Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (4): 744-750.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20230524.002
Previous Articles Next Articles
Uncovering pharmacological mechanisms of Phellinus linteus on focal segmental glomeruloscleosis rats through tandem mass tag-based quantitative proteomic analysis, network pharmacology analysis and experimental validation
WAN Feng, YANG Ruchun( ), TANG Yuewen
), TANG Yuewen
- Department of Nephrology, Key Laboratory of Kidney Disease Prevention and Control Technology, Hangzhou TCM Hospital Affiliated to Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, Hangzhou 310007, China
-
Received:2022-04-11Accepted:2022-08-15Online:2023-08-15Published:2023-05-24 -
Contact:Prof. YANG Ruchun, Department of Nephrology, Key Laboratory of Kidney Disease Prevention and Control Technology, Hangzhou TCM Hospital Affiliated to Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, Hangzhou 310007, China. yangruchunhz@163.com. Telephone: +86-571-85827871, 15167106095 -
Supported by:Public Welfare Technology Application Research Program of Zhejiang Province: Study on the Application of Phellinus linteus Protocatechualdehyde in Inhibiting Glomerular Extracellular Matrix Accumulation based on TSP-1 Double Luciferase Reporting System(LGC21H290002);Key Projects of Zhejiang Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine: Quality and Safety Evaluation of Cultivated Phellinus linteus in Zhejiang Province and its Comprehensive Application in the Prevention and Treatment of Kidney Disease(2020ZZ016)
Cite this article
