Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (1): 49-56.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2025.01.005
Previous Articles Next Articles
Antidepressive and anxiolytic effects of a combination of Saffron and Chamomile in rats and their relationship with serotonin using in vivo methods
Faiq Amin1, Saara Ahmad1( ), Muhammad Wasim2(
), Muhammad Wasim2( ), Asra Khan1, Fazal Manzoor Arain1, Zehra Batool3, Saiqa Tabassum4, Saima Khaliq5, Noreen Samad6, Saida Haider7
), Asra Khan1, Fazal Manzoor Arain1, Zehra Batool3, Saiqa Tabassum4, Saima Khaliq5, Noreen Samad6, Saida Haider7
- 1 Department of Biological and Biomedical Sciences, the Aga Khan University, Karachi 74800, Pakistan
2 Maternal and Children's Health Research Institute, Shunde Women and Children's Hospital, Guangdong Medical University, Foshan 528300, China
3 Dr. Panjwani Center for Molecular Medicine and Drug Research, International Center for Chemical and Biological Sciences, University of Karachi, Karachi 74800, Pakistan
4 Department of Biosciences, Shaheed Zulfikar Ali Bhutto Institute of Science and Technology, Karachi 74800, Pakistan
5 Department of Biochemistry, Federal Urdu University of Science, Arts and Technology, Karachi 74800, Pakistan
6 Department of Biochemistry, Bahauddin Zakariya University, Multan 60800, Pakistan
7 Department of Biochemistry, University of Karachi, Karachi 74800, Pakistan
-
Received:2023-11-22Accepted:2024-05-15Online:2025-02-15Published:2025-01-10 -
Contact:Dr. Saara Ahmad, Department of Biological and Biomedical Sciences, the Aga Khan University, Karachi 74800, Pakistan.saara_ahmad@hotmail.com ;saara.muddasir@aku.edu ; Dr. Muhammad Wasim, Maternal and Children's Health Research Institute, Shunde Women and Children's Hospital, Guangdong Medical University, Foshan 528300, China.mm.waseeemjee@gmail.com Telephone: +92-21-36642030; +92-334-3448258; +86-136-12624969 -
Supported by:the Higher Education Commission, Islamabad, Pakistan(9447/Sindh/NRPU/R&D/HEC/2017);Aga Khan University Dean’s Startup Fund, Role of Natural Remedies on Psycho-neurological Deficits in Murine Model as Preclinical Studies Associated with or without Diabetes(2017-2021)
Cite this article
Faiq Amin, Saara Ahmad, Muhammad Wasim, Asra Khan, Fazal Manzoor Arain, Zehra Batool, Saiqa Tabassum, Saima Khaliq, Noreen Samad, Saida Haider. Antidepressive and anxiolytic effects of a combination of Saffron and Chamomile in rats and their relationship with serotonin using in vivo methods[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(1): 49-56.
