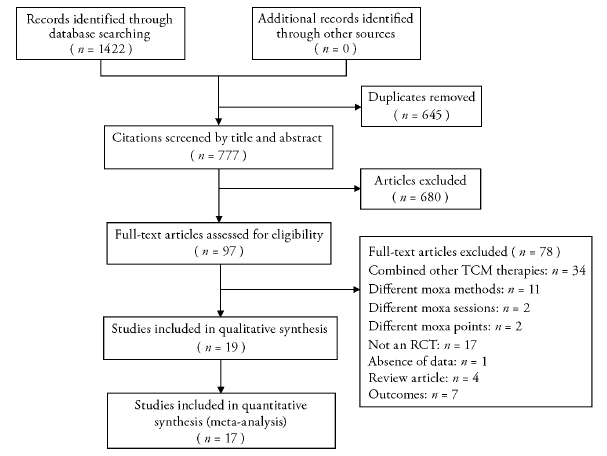
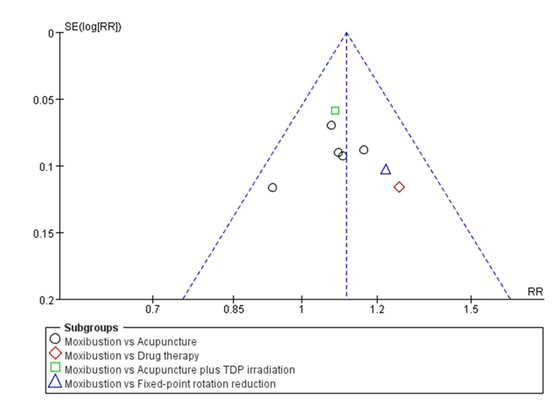
Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (1): 14-26.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20221108.001
• Meta-analysises • Previous Articles Next Articles
Effectiveness of moxibustion alone on lumbar disc herniation: a Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
YAO Yao1, ZHAO Zhenni1, CHEN Fengqin2, LENG Yufei3, PANG Xiangtian1, XU Xiao4, SUN Zhiling1( )
)
- 1 School of Nursing, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210023, China
2 Office of Academic Affairs, Nanjing Normal University of Special Education, Nanjing 210038, China
3 Auxiliary Teaching Center, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200025, China
4 School of Nursing, Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, Hangzhou 310053, China
-
Received:2021-12-16Accepted:2022-03-28Online:2023-02-15Published:2023-01-10 -
Contact:SUN Zhiling -
About author:Prof. SUN Zhiling, School of Nursing, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210023, China.szl@njucm.edu.cn.Telephone,Telephone:+86-25-85811639
-
Supported by:The National Natural Science Foundation of China: Study on Multi-target Regulation Mechanism of Moxibustion on Rheumatoid Arthritis Based on Signal Pathway of Lipid Metabolism Network(81774383);Study on the Multi target Effect Mechanism of Moxibustion Intervention on Ankylosing Spondylitis Based on Metabolic Proteomics and System Bioinformatics Cross linking Analysis between Genomics(81904274);The "Research and Innovation Plan for Postgraduates in Jiangsu Province" of the Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine: Clinical Experimental Study on the Effect of Different Moxibustion Duration on Lumbar Disc Herniation(SJCX20_0524);Clinical Study on the Treatment of Lumbar Disc Herniation with Thunder Fire Moxibustion and Common Moxibustion(SJCX20_0525)
Cite this article
YAO Yao, ZHAO Zhenni, CHEN Fengqin, LENG Yufei, PANG Xiangtian, XU Xiao, SUN Zhiling. Effectiveness of moxibustion alone on lumbar disc herniation: a Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(1): 14-26.
share this article
| Study | Sample size | Mean age (years) | Duration (months) | Intervention | Follow up | Adverse events | Outcomes | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Experimental group | Control group | ||||||||||||||||||
| Chen RX et al 201438 | 456 | E1: 45.5±10.6 E2: 47.3±11.2 C: 46.6±10.5 | n.r. | (E1) Suspended moxa (2 times daily in the first 4 d, one time daily in remaining 10 d, 2 weeks, n = 152) (E2) Suspended moxa (1session = 45 min, 2 times daily in the first 4 d, 1 time daily in the remaining 10 d, 2 weeks, n = 152) | Drug therapy (20% mannitol, Voltaren tablets in the first 3 d. Voltaren tablets in subsequent 11 d.) Plus acupuncture (1session = 30 min, 1/d, 2 weeks, n = 152) | 2 weeks, 6 months | None related to moxa. | JOA | |||||||||||
| Fu Y et al 201437 | 180 | E1: 54.55±6.24 E2: 57.22±6.37 C: 56.21±5.27 | E1: 5.45±3.46 E2: 5.00±2.12 C: 5.32±3.18 | (E1) Suspended moxa (2 times daily in the first four days, 1 time daily in the remaining 10 d, 2 weeks, n = 60) (E2) Suspended moxa (1 session = 30 min, 2 times daily in the first 4 d, 1 time daily in the remaining 10 d, 2 weeks, n = 60) | Drug therapy (20% mannitol, 1/d, fortalin tablets, in the first 3 d, only taken fortalin tablets in subsequent 11 d.) Plus acupuncture, (1 session = 30 min, once daily, 2 weeks, n = 60) | 2 weeks, 6 months | n.r. | JOA | |||||||||||
| Hu XW et al 201925 | 90 | E: 40.19±5.16 C1: 38.32±6.71 C2: 40.32±7.92 | E: 10.58±2.33 C1: 8.90±1.80 C2: 9.68±1.74 | Indirect moxa (once a week, 1 month, n = 31) | (C1) Acupuncture (1 session = 30 min, 1/d, 10 times as a course, rest for 2 d between courses, 1 month, n = 28) (C2) Drug therapy (Diclofenac sodium tablets, 25 mg, 3 times a day, 1 month, n = 31) | 1 month | n.r. | Response rate; VAS; ODI; | |||||||||||
