Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (4): 670-679.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20240626.002
• Original articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Luteolin promotes neuronogenesis in hippocampus of chronic unpredictable mild stress rats and primary hippocampus of fetal rats
LIU Tongtong1, ZHANG Xi2, YANG Hui3, LIN Xiaoyuan3, LIU Jian3, ZHANG Xiuli1, GUO Dongwei2, ZHAO Hongqing1, ZOU Manshu1, LEI Chang1, LONG Hongping3, LUO Yan1, XIANG Yun1, GE Jinwen4, WANG Yuhong1, MENG Pan1( )
)
- 1 Institute of Innovation and Applied Research in Chinese Medicine, Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha 410208, China
2 the Second People's Hospital of Hunan Province, Changsha 410007, China
3 The First Affiliated Hospital, Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha 410007, China
4 Hunan Academy of Chinese Medicine, Changsha 410013, China
-
Received:2023-01-12Accepted:2023-08-22Online:2024-08-15Published:2024-06-26 -
Contact:MENG Pan, Institute of Innovation and Applied Research in Chinese Medicine, Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha 410208, China.mengpan@hnucm.edu.cn Telephone: +86-15873153921 -
Supported by:Outstanding Youth Project of Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province: Mechanisms of Emotional-behavioural and Cognitive Impairment in Depression and Intervention with Traditional Chinese Medicine(2020JJ3027);Training Plan of Outstanding Innovative Youth of Changsha(kq2009018);Key Projects of Hunan Provincial Department of Education: Hspa5/PrPc-based Study on the Mechanism of Lymphoid System Damage in Cerebral Small Vessel Disease with Depression and Intervention with Traditional Chinese Medicine(23A0281);Traditional Chinese Medicine Research Program Project of Hunan Province: Mechanisms of Impairment of Ventral and Dorsal Hippocampal Differential Function in Depression based on Sonic Hedgehog/Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Signalling-Mediated Synaptogenesis in Newborn Neurons and Intervention with Traditional Chinese Medicine(B2023021);Open Fund Project of State Key Laboratory of Traditional Chinese Medicine Powder and Innovative Drugs: Mechanisms of Glymphatic Iinjury in Cerebral Small Vessel Disease with Depression Based on Aquaporin Protein-4 Signalling-Mediated Astrocyte-Responsive Hyperplasia and Intervention with Traditional Chinese Medicine(23PTKF1013)
Cite this article
LIU Tongtong, ZHANG Xi, YANG Hui, LIN Xiaoyuan, LIU Jian, ZHANG Xiuli, GUO Dongwei, ZHAO Hongqing, ZOU Manshu, LEI Chang, LONG Hongping, LUO Yan, XIANG Yun, GE Jinwen, WANG Yuhong, MENG Pan. Luteolin promotes neuronogenesis in hippocampus of chronic unpredictable mild stress rats and primary hippocampus of fetal rats[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(4): 670-679.
share this article