share this article
| Item | Healthy control (n = 6) | Disease control (n = 6) | Fluoxetine (n = 6) | Saffron (n = 6) | Chamomile (n = 6) | Saffron + chamomile (n = 6) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blood glucose (mg/dL) | 92.80±10.11ab | 147.00±35.50 | 134.90±35.70 | 119.61±4.00 | 126.82±6.10 | 99.80±7.91a |
| FST (s) | 75.81±7.50abc | 31.82±4.70 | 42.01±4.30 | 67.05±6.02abc | 77.81±9.80ab | 96.13±4.71ab |
| Tryptophan (μg/mL) | 9.00±0.82a | 5.81±0.40 | 8.61±1.40a | 8.80±0.30a | 8.11±0.51a | 9.14±0.30a |
| CRP (ng/mL) | 1.80±0.40abc | 3.31±0.11 | 4.61±0.80ac | 5.30±0.11ac | 6.13±0.11ac | 7.42±0.31ab |
Table 1 Biochemical and behavioral analyses ($\bar{x}±s$)
| Item | Healthy control (n = 6) | Disease control (n = 6) | Fluoxetine (n = 6) | Saffron (n = 6) | Chamomile (n = 6) | Saffron + chamomile (n = 6) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blood glucose (mg/dL) | 92.80±10.11ab | 147.00±35.50 | 134.90±35.70 | 119.61±4.00 | 126.82±6.10 | 99.80±7.91a |
| FST (s) | 75.81±7.50abc | 31.82±4.70 | 42.01±4.30 | 67.05±6.02abc | 77.81±9.80ab | 96.13±4.71ab |
| Tryptophan (μg/mL) | 9.00±0.82a | 5.81±0.40 | 8.61±1.40a | 8.80±0.30a | 8.11±0.51a | 9.14±0.30a |
| CRP (ng/mL) | 1.80±0.40abc | 3.31±0.11 | 4.61±0.80ac | 5.30±0.11ac | 6.13±0.11ac | 7.42±0.31ab |
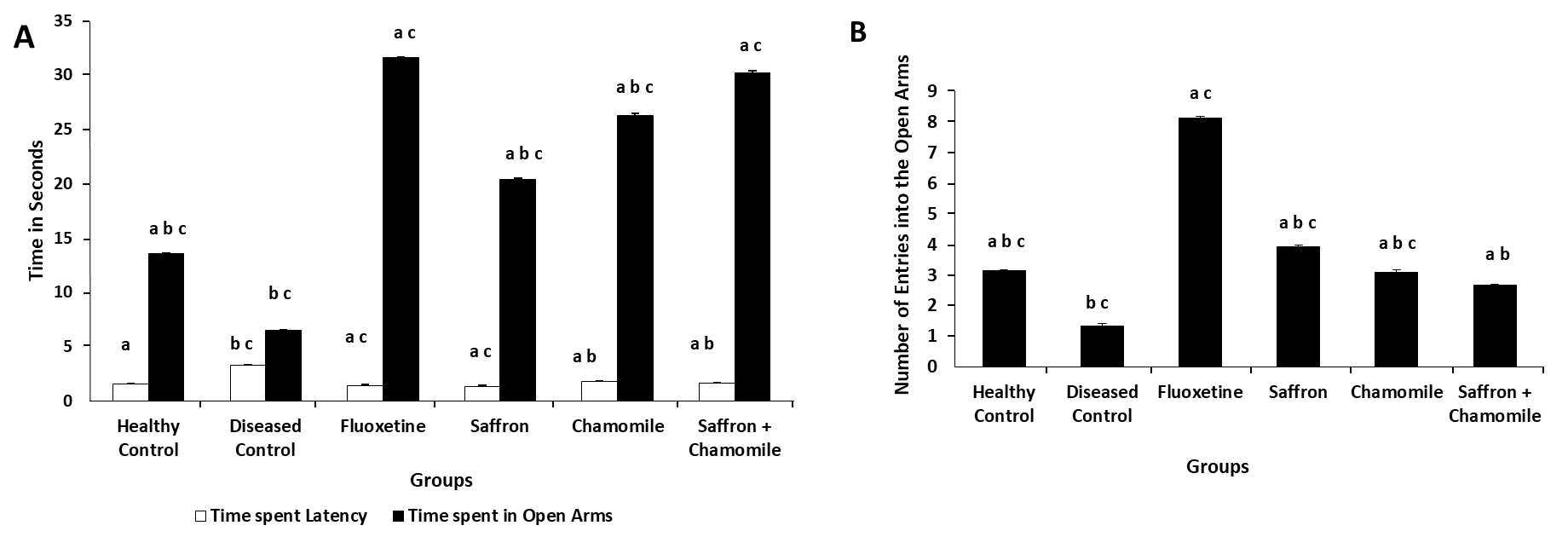
Figure 1 Effects of treatments on EPMT parameters A: EPMT latency and time spent in open arms in seconds; B: EPMT number of entries in the open arms for all the groups. The animals were divided into six groups (n = 6): healthy control (standard chow and water), disease control (diabetic without treatment), positive control (diabetic with Fluoxetine 5 mg·kg-1·d-1), saffron group (diabetic with saffron 10 mg·kg-1·d-1), chamomile group (diabetic with chamomile 30 mg·kg-1·d-1), and combination group (diabetic with saffron 5 mg·kg-1·d-1 and chamomile 15 mg·kg-1·d-1). All treatments were administered via oral gavage, with decoctions prepared fresh daily. After three weeks of treatment duration, analysis performed. EPMT: elevated plus maze test; ANOVA: analysis of variance. The bar values in average and error bars are standard deviation. ANOVA followed by Tukey's test revealed statistically significant differences (P < 0.05), denoted by the following legends: aindicates comparison with the diseased control group, bindicates comparison with the fluoxetine group, and c indicates comparison with the combination of saffron and + chamomile group.

