Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (4): 760-769.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20230608.003
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of Shenlian formula (参连方) on microbiota and inflammatory cytokines in adults with type 2 diabetes: a double-blind randomized clinical trial
JIANG Li, FU Qiang( ), WANG Shidong(
), WANG Shidong( ), ZHAO Jinxi, CHEN Yu, LI Jiayue, XIAO Yonghua, HUANG Weijun, SUN Ruixi, XIAO Yao, SHEN Aijia, WANG Junheng, LIU Jiangteng, FU Xiaozhe, LI Yuanyuan, ZHAO Yu, XUE Taiqi
), ZHAO Jinxi, CHEN Yu, LI Jiayue, XIAO Yonghua, HUANG Weijun, SUN Ruixi, XIAO Yao, SHEN Aijia, WANG Junheng, LIU Jiangteng, FU Xiaozhe, LI Yuanyuan, ZHAO Yu, XUE Taiqi
- Section Ⅱ Department of Endocrinology and Nephropathy, Dongzhimen Hospital affiliated to Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100700, China
-
Received:2021-11-22Accepted:2022-05-23Online:2023-08-15Published:2023-06-08 -
Contact:Prof. WANG Shidong, SectionⅡ Department of Endocrinology and Nephropathy, Dongzhimen Hospital affiliated to Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100700, China. wsd3122@126.com.Telephone: +86-1850122059; +86-1910965659
Prof. FU Qiang, Section ⅡDepartment of Endocrinology and Nephropathy, Dongzhimen Hospital affiliated to Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100700, China. 13693332059@163.com -
Supported by:National Key R&D Program of China: the Study on Syndrome Differentiation Standard of Yin Deficiency Syndrome in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus(2018YFC1704402);Project for Young Teachers of Beijing University of Chinese Medicine: Clinical Study on Intervention of Shenlian Formula based on Microbiota in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus(2018-JYBZZ-JS062)
Cite this article
JIANG Li, FU Qiang, WANG Shidong, ZHAO Jinxi, CHEN Yu, LI Jiayue, XIAO Yonghua, HUANG Weijun, SUN Ruixi, XIAO Yao, SHEN Aijia, WANG Junheng, LIU Jiangteng, FU Xiaozhe, LI Yuanyuan, ZHAO Yu, XUE Taiqi. Effects of Shenlian formula (参连方) on microbiota and inflammatory cytokines in adults with type 2 diabetes: a double-blind randomized clinical trial[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(4): 760-769.
share this article
| Item | Total (n = 31) | Sl group (n = 16) | Placebo group (n = 15) | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 54.8±10.6 | 52.4±8.4 | 56.9±12.4 | 0.38 | |
| Gender [n (%)] | Male | 15 (48.4) | 8 (50.0) | 7 (46.7) | 0.87 |