| Group | n | Open field | Latency to feed (s) | Sugar preference (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Horizontal | Vertical | ||||
| Control | 8 | 114.5±9.4 | 9.6±1.6 | 10.6±10.6 | 77.2±3.5 |
| CUMS | 8 | 10.0±2.7a | 1.7±0.5a | 90.7±19.4a | 28.1±3.6a |
| Luteolin-H | 8 | 97.6±19.1b | 7.9±1.7b | 7.2±4.0b | 70.9±3.0b |
| Luteolin-L | 8 | 16.1±1.7 | 4.4±1.3 | 45.4±14.6 | 36.1±2.2 |
| Fluoxetine | 8 | 77.4±7.0b | 6.9±0.9b | 10.9±7.4b | 68.7±3.2b |
Table 1 Behavior scores in each group
| Group | n | Open field | Latency to feed (s) | Sugar preference (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Horizontal | Vertical | ||||
| Control | 8 | 114.5±9.4 | 9.6±1.6 | 10.6±10.6 | 77.2±3.5 |
| CUMS | 8 | 10.0±2.7a | 1.7±0.5a | 90.7±19.4a | 28.1±3.6a |
| Luteolin-H | 8 | 97.6±19.1b | 7.9±1.7b | 7.2±4.0b | 70.9±3.0b |
| Luteolin-L | 8 | 16.1±1.7 | 4.4±1.3 | 45.4±14.6 | 36.1±2.2 |
| Fluoxetine | 8 | 77.4±7.0b | 6.9±0.9b | 10.9±7.4b | 68.7±3.2b |
| Group | n | 1 week | 2 weeks | 3 weeks | 4 weeks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 8 | 214.1±2.5 | 274.2±3.3 | 333.0±5.1 | 404.5±5.4 |
| CUMS | 8 | 217.5±2.5 | 240.1±4.6a | 272.6±4.7a | 301.5±3.8a |
| Luteolin-H | 8 | 209.2±4.1 | 247.8±2.7 | 290.6±4.8b | 346.4±7.0c |
| Luteolin-L | 8 | 216.9±3.4 | 241.6±4.8 | 280.6±6.2 | 310.1±10.5 |
| Fluoxetine | 8 | 215.9±4.4 | 244.9±6.1 | 301.8±9.3c | 342.8±4.1c |
Table 2 Body weight in each group (g)
| Group | n | 1 week | 2 weeks | 3 weeks | 4 weeks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 8 | 214.1±2.5 | 274.2±3.3 | 333.0±5.1 | 404.5±5.4 |
| CUMS | 8 | 217.5±2.5 | 240.1±4.6a | 272.6±4.7a | 301.5±3.8a |
| Luteolin-H | 8 | 209.2±4.1 | 247.8±2.7 | 290.6±4.8b | 346.4±7.0c |
| Luteolin-L | 8 | 216.9±3.4 | 241.6±4.8 | 280.6±6.2 | 310.1±10.5 |
| Fluoxetine | 8 | 215.9±4.4 | 244.9±6.1 | 301.8±9.3c | 342.8±4.1c |
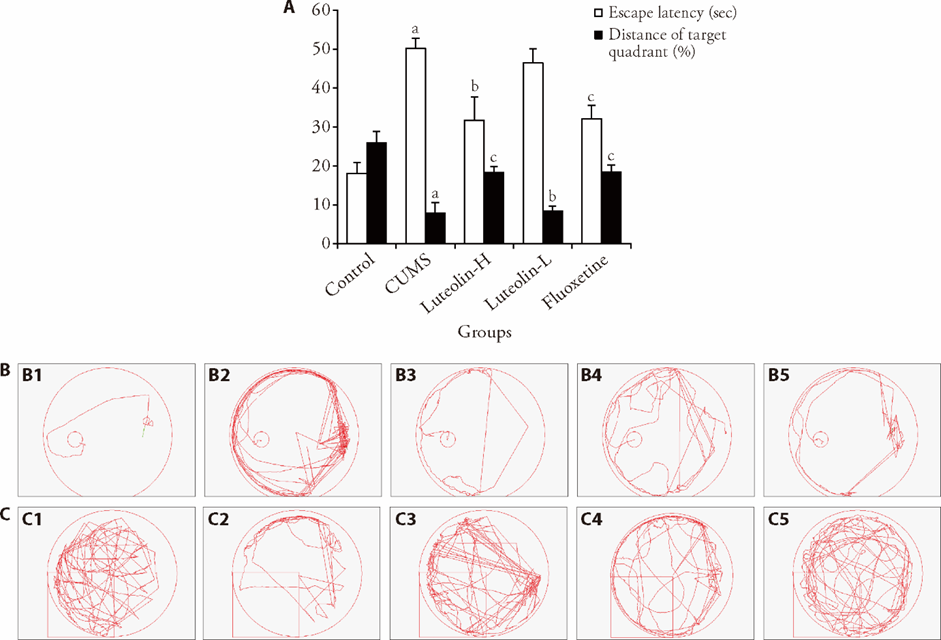
Figure 1 Escape latency and crossing distance of the platform position in each group A: the results of Morris Water maze test of each group; B: trace plot of escape latency of control (B1), CUMS (B2), luteolin-H (B3), luteolin-L (B4), fluoxetine (B5) groups.; C: trace plot of Crossing distance of the platform position of control (C1), CUMS (C2), luteolin-H (C3), luteolin-L (C4), fluoxetine (C5) groups. Control: unstressed and intragastrically given 2 mL distilled water daily. CUMS: were intragastrically with distilled water. Luteolin-H: were intragastrically with luteolin at 20 mg·kg-1·d-1. Luteolin-L: were intragastrically with luteolin at 10 mg·kg-1·d-1. Fluoxetine: were intragastrically with fluoxetine at 5.4 mg·kg-1·d-1. CUMS: chronic unpredictable mild stress. Statistical significance among groups was conducted using one-way analysis of variance. Data were presented as mean ± standard error of mean (n = 8). aP < 0.0,1 compared with the control group; bP < 0.05, cP < 0.01, compared with the CUMS group.