Figure 2 5HT2C receptor expression in the cortex and hippocampus The animals were divided into six groups (n = 6): healthy control (standard chow and water), disease control (diabetic without treatment), positive control (diabetic with Fluoxetine 5 mg·kg-1·d-1), saffron group (diabetic with saffron 10 mg·kg-1·d-1), chamomile group (diabetic with chamomile 30 mg·kg-1·d-1), and combination group (diabetic with saffron 5 mg·kg-1·d-1 and chamomile 15 mg·kg-1·d-1). All treatments were administered via oral gavage, with decoctions prepared fresh daily. After three weeks of treatment duration, analysis performed. 5HT2C: 5-hydroxytryptamine 2C; ANOVA: analysis of variance. The bar values in average and error bars are standard deviation. ANOVA followed by Tukey's test revealed statistically significant differences (P < 0.05), denoted by the following legends: aindicates comparison with the diseased control group, b indicates comparison with the fluoxetine group, and c indicates comparison with the combination of saffron and + chamomile group.

Figure 3 BDNF expression in the cortex and hippocampus The animals were divided into six groups (n = 6): healthy control (standard chow and water), disease control (diabetic without treatment), positive control (diabetic with Fluoxetine 5 mg·kg-1·d-1), saffron group (diabetic with saffron 10 mg·kg-1·d-1), chamomile group (diabetic with chamomile 30 mg·kg-1·d-1), and combination group (diabetic with saffron 5 mg·kg-1·d-1 and chamomile 15 mg·kg-1·d-1). All treatments were administered via oral gavage, with decoctions prepared fresh daily. After three weeks of treatment duration, analysis performed. BDNF: brain-derived neurotrophic factor; The bar values in average and error bars are standard deviation. ANOVA followed by Tukey's test revealed statistically significant differences (P < 0.05), denoted by the following legends: aindicates comparison with the diseased control group, bindicates comparison with the fluoxetine group, and cindicates comparison with the combination of saffron and + chamomile group.
| 1. | Murphy JA, Byrne GJ. Prevalence and correlates of the proposed DSM-5 diagnosis of chronic depressive disorder. J Affect Disord 2012; 139: 172-80. |
| 2. | Angst J, Gamma A, Rossler W, Ajdacic V, Klein DN. Long-term depression versus episodic major depression: results from the prospective Zurich study of a community sample. J Affect Disord 2009; 115: 112-21. |
| 3. | Satyanarayana S, Enns MW, Cox BJ, Sareen J. Prevalence and correlates of chronic depression in the canadian community health survey: mental health and well-being. Can J Psychiatry 2009; 54: 389-98. |
| 4. | Ventriglio A, Bhugra D, Sampogna G, et al. From dysthymia to treatment-resistant depression: evolution of a psychopathological construct. Int Rev Psychiatry 2020; 32: 471-6. |
| 5. | Al-Harbi KS. Treatment-resistant depression: therapeutic trends, challenges, and future directions. Patient Prefer Adherence 2012; 6: 369-88. |
| 6. | Hung CI, Liu CY, Yang CH. Persistent depressive disorder has long-term negative impacts on depression, anxiety, and somatic symptoms at 10-year follow-up among patients with major depressive disorder. J Affect Disord 2019; 243: 255-61. |
| 7. |
Ivanova JI, Birnbaum HG, Kidolezi Y, et al. Direct and indirect costs of employees with treatment-resistant and non-treatment-resistant major depressive disorder. Curr Med Res Opin 2010; 26: 2475-84.
