Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (2): 291-302.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2025.02.016
• Original articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Mechanism of Huayu Qutan recipe (化瘀祛痰方) anti-atherosclerosis mediates lipophagy via mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1/ transcription factor EB signaling pathway in ApoE-/-mice
LI Yue1,2, PAN Jiaxiang1, YANG Guanlin3, YU Jiajia4, WU Xize5, MIN Dongyu6, CHENG Meijia6, YU Dongdong7, NAN Minghua8,9, GAO Xiaoyu10, PANG Linlin1, GONG Lihong1,2( ), JIA Lianqun3(
), JIA Lianqun3( )
)
- 1 Department of Cardiology, the Affiliated Hospital of Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenyang 110032, China
2 Liaoning Provincial Key Laboratory of TCM Geriatric Cardio-Cerebrovascular Diseases, Shenyang 110032, China
3 Innovation Engineering Technology Center of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenyang 110847, China
4 Postdoctoral Program of Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenyang 110847, China
5 Graduate School of Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenyang 110847, China
6 Experimental Center of Traditional Chinese Medicine, the Affiliated Hospital of Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenyang 110032, China
7 Department of Osteology, Affiliated Hospital of Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenyang 110032, China
8 Key Laboratory of Ministry of Education for TCM Viscera-State Theory and Applications of Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenyang 110847, China
9 Second Affiliated Hospital of Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenyang 110000, China
10 Department of Oncology department, Shengjing Hospital affiliated to China Medical University, Shenyang 110000, China
-
Received:2023-12-12Accepted:2024-05-15Online:2025-04-15Published:2025-03-10 -
Contact:Prof. JIA Lianqun, Department of Academic Affairs Office, Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenyang 110847, China. jlq-8@163.com; Prof. GONG Lihong, Department of Cardiology, Affiliated Hospital of Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenyang 110032, China. 215922524@qq.com, Telephone: +86-24-82961157 -
Supported by:Science and Technology Research Project of Education Department of Liaoning Province: the Mechanism of Regulating Lipophagy and Affecting Cholesterol Efflux in Human Promyelocytic Leukemia Cell Line Macrophages by Huayu Qutan Recipe based on the Theory of "Laoxia Shengtan"(L202048);Youth Project of Basic Scientific Research Project of Education Department of Liaoning Province: Mechanism of Mitochondrial Autophagy and Apoptosis in L02 Hepatocytes Regulated by miR-7043-3p based on the Theory of "Spleen Qi Dispersing Essence" of Huayu Qutan Recipe(LJKQZ2021064)
Cite this article
LI Yue, PAN Jiaxiang, YANG Guanlin, YU Jiajia, WU Xize, MIN Dongyu, CHENG Meijia, YU Dongdong, NAN Minghua, GAO Xiaoyu, PANG Linlin, GONG Lihong, JIA Lianqun. Mechanism of Huayu Qutan recipe (化瘀祛痰方) anti-atherosclerosis mediates lipophagy via mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1/ transcription factor EB signaling pathway in ApoE-/-mice[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(2): 291-302.