| Li H et al 201231 | 60 | E: 41.7 C: 41.9 | E: 7.4 C: 7.2 | Suspended moxa (2 times daily in the first 4 d, 1 time daily in the remaining 10 d, 2 weeks, n = 30) | Acupuncture (1 session = 30 min, 1/d, 6 times/ week, 8 weeks, n = 30) | 2 weeks | n.r. | Response rate | |||||||||||
| Li L 201634 | 60 | E: 39.62±5.26 C: 40.80±4.68 | E (yr): 3.60±1.09 C(yr): 3.57±1.12 | Indirect moxa (1 session = 1.5 h, 2 times/week, 8 weeks, n = 30) | Acupuncture (1 session = 30 min, 1/d, 6 times/ week, 8 weeks, n = 30) | 8 weeks | n.r. | VAS; JOA | |||||||||||
| Lin WP 201236 | 60 | E: 42.73±11.77 C: 41.73±10.65 | E(d): 18.77±19.58 C(d): 20.53±23.56 | Indirect moxa (1 session = 50 min, once daily, 10 d, n = 30) | Acupuncture (1session = 30 min, plus cup, 1 session = 30 min, 1/d, 10 d, n = 30) | 10 d | n.r. | Response rate | |||||||||||
| Liu Q et al 201239 | 80 | E: 43.20±10.26 C: 42.77±10.50 | E (yr): 4.81±2.96 C (yr): 4.67±3.16 | Indirect moxa (once every other one day, 3 times/week, 3 weeks, n = 40) | Acupuncture plus TDP irradiation (1 session = 30 min, 1/d, 5 times/ week, 3 weeks, n = 40) | 3 weeks | n.r. | Response rate | |||||||||||
| Liu CY et al 202140 | 60 | E: 52.42±3.17 C: 52.38±3.25 | n.r. | Suspended moxa (1 session = 15 min, 1/d, 6 d/course, rest for 1 d between courses, 4 weeks, n = 30) | Drug therapy (Citicoline sodium injection 0.5 g, salvia miltiorrhiza injection 20 mL, respectively, added to 5% of the glucose solution 250 mL intravenous injection,1/d, 4 weeks, n = 30) | 4 weeks | n.r. | VAS; JOA | |||||||||||
| Lu YJ 201535 | 60 | E: 52.20±7.14 C: 52.53±7.53 | E(yr): 5.63±2.94 C(yr): 5.57±2.87 | Indirect moxa (1 session = 1.5 h, 2 times/week, 8 weeks, n = 30) | Acupuncture (1 session = 25 min, 1/d, 6 times/week, 8 weeks, n = 30) | 8 weeks | n.r. | VAS; JOA | |||||||||||
| Ma S et al 201033 | 120 | E1: 41.5±12.8 E2: 38.3±11.3 C: 37.9±11.2 | E1(d): 261.2±47.7 E2(d): 267.3±34.5 C(d): 274.8±50.2 | (E1) Indirect moxa (once daily, 3 weeks, n = 30) (E2) Indirect moxa plus Acupuncture, (3 weeks, n = 60) | Acupuncture (1session = 30 min, 1/d, 3 weeks, n = 30) | 3 weeks | n.r. | ||||||||||||
| Ma S et al 201033 | 120 | E1: 41.5±12.8 E2: 38.3±11.3 C: 37.9±11.2 | E1(d): 261.2±47.7 E2(d): 267.3±34.5 C(d): 274.8±50.2 | (E1) Indirect moxa (once daily, 3 weeks, n = 30) (E2) Indirect moxa plus Acupuncture, (3 weeks, n = 60) | Acupuncture (1session = 30 min, 1/d, 3 weeks, n = 30) | 3 weeks | n.r. | JOA | |||||||||||
| Mai ZM, Tang JD 201729 | 94 | E: 42.81±9.31 C: 43.17±9.63 | E: 13.45±6.41 C: 13.63±6.55 | Suspended moxa (1 session = 40 min, 1/d, 5 d/course, rest for 2 d between courses, 4 weeks, n = 47) | Acupuncture (1 session = 30 min, 1/d, 5 d/course, rest for 2 d between courses, 4 weeks, n = 47) | 4 weeks | n.r. | VAS; JOA | |||||||||||
| Mao LF 201726 | 60 | E: 51.53±8.66 C: 51.93±11.30 | n.r. | Suspended moxa (5 d/course, rest for 2 d between courses of treatment, n = 30) | Drug therapy (Yaotongning capsule, 4-6 pieces, 3/d, 10 d, n = 30) | 10 d | 5 patients developed dry and thirst, normal after hydration | JOA | |||||||||||
| Song LJ et al 201622 | 60 | E: 27.76±3.67 C: 28.83±3.33 | E: 15 d-3 yr C: 20 d-2.5 yr | Suspended moxa (1session = 15-20 min, 1/d, 5 d/course, 10 d, n = 30) | Conventional therapy (10 d, n = 30) | 10 d | n.r. | ODI | |||||||||||
| Wang XY 200828 | 72 | E: 48.8±11.8 C: 46.8±13.7 | n.r. | Indirect moxa (once every other one day, 3 weeks, n = 36) | Acupuncture (1 session = 30 min, once every other one day, 3 weeks, n = 36) | 1/2/3 week(s), 1 month | None related to moxa. | Response rate; JOA | |||||||||||
| Xu JF et al 201227 | 60 | E: 41.1±11.6 C: 40.1±10.1 | E: 29.2±8.4 C: 32.3±8.2 | Suspended moxa (1 session = 1 h, 1/d, 3 weeks, n = 30) | Acupuncture (1 session = 30 min, 1/d, 3 weeks, n = 30) | 3 weeks | n.r. | VAS; JOA | |||||||||||
| Yang DL et al 201432 | 40 | E: 42±13 C: 45±12 | E: 29.2±8.4 C: 32.3±8.2 | Suspended moxa (1 session = 1 h, 1/d, 3 weeks, n = 20) | Acupuncture (1 session = 30 min, 1/d, 3 weeks, n = 20) | 3 weeks | n.r. | JOA | |||||||||||
