Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (4): 852-859.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2025.04.014
• Original Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
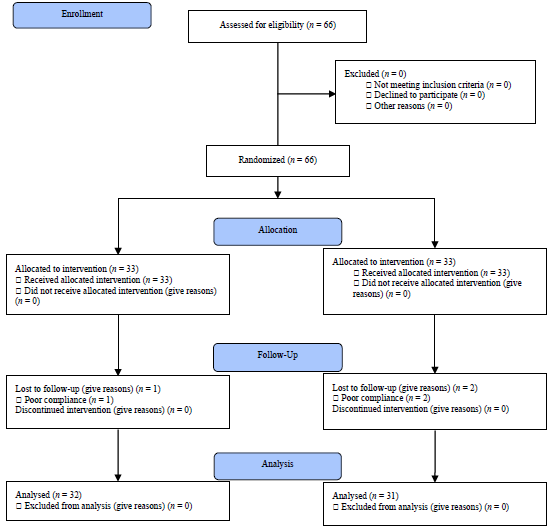
Electroacupuncture versus conventional acupuncture of scalp motor area for post-stroke wrist dyskinesia and its effect on muscle function: a randomized, controlled clinical trial
ZHENG Ruwen1, DONG Xu2, WANG Tianyi1, FENG Liyuan2, ZHANG Hongyan2, HUO Hong2, ZHANG Ying2, ZHANG Qianshi1, ZHU Xingyan1, WANG Dongyan2( )
)
- 1 the Second Clinical Medical College, Heilongjiang University of Chinese Medicine, Harbin 150040, China
2 Department of Acupuncture Ⅲ, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Heilongjiang University of Chinese Medicine, Harbin 150000, China
-
Received:2024-04-12Accepted:2024-11-22Online:2025-08-15Published:2025-07-25 -
Contact:WANG Dongyan -
About author:WANG Dongyan, Department of Acupuncture Ⅲ, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Heilongjiang University of Chinese Medicine, Harbin, 150000, China. doctwdy@163.com,Telephone: +86-17862969310
-
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China: Exploration of Key Factors and Mechanisms of Modulating Motor Function Reconstruction After Cerebral Infarction Through Multimodal Brain Functional Connectivity Perspective in Procedural Acupoint Electrical Stimulation Research(82374601);Jointly Guided Program of Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province: Quantitative Study on the Role of Scalp Acupuncture in the Motor Area in Promoting Motor Function Reconstruction after Stroke(LH2019H113);Innovation Team Construction Project of Heilongjiang University of Chinese Medicine: Construction of a Doctoral Research and Innovation Team in Acupuncture Science(2017sit01);Traditional Chinese Medicine Research Project of Heilongjiang Province: Clinical Study on the Promotion of Upper Limb Motor Function Reconstruction in Post-Stroke Patients Using Optimal Limb Positioning with Electroacupuncture(ZHY2022-171)
Cite this article
ZHENG Ruwen, DONG Xu, WANG Tianyi, FENG Liyuan, ZHANG Hongyan, HUO Hong, ZHANG Ying, ZHANG Qianshi, ZHU Xingyan, WANG Dongyan. Electroacupuncture versus conventional acupuncture of scalp motor area for post-stroke wrist dyskinesia and its effect on muscle function: a randomized, controlled clinical trial[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(4): 852-859.
