Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (6): 980-987.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20220817.001
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Efficacy of Moxa-burning heat stimulating Zusanli (ST36) and Shenshu (BL23) on expressions of macrophage migration inhibitory factor and macrophage apoptosis in rabbits with adjuvant-induced arthritis
ZHOU Haiyan, ZHONG Yumei2, GAO Xiuhua3, WU Fei4, JIA Min5( ), YANG Xin6(
), YANG Xin6( )
)
- 1 School of Acupuncture-Moxibustion and Tuina, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu 610075, China
2 Pain Department, Chengdu First People's Hospital/ Chengdu Integrated TCM & Western Medicine Hospital, Chengdu 610095, China
3 Centre of Preventive Treatment of Disease, Teaching Hospital of Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu 610075, China
4 Foreign Languages School, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu 610075, China
5 Acupuncture Department, Second Affiliated Hospital of Baotou Medical College, Baotou 014030, China
6 Health Rehabilitation School, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu 610075, China
-
Received:2021-09-16Accepted:2021-12-21Online:2022-12-15Published:2022-08-17 -
Contact:JIA Min,YANG Xin -
About author:Associate Prof. YANG Xin, Health Rehabilitation School, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu 610075, China. yangxin@cdutcm.edu.cn,Telephone: +86-13551039390
Associate chief doctor JIA Min, Acupuncture Department, Second Affiliated Hospital of Baotou Medical College, Baotou 014030, China. 401877133@qq.com;
-
Supported by:Study on the Immune Mechanisms of Macrophage M1/M2 Polarization in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis by Moxibustion “Strengthening Body Resistance and Eliminating Evil”(81973959);Research on “Immune-Inflammation” Molecular Signal Regulation of NLRP3 Inflammasomes in RA with Moxibustion Treatment(81774435);Research on the Functional Characterics of “Special Effect” and “Common Effect” of Acupoints(2019YFC1709001);Research on MIF-GC Rhythm Regulation Mechanism of Moxibustion in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis(2018JC007);Research on the Mechanism of “MIF-target Protein-GC-inflammation” of Anti-inflammatory Effect of Moxibustion on Rheumatoid Arthritis(QNXZ2018034)
Cite this article
ZHOU Haiyan, ZHONG Yumei, GAO Xiuhua, WU Fei, JIA Min, YANG Xin. Efficacy of Moxa-burning heat stimulating Zusanli (ST36) and Shenshu (BL23) on expressions of macrophage migration inhibitory factor and macrophage apoptosis in rabbits with adjuvant-induced arthritis[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(6): 980-987.
share this article

Figure 1 Apoptosis rate of macrophages in control, RA and Moxibustion group A-C: terminal deoxynucleotide transferase-mediated dUTP nick end labeling staining (× 400). A to C representative images show the apoptosis of macrophages in control (A), RA (B) and moxibustion (C) group. Black arrow indicates the apoptosis of macrophages. D showed the statistical analysis of the apoptosis of macrophages. n =10 for each group. RA group and Moxa group were established by injecting FCA (0.5 mL/kg) into the bilateral posterior knee joints. Control group was injected with the same volume sterile normal saline in the same way. Moxa group was treated by moxa-burning heat on Zusanli (ST36) and Shenshu (BL23) once 1 d for 3 courses after FCA injection. Other two groups were fixed with the same method for the same time without moxibustion. Data were expressed as the mean ± standard deviation. Compared with the Control group, aP < 0.01; compared with the RA group, bP < 0.05. RA: rheumatoid arthritis; FCA: Freund’s complete adjuvant.

Figure 2 Immunohistochemical assessment the expression of ERK2 in control, RA, and moxibustion group A-C: immunohistochemistry (S-P) analysis (×400). Representative images show the expression of ERK2 in synovial tissues of control (A), RA (B) and moxibustion (C) group. Black arrow indicates the position expression of ERK2. D represented the statistical analysis of the expression of ERK2. n =10 for each group. RA group and Moxa group were established by injecting FCA (0.5 mL/kg) into the bilateral posterior knee joints. Control group was injected with the same volume sterile normal saline in the same way. Moxa group was treated by moxa-burning heat on Zusanli (ST36) and Shenshu (BL23) once 1day for 3 courses after FCA injection. Other two groups were fixed with the same method for the same time without moxibustion. Data were expressed as the mean ± standard deviation. Compared with the Control group, aP < 0.01; compared with the RA group, bP < 0.05. ERK: extracellular regulated protein kinases; RA: rheumatoid arthritis; FCA: Freund’s complete adjuvant.