| Yi GQ et al 201530 | 70 | E: 47.09±9.06 C: 45.49±10.48 | E: 14.40±16.83 C: 11.49±17.70 | Suspended moxa (1 session = 30 min, 1/d, 5 d/course, rest for 2 d between courses, 3 weeks, n = 35) | Acupuncture (1 session = 30 min, 1/d, 5 d/course, rest for 2 d between courses, 3 weeks, n = 35) | 3 weeks | n.r. | Response rate; VAS; JOA | |||||||||||
| Zhang LZ 201823 | 106 | E: 47.58±10.30 C: 47.15±10.07 | E (yr): 6.08±3.64 C(yr): 6.34±3.51 | Suspended moxa (1 session = 20-30 min, 1/d, n = 53), plus Conventional therapy | Conventional therapy (n = 53) | 14-21 d | n.r. | VAS | |||||||||||
| Zheng CH et al 201924 | 100 | E: 54.26±8.24 C: 54.49±8.19 | E: 3.79±2.88 C: 3.86±2.91 | Suspended moxa (5 times every week, 2 weeks, n = 50) | Fixed-point rotation reduction (once every other one day, 2 weeks, n = 50) | 2 weeks | n.r. | Response rate; VAS; JOA; ODI | |||||||||||
Table 1 Summary of the 19 included studies
| Study | Sample size | Mean age (years) | Duration (months) | Intervention | Follow up | Adverse events | Outcomes | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Experimental group | Control group | ||||||||||||||||||
| Chen RX et al 201438 | 456 | E1: 45.5±10.6 E2: 47.3±11.2 C: 46.6±10.5 | n.r. | (E1) Suspended moxa (2 times daily in the first 4 d, one time daily in remaining 10 d, 2 weeks, n = 152) (E2) Suspended moxa (1session = 45 min, 2 times daily in the first 4 d, 1 time daily in the remaining 10 d, 2 weeks, n = 152) | Drug therapy (20% mannitol, Voltaren tablets in the first 3 d. Voltaren tablets in subsequent 11 d.) Plus acupuncture (1session = 30 min, 1/d, 2 weeks, n = 152) | 2 weeks, 6 months | None related to moxa. | JOA | |||||||||||
| Fu Y et al 201437 | 180 | E1: 54.55±6.24 E2: 57.22±6.37 C: 56.21±5.27 | E1: 5.45±3.46 E2: 5.00±2.12 C: 5.32±3.18 | (E1) Suspended moxa (2 times daily in the first four days, 1 time daily in the remaining 10 d, 2 weeks, n = 60) (E2) Suspended moxa (1 session = 30 min, 2 times daily in the first 4 d, 1 time daily in the remaining 10 d, 2 weeks, n = 60) | Drug therapy (20% mannitol, 1/d, fortalin tablets, in the first 3 d, only taken fortalin tablets in subsequent 11 d.) Plus acupuncture, (1 session = 30 min, once daily, 2 weeks, n = 60) | 2 weeks, 6 months | n.r. | JOA | |||||||||||
| Hu XW et al 201925 | 90 | E: 40.19±5.16 C1: 38.32±6.71 C2: 40.32±7.92 | E: 10.58±2.33 C1: 8.90±1.80 C2: 9.68±1.74 | Indirect moxa (once a week, 1 month, n = 31) | (C1) Acupuncture (1 session = 30 min, 1/d, 10 times as a course, rest for 2 d between courses, 1 month, n = 28) (C2) Drug therapy (Diclofenac sodium tablets, 25 mg, 3 times a day, 1 month, n = 31) | 1 month | n.r. | Response rate; VAS; ODI; | |||||||||||
| Li H et al 201231 | 60 | E: 41.7 C: 41.9 | E: 7.4 C: 7.2 | Suspended moxa (2 times daily in the first 4 d, 1 time daily in the remaining 10 d, 2 weeks, n = 30) | Acupuncture (1 session = 30 min, 1/d, 6 times/ week, 8 weeks, n = 30) | 2 weeks | n.r. | Response rate | |||||||||||
| Li L 201634 | 60 | E: 39.62±5.26 C: 40.80±4.68 | E (yr): 3.60±1.09 C(yr): 3.57±1.12 | Indirect moxa (1 session = 1.5 h, 2 times/week, 8 weeks, n = 30) | Acupuncture (1 session = 30 min, 1/d, 6 times/ week, 8 weeks, n = 30) | 8 weeks | n.r. | VAS; JOA | |||||||||||
| Lin WP 201236 | 60 | E: 42.73±11.77 C: 41.73±10.65 | E(d): 18.77±19.58 C(d): 20.53±23.56 | Indirect moxa (1 session = 50 min, once daily, 10 d, n = 30) | Acupuncture (1session = 30 min, plus cup, 1 session = 30 min, 1/d, 10 d, n = 30) | 10 d | n.r. | Response rate | |||||||||||
| Liu Q et al 201239 | 80 | E: 43.20±10.26 C: 42.77±10.50 | E (yr): 4.81±2.96 C (yr): 4.67±3.16 | Indirect moxa (once every other one day, 3 times/week, 3 weeks, n = 40) | Acupuncture plus TDP irradiation (1 session = 30 min, 1/d, 5 times/ week, 3 weeks, n = 40) | 3 weeks | n.r. | Response rate | |||||||||||