share this article
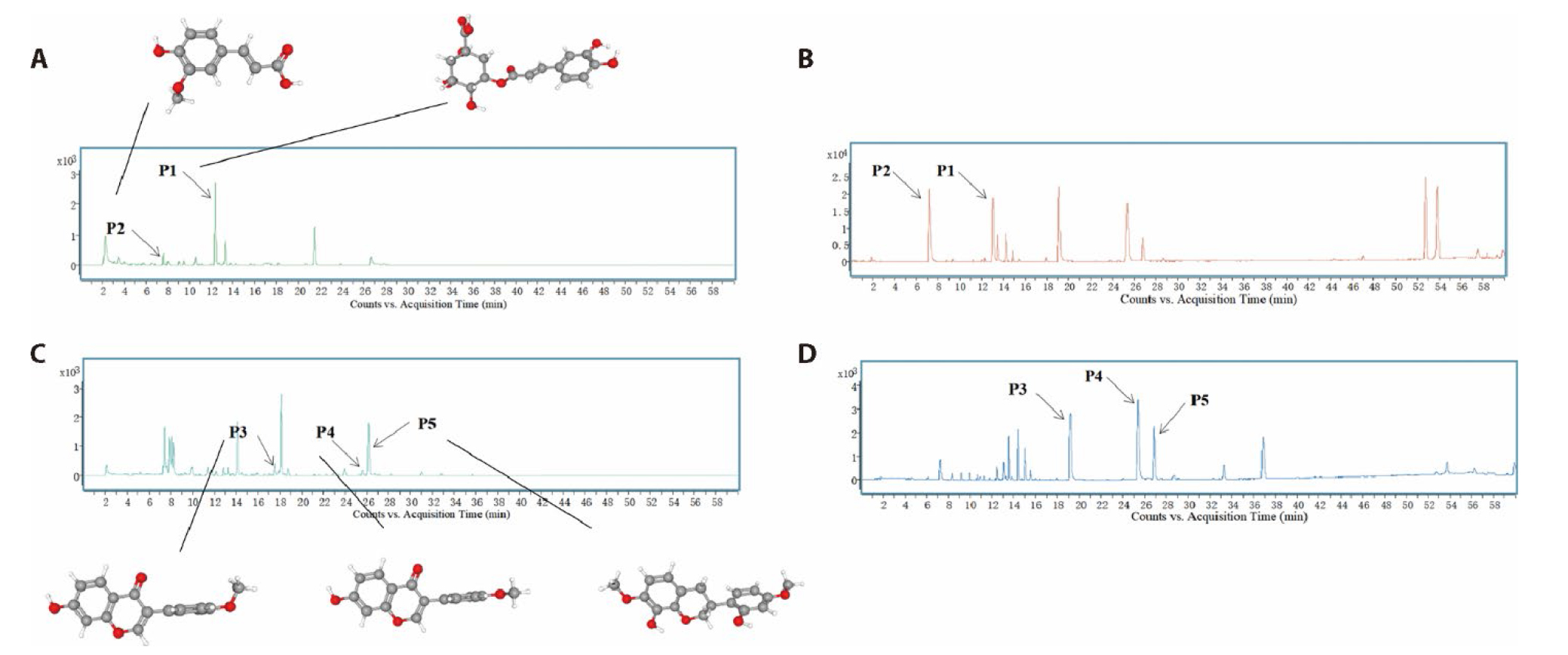
Figure 1 The extracted ion chromatograms of HYQT A: the extracted ion chromatograms of HYQT. A1: the total ion flow diagram of UPLC-Q/TOF-MS negative-ion mode of mixed standards; A2: the total ion flow diagram of UPLC-Q/TOF-MS negative-ion mode of HYQT sample; A3: the total ion flow diagram of UPLC-Q/TOF-MS positive-ion mode of mixed standards; A4: the total ion flow diagram of UPLC-Q/TOF-MS positive-ion mode of HYQT sample; P1: Ferulic acid; P2: Chlorogenic acid; P3: Calyx isoflavone; P4: Formononetin; P5: 8,2 '-dihydroxy-7,4' -dimethoxy-isoflavane. HYQT: Huayu Qutan recipe; UPLC-Q/TOF-MS: high performance liquid chromatography of quadrupole time of flight-tandem mass spectrometry.