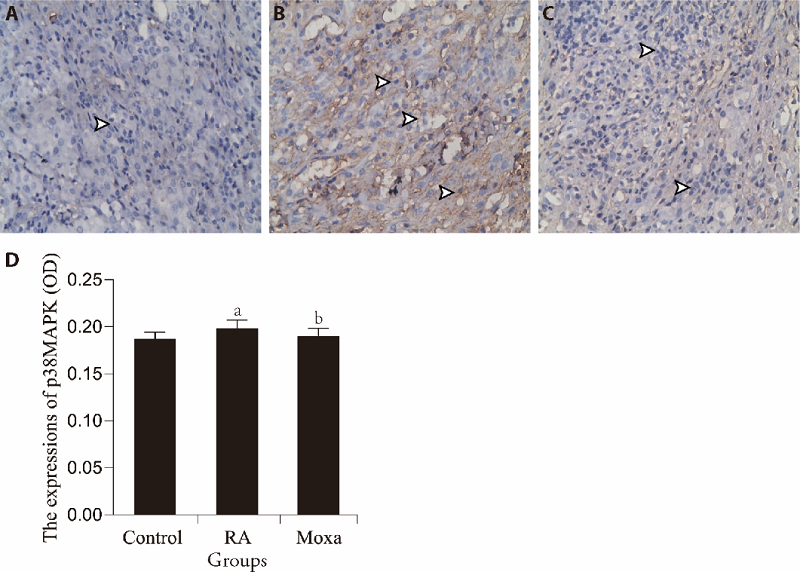
Figure 3 Immunohistochemical assessment the expression of p38MAPK in control, RA and Moxa group A-C: immunohistochemistry (S-P) analysis (× 400). A to C representative images show the expression of p38MAPK in synovial tissues of control (A), RA (B) and moxibustion (C) group. D represented the statistical analysis of the expression of p38MAPK. n =10 for each group. RA group and moxa group were established by injecting FCA (0.5 mL/kg) into the bilateral posterior knee joints. Control group was injected with the same volume sterile normal saline in the same way. Moxa group was treated by moxa-burning heat on Zusanli (ST36) and Shenshu (BL23) once 1 d for 3 courses after FCA injection. Other two groups were fixed with the same method for the same time without moxibustion. Data were expressed as the mean ± standard deviation. Compared with the control group, aP < 0.01; compared with RA group, bP < 0.05. MAPK: mitogen-activated protein kinase; RA: rheumatoid arthritis; FCA: Freund’s complete adjuvant.

Figure 4 Immunohistochemical assessment the expression of NF-κBp65 in control, RA, and moxibustion group A-C: Immunohistochemistry (S-P) analysis (× 400). A to C representative images show the expression of NF-κBp65 in synovial tissues of control (A), RA (B) and moxibustion (C) group. Black arrow indicates the position expression of NF-κBp65. D represented the statistical analysis of the expression of NF-κBp65. n =10 for each group. RA group and Moxa group were established by injecting FCA (0.5 mL/kg) into the bilateral posterior knee joints. Control group was injected with the same volume sterile normal saline in the same way. Moxa group was treated by moxa-burning heat on Zusanli (ST36) and Shenshu (BL23) once 1day for 3 courses after FCA injection. Other two groups were fixed with the same method for the same time without moxibustion. Data were expressed as the mean ± standard deviation. Compared with the Control group, aP < 0.05; compared with the RA group, bP < 0.05. NF-κB: nuclear factor-κ-gene binding; RA: rheumatoid arthritis; FCA: Freund’s complete adjuvant.
| [1] |
Sparks JA. Rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Intern Med 2019; 170: ITC1-16.
DOI |
| [2] |
Aletaha D, Smolen JS. Diagnosis and management of rheumatoid arthritis: a review. JAMA 2018; 320: 1360-72.
DOI PMID |
| [3] |
De R, Sarkar S, Mazumder S, et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor regulates mitochondrial dynamics and cell growth of human cancer cell lines through CD74-NF-kappaB signaling. J Biol Chem 2018; 293: 19740-60.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
Morand EF, Leech M, Bernhagen J. MIF: a new cytokine link between rheumatoid arthritis and atherosclerosis. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2006; 5: 399-410.
PMID |
| [5] |
Kim KW, Kim HR. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor: a potential therapeutic target for rheumatoid arthritis. Korean J Intern Med 2016; 31: 634-42.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
Bilsborrow JB, Doherty E, Tilstam PV, Bucala R. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) as a therapeutic target for rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Expert Opin Ther Targets 2019; 23: 733-44.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
Jankauskas SS, Wong DWL, Bucala R, Djudjaj S, Boor P. Evolving complexity of MIF signaling. Cell Signal 2019; 57: 76-88.
