Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (6): 1168-1175.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20230814.002
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Jianpi Qutan Fang (健脾祛痰方) induces anti-atherosclerosis and ameliorates endothelial cell injury in high-fat diet rats via an anti-inflammatory and inhibiting Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription signaling pathway
LIU Yue1, ZHANG Fan2, HAN Xiaomeng2, XU Ningyang2, ZHAO Yu2, WANG Qige2, WANG Jianan2, LU Bingjiu3( ), Zhang Yan4(
), Zhang Yan4( )
)
- 1 Studio of Prestigious Chinese physician Zhang Yan, Affiliated hospital, Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenyang 110000, China
2 Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenyang 110000, China
3 Department of Infectious Disease, Affiliated hospital, Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenyang 110000, China
4 Studio of Prestigious Chinese physician Zhang Yan, Department of Cardiopulmonary Rehabilitation, Affiliated hospital, Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenyang 110000, China
-
Received:2022-06-12Accepted:2022-10-22Online:2023-10-25Published:2023-08-14 -
Contact:LU Bingjiu, Department of Infectious Disease, Affiliated Hospital, Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenyang 110000, China. lubingjiu@163.com; ZHANG Yan, Department of Cardiopulmonary rehabilitation, Affiliated hospital, Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenyang 110000, China. Yanzhang1016@163.com. Telephone: +86-24-31961603 -
Supported by:Explore the Regulatory Mechanism of Coronary Endothelial Immune Inflammation Mediated by MicroRNA155-SOCS1 Axis in Bama Pigs based on “Xin Shou Qi Yu Pi”(81703970);Study on the Therapeutic Mechanism and Rule of Treating Angina Pectoris based on “Cong Pi Lun Zhi”(2013CB531704)
Cite this article
LIU Yue, ZHANG Fan, HAN Xiaomeng, XU Ningyang, ZHAO Yu, WANG Qige, WANG Jianan, LU Bingjiu, Zhang Yan. Jianpi Qutan Fang (健脾祛痰方) induces anti-atherosclerosis and ameliorates endothelial cell injury in high-fat diet rats via an anti-inflammatory and inhibiting Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription signaling pathway[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1168-1175.
share this article
| Group | n | TC | TG | LDL | HDL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 6 | 198.5±34.7a | 36.7±7.3a | 32.0±4.5a | 73.6±4.6a |
| Model | 6 | 569.4±56.5b | 103.1±3.2b | 90.4±9.6b | 17.9±3.1b |
| Atorvastatin | 6 | 438.0±27.1ab | 90.0±4.6ab | 64.3±5.7ab | 49.5±2.6ab |
| Quarter-dose JPQT | 6 | 510.7±28.3ac | 102.2±3.0d | 87.0±3.0d | 32.5±1.8ab |
| Half-dose JPQT | 6 | 467.2±21.8ab | 97.5±1.7d | 76.6±2.4ab | 33.4±2.8ab |
| JPQT | 6 | 367.2±43.5ab | 90.6±3.7ab | 63.6±5.6ab | 48.5±3.2ab |
| Double-dose JPQT | 6 | 321.1±42.9ab | 76.4±7.1ab | 53.5±4.6ab | 61.4±2.8ab |