WAN Feng, YANG Ruchun, TANG Yuewen. Uncovering pharmacological mechanisms of Phellinus linteus on focal segmental glomeruloscleosis rats through tandem mass tag-based quantitative proteomic analysis, network pharmacology analysis and experimental validation[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(4): 744-750.
share this article
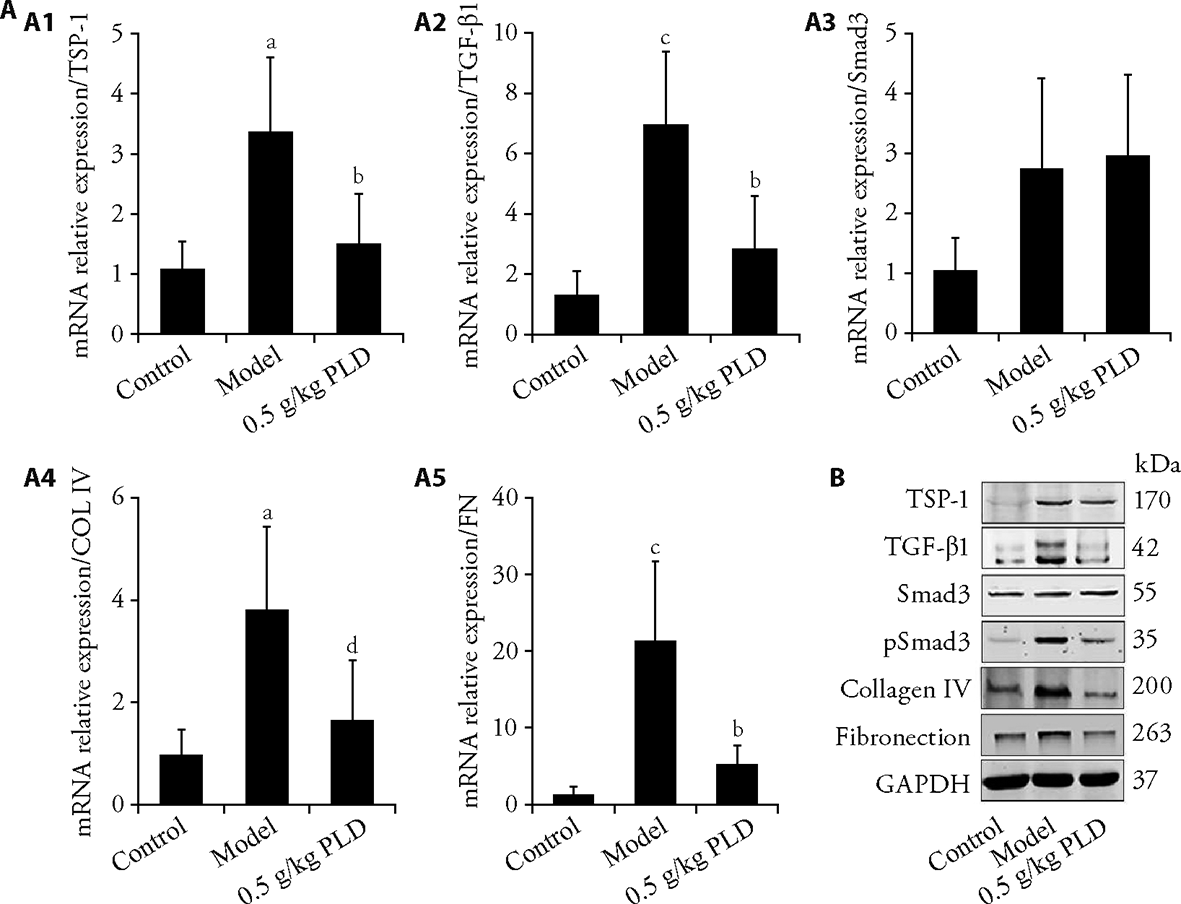
Figure 1 Validation of DEPs using qRT-PCR and Western blotting DEPs, including TSP-1/TGF-β1 signaling pathway and the ECM components, were determined using qRT-PCR. A1: mRNA expression level of TSP-1; A2: mRNA expression level of TGF-β1; A3: mRNA expression level of smad3; A4: mRNA expression level of COL IV; A5: mRNA expression level of FN. The relative gene expression was normalized to that of GAPDH. DEPs: differentially expressed proteins; qRT-PCR: quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction; TSP-1: thrombospondin-1; TGF-β1: transforming growth factor-β1; ECM: extracellular matrix; COL IV: collagen IV, FN: fibronection; GAPDH: glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Quantitative data are shown as the mean ± standard deviation (n = 6). aP < 0.01, cP < 0.001, compared with the control group. bP < 0.01, dP < 0.05, compared with the model group. B: Western blotting analyses of the TSP-1/TGF-β1 signaling pathway and ECM components. Control: control group; model: model group; PLD: P. linteus decoction intervention group (0.5 g/kg), daily gavage, 8 weeks.

Figure 2 Compound-target network Orange diamonds represent each compound in Phellinus linteus; Blue round nodes represent the putative targets of these compounds. Red square nodes represent the known targets for FSGS obtained from the GeneCards database. FSGS: focal segmental glomeruloscleosis.