share this article
| Parameter | EA group (n=32) | Conventional scalp acupuncture group (n=31) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 64.0 (53.5, 67.7) | 65.0 (57.0, 69.0) | 0.335a |
| Sex (male/female, n) | 20/12 | 22/9 | 0.476b |
| Disease duration (days) | 74.5 (56.5, 105.0) | 82.00 (66.0, 132.0) | 0.169a |
| Hemiplegic side (left/right, n) | 17/15 | 19/12 | 0.513b |
| CSS (points) | 6.5±1.3 | 6.6±1.6 | 0.893c |
| Upper limb-related BI (points) | 25.0 (20.0, 30.0) | 25.0 (20.0, 30.0) | 0.943a |
| AROM of wrist dorsiflexion (°) | 35.0±11.2 | 32.9±10.6 | 0.441c |
| AROM of wrist flexion (°) | 48.6±10.8 | 46.7±10.5 | 0.482c |
| RMS of ECRL (μV) | 80.5±28.9 | 83.5±21.5 | 0.647c |
| RMS of ED (μV) | 44.3 (28.4, 65.6) | 55.3 (33.1, 75.4) | 0.343a |
| RMS of FCR (μV) | 11.2 (8.7, 15.1) | 12.1 (9.6, 15.9) | 0.523a |
| RMS of FCU (μV) | 45.9±22.5 | 49.0±19.2 | 0.552c |
Table 1 Baseline characteristics of patients
| Parameter | EA group (n=32) | Conventional scalp acupuncture group (n=31) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 64.0 (53.5, 67.7) | 65.0 (57.0, 69.0) | 0.335a |
| Sex (male/female, n) | 20/12 | 22/9 | 0.476b |
| Disease duration (days) | 74.5 (56.5, 105.0) | 82.00 (66.0, 132.0) | 0.169a |
| Hemiplegic side (left/right, n) | 17/15 | 19/12 | 0.513b |
| CSS (points) | 6.5±1.3 | 6.6±1.6 | 0.893c |
| Upper limb-related BI (points) | 25.0 (20.0, 30.0) | 25.0 (20.0, 30.0) | 0.943a |
| AROM of wrist dorsiflexion (°) | 35.0±11.2 | 32.9±10.6 | 0.441c |
| AROM of wrist flexion (°) | 48.6±10.8 | 46.7±10.5 | 0.482c |
| RMS of ECRL (μV) | 80.5±28.9 | 83.5±21.5 | 0.647c |
| RMS of ED (μV) | 44.3 (28.4, 65.6) | 55.3 (33.1, 75.4) | 0.343a |
| RMS of FCR (μV) | 11.2 (8.7, 15.1) | 12.1 (9.6, 15.9) | 0.523a |
| RMS of FCU (μV) | 45.9±22.5 | 49.0±19.2 | 0.552c |
| Parameter | EA group (n = 32) | Conventional scalp acupuncture group (n = 31) | t/Z value | P valueb | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | After 3 weeks | t/Z value | P valuea | Baseline | After 3 weeks | t/Z value | P valuea | ||||
| CSS (points) | 6.5 (6.0, 7.0) | 4.0 (3.0, 5.0) | 4.923 | <0.001 | 7.0 (6.0, 7.0) | 4.0 (4.0, 5.0) | 4.610 | <0.001 | 2.079 | 0.038 | |
| Upper limb-related BI (points) | 25.0 (20.0, 30.0) | 32.5 (30.0, 35.0) | 4.906 | <0.001 | 25.0 (20.0, 30.0) | 30.0 (30.0, 35.0) | 4.862 | <0.001 | 0.515 | 0.606 | |
| AROM of wrist dorsiflexion (°) | 35.0±11.2 | 44.4±10.7 | 12.056 | <0.001 | 32.9±10.6 | 39.1±10.4 | 20.747 | <0.001 | 2.023 | 0.047 | |
| AROM of wrist flexion (°) | 48.5 (41.6, 58.7) | 56.7 (51.5, 66.4) | 4.937 | <0.001 | 46.7±10.5 | 54.4±9.8 | 10.265 | <0.001 | 1.805 | 0.076 | |
Table 2 Changes in CSS scores, upper limb-related BI scores, and wrist AROM after 3 weeks of treatment
| Parameter | EA group (n = 32) | Conventional scalp acupuncture group (n = 31) | t/Z value | P valueb | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | After 3 weeks | t/Z value | P valuea | Baseline | After 3 weeks | t/Z value | P valuea | ||||
| CSS (points) | 6.5 (6.0, 7.0) | 4.0 (3.0, 5.0) | 4.923 | <0.001 | 7.0 (6.0, 7.0) | 4.0 (4.0, 5.0) | 4.610 | <0.001 | 2.079 | 0.038 | |