DOI PMID |
| [8] | Santoscoy-Ascencio G, Banos-Hernandez CJ, Navarro-Zarza JE, et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor promoter polymorphisms are associated with disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis patients from Southern Mexico. Mol Genet Genomic Med 2020; 8: e1037. |
| [9] | Gong Y, Yu Z, Wang Y, et al. Effect of moxibustion on HIF-1alpha and VEGF levels in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Pain Res Manag 2019; 2019: 4705247. |
| [10] |
Sun ZL, Xu X, Du SZ, Jiang X. Moxibustion for treating rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Eur J Integr Med 2014; 6: 621-30.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
Seca S, Miranda D, Cardoso D, et al. Effectiveness of acupuncture on pain, physical function and health-related quality of life in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review of quantitative evidence. Chin J Integr Med 2019; 25: 704-9.
DOI PMID |
| [12] | Zhou DP, Jiang X, Ji W, Xu X, Sun ZL. bibliometric analysis on moxibustion for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Beijing Zhong Yi Yao 2015; 34: 434-7. |
| [13] | Zhu TT, Zhao ZT, Zhao YK, Yan XK. Review on modern repair mechanism of moxibustion for treating inflammatory damage of rheumatoid arthritis. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu 2017; 42: 271-4. |
| [14] | Gao XH, Liu XG, Jin S, et al. Effect of moxibustion therapy on the balance of Th17/Treg in rabbits with rheumatoid arthritis. Journal of Basic Chinese Medicine 2019; 25: 1404-06,19. |
| [15] | Ma WB, Liu XG, Zhou HY. Effects of chronological moxibustion on circadian rhythm activities of hypothalamus-pituitary-axis in rheumatoid arthritis rats. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu 2016; 41: 100-7. |
| [16] | Chen Y, Li H, Luo X, et al. Moxibustion of Zusanli (ST36) and Shenshu (BL23) alleviates cartilage degradation through RANKL/OPG signaling in a rabbit model of rheumatoid arthritis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2019; 2019: 6436420. |
| [17] | Li Z, Experimental acupuncture and moxibustion. Beijing: China Press of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2003: 314-6. |
| [18] |
Liu H, Huang Q, Shi B, Eksarko P, Temkin V, Pope RM. Regulation of Mcl-1 expression in rheumatoid arthritis synovial macrophages. Arthritis Rheum 2006; 54: 3174-81.
DOI URL |
| [19] | Yang X, Chang Y, Wei W. Emerging role of targeting macrophages in rheumatoid arthritis: focus on polarization, metabolism and apoptosis. Cell Prolif 2020; 53: e12854. |
| [20] |
Thornton S, Boivin GP, Kim KN, Finkelman FD, Hirsch R. Heterogeneous effects of IL-2 on collagen-induced arthritis. J Immunol 2000; 165: 1557-63.
PMID |
| [21] |
Teixeira JH, Silva AM, Almeida MI, et al. The systemic immune response to collagen-induced arthritis and the impact of bone injury in inflammatory conditions. Int J Mol Sci 2019; 20: 5436.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
Brennan FM, McInnes IB. Evidence that cytokines play a role in rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest 2008; 118: 3537-45.
DOI PMID |
| [23] |
Zhang J, Zhang G, Yang S, et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor regulating the expression of VEGF-C through MAPK signal pathways in breast cancer MCF-7 cell. World J Surg Oncol 2016; 14: 51.
DOI PMID |
| [24] |
Singh H, Chetha AS, Shalikar H. Moxibustion-septic shock and necrotizing fasciitis. IDCases 2020; 22: e00990.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
Wu Z, Xu G, Xiong J, Zuo Z, Yu X, Xie Q. Moxibustion therapy on myofascial pain syndrome: an evidence-based clinical practice guideline. Medicine (Baltimore) 2020; 99: e22342.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
Xue N, Fu X, Zhu Y, Da N, Zhang J. Moxibustion enhances chemotherapy of breast cancer by affecting tumor microenvironment. Cancer Manag Res 2020; 12: 8015-22.
DOI PMID |
| [27] |
Xu J, Pan LJ, Jia CS. Exploration on the feasibility of moxibustion in prevention and treatment of COVID-19 from the perspective of modern medical mechanism. World J Acupunct Moxibustion 2020; 30: 81-4.