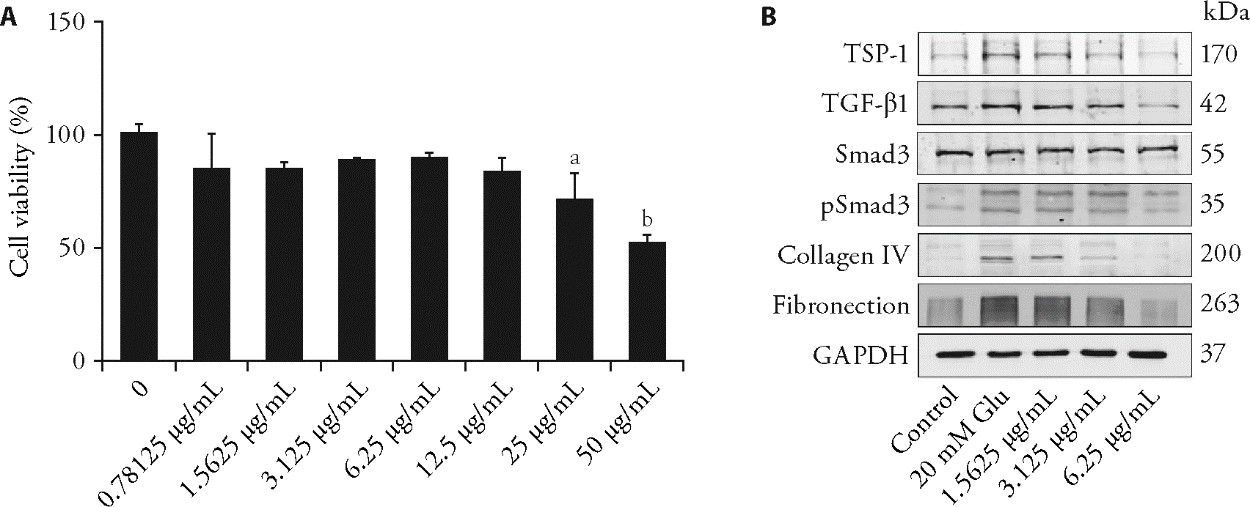
Figure 3 PCA inhibits the TSP-1/TGF-β1 signaling pathway in RMCs A: effects of different concentrations of PCA on the cell proliferation of RMCs were determined using the CCK-8 assay. Quantitative data are represented as the mean ± standard deviation (n = 3). PCA: protocatechualdehyde. 0.78125, 1.5625, 3.125, 6.25, 12.5, 25, 50 μg/mL: cells were treated with PCA for 24 h, aP < 0.01, bP < 0.0001, compared with the control group; B: Western blotting analyses of the TSP-1/TGF-β1 signaling and ECM components. RMCs: rat mesangial cells; CCK-8: cell counting kit-8; TSP-1: thrombospondin-1; TGF-β1: transforming growth factor-β1; ECM: extracellular matrix. Control: control group; 20 mM Glu: high glucose stimulation group; 1.5625, 3.125, 6.25 μg/mL: PCA low-dose, medium-dose, and high-dose group, cells were treated with PCA for 48 h.

Figure 4 Knockdown of TSP-1 protein affects the TGF-β1 signaling pathway A: efficacies of shRNAs were determined in 293T cells by observing the GFP fluorescence intensity under a fluorescence microscope (Olympus IX53). A1: control shRNA; A2: TSP-1 shRNA1; A3: TSP-1 shRNA2; A4: TSP-1 shRNA3. 48 h stimulation, scale bars, 200 μm. B: relative mRNA levels of TSP-1 in 293T cells treated with shRNAs 1-3 for 48 h, respectively. Three independent experiments were analyzed. Quantitative data are represented as the mean ± standard deviation (n = 3). aP < 0.01, compared with the control group, C: protein levels of TSP-1 in 293T cells treated with shRNAs targeting for 48 h. D: efficacy of lentivirus-mediated shRNA interference on TSP-1 was determined in RMCs by observing the GFP fluorescence under a fluorescence microscope (Olympus IX53). D1: control lv, 3 × 108 TU/mL; D2: TSP-1 Lv, 3 × 108 TU/mL. 72 h stimulation, scale bars, 100 μm. E: protein levels of TGF-β1 signaling and ECM components in RMCs treated with the lentivirus targeting TSP-1 for 72 h and the control lentivirus were determined using Western blotting. Control lv: control lentivirus; TSP-1 Lv: Lv carrying TSP-1 shRNA. TSP-1: thrombospondin-1; TGF-β1: transforming growth factor-β 1; GFP: green fluorescent protein; RMCs: rat mesangial cells; ECM: extracellular matrix.
| 1. |
Schwartzman M, Reginensi A, Wong JS, et al. Podocyte-specific deletion of yes-associated protein causes FSGS and progressive renal failure. J Am Soc Nephrol 2016; 27: 216-26.
DOI PMID |
| 2. |
Malaga-Dieguez L, Bouhassira D, Gipson D, Trachtman H. Novel therapies for FSGS: preclinical and clinical studies. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis 2015; 22: e1-6.