| Group | n | BDNF | 5-HT | NE | DA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 8 | 38.3±1.9 | 75.8±2.0 | 22.5±1.1 | 45.2±0.8 |
| CUMS | 8 | 17.5±0.7a | 35.6±3.0a | 13.2±0.7a | 20.5±0.3a |
| Luteolin-H | 8 | 32.6±1.9b | 63.5±4.9b | 22.9±1.2b | 45.3±0.6b |
| Luteolin-L | 8 | 19.4±0.8 | 46.8±3.2c | 13.9±0.8 | 19.9±0.2 |
| Fluoxetine | 8 | 33.9±2.1b | 65.2±4.3d | 24.4±1.0b | 45.8±0.7b |
Table 3 Content of BDNF, 5-HT, NE and DA in serum in each group (ng/mL)
| Group | n | BDNF | 5-HT | NE | DA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 8 | 38.3±1.9 | 75.8±2.0 | 22.5±1.1 | 45.2±0.8 |
| CUMS | 8 | 17.5±0.7a | 35.6±3.0a | 13.2±0.7a | 20.5±0.3a |
| Luteolin-H | 8 | 32.6±1.9b | 63.5±4.9b | 22.9±1.2b | 45.3±0.6b |
| Luteolin-L | 8 | 19.4±0.8 | 46.8±3.2c | 13.9±0.8 | 19.9±0.2 |
| Fluoxetine | 8 | 33.9±2.1b | 65.2±4.3d | 24.4±1.0b | 45.8±0.7b |
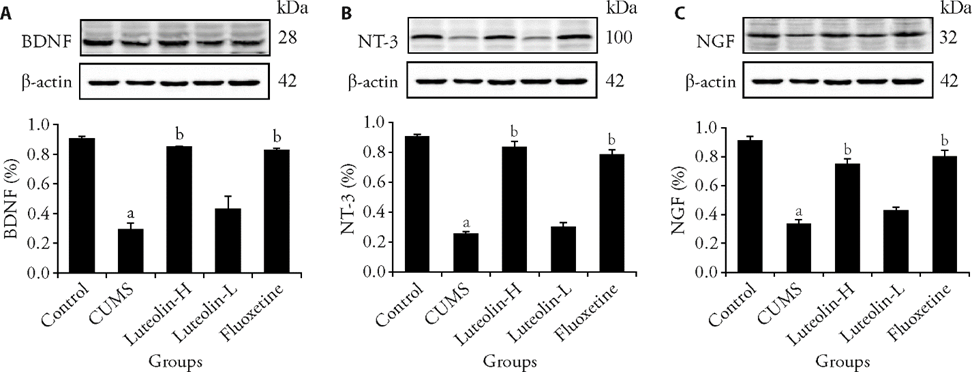
Figure 2 Expression of BDNF, NT-3, NGF in the dentate gyrus of hippocampus A: gray value of BDNF; B: gray value of NT-3; C: gray value of NGF. Control: unstressed and intragastrically given 2 mL distilled water daily. CUMS: were intragastrically with distilled water. Luteolin-H: were intragastrically with luteolin at 20 mg·kg-1·d-1. Luteolin-L: were intragastrically with luteolin at 10 mg·kg-1·d-1. Fluoxetine: were intragastrically with fluoxetine at 5.4 mg·kg-1·d-1. CUMS: chronic unpredictable mild stress; BDNF: brain derived neurotrophic factor; NT-3: neurotrophin-3; NGF: nerve growth factor. Statistical significance among groups was conducted using one-way analysis of variance. Data are expressed as mean ± standard error of mean (n = 3). aP < 0.01, compared with the control group; bP < 0.01, compared with the CUMS group.
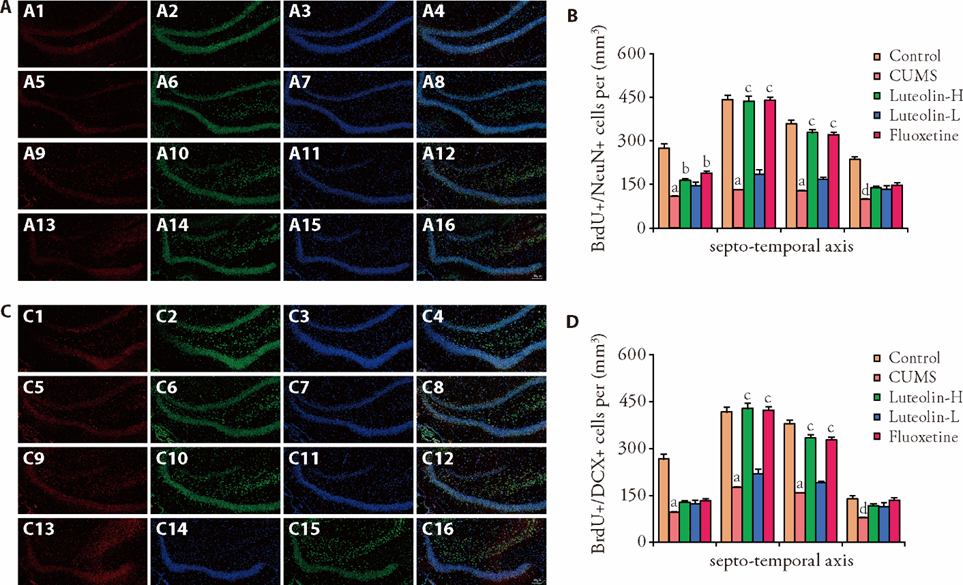
Figure 3 Neuronal differentiation and migration along the septo-temporal axis of hippocampus in each group Magnification of pictures is 100 ×. A: Representative pictures of BrdU+/NeuN+ cells. A1: expression of BrdU in the S1; A2: expression of NeuN in the S1; A3: expression of DAPI in the S1; A4: merged expression of BrdU, NeuN, and DAPI in the S1; A5: expression of BrdU in the S2; A6: expression of NeuN in the S2; A7: expression of DAPI in the S2; A8: merged expression of BrdU, NeuN, and DAPI in the S2; A9: expression of BrdU in the T3; A10: expression of NeuN in the T3; A11: expression of DAPI in the T3; A12: merged expression of BrdU, NeuN, and DAPI in the T3; A13: expression of BrdU in the T4; A14: expression of NeuN in the T4; A15: expression of DAPI in the T4; A16: merged expression of BrdU, NeuN, and DAPI in the T4; B: BrdU+/ NeuN+ cells per mm3. C: representative pictures of BrdU+/ DCX+ cells. C1: expression of BrdU in the S1; C2: expression of DCX in the S1; C3: expression of DAPI in the S1; C4: merged expression of