| Upper limb-related BI (points) | 25.0 (20.0, 30.0) | 32.5 (30.0, 35.0) | 4.906 | <0.001 | 25.0 (20.0, 30.0) | 30.0 (30.0, 35.0) | 4.862 | <0.001 | 0.515 | 0.606 | |
| AROM of wrist dorsiflexion (°) | 35.0±11.2 | 44.4±10.7 | 12.056 | <0.001 | 32.9±10.6 | 39.1±10.4 | 20.747 | <0.001 | 2.023 | 0.047 | |
| AROM of wrist flexion (°) | 48.5 (41.6, 58.7) | 56.7 (51.5, 66.4) | 4.937 | <0.001 | 46.7±10.5 | 54.4±9.8 | 10.265 | <0.001 | 1.805 | 0.076 | |
| Parameter | EA group (n=32) | Conventional scalp acupuncture group (n=31) | t/Z value | P valueb | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | After 3 weeks | t value | P valuea | Baseline | After 3 weeks | t/Z value | P valuea | ||||
| RMS of ECRL (μV) | 80.5±28.9 | 111.2±37.8 | 6.708 | <0.001 | 83.5±21.5 | 94.0±28.8 | 3.122 | 0.004 | 2.032 | 0.047 | |
| RMS of ED (μV) | 48.2±22.2 | 74.9±23.4 | 6.194 | <0.001 | 55.4 (33.1, 75.4) | 62.0 (45.9, 79.4) | 2.312 | 0.021 | 2.020 | 0.048 | |
| RMS of FCR (μV) | 13.4±6.9 | 17.9±6.7 | 4.025 | <0.001 | 12.8±4.4 | 15.0±5.2 | 2.228 | 0.033 | 1.966 | 0.049 | |
| RMS of FCU (μV) | 45.9±22.6 | 67.8±21.3 | 5.761 | <0.001 | 49.0±19.2 | 56.9±21.5 | 2.634 | 0.013 | 2.030 | 0.047 | |
Table 3 Changes in RMS of agonistic muscles associated with wrist movement on the hemiplegic side of patients after 3 weeks of treatment
| Parameter | EA group (n=32) | Conventional scalp acupuncture group (n=31) | t/Z value | P valueb | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | After 3 weeks | t value | P valuea | Baseline | After 3 weeks | t/Z value | P valuea | ||||
| RMS of ECRL (μV) | 80.5±28.9 | 111.2±37.8 | 6.708 | <0.001 | 83.5±21.5 | 94.0±28.8 | 3.122 | 0.004 | 2.032 | 0.047 | |
| RMS of ED (μV) | 48.2±22.2 | 74.9±23.4 | 6.194 | <0.001 | 55.4 (33.1, 75.4) | 62.0 (45.9, 79.4) | 2.312 | 0.021 | 2.020 | 0.048 | |
| RMS of FCR (μV) | 13.4±6.9 | 17.9±6.7 | 4.025 | <0.001 | 12.8±4.4 | 15.0±5.2 | 2.228 | 0.033 | 1.966 | 0.049 | |
| RMS of FCU (μV) | 45.9±22.6 | 67.8±21.3 | 5.761 | <0.001 | 49.0±19.2 | 56.9±21.5 | 2.634 | 0.013 | 2.030 | 0.047 | |
| 1. | Prevention RoS, Group TiCW. Brief report on stroke prevention and treatment in China, 2021. Zhong Guo Nao Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi 2023; 20: 783-93. |
| 2. | Tang Z, Liu T, Liu Y, et al. Different doses of intermittent theta burst stimulation for upper limb motor dysfunction after stroke: a study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Front Neurosci 2023; 17: 1259872. |
| 3. | Tang Q, Yang X, Sun M, et al. Research trends and hotspots of post-stroke upper limb dysfunction: a bibliometric and visualization analysis. Front Neurol 2024; 15: 1449729. |
| 4. | Zhao Q, Jia G, Jia L, et al. Effects of electromyography bridge on upper limb motor functions in stroke participants: an exploratory randomized controlled trial. Brain Sci 2022; 12: 870. |
| 5. |
Xu Y, Wu C, Yu W, et al. Systematic review and Meta-analysis of brain plasticity associated with electroacupuncture in experimental ischemic stroke. J Tradit Chin Med 2024; 44: 859-70.