| Liu CY et al 202140 | 60 | E: 52.42±3.17 C: 52.38±3.25 | n.r. | Suspended moxa (1 session = 15 min, 1/d, 6 d/course, rest for 1 d between courses, 4 weeks, n = 30) | Drug therapy (Citicoline sodium injection 0.5 g, salvia miltiorrhiza injection 20 mL, respectively, added to 5% of the glucose solution 250 mL intravenous injection,1/d, 4 weeks, n = 30) | 4 weeks | n.r. | VAS; JOA | |||||||||||
| Lu YJ 201535 | 60 | E: 52.20±7.14 C: 52.53±7.53 | E(yr): 5.63±2.94 C(yr): 5.57±2.87 | Indirect moxa (1 session = 1.5 h, 2 times/week, 8 weeks, n = 30) | Acupuncture (1 session = 25 min, 1/d, 6 times/week, 8 weeks, n = 30) | 8 weeks | n.r. | VAS; JOA | |||||||||||
| Ma S et al 201033 | 120 | E1: 41.5±12.8 E2: 38.3±11.3 C: 37.9±11.2 | E1(d): 261.2±47.7 E2(d): 267.3±34.5 C(d): 274.8±50.2 | (E1) Indirect moxa (once daily, 3 weeks, n = 30) (E2) Indirect moxa plus Acupuncture, (3 weeks, n = 60) | Acupuncture (1session = 30 min, 1/d, 3 weeks, n = 30) | 3 weeks | n.r. | ||||||||||||
| Ma S et al 201033 | 120 | E1: 41.5±12.8 E2: 38.3±11.3 C: 37.9±11.2 | E1(d): 261.2±47.7 E2(d): 267.3±34.5 C(d): 274.8±50.2 | (E1) Indirect moxa (once daily, 3 weeks, n = 30) (E2) Indirect moxa plus Acupuncture, (3 weeks, n = 60) | Acupuncture (1session = 30 min, 1/d, 3 weeks, n = 30) | 3 weeks | n.r. | JOA | |||||||||||
| Mai ZM, Tang JD 201729 | 94 | E: 42.81±9.31 C: 43.17±9.63 | E: 13.45±6.41 C: 13.63±6.55 | Suspended moxa (1 session = 40 min, 1/d, 5 d/course, rest for 2 d between courses, 4 weeks, n = 47) | Acupuncture (1 session = 30 min, 1/d, 5 d/course, rest for 2 d between courses, 4 weeks, n = 47) | 4 weeks | n.r. | VAS; JOA | |||||||||||
| Mao LF 201726 | 60 | E: 51.53±8.66 C: 51.93±11.30 | n.r. | Suspended moxa (5 d/course, rest for 2 d between courses of treatment, n = 30) | Drug therapy (Yaotongning capsule, 4-6 pieces, 3/d, 10 d, n = 30) | 10 d | 5 patients developed dry and thirst, normal after hydration | JOA | |||||||||||
| Song LJ et al 201622 | 60 | E: 27.76±3.67 C: 28.83±3.33 | E: 15 d-3 yr C: 20 d-2.5 yr | Suspended moxa (1session = 15-20 min, 1/d, 5 d/course, 10 d, n = 30) | Conventional therapy (10 d, n = 30) | 10 d | n.r. | ODI | |||||||||||
| Wang XY 200828 | 72 | E: 48.8±11.8 C: 46.8±13.7 | n.r. | Indirect moxa (once every other one day, 3 weeks, n = 36) | Acupuncture (1 session = 30 min, once every other one day, 3 weeks, n = 36) | 1/2/3 week(s), 1 month | None related to moxa. | Response rate; JOA | |||||||||||
| Xu JF et al 201227 | 60 | E: 41.1±11.6 C: 40.1±10.1 | E: 29.2±8.4 C: 32.3±8.2 | Suspended moxa (1 session = 1 h, 1/d, 3 weeks, n = 30) | Acupuncture (1 session = 30 min, 1/d, 3 weeks, n = 30) | 3 weeks | n.r. | VAS; JOA | |||||||||||
| Yang DL et al 201432 | 40 | E: 42±13 C: 45±12 | E: 29.2±8.4 C: 32.3±8.2 | Suspended moxa (1 session = 1 h, 1/d, 3 weeks, n = 20) | Acupuncture (1 session = 30 min, 1/d, 3 weeks, n = 20) | 3 weeks | n.r. | JOA | |||||||||||
| Yi GQ et al 201530 | 70 | E: 47.09±9.06 C: 45.49±10.48 | E: 14.40±16.83 C: 11.49±17.70 | Suspended moxa (1 session = 30 min, 1/d, 5 d/course, rest for 2 d between courses, 3 weeks, n = 35) | Acupuncture (1 session = 30 min, 1/d, 5 d/course, rest for 2 d between courses, 3 weeks, n = 35) | 3 weeks | n.r. | Response rate; VAS; JOA | |||||||||||
| Zhang LZ 201823 | 106 | E: 47.58±10.30 C: 47.15±10.07 | E (yr): 6.08±3.64 C(yr): 6.34±3.51 | Suspended moxa (1 session = 20-30 min, 1/d, n = 53), plus Conventional therapy | Conventional therapy (n = 53) | 14-21 d | n.r. | VAS | |||||||||||
| Zheng CH et al 201924 | 100 | E: 54.26±8.24 C: 54.49±8.19 | E: 3.79±2.88 C: 3.86±2.91 | Suspended moxa (5 times every week, 2 weeks, n = 50) | Fixed-point rotation reduction (once every other one day, 2 weeks, n = 50) | 2 weeks | n.r. | Response rate; VAS; JOA; ODI | |||||||||||
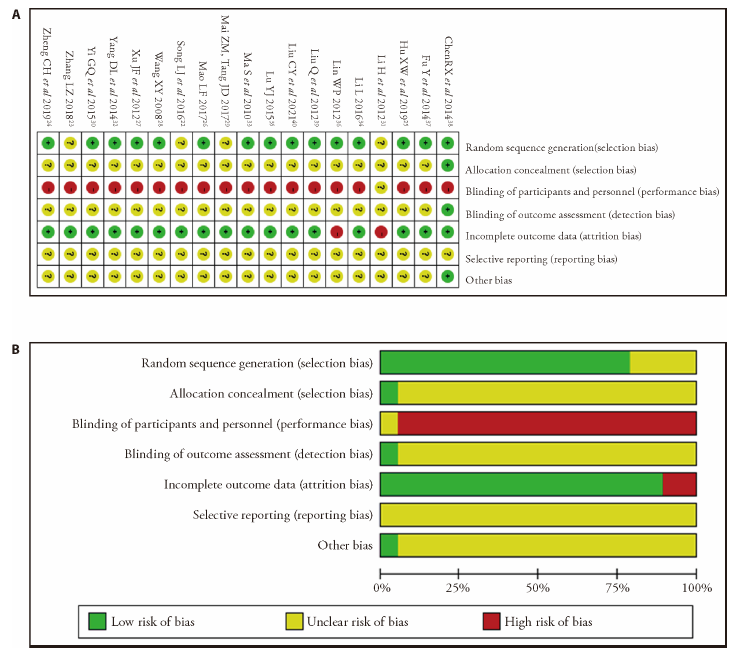
Figure 2 Risk of bias graph and summary A: risk of bias analysis of each included studies; B: overall risk of bias analysis of included studies. “?”: unclear risk of bias; “+”: low risk of bias; “-”: high risk of bias.