BrdU, DCX, and DAPI in the S1; C5: expression of BrdU in the S2; C6: expression of DCX in the S2; C7: expression of DAPI in the S2; C8: merged expression of BrdU, DCX, and DAPI in the S2; C9: expression of BrdU in the T3; C10: expression of DCX in the T3; C11: expression of DAPI in the T3; C12: merged expression of BrdU, DCX, and DAPI in the T3; C13: expression of BrdU in the T4; C14: expression of DCX in the T4; C15: expression of DAPI in the T4; C16: merged expression of BrdU, DCX, and DAPI in the T4; D: BrdU+/ DCX+ cells per mm3. Control: unstressed and intragastrically given 2 mL distilled water daily. CUMS: were intragastrically with distilled water. Luteolin-H: were intragastrically with luteolin at 20 mg·kg-1·d-1. Luteolin-L: were intragastrically with luteolin at 10 mg·kg-1·d-1. Fluoxetine: were intragastrically with fluoxetine at 5.4 mg·kg-1·d-1. CUMS: chronic unpredictable mild stress; BrdU: 5-bromo-2-deoxyuridine; DAPI: 4’,6-Diamidino-2’-phenylindole; NeuN: Neuron specific nuclear protein antigen; DCX: doublecortin; S1: septal; S2: mid-septal; T3: mid-temporal; T4: temporal. Statistical significance among groups was conducted using one-way analysis of variance. Data were shown as mean ± standard error of mean (n = 3). aP < 0.01, dP < 0.05, compared with the control group; bP < 0.05, cP < 0.01, compared with the CUMS group.
| Group | n | Average fluorescence intensity of BDNF | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | S2 | T3 | T4 | ||
| Control | 8 | 0.403±0.023 | 0.600±0.023 | 0.577±0.023 | 0.233±0.022 |
| CUMS | 8 | 0.273±0.023a | 0.297±0.020c | 0.213±0.032c | 0.117±0.018a |
| Luteolin-H | 8 | 0.383±0.020b | 0.507±0.018d | 0.440±0.021d | 0.190±0.012 |
| Luteolin-L | 8 | 0.217±0.015 | 0.337±0.026 | 0.277±0.027 | 0.153±0.015 |
| Fluoxetine | 8 | 0.403±0.030b | 0.540±0.044d | 0.477±0.023d | 0.183±0.019 |
Table 4 Expression of BDNF along the septo-temporal axis of hippocampus in the indicated groups
| Group | n | Average fluorescence intensity of BDNF | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | S2 | T3 | T4 | ||
| Control | 8 | 0.403±0.023 | 0.600±0.023 | 0.577±0.023 | 0.233±0.022 |
| CUMS | 8 | 0.273±0.023a | 0.297±0.020c | 0.213±0.032c | 0.117±0.018a |
| Luteolin-H | 8 | 0.383±0.020b | 0.507±0.018d | 0.440±0.021d | 0.190±0.012 |
| Luteolin-L | 8 | 0.217±0.015 | 0.337±0.026 | 0.277±0.027 | 0.153±0.015 |
| Fluoxetine | 8 | 0.403±0.030b | 0.540±0.044d | 0.477±0.023d | 0.183±0.019 |
| Group | n | S1 | S2 | T3 | T4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 8 | 0.450±0.012 | 0.593±0.026 | 0.553±0.020 | 0.280±0.017 |
| CUMS | 8 | 0.183±0.020a | 0.293±0.015a | 0.207±0.029a | 0.197±0.018d |
| Luteolin-H | 8 | 0.277±0.020b | 0.493±0.015c | 0.493±0.026c | 0.213±0.015 |
| Luteolin-L | 8 | 0.227±0.015 | 0.313±0.020 | 0.327±0.035 | 0.203±0.015 |
