Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (6): 1330-1341.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2025.06.012
• Original Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Network pharmacology combined with in vivo experiments to explore the molecular mechanism of Jiawei Erzhi pill (加味二至丸) protects against atherosclerosis by inhibiting ferroptosis
MA Guiping1, CHEN Ran2, LI Junlong3, SUN Le3, HU Shiping1, ZHANG Yiyi2( ), HONG Chuangxiong3(
), HONG Chuangxiong3( )
)
- 1 Beijing University of Chinese Medicine Affiliated Shenzhen Hospital, Central laboratory, Shenzhen 518172, China
2 Longhua Hospital, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Intensive care unit, Shanghai 200030, China
3 The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Department of cardiology, Guangzhou 510400, China
-
Received:2024-10-12Accepted:2025-01-25Online:2025-12-15Published:2025-11-24 -
Contact:Prof. HONG Chuangxiong, the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Department of cardiology, Guangzhou 510400, China. 787109008@qq.com, Telephone: +86-18320070508;
Prof. ZHANG Yiyi, Longhua Hospital, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200030, China. eezh@msn.com -
Supported by:Mechanism of Modified Erzhi Pills Up-regulating Adiponectin to Improve the Anti-vasoconstriction Function of Active Perivascular Fat in Menopausal Rats(81373799)
Cite this article
MA Guiping, CHEN Ran, LI Junlong, SUN Le, HU Shiping, ZHANG Yiyi, HONG Chuangxiong. Network pharmacology combined with in vivo experiments to explore the molecular mechanism of Jiawei Erzhi pill (加味二至丸) protects against atherosclerosis by inhibiting ferroptosis[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(6): 1330-1341.
share this article
| Group | n | TC | TG | HDL-C | LDL-C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CON | 10 | 3.523±0.113a | 2.518±0.297 | 2.841±0.063a | 0.363±0.022a |
| MOD | 10 | 48.706±2.770b | 3.685±0.30 | 1.583±0.115b | 35.021±1.109b |
| SIM | 10 | 37.045±3.721ab | 2.961±0.932 | 1.801±0.067bc | 26.905±4.955ab |
| L-JWEZP | 10 | 43.981±2.871b | 3.293±1.437 | 1.771±0.191b | 34.682±2.277b |
| M-JWEZP | 10 | 43.735±1.765b | 2.910±0.403 | 1.998±0.236ab | 30.428±3.337ab |
| H-JWEZP | 10 | 40.393±2.883bc | 3.556±0.958 | 1.930±0.305ab | 29.086±1.896ab |
Table 1 Effects of JWEZP on blood lipids of mice ($\bar{x}$ ± s, mmol/L)
| Group | n | TC | TG | HDL-C | LDL-C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CON | 10 | 3.523±0.113a | 2.518±0.297 | 2.841±0.063a | 0.363±0.022a |
| MOD | 10 | 48.706±2.770b | 3.685±0.30 | 1.583±0.115b | 35.021±1.109b |
| SIM | 10 | 37.045±3.721ab | 2.961±0.932 | 1.801±0.067bc | 26.905±4.955ab |
| L-JWEZP | 10 | 43.981±2.871b | 3.293±1.437 | 1.771±0.191b | 34.682±2.277b |
| M-JWEZP | 10 | 43.735±1.765b | 2.910±0.403 | 1.998±0.236ab | 30.428±3.337ab |
| H-JWEZP | 10 | 40.393±2.883bc | 3.556±0.958 | 1.930±0.305ab | 29.086±1.896ab |

Figure 1 JWEZP improves AS in ApoE-/- mice A: body weight change trend in mice from week 12 to week 22; B: body weight of mice at week 12; C: body weight of mice at week 22; D: Oil-red O staining of aorta; E: HE staining of the aortic sinus (magnification at × 400; scale bar, 50 μm. F: Masson staining of the aortic sinus (magnification at × 400; scale bar, 50 μm); G: percentages of plaque lesions in the aorta; H: atherosclerotic plaque areas in the aortic sinus; I: collagen fiber positive areas in the aortic sinus; D1, E1, F1: CON group; D2, E2, F2: MOD group; D3, E3, F3: SIM group; D4, E4, F4: L-JWEZP group; D5, E5, F5: M-JWEZP group; D6, E6, F6: H-JWEZP group. CON: treated only with physiological saline; MOD: treated only with physiological saline; SIM: treated with simvastatin by gavage (2.6 mg·kg?1·d?1); L-JWEZP: treated with low-dose Jiawei Erzhi pill by gavage (3.9 g·kg?1·d?1); M-JWEZP: treated with medium-dose Jiawei Erzhi pill by gavage (7.8 g·kg?1·d?1); H-JWEZP: treated with high-dose Jiawei Erzhi pill by gavage (15.6 g·kg?1·d?1). CON: control group; MOD: model group; SIM: simvastatin group; L-JWEZP: low-dose Jiawei Erzhi pill; M-JWEZP: medium-dose Jiawei Erzhi pill; H-JWEZP: high-dose Jiawei Erzhi pill. The results are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (n = 3), and the groups were compared using one-way analysis of variance. aP < 0.01, compared with model group; bP < 0.01, compared with control group; cP < 0.05, compared with model group.