DOI URL |
| [28] | Huang A, Pang Y, Tang Q, Xu J, Lin J, Li J. Clinical therapeutic effects on rheumatoid arthritis treated with the assisted therapy of acupuncture at the points detected with thermosensitive moxibustion in Zhuang medicine. Zhong Guo Zhen Jiu 2018; 38: 245-50. |
| [29] | Liu J, Huang Z, Zhang GH. Involvement of NF-kappa B signal pathway in acupuncture treatment of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu 2020; 45: 914-9. |
| [30] | Yu Z, Wang Y, Li Y, et al. Effect of moxibustion on the serum levels of MMP-1, MMP-3, and VEGF in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2020; 2020: 7150605. |
| [31] |
Su X, Zhang H, Wang H, Sun P. MiR-130a/Ndrg2 axis inhibits the proliferation of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. Inflammation 2020; 43: 2048-60.
DOI URL |
| [32] | Zhang CY, Hu L, Cai RL, Peng CY, Yuan J. Toll-like receptor 4/nuclear factor-kappaB signaling in synovial tissue is involved in the anti-inflammatory effect of moxibustion in rats with rheumatoid arthritis. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu 2018; 43: 687-91. |
| [33] | Liu Z, Li X, Zhao C, et al. Effects of moxibustion on Treg/Th17 cell and its signal pathway in mice with rheumatoid arthritis. Zhong Guo Zhen Jiu 2017; 37: 1083-91. |
| [34] | Zhang CY, Shao FR, Cai RL, Yuan J, Yin G, Tang ZL. Effects of moxibustion on expression of STAT 1, SOCS mRNA in synovium of rats with rheumatoid arthritis. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu 2015; 40: 205-9. |
| [35] | Yang X, Liu XG, Wang Y, Yang SQ, Jin RJ. Effects of moxibustion intervention on inflammatory reactions and expression of suppressor of cytokine signaling proteins of synovium cells in rheumatoid arthritis rabbits. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu 2013; 38: 129-33, 57. |
| [36] | Yoo SA, Leng L, Kim BJ, et al. MIF allele-dependent regulation of the MIF coreceptor CD44 and role in rheumatoid arthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2016; 113: E7917-26. |
| [37] | Zhong YM, Cheng B, Zhang LL, Lu WT, Shang YN, Zhou HY. Effect of moxibustion on inflammatory cytokines in animals with rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2020; 2020: 6108619. |
| [38] | Zhao C, Li X, Yang Y, et al. An analysis of Treg/Th 17 cells imbalance associated microRNA networks regulated by moxibustion therapy on Zusanli (ST36) and Shenshu (BL23) in mice with collagen induced arthritis. Am J Transl Res 2019; 11: 4029-45. |
| [39] | He TF, Yang WJ, Zhang SH, Zhang CY, Li LB, Chen YF. Electroacupuncture inhibits inflammation reaction by upregulating vasoactive intestinal peptide in rats with adjuvant-induced arthritis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2011; 2011. |
| [40] | Yang X, Yang SQ, Zhou HY, et al. The influence on MAPK signal pathway in RA synovial cell of experimental rabbits by moxibustion. Zhong Hua Zhong Yi Yao Xue Kan 2007; 25: 470-4. |
| [41] | Gao J, Liu XG, Huang DJ, et al. Involvement of the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis in moxibustion-induced changes of NF-kB signaling in the synovial tissue in rheumatic arthritis rats. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu 2010; 35: 198-203. |
| [42] | Zhang CY, Cai RL, Tang ZL. Influences of moxibustion on inflammatory factors and synoviocytes in rats with rheumatoid arthritis. Beijing Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue Xue Bao 2014; 37: 190-5. |
| [1] | LI Chaoran, YANG Yan, FENG Chuwen, LI Heng, QU Yuanyuan, WANG Yulin, WANG Delong, WANG Qingyong, GUO Jing, SHI Tianyu, SUN Xiaowei, WANG Xue, HOU Yunlong, SUN Zhongren, YANG Tiansong. Integrated 'omics analysis for the gut microbiota response to moxibustion in a rat model of chronic fatigue syndrome [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1176-1189. |
| [2] | WANG Miao, ZHU Yan, ZHAO Hui, ZHAO Hongfang. Moxibustion enables protective effects on rheumatoid arthritis-induced myocardial injury via transforming growth factor beta1 signaling and metabolic reprogramming [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1190-1199. |