| Female | 16 (51.6) | 8 (50.0) | 8 (53.3) | ||
| Course of disease (years) | 7.2±0.4 | 6.9±2.3 | 7.5±2.6 | 0.55 | |
| Weight (kg) | 72.5±11.7 | 73.2±12.0 | 71.8±11.8 | 0.74 |
Table 1 baseline characteristics presented by the two groups ($\bar{x}±s$)
| Item | Total (n = 31) | Sl group (n = 16) | Placebo group (n = 15) | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 54.8±10.6 | 52.4±8.4 | 56.9±12.4 | 0.38 | |
| Gender [n (%)] | Male | 15 (48.4) | 8 (50.0) | 7 (46.7) | 0.87 |
| Female | 16 (51.6) | 8 (50.0) | 8 (53.3) | ||
| Course of disease (years) | 7.2±0.4 | 6.9±2.3 | 7.5±2.6 | 0.55 | |
| Weight (kg) | 72.5±11.7 | 73.2±12.0 | 71.8±11.8 | 0.74 |
| Item | Group | n | At baseline | At 12 weeks | Baseline-week 12 | P valuesa | P values between groupsb | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glycemic biomarkers | HbA1c (%) | SL formula | 16 | 9.035±1.933 | 6.950±1.370a | 2.085±1.822 | <0.001 | 0.97 |
| Placebo | 15 | 8.960±2.329 | 6.853±0.795a | 2.107±2.081 | 0.002 | |||
| FPG (mmol/L) | SL formula | 16 | 6.964±1.290 | 6.597±1.732 | 0.367±1.323b | 0.28 | 0.04 | |
| Placebo | 15 | 5.456±1.399 | 6.317±1.543 | —0.861±1.914 | 0.10 | |||
| PBG (mmol/L) | SL formula | 16 | 9.660±0.906 | 8.342±1.081a | 1.318±0.772c | <0.001 | 0.003 | |
| Placebo | 15 | 9.075±1.720 | 9.067±1.074 | 0.008±1.404 | 0.98 | |||
| FIL (μIU/mL) | SL formula | 16 | 16.962±24.341 | 15.335±19.176 | 1.627±6.268b | 0.32 | 0.02 | |
| Placebo | 15 | 8.541±4.861 | 12.517±9.500 | —3.976±6.855 | 0.32 | |||
| C-P (ng/mL) | SL formula | 16 | 2.577±2.356 | 2.537±1.732 | 0.040±0.872 | 0.85 | 0.62 | |
| Placebo | 15 | 1.833±0.856 | 1.950±1.054 | —0.117±0.888 | 0.61 | |||
| HOMA-IR | SL formula | 16 | 5.682±8.608 | 5.152±7.948 | 0.530±1.461c | 0.17 | 0.006 | |
| Placebo | 15 | 2.093±1.331 | 3.604±2.745 | —1.511±2.288 | 0.02 | |||
| Blood lipid indices | TG (mmol/L) | SL formula | 16 | 1.780±1.210 | 1.633±1.213 | 0.147±1.143 | 0.62 | 0.40 |
| Placebo | 15 | 1.053±0.499 | 1.185±0.460 | —0.132±0.551 | 0.37 | |||
| LDL-C (mmol/L) | SL formula | 16 | 2.572±0.990 | 2.239±0.899 | 0.333±1.103 | 0.24 | 0.35 | |
| Placebo | 15 | 1.997±0.835 | 2.025±0.730 | —0.028±1.029 | 0.92 | |||
| BMI (kg/m2) | SL formula | 16 | 26.504±3.657 | 25.893±3.624a | 0.611±0.524c | <0.001 | 0.01 | |
| Placebo | 15 | 25.718±3.517 | 26.675±3.623 | —0.957±2.212 | 0.12 | |||
| Inflammatory Cytokines | TNF-α (pg/mL) | SL formula | 16 | 672.632±78.018 | 595.746±68.302a | 76.886±46.244 | <0.001 | 0.26 |
| Placebo | 15 | 668.096±88.240 | 610.399±68.329a | 57.697±41.381 | <0.001 | |||