Figure 2 JWEZP ameliorates ferroptosis in arterial tissues of mice A: content of GSH in the aortas of mice; B: content of LPO in the aortas of mice; C: content of MDA in the aortas of mice; D: content of NADPH in the aortas of mice; E: content of GSH-PX in the aortas of mice; F: content of iron in the aortas of mice; G: expression of ROS in thoracic aortic tissues; H: expression of GPX4 in thoracic aortic tissues were evaluated by immunofluorescence. G1, H1, I1, J1: CON group; G2, H2, I2, J2: MOD group; G3, H3, I3, J3: SIM group; G4, H4, I4, J4: L-JWEZP group; G5, H5, I5, J5: M-JWEZP group; G6, H6, I6, J6: H-JWEZP group. CON: treated only with physiological saline; MOD: treated only with physiological saline; SIM: treated with simvastatin by gavage (2.6 mg·kg?1·d?1); L-JWEZP: treated with low-dose Jiawei Erzhi pill by gavage (3.9 g·kg?1·d?1); M-JWEZP: treated with medium-dose Jiawei Erzhi pill by gavage (7.8 g·kg?1·d?1); H-JWEZP: treated with high-dose Jiawei Erzhi pill by gavage (15.6 g·kg?1·d?1). CON: control group; MOD: model group; SIM: simvastatin group; L-JWEZP: low-dose Jiawei Erzhi pill; M-JWEZP: medium-dose Jiawei Erzhi pill; H-JWEZP: high-dose Jiawei Erzhi pill; GSH: glutathione; LPO: lipid peroxide; MDA: malondialdehyde; NADPH: nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; ROS: reactive oxygen species; DAPI: 4',6-Diamidino-2-Phenylindole; GPX4: glutathione peroxidase 4. The results are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (n = 3), and the groups were compared using one-way analysis of variance. aP < 0.01, compared with model group; bP < 0.01, compared with control group; cP < 0.05, compared with model group.

Figure 3 Target-pathway network for JWEZP in ferroptosis A: venn diagram of JWEZP and ferroptosis targets; B: protein-protein interaction network of JWEZP and ferroptosis; C: results of KEGG enrichment analysis. JWEZP: Jiawei Erzhi pill; KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes.