| Fluoxetine | 8 | 0.290±0.012b | 0.507±0.035c | 0.463±0.026c | 0.273±0.026 |
Table 5 Expression of NT-3 along the septo-temporal axis of hippocampus in the indicated groups
| Group | n | S1 | S2 | T3 | T4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 8 | 0.450±0.012 | 0.593±0.026 | 0.553±0.020 | 0.280±0.017 |
| CUMS | 8 | 0.183±0.020a | 0.293±0.015a | 0.207±0.029a | 0.197±0.018d |
| Luteolin-H | 8 | 0.277±0.020b | 0.493±0.015c | 0.493±0.026c | 0.213±0.015 |
| Luteolin-L | 8 | 0.227±0.015 | 0.313±0.020 | 0.327±0.035 | 0.203±0.015 |
| Fluoxetine | 8 | 0.290±0.012b | 0.507±0.035c | 0.463±0.026c | 0.273±0.026 |
| Group | n | Average fluorescence intensity of NGF | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | S2 | T3 | T4 | ||
| Control | 8 | 0.447±0.020 | 0.550±0.023 | 0.523±0.015 | 0.297±0.020 |
| CUMS | 8 | 0.237±0.018a | 0.277±0.020a | 0.293±0.032a | 0.197±0.018a |
| Luteolin-H | 8 | 0.277±0.018 | 0.493±0.015b | 0.490±0.015b | 0.263±0.026 |
| Luteolin-L | 8 | 0.263±0.009 | 0.343±0.020 | 0.327±0.035 | 0.223±0.015 |
| Fluoxetine | 8 | 0.317±0.015 | 0.540±0.038b | 0.487±0.023b | 0.283±0.026 |
Table 6 Expression of NGF along the septo-temporal axis of hippocampus in the indicated groups
| Group | n | Average fluorescence intensity of NGF | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | S2 | T3 | T4 | ||
| Control | 8 | 0.447±0.020 | 0.550±0.023 | 0.523±0.015 | 0.297±0.020 |
| CUMS | 8 | 0.237±0.018a | 0.277±0.020a | 0.293±0.032a | 0.197±0.018a |
| Luteolin-H | 8 | 0.277±0.018 | 0.493±0.015b | 0.490±0.015b | 0.263±0.026 |
| Luteolin-L | 8 | 0.263±0.009 | 0.343±0.020 | 0.327±0.035 | 0.223±0.015 |
| Fluoxetine | 8 | 0.317±0.015 | 0.540±0.038b | 0.487±0.023b | 0.283±0.026 |
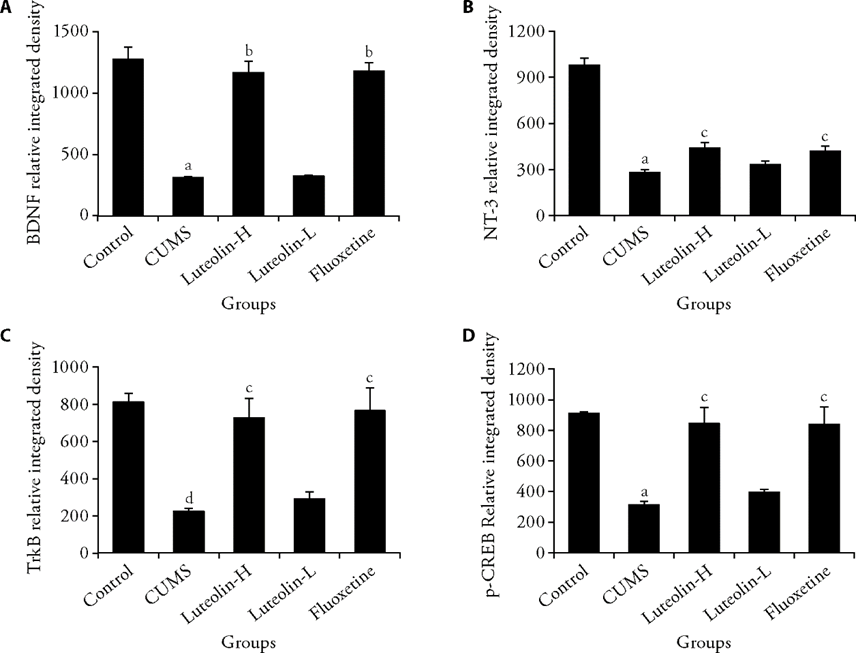
Figure 4 Expression of BDNF, NT-3, TrkB, and p-CREB in primary cells in the indicated groups Magnification of pictures is ×400. A: relative integrated density of BDNF; B: relative integrated density of NT-3; C: relative integrated density of TrkB; D: relative integrated density of p-CREB. Control: unstressed and intragastrically given 2 mL distilled water daily. CUMS: were intragastrically with distilled water. Luteolin-H: were intragastrically with luteolin at 20 mg·kg-1·d-1. Luteolin-L: were intragastrically with luteolin at 10 mg·kg-1·d-1. Fluoxetine: were intragastrically with fluoxetine at 5.4 mg·kg-1·d-1. CUMS: chronic unpredictable mild stress; BDNF: brain derived neurotrophic factor; NT-3: neurotrophin-3; TrkB: tropomyosin receptor kinase B; p-CREB: phosphorylated cAMP responsive element binding protein. Statistical significance among groups was conducted using one-way analysis of variance. Data were shown as mean ± standard error of mean (n = 3). aP < 0.01, dP < 0.05, compared with the control group; bP < 0.01, cP < 0.05, compared with the CUMS group.