| IL-6 (pg/mL) | SL formula | 16 | 55.380±5.129 | 47.281±6.223a | 8.099±5.883 | <0.001 | 0.10 | |
| Placebo | 15 | 52.651±5.957 | 47.509±5.545a | 5.142±2.845 | <0.001 | |||
| CRP (mg/L) | SL formula | 16 | 6.129±1.110 | 4.822±1.316a | 1.307±0.684b | <0.001 | 0.04 | |
| Placebo | 15 | 5.337±1.334 | 4.509±1.230a | 0.828±0.557 | <0.001 | |||
| Safety indicators | ALT (mmol/L) | SL formula | 16 | 19.131±11.522 | 17.944±7.914 | 1.187±9.523 | 0.62 | 0.39 |
| Placebo | 15 | 17.900±6.264 | 21.420±19.112 | —3.520±19.437 | 0.49 | |||
| AST (mmol/L) | SL formula | 16 | 17.763±7.168 | 16.056±5.233 | 1.707±7.413 | 0.37 | 0.77 | |
| Placebo | 15 | 18.220±5.808 | 17.253±7.415 | 0.967±6.524 | 0.58 | |||
| BU (mmol/L) | SL formula | 16 | 4.641±1.408 | 4.728±1.650 | —0.087±1.333 | 0.78 | 0.50 | |
| Placebo | 15 | 4.217±1.271 | 4.707±1.603 | —0.49±1.892 | 0.33 | |||
| Cr (μmol/mL) | SL formula | 16 | 52.994±11.469 | 51.438±11.708 | 1.556±9.921 | 0.54 | 0.49 | |
| Placebo | 15 | 53.313±14.676 | 54.787±9.865 | —1.474±14.183 | 0.70 |
Table 2 Biochemical characteristics and physical index at the baseline, after 12 weeks of intervention in SL group and placebo group ($\bar{x}±s$)
| Item | Group | n | At baseline | At 12 weeks | Baseline-week 12 | P valuesa | P values between groupsb | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glycemic biomarkers | HbA1c (%) | SL formula | 16 | 9.035±1.933 | 6.950±1.370a | 2.085±1.822 | <0.001 | 0.97 |
| Placebo | 15 | 8.960±2.329 | 6.853±0.795a | 2.107±2.081 | 0.002 | |||
| FPG (mmol/L) | SL formula | 16 | 6.964±1.290 | 6.597±1.732 | 0.367±1.323b | 0.28 | 0.04 | |
| Placebo | 15 | 5.456±1.399 | 6.317±1.543 | —0.861±1.914 | 0.10 | |||
| PBG (mmol/L) | SL formula | 16 | 9.660±0.906 | 8.342±1.081a | 1.318±0.772c | <0.001 | 0.003 | |
| Placebo | 15 | 9.075±1.720 | 9.067±1.074 | 0.008±1.404 | 0.98 | |||
| FIL (μIU/mL) | SL formula | 16 | 16.962±24.341 | 15.335±19.176 | 1.627±6.268b | 0.32 | 0.02 | |
| Placebo | 15 | 8.541±4.861 | 12.517±9.500 | —3.976±6.855 | 0.32 | |||
| C-P (ng/mL) | SL formula | 16 | 2.577±2.356 | 2.537±1.732 | 0.040±0.872 | 0.85 | 0.62 | |
| Placebo | 15 | 1.833±0.856 | 1.950±1.054 | —0.117±0.888 | 0.61 | |||
| HOMA-IR | SL formula | 16 | 5.682±8.608 | 5.152±7.948 | 0.530±1.461c | 0.17 | 0.006 | |
| Placebo | 15 | 2.093±1.331 | 3.604±2.745 | —1.511±2.288 | 0.02 | |||
| Blood lipid indices | TG (mmol/L) | SL formula | 16 | 1.780±1.210 | 1.633±1.213 | 0.147±1.143 | 0.62 | 0.40 |
