Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (1): 1-8.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20210425.001
• Meta-analysis • Next Articles
Flavonoids from traditional Chinese herbs for diabetes in rats: a network Meta-analysis
You WU, Yuli HU, Wei LIU, Boju SUN, Chengfei ZHANG, Lili WU( ), Tonghua LIU(
), Tonghua LIU( )
)
- Key Laboratory of Health Cultivation of the Ministry of Education, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100029, China
-
Received:2020-11-22Accepted:2021-02-06Online:2022-02-15Published:2021-04-25 -
Contact:Lili WU,Tonghua LIU -
About author:WU Lili, Key Laboratory of Health Cultivation of the Ministry of Education, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100029, China. Qingniao_566@163.com
LIU Tonghua, Key Laboratory of Health Cultivation of the Ministry of Education, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100029, China. thliu@vip.163.com;
-
Supported by:International Cooperation Base for the Prevention and Treatment of Chronic Diseases by Traditional Chinese Medicine(GZYYGJ2019034);National Center for International Research(2015B01022)
Cite this article
You WU, Yuli HU, Wei LIU, Boju SUN, Chengfei ZHANG, Lili WU, Tonghua LIU. Flavonoids from traditional Chinese herbs for diabetes in rats: a network Meta-analysis[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(1): 1-8.
share this article
| Baicalein | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| -2.63 (-133.87, 127.00) | Kaempferol | ||||||
| -29.63 (-163.37, 104.77) | -26.82 (-145.01, 90.10) | Luteolin | |||||
| -27.54 (-156.63, 97.98) | -25.89 (-129.99, 78.58) | 0.73 (-113.72, 117.55) | Metformin | ||||
| -11.47 (-123.20, 104.36) | -7.83 (-105.10, 86.88) | 18.68 (-85.70, 123.21) | 17.32 (-68.07, 101.15) | Naringenin | |||
| -141.24 (-240.81, -36.43) | -138.37 (-219.65, -55.54) | -111.02 (-198.59, -22.41) | -112.20 (-185.78, -36.85) | -129.42 (-182.69, -77.07) | Placebo | ||
| -15.64 (-136.02, 108.60) | -12.77 (-118.18, 92.85) | 14.23 (-97.88, 126.48) | 13.54 (-78.60, 105.39) | -3.81 (-90.85, 80.55) | 125.74 (54.89, 195.28) | Puerarin | |
Table 1 League table showing the results of the network Meta-analysis comparing the effect of flavonoid treatments on blood glucose level in diabetic rat modelsa
| Baicalein | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| -2.63 (-133.87, 127.00) | Kaempferol | ||||||
| -29.63 (-163.37, 104.77) | -26.82 (-145.01, 90.10) | Luteolin | |||||
| -27.54 (-156.63, 97.98) | -25.89 (-129.99, 78.58) | 0.73 (-113.72, 117.55) | Metformin | ||||
| -11.47 (-123.20, 104.36) | -7.83 (-105.10, 86.88) | 18.68 (-85.70, 123.21) | 17.32 (-68.07, 101.15) | Naringenin | |||
| -141.24 (-240.81, -36.43) | -138.37 (-219.65, -55.54) | -111.02 (-198.59, -22.41) | -112.20 (-185.78, -36.85) | -129.42 (-182.69, -77.07) | Placebo | ||
| -15.64 (-136.02, 108.60) | -12.77 (-118.18, 92.85) | 14.23 (-97.88, 126.48) | 13.54 (-78.60, 105.39) | -3.81 (-90.85, 80.55) | 125.74 (54.89, 195.28) | Puerarin | |
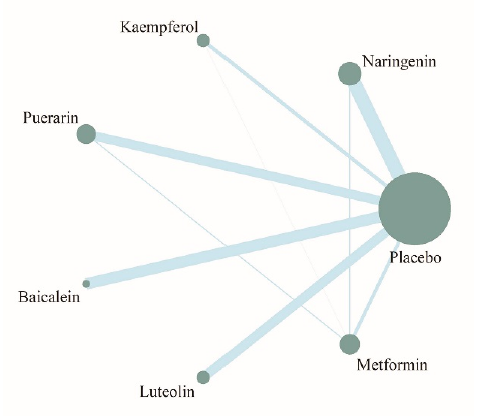
Figure 1 Network diagram of the network Meta-analysis The size of nodes corresponds to the total number of studies in each group, and line thickness represents the total number of studies between connected treatment groups.
