| 11. | He LZ, Zhang Q, Wang SC. Clinical study on treatment of gastric ulcer with Qingwei Zhitong pill. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi 2001; 21: 422-3. |
| 12. | Paavola M, Kanto K, Ranstam J, et al. Subacromial decompression versus diagnostic arthroscopy for shoulder impingement: a 5-year follow-up of a randomised, placebo surgery controlled clinical trial. Br J Sports Med 2021; 55: 99-107. |
| 13. | Ren C, Mai ZJ, Jin Y, et al. Anti-PD-1 antibody SHR-1210 plus apatinib for metastatic colorectal cancer: a prospective, single-arm, open-label, phase Ⅱ trial. Am J Cancer Res 2020; 10: 2946-54. |
| 14. | Bang CS, Lim H, Jeong HM, et al. Amoxicillin or tetracycline in bismuth-containing quadruple therapy as first-line treatment for Helicobacter pylori infection. Gut Microbes 2020; 11: 1314-23. |
| 15. | Yang JC, Lin CJ, Wang HL, et al. High-dose dual therapy is superior to standard first-line or rescue therapy for Helicobacter pylori infection. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2015; 13: 895-905. |
| 16. | Zhou L, Lu H, Song Z, et al. 2022 Chinese national clinical practice guideline on Helicobacter pylori eradication treatment. Chin Med J (Engl) 2022; 135: 2899-2910. |
| 17. | Murakami K, Sakurai Y, Shiino M, et al. Vonoprazan, a novel potassium-competitive acid blocker, as a component of first-line and second-line triple therapy for Helicobacter pylori eradication: a phase Ⅲ, randomised, double-blind study. Gut 2016; 65: 1439-46. |
| 18. | Hsu PI, Lin PC, Graham DY. Hybrid therapy for Helicobacter pylori infection: a systemic review and Meta-analysis. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21: 12954-62. |
| 19. | Hwang JJ, Lee DH, Lee AR, et al. Fourteen- vs seven-day bismuth-based quadruple therapy for second-line Helicobacter pylori eradication. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21: 8132-39. |
| 20. | Chey WD, Wong BCY, Gastroenterology PPCotACo. American college of gastroenterology guideline on the management of Helicobacter pylori infection. Am J Gastroenterol 2007; 102: 1808-25. |
| 21. | Malfertheiner P, Megraud F, O'Morain CA, et al. Management of Helicobacter pylori infection — the Maastricht Ⅳ / Florence consensus report. Gut 2012; 61: 646-64. |
| 22. | Wang L, Lin Z, Chen S, et al. Ten-day bismuth-containing quadruple therapy is effective as first-line therapy for Helicobacter pylori-related chronic gastritis: a prospective randomized study in China. Clin Microbiol Infect 2017; 23: 391-5. |
| 23. | Huang Y, Wang QL, Cheng DD, et al. Adhesion and invasion of gastric mucosa epithelial cells by Helicobacter pylori. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2016; 6: 159. |
| 24. | Hu Q, Peng Z, Li L, et al. The efficacy of berberine-containing quadruple therapy on Helicobacter Pylori eradication in China: a systematic review and Meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Front Pharmacol 2019; 10: 1694. |
| 25. | Nagaraja V, Eslick GD. Evidence-based assessment of proton-pump inhibitors in Helicobacter pylori eradication: a systematic review. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20: 1427-36. |
| 26. | Jing JJ, Liu HY, Hao JK, et al. Gastric cancer incidence and mortality in Zhuanghe, China, between 2005 and 2010. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18: 1262-69. |
| 27. | Jiao Y, Yang H, Qian J, et al. miR-3664-5P suppresses the proliferation and metastasis of gastric cancer by attenuating the NF-κB signaling pathway through targeting MTDH. Int J Oncol 2019; 54: 845-58. |
| 28. | Yen CH, Chiu HF, Huang SY, et al. Beneficial effect of Burdock complex on asymptomatic Helicobacter pylori-infected subjects: a randomized, double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial. Helicobacter 2018; 23: e12469. |