DOI PMID |
| 8. |
Olchanski N, McInnis Myers M, Halseth M, et al. The economic burden of treatment-resistant depression. Clin Ther 2013; 35: 512-22.
DOI PMID |
| 9. |
Dunner DL, Rush AJ, Russell JM, et al. Prospective, long-term, multicenter study of the naturalistic outcomes of patients with treatment-resistant depression. J Clin Psychiatry 2006; 67: 688-95.
DOI PMID |
| 10. | Hantouche E, Angst J, Azorin JM. Explained factors of suicide attempts in major depression. J Affect Disord 2010; 127: 305-8. |
| 11. | Bernal M, Haro JM, Bernert S, et al. Risk factors for suicidality in Europe: results from the ESEMED study. J Affect Disord 2007; 101: 27-34. |
| 12. | Chen YW, Dilsaver SC. Lifetime rates of suicide attempts among subjects with bipolar and unipolar disorders relative to subjects with other Axis I disorders. Biol Psychiatry 1996; 39: 896-9. |
| 13. | Berge LI, Riise T. Comorbidity between type 2 diabetes and depression in the adult population: directions of the association and its possible pathophysiological mechanisms. Int J Endocrinol 2015; 2015: 164760. |
| 14. | Moulton CD, Pickup JC, Ismail K. The link between depression and diabetes: the search for shared mechanisms. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2015; 3: 461-71. |
| 15. |
Ho N, Balu DT, Hilario MR, Blendy JA, Lucki I. Depressive phenotypes evoked by experimental diabetes are reversed by insulin. Physiol Behav 2012; 105: 702-8.
DOI PMID |
| 16. | Liu K, Zhao L, Xu W, et al. Metabolic changes associated with a rat model of diabetic depression detected by Ex Vivo (1)H nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy in the prefrontal cortex, hippocampus, and hypothalamus. Neural Plast 2018; 2018: 6473728. |
| 17. | Miraj S, Alesaeidi S. A systematic review study of therapeutic effects of Matricaria recuitta chamomile (chamomile). Electron Physician 2016; 8: 3024-31. |
| 18. |
Schmidt M, Betti G, Hensel A. Saffron in phytotherapy: pharmacology and clinical uses. Wien Med Wochenschr 2007; 157: 315-9.
DOI PMID |
| 19. |
Javadi B, Sahebkar A, Emami SA. A survey on saffron in major islamic traditional medicine books. Iran J Basic Med Sci 2013; 16: 1-11.
PMID |
| 20. |
Pitsikas N. Constituents of Saffron (Crocus sativus L.) as potential candidates for the treatment of anxiety disorders and schizophrenia. Molecules 2016; 21: 303.
DOI PMID |
| 21. | Salehi B, Venditti A, Sharifi-Rad M, et al. The therapeutic potential of apigenin. Int J Mol Sci 2019; 20: 1305. |
| 22. | Amin F, Ibrahim MAA, Rizwan-Ul-Hasan S, et al. Interactions of apigenin and safranal with the 5HT1A and 5HT2A receptors and behavioral effects in depression and anxiety: a molecular docking, lipid-mediated molecular dynamics, and in vivo analysis. Molecules 2022; 27: 8658. |
| 23. |
Hannon J, Hoyer D. Molecular biology of 5-HT receptors. Behav Brain Res 2008; 195: 198-213.
DOI PMID |
| 24. |
Zmudzka E, Salaciak K, Sapa J, Pytka K. Serotonin receptors in depression and anxiety: insights from animal studies. Life Sci 2018; 210: 106-24.