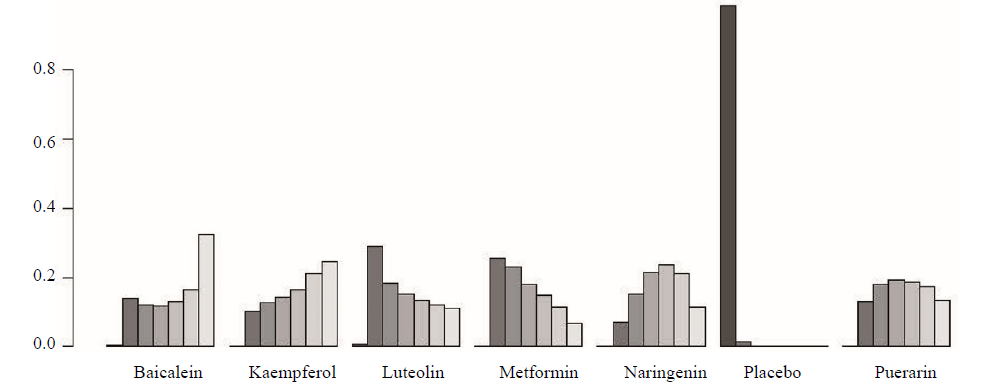
Figure 2 Rank probability plot for network Meta-analysis The columns show the P values of each treatment for rankings from left to right (ie, from lowest to highest rank).
| [1] | American Diabetes Association. 2. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: standards of medical care in diabetes-2020. Diabetes Care 2020;43:S14-31. |
| [2] | Saeedi P, Petersohn I, Salpea P, et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th ed. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2019;157:107843. |
| [3] | Cheng AY, Fantus IG. Oral antihyperglycemic therapy for type 2 diabetes mellitus. Can Med Assoc J 2005;172:213-226. |
| [4] | Xiao E, Luo L. Alternative therapies for diabetes: a comparison of western and Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) approaches. Curr Diabetes Rev 2018;14:487-96. |
| [5] | Necyk C, Zubach-Cassano L. Natural health products and diabetes: A practical review. Can J Diabetes 2017;41:642-47. |
| [6] | Wang H, Shi S, Wang S. Can highly cited herbs in ancient Traditional Chinese Medicine formulas and modern publications predict therapeutic targets for diabetes mellitus? J Ethnopharmacol 2018;213:101-10. |
| [7] | Tian J, Jin D, Bao Q, et al. Evidence and potential mechanisms of Traditional Chinese Medicine for the treatment of type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. Diabetes Obes Metab 2019;21:1801-16. |
| [8] | Perez-Vizcaino F, Fraga CG. Research trends in flavonoids and health. Arch Biochem Biophys 2018;646:107-12. |
| [9] | Santos-Buelga C, Feliciano AS. Flavonoids: from structure to health issues. Molecules 2017;22:477. |
| [10] | Oteiza PI, Fraga CG, Mills DA, Taft DH. Flavonoids and the gastrointestinal tract: local and systemic effects. Mol Aspects Med 2018;61:41-9. |
| [11] | Imran M, Rauf A, Abu-Izneid T, et al. Luteolin, a flavonoid, as an anticancer agent: a review. Biomed Pharmacother 2019;112:108612. |
| [12] | Yi YS. Regulatory roles of flavonoids on inflammasome activation during inflammatory responses. Mol Nutr Food Res 2018;62:e1800147. |
| [13] | Bubols GB, Vianna Dda R, Medina-Remon A, et al. The antioxidant activity of coumarins and flavonoids. Mini- Rev Med Chem 2013;13:318-334. |
| [14] | Afshari K, Haddadi NS, Haj-Mirzaian A, et al. Natural flavonoids for the prevention of colon cancer: a comprehensive review of preclinical and clinical studies. J Cell Physiol 2019;234(12):21519-46. |
| [15] | Bansal Y, Singh R, Saroj P, Sodhi RK, Kuhad A. Naringenin protects against oxido-inflammatory aberrations and altered tryptophan metabolism in olfactory bulbectomized-mice model of depression. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 2018;355:257-68. |
| [16] | Ahmed OM, Hassan MA, Abdel-Twab SM, Abdel Azeem MN. Navel orange peel hydroethanolic extract, naringin and naringenin have anti-diabetic potentials in type 2 diabetic rats. Biomed Pharmacother 2017;94:197-205. |
| [17] | Wang Y, Chen H, Zhang H. Kaempferol promotes proliferation, migration and differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells via up-regulation of microRNA-101. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 2019;47:1050-56. |