DOI URL |
| 3. |
Lau E, Ma P, Wu X, Chung V, Wong S. Mycophenolate mofetil for primary focal segmental glomerulosclerosis: systematic review. Renal Failure 2013; 35: 914-29.
DOI URL |
| 4. |
Wan F, Yang RC, Shi YP, et al. The protective effect of Phellinus linteus decoction on podocyte injury in the kidney of FSGS rats. BMC Complement Altern Med 2019; 19: 272.
DOI |
| 5. |
Xiao SX, Li SJ, Fang WX, Chen J, Li HJ, Situ YL. Exploring the mechanism of Tripterygium wilfordii against cancer using network pharmacology and molecular docking. World J Tradit Chin Med 2022; 8: 417-25.
DOI URL |
| 6. |
Zhou H, Finkemeier I, Guan W, et al. Oxidative stress-triggered interactions between the succinyl- and acetyl-proteomes of rice leaves. Plant Cell Environ 2018; 41: 1139-53.
DOI URL |
| 7. |
Wang H, Cheng Q, Li X, et al. Loss of TIGAR induces oxidative stress and meiotic defects in oocytes from obese mice. Mol Cell Proteomics 2018; 17: 1354-64.
DOI PMID |
| 8. |
Chen H, Tian T, Miao H, Zhao YY. Traditional uses, fermentation, phytochemistry and pharmacology of Phellinus linteus: a review. Fitoterapia 2016; 113: 6-26.
DOI PMID |
| 9. |
Huo J, Zhong S, Du X, et al. Whole-genome sequence of Phellinus gilvus (mulberry Sanghuang) reveals its unique medicinal values. J Adv Res 2020; 24: 325-35.
DOI URL |
| 10. |
Hugo C, Shankland SJ, Pichler RH, Couser WG, Johnson RJ. Thrombospondin 1 precedes and predicts the development of tubulointerstitial fibrosis in glomerular disease in the rat. Kidney Int 1998; 53: 302-11.
PMID |
| 11. |
Daniel C, Takabatake Y, Mizui M, et al. Antisense oligonucleotides against thrombospondin-1 inhibit activation of tgf-beta in fibrotic renal disease in the rat in vivo. Am J Pathol 2003; 163: 1185-92.
DOI URL |
| 12. |
Murphy-Ullrich JE. Thrombospondin 1 and its diverse roles as a regulator of extracellular matrix in fibrotic disease. J Histochem Cytochem 2019; 67: 683-99.
DOI PMID |
| 13. | Xu L, Zhang Y, Chen J, Xu Y. Thrombospondin-1: a key protein that induces fibrosis in diabetic complications. J Diabetes Res 2020; 2020: 8043135. |
| 14. | Murphy-Ullrich JE, Suto MJ. Thrombospondin-1 regulation of latent TGF-β activation: a therapeutic target for fibrotic disease. Matrix Biol 2018; 68- 69: 28-43. |
| 15. |
Daniel C, Schaub K, Amann K, Lawler J, Hugo C. Throm-bospondin-1 is an endogenous activator of TGF-beta in experimental diabetic nephropathy in vivo. Diabetes 2007; 56: 2982-9.
DOI URL |
| 16. | Suto MJ, Gupta V, Mathew B, Zhang W, Pallero MA, Murphy-Ullrich JE. Identification of inhibitors of thrombospondin 1 activation of TGF-β. ACS Med Chem Lett 2020; 11: 1130-36. |
| 17. |
Gifford CC, Tang J, Costello A, et al. Negative regulators of TGF-β1 signaling in renal fibrosis; pathological mechanisms and novel therapeutic opportunities. Clin Sci (Lond) 2021; 135: 275-303.
DOI PMID |
| 18. |
Kim JH, Kim BK, Moon KC, Hong HK, Lee HS. Activation of the TGF-beta/Smad signaling pathway in focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Kidney Int 2003; 64: 1715-21.