| Quadruple-dose JPQT | 6 | 208.2±38.8a | 56.1±6.1ab | 46.9±2.7ab | 70.3±5.3a |
| F value | 76.395 | 137.444 | 37.491 | 194.175 | |
| P value | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
Table 1 Effect of JPQT on rat serum lipid levels (μmol/L, $\bar{x}$ ± s)
| Group | n | TC | TG | LDL | HDL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 6 | 198.5±34.7a | 36.7±7.3a | 32.0±4.5a | 73.6±4.6a |
| Model | 6 | 569.4±56.5b | 103.1±3.2b | 90.4±9.6b | 17.9±3.1b |
| Atorvastatin | 6 | 438.0±27.1ab | 90.0±4.6ab | 64.3±5.7ab | 49.5±2.6ab |
| Quarter-dose JPQT | 6 | 510.7±28.3ac | 102.2±3.0d | 87.0±3.0d | 32.5±1.8ab |
| Half-dose JPQT | 6 | 467.2±21.8ab | 97.5±1.7d | 76.6±2.4ab | 33.4±2.8ab |
| JPQT | 6 | 367.2±43.5ab | 90.6±3.7ab | 63.6±5.6ab | 48.5±3.2ab |
| Double-dose JPQT | 6 | 321.1±42.9ab | 76.4±7.1ab | 53.5±4.6ab | 61.4±2.8ab |
| Quadruple-dose JPQT | 6 | 208.2±38.8a | 56.1±6.1ab | 46.9±2.7ab | 70.3±5.3a |
| F value | 76.395 | 137.444 | 37.491 | 194.175 | |
| P value | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Group | n | IL-1β (ng/L) | IL-6 (pg/mL) | IL-8 (ng/L) | IL-10 (ng/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 6 | 12.8±1.8a | 26.9±2.1a | 138.3±6.8a | 47.4±2.1a |
| Model | 6 | 29.8±0.9b | 76.0±1.6b | 317.1±9.1b | 18.3±1.5b |
| Atorvastatin | 6 | 22.0±0.5ab | 56.0±1.7ab | 253.1±18.1ab | 41.2±1.9ab |
| Quarter-dose JPQT | 6 | 27.1±1.5ab | 68.4±1.8ab | 284.5±11.8ab | 28.6±2.1ab |
| Half-dose JPQT | 6 | 23.5±1.2ab | 63.6±1.8ab | 284.0±6.7ab | 32.3±2.2ab |
| JPQT | 6 | 21.7±0.5ab | 55.4±2.5ab | 249.9±9.4ab | 38.5±1.1ab |
| Double-dose JPQT | 6 | 19.5±0.7ab | 47.2±2.0ab | 203.4±14.9ab | 41.3±1.4ab |
| Quadruple-dose JPQT | 6 | 18.5±1.2ab | 40.3±3.7ab | 174.4±8.4ab | 46.2±1.2ab |
| F value | 127.489 | 296.516 | 174.695 | 131.482 | |
| P value | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
Table 2 Effect of JPQT on rat serum inflammatory cytokines levels ($\bar{x}$ ± s)
| Group | n | IL-1β (ng/L) | IL-6 (pg/mL) | IL-8 (ng/L) | IL-10 (ng/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 6 | 12.8±1.8a | 26.9±2.1a | 138.3±6.8a | 47.4±2.1a |
| Model | 6 | 29.8±0.9b | 76.0±1.6b | 317.1±9.1b | 18.3±1.5b |
| Atorvastatin | 6 | 22.0±0.5ab | 56.0±1.7ab | 253.1±18.1ab | 41.2±1.9ab |
| Quarter-dose JPQT | 6 | 27.1±1.5ab | 68.4±1.8ab | 284.5±11.8ab | 28.6±2.1ab |
| Half-dose JPQT | 6 | 23.5±1.2ab | 63.6±1.8ab | 284.0±6.7ab | 32.3±2.2ab |
| JPQT | 6 | 21.7±0.5ab | 55.4±2.5ab | 249.9±9.4ab | 38.5±1.1ab |
| Double-dose JPQT | 6 | 19.5±0.7ab | 47.2±2.0ab | 203.4±14.9ab | 41.3±1.4ab |
| Quadruple-dose JPQT | 6 | 18.5±1.2ab | 40.3±3.7ab | 174.4±8.4ab | 46.2±1.2ab |
| F value | 127.489 | 296.516 | 174.695 | 131.482 | |
| P value | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Group | n | Complex I | Complex Ⅱ | Complex Ⅲ | Complex Ⅳ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 6 | 6375±261a | 1265±202a | 1011±63a | 4608±215a |