| [18] | Devi KP, Malar DS, Nabavi SF, et al. Kaempferol and inflammation: from chemistry to medicine. Pharmacol Res 2015;99:1-10. |
| [19] | She S, Liu W, Li T, Hong Y. Effects of puerarin in STZ-induced diabetic rats by oxidative stress and the TGF-β1/Smad2 pathway. Food Funct 2014;5:944-950. |
| [20] | Wu C, Xu Q, Chen X, Liu J. Delivery luteolin with folacin-modified nanoparticle for glioma therapy. Int J Nanomedicine 2019;14:7515-31. |
| [21] | Ye S, Liu H, Chen Y, et al. A novel immunosuppressant, luteolin, modulates alloimmunity and suppresses murine allograft rejection. J Immunol 2019;203:3436-46. |
| [22] | Bai L, Li X, He L, et al. Antidiabetic potential of flavonoids from traditional Chinese medicine: A review. Am J Chin Med 2019;47:933-57. |
| [23] | Hooijmans CR, IntHout J, Ritskes-Hoitinga M, Rovers MM. Meta-analyses of animal studies: an introduction of a valuable instrument to further improve healthcare. ILAR J 2014;55:418-426. |
| [24] | Schwingshackl L, Chaimani A, Hoffmann G, Schwedhelm C, Boeing H. A network Meta-analysis on the comparative efficacy of different dietary approaches on glycaemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Eur J Epidemiol 2018;33:157-70. |
| [25] | Hutton B, Salanti G, Caldwell DM, et al. The PRISMA extension statement for reporting of systematic reviews incorporating network Meta-analyses of health care interventions: checklist and explanations. Ann Intern Med 2015;162:777-84. |
| [26] | Hooijmans CR, Rovers MM, de Vries RB, Leenaars M, Ritskes-Hoitinga M, Langendam MW. SYRCLE’s risk of bias tool for animal studies. BMC Med Res Methodol 2014;14:43. |
| [27] | Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Measuring inconsistency in Meta-analyses. BMJ 2003;327:557-60. |
| [28] | Van Valkenhoef G, Tervonen T, Zwinkels T, de Brock B, Hillege H. ADDIS: a decision support system for evidence-based medicine. Decision Support Systems 2013;55:459-75. |
| [29] | Chaimani A, Higgins JP, Mavridis D, Spyridonos P, Salanti G. Graphical tools for network Meta-analysis in STATA. PLoS One 2013;8:e76654. |
| [30] | Ahad A, Mujeeb M, Ahsan H, Siddiqui WA. Prophylactic effect of baicalein against renal dysfunction in type 2 diabetic rats. Biochimie 2014;106:101-10. |
| [31] | Al-Numair KS, Chandramohan G, Veeramani C, Alsaif MA. Ameliorative effect of kaempferol, a flavonoid, on oxidative stress in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Redox Rep 2015;20:198-209. |
| [32] | Al-Rejaie SS, Aleisa AM, Abuohashish HM, et al. Naringenin neutralises oxidative stress and nerve growth factor discrepancy in experimental diabetic neuropathy. Neurol Res 2015;37:924-33. |
| [33] | Annadurai T, Muralidharan AR, Joseph T, Hsu MJ, Thomas PA, Geraldine P. Antihyperglycemic and antioxidant effects of a flavanone, naringenin, in streptozotocin-nicotinamide-induced experimental diabetic rats. J Physiol Biochem 2012;68:307-18. |
| [34] | Cao L, Mao CP, Gu ZL, Zhou WX, Guo CY. Influence of insulin sensitivity on insulin resistance rats treated by puerarin. Chin Pharmacol Bull 2007; 23: 1598-600+601. |