| 29. | Hojo M, Asaoka D, Takeda T, et al. Randomized controlled study on the effects of triple therapy including vonoprazan or rabeprazole for the second-line treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection. Therap Adv Gastroenterol 2020; 13: 1756284820966247. |
| 30. | Li C, Huang P, Wong K, et al. Coptisine-induced inhibition of Helicobacter pylori: elucidation of specific mechanisms by probing urease active site and its maturation process. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 2018; 33: 1362-75. |
| 31. | Li Q, Qu X, Pang X, et al. Berberine protects mice against dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis by activating mTORC 1 pathway. Front Pharmacol 2019; 10: 786. |
| 32. | Tan L, Li C, Chen H, et al. Epiberberine, a natural protoberberine alkaloid, inhibits urease of Helicobacter pylori and jack bean: susceptibility and mechanism. Eur J Pharm Sci 2017; 110: 77-86. |
| 33. | Lin YH, Lin JH, Chou SC, et al. Berberine-loaded targeted nanoparticles as specific Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy: in vitro and in vivo study. Nanomedicine (Lond) 2015; 10: 57-71. |
| 34. | Chang CH, Huang WY, Lai CH, et al. Development of novel nanoparticles shelled with heparin for berberine delivery to treat Helicobacter pylori. Acta Biomater 2011; 7: 593-603. |
| 35. | Zhang D, Ke L, Ni Z, et al. Berberine containing quadruple therapy for initial Helicobacter pylori eradication: an open-label randomized phase IV trial. Medicine (Baltimore) 2017; 96: e7697. |
| 36. | Liang CM, Tai WC, Hsu PI, et al. Trend of changes in antibiotic resistance in Helicobacter pylori from 2013 to 2019:a multicentre report from Taiwan. Therap Adv Gastroenterol 2020; 13: 1756284820976990. |
| 37. | Zhang YX, Zhou LY, Song ZQ, et al. Primary antibiotic resistance of Helicobacter pylori strains isolated from patients with dyspeptic symptoms in Beijing: a prospective serial study. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21: 2786-92. |
| 38. | Li SY, Li J, Dong XH, et al. The effect of previous eradication failure on antibiotic resistance of Helicobacter pylori: a retrospective study over 8 years in Beijing. Helicobacter 2021; 26: e12804. |
| 39. | Megraud F, Coenen S, Versporten A, et al. Helicobacter pylori resistance to antibiotics in Europe and its relationship to antibiotic consumption. Gut 2013; 62: 34-42. |
| 40. | Savoldi A, Carrara E, Graham DY, et al. Prevalence of antibiotic resistance in Helicobacter pylori: a systematic review and Meta-analysis in World Health Organization regions. Gastroenterology 2018; 155: 1372-82. |
| 41. |
Emara MH, Mohamed SY, Abdel-Aziz HR. Lactobacillus reuteri in management of Helicobacter pylori infection in dyspeptic patients: a double-blind placebo-controlled randomized clinical trial. Therap Adv Gastroenterol 2014; 7: 4-13
DOI PMID |
| [1] | XIAO Jing, SONG Danlei, LIANG Caiming, HE Yinuo, ZHENG Weifang, WU Xiaqiu. Efficacy of Jianpi formulas (健脾剂) in reducing the recurrence of colorectal adenoma after polypectomy: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(2): 225-233. |
| [2] | LAI Xiaolei, SHANG Juju, LIU Hongxu, HU Jing, LI Xiang, ZHANG Zhenmin, XING Wenlong. Clinical efficacy of Angong Jiangya pill (安宫降压丸) for grade 2 hypertension with liver-fire hyperactivity syndrome: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(2): 422-429. |
| [3] | Nima Vaziri, Gholamreza Dehghannoudeh, Fariba Sharififar, Fatemeh Dabaghzadeh, Farhad Sarafzadeh, Bizhan Ahmadi. Salvia mirzayanii Rech. f. & Esfand as adjunctive therapy for Helicobacter pylori eradication: a randomized controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(2): 437-442. |