| Placebo | 15 | 1.053±0.499 | 1.185±0.460 | —0.132±0.551 | 0.37 | |||
| LDL-C (mmol/L) | SL formula | 16 | 2.572±0.990 | 2.239±0.899 | 0.333±1.103 | 0.24 | 0.35 | |
| Placebo | 15 | 1.997±0.835 | 2.025±0.730 | —0.028±1.029 | 0.92 | |||
| BMI (kg/m2) | SL formula | 16 | 26.504±3.657 | 25.893±3.624a | 0.611±0.524c | <0.001 | 0.01 | |
| Placebo | 15 | 25.718±3.517 | 26.675±3.623 | —0.957±2.212 | 0.12 | |||
| Inflammatory Cytokines | TNF-α (pg/mL) | SL formula | 16 | 672.632±78.018 | 595.746±68.302a | 76.886±46.244 | <0.001 | 0.26 |
| Placebo | 15 | 668.096±88.240 | 610.399±68.329a | 57.697±41.381 | <0.001 | |||
| IL-6 (pg/mL) | SL formula | 16 | 55.380±5.129 | 47.281±6.223a | 8.099±5.883 | <0.001 | 0.10 | |
| Placebo | 15 | 52.651±5.957 | 47.509±5.545a | 5.142±2.845 | <0.001 | |||
| CRP (mg/L) | SL formula | 16 | 6.129±1.110 | 4.822±1.316a | 1.307±0.684b | <0.001 | 0.04 | |
| Placebo | 15 | 5.337±1.334 | 4.509±1.230a | 0.828±0.557 | <0.001 | |||
| Safety indicators | ALT (mmol/L) | SL formula | 16 | 19.131±11.522 | 17.944±7.914 | 1.187±9.523 | 0.62 | 0.39 |
| Placebo | 15 | 17.900±6.264 | 21.420±19.112 | —3.520±19.437 | 0.49 | |||
| AST (mmol/L) | SL formula | 16 | 17.763±7.168 | 16.056±5.233 | 1.707±7.413 | 0.37 | 0.77 | |
| Placebo | 15 | 18.220±5.808 | 17.253±7.415 | 0.967±6.524 | 0.58 | |||
| BU (mmol/L) | SL formula | 16 | 4.641±1.408 | 4.728±1.650 | —0.087±1.333 | 0.78 | 0.50 | |
| Placebo | 15 | 4.217±1.271 | 4.707±1.603 | —0.49±1.892 | 0.33 | |||
| Cr (μmol/mL) | SL formula | 16 | 52.994±11.469 | 51.438±11.708 | 1.556±9.921 | 0.54 | 0.49 | |
| Placebo | 15 | 53.313±14.676 | 54.787±9.865 | —1.474±14.183 | 0.70 |
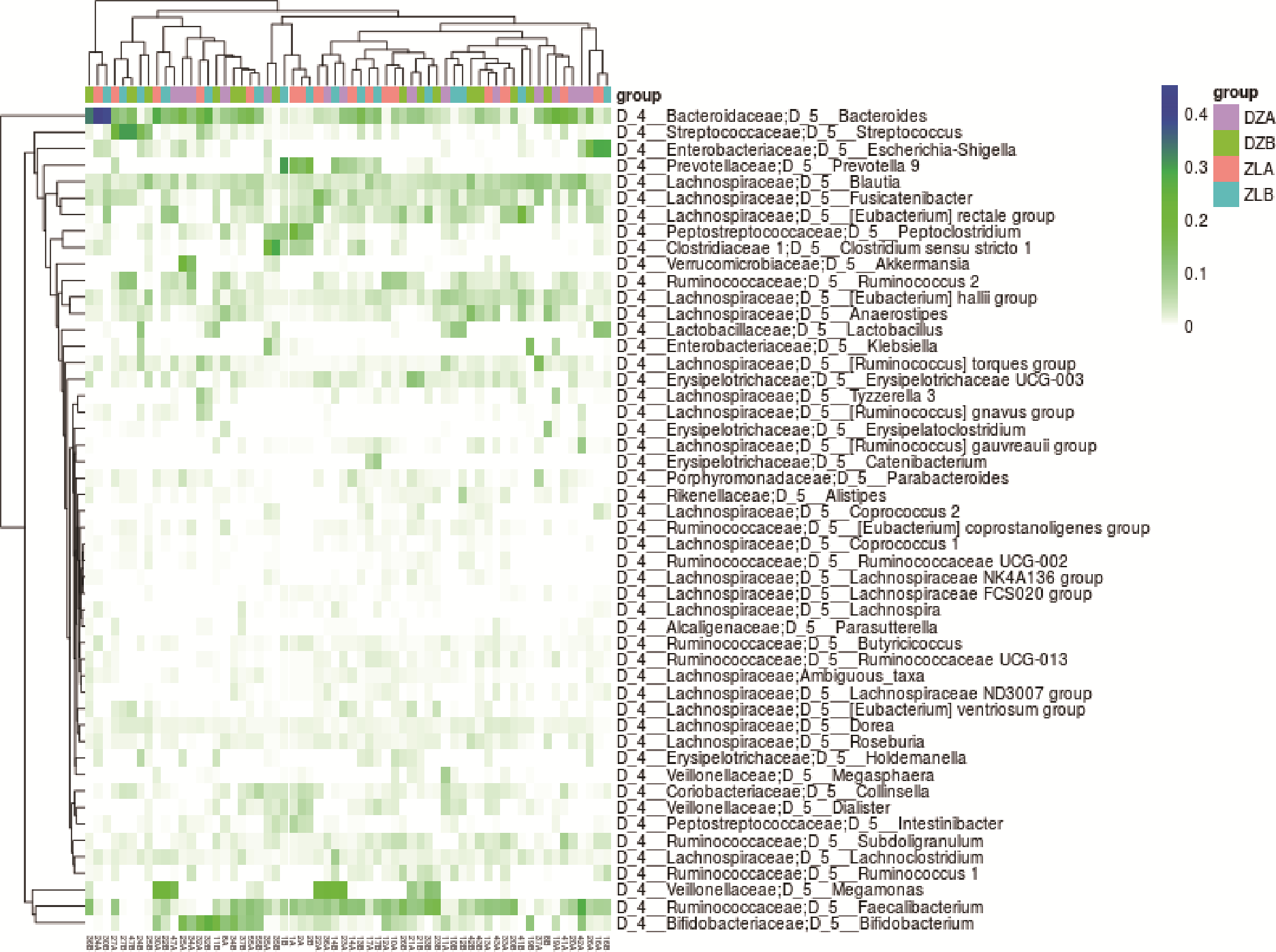
Figure 2 Clustering heat map DZA: baseline of placebo group; DZB: endpoint of placebo group; ZLB: baseline of SL group; ZLB: endpoint of SL group; SL: Shenlian. The group with high clustering correlation was SL group at baseline and after treatment, and the associated bacteria genus was bacteroides, followed by Escherichia-Shigella, suggesting that Bacteroides and Escherichia-Shigella were not sensitive to therapeutic intervention of SL formula.

Figure 3 α-diversity analysis A: observed species; B: Chao1; C: Shannon-Wiener; D: Simpson, index. DZA: baseline of placebo group; DZB: endpoint of placebo group; ZLA: baseline of SL group; ZLB: endpoint of SL group; SL: Shenlian. P values comes from paired t-test. There was significant increasing richness of bacteria in the placebo group and decreasing evenness of bacteria in the SL treatment group.