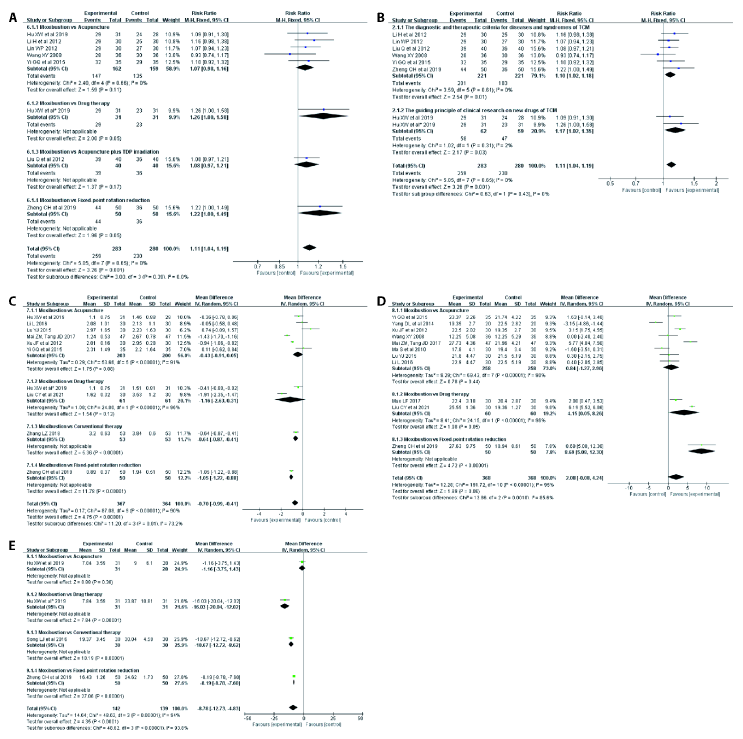
Figure 3 Results of the Meta-analysis A: forest plot of moxibustion on response rate (1); B: forest plot of moxibustion on response rate (2); C: forest plot of moxibustion on VAS score; D: forest plot of moxibustion on JOA score; E: forest plot of moxibustion on ODI score. VAS: Visual Analogue Scale; JOA: Japanese Orthopaedic Association; ODI: Oswestry Disability Index.
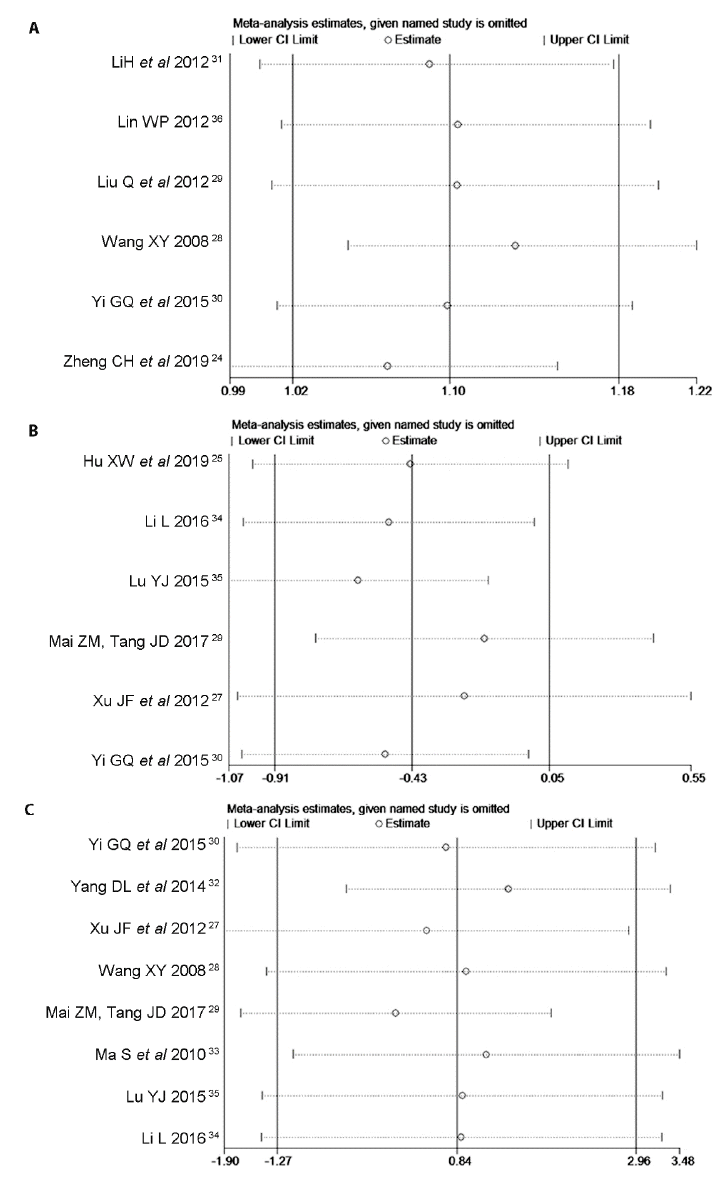
Figure 4 Sensitivity analysis A: sensitivity analysis of the response rate; B: sensitivity analysis of the VAS score; C: sensitivity analysis of the JOA score. VAS: Visual Analogue Scale; JOA: Japanese Orthopaedic Association.
| Item | Effect size (95% CI) | No. of participants (studies) | Quality of the evidence (GRADE) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Response rate | Moxibustion vs Acupuncture | RR 1.07 higher (0.98 higher to 1.16 higher) | 321 (5 RCTs) | ⊕○○○ VERY LOW |
| Moxibustion vs Drug therapy | RR 1.26 higher (1.00 higher to 1.58 higher) | 62 (1 RCTs) | ⊕○○○ VERY LOW | |
| Moxibustion vs Acupuncture plus TDP irradiation | RR 1.08 higher (0.97 higher to 1.21 higher) | 80 (1 RCTs) | ⊕○○○ VERY LOW | |
| Moxibustion vs Fixed-point rotation reduction | RR 1.22 higher (1.00 higher to 1.49 higher) | 100 (1 RCTs) | ⊕○○○ VERY LOW | |
| The diagnostic and therapeutic criteria for diseases and syndrome patterns of TCM | RR 1.10 higher (1.02 higher to 1.18 higher) | 442 (6 RCTs) | ⊕⊕○○ LOW | |
| The guiding principle of clinical research on new drugs of TCM | RR 1.17 higher (1.02 higher to 1.35 higher) | 121 (1 RCTs) | ⊕○○○ VERY LOW | |
| VAS score | Moxibustion vs Acupuncture | MD 0.43 lower (0.91 lower to 0.05 higher) | 403 (6 RCTs) | ⊕○○○ VERY LOW |
| Moxibustion vs Drug therapy | MD 1.16 lower (2.63 lower to 0.31 higher) | 122 (2 RCTs) | ⊕○○○ VERY LOW | |
| Moxibustion vs Conventional therapy | MD 0.64 lower (0.87 lower to 0.41 lower) | 106 (1 RCTs) | ⊕○○○ VERY LOW | |
| Moxibustion vs Fixed-point rotation reduction | MD 1.05 lower (1.22 lower to 0.88 lower) | 100 (1 RCTs) | ⊕○○○ VERY LOW | |
| JOA score | Moxibustion vs Acupuncture | MD 0.84 higher (1.27 lower to 2.96 higher) | 516 (8 RCTs) | ⊕⊕○○ LOW |
| Moxibustion vs Drug therapy | MD 4.15 higher (0.05 higher to 8.26 higher) | 120 (2 RCTs) | ⊕○○○ VERY LOW | |
| Moxibustion vs Fixed-point rotation reduction | MD 8.69 higher (5.08 higher to 12.30 higher) | 100 (1 RCTs) | ⊕○○○ VERY LOW | |
| ODI score | Moxibustion vs Acupuncture | MD 1.16 lower (3.75 lower to 1.43 higher) | 59 (1 RCTs) | ⊕○○○ VERY LOW |
| Moxibustion vs Drug therapy | MD 16.03 lower (20.04 lower to 12.02 lower) | 62 (1 RCTs) | ⊕○○○ VERY LOW | |
| Moxibustion vs Conventional therapy | MD 10.67 lower (12.72 lower to 8.62 lower) | 60 (1 RCTs) | ⊕○○○ VERY LOW | |
| Moxibustion vs Fixed-point rotation reduction | MD 8.19 lower (8.78 lower to 7.60 lower) | 100 (1 RCTs) | ⊕○○○ VERY LOW | |
Table 2 Summary of findings and quality of evidence for all outcomes included in this review
| Item | Effect size (95% CI) | No. of participants (studies) | Quality of the evidence (GRADE) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Response rate | Moxibustion vs Acupuncture | RR 1.07 higher (0.98 higher to 1.16 higher) | 321 (5 RCTs) | ⊕○○○ VERY LOW |
| Moxibustion vs Drug therapy | RR 1.26 higher (1.00 higher to 1.58 higher) | 62 (1 RCTs) | ⊕○○○ VERY LOW | |
| Moxibustion vs Acupuncture plus TDP irradiation | RR 1.08 higher (0.97 higher to 1.21 higher) | 80 (1 RCTs) | ⊕○○○ VERY LOW | |