| [3] | LI Xingjie, LIU Qiqi, XIA Rui, LIU Jun, WANG Dan, SHI Jiao, KUANG Yuxing, DAI Yalan, HUANG Haoyu, TANG Wei, CHEN Shangjie. Moxibustion modulates working memory in patients with amnestic mild cognitive impairment: a functional magnetic resonance imaging study [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(4): 801-808. |
| [4] | MA Fangfang, ZHANG Hewei, LI Bingxue, CHENG Peiyu, YU Mingwei, WANG Xiaomin. Acupuncture and moxibustion for malignant tumor patients with psychological symptoms of insomnia, anxiety and depression: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(3): 441-456. |
| [5] | XIONG Yunzhao, LIU Lingjin, LIU Ziqian, CHEN Gege, HAO Juan, GAO Xiaomeng, QIANG Panpan, WANG Zheng, XU Qingyou. Huoxue Jiedu Huayu recipe (活血解毒化瘀方) alleviates contralateral renal fibrosis in unilateral ureteral obstruction rats by inhibiting the transformation of macrophages to myofibroblast [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(1): 105-112. |
| [6] | MIN Youjiang, YAO Haihua, WANG Zhiqin, LUO Kaitao, SUN Jie, YUAN Zheng, WU Huiqi, CHENG Lihong. Efficacy of suspended moxibustion stimulating Shenshu (BL23) and Guanyuan (CV4) on the amygdala-HPA axis in rats with kidney-Yang deficiency symptom pattern induced by hydrocortisone [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(1): 113-123. |
| [7] | YAO Yao, ZHAO Zhenni, CHEN Fengqin, LENG Yufei, PANG Xiangtian, XU Xiao, SUN Zhiling. Effectiveness of moxibustion alone on lumbar disc herniation: a Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(1): 14-26. |
| [8] | YANG Jun, XIONG Jun, XU Shaozhong, XIE Hongwu, XIANG Jie. Effect and cerebral mechanism of moxibustion at heat-sensitized Yaoyangguan (GV3) in patients with lumbar disc herniation and myofascial pain syndrome by resting-state functionality magnetic resonance imaging: protocol for an observational study [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(1): 175-180. |
| [9] | HE Lianhua, LUAN Huijie, QIN Qingxia, HE Juan, CHEN Jian, HU Yiping, CAI Yueming, SUN Desheng, SHI Yu, WANG Qingwen. Shikonin alleviates collagen-induced arthritis mice by inhibiting M1 macrophage polarization [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(6): 932-939. |
| [10] | FANG Jing, PAN Wen, WANG Xiangyun, LI Fengxing, ZHAO Ling, HUANG Zouqin, SHEN Xueyong. Efficacy of stimulating Mingmen (GV4) and Guanyuan (CV4) on kidney Yang deficiency in rat model: laser irradiation vs traditional moxibustion [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(6): 972-979. |
| [11] | WANG Wei, LI Qingling, MA Qiang, XIA Ran, GAO Bing, WANG Yi, WANG Jing. Effects of moxibustion at bilateral Feishu (BL13) and Xinshu (BL15) combined with benazepril on myocardial cells apoptosis index and apoptosis-related proteins cytochrome c and apoptosis-inducing factor in rats with chronic heart failure [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(2): 227-233. |
| [12] | MA Tingting, WU Jie, YANG Lijie, FENG Fen, YANG Huilin, ZHANG Jinhua, ZHONG Yanjin, NING Qing, HUANG Lirong, LIN Youbing, YAN Jue, CHEN Guiquan, HOU Tianshu, WANG Li, REN Yuanfang, TAN Jing. Ginger-indirect moxibustion plus acupuncture versus acupuncture alone for chronic fatigue syndrome: a randomized controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(2): 242-249. |
| [13] | Feng HAO, Qiang WANG, Lei LIU, Libin WU, Ronglin CAI, Jiajia SANG, Jun HU, Jie WANG, Qing YU, Lu HE, Yingchao SHEN, Yiming MIAO, Ling HU, Zijian WU. Effect of moxibustion on autophagy and the inflammatory response of synovial cells in rheumatoid arthritis model rats [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(1): 73-82. |
| [14] | PAN Lijia, MA Shuya, WEN Jing, ZHANG Xiaoqi, XING Haijiao, JIA Chunsheng. Direct contact moxibustion promotes apoptosis of gastric cancer cells in rats by regulating intestinal flora [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(6): 943-952. |
| [15] | LIU Di, WU Yongli, LI Chun, WANG Minglei, MA Xiaoxiu, LIU Junwei, ZHANG Yanling, YANG Lei. Warming moxibustion attenuates inflammation and cartilage degradation in experimental rabbit knee osteoarthritis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(6): 959-967. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