DOI PMID |
| 25. | Popova NK, Naumenko VS. Neuronal and behavioral plasticity: the role of serotonin and BDNF systems tandem. Expert Opin Ther Targets 2019; 23: 227-39. |
| 26. | Caviedes A, Lafourcade C, Soto C, Wyneken U. BDNF/NF-kappaB signaling in the neurobiology of depression. Curr Pharm Des 2017; 23: 3154-63. |
| 27. | Dionisie V, Ciobanu AM, Toma VA, et al. Escitalopram targets oxidative stress, caspase-3, BDNF and MeCP 2 in the hippocampus and frontal cortex of a rat model of depression induced by chronic unpredictable mild stress. Int J Mol Sci 2021; 22: 7483. |
| 28. | Ahmad S, Khan A, Batool Z, et al. Medicinal effects of saffron and chamomile on diabetes mellitus and associated hyperlipidemia and memory impairment. Pak J Pharm Sci 2020; 33: 1191-8. |
| 29. | Ahmad S, Khan A, Tabassum S, et al. Co-administration of saffron and chamomile give additive effects of antidiabetic and antioxidant activity with in vivo augmentation of brain BDNF, acetylcholine levels and cognitive functions in streptozotocininduced diabetic rats. Curr Psychopharmacol 2022; 11: 56-69. |
| 30. |
Okyar A, Can A, Akev N, Baktir G, Sutlupinar N. Effect of Aloe vera leaves on blood glucose level in type Ⅰ and type Ⅱ diabetic rat models. Phytother Res 2001; 15: 157-61.
DOI PMID |
| 31. | Ceretta LB, Reus GZ, Stringari RB, et al. Imipramine treatment reverses depressive-like behavior in alloxan-diabetic rats. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 2012; 28: 139-44. |
| 32. |
Shivavedi N, Charan Tej GNV, Neogi K, Nayak PK. Ascorbic acid therapy: a potential strategy against comorbid depression-like behavior in streptozotocin-nicotinamide-induced diabetic rats. Biomed Pharmacother 2019; 109: 351-9.
DOI PMID |
| 33. |
McIntyre RS, Soczynska JK, Konarski JZ, Kennedy SH. The effect of antidepressants on glucose homeostasis and insulin sensitivity: synthesis and mechanisms. Expert Opin Drug Saf 2006; 5: 157-68.
PMID |
| 34. | Bolo NR, Jacobson AM, Musen G, Keshavan MS, Simonson DC.Acute hyperglycemia increases brain pregenual anterior cingulate cortex glutamate concentrations in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 2020; 69: 1528-39. |
| 35. |
Yu E, Papandreou C, Ruiz-Canela M, et al. Association of tryptophan metabolites with incident type 2 diabetes in the PREDIMED Trial: a case-cohort study. Clin Chem 2018; 64: 1211-20.
DOI PMID |
| 36. | Ahmad S, Rafiq H, Khan A, et al. Ameliorative effects of half-dose saffron and chamomile combination on Psycho-endocrinological changes in a diabetic murine model. PLoS One 2022; 17: e0276236. |
| 37. |
Belovicova K, Bogi E, Csatlosova K, Dubovicky M. Animal tests for anxiety-like and depression-like behavior in rats. Interdiscip Toxicol 2017; 10: 40-3.
DOI PMID |
| 38. | Orio L, Alen F, Ballesta A, Martin R, Gomez de Heras R. Antianhedonic and antidepressant effects of affron ((R)), a standardized saffron (Crocus Sativus L.) extract. Molecules 2020; 25: 3207. |
| 39. | Hawiset T, Sriraksa N, Kamsrijai U, Wanchai K, Inkaew P. Anxiolytic and antidepressant-like activities of aqueous extract of Azadirachta indica A. Juss. flower in the stressed rats. Heliyon 2022; 8: e08881. |
| 40. |
Giffen PS, Turton J, Andrews CM, et al. Markers of experimental acute inflammation in the Wistar Han rat with particular reference to haptoglobin and C-reactive protein. Arch Toxicol 2003; 77: 392-402.