DOI PMID |
| 19. |
Zhong S, Jin Q, Yu T, Zhu J, Li Y. Phellinus gilvus-derived protocatechualdehyde induces G0/G1 phase arrest and apoptosis in murine B16-F10 cells. Mol Med Rep 2020; 21: 1107-14.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | WANG Miao, ZHU Yan, ZHAO Hui, ZHAO Hongfang. Moxibustion enables protective effects on rheumatoid arthritis-induced myocardial injury via transforming growth factor beta1 signaling and metabolic reprogramming [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1190-1199. |
| [2] | SU Chengguo, ZHAO Xiaoyan, YE Jiangnan, ZHANG Xin, JIANG Yuqing, GUO Junjie, ZHANG Xiyuan, QI Wenchuan, ZHU Jun. Effect of Tuina along “bladder meridian” alleviating intervertebral disc degeneration by regulating the transforming growth factor-β1/Smad signaling pathway in a rabbit model [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 991-1000. |
| [3] | ZHAO Ye, WANG Xian, GU Ling, LI Zihang, ZHU Jingtian, WANG Wenkai, ZHANG Liang, XUE Mei. Efficacy of Danggui Buxue decoction (当归补血汤) on diabetic nephropathy-induced renal fibrosis in rats and possible mechanism [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(3): 507-513. |
| [4] | ZHAO Jie, WANG Li, CAO Ai-li, WANG Yun-man, CHI Yang-feng, WANG Yi, WANG Hao, PENG Wen. Huangqi decoction (黄芪汤) attenuates renal interstitial fibrosis via transforming growth factor-β1/mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways in 5/6 nephrectomy mice [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(5): 723-731. |
| [5] | HU Xijiao, CHENG Yinglong, KANG Huanan, LI Shuoxi, WANG Yawen, LIU Jinzhe, SUN Yiming, LIU Li. Electroacupuncture attenuates chronic salpingitis via transforming growth factor-β1/p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(5): 781-787. |
| [6] | Jiaru LIN, Li WANG, Bo CHEN, Santao OU, Jianhua QIN, Junming FAN. Shenweifang-containing serum inhibits transforming growth factor-β1-induced myofibroblast differentiation in normal rat kidney interstitial fibroblast cells [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(1): 39-48. |
| [7] | Xia Xichao, Mao Dongxue, Dai Hongmei, Wu Xi, Zhang Zuyuan, Wang Huaying, Zhou Wenwen, Dong Yanmei, Wang Mengqi, Li Yuan, Shao Xiangyang, Ouyang Jingfeng. Effect of Cyclocarya paliurus polysaccharides on streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy in rats [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020, 40(6): 956-964. |
| [8] | Wang Jiepeng, Fang Chaoyi, Wang Shaoxian, Fang Fang, Chu Xinqiao, Liu Na, Lu Chenxi, Wang Shuo, Li Wei. Danggui Buxue Tang ameliorates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats through inhibiting transforming growth factor-β1/Smad3/plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020, 40(2): 236-244. |
| [9] | Zhang Yali, Wang Bingyu, Guo Xueying, Yang Lei, Li Dandan, Yuan Xingxing. Wulong Xiaozheng Wan medicated serum inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human gastric carcinoma cell line BGC823 by modulation of transforming growth factor-β_1/Smad signaling [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2019, 39(03): 380-392. |
| [10] | Shi Yueping, Zhai Jianli, Liu Chunxiao. Effect of Sini decoction on angiotensin Ⅱ, transforming growth factor β_1 and connective tissue growth factor in rats with myocardial fibrosis-induced banding of the abdominal aorta [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2018, 38(03): 427-432. |
| [11] | Chunxia Zuo, Xiaoyue Tan, Shengqin Jia, Mianzhi Zhang, Daning Zhang. Influence of Bushenhuoxue on podocytes of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis mice [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2014, 34(05): 591-596. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