| 1. |
Zhu Y, Duan X, Cheng X, et al. Kai-Xin-San, a standardized Traditional Chinese Medicine formula, up-regulates the expressions of synaptic proteins on hippocampus of chronic mild stress induced depressive rats and primary cultured rat hippocampal neuron. J Ethnopharmacol 2016; 193: 423-32.
DOI PMID |
| 2. | Tiger M, Varnäs K, Okubo Y, Lundberg J. The 5-HT1B receptor-a potential target for antidepressant treatment. Psychopharm-acology (Berl) 2018; 235: 1317-34. |
| 3. | Belleau EL, Treadway MT, Pizzagalli DA. The impact of stress and major depressive disorder on hippocampal and medial prefrontal cortex morphology. Biol psychiatry 2019; 85: 443-53. |
| 4. |
Tanti A, Belzung C. Neurogenesis along the septo-temporal axis of the hippocampus: are depression and the action of antidepressants region-specific. Neuroscience 2013; 252: 234-52.
DOI PMID |
| 5. | Kim IB, Park SC. Neural circuitry-neurogenesis coupling model of depression. Int J Mol Sci 2021; 22: 2468. |
| 6. | Drew MR, Hen R. Adult hippocampal neurogenesis as target for the treatment of depression. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 2007; 6: 205-18. |
| 7. | Li Y, Shen M, Stockton ME, Zhao X. Hippocampal deficits in neurodevelopmental disorders. Neurobiol Learn Mem 2019; 165: 106945. |
| 8. |
Snyder JS, Ramchand P, Rabbett S, Radik R, Wojtowicz JM, Cameron HA. Septo-temporal gradients of neurogenesis and activity in 13-month-old rats. Neurobiol Aging 2011; 32: 1149-56.
DOI PMID |
| 9. |
Chen H, Lin Q, Lin T, et al. A controlled study of the efficacy and safety of tandospirone citrate combined with escitalopram in the treatment of vascular depression: a pilot randomized controlled trial at a single-center in China. J Psychiatr Res 2019; 114: 133-40.
DOI PMID |
| 10. |
Adzic M, Brkic Z, Mitic M, et al. Therapeutic strategies for treatment of inflammation-related depression. Curr Neuropharmacol 2018; 16: 176-209.
DOI PMID |
| 11. | Achour M, Mateos R, Ben Fredj M, Mtiraoui A, Bravo L, Saguem S. A comprehensive characterisation of rosemary tea obtained from rosmarinus officinalis l. Collected in a sub-Humid Area of Tunisia. Phytochem Anal 2018; 29: 87-100. |
| 12. | Miean KH, Mohamed S. Flavonoid (myricetin, quercetin, kaempferol, luteolin, and apigenin) content of edible tropical plants. J Agric Food Chem 2001; 49: 3106-12. |
| 13. |
Imran M, Rauf A, Abu-Izneid T, et al. Luteolin, a flavonoid, as an anticancer agent: a review. Biomed Pharmacother 2019; 112: 108612.
DOI |
| 14. |
Albarakati A, Baty RS, Aljoudi AM, et al. Luteolin protects against lead acetate-induced nephrotoxicity through antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-apoptotic, and Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathways. Mol Biol Rep 2020; 47: 2591-603.
DOI PMID |
| 15. | Sur B, Lee B. Luteolin reduces fear, anxiety, and depression in rats with post-traumatic stress disorder. Anim Cells Syst (Seoul) 2022; 26: 174-82. |
| 16. |
Sawmiller D, Li S, Shahaduzzaman M, et al. Luteolin reduces Alzheimer's disease pathologies induced by traumatic brain injury. Int J Mol Sci 2014; 15: 895-904.