| Moxibustion vs Fixed-point rotation reduction | RR 1.22 higher (1.00 higher to 1.49 higher) | 100 (1 RCTs) | ⊕○○○ VERY LOW | |
| The diagnostic and therapeutic criteria for diseases and syndrome patterns of TCM | RR 1.10 higher (1.02 higher to 1.18 higher) | 442 (6 RCTs) | ⊕⊕○○ LOW | |
| The guiding principle of clinical research on new drugs of TCM | RR 1.17 higher (1.02 higher to 1.35 higher) | 121 (1 RCTs) | ⊕○○○ VERY LOW | |
| VAS score | Moxibustion vs Acupuncture | MD 0.43 lower (0.91 lower to 0.05 higher) | 403 (6 RCTs) | ⊕○○○ VERY LOW |
| Moxibustion vs Drug therapy | MD 1.16 lower (2.63 lower to 0.31 higher) | 122 (2 RCTs) | ⊕○○○ VERY LOW | |
| Moxibustion vs Conventional therapy | MD 0.64 lower (0.87 lower to 0.41 lower) | 106 (1 RCTs) | ⊕○○○ VERY LOW | |
| Moxibustion vs Fixed-point rotation reduction | MD 1.05 lower (1.22 lower to 0.88 lower) | 100 (1 RCTs) | ⊕○○○ VERY LOW | |
| JOA score | Moxibustion vs Acupuncture | MD 0.84 higher (1.27 lower to 2.96 higher) | 516 (8 RCTs) | ⊕⊕○○ LOW |
| Moxibustion vs Drug therapy | MD 4.15 higher (0.05 higher to 8.26 higher) | 120 (2 RCTs) | ⊕○○○ VERY LOW | |
| Moxibustion vs Fixed-point rotation reduction | MD 8.69 higher (5.08 higher to 12.30 higher) | 100 (1 RCTs) | ⊕○○○ VERY LOW | |
| ODI score | Moxibustion vs Acupuncture | MD 1.16 lower (3.75 lower to 1.43 higher) | 59 (1 RCTs) | ⊕○○○ VERY LOW |
| Moxibustion vs Drug therapy | MD 16.03 lower (20.04 lower to 12.02 lower) | 62 (1 RCTs) | ⊕○○○ VERY LOW | |
| Moxibustion vs Conventional therapy | MD 10.67 lower (12.72 lower to 8.62 lower) | 60 (1 RCTs) | ⊕○○○ VERY LOW | |
| Moxibustion vs Fixed-point rotation reduction | MD 8.19 lower (8.78 lower to 7.60 lower) | 100 (1 RCTs) | ⊕○○○ VERY LOW | |
| 1 | Zuo MM, Chen XP, Liu JF. Research progress of epidural drug injection in treatment of lumbar disc herniation. Zhong Guo Teng Tong Yi Xue Za Zhi 2017; 23: 299-302. |
| 2 |
Tang S, Mo Z, Zhang R. Acupuncture for lumbar disc herniation: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. Acupunct Med 2018; 36: 62-70.
DOI PMID |
| 3 |
Mu W, Shang Y, Zhang C, Tang S. Analysis of the depression and anxiety status and related risk factors in patients with lumbar disc herniation. Pak J Med Sci 2019; 35: 658-62.
DOI PMID |
| 4 | Shin BJ. Risk factors for recurrent lumbar disc herniations. Asian Spine J 2014; 8: 211-5. |
| 5 | Shen SY, Li CJ. Efficacy analysis of conservative treatment in lumbar disc herniation. Shi Zhen Guo Yi Guo Yao 2014; 25: 1670-1. |
| 6 |
Masui T, Yukawa Y, Nakamura S, et al. Natural history of patients with lumbar disc herniation observed by magnetic resonance imaging for minimum 7 years. J Spinal Disord Tech 2005; 18: 121-6.
PMID |
| 7 | Wilkinson I, Cohen SP. Epidural steroids for spinal pain and radiculopathy: a narrative, evidence-based review. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol 2013; 26: 562-72. |
| 8 | Yang M, Jiang L, Xu GH. Traditional Chinese medicine for lumbar disc herniation: an overview of systematic review and Meta-analysis. Zhong Hua Zhong Yi Yao Xue Kan 2016; 34: 2897-901. |
| 9 | Pei XH, Qin Y, Li ZQ, Tian YX, Zhao JX. Visual analysis of common acupoints for moxibustion in the treatment of lumbar disc herniation. Shi Jie Ke Xue Ji Shu Zhong Yi Yao Xian Dai Hua 2018; 20: 1860-6. |
| 10 |
Wang Y, Zhang HL, Xia LP, Sun ZL, Xu X, Du SZ. Effectiveness and safety of moxibustion in treatment of lumbar disc herniation: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. J Tradit Chin Med 2019; 39: 599-608.