| Model | 6 | 1618±407b | 199±38b | 231±27b | 555±70b |
| Atorvastatin | 6 | 4848±164ab | 762±44ab | 516±26ab | 2839±153ab |
| Quarter-dose JPQT | 6 | 3207±193ab | 257±29b | 323±20ab | 1003±158ab |
| Half-dose JPQT | 6 | 3992±241ab | 609±13ab | 354±29ab | 1561±169ab |
| JPQT | 6 | 4572±145ab | 687±81ab | 452±23ab | 2351±130ab |
| Double-dose JPQT | 6 | 5186±137ab | 944±55ab | 647±34ab | 3150±144ab |
| Quadruple-dose JPQT | 6 | 5918±233ab | 1029±44ab | 873±34ab | 3763±249ab |
| F value | 249.455 | 114.437 | 380.62 | 406.357 | |
| P value | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
Table 3 Measurement of mitochondrial respiratory enzyme activity (U/g, $\bar{x}$ ± s)
| Group | n | Complex I | Complex Ⅱ | Complex Ⅲ | Complex Ⅳ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 6 | 6375±261a | 1265±202a | 1011±63a | 4608±215a |
| Model | 6 | 1618±407b | 199±38b | 231±27b | 555±70b |
| Atorvastatin | 6 | 4848±164ab | 762±44ab | 516±26ab | 2839±153ab |
| Quarter-dose JPQT | 6 | 3207±193ab | 257±29b | 323±20ab | 1003±158ab |
| Half-dose JPQT | 6 | 3992±241ab | 609±13ab | 354±29ab | 1561±169ab |
| JPQT | 6 | 4572±145ab | 687±81ab | 452±23ab | 2351±130ab |
| Double-dose JPQT | 6 | 5186±137ab | 944±55ab | 647±34ab | 3150±144ab |
| Quadruple-dose JPQT | 6 | 5918±233ab | 1029±44ab | 873±34ab | 3763±249ab |
| F value | 249.455 | 114.437 | 380.62 | 406.357 | |
| P value | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |

Figure 1 JPQT ameliorated histopathological changes in rat aorta (HE staining, ×200) A: normal control group (normal diet + normal saline); B: model group (HFD + normal saline); C: Atorvastatin group (8 weeks, HFD + 10 mg/kg Atorvastatin); D: Quarter-dose Jianpi Qutan Fang (8 weeks, HFD + 2.225 g/kg Jianpi Qutan Fang); E: Half-dose Jianpi Qutan Fang (8 weeks, HFD + 4.45 g/kg Jianpi Qutan Fang); F: Jianpi Qutan Fang (8 weeks, HFD + 8.9 g/kg Jianpi Qutan Fang); G: Double-dose Jianpi Qutan Fang (8 weeks, HFD + 17.8 g/kg Jianpi Qutan Fang); H: Quadruple-dose Jianpi Qutan Fang (8 weeks, HFD + 35.6 g/kg Jianpi Qutan Fang). JPQT: Jianpi Qutan Fang; HE: hematoxylin-eosin staining.
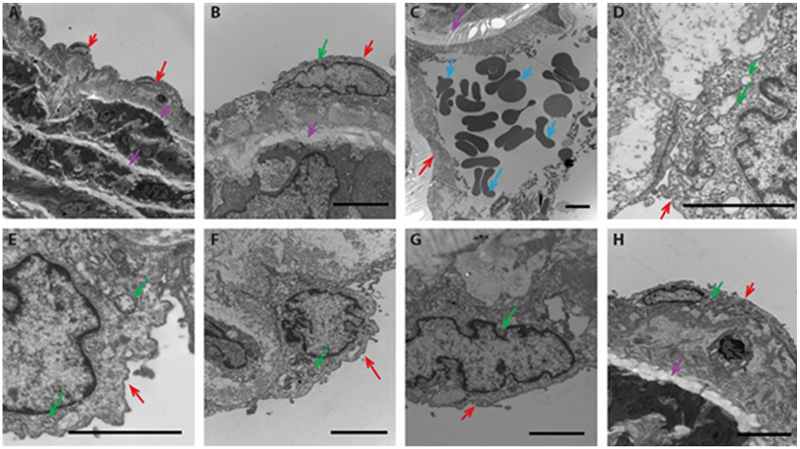
Figure 2 JPQT ameliorated ultrastructural changes in rat aorta Transmission electron microscope observe the subcellular structure of the thoracic aorta. A-B: normal control group (normal diet + normal saline), C-D: model group (HFD + normal saline), E: atorvastatin group (8 weeks, HFD + 10 mg/kg Atorvastatin), F: JPQT group (8 weeks, HFD + 8.9 g/kg JPQT), G: double-dose JPQT group (8 weeks, HFD + 17.8 g/kg JPQT), H: quadruple-dose JPQT group (8 weeks, HFD + 35.6 g/kg JPQT). Scale bar = 2 μm. Red arrow: the endothelial cells; blue arrow: the blood cells; pink arrow: elastic fibers and collagen fibers; green arrow: mitochondria.