DOI PMID |
| 17. | Xu T, Li D, Jiang D. Targeting cell signaling and apoptotic pathways by luteolin: cardioprotective role in rat cardiomyocytes following ischemia/reperfusion. Nutrients 2012; 4: 2008-19. |
| 18. |
Ding F, Wu J, Liu C, et al. Effect of Xiaoyaosan on colon morphology and intestinal permeability in rats with chronic unpredictable mild stress. Front Pharmacol 2020; 11: 1069.
DOI PMID |
| 19. |
Wang D, An SC, Zhang X. Prevention of chronic stress-induced depression-like behavior by inducible nitric oxide inhibitor. Neurosci Lett 2008; 433: 59-64.
DOI PMID |
| 20. | Wang C, Guo J, Guo R. Effect of Xingpi Jieyu decoction on spatial learning and memory and cAMP-PKA-CREB-BDNF pathway in rat model of depression through chronic unpredictable stress. BMC Complement Altern Med 2017; 17: 73. |
| 21. | Levy M, Boulle F, Steinbusch HW, van den Hove D, Kenis G, Lanfumey L. Neurotrophic factors and neuroplasticity pathways in the pathophysiology and treatment of depression. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2018; 235: 2195-220. |
| 22. | Chen YP, Wang C, Xu JP. Chronic unpredictable mild stress induced depression-like behaviours and glutamate-glutamine cycling dysfunctions in both blood and brain of mice. Pharm Biol 2019; 57: 280-6. |
| 23. | Ekeanyanwu RC, Njoku OU. Flavonoid-rich fraction of the Monodora tenuifolia seed extract attenuates behavioural alterations and oxidative damage in forced-swim stressed rats. Chin J Nat Med 2015; 13: 183-91. |
| 24. |
Yu X, Zhang F, Shi J. Sevoflurane anesthesia impairs metabotropic glutamate receptor-dependent long-term depression and cognitive functions in senile mice. Geriatr Gerontol Int 2019; 19: 357-62.
DOI PMID |
| 25. |
Tanti A, Westphal WP, Girault V, et al. Region-dependent and stage-specific effects of stress, environmental enrichment, and antidepressant treatment on hippocampal neurogenesis. Hippocampus 2013; 23: 797-811.
DOI PMID |
| 26. |
McAvoy K, Russo C, Kim S, Rankin G, Sahay A. Fluoxetine induces input-specific hippocampal dendritic spine remodeling along the septotemporal axis in adulthood and middle age. Hippocampus 2015; 25: 1429-46.
DOI PMID |
| 27. |
Powers BE, Santiago NA, Strupp BJ. Rapid forgetting of social learning in the Ts65Dn mouse model of Down syndrome: new evidence for hippocampal dysfunction. Behav Neurosci 2018; 132: 51-6.
DOI PMID |
| 28. |
Bortolotto V, Bondi H, Cuccurazzu B, Rinaldi M, Canonico PL, Grilli M. Salmeterol, a β2 adrenergic agonist, promotes adult hippocampal neurogenesis in a region-specific manner. Front Pharmacol 2019; 10: 1000.
DOI PMID |
| 29. |
Ricken R, Adli M, Lange C, et al. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor serum concentrations in acute depressive patients increase during lithium augmentation of antidepressants. J Clin Psychopharmacol 2013; 33: 806-9.
DOI PMID |
| 30. |
Jiang C, Salton SR. The role of neurotrophins in major depressive disorder. Transl Neurosci 2013; 4: 46-58.
PMID |
| 31. | Ghosh HS. Adult neurogenesis and the promise of adult neural stem cells. J Exp Neurosci 2019; 13: 1179069519856876. |
| 32. | Carli M, Aringhieri S, Kolachalam S, et al. Is adult hippocampal neurogenesis really relevant for the treatment of psychiatric disorders. Curr neuropharmacol 2021; 19: 1640-60. |
| 33. |
Ewin SE, Morgan JW, Niere F, et al. Chronic intermittent ethanol exposure selectively increases synaptic excitability in the ventral domain of the rat hippocampus. Neuroscience 2019; 398: 144-57.
DOI PMID |
| 34. |
Shirayama Y, Chen AC, Nakagawa S, Russell DS, Duman RS. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor produces antidepressant effects in behavioral models of depression. J Neurosci 2002; 22: 3251-61.
PMID |
| 35. | Casarotto PC, Girych M, Fred SM, et al. Antidepressant drugs act by directly binding to TRKB neurotrophin receptors. Cell 2021; 184: 1299-313.e19. |
| 36. |
Polyakova M, Beyer F, Mueller K, et al. Serum BDNF levels correlate with regional cortical thickness in minor depression: a pilot study. Sci Rep 2020; 10: 14524.