| Time | n | CTRL | ND | HFD | L-HYQT | M-HYQT | H-HYQT | SIM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 week | 10 | 17.50±0.90 | 17.3±0.96 | 17.4±0.56 | 17.23±1.15 | 17.23±0.35 | 17.73±0.23 | 17.46±0.70 |
| 4 weeks | 10 | 20.13±1.36 | 20.73±1.30 | 22.00±0.87 | 20.97±1.19 | 20.33±1.15 | 20.67±1.27 | 20.97±1.31 |
| 8 weeks | 10 | 22.47±1.60 | 23.13±2.11 | 25.73±0.67ab | 24.63±1.94cd | 24.67±0.58cd | 23.94±1.46 | 24.70±1.62 |
| 12 weeks | 10 | 25.20±0.96 | 25.63±0.75 | 29.47±0.40ab | 28.27±0.51ab | 28.21±0.71cd | 27.28±0.93bc | 27.52±1.37cde |
| 16 weeks | 10 | 27.67±0.50 | 27.73±0.40 | 33.60±1.14ab | 32.93±0.67ab | 30.93±0.59abf | 30.80±0.40abdfg | 30.80±1.40 abdfg |
Table 1 Mice were weighted weekly for the 7 groups
| Time | n | CTRL | ND | HFD | L-HYQT | M-HYQT | H-HYQT | SIM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 week | 10 | 17.50±0.90 | 17.3±0.96 | 17.4±0.56 | 17.23±1.15 | 17.23±0.35 | 17.73±0.23 | 17.46±0.70 |
| 4 weeks | 10 | 20.13±1.36 | 20.73±1.30 | 22.00±0.87 | 20.97±1.19 | 20.33±1.15 | 20.67±1.27 | 20.97±1.31 |
| 8 weeks | 10 | 22.47±1.60 | 23.13±2.11 | 25.73±0.67ab | 24.63±1.94cd | 24.67±0.58cd | 23.94±1.46 | 24.70±1.62 |
| 12 weeks | 10 | 25.20±0.96 | 25.63±0.75 | 29.47±0.40ab | 28.27±0.51ab | 28.21±0.71cd | 27.28±0.93bc | 27.52±1.37cde |
| 16 weeks | 10 | 27.67±0.50 | 27.73±0.40 | 33.60±1.14ab | 32.93±0.67ab | 30.93±0.59abf | 30.80±0.40abdfg | 30.80±1.40 abdfg |

Figure 2 Effects of HYQT on atherosclerosis ORO and HE staining were performed. A: full-length aorta containing most of the thoracic aorta, and abdominal aorta with ORO staining; B: image analysis of ORO (n = 3 per group). C: HE stains of aortas (Scale bar: 50 μm), C1-C7: Pathological changes of aorta of CTRL, ND, HFD, L-HYQT, M-HYQT, H-HYQT, and SIM group in week 16. D: ORO stains of aortas (Scale bar: 50 μm), D1-D7: ORO stains of CTRL, ND, HFD, L-HYQT, M-HYQT, H-HYQT, and SIM group in week 16. CTRL group: C57/BL6J mice, normal diet for 16 weeks; ND group: ApoE-/- mice, normal diet for 16 weeks; HFD group: ApoE-/- mice, HFD for 16 weeks; L-HYQT group: ApoE-/- mice, HFD for 16 weeks and received HYQT for 8 weeks (10.27 g·kg-1·d-1); M-HYQT group: ApoE-/- mice, HFD for 16 weeks, received HYQT for 8 weeks (20.54 g·kg-1·d-1); H-HYQT group: ApoE-/- mice, HFD for 16 weeks, received HYQT for 8 weeks (41.08 g·kg-1·d-1); SIM group: ApoE-/- mice, HFD for 16 weeks, received SIM for 8 weeks (10 mg·kg-1·d-1). ORO: oil red O; HE: hematoxylin-eosin; CTRL: control; ND: normal diet; HFD: high fat diet; HYQT: Huayu Qutan recipe; L-HYQT: low dose of Huayu Qutan recipe; M-HYQT: middle dose of Huayu Qutan recipe; H-HYQT: high dose of Huayu Qutan recipe; ANOVA: one-way analysis of variance; SEM: standard error of mean. ANOVA was performed for normal distribution data. The data were presented as the mean ± SEM from 3 independent experiments. aP < 0.01 vs ND group, bP < 0.05 vs HFD group, cP < 0.05 vs L-HYQT group.