PMID |
| 41. | Ghaderi A, Asbaghi O, Reiner Z, et al. The effects of saffron (Crocus sativus L.) on mental health parameters and C-reactive protein: a Meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Complement Ther Med 2020; 48: 102250. |
| 42. | Dixon JB, Hayden MJ, Lambert GW, et al. Raised CRP levels in obese patients: symptoms of depression have an independent positive association. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2008; 16: 2010-5. |
| 43. |
Messaoud A, Mensi R, Douki W, et al. Reduced peripheral availability of tryptophan and increased activation of the kynurenine pathway and cortisol correlate with major depression and suicide. World J Biol Psychiatry 2019; 20: 703-11.
DOI PMID |
| 44. |
Lukic I, Getselter D, Koren O, Elliott E. Role of tryptophan in microbiota-induced depressive-like behavior: evidence from tryptophan depletion study. Front Behav Neurosci 2019; 13: 123.
DOI PMID |
| 45. | Mackay GM, Forrest CM, Christofides J, et al. Kynurenine metabolites and inflammation markers in depressed patients treated with fluoxetine or counselling. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 2009; 36: 425-35. |
| 46. |
Wold EA, Wild CT, Cunningham KA, Zhou J. Targeting the 5-HT2C receptor in biological context and the current state of 5-HT2C receptor ligand development. Curr Top Med Chem 2019; 19: 1381-98.
DOI PMID |
| 47. |
Martin CB, Hamon M, Lanfumey L, Mongeau R. Controversies on the role of 5-HT(2C) receptors in the mechanisms of action of antidepressant drugs. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 2014; 42: 208-23.
DOI PMID |
| 48. | Yan L, Xu X, He Z, et al. Antidepressant-like effects and cognitive enhancement of coadministration of Chaihu Shugan San and fluoxetine: dependent on the BDNF-ERK-CREB signaling pathway in the hippocampus and frontal cortex. Biomed Res Int 2020; 2020: 2794263. |
| 49. | Diniz DM, Calabrese F, Brivio P, et al. BDNF overexpression in the ventral hippocampus promotes antidepressant- and anxiolytic-like activity in serotonin transporter knockout rats. Int J Mol Sci 2021; 22: 5040. |
| 50. | Lymperopoulou C, Lamari F. Saffron safety in humans: lessons from the animal and clinical studies. Med Aromat Plants 2015; 4: 4-6. |
| [1] | LI Yajing, WANG Baoying, SHAO Wenxue, LU Shuaifei, SU Pan, BAI Ming, XU Erping, LI Yucheng. Quantitative proteomic analysis of the brain reveals the potential antidepressant mechanism of Jiawei Danzhi Xiaoyao San (加味丹栀逍遥散) in a chronic unpredictable mild stress mouse model of depression [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(1): 22-31. |
| [2] | YAN Kai, WANG Wei, WANG Yan, GAO Huijuan, FENG Xingzhong. Network pharmacology-based study on the mechanism of Tangfukang formula (糖复康方) against type 2 diabetes mellitus [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(1): 76-88. |
| [3] | DENG Deqiang, XIAO Yan, MA Dan, QIU Jinling, HAO Congli, WANG Di, ZHANG Miao. Role of toll-like receptor 4/mutant myeloid differentiation primary response 88/nuclear factor kappa-B mediated inflammation in diabetes mellitus with Northwest dryness syndrome [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(5): 963-973. |
| [4] | LIU Tongtong, ZHANG Xi, YANG Hui, LIN Xiaoyuan, LIU Jian, ZHANG Xiuli, GUO Dongwei, ZHAO Hongqing, ZOU Manshu, LEI Chang, LONG Hongping, LUO Yan, XIANG Yun, GE Jinwen, WANG Yuhong, MENG Pan. Luteolin promotes neuronogenesis in hippocampus of chronic unpredictable mild stress rats and primary hippocampus of fetal rats [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(4): 670-679. |