Figure 4 LDA effect size LDA: linear discriminant analysis; DZA: baseline of placebo group. DZB: endpoint of placebo group; ZLA: baseline of SL group. ZLB: endpoint of SL group; SL: Shenlian; D_1: Order lvel; D_2: Family level; D_3: D_4: Genu level; D_5: Species level. A: LDA score analysis between SL group and placebo group at endpoint. B: LDA score analysis within SL group. The colony most closely associated with SL treatment were Bacilli, Lactobacillales and Ruminiclostridium9.
| 1. | Chinese Diabetes Society. Guidelines for the prevention and control of type 2 diabetes in China (2017 Edition). Zhong Guo Shi Yong Nei Ke Za Zhi 2018; 38: 292-4. |
| 2. | Cannon A, Handelsman Y, Heile M, et al. Burden of illness in type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Manag Care Spec Pharm 2018; 24: S5-13. |
| 3. | Qin J, Li Y, Cai Z, et al. A metagenome-wide association study of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes. Nature 2012; 490: 55-60. |
| 4. |
Ley RE, Turnbaugh PJ, Klein S, Gordon JI. Microbial ecology: human gut microbes associated with obesity. Nature 2006; 444: 1022-3.
DOI |
| 5. |
Ley RE, Bäckhed F, Turnbaugh P, Lozupone CA, Knight RD, Gordon JI. Obesity alters gut microbial ecology. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005; 102: 11070-5.
DOI PMID |
| 6. | Salgaço MK, Oliveira LGS, Costa GN, et al. Relationship between gut microbiota, probiotics, and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 2019; 103: 9229-38. |
| 7. |
LeRoith D, Shiloach J, Roth J, et al. Insulin or a closely related molecule is native to Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 1981; 256: 6533-6.
PMID |
| 8. |
Jumpertz R, Le DS, Turnbaugh PJ, et al. Energy-balance studies reveal associations between gut microbes, caloric load, and nutrient absorption in humans. Am J Clin Nutr 2011; 94: 58-65.
DOI PMID |
| 9. |
Xiong Y, Miyamoto N, Shibata K, et al. Short-chain fatty acids stimulate leptin production in adipocytes through the G protein-coupled receptor GPR41. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101: 1045-50.
DOI PMID |
| 10. |
Bäckhed F, Ding H, Wang T, et al. The gut microbiota as an environmental factor that regulates fat storage. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101: 15718-23.
DOI PMID |
| 11. |
Bäckhed F, Manchester JK, Semenkovich CF, et al. Mechanisms underlying the resistance to diet-induced obesity in germ-free mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007; 104: 979-84.
DOI PMID |
| 12. | Aornsson L, Hunag Y, Parini P, et al. Decreased fat storage by Lactobacillus paraeasei is associated with increased levels of an giopoietin-like 4 protein (ANGPTIA). PLoS One 2010; 12: e13087. |
| 13. |
Cani PD, Amar J, Iglesias MA, et al. Metabolic endotoxemia initiates obesity and insulin resistance. Diabetes 2007; 56: 1761-72.
DOI PMID |
| 14. | Xu J, Lian F, Zhao L, et al. Structural modulation of gut microbiota during alleviation of type 2 diabetes with a Chinese herbal formula. ISME 2015; 5: 552-62. |
| 15. | Tong X, Xu J, Lian F, et al. Structural alteration of gut microbiota during the amelioration of human type 2 diabetes with hyperlipidemia by metformin and a traditional Chinese herbal formula: a multicenter, randomized, open label clinical trial. mBio 2018; 9: e02392-17. |
| 16. | Tang S, Sun J, Zhang H. Effects of ginseng coptis root on α-glucosidase. Jilin Zhong Yi Yao 2012; 32: 192-4. |
| 17. | Wang SD. the mechanism of the combination of Clearing Heat and Supplementing Qi in the treatment of Type 2 diabetes. Beijing: Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, 2007: 108-16. |
| 18. | Chinese Diabetes Society. Guidelines for the prevention and control of type 2 diabetes in China (2020 Edition). Zhong Guo Shi Yong Nei Ke Za Zhi 2021; 37: 311-98. |
| 19. | Pandis N, Chung B, Scherrer R, et al. CONSORT extension for reporting within-person randomised trials. BMJ 2017; 11: 1-22. |
| 20. |
Vuksan V, Zenith ZX, Jovanovski E, et al. Efficacy and safety of American ginseng extract on glycemic control and cardiovascular risk factors in individuals with type 2 diabetes: a double-blind, randomized, cross-over clinical trial. Eur J Nutr 2019; 58: 1237-45.
DOI |
| 21. | Dong H, Wang N, Zhao L, et al. Berberine in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systemic review and Meta-analysis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2012; 2012: 591654. |
| 22. |
Kassaian N, Feizi A, Aminorroaya A. et al. The effects of probiotics and synbiotic supplementation on glucose and insulin metabolism in adults with prediabetes: a double-blind randomized clinical trial. Acta Diabetol 2018; 55: 1019-28.