| [35] | Chen Y, Sun XB, Lu HE, Wang F, Fan XH. Effect of luteoin in delaying cataract in STZ-induced diabetic rats. Arch Pharm Res 2015;40:88-95. |
| [36] | El-Bassossy HM, Abo-Warda SM, Fahmy A. Chrysin and luteolin alleviate vascular complications associated with insulin resistance mainly through PPAR-γ activation. Am J Chin Med 2014;42:1153-67. |
| [37] | Gong ZG, Zhu D, Zheng SB, Zhang Y. Changes in nitrogen monoxide and nitric oxide synthase content in diabetic rats intervention of puerarin and exercise. Zhong Guo Lin Chuang Kang Fu 2006;10:95-7. |
| [38] | Hasanein P, Fazeli F. Role of naringenin in protection against diabetic hyperalgesia and tactile allodynia in male wistar rats. J Physiol Biochem 2014;70:997-1006. |
| [39] | Kannappan S, Anuradha CV. Naringenin enhances insulin-stimulated tyrosine phosphorylation and improves the cellular actions of insulin in a dietary model of metabolic syndrome. Eur J Nutr 2010;49:101-09. |
| [40] | Kannappan S, Palanisamy N, Anuradha CV. Suppression of hepatic oxidative events and regulation of eNOS expression in the liver by naringenin in fructose-administered rats. Eur J Pharmacol 2010;645:177-84. |
| [41] | Li Y, Chen Q, Ran D, et al. Changes in the levels of 12/15-lipoxygenase, apoptosis-related proteins and inflammatory factors in the cortex of diabetic rats and the neuroprotection of baicalein. Free Radic Biol Med 2019;134:239-47. |
| [42] | Liu Y, Tian X, Gou L, Sun L, Ling X, Yin X. Luteolin attenuates diabetes-associated cognitive decline in rats. Brain Res Bull 2013;94:23-9. |
| [43] | Lu HE, Chen Y, Sun XB, Tong B, Fan XH. Effects of luteolin on retinal oxidative stress and inflammation in diabetes. RSC Adv 2015;5:4898-904. |
| [44] | Luo C, Yang H, Tang CY, et al. Kaempferol alleviates insulin resistance via hepatic IKK/NF-κB signal in type 2 diabetic rats. Int Immunopharmacol 2015;28:744-50. |
| [45] | Mao CP, Gu ZL. Experimental effect of puerarin on the formation of advanced glycation end products and expression of RAGE in the aorta of diabetic rats. Chin Pharmacol Bull 2004;20:393-7. |
| [46] | Mato EPM, Essop MF, Owira PMO. Effects of naringenin on renal expression of organic cation transporter 1 and 2 proteins and metformin disposition in diabetic rats. J Funct Foods 2019;59:1-7. |
| [47] | Priscilla DH, Jayakumar M, Thirumurugan K. Flavanone naringenin: an effective antihyperglycemic and anti-hyperlipidemic nutraceutical agent on high fat diet fed streptozotocin induced type 2 diabetic rats. J Funct Foods 2015;14:363-73. |
| [48] | Qian LB, Lu JF, Ye ZG, Wang HP, Xia Q. Luteolin reduces cardiac dysfunctions in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Zhong Guo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi 2011;27:409-14. |
| [49] | Radika MK, Anuradha CV. Polyphenols activate energy sensing network in insulin resistant models. Chem Biol Interact 2017;275:95-107. |
| [50] | Rahigude A, Bhutada P, Kaulaskar S, Aswar M, Otari K. Participation of antioxidant and cholinergic system in protective effect of naringenin against type-2 diabetes-induced memory dysfunction in rats. Neuroscience 2012;226:62-72. |
| [51] | Sarkar P, Nath K, Banu S. Modulatory effect of baicalein on gene expression and activity of antioxidant enzymes in streptozotocin-nicotinamide induced diabetic rats. Braz J Pharm Sci 2019;55. |