Figure 3 HYQT promoted lipophagy in aortic tissue A: fluorescence images of CD68-LC3B in aortic root sections obtained from mice in week 16 (scale bar: 50 μm). A1-A3: CD68-LC3B in aortic root of CTRL group; A4-A6: CD68-LC3B in aortic root of ND group; A7-A9: CD68-LC3B in aortic root of HFD group; A10-A12: CD68-LC3B in aortic root of L-HYQT; A13-A15: CD68-LC3B in aortic root of M-HYQT group; A16-A18: CD68-LC3B in aortic root of H-HYQT group; A19-A21: CD68-LC3B in aortic root of SIM group. B: TEM image of 1 μm (the yellow arrow points to the lysosome and the yellow star locats lipophagy, scale bar: 2.0 μm). B: the formation of autophagosomes and lipid droplets was observed by transmission electron microscopy in week 16. B1: CTRL group; B2: ND group; B3: HFD group; B4: L-HYQT group; B5: M-HYQT group; B6: H-HYQT group; B7: SIM group. CTRL group: C57/BL6J mice, normal diet for 16 weeks; ND group: ApoE-/- mice, normal diet for 16 weeks; HFD group: ApoE-/- mice, HFD for 16 weeks; L-HYQT group: ApoE-/- mice, HFD for 16 weeks and received HYQT for 8 weeks (10.27 g·kg-1·d-1); M-HYQT group: ApoE-/- mice, HFD for 16 weeks, received HYQT for 8 weeks (20.54 g·kg-1·d-1); H-HYQT group: ApoE-/- mice, HFD for 16 weeks, received HYQT for 8 weeks (41.08 g·kg-1·d-1); SIM group: ApoE-/- mice, HFD for 16 weeks, received SIM for 8 weeks (10 mg·kg-1·d-1). CTRL: control; ND: normal diet; HFD: high fat diet; HYQT: Huayu Qutan recipe; L-HYQT: low dose of Huayu Qutan recipe; M-HYQT: middle dose of Huayu Qutan recipe; H-HYQT: high dose of Huayu Qutan recipe; SIM: simvastatin; CD68: macrophage Antigen CD68; LC3B: Microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3 beta; TEM: transmission electron microscopy.

Figure 4 HYQT regulated lipophagy through the mTORC1/TFEB signaling pathway, and ABCA1 genes and proteins expression in aortic. A: the expression level of Beclin1 mRNA; B: the expression level of p62 mRNA; C: the expression level of Lamp1 mRNA. The data were detected by reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR) of aortic in week 16; D: the expression level of LC3A/B, Beclin1, p62 and Lamp1 were determined by Western blotting, using β‐actin as a loading control; E: Western blot analysis of LC3 A/B; F: Western blot analysis of Beclin1;G: Western blot analysis of p62; H: Western blot analysis of Lamp1; I: mTOR, p-mTOR, ABCA1 expression detected by Western blot; J: relative expression level of mTOR protein; K: p-mTOR protein; L: p-mTOR/mTOR protein; M: the expression level of ABCA1 mRNA; N: the expression level of ABCA1 protein. CTRL group: C57/BL6J mice, normal diet for 16 weeks; ND group: ApoE-/- mice, normal diet for 16 weeks; HFD group: ApoE-/- mice, HFD for 16 weeks; L-HYQT group: ApoE-/- mice, HFD for 16 weeks and received HYQT for 8 weeks (10.27 g·kg-1·d-1); M-HYQT group: ApoE-/- mice, HFD for 16 weeks, received HYQT for 8 weeks (20.54 g·kg-1·d-1); H-HYQT group: ApoE-/- mice, HFD for 16 weeks, received HYQT for 8 weeks (41.08 g·kg-1·d-1); SIM group: ApoE-/- mice, HFD for 16 weeks, received SIM for 8 weeks (10 mg·kg-1·d-1). Beclin1: recombinant beclin 1; p62: sequestosome 1??; mTORC1: mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1; p-mTOR: phosphorylated mammalian target of rapamycin; Lamp1: recombinant lysosomal associated membrane protein 1; LC3 A/B: autophagy related protein LC3 A/B; ABCA1: ATP-binding cassette transporter A1; ANOVA: one-way analysis of variance; SEM: standard error of mean. ANOVA was performed for normal distribution data. The data were presented as the mean ± SEM from 3 independent experiments. aP < 0.01, eP < 0.05, vs HFD group; bP < 0.01, fP < 0.05, vs L-HYQT group; cP < 0.01 vs CTRL group, dP < 0.01, gP < 0.05, vs ND group.
| 1. | World Health Organization. Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs), 2020-03-14, cited 2021-06-11. Available from URL: https://www.who.int/zh/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cardiovascular-diseases-(cvds). |
| 2. |
Libby P, Buring JE, Badimon L, et al. Atherosclerosis. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2019; 5: 56.