DOI |
| 6. | Huang YJ, Huang CS, Leng KF, Sung JY, Cheng SW. Efficacy of scalp acupuncture in patients with post-stroke hemiparesis: Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front Neurol 2021; 12: 746567. |
| 7. | Lu SY, Wang DY, Yang HY, Ma CC, Chen C, Zhao YN. Effect of scalp electro-acupuncture on metabonomics of urine in rats with cerebra infarction. Zhen Jiu Lin Chuang Za Zhi 2021; 37: 52-9. |
| 8. | Ma CC, Wang DY. Effect of head electroacupuncture with different frequency on the expression of NRG-1 in rats with cerebral infarction. Liaoning Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue Xue Bao 2021; 23: 54-8. |
| 9. | Ji Y. Clinical observation of electroacupuncture combined with scalp acupuncture in the treatment of ischemic stroke. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine; 2017: 20-5. |
| 10. | Wu MH, Shi Y. Internal medicine of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Beijing: China Press of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021: 145-52. |
| 11. | Neurology CSo, Neurology CDGotCSo. Chinese guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of acute intracerebral hemorrhage 2019. Zhong Hua Shen Jing Ke Za Zhi 2019; 52: 994-1005. |
| 12. | Neurology CSo, Neurology CDGotCSo. Chinese guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of acute ischemic stroke 2018. Zhong Hua Shen Jing Ke Za Zhi 2018; 51: 666-82. |
| 13. | Region WHOWP. WHO standard acupuncture point locations in the western pacific region. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2008: 174, 214. |
| 14. | Tao ZR. Reliability, validity and sensitivity of Chinese scale for clinical neurological deficit of stroke patients. Di Er Jun Yi Da Xue Xue Bao 2009; 30: 283-5. |
| 15. |
Buurman BM, van Munster BC, Korevaar JC, de Haan RJ, de Rooij SE. Variability in measuring (instrumental) activities of daily living functioning and functional decline in hospitalized older medical patients: a systematic review. J Clin Epidemiol 2011; 64: 619-27.
DOI PMID |
| 16. | Huang XL, Yan TB. Rehabilitation medicine. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House, 2018: 46-8. |
| 17. | Sung JH, Baek SH, Park JW, Rho JH, Kim BJ. Surface electromyography-driven parameters for representing muscle mass and strength. Sensors (Basel) 2023; 23: 5490. |
| 18. | Society CN. Scoring criteria for the degree of clinical neurological deficits in stroke patients (1995). Zhong Hua Shen Jing Ke Za Zhi 1996; 29: 62-4. |
| 19. | Wang SY, Wang J, Liu K, et al. The shortcut pathway between scalp acupuncture and brain. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu 2020; 45: 947-53. |
| 20. | Chen G. Study on the localization of head needle motor area based on 3D printing technology. Harbin: Heilongjiang University of Chinese Medicine; 2022: 33-7. |
| 21. | Tang J, Xi X, Wang T, Wang J, Li L, Lyu Z. Analysis of corticomuscular-cortical functional network based on time-delayed maximal information spectral coefficient. J Neural Eng 2023; 20: 10.1088/1741-2552/acf7f7. |
| 22. | Lin D, Gao J, Lu M, et al. Scalp acupuncture regulates functional connectivity of cerebral hemispheres in patients with hemiplegia after stroke. Front Neurol 2023; 14: 1083066. |
| 23. | Lang Y, Li KS, Yang JY, Cui FY, Bai W, Liang CX. Effect of acupuncture at the anterior oblique parietotemporal line on gray matter remodeling in patients with hemiplegia of cerebral infarction. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu 2020; 45: 141-7. |
| 24. |
Chen YL, Ouyang L, Meng LL, et al. Electroacupuncture ameliorates blood-brain barrier disruption after ischemic stroke through histone acetylation regulation at the matrix metalloproteinase 9 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 2 genes. J Tradit Chin Med 2024; 44: 734-44.
DOI |
| 25. | Chen C. Effects of different frequency of scalp electroacupuncture on motor function and expression of VEGF protein in ischemic region in rats with cerebral infarction. Harbin: Heilongjiang University of Chinese Medicine, 2020: 23-37. |
| 26. | Cao BQ, Tan F, Fang MF, Huo QW. Effects of electroacupuncture on neurological rehabilitation and serum NLRP3 and lL-18 levels in patients with anterior cerebral infarction. Shanghai Zhen Jiu Za Zhi 2022; 41: 1071-6. |
| 27. | Meng L, Yang S, Zhong QH, et al. Clinical study of rehabilitation robot gloves combined with electroacupuncture to treat patients with phlegm-stasis blocking collaterals stroke hand dysfunction. Hunan Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue Xue Bao 2022; 42: 387-92. |
| 28. | Yin LB. The analysis of parameters of electroacupuncture device (EAD) and relevant factors. Guangzhou: Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, 2010: 64-88. |