| [52] | Singh P, Bansal S, Kuhad A, Kumar A, Chopra K. Naringenin ameliorates diabetic neuropathic pain by modulation of oxidative-nitrosative stress, cytokines and MMP-9 levels. Food Funct 2020;11:4548-60. |
| [53] | Wojnar W, Zych M, Kaczmarczyk-Sedlak I. Antioxidative effect of flavonoid naringenin in the lenses of type 1 diabetic rats. Biomed Pharmacother 2018;108:974-84. |
| [54] | Wu QM, Jin YM, Ni HX. Effect of kaempferol on correlation factors of chronic complications of type 2 diabetic rats. Zhong Cao Yao 2015;46:1806-9. |
| [55] | Yan N, Wen L, Peng R, et al. Naringenin ameliorated kidney injury through Let-7a/TGFBR1 signaling in diabetic nephropathy. J Diabetes Res 2016;2016:8738760. |
| [56] | Yang F, Dong XX, Guo Y. Effects of puerarin on rats with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Zhong Guo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi 2019;35:355-8. |
| [57] | Yang LP, Sun HL, Wu LM, et al. Baicalein reduces inflammatory process in a rodent model of diabetic retinopathy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2009;50:2319-2327. |
| [58] | Yu Q, Han W, Zhu Y, Zhai H. Effect of puerarin on typeⅡ diabetes mellitus with orthopaedic footwear. Pak J Pharm Sci 2017;30:1899-903. |
| [59] | Zhang L, Guo Z, Wang Y, Geng J, Han S. The protective effect of kaempferol on heart via the regulation of Nrf2, NF-κβ, and PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β signaling pathways in isoproterenol-induced heart failure in diabetic rats. Drug Dev Res 2019;80:294-309. |
| [60] | Kapoor R, Kakkar P. Naringenin accords hepatoprotection from streptozotocin induced diabetes in vivo by modulating mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptotic signaling cascade. Toxicol Rep 2014;1:569-81. |
| [61] | Kishore L, Kaur N, Singh R. Effect of Kaempferol isolated from seeds of Eruca sativa on changes of pain sensitivity in streptozotocin-induced diabetic neuropathy. Inflammophar-macology 2018;26:993-1003. |
| [62] | Dias S, Welton NJ, Caldwell DM, Ades AE. Checking consistency in mixed treatment comparison Meta-analysis. Stat Med 2010;29:932-44. |
| [63] | Kleinert M, Clemmensen C, Hofmann SM, et al. Animal models of obesity and diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2018;14:140-62. |
| [64] | Goyal SN, Reddy NM, Patil KR, et al. Challenges and issues with streptozotocin-induced diabetes-a clinically relevant animal model to understand the diabetes pathogenesis and evaluate therapeutics. Chem Biol Interact 2016;244:49-63. |
| [65] | Jennions MD, Møller AP. Publication bias in ecology and evolution: an empirical assessment using the ‘trim and fill’ method. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc 2002;77:211-22. |
| [66] | Thomas JS. Nonparametric trim and fill analysis of publication bias in Meta-analysis. Stata Technical Bulletin 2000;10:8-14 |
| [67] | DiMeglio LA, Evans-Molina C, Oram RA. Type 1 diabetes. Lancet 2018;391:2449-462. |
| [68] | Eizirik DL, Colli ML, Ortis F. The role of inflammation in insulitis and β-cell loss in type 1 diabetes. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2009;5:219-26. |