DOI PMID |
| 23. | Gong TX Ming dynasty. Wan Bing Hui Chun·dysentery. Beijing: China Traditional Chinese Medicine Press, 2007: 321-3. |
| 24. | Zhang JY Ming dynasty. Jing Yue Quan Shu·Gu Fang Ba Zhen. Beijing: China Traditional Chinese Medicine Press, 2007: 436-7. |
| 25. | Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, et al. Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and β-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 1985; 28: 412-19. |
| 26. |
Yang Y, Peng J, Li F, et al. Determination of alkaloid contents in various tissues of Coptis Chinensis Franch by reversed phase-high performance liquid chromatography and ultraviolet spectrophotometry. Chromatogr Sci 2017; 55: 556-63.
DOI URL |
| 27. |
Xie W, Du L. Diabetes is an inflammatory disease: evidence from Traditional Chinese Medicines. Diabetes Obes Metab 2011; 13: 289-301.
DOI PMID |
| 28. | Wang J, Gao WY, Zhang J, et al. Advances in study of ginsenoside biosynthesis pathway in Panax ginseng CA Meyer. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum 2012; 11: 397-403. |
| 29. |
Kheir MM, Wang Y, Hua L, et al. Acute toxicity of berberine and its correlation with the blood concentration in mice. Food Chem Toxicol 2010; 48: 1105-10.
DOI PMID |
| 30. |
Mancuso C, Santangelo R. Panax ginseng and Panax quinquefolius: from pharmacology to toxicology. Food Chem Toxicol 2017; 107: 362-72.
DOI PMID |
| 31. |
Zhang H, Wei J, Xue R, et al. Berberine lowers blood glucose in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients through increasing insulin receptor expression. Metabolism 2010; 59: 285-9.
DOI URL |
| 32. |
Zhang Y, Li X, Zou D, et al. Treatment of type 2 diabetes and dyslipidemia with the natural plant alkaloid berberine. Clin Endocrinol Metab 2008; 93: 2559-65.
DOI URL |
| 33. | Hasegawa H. Proof of the mysterious efficacy of ginseng: basic and clinical trials: metabolic activation of ginsenoside: deglycosylation by intestinal bacteria and esterification with fatty acid. Pharmacol Sci 2004; 12: 153-7. |
| 34. | Baska A, Leis K, Gałązka P. Berberine in the treatment of diabetes mellitus: a review. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets 2021; 21: 1379-86. |
| 35. | Duan Y, Liu T, Zhou Y, et al. Glycoside hydrolase family 18 and 20 enzymes are novel targets of the traditional medicine berberine. Biol Chem 2018; 293: 15429-38. |
| 36. |
Onomura M, Tsukada H, Fukuda K, et al. Effects of ginseng radix on sugar absorption in the small intestine. Am J Chin Med 1999; 27: 347-54.
DOI URL |
| 37. |
Suzuki Y, Ito Y, Konno C, et al. Effects of tissue cultured ginseng on gastric secretion and pepsin activity. Yakugaku zasshi 1991; 111: 770-4.
PMID |
| 38. |
Oh MR, Park SH, Kim SY, et al. Postprandial glucose-lowering effects of fermented red ginseng in subjects with impaired fasting glucose or type 2 diabetes: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. BMC Complement Altern Med 2014; 7: 14-7.
DOI URL |
| 39. | Zhou DY. Study on the correlation between the pathogenesis of fever and metabolic indexes of type 2 diabetes mellitus and the action mechanism of Traditional Chinese Medicine for clearing heat and replenishing Qi. Beijing: Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, 2013: 23-6. |
| 40. |
Cao Y, Pan Q, Cai W, et al. Modulation of gut microbiota by berberine improves steatohepatitis in high-fat diet-fed BALB/C mice. Arch Iran Med 2016; 19: 197-203.
DOI PMID |
| 41. |
Guo Y, Zhang Y, Huang W, Selwyn FP, Klaassen CD. Dose-response effect of berberine on bile acid profile and gut microbiota in mice. BMC Complement Altern Med 2016; 16: 394.
DOI |
| 42. | Guarino G, Strollo F, Carbone L, et al. Bioimpedance analysis, metabolic effects and safety of the association Berberis aristata/Bilybum marianum: a 52-week double-blind, placebo-controlled study in obese patients with type 2 diabetes. Biol Regul Homeost Agents 2017; 31: 495-502. |
| 43. | Siraj FM, Kim YJ, Natarajan S, et al. Ginseng and obesity: observations from assorted perspectives. Food Sci Biotechnol 2014; 11: 1007-16. |
| 44. |
Behrouz V, Sohrab G, Hedayati M, et al. Inflammatory markers response to crocin supplementation in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized controlled trial. Phytother Res 2021; 35: 4022-31.