| [5] | JIN Shenyi, LIU Yahua, HAN Xu, CAI Mengjie, XU Jiatuo, LU Hao, CHEN Qingguang. Dark red tongue color formation caused by hyperglycemia is attributed to decreased blood flow of tongue tissue partially due to nuclear factor-kappa B pathway activation [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1118-1125. |
| [6] | HENG Xianpei, WANG Zhita, YANG Liuqing, LI Liang, HUANG Suping. Dangua Fang (丹瓜方) regulating tricarboxylic acid cycle and respiratory chain and its mechanism in diabetic rats [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1150-1159. |
| [7] | QIN Xihui, PANG Jianli, XIONG Guan, FENG Jie. Bo′s abdominal acupuncture improves disordered metabolism in obese type 2 diabetic rats through regulating fibroblast growth factor 21 and its related adipokines [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1200-1208. |
| [8] | WANG Yaqi, ZHAO Weibo, WANG Yixing, ZHAO Haihong, ZHOU Yaoyao, YAN Yun, WU Taotao, LUO Bin, WANG Ji. Traditional Chinese Medicine constitution among patients with allergic rhinitis and its correlation with anxiety and depression [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1252-1258. |
| [9] | JIANG Li, FU Qiang, WANG Shidong, ZHAO Jinxi, CHEN Yu, LI Jiayue, XIAO Yonghua, HUANG Weijun, SUN Ruixi, XIAO Yao, SHEN Aijia, WANG Junheng, LIU Jiangteng, FU Xiaozhe, LI Yuanyuan, ZHAO Yu, XUE Taiqi. Effects of Shenlian formula (参连方) on microbiota and inflammatory cytokines in adults with type 2 diabetes: a double-blind randomized clinical trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(4): 760-769. |
| [10] | MA Fangfang, ZHANG Hewei, LI Bingxue, CHENG Peiyu, YU Mingwei, WANG Xiaomin. Acupuncture and moxibustion for malignant tumor patients with psychological symptoms of insomnia, anxiety and depression: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(3): 441-456. |
| [11] | QU Yilun, CHENG Haimei, WANG Qian, LI Shuang, DUAN Shuwei, FENG Zhe, LI Weizhen, JIANG Shuangshuang, YANG Hongtao, MAO Yonghui, GENG Yanqiu, LI Jijun, LIU Yuning, TIAN Jinzhou, LIU Hongfang, DONG Zheyi, CHEN Xiangmei. Noninvasive identificational diagnosis of diabetic nephropathy and non-diabetic renal disease based on clinical characteristics of Traditional Chinese Medicine symptom pattern and conventional medicine [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(3): 588-593. |
| [12] | ZOU Xinshuang, SHI Lei, YIN Hailong, LI Haiping, WANG Mengheng, SONG Wanci, LUO Laichun, WU Hezhen, YANG Yanfang, ZAN Junfeng, LIU Yanwen, DAN Hanxiong, YIN Qiang, YOU Pengtao. Compound Gaoziban tablet (复方高滋斑片) alleviates depression via toll-like receptor 4/myeloid differentiation factor 88/nuclear factor-kappa B pathway [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(6): 956-964. |
| [13] | CHEN Limei, SUN Jifei, GUO Chunlei, LI Xiaojiao, WANG Zhi, Hong Yang, FANG Jiliang. Preliminary single-arm study of brain effects during transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation treatment of recurrent depression by resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(5): 818-824. |
| [14] | You WU, Yuli HU, Wei LIU, Boju SUN, Chengfei ZHANG, Lili WU, Tonghua LIU. Flavonoids from traditional Chinese herbs for diabetes in rats: a network Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(1): 1-8. |
| [15] | LI Ganggang, LU Ye, HE Pei, ZHANG Shiyue, CHENG Yating, ZHANG Shaodan, PEI Lin. Target prediction and activity verification for the antidepressant action of Huangqin(Radix Scutellariae Baicalensis) [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(6): 845-852. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