| [69] | Czech MP. Insulin action and resistance in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Nat Med 2017;23:804-14. |
| [70] | Petersen MC, Shulman GI. Mechanisms of insulin action and insulin resistance. Physiol Rev 2018;98:2133-223. |
| [71] | Forbes JM, Cooper ME. Mechanisms of diabetic complications. Physiol Rev 2013;93:137-88. |
| [72] | Zhou Y, Wang T, Song D, Wang A. Dietary intake of flavonoid subclasses and risk of type 2 diabetes in prospective cohort studies: a dose-response Meta-analysis. Clin Nutr 2018;37:2294-98. |
| [73] | Millar CL, Duclos Q, Blesso CN. Effects of dietary flavonoids on reverse cholesterol transport, HDL metabolism, and HDL function. Adv Nutr 2017;8:226-39. |
| [74] | Gil-Cardoso K, Ginés I, Pinent M, Ardévol A, Blay M, Terra X. Effects of flavonoids on intestinal inflammation, barrier integrity and changes in gut microbiota during diet-induced obesity. Nutr Res Rev 2016;29:234-48. |
| [75] | Zaidun NH, Sahema ZCT, Mardiana AA, Santhana RL, Latiff AA, Syed Ahmad Fuad SB. Effects of naringenin on vascular changes in prolonged hyperglycaemia in fructose-STZ diabetic rat model. Drug Discov Ther 2019;13:212-21. |
| [76] | Ighodaro OM. Molecular pathways associated with oxidative stress in diabetes mellitus. Biomed Pharmacother 2018;108:656-62. |
| [77] | Samie A, Sedaghat R, Baluchnejadmojarad T, Roghani M. Hesperetin, a citrus flavonoid, attenuates testicular damage in diabetic rats via inhibition of oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis. Life Sci 2018;210:132-9. |
| [78] | Ren B, Qin W, Wu F, et al. Apigenin and naringenin regulate glucose and lipid metabolism, and ameliorate vascular dysfunction in type 2 diabetic rats. Eur J Pharmacol 2016;773:13-23. |
| [79] | Govindasamy C, Al-Numair KS, Alsaif M. Ameliorative effect of kaempferol a flavonoid against streptozotocin-generated oxidative stress induced diabetic rats. Obes Res Clin Pract 2014;8:39. |
| [80] | Cai Y, Zhang X, Xu X, Yu Y. Effects of puerarin on the retina and STAT3 expression in diabetic rats. Exp Ther Med 2017;14:5480-4. |
| [81] | Chen F, Zhang HQ, Zhu J, et al. Puerarin enhances superoxide dismutase activity and inhibits RAGE and VEGF expression in retinas of STZ-induced early diabetic rats. Asian Pac J Trop Med 2012;5:891-6. |
| [82] | Ma L, Li XP, Ji HS, Liu YF, Li EZ. Baicalein protects rats with diabetic cardiomyopathy against oxidative stress and infla-mmation injury via phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) / AKT pathway. Med Sci Monit 2018;24:5368-75. |
| [83] | Wang G, Li W, Lu X, Bao P, Zhao X. Luteolin ameliorates cardiac failure in type I diabetic cardiomyopathy. J Diabetes Complications 2012;26:259-65. |
| [84] | Xiao C, Xia ML, Wang J, et al. Luteolin attenuates cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury in diabetic rats by modulating Nrf2 antioxidative function. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2019;2019:2719252. |
| [85] | Yaribeygi H, Farrokhi FR, Butler AE, Sahebkar A. Insulin resistance: Review of the underlying molecular mechanisms. J Cell Physiol 2019;234:8152-61. |