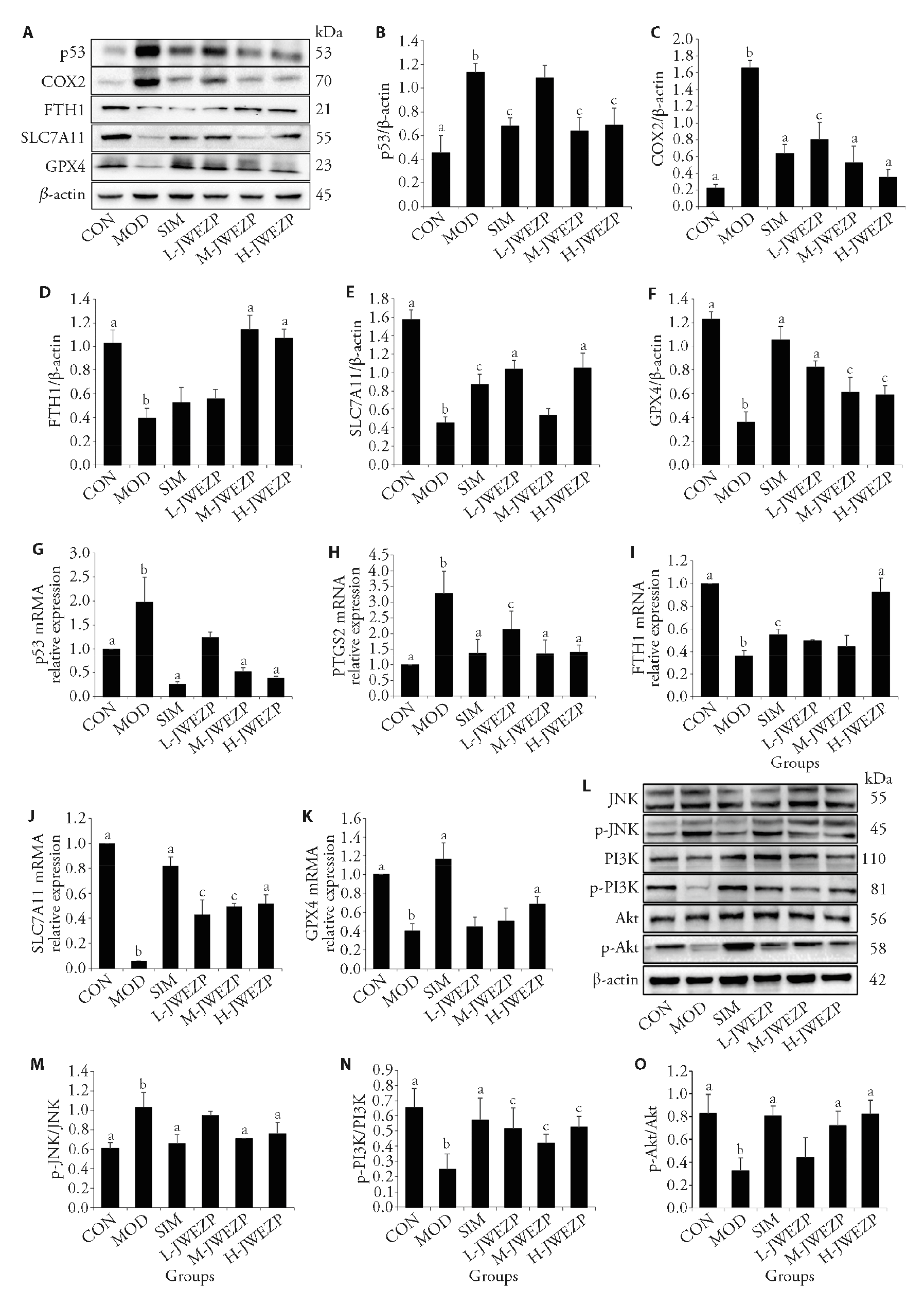
Figure 4 JWEZP inhibits ferroptosis via p53, MAPK and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways against AS A: protein expression of p53 signaling pathway; B: protein expression of p53; C: protein expression of COX2; D: protein expression of FTH1; E: protein expression of SLC7A11; F: protein expression of GPX4; G: mRNA expression of p53; H: mRNA expression of PTGS2; I: mRNA expression of FTH1; J: mRNA expression of SLC7A11; K: mRNA expression of GPX4; L: protein expression of MAPK and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways; M: protein expression of p-JNK/JNK; N: protein expression of p-PI3K/PI3K; O: protein expression of p-Akt/Akt. CON: treated only with physiological saline; MOD: treated only with physiological saline; SIM: treated with simvastatin by gavage (2.6 mg·kg?1·d?1); L-JWEZP: treated with low-dose Jiawei Erzhi pill by gavage (3.9 g·kg?1·d?1); M-JWEZP: treated with medium-dose Jiawei Erzhi pill by gavage (7.8 g·kg?1·d?1); H-JWEZP: treated with high-dose Jiawei Erzhi pill by gavage (15.6 g·kg?1·d?1). CON: control group; MOD: model group; SIM: simvastatin group; L-JWEZP: low-dose Jiawei Erzhi pill; M-JWEZP: medium-dose Jiawei Erzhi pill; H-JWEZP: high-dose Jiawei Erzhi pill; COX2: cyclooxygenase-2; FTH1: ferritin heavy chain 1; SLC7A11: solute carrier family 7 member 11; GPX4: glutathione peroxidase 4; JNK: c-Jun N-terminal kinase; PI3K: phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; Akt: protein Kinase B; MAPK: mitogen-activated protein kinase. The results are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (n = 3), and the groups were compared using one-way analysis of variance. aP < 0.01, compared with model group; bP < 0.01, compared with control group; cP < 0.05, compared with model group.