| [1] | CHEN Ziying, ZHAO Xiaoping, FAN Xiaoxuan, TANG Didi, SUN Wen, LYU Jing, HUANG Lan, QI Fan. Seven Traditional Chinese Medicine external treatments combined with rehabilitation training on the functional recovery of limbs in patients with cerebral hemorrhage: a network Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(4): 711-719. |
| [2] | ZHAO Ping, HE Xingbo, HAN Xudong, CHEN Xinyue, LI Zhanglong, SONG Jike, XING Wenjia, WU Jiangfeng, GUO Bin, BI Hongsheng. Mechanism of electroacupuncture involve in lens-induced myopia guinea pigs by inhibiting wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(4): 796-805. |
| [3] | ZHAO Weibo, WANG Yaqi, KONG Lingyao, WANG Tianyi, ZHAO Haihong, ZHANG Ying, LUO Bin, WANG Ji, WANG Qi. Efficacy and safety of Tuomin Zhiti decoction (脱敏止嚏汤) on patients with seasonal allergic rhinitis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(4): 829-835. |
| [4] | LI Yuxuan, LI Yan, WANG Wujiao, CUI Xiaoyun, WAN Jie, ZHOU Kun, LU Jinjin, LIU Jing, LIN Qian, LI Dong. Clinical study of Yiqi Liangxue Shengji prescription (益气凉血生肌方) for improving cardiac function after myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury in patients with acute myocardial infarction: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(4): 836-844. |
| [5] | SONG Jianfei, QIN Zhengyuan, GU Xinlu, ZHANG Yan, LI Xingrui. Efficacy of acupuncture combined with upper limb rehabilitation robot-assisted training for neuroplasticity and functional recovery of patients with stroke: a prospective cohort study based on functional near-infrared spectroscopy technology [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(4): 860-866. |
| [6] | SUN Jiao, WANG Yueming, LYU Jian, LIU Xin, YUE Bingnan, LI Yinyin, LIU Jipeng, SUN Yize, LIU Qingguo, YAN Liu. Effect of electroacupuncture on hypertensive and sympathetic excitability mechanism mediated by the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus in spontaneous hypertensive rats [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(3): 586-596. |
| [7] | XIAO Jing, SONG Danlei, LIANG Caiming, HE Yinuo, ZHENG Weifang, WU Xiaqiu. Efficacy of Jianpi formulas (健脾剂) in reducing the recurrence of colorectal adenoma after polypectomy: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(2): 225-233. |
| [8] | LI Yongfeng, CHEN Xinyi, REN Wei, QIAO Haifa. Electroacupuncture stimulation of auricular concha region improves loss of control over stress induced depression-like behavior by modulating 5-hydroxytryptamine 1A receptor [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(2): 326-334. |
| [9] | HU Junwei, FENG Jiwei, LI Wen, LIU Lumin, LI Xu, XU Ge, LIU Jiandang, CHEN Yuelai. Electroacupuncture improves cyclophosphamide-induced bladder overactivity by reducing mechanotransduction in the rat urothelium [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(2): 348-358. |
| [10] | LAI Xiaolei, SHANG Juju, LIU Hongxu, HU Jing, LI Xiang, ZHANG Zhenmin, XING Wenlong. Clinical efficacy of Angong Jiangya pill (安宫降压丸) for grade 2 hypertension with liver-fire hyperactivity syndrome: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(2): 422-429. |
| [11] | CHENG Jianping, FAN Chanjuan, ZHAI Lili, WANG Hui, XIE Dongling, CAI Yong, LI Zhen, HUANG Kun, BAI Qixuan. Efficacy and safety of Qingwei Zhitong pellets (清胃止痛微丸)-containing quadruple therapy for Helicobacter pylori eradication: a prospective, single-center, randomized trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(2): 430-436. |
| [12] | LI Siting, WANG Shaojun, YIN Yehui, DE Gejing, LI Caicai, WANG Ziyan, CAO Wenjie. Electroacupuncture alleviates zymosan-induced colorectal hypersensitivity [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(1): 32-38. |
| [13] | YE Wujie, YANG Yawei, ZHANG Da, TANG Ling, CUI Minying, FU Bin, ZHANG Meng, HU Xingang, ZHAO Yan. Effectiveness of combining Qingyanyin formulated granules (轻燕饮配方颗粒) with press needles in treating abdominal obesity: a multicenter randomized controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(1): 107-114. |
| [14] | LANG Jiawang, JIN Lingqing, LUO Jianchang, LANG Boxu. Effects of acupuncture combined with bone-setting therapy to treat tourette syndrome: a three-arm randomized controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(1): 176-183. |
| [15] | Emre Bulut, Didem Özkal Eminoğlu, Yasemin Çayır. Effect of electroacupuncture on pain after periodontal flap surgery: a randomized controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(1): 184-191. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||