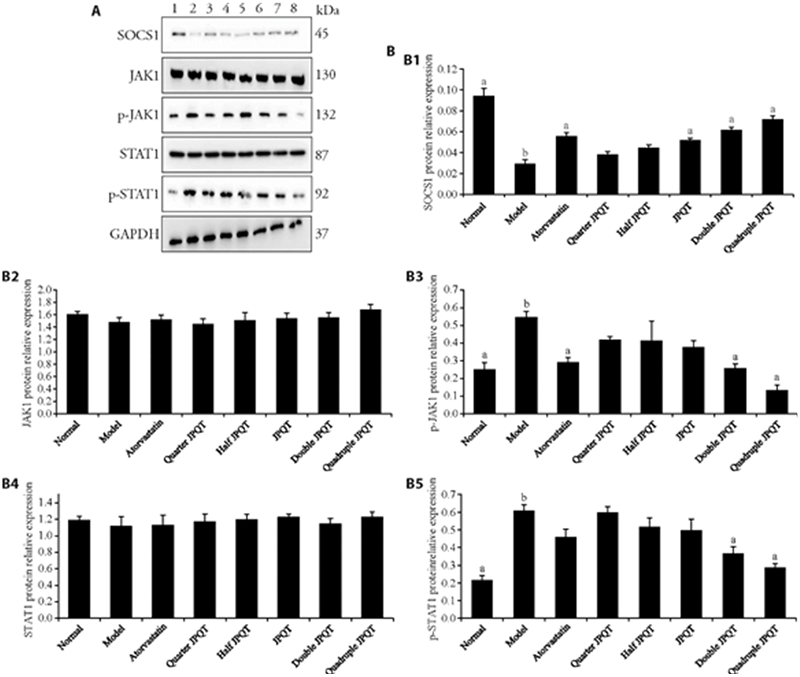
Figure 3 JPQT inhibited JAK/STAT signaling pathway via upregulating SOCS1 protein expression in the aortic tissues of HFD fed rat A: expression of aortic SOCS1/JAK1/STAT1 signaling pathway proteins levels by Western blot; B: normalized against GAPDH. 1: Normal: normal control group (normal diet + normal saline); 2: Model: model group (HFD + normal saline); 3: Atorvastatin: atorvastatin group (HFD + 10 mg/kg Atorvastatin); 4: Quarter-dose JPQT: quarter-dose Jianpi Qutan Fang (HFD + 2.225 g/kg JPQT); 5: Half-dose JPQT: half-dose Jianpi Qutan Fang (HFD + 4.45 g/kg JPQT); 6: JPQT: Jianpi Qutan Fang (HFD + 8.9 g/kg JPQT); 7: Double-dose JPQT: double-doseJianpi Qutan Fang (HFD + 17.8 g/kg JPQT); 8: Quadruple-dose JPQT: quadruple-dose Jianpi Qutan Fang (HFD + 35.6 g/kg JPQT). JPQT: Jianpi Qutan Fang; JAK: Janus kinase; STAT: signal transducer and activator of transcription; SOCS1: suppressor of cytokine signaling 1; HFD: high-fat diet. Student t-test and one-way analysis of variance were used for comparison analysis. aP < 0.01 compared with model group; bP < 0. 01 compared with the normal group; cP < 0.05 compared with model group; dP < 0.05 compared with the normal group. Statistical significance between the groups was determined by one-way analysis of variance. The sample size for each group was 5.
| 1. | Benjamin EJ, Virani SS, Callaway CW, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2018 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2018; 137: e67-492. |
| 2. | Benjamin EJ, Blaha MJ, Chiuve SE, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2017 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2017; 135: e146-603. |
| 3. |
Emerging Risk Factors Collaboration, Di Angelantonio E, Sarwar N, et al. Major lipids, apolipoproteins, and risk of vascular disease. JAMA 2009; 302: 1993-2000.
DOI PMID |
| 4. |
Zhao XX, Liu J, Zhao H, et al. The effect of cardiovascular risk factors on the carotid intima-media thickness in an old-aged cohort with hypertension: a longitudinal evolution with 4-year follow-up of a random clinical trial. Clin Exp Hypertens 2019; 41: 49-57.
DOI URL |
| 5. |
Toth PP. Triglyceride-rich lipoproteins as a causal factor for cardiovascular disease. Vasc Health Risk Manag 2016; 12: 171-83.
DOI PMID |
| 6. |
Poznyak A, Grechko AV, Poggio P, et al. The diabetes mellitus-atherosclerosis connection: the role of lipid and glucose metabolism and chronic inflammation. Int J Mol Sci 2020; 21: 1835.
DOI URL |
| 7. |
Nimai C Chandra. Atherosclerosis and carcinoma: two facets of dysfunctional cholesterol homeostasis. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 2020; 34: e22595.
DOI URL |
| 8. |
Meurer L, Cohen SM. Drug-induced liver injury from statins. Clin Liver Dis 2020; 24: 107-19.
DOI PMID |
| 9. |
Vinci P, Panizon E, Tosoni LM, et al. Statin-associated myopathy: emphasis on mechanisms and targeted therapy. Int J Mol Sci 2021; 22: 11687.