| 1. |
Conte SM, Vale, PR. Peripheral arterial disease. Heart Lung Circ 2018; 27: 427-32.
DOI PMID |
| 2. |
Emini Veseli B, Perrotta P, De Meyer GRA, et al. Animal models of atherosclerosis. Eur J Pharmacol 2017; 816: 3-13.
DOI PMID |
| 3. |
Moore KJ, Tabas I. Macrophages in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Cell 2011; 145: 341-55.
DOI PMID |
| 4. | Zhong S, Li L, Shen X, et al. An update on lipid oxidation and inflammation in cardiovascular diseases. Free Radic Biol Med 2019; 144: 266-78. |
| 5. |
Shibata T, Shimizu K, Hirano K, et al. Adductome-based identification of biomarkers for lipid peroxidation. J Biol Chem 2017; 292: 8223-35.
DOI PMID |
| 6. |
Hammad SM, Twal WO, Barth JL, et al. Oxidized LDL immune complexes and oxidized LDL differentially affect the expression of genes involved with inflammation and survival in human U937 monocytic cells. Atherosclerosis 2009; 202: 394-404.
DOI PMID |
| 7. |
Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR, et al. Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell 2012; 149: 1060-72.
DOI PMID |
| 8. |
Latunde-Dada GO. Ferroptosis: role of lipid peroxidation, iron and ferritinophagy. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj 2017; 1861: 1893-900.
DOI URL |
| 9. |
Stockwell BR, Friedmann Angeli JP, Bayir H, et al. Ferroptosis: a regulated cell death nexus linking metabolism, redox biology, and disease. Cell 2017; 171: 273-85.
DOI PMID |
| 10. |
Bai T, Li MX, Liu YF, Qiao ZT, Wang ZW. Inhibition of ferroptosis alleviates atherosclerosis through attenuating lipid peroxidation and endothelial dysfunction in mouse aortic endothelial cell. Free Radic Biol Med 2020; 160: 92-102.
DOI URL |
| 11. |
Sullivan JL. Iron in arterial plaque: modifiable risk factor for atherosclerosis. Biochim Biophys Acta 2009; 1790: 718-23.
DOI PMID |
| 12. | Lei W, Shen F, Chang N, et al. Chemical proteomics reveals ligustilide targets SMAD3, inhibiting collagen synthesis in aortic endothelial cells. Chin Chem Lett 2021; 32: 190-3. |
| 13. | Zuo JY, Park C, Doschak M, Löbenberg R. Are the release characteristics of Erzhi pills in line with Traditional Chinese Medicine theory? A quantitative study. J Integr Med 2021; 19: 50-5. |
| 14. | Huang S, Mu F, Li F, et al. A network-based approach to explore the mechanism and bioactive compounds of Erzhi pill against metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease. J Diabetes Res 2020; 2020: 1-15. |
| 15. | Peng M, Xia T, Zhong Y, et al. Integrative pharmacology reveals the mechanisms of Erzhi pill, a traditional Chinese formulation, against diabetic cardiomyopathy. J Ethnopharmacol 2022; 296: 115474. |
| 16. |
Xia J, Hu J, Zhang R, et al. Icariin exhibits protective effects on cisplatin-induced cardiotoxicity via ROS-mediated oxidative stress injury in vivo and in vitro. Phytomedicine 2022; 104: 154331.