| [4] | YE Wujie, YANG Yawei, ZHANG Da, TANG Ling, CUI Minying, FU Bin, ZHANG Meng, HU Xingang, ZHAO Yan. Effectiveness of combining Qingyanyin formulated granules (轻燕饮配方颗粒) with press needles in treating abdominal obesity: a multicenter randomized controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(1): 107-114. |
| [5] | LANG Jiawang, JIN Lingqing, LUO Jianchang, LANG Boxu. Effects of acupuncture combined with bone-setting therapy to treat tourette syndrome: a three-arm randomized controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(1): 176-183. |
| [6] | Emre Bulut, Didem Özkal Eminoğlu, Yasemin Çayır. Effect of electroacupuncture on pain after periodontal flap surgery: a randomized controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(1): 184-191. |
| [7] | WU Qiaomin, GUAN Xuanke, LIU Jinfeng, WANG Yanli, CHANG Xing, LIU Zhiming, LIU Ruxiu. Compound Tongyang Fumai decoction (通阳复脉方) improves quality of life in sick sinus syndrome: a randomized controlled study [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(6): 1247-1253. |
| [8] | QIAN Jianan, XU Yan, HU Hongyi, ZHAO Aiguang. Clinical efficacy and safety evaluation of Buzhongyiqi pills (补中益气丸) on appetite improvement in patients with colorectal cancer receiving chemotherapy: a pilot randomized cross-over clinical trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(6): 1254-1267. |
| [9] | DENG Yasheng, HAN Siyin, XI Lanhua, HUANG Hui, LIANG Tianwei, ZHENG Yiqing, FAN Yanping, LIN Jiang. Traditional Chinese Medicine in the treatment of recurrent respiratory tract infections in children: an overview of systematic reviews and Meta-analyses [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(5): 871-884. |
| [10] | GU Xiangchen, QIU Meisi, XIE Lin, CHEN Min, DENG Yueyi, ZHANG Changming, JIAN Guihua, WANG Chen, WANG Yi. Individualized Traditional Chinese Medicine treatment vs antibiotics for recurrent urinary tract infections: a multicenter, randomized controlled study [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(3): 524-529. |
| [11] | TIAN Haolin, YANG Yuanbin, ZHANG Hu, ZHAO Wenjing, ZHOU Jing, TIAN Jingfeng, HE Long, LI Xuechao, SHEN Qinxuan, SHUAI Mei. Efficacy of Daoyin combined with lower limb robot as a comprehensive rehabilitation intervention for stroke patients: a randomized controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(3): 530-536. |
| [12] | LI Xiyu, YANG Yanhong, SUN Jian, NIE Quanfang, LIU Lifen, LI Guifen, YU Junping, ZHANG Zhuangjin, XU Yi, ZOU Ting, SHI Yun. Effectiveness and safety of Jiawei Xiaoyao pill (加味逍遥丸) in the treatment of premenstrual syndrome (liver depression, spleen deficiency, and blood-heat syndrome): a multi-center, randomized, placebo-controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(2): 373-380. |
| [13] | YU Zhengqiu, YU Liuda, CHEN Ye, LI Mingjing, CAI Wanru. Effectiveness and safety of Qidong Huoxue decoction (芪冬活血饮) in treatment of acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome: a randomized, controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(2): 381-387. |
| [14] | WANG Shaosong, SUN Jingqing, FENG Qingyin, LI Bin, WANG Xin, YUAN Fan, CUI Yingxue. Effectivenss of electroacupuncture for skeletal muscle pain in Parkinson's disease: a Clinical randomized controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(2): 388-395. |
| [15] | ZHOU Mingwang, DONG Zhuanli, WEI Changhao, FENG Lufang, WANG Xiaoping, LIU Haiping, JI Xing, YANG Kehu, LI Shenghua. Efficacy and safety of extracorporeal shock wave therapy combined with sodium hyaluronate in treatment of knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(2): 243-250. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