DOI PMID |
| 45. | Garcia-Carretero R, Vigil-Medina L, Barquero-Perez O. The use of machine learning techniques to determine the predictive value of inflammatory biomarkers in the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Metab Syndr Relat Disord 2021; 2: 44. |
| 46. | Maithilikarpagaselvi N, Sridhar MG, Swaminathan RP, et al. Curcumin prevents inflammatory response, oxidative stress and insulin resistance in high fructose fed male Wistar rats: potential role of serine kinases. Chem Biol Interact 2016; 1: 187-94. |
| 47. |
Karbalaee-Hasani A, Khadive T, Eskandari M, et al. Effect of metformin on circulating levels of inflammatory markers in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Ann Pharmacother 2021; 55: 1096-109.
DOI PMID |
| 48. |
Agho ET, Owotade FJ, Kolawole BA, et al. Salivary inflammatory biomarkers and glycated haemoglobin among patients with type 2 diabetic mellitus. BMC Oral Health 2021; 21: 101.
DOI PMID |
| 49. |
Wei X, Tao J, Xiao S, et al. Xiexin Tang improves the symptom of type 2 diabetic rats by modulation of the gut microbiota. Sci Rep 2018; 8: 3685.
DOI PMID |
| 50. | Chen M, Liao Z, Lu B, et al. Huang-Lian-Jie-Du-decoction ameliorates hyperglycemia and insulin resistant in association with gut microbiota modulation. Front Microbiol 2018; 11: 2380. |
| 51. |
da Silva Duarte V, Dos Santos Cruz BC, Tarrah A, et al. Chemoprevention of DMH-induced early colon carcinogenesis in male BALB/c mice by administration of lactobacillus paracasei DTA81. Microorganism 2020; 8: 1994.
DOI URL |
| 52. |
Li K, Zhang L, Xue J, et al. Dietary inulin alleviates diverse stages of type 2 diabetes mellitus via anti-inflammation and modulating gut microbiota in db/db mice. Food Funct 2019; 10: 1915-27.
DOI URL |
| 53. | Liu Q, Cai BY, Zhu LX, et al. Liraglutide modulates gut microbiome and attenuates nonalcoholic fatty liver in db/db mice. Life Sci 2020; 12: 118457. |
| 54. |
Zhang X, Zhao Y, Zhang M, et al. Structural changes of gut microbiota during berberine-mediated prevention of obesity and insulin resistance in high-fat diet-fed rats. PLoS One 2012; 7: e42529.
DOI URL |
| 55. |
Horie M, Miura T, Hirakata S, et al. Comparative analysis of the intestinal flora in type 2 diabetes and nondiabetic mice. Exp Anim 2017; 66: 405-16.
DOI URL |
| 56. |
Adachi K, Sugiyama T, Yamaguchi Y, et al. Gut microbiota disorders cause type 2 diabetes mellitus and homeostatic disturbances in gut-related metabolism in Japanese subjects. Clin Biochem Nutr 2019; 64: 231-8.
DOI URL |
| 57. | Sasaki M, Ogasawara N, Funaki Y, et al. Transglucosidase improves the gut microbiota profile of type 2 diabetes mellitus patients: a randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled study. BMC Gastroenterol 2013; 5: 81. |
| 58. |
Kim ST, Kim HB, Lee KH, et al. Steam-dried ginseng berry fermented with Lactobacillus plantarum controls the increase of blood glucose and body weight in type 2 obese diabetic db/db mice. Agric Food Chem 2012; 60: 5438-45.