DOI URL |
| 17. |
Huwait EA, Saddeek SY, Al-Massabi RF, Almowallad SJ, Pushparaj PN, Kalamegam G. Antiatherogenic effects of quercetin in the THP-1 macrophage model in vitro, with insights into its signaling mechanisms using in silico analysis. Front Pharmacol 2021; 12: 698138.
DOI URL |
| 18. | Li H, Xiao L, He H, et al. Quercetin attenuates atherosclerotic inflammation by inhibiting galectin-3-NLRP 3 signaling pathway. Mol Nutr Food Res 2021; 65: e2000746. |
| 19. | Zhang Y, Xu D, Huang P, et al. Essential role of protein kinase C betaI in icariin-mediated protection against atherosclerosis. J Pharm Pharmacol 2021; 73: 1169-79. |
| 20. |
Zeng Y, Xiong Y, Yang T, et al. Icariin and its metabolites as potential protective phytochemicals against cardiovascular disease: from effects to molecular mechanisms. Biomed Pharmacother 2022; 147: 112642.
DOI URL |
| 21. |
Luo H, Zhang R. Icariin enhances cell survival in lipopolysaccharide-induced synoviocytes by suppressing ferroptosis via the Xc-/GPX4 axis. Exp Ther Med 2021; 21: 72.
DOI URL |
| 22. |
Liu X, Ma Y, Luo L, et al. Dihydroquercetin suppresses cigarette smoke induced ferroptosis in the pathogenesis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease by activating Nrf2-mediated pathway. Phytomedicine 2022; 96: 153894.
DOI URL |
| 23. | Wang ZX, Ma J, Li XY, et al. Quercetin induces p53-independent cancer cell death through lysosome activation by the transcription factor EB and reactive oxygen species-dependent ferroptosis. Br J Pharmacol 2021; 178: 1133-48. |
| 24. | Fang Y, Liu J, Xin L, et al. Radix Salvia miltiorrhiza for ankylosing spondylitis: determining potential inflammatory molecular targets and mechanism using network pharmacology. Biomed Res Int 2022; 2022: 1-13. |
| 25. |
Xu X, Zhang W, Huang C, et al. A novel chemometric method for the prediction of human oral bioavailability. Int J Mol Sci 2012; 13: 6964-82.
DOI PMID |
| 26. | Jia CY, Li JY, Hao GF, Yang GF. A drug-likeness toolbox facilitates ADMET study in drug discovery. Drug Discov Today 2020; 25: 248-58. |
| 27. | Jiang L, Kon N, Li T, et al. Ferroptosis as a p53-mediated activity during tumour suppression. Nature 2015; 520: 57-62. |
| 28. |
Kobayashi M, Suhara T, Baba Y, Kawasaki NK, Higa JK, Matsui T. Pathological roles of iron in cardiovascular disease. Curr Drug Targets 2018; 19: 1068-76.
DOI PMID |
| 29. | Ayala A, Muñoz M, Argüelles S. Lipid peroxidation: production, metabolism, and signaling mechanisms of malondialdehyde and 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2014; 2014: 360438. |
| 30. |
Gianazza E, Brioschi M, Martinez Fernandez A, et al. Lipid peroxidation in atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases. Antioxid Redox Signal 2021; 34: 49-98.
DOI URL |
| 31. | Dev S, Babitt JL. Overview of iron metabolism in health and disease. Hemodial Int 2017; 21 Suppl 1: S6-S20. |
| 32. |
Wunderer F, Traeger L, Sigurslid HH, et al. The role of hepcidin and iron homeostasis in atherosclerosis. Pharmacol Res 2020; 153: 104664.
DOI URL |
| 33. |
Seibt TM, Proneth B, Conrad M. Role of GPX4 in ferroptosis and its pharmacological implication. Free Radic Biol Med 2019; 133: 144-52.
DOI URL |
| 34. |
Luo TT, Lu Y, Yan SK, Xiao X, Rong XL, Guo J. Network pharmacology in research of Chinese medicine formula: methodology, application and prospective. Chin J Integr Med 2020; 26: 72-80.