DOI URL |
| 10. | Wu PS (Wei dynasty), Sun XY (Qing dynasty), Feng MY (Qing dynasty. Shen Nong Ben Cao Jing. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House, 1984: 27. |
| 11. |
Wang Y, Liu L, Ma Y, et al. Chemical discrimination of Astragalus mongholicus and Astragalus membranaceus based on metabolomics using UHPLC-ESI-Q-TOF-MS/MS Approach. Molecules 2019; 24: 4064.
DOI URL |
| 12. |
Zhu Z, Li J, Zhang X. Astragaloside Ⅳ protects against oxidized low-density lipoprotein (ox-LDL)-induced endothelial cell injury by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation. Med Sci Monit 2019; 25: 2132-40.
DOI URL |
| 13. | Yang Y, Pei K, Zhang Q, et al. Salvianolic acid B ameliorates atherosclerosis via inhibiting YAP/TAZ/JNK signaling pathway in endothelial cells and pericytes. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids 2020; 1865: 158779. |
| 14. |
Wang YL, Zhang Q, Yin SJ, et al. Screening of blood-activating active components from Danshen-Honghua herbal pair by spectrum-effect relationship analysis. Phytomedicine 2019; 54: 149-58.
DOI URL |
| 15. |
Li ZM, Xu SW, Liu PQ. Salvia miltiorrhiza Burge (Danshen): a golden herbal medicine in cardiovascular therapeutics. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2018; 39: 802-24.
DOI URL |
| 16. | Aguilar-Ballester M, Herrero-Cervera A, Vinué Á, Martínez-Hervás S, González-Navarro H. Impact of cholesterol metabolism in immune cell function and atherosclerosis. Nutrients 2020; 12: 2021. |
| 17. |
Wojda A, Janczy A, Małgorzewicz S. Mediterranean, vegetarian and vegan diets as practical outtakes of EAS and ACC/AHA recommendations for lowering lipid profile. Acta Biochim Pol 2021; 68: 41-8.
DOI PMID |
| 18. | Ouchi Y, Sasaki J, Arai H, et al. Ezetimibe lipid-lowering trial on prevention of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in 75 or older (EWTOPIA 75): a randomized, controlled trial. Circulation 2019;140: 992-1003. |
| 19. |
Xu Y, Li F, Zhao X, et al. Methionine sulfoxide reductase a attenuates atherosclerosis via repairing dysfunctional HDL in scavenger receptor class B type I deficient mice. FASEB J 2020; 34: 3805-19.
DOI URL |
| 20. |
Pownall HJ, Rosales C, Gillard BK, Gotto AM Jr. High-density lipoproteins, reverse cholesterol transport and atherogenesis. Nat Rev Cardiol 2021; 18: 712-23.
DOI PMID |
| 21. |
Bonaventura A, Montecucco F, Dallegri F, et al. Novel findings in neutrophil biology and their impact on cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc Res 2019; 115: 1266-85.
DOI PMID |
| 22. |
Persson J, Nilsson J, Lindholm MW. Interleukin-1beta and tumour necrosis factor-alpha impede neutral lipid turnover in macrophage-derived foam cells. BMC Immunol 2008; 9: 70.
DOI PMID |
| 23. |
Hartman J, Frishman WH. Inflammation and atherosclerosis: a review of the role of interleukin-6 in the development of atherosclerosis and the potential for targeted drug therapy. Cardiol Rev 2014; 22: 147-51.
DOI PMID |
| 24. | Zhang L, Li HY, Li H, et al. Lipopolysaccharide activated phosphatidylcholine -specific phospholipase C and induced IL-8 and MCP-1 production in vascular endothelial cells. J Cell Physiol 2011;226: 1694-701. |
| 25. | Kamari Y, Shaish A, Shemesh S, et al. Reduced atherosclerosis and inflammatory cytokines in apolipoprotein-E-deficient mice lacking bone marrow-derived interleukin-1α. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2011; 405: 197-203. |
| 26. |
Kahraman S, Yilmaz R, Arici M, et al. IL-10 genotype predicts serum levels of adhesion molecules, inflammation and athero-sclerosis in hemodialysis patients. J Nephrol 2006; 19: 50-6.
PMID |
| 27. |
Yu CR, Mahdi RR, Oh HM, et al. Suppressor of cytokine signaling-1 (SOCS1) inhibits lymphocyte recruitment into the retina and protects SOCS1 transgenic rats and mice from ocular inflammation. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2011; 52: 6978-86.
DOI URL |
| 28. | Baldini C, Moriconi FR, Galimberti S, Libby P, De Caterina R. The JAK-STAT pathway: an emerging target for cardiovascular disease in rheumatoid arthritis and myeloproliferative neoplasms. Eur Heart J 2021;4 2: 4389-400. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