PMID |
| 11 | Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021; 372: n71. |
| 12 | Medicine NAoTC. The Politics of Medicine in the People’s Republic of China. Diagnostic and therapeutic criteria of Traditional Chinese Medicine syndrome. Nanjing Da Xue Chu Ban She 1994: 201-3. |
| 13 | Zheng XY. Guiding principle of clinical research on new drugs of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Zhong Guo Yi Yao Ke Ji Chu Ban She 1997: 145-7. |
| 14 |
Kreiner DS, Hwang SW, Easa JE, et al. An evidence-based clinical guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of lumbar disc herniation with radiculopathy. Spine J 2014; 14: 180-91.
DOI PMID |
| 15 | Breivik H. Fifty years on the Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) for pain-intensity is still good for acute pain. But multidimensional assessment is needed for chronic pain. Scand J Pain 2016; 11: 150-2. |
| 16 | Yonenobu K, Abumi K, Nagata K, Taketomi E, Ueyama K. Interobserver and intraobserver reliability of the Japanese orthopaedic association scoring system for evaluation of cervical compression myelopathy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2001; 26: 1890-4. |
| 17 | Fairbank JC, Pynsent PB. The oswestry disability index. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2000; 25: 2940-52. |
| 18 | Higgins JP, Thompson SG. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 5.1 0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration 2011; |
| 19 |
Higgins JP, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a Meta-analysis. Stat Med 2002; 21: 1539-58.
DOI PMID |
| 20 | Schunemann HJ, Mustafa RA, Brozek J, et al. GRADE guidelines: 21 part 1. Study design, risk of bias, and indirectness in rating the certainty across a body of evidence for test accuracy. J Clin Epidemiol 2020;122: 129-41. |
| 21 | Schunemann HJ, Mustafa RA, Brozek J, et al. GRADE guidelines: 21 part 2. Test accuracy: inconsistency, imprecision, publication bias, and other domains for rating the certainty of evidence and presenting it in evidence profiles and summary of findings tables. J Clin Epidemiol 2020;122: 142-52. |
| 22 | Song LJ, Xie F, Gao CL. Nursing effect of point moxibustion on lumbar disc herniation of blood Stasis and Qi stagnation types. Dang Dai Hu Shi 2016; 24: 80-1. |
| 23 | Zhang LZ. Effect of comprehensive nursing combined with mox-ibustion on pain and quality of life of patients with lumbar disc herniation. Xian Dai Zhen Duan Yu Zhi Liao 2018; 29: 2336-8. |
| 24 | Zheng CH, Luo Z, Huang ZJ. Effects of fixed point rotation reduction combined with thunder fire moxibustion on spinal stability in patients with lumbar disc herniation. Shi Jie Zhong Yi Yao 2019; 14: 1302-5. |
| 25 | Hu XW, Deng CY, Qiu FF, et al. Efficacy observation on long snake moxibustion for lumbar disc herniation with cold-dampness syndrome. World J Acupunct Moxibust 2019; 29: 97-102. |
| 26 | Mao LF. The clinical efficacy of moxibustion Ashi point in the cold and humid type lumbar disc herniation. Fujian Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue 2017: 1-36. |
| 27 | Xu JF, Lin RZ, Niu ZZ, Zhang YQ, Wu YL. Observations on the efficacy of moxibustion at guanyuan point in treating 30 cases of lumbar disc herniation. Gansu Zhong Yi Xue Yuan Xue Bao 2012; 29: 55-8. |
| 28 | Wang XY. Clinical studies of medicine-separated moxibustion repeated at “Shenque” to treat lumbar intervertebral disc protrusion. Henan Zhong Yi Xue Yuan 2008: 1-47. |
| 29 | Mai ZM, Tang JD. Comparison of therapeutic effects of warming Yang moxibustion and filiform needle acupuncture on blood stasis type lumbar disc herniation. Neimenggu Zhong Yi Yao 2017; 36: 128-9. |
| 30 | Yi GQ, Zhou JH, Huang YX. 35 cases of blood stasis type lumbar disc herniation treated by warming Yang and moxibustion. Zhong Yi Wai Zhi Za Zhi 2015; 24: 38-40. |
| 31 | Li H, Xiao Y, Zhou JL. Therapeutic observation of treating 30 cases of lumbar disc herniation patients by using thermal moxibustion. Sichuan Zhong Yi 2012; 30: 112-4. |
| 32 | Yang DL, Zhou WQ, Li J, Ruan CL, Zhang YS, Wang ZX. Comparative study on function and surface electromyography in patients of lumbar disc herniation treated with acupunctrue and moxibustion. Zhong Guo Zhen Jiu 2014; 34: 341-6. |
| 33 | Ma S, Ma J, Pan JN, Zhang XS. Comparative research of lumbar disc herniation treated with acupuncture and snake moxibustion. Zhong Guo Zhen Jiu 2010; 30: 563-6. |
| 34 | Li L. Clinical research of navel-moxibustion with Chinese medicine on treating lumbar intervertebral disc protrusion with blood stasis type. Jinan: Shandong Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue 2016: 1-50. |
| 35 | Lu YJ. Clinical research of navel-moxibustion with Chinese medicine on treating lumbar intervertebral disc protrusion with cold-dampness syndrome. Jinan: Shandong Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue 2015: 1-31. |
| 36 | Lin WP. Therapeutic observation of moxibustion with salt in bamboo circle on treating lumbar disc herniation. Fuzhou: Fujian Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue 2012: 1-29. |
| 37 | Fu Y, Zhang HF, Xiong J, Zhang W, Zhou XP, Xu HB. Study on the curative effect of thermal moxibustion treating lumbar disc herniation. Nanjing: Nanjing Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue Xue Bao 2014; 30: 120-3. |
| 38 | Chen RX, Chen MR, Su TS, et al. A 3-arm, randomized, controlled trial of heat-sensitive moxibustion therapy to determine superior effect among patients with lumbar disc herniation. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2014; 2014: 154941. |
| 39 | Liu Q, Zhao BY, Qin XG, Luo CL, Zhao ZT, He TY. 40 cases of cold-dampness lumbar disc herniation treated by Ho's drug moxibustion therapy. Zhong Yi Yan Jiu 2012; 25: 46-8. |
| 40 | Liu CY, Lu MJ, Kang ZZ, et al. Effect of thunder fire moxibustion at Mang Shu point on the pain degree and plasma substance P level of patients with lumbar intervertebral disc herniation. Xian Dai Yi Xue Yu Jian Kang Yan Jiu 2021; 5: 138-40. |