DOI |
| 35. | Bi Z, Zhang W, Yan X. Anti-inflammatory and immunoregulatory effects of icariin and icaritin. Biomed Pharmacother 2022; 151: 113180. |
| 36. | Chen Y, Gan Y, Yu J, Ye X, Yu W. Key ingredients in Verbena officinalis and determination of their anti-atherosclerotic effect using a computer-aided drug design approach. Front Plant Sci 2023; 14: 1154266. |
| 37. |
Luo G, Xiang L, Xiao L. Quercetin alleviates atherosclerosis by suppressing oxidized LDL-induced senescence in plaque macrophage via inhibiting the p38MAPK/p16 pathway. J Nutr Biochem 2023; 116: 109314.
DOI URL |
| 38. |
Wang IC, Lin JH, Lee WS, Liu CH, Lin TY, Yang KT. Baicalein and luteolin inhibit ischemia/ reperfusion-induced ferroptosis in rat cardiomyocytes. Int J Cardiol 2023; 375: 74-86.
DOI URL |
| 39. |
Wang SJ, Li D, Ou Y, et al. Acetylation is crucial for p53-mediated ferroptosis and tumor suppression. Cell Rep 2016; 17: 366-73.
DOI URL |
| 40. |
Yang WS, SriRamaratnam R, Welsch ME, et al. Regulation of ferroptotic cancer cell death by GPX4. Cell 2014; 156: 317-31.
DOI PMID |
| 41. | Lagares MH, Silva KSF, Barbosa AM, et al. Analysis of p53 gene polymorphism (codon 72) in symptomatic patients with atherosclerosis. Genet Mol Res 2017; 16: 1-10. |
| 42. | Iwabayashi M, Taniyama Y, Sanada F, et al. Inhibition of Lp(a)-induced functional impairment of endothelial cells and endothelial progenitor cells by hepatocyte growth factor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2012; 423: 79-84. |
| 43. | Konstorum A, Tesfay L, Paul BT, Torti FM, Laubenbacher RC, Torti SV. Systems biology of ferroptosis: a modeling approach. J Theor Biol 2020; 493: 110222. |
| 44. | Wang Y, Zhao Y, Ye T, Yang L, Shen Y, Li H. Ferroptosis signaling and regulators in atherosclerosis. Front Cell Dev Biol 2021; 9: 809457. |
| 45. |
Funauchi Y, Tanikawa C, Yi Lo PH, et al. Regulation of iron homeostasis by the p53-ISCU pathway. Sci Rep 2015; 5: 16497.
DOI PMID |
| 46. |
Zhang F, Wang W, Tsuji Y, Torti SV, Torti FM. Post-transcriptional modulation of iron homeostasis during p53-dependent growth arrest. J Biol Chem 2008; 283: 33911-8.
DOI PMID |
| 47. |
Chen WX, Zhang Y, Wang ZX, et al. Dapagliflozin alleviates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by reducing ferroptosis MAPK signaling inhibition. Front Pharmacol 2023; 14: 1078205.
DOI URL |
| 48. |
Sarmiento-Salinas FL, Perez-Gonzalez A, Acosta-Casique A, et al. Reactive oxygen species: role in carcinogenesis, cancer cell signaling and tumor progression. Life Sci 2021; 284: 119942.
DOI URL |
| 49. |
Son Y, Kim S, Chung HT, Pae HO. Reactive oxygen species in the activation of MAP kinases. Methods Enzymol 2013; 528: 27-48.
DOI PMID |
| 50. |
Liu R, Sun Y, Di D, Zhang X, Zhu B, Wu H. PI3K/AKT/SERBP-1 pathway regulates Alisma orientalis beverage treatment of atherosclerosis in APOE-/- high-fat diet mice. Pharm Biol 2023; 61: 473-87.
DOI URL |
| 51. |
Li J, Jiang J, Chen Y, Lu WQ. KLF 2 inhibits colorectal cancer progression and metastasis by inducing ferroptosis via the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. J Pathol Clin Res 2023; 9: 423-35.
DOI URL |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