DOI PMID |
| 37. | Arosio B, Guerini FR, Voshaar R, Aprahamian I. Blood brain-derived neurotrophic factor (bdnf) and major depression: do we have a translational perspective. Front Behav Neurosci 2021; 15: 626906. |
| 38. | Groves N, O'Keeffe I, Keeffe I, et al. Blockade of TrkB but not p75NTR activates a subpopulation of quiescent neural precursor cells and enhances neurogenesis in the adult mouse hippocampus. Dev Neurobiol 2019; 79: 868-79. |
| 39. | Mateus-Pinheiro A, Pinto L, Bessa JM, et al. Sustained remission from depressive-like behavior depends on hippocampal neuro-genesis. Transl Psychiatry 2013; 3: e210. |
| 40. | Lee YJ, Kim HR, Lee CY, et al. 2-Phenylethylamine (PEA) ameliorates corticosterone-induced depression-like phenotype via the BDNF/TrkB/CREB signaling pathway. Int J Mol Sci 2020; 21: 9103. |
| 41. | Zhang Z, Deng T, Wu M, Zhu A, Zhu G. Botanicals as modulators of depression and mechanisms involved. Chin Med 2019; 14: 24. |
| [1] | WANG Yaqi, ZHAO Weibo, WANG Yixing, ZHAO Haihong, ZHOU Yaoyao, YAN Yun, WU Taotao, LUO Bin, WANG Ji. Traditional Chinese Medicine constitution among patients with allergic rhinitis and its correlation with anxiety and depression [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1252-1258. |
| [2] | MA Fangfang, ZHANG Hewei, LI Bingxue, CHENG Peiyu, YU Mingwei, WANG Xiaomin. Acupuncture and moxibustion for malignant tumor patients with psychological symptoms of insomnia, anxiety and depression: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(3): 441-456. |
| [3] | DING Yajie, LIU Feng, LI Zhaoyan, Xu Yan, CAO Nida, ZHANG Guangao, WANG Rui, ZHAO Aiguang. Efficacy of luteolin on the human gastric cancer cell line MKN45 and underlying mechanism [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(1): 34-41. |
| [4] | ZOU Xinshuang, SHI Lei, YIN Hailong, LI Haiping, WANG Mengheng, SONG Wanci, LUO Laichun, WU Hezhen, YANG Yanfang, ZAN Junfeng, LIU Yanwen, DAN Hanxiong, YIN Qiang, YOU Pengtao. Compound Gaoziban tablet (复方高滋斑片) alleviates depression via toll-like receptor 4/myeloid differentiation factor 88/nuclear factor-kappa B pathway [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(6): 956-964. |
| [5] | CHEN Limei, SUN Jifei, GUO Chunlei, LI Xiaojiao, WANG Zhi, Hong Yang, FANG Jiliang. Preliminary single-arm study of brain effects during transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation treatment of recurrent depression by resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(5): 818-824. |
| [6] | You WU, Yuli HU, Wei LIU, Boju SUN, Chengfei ZHANG, Lili WU, Tonghua LIU. Flavonoids from traditional Chinese herbs for diabetes in rats: a network Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(1): 1-8. |
| [7] | Jing ZHANG, Jingjing ZHU, Siqi HE, Jianxun WANG. Efficacy of glucocorticoids, chloroquine and vitamin A on cytokine release syndrome: a network pharmacology study [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(1): 116-121. |
| [8] | LI Ganggang, LU Ye, HE Pei, ZHANG Shiyue, CHENG Yating, ZHANG Shaodan, PEI Lin. Target prediction and activity verification for the antidepressant action of Huangqin(Radix Scutellariae Baicalensis) [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(6): 845-852. |
| [9] | WANG Xue, XIONG Jun, YANG Jun, YUAN Ting, JIANG Yunfeng, ZHOU Xiaohong, LIAO Kai, XU Lingling. Meta-analysis of the clinical effectiveness of combined acupuncture and Western Medicine to treat post-stroke depression [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(1): 6-16. |
| [10] | You Yanli, Zhang Tianfang, Shu Shi, Qian Xiaolu, Zhou Shuang, Yao Fei. Wrist-ankle acupuncture and Fluoxetine in the treatment of post-stroke depression: a randomized controlled clinical trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020, 40(3): 455-460. |
| [11] | Cheng Hsuesh-Yu, Carol Shieh, Wu Bei-Yu, Cheng Yu-Fen. Effect of acupressure on postpartum low back pain, salivary cortisol, physical limitations, and depression: a randomized controlled pilot study [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020, 40(1): 128-136. |
| [12] | Yan Yongmei, Li Tao, Wang Dou, Zhao Bingbing, Zhou Qi. Antidepressant effect of Xingnao Jieyu decoction mediated by alleviating neuroinflammation in a rat model of post-stroke depression [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2019, 39(05): 658-666. |
| [13] | Mahin Maleki, Ali Aidy, Elahe Karimi, Shaahin Shahbazi, Nader Safarian, Naser Abbasi. Synthesis of a copolymer carrier for anticancer drug luteolