Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (3): 618-627.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20250515.001
Previous Articles Next Articles
Weifuchun (胃复春 ) exerts therapeutic effects on gastric fundic gland polyps by promoting ferroptosis
LI Yue1( ), DENG Jinyan1(
), DENG Jinyan1( ), PI Shanshan1, ZHANG Yingjuan1, ZHAO Dan1, GUO Yi1, YE Yong’an2,3, ZAO Xiaobin4,5(
), PI Shanshan1, ZHANG Yingjuan1, ZHAO Dan1, GUO Yi1, YE Yong’an2,3, ZAO Xiaobin4,5( ), DU Hongbo2,3(
), DU Hongbo2,3( )
)
- 1 Gastroenterology Department, Dongzhimen Hospital, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100700, China
2 Gastroenterology Department, Dongzhimen Hospital, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100700, China
3 Institute of Liver Diseases, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100700, China
4 Institute of Liver Diseases, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100700, China
5 Key Laboratory of Chinese Internal Medicine of Ministry of Education and Beijing, Dongzhimen Hospital, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100700, China
-
Received:2024-11-02Accepted:2025-01-24Online:2025-06-15Published:2025-05-15 -
Contact:DU Hongbo, Gastroenterology Department, Dongzhimen Hospital, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100700, China; Institute of Liver Diseases, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100700, China. duhongbtcm@126.com;ZAO Xiaobin, Institute of Liver Diseases, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100700, China; Key Laboratory of Chinese Internal Medicine of Ministry of Education and Beijing, Dongzhimen Hospital, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100700, China. A3417@bucm.edu.cn,Telephone: +86-10-84015592 -
Supported by:National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine Letter([2022]-1);Dongzhimen Hospital Horizontal Project: Exploring the Effects of Weifuchun on Key Mechanisms of Different Types of Gastric Polyps based on Human Organoid Culture Technology(HX-DZM-202239);Qihuang Talent Program for Renowned Physician Cultivation at Beijing University of Chinese Medicine(Y2023A06)
Cite this article
LI Yue, DENG Jinyan, PI Shanshan, ZHANG Yingjuan, ZHAO Dan, GUO Yi, YE Yong’an, ZAO Xiaobin, DU Hongbo. Weifuchun (胃复春 ) exerts therapeutic effects on gastric fundic gland polyps by promoting ferroptosis[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(3): 618-627.
share this article

Figure 1 Morphology and histopathology features of FGP-PDOs A: morphology of primary, passaged, and thawed organoids under bright-field microscopy at different magnifications. A1-A3: bright-field microscope × 50; A4-A6: bright-field microscope × 100. B: HE staining of the three constructed organoid lines was consistent with that of the primary tissue. B1-B3: FGPs; B4-B6: FGPs-PDO. Primary organoids group: A1, A4; passage 4 (P4) organoids group: A2, A5; organoids at passage 1 after thawed group: A3, A6. Patient 1: B1, B4; Patient 2: B2, B5; Patient 3: B3, B6. Scale bar: 100 μm. FGPs: fundic gland polyps; PDO: patient-derived organoids.HE: hematoxylin-eosin staining.
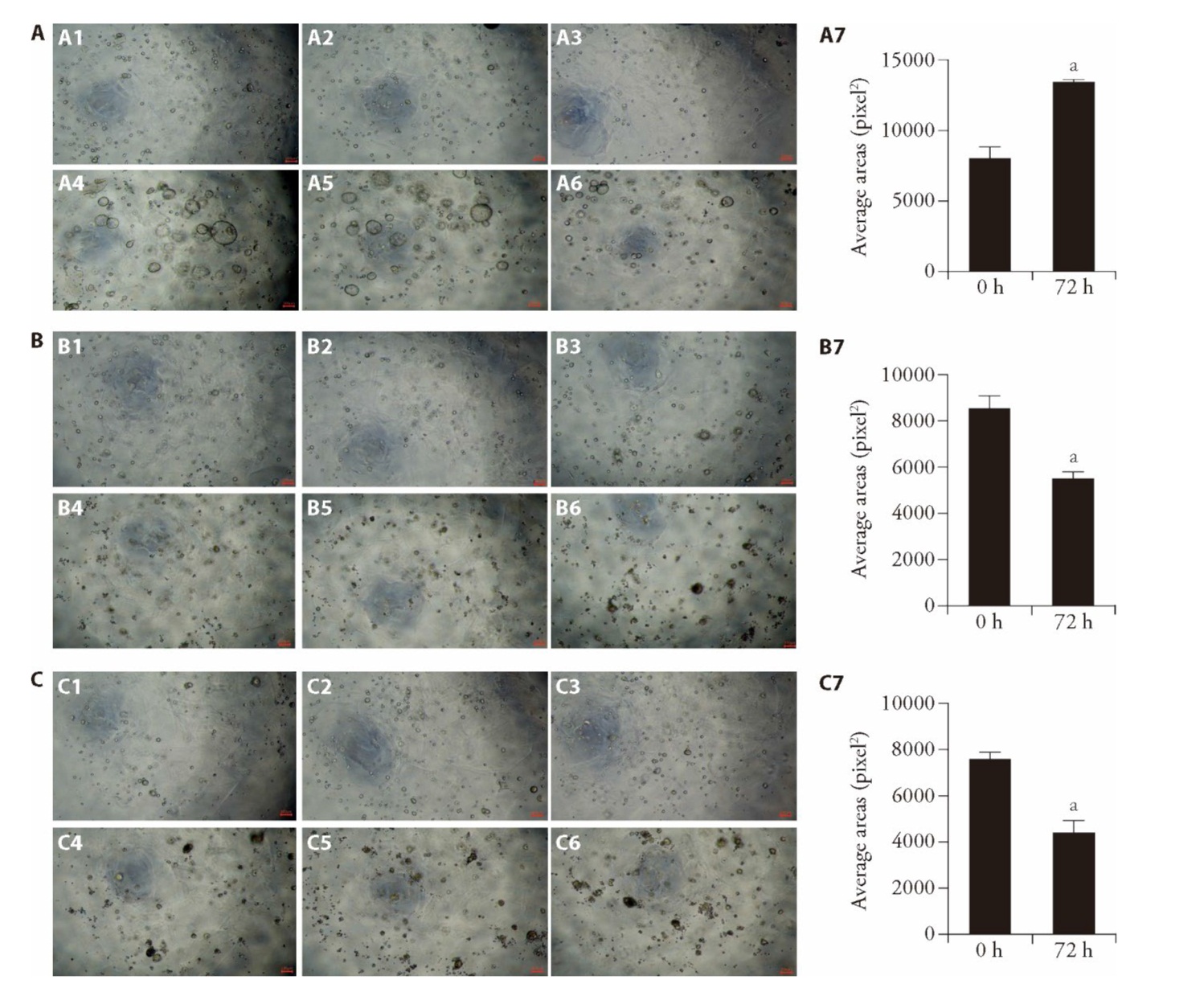
Figure 2 Effect of WFC on FGPs-PDO cell activity A: bright-field images of three organoid lines in the control group at 0 and 72 h. A1-A3 are bright-field images at 0 h after drug administration; A4-A6 are bright-field images at 72 h after drug administration. A1, A4: Organoid 1; A2, A5: Organoid 2; A3, A6: Organoid 3; A7: the statistical analysis of the average organoid area at 0, 72 h. B: bright-field images of three organoid lines treated with 10 μM sorafenib at 0, 72 h. B1-B3 are bright-field images at 0 h after drug administration; B4-B6 are bright-field images at 72 h after drug administration. B1, B4: Organoid 1; B2, B5: Organoid 2; B3, B6: Organoid 3; B7: the statistical analysis of the average organoid area at 0 and 72 h under sorafenib treatment. C: bright-field images of three organoid lines treated with 250 μg/mL WFC at 0 and 72 h. C1-C3 are bright-field images at 0h after drug administration; C4-C6 are bright-field images at 72 h after drug administration. C1, C4: Organoid 1; C2, C5: Organoid 2; C3, C6: Organoid 3; C7: the statistical analysis of the average organoid area at 0 and 72 h under WFC treatment. A: the control group; no treatment; B: the sorafenib group; treated with 10 μM sorafenib for 72 h; C: the WFC group: treated with 250 μg/mL WFC for 72 h. Scale bar: 100 μm, FGPs: fundic gland polyps; PDO: patient-derived organoids. The unpaired t-test was used to evaluate the differences between the two groups. Data are presented as mean ± standard error of mean (n = 3). aP < 0.001, compared with 0 h.
| Serial No. | Name | Source plant | Serial No. | Name | Source plant |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| XCC1 | Ferulic acid | Herba seu Radix Isodi Amethystoidis | XCC11 | Dibutyl terephthalate | Herba seu Radix Isodi Amethystoidis |
| XCC2 | Caffeic acid | Herba seu Radix Isodi Amethystoidis | XCC12 | Quercetin | Herba seu Radix Isodi Amethystoidis |
| XCC3 | Lariciresinol | Herba seu Radix Isodi Amethystoidis | ZQ1 | Hesperetin | Fructus Aurantii Submaturus |
| XCC4 | Glaucocalyxin A | Herba seu Radix Isodi Amethystoidis | A | beta-sitosterol | Fructus Aurantii Submaturus, Panax ginseng |
| XCC5 | Melissoidesin U | Herba seu Radix Isodi Amethystoidis | ZQ2 | naringenin | Fructus Aurantii Submaturus |
| XCC6 | Pomiferin F | Herba seu Radix Isodi Amethystoidis | ZQ3 | nobiletin | Fructus Aurantii Submaturus |
| XCC7 | Angustifolin | Herba seu Radix Isodi Amethystoidis | HS1 | Dioctyl Phthalate | Panax Ginseng Rubra |
| XCC8 | Glaucocalyxin B | Herba seu Radix Isodi Amethystoidis | HS2 | (6Z,10E,14E,18E)-2,6,10,15, 19,23 hexa-methyltetra-cosa-2,6,10,14,18, 22-hexaene | Panax Ginseng Rubra |
| XCC9 | Melissoidesin M | Herba seu Radix Isodi Amethystoidis | |||
| XCC10 | Melissoidesin O | Herba seu Radix Isodi Amethystoidis | HS3 | ginsenoside rh2 | Panax Ginseng Rubra |
Table 1 Active components of WFC
| Serial No. | Name | Source plant | Serial No. | Name | Source plant |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| XCC1 | Ferulic acid | Herba seu Radix Isodi Amethystoidis | XCC11 | Dibutyl terephthalate | Herba seu Radix Isodi Amethystoidis |
| XCC2 | Caffeic acid | Herba seu Radix Isodi Amethystoidis | XCC12 | Quercetin | Herba seu Radix Isodi Amethystoidis |
| XCC3 | Lariciresinol | Herba seu Radix Isodi Amethystoidis | ZQ1 | Hesperetin | Fructus Aurantii Submaturus |
| XCC4 | Glaucocalyxin A | Herba seu Radix Isodi Amethystoidis | A | beta-sitosterol | Fructus Aurantii Submaturus, Panax ginseng |
| XCC5 | Melissoidesin U | Herba seu Radix Isodi Amethystoidis | ZQ2 | naringenin | Fructus Aurantii Submaturus |
| XCC6 | Pomiferin F | Herba seu Radix Isodi Amethystoidis | ZQ3 | nobiletin | Fructus Aurantii Submaturus |
| XCC7 | Angustifolin | Herba seu Radix Isodi Amethystoidis | HS1 | Dioctyl Phthalate | Panax Ginseng Rubra |
| XCC8 | Glaucocalyxin B | Herba seu Radix Isodi Amethystoidis | HS2 | (6Z,10E,14E,18E)-2,6,10,15, 19,23 hexa-methyltetra-cosa-2,6,10,14,18, 22-hexaene | Panax Ginseng Rubra |
| XCC9 | Melissoidesin M | Herba seu Radix Isodi Amethystoidis | |||
| XCC10 | Melissoidesin O | Herba seu Radix Isodi Amethystoidis | HS3 | ginsenoside rh2 | Panax Ginseng Rubra |

Figure 3 WFC's Co-targets and Interaction Network with FGPs A: venn diagram showing the intersection of FGPs disease genes and WFC target genes; B: network diagram illustrating the drug-active ingredient-intersection target relationship between FGPs and WFC; C: PPI network of WFC-FGPs-related targets; D: bubble chart displaying the top 10 enriched pathways from KEGG pathway. WFC: Weifuchun; FGPs: undic gland polyps; PPI: protein-protein interaction; KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes.
| Active Component | Degree Value | Betweenness Centrality | Closeness Centrality |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quercetin | 53 | 0.25 | 0.42 |
| Glaucocalyxin B | 46 | 0.17 | 0.41 |
| Melissoidesin U | 45 | 0.15 | 0.41 |
| Melissoidesin O | 42 | 0.16 | 0.40 |
| Hesperetin | 42 | 0.17 | 0.37 |
| Glaucocalyxin A | 40 | 0.12 | 0.40 |
| Angustifolin | 28 | 0.08 | 0.37 |
| Melissoidesin M | 28 | 0.08 | 0.37 |
| Dioctyl Phthalate | 24 | 0.12 | 0.36 |
| beta-sitosterol | 18 | 0.10 | 0.34 |
Table 2 Top 10 active components by degree value
| Active Component | Degree Value | Betweenness Centrality | Closeness Centrality |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quercetin | 53 | 0.25 | 0.42 |
| Glaucocalyxin B | 46 | 0.17 | 0.41 |
| Melissoidesin U | 45 | 0.15 | 0.41 |
| Melissoidesin O | 42 | 0.16 | 0.40 |
| Hesperetin | 42 | 0.17 | 0.37 |
| Glaucocalyxin A | 40 | 0.12 | 0.40 |
| Angustifolin | 28 | 0.08 | 0.37 |
| Melissoidesin M | 28 | 0.08 | 0.37 |
| Dioctyl Phthalate | 24 | 0.12 | 0.36 |
| beta-sitosterol | 18 | 0.10 | 0.34 |

Figure 4 Organoid morphology and mRNA expression of key ferroptosis-related genes after WFC treatment A: after 2 d of organoid passaging, drug interventions were performed, followed by bright-field morphological observations at 0 and 72 h. A1-A5 are bright-field images at 0 h after drug administration; A6-A10 are bright-field images at 72 h after drug administration. B: mRNA expression levels of SLC7A11 in the control, Erastin, and WFC groups after 72 h of drug treatment. C: mRNA expression levels of ACSL4 in the control, Erastin, and WFC groups after 72 h of drug treatment. D: mRNA expression levels of SLC7A11 in three organoid lines after 72 h of WFC treatment. E: mRNA expression levels of ACSL4 in three organoid lines after 72 h of WFC treatment. F: mRNA expression levels of ALOX5B in three organoid lines after 72 h of WFC treatment. the control group: A1, A6, treated with 0.1% DMSO; Erastin group: A2, A7, treated with the 5 μM Erastin dissolved in DMSO; Fer-1 + erastin group:A3, A8, the group pretreated with 10 μM Fer-1 for 24 h followed by Erastin treatment; WFC group: A4, A9, the group treated with 250 μg/mL WFC dissolved in DMSO; Fer-1+WFC group: A5, A10, the group pretreated with 10 μM Fer-1 for 24 h followed by WFC treatment. Scale bar: 100 μm. WFC: Weifuchun; DMSO: dimethyl sulfoxide; Fer-1: Ferrostin-1. The unpaired t-test was used to evaluate the differences between the two groups. Data are presented as mean ± standard error of mean (n = 3). Compared with control, aP < 0.0001, bP < 0.05, cP < 0.001.
| 1. | Carmack SW, Genta RM, Schuler CM, Saboorian MH. The current spectrum of gastric polyps: a 1-year national study of over 120 000 patients. Am J Gastroenterol 2009; 104: 1524-32. |
| 2. | Yacoub H, Bibani N, Sabbah M, et al. Gastric polyps: a 10-year analysis of 18 496 upper endoscopies. BMC gastroenterology 2022; 22: 1-7. |
| 3. | Sonnenberg A, Genta RM. Genta RM. Prevalence of benign gastric polyps in a large pathology database. Dig Liver Dis 2015; 47: 164-9. |
| 4. | Martin FC, Chenevix-Trench G, Yeomans ND. Systematic review with23 Meta-analysis: fundic gland polyps and proton pump inhibitors. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2016; 44: 915-25. |
| 5. |
Velázquez-Dohorn ME, López-Durand CF, Gamboa-Domínguez A. Changing trends in gastric polyps. Rev Invest Clin 2018; 70: 40-5.
DOI PMID |
| 6. | Skat-Rørdam PA, Kaya Y, Qvist N, et al. Gastrointestinal manifestations in patients with gastric adenocarcinoma and proximal polyposis of the stomach (GAPPS): a systematic review with analysis of individual patient data. Hered Cancer Clin Pract 2024; 22: 12. |
| 7. |
Fukuda M, Ishigaki H, Sugimoto M, et al. Histological analysis of fundic gland polyps secondary to PPI therapy. Histopathology 2019; 75: 537-45.
DOI PMID |
| 8. | Mankaney GN, Cruise M, Sarvepalli S, Bhatt A, Liska D, Burke CA. Identifying factors associated with detection of sessile gastric polyps in patients with familial adenomatous polyposis. Endosc Int Open 2022; 10: 1080-7. |
| 9. | Kroupa R, Pavlik T, Konecny S, et al. The association between duration of and indications for proton pump inhibitor use and risk of gastric polyps. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2023; 35: 829-35. |
| 10. | Notsu T, Adachi K, Mishiro T, Ishimura N, Ishihara S. Fundic gland polyp prevalence according to Helicobacter pylori infection status. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2020; 35: 1158-62. |
| 11. |
Levy MD, Bhattacharya B. Sporadic fundic gland polyps with low-grade dysplasia: a large case series evaluating pathologic and immunohistochemical findings and clinical behavior. Am J Clin Pathol 2015; 144: 592-600.
DOI PMID |
| 12. | Nam SY, Park BJ, Ryu KH, Nam JH. Effect of Helicobacter pylori infection and its eradication on the fate of gastric polyps. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2016; 28: 449-54. |
| 13. |
Straub SF, Drage MG, Gonzalez RS. Comparison of dysplastic fundic gland polyps in patients with and without familial adenomatous polyposis. Histopathology 2018; 72: 1172-9.
DOI PMID |
| 14. | Togo K, Ueo T, Yonemasu H, et al. Two cases of adenocarcinoma occurring in sporadic fundic gland polyps observed by magnifying endoscopy with narrow band imaging. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22: 9028-34. |
| 15. | Shibukawa N, Wakahara Y, Ouchi S, Wakamatsu S, Kaneko A. Synchronous three gastric fundic gland polyps with low-grade dysplasia treated with endoscopic mucosal resection after being diagnosed to be tubular adenocarcinoma based on a biopsy specimen. Intern Med 2019; 58: 1871-5. |
| 16. | Yasuda T, Omatsu T, Yagi N. Fundic gland type adenocarcinoma in fundic gland polyps. Intern Med 2020; 59: 455-6. |
| 17. |
Lee HS, Choi Y, Jung JY, et al. Do we need colonoscopy verification in patients with fundic gland polyp? Intest Res 2016; 14: 172-7.
DOI PMID |
| 18. | Shi XX, Yu DH, Zheng SB. A study on the clinical and pathological features of 1200 cases of gastric fundus gland polyps. Zhong Guo Quan Ke Yi Xue 2020; 23: 1436-9. |
| 19. | Niu M, Deng YH, Zhou Y, et al. Analysis of clinical and pathological features of 1170 cases of gastric polyps in Ningxia region from 2012 to 2019. Zhong Guo Lin Chuang Yi Xue 2021; 28: 853-7. |
| 20. | Cao JX, Nian YY, Li HY, et al. Analysis of the clinical and pathogenesis of multiple fundic gland polyps. Lin Chuang Xiao Hua Bing Za Zhi 2023; 35: 13-5. |
| 21. | Tu HF, Wang YH, Wang ML, Fei SJ. Expression and significance of PGⅠ, PGⅡ, G-17 in the serum of patients with fundic gland polyps and gastric cancer. Zhong Guo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xiao Hua Za Zhi 2019; 27: 622-4. |
| 22. | Yan XL, Zhou BG, Mei YZ, Han L, Ai YW. Analysis of clinical endoscopic features and concomitant diseases of fundic gland polyps. Zhong Guo Shi Yong Nei Ke Za Zhi 2020; 40: 836-9. |
| 23. | Sun SW, Zhuang LW, Mi LN, Bo WL, Li X. Research progress on fundic gland polyps. Xian Dai Sheng Wu Xue Jin Zhan 2018, 18: 1597-600. |
| 24. |
Wensink GE, Elias SG, Mullenders J, et al. Patient-derived organoids as a predictive biomarker for treatment response in cancer patients. NPJ Precis Oncol 2021; 5: 30.
DOI PMID |
| 25. |
Vlachogiannis G, Hedayat S, Vatsiou A, et al. Patient-derived organoids model treatment response of metastatic gastrointestinal cancers. Science 2018; 359: 920-6.
DOI PMID |
| 26. | Ooft SN, Weeber F, Dijkstra KK, et al. Patient-derived organoids can predict response to chemotherapy in metastatic colorectal cancer patients. Sci Transl Med 2019; 11: 2574. |
| 27. |
Puca L, Bareja R, Prandi D, et al. Patient derived organoids to model rare prostate cancer phenotypes. Nat commun 2018; 9: 2404.
DOI PMID |
| 28. |
Yao Y, Xu X, Yang L, et al. Patient-derived organoids predict chemoradiation responses of locally advanced rectal cancer. Cell stem cell 2020; 26: 17-26.
DOI PMID |
| 29. | Ding X, Wang L, Liu DM, Yuan F, Li LL. Discussion on the pathogenesis and prevention and treatment of gastric polyps based on "Yanghuaqi, Yin Chengxing". Xian Dai Zhong Yi Lin Chuang 2023; 30: 54-7. |
| 30. | Huang YC, Zou YS, Huang CY, et al. Literature research on the syndrome and medication rules of gastric polyps. Shi Jie Zhong Yi Yao 2023; 18: 537-41. |
| 31. | Zhang FX, Wang YJ, Yu LL, Hou T. Medication rules for the treatment of gastric polyps with Traditional Chinese Medicine based on cluster analysis and association rules. Zhejiang Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue Xue Bao 2022; 46: 187-92. |
| 32. | Li JX, Chen J, Lyu B, Wu YL. Consensus opinion on the diagnosis and treatment of chronic atrophic gastritis with integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine (2017). Zhong Guo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xiao Hua Za Zhi 2018; 26: 121-31. |
| 33. | Li JX, Liu ZL, Han X. Expert consensus on the clinical application of Weifuchun in the treatment of precancerous lesions of atrophic gastritis. Zhong Yi Za Zhi 2023; 64: 212-6. |
| 34. | Pan HC, Chen LH, Wang LY. Discussion on the mechanism of Weifuchun in the treatment of low-grade gastric intraepithelial neoplasia based on GEO chip combined with network pharmacology. Zhong Guo Zhong Yi Yao Tu Shu Qing Bao Za Zhi 2023; 47: 32-9. |
| 35. | Pan HC, Qi DQ, Chen LH, Wang LY, Wan LC. Weifuchun capsule promotes the apoptosis of human gastric cancer cells through the STAT3 signaling pathway. Zhejiang Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue Xue Bao 2023; 47: 227-33. |
| 36. | Lyu B, Wang YG, Hu Y, Liu SW, Li JX. Consensus opinion on the diagnosis and treatment of chronic atrophic gastritis with integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine (2025). Zhong Guo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xiao Hua Za Zhi 2025; 33:230-40. |
| 37. | Wang Y, Guan WX, Zhou Y, Zhang XY, Zhao HJ. Red ginseng polysaccharide promotes ferroptosis in gastric cancer cells by inhibiting PI3K/Akt pathway through down-regulation of AQP3. Cancer Biol Ther 2024; 25: 2284849. |
| 38. | Li N, Duan YH, Chen L, Zhang K. Iron metabolism: an emerging therapeutic target underlying the anti-Alzheimer's disease effect of ginseng. J Trace Elem Med Biol 2023; 79: 127252. |
| 39. | ClinicalTrials.gov. A study to assess the safety and efficacy of SAR445088 in adults with CIDP. Clinical trial registry online, 2020-12-10, cited 2024-08-31; NCT04658472: 1 study record. Available from URL: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04658472. |
| 40. |
Gao M, Lin M, Rao M, et al. Development of patient-derived gastric cancer organoids from endoscopic biopsies and surgical tissues. Ann Surg Oncol 2018; 25: 2767-75.
DOI PMID |
| 41. | Song H, Park J Y, Kim J H, et al. Establishment of patient-derived gastric cancer organoid model from tissue obtained by endoscopic biopsies. J Korean Med Sci 2022; 37: 220. |
| 42. | Yu YY, Zhu YJ, Xiao ZZ, et al. The pivotal application of patient-derived organoid biobanks for personalized treatment of gastrointestinal cancers. Biomark Res 2022; 10: 73. |
| 43. | Eicher AK, Kechele DO, Sundaram N, et al. Functional human gastrointestinal organoids can be engineered from three primary germ layers derived separately from pluripotent stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 2022; 29: 36-51. |
| 44. |
Seidlitz T, Koo BK, Stange DE. Gastric organoids—an in vitro model system for the study of gastric development and road to personalized medicine. Cell Death Differ 2021; 28: 68-83.
DOI PMID |
| 45. | Xiao S, Zhou L. Gastric stem cells: physiological and pathological perspectives. Front Cell Dev Biol 2020; 8: 571536. |
| 46. |
Hang Y, Swanda RV, Nie L, et al. mTORC1 couples cyst(e)ine availability with GPX4 protein synthesis and ferroptosis regulation. Nat Commun 2021; 12: 1589.
DOI PMID |
| 47. | Yi J, Zhu J, Wu J, Thompson CB, Jiang X. Oncogenic activation of PI3K-AKT-mTOR signaling suppresses ferroptosis via SREBP-mediated lipogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2020; 117: 31189-97. |
| 48. | Hayes JD, Chowdhry S, Dinkova-Kostova AT, Sutherland C. Dual regulation of transcription factor Nrf2 by Keap1 and by the combined actions of β-TrCP and GSK-3. Biochem Soc Trans 2015; 43: 611-20. |
| 49. | Cao XC, Zhang WR, Cao WF, et al. Aquaporin 3 is required for FGF-2-induced migration of human breast cancers. PLoS One 2013; 8: 56735. |
| 50. | Zhang Y, Ding S, Shen Q, Wu J, Zhu X. The expression and regulation of aquaporins in placenta and fetal membranes. Front Biosci 2012; 17: 2371-82. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