| 41 | Guo XF. Clinical effects and security of lumbar disc herniation by the treatment of moxibustion: a Meta-analysis. Liaoning Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue 2017: 1-37. |
| 42 | Chen FQ, Ge JF, Leng YF, Li C, Chen B, Sun ZL. Efficacy and safety of moxibustion for chronic low back pain: a systematic review and Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Complement Ther Clin Pract 2020; 39: 101130. |
| 43 | Sun ZL, Xu X, Du SZ, et al. Moxibustion for treating rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Eur J Integr Med 2014; 6: 621-30. |
| 44 | Ni Y, Lu WL, Li JM, Hu LZ, Wang DP, Zhou WH. Mechanism and research progress of moxibustion in treatment of inflammatory diseases. Liaoning Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue Xue Bao 2018; 20: 215-8. |
| 45 | Wang TT, Zhu ML, Zhang GY, et al. Anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects of moxibustion in experimental rats with radicular neuritis. Zhong Guo Zhong Yi Ji Chu Yi Xue Za Zhi 2018; 24: 1750-2. |
| 46 | Wang L, Li XW, Zhang L. Research progress on mechanism of moxibustion therapy at home and abroad. Zhong Guo Zhen Jiu 2001; 9: 56-9. |
| 47 | Huang KY, Liang S, Sun Z, Zhang JB. Start up mechanism of moxibustion warming and dredging Function. Zhong Guo Zhen Jiu 2017; 37: 1023-6. |
| [1] | QIN Xiaoyu, WANG Chunai, XUE Jianjun, ZHANG Jie, LU Xiaoting, DING Shengshuang, GE Long, WANG Minzhen. Efficacy of electroacupuncture on myocardial protection and postoperative rehabilitation in patients undergoing cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 1-15. |
| [2] | DAI Xiaoling, ZHANG Anming, LIN Hui, SHI Bei, REN Yi, WEN Hongzhu, FEI Xiaoyan, LIN Jiang. Qingchang suppositry (清肠栓) induced remission in patients with mild-to-moderate ulcerative proctitis: a multicenter, prospective, randomized, parallel-controlled clinical trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 156-162. |
| [3] | LIU Tingting, LIU Tongou, LIU Mingfu. Effectiveness and safety of acupuncture in treatment of pregnancy-related symptoms: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 16-26. |
| [4] | WANG Yichen, WU Shiyi, WANG Zhengyan, CHANG Wenling, XIE Zhihao, TANG Xing, ZHAO Songmei, ZHOU Jing, CHEN Zehong, WANG Chao, YANG Chunxia. Efficacy of Zhumian Tang formula granules (助眠汤配方颗粒) combined with eszopiclone for the treatment of poor sleep quality: a multi-center, randomized controlled, superiority trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 163-171. |
| [5] | YANG Yi, YE Huijun, ZHENG Huiling, JIN Lihua. Clinical observation on 90 cases of primary dysmenorrhea treated by buccal acupuncture therapy: a randomized controlled study [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 172-181. |
| [6] | WANG Jiabao, ZHANG Lishuang, NIU Baihan, YU Yajun, YANG Fengwen, MIAO Lin, CHAI Lijuan, DING Xinya, SUN Yingjie, WANG Yujing, WANG Lin, ZHANG Han, WANG Yi, LI Lin. Efficacy and safety of Weichang’ an pill (胃肠安丸) combined with Western Medicine on gastrointestinal diseases: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1057-1067. |
| [7] | FAN Rong, HE Haoyu, TANG Tao, CUI Hanjin. Long-term effects of Qingfei Paidu decoction (清肺排毒汤) in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 acute pneumonia after treatment: a protocol for systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1068-1071. |
| [8] | LI Chaoran, YANG Yan, FENG Chuwen, LI Heng, QU Yuanyuan, WANG Yulin, WANG Delong, WANG Qingyong, GUO Jing, SHI Tianyu, SUN Xiaowei, WANG Xue, HOU Yunlong, SUN Zhongren, YANG Tiansong. Integrated 'omics analysis for the gut microbiota response to moxibustion in a rat model of chronic fatigue syndrome [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1176-1189. |
| [9] | WANG Miao, ZHU Yan, ZHAO Hui, ZHAO Hongfang. Moxibustion enables protective effects on rheumatoid arthritis-induced myocardial injury via transforming growth factor beta1 signaling and metabolic reprogramming [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1190-1199. |
| [10] | DAI Zeqi, LIAO Xing, GUAN Yueyue, ZENG Zixiu, TANG Jun, HU Jing. Bloodletting puncture in the treatment of acute ischemic stroke: protocol for a mixed-method study of a multi-center randomized controlled trial and focus group [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1259-1267. |
| [11] | XU Yani, ZHANG Yutong, HE Weile, DAI Linglin, TANG Ding, WANG Jialing, ZHANG Xufen, CHEN Qin, CHEN Lifang, WANG Zhanglian, ZHAN Mingjie. Efficiency and safety of acupuncture for women with premature ovarian insufficiency: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1268-1274. |
| [12] | XU Xiangru, ZHOU Yi, CHEN Gang, LEI Ming, ZHANG Wen, WU Xinxin, PU Yuting, CHEN Caiyu, SUN Yuting, ZHOU Shuang, FANG Bangjiang. Clinical efficacy of Buzhong Yiqi decoction (补中益气汤) in the treatment of hospital-acquired pneumonia with multi-drug resistant bacteria: a prospective, randomized, multicenter controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 1010-1018. |
| [13] | ZHAO Ming, LUO Yimiao, WANG Huichan, CAO Yu, MA Lina, PEI Hui, LI Hao. Guilingji capsule (龟龄集胶囊) for Alzheimer's disease: secondary analysis of a randomized non-inferiority controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 1019-1025. |
| [14] | ZHANG Meizhen, HAO Xiaohui, TANG Yiting, CHEN Yupeng, HE Puyu, ZHAO Liming, PANG Bing, NI Qing. Efficacy and safety of Buyang Huanwu decoction (补阳还五汤) for diabetic peripheral neuropathy: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 841-850. |
| [15] | YANG Yuqing, CHEN Yuhuan, LI Chunxiao, LING Xiao, WANG Panpan, GUO Jing, ZHANG Yingying. Effectiveness and safety of Pingxiao capsule (平消胶囊) as adjuvant therapy in treatment of breast cancer: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 851-859. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||