| [86] | Annadurai T, Thomas PA, Geraldine P. Ameliorative effect of naringenin on hyperglycemia-mediated inflammation in hepatic and pancreatic tissues of Wistar rats with streptozotocin-nicotinamide-induced experimental diabetes mellitus. Free Radic Res 2013;47(10):793-803. |
| [87] | Hou BY, Zhao YR, Qiang GF, et al. Puerarin mitigates diabetic hepatic steatosis and fibrosis by inhibiting TGF-β signaling pathway activation in tune 2 diabetic rats. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2018;2018:4545321. |
| [88] | Jeon SM. Regulation and function of AMPK in physiology and diseases. Exp Mol Med 2016;48:e245. |
| [89] | Singh AK, Raj V, Keshari AK, et al. Isolated mangiferin and naringenin exert antidiabetic effect via PPARγ/GLUT4 dual agonistic action with strong metabolic regulation. Chem Biol Interact 2018;280:33-44. |
| [90] | Chen WC, Hayakawa S, Yamamoto T, Su HC, Liu IM, Cheng JT. Mediation of β-endorphin by the isoflavone puerarin to lower plasma glucose in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Planta Med 2004;70:113-6. |
| [91] | Chen XF, Wang L, Fan SS, et al. Puerarin acts on the skeletal muscle to improve insulin sensitivity in diabetic rats involving μ-opioid receptor. Eur J Pharmacol 2018;818:115-23. |
| [92] | Cheng KC, Asakawa A, Li YX, et al. Opioid μ-receptors as new target for insulin resistance. Pharmacol Ther 2013;139:334-40. |
| [93] | Saklayen MG. The global epidemic of the metabolic syndrome. Curr Hypertens Rep 2018;20:12. |
| [94] | Akiyama S, Katsumata SI, Suzuki K, Ishimi Y, Wu J, Uehara M. Dietary hesperidin exerts hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic effects in streptozotocin-induced marginal type 1 diabetic rats. J Clin Biochem Nutr 2010;46:87-92. |
| [95] | Al-Numair KS, Veeramani C, Alsaif MA, Chandramohan G. Influence of kaempferol on lipid metabolic changes in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Prog Nutr 2013;15:255-64. |
| [96] | Liu YM, Feng QJ, Niu X, Song QA, Zhang X, Kang YM. Puerarin reduces blood sugar in the diabetic mice and improves hyperlipidemia in rats. FASEB J 2006;20:A298-A298. |
| [97] | Pu P, Wang XA, Salim M, et al. Baicalein, a natural product, selectively activating AMPKα2 and ameliorates metabolic disorder in diet-induced mice. Mol Cell Endocrinol 2012;362:128-38. |
| [98] | Wang J, Gao T, Wang F, Xue J, Ye H, Xie M. Luteolin improves myocardial cell glucolipid metabolism by inhibiting hypoxia inducible factor-1α expression in angiotensin II/hypoxia-induced hypertrophic H9c2 cells. Nutr Res 2019;65:63-70. |
| [99] | Melmer A, Laimer M. Treatment goals in diabetes. Endocr Dev 2016;31:1-27. |
| [100] | Mueller KF, Briel M, Strech D, et al. Dissemination bias in systematic reviews of animal research: A systematic review. PLoS One 2014;9(12):e116016. |
| [101] | Bebarta V, Luyten D, Heard K. Emergency medicine animal research: does use of randomization and blinding affect the results? Acad Emerg Med 2003;10:684-7. |
| [102] | Pound P, Ebrahim S, Sandercock P, Bracken MB, Roberts I. Where is the evidence that animal research benefits humans? BMJ 2004;328:514-7 |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