DOI PMID |
| 3. |
Ward NC, Watts GF, Eckel RH. Statin toxicity. Circ Res 2019; 124: 328-50.
DOI PMID |
| 4. | Li YC (Qing dynasty). Zheng Zhi Hui Bu. Beijing: China Traditional Chinese Medicine Press, 2005: 15. |
| 5. | Zhang Z, Hu J. Recent advances and perspective of studies on phlegm syndrome in Chinese Medicine. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2016; 2016: 6463270. |
| 6. |
Bai D, Song J. Plasma metabolic biomarkers for syndrome of phlegm and blood stasis in hyperlipidemia and atherosclerosis. J Tradit Chin Med 2012; 32: 578-83.
DOI |
| 7. | Su C, Li N, Ren R, et al. Progress in the medicinal value, bioactive compounds, and pharmacological activities of gynostemma pentaphyllum. Molecules 2021; 26: 6249. |
| 8. | Huang W, Yang Y, Zeng Z, et al. Effect of Salvia Miltiorrhiza and ligustrazine injection on myocardial ischemia/reperfusion and hypoxia/reoxygenation injury. Mol Med Rep 2016; 144537-44. |
| 9. | Wang Q, Yuan LL, Zhang YL, et al. Research on network pharmacology of Acori Tatarinowii Rhizoma combined with Curcumae Radix in treating epilepsy. Zhong Guo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2019; 44: 2701-8. |
| 10. | Man YC, Yang C, Wang XT, et al. Effect of Huayu Qutan decoction recipe on liver lipid injury in atherosclerotic rabbits by regulating autophagy through PI3K/Akt/mTOR signal pathway. Zhong Hua Zhong Yi Yao Xue Kan 2019; 37: 1913-6+2058. |
| 11. | Pei YP, Chen ZH, Meng XY, et al. Mechanism of prevention and treatment of arteriosclerosis by Jianpi Qutan Huayu formula regulating miR-155/Rheb/mTOR pathway to mediate autophagy of endothelial cells. Zhong Hua Zhong Yi Yao Xue Kan 2022; 40: 29-34+262-3. |
| 12. | Sun YM, Jia LQ, Zhang N, et al. Effect of Huayu Qutan recipe on liver mediated autophagy related gene mTOR in hyperlipidemia rats. Zhong Hua Zhong Yi Yao Xue Kan 2017; 35: 3143-6. |
| 13. | Zheng Q, Jia LQ, Song N, et al. Study on inhibitory effect of Huayu Qutan recipe on myocardial fibrosis in atherosclerotic rabbits based on mitochondrial Fusion-lysis. Zhong Guo Shi Yan Fang Ji Xue Za Zhi 2020; 26: 71-7. |
| 14. | Pi S, Mao L, Chen J, et al. The P2RY12 receptor promotes VSMC-derived foam cell formation by inhibiting autophagy in advanced atherosclerosis. Autophagy 2021; 17: 980-1000. |
| 15. |
Wang N, Westerterp M. ABC Transporters, Cholesterol efflux, and implications for cardiovascular diseases. Adv Exp Med Biol 2020; 1276: 67-83.
DOI PMID |
| 16. |
Chistiakov DA, Melnichenko AA, Myasoedova VA, et al. Mechanisms of foam cell formation in atherosclerosis. J Mol Med (Berl) 2017; 95: 1153-65.
DOI PMID |
| 17. |
Kim YC, Guan KL. mTOR: a pharmacologic target for autophagy regulation. J Clin Invest 2015; 125: 25-32.
DOI PMID |
| 18. | Roczniak-Ferguson A, Petit CS, Froehlich F, et al. The transcription factor TFEB links mTORC 1 signaling to transcriptional control of lysosome homeostasis. Sci Signal 2012; 5: ra42. |
| 19. |
Settembre C, Zoncu R, Medina DL, et al. A lysosome-to-nucleus signalling mechanism senses and regulates the lysosome via mTOR and TFEB. Embo J 2012; 31: 1095-108.
DOI PMID |
| 20. |
Martina JA, Diab HI, Brady OA, et al. TFEB and TFE3 are novel components of the integrated stress response. Embo J 2016; 35: 479-95.
DOI PMID |
| 21. |
Nezich CL, Wang C, Fogel AI, et al. MiT/TFE transcription factors are activated during mitophagy downstream of Parkin and Atg5. J Cell Biol 2015; 210: 435-50.
DOI PMID |
| 22. |
Raben N, Puertollano R. TFEB and TFE3: linking lysosomes to cellular adaptation to stress. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 2016; 32: 255-78.
PMID |
| 23. | Ren H, Wang D, Zhang L, et al. Catalpol induces autophagy and attenuates liver steatosis in ob/ob and high-fat diet-induced obese mice. Aging (Albany NY) 2019; 11: 9461-77. |
| 24. | Wang D, Hiebl V, Xu T, et al. Impact of natural products on the cholesterol transporter ABCA1. J Ethnopharmacol 2020; 249: 112444. |
| 25. |
Ahmadi A, Argulian E, Leipsic J, et al. From subclinical atherosclerosis to plaque progression and acute coronary events: JACC state-of-the-art review. J Am Coll Cardiol 2019; 74: 1608-17.
DOI PMID |
| 26. | Bai T, Li M, Liu Y, et al. Inhibition of ferroptosis alleviates atherosclerosis through attenuating lipid peroxidation and endothelial dysfunction in mouse aortic endothelial cell. Free Radic Biol Med 2020; 160: 92-102. |
| 27. |
Zhang Z, Zhang T, Dong K. Icariin upregulates phosphorylated cyclic adenosine monophosphate response element binding protein levels in the hippocampus of the senescence- accelerated mouse. Neural Regen Res 2012; 7: 885-90.
DOI PMID |
| 28. | Bigford GE, Szeto A, Kimball J, et al. Cardiometabolic risks and atherosclerotic disease in ApoE knockout mice: effect of spinal cord injury and salsalate anti-inflammatory pharmacotherapy. PLoS One 2021; 16: e0246601. |
| 29. | Li D, Rui YX, Guo SD, et al. Ferulic acid: a review of its pharmacology, pharmacokinetics and derivatives. Life Sci 2021; 284: 119921. |
| 30. |
Lukitasari M, Saifur Rohman M, Nugroho DA, et al. Cardiovascular protection effect of chlorogenic acid: focus on the molecular mechanism. F1000Res 2020; 9: 1462.
DOI PMID |
| 31. | Wu C, Luan H, Zhang X, et al. Chlorogenic acid protects against atherosclerosis in ApoE-/- mice and promotes cholesterol efflux from RAW264.7 macrophages. PLoS One 2014; 9: e95452. |
| 32. | Pan L, Zhang XF, Wei WS, et al. The cardiovascular protective effect and mechanism of calycosin and its derivatives. Chin J Nat Med 2020; 18: 907-15. |
| 33. | Ma C, Xia R, Yang S, et al. Formononetin attenuates atherosclerosis via regulating interaction between KLF4 and SRA in apoE(-/-) mice. Theranostics 2020; 10: 1090-106. |
| 34. |
Fardoun MM, Maaliki D, Halabi N, et al. Flavonoids in adipose tissue inflammation and atherosclerosis: one arrow, two targets. Clin Sci (Lond) 2020; 134: 1403-32.
DOI PMID |
| 35. | Zhao J, Yu QT, Li P, et al. Determination of nine active components in Radix Hedysari and Radix Astragali using capillary HPLC with diode array detection and MS detection. J Sep Sci 2008; 31: 255-61. |
| 36. |
He J, Zhang G, Pang Q, et al. SIRT6 reduces macrophage foam cell formation by inducing autophagy and cholesterol efflux under ox-LDL condition. FEBS J 2017; 284: 1324-37.
DOI PMID |
| 37. |
Li X, Xu M, Pitzer AL, et al. Control of autophagy maturation by acid sphingomyelinase in mouse coronary arterial smooth muscle cells: protective role in atherosclerosis. J Mol Med (Berl) 2014; 92: 473-85.
DOI PMID |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