DOI URL |
| [1] | ZHANG Qi, CHEN Dexuan, ZHU Guixiang, ZHANG Shihu, FENG Xiao, MA Chaoqun, ZHANG Yi. Efficacy of Tounongsan decoction (透脓散方) on pyogenic liver abscess: network pharmacology and clinical trial validation [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 145-155. |
| [2] | LI Menghan, YAN Yan, DENG Shizhe, WANG Yu, FU Yu, SHI Lei, YANG Jin, ZHANG Chunhong. Contralateral needling at the foot of unaffected side combining with rehabilitation treatment for motor dysfunction of hand after ischemic stroke: study protocol for a randomized controlled pilot trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 1034-1039. |
| [3] | Minh Duc Nguyen, Thanh Van Tran, Quoc Vinh Nguyen, Cay Doan Ha, Linh Vu Phuong Dang. Effectiveness of bee venom acupuncture for patients suffering from periarthritis humeroscapularis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(4): 795-800. |
| [4] | SUN Mengzhu, ZHANG Yujie, SONG Yafang, GUO Jing, WANG Yuhang, XIN Chen, GU Dongmei, SUN Jianhua, PEI Lixia. Electroacupuncture alleviates water avoidance stress-induced irritable bowel syndrome in mice by improving intestinal barrier functions and suppressing the expression of inflammatory cytokines [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(3): 494-500. |
| [5] | CHEN Wenlin, LIANG Fang, ZHANG Yuncheng, LV Jinzhen, YANG Daguo. Effects of Zhenggan Huayu decoction (正肝化瘀方) combined with entecavir on gut microbiota in patients with chronic hepatitis B fibrosis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(3): 559-567. |
| [6] | GONG Hui, LI Yang, FENG Lei, XIAO Yujie, HUANG Lizhong, MAO Dan, ZHANG Hui. Yanghe decoction (阳和汤) attenuated pain hypersensitivity induced by michigan cancer foundation-7 injection in rats with bone metastases from breast cancer by inhibiting transient receptor potential ankyrin 1 [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(6): 948-955. |
| [7] | XU Chang, LI Na, WU Xiaoling, DAI Xingye, YANG Zhiwen, SUN Qianhui, SHI Tianyu, CHAI Yemao, PANG Dandan, CHENG Kai. Effect of electroacupuncture on inflammatory signal expression in local tissues of rats with chronic pelvic pain syndrome based on purinergic 2X7 receptor/NOD-like receptor pyrin domain-containing 3 signal pathway [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(6): 965-971. |
| [8] | DENG Qianlan, LU Yueting, YAN Lijuan, LU Hualin, JIN Ruizhe, XU Yanzhi, SONG Jing, LIU Tiejun. Mechanism of Huashi Xingyu Qingre recipe (化湿行淤清热方) in treating oral lichen planus based on network pharmacology and clinical trial verification [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(2): 304-313. |
| [9] | Jingjing WEI, Rongjuan GUO, Guojing FU, Xiao LIANG, Zhenmin XU, Min JIA, Zixiu ZENG, Wanqing DU, Weiwei JIAO, Linjuan SUN, Hongmei LIU, Chunli GUO, Chenguang TONG, Yunling ZHANG, Xing LIAO. Registration of intervention trials of Traditional Chinese Medicine for four neurological diseases on Chinese Clinical Trial Registry and ClinicalTrials.gov: a narrative review [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(1): 148-153. |
| [10] | YANG Liang, HUANG Guangyao, WANG Yuguang, HAN Baoqi, ZHENG Bin, ZHU Jinmiao, GAO Shan, GAO Yue. Efficacy of Renshen(Radix Ginseng) plus Fuzi(Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata) on myocardial infarction by enhancing autophagy in rats [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(6): 909-918. |
| [11] | Elham Shokati, Mohammad-Reza Shokri, Kobra Entezami, Samaneh Khorrami, Mona Amani, Morteza Motallebnezhad, Elahe Safari. Immunomodulatory effects of astragalus polysaccharide on Human peripheral blood mononuclear cells co-cultured with cervical cancer cell line [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(5): 684-694. |
| [12] | BI Yingfei, WANG Xianliang, ZHANG Xuan, HOU Yazhu, ZHAO Zhiqiang, REN Xiaoyu, YANG Zhihua, MAO Jingyuan. Protocol to study the effects of Traditional Chinese Medicine on patients with coronary heart disease showing phlegm-heat-stasis symptom pattern [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(5): 826-832. |
| [13] | ZHANG Zhouji, ZHANG Ming, WU Xiaoting, CUI Qing, GUO Yijun. Zhengyuan capsule(正元胶囊)for the treatment of cancer-related fatigue in lung cancer patients undergoing operation:a study protocol for a randomized controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(3): 485-490. |
| [14] | Chien Yi Koay;Anna Pick Kiong Ling;Ying Pei Wong;Rhun Yian Koh;Sobri Hussein;. Anti-neuroinflammatory responses in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated BV2 microglial cells upon treatment with methanol extract of Panax ginseng root [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(2): 185-193. |
| [15] | Mehdi Zobeiri;Fatemeh Parvizi;Roja Rahimi;Fatemeh Heydarpour;Hamid Reza Sheikhan;Jafar Navabi;Mohammad Hosein Farzaei;. Efficacy and safety of Hemoheal cream in patients with hemorrhoids: a randomized double-blind placebo controlled clinical trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(2): 301-307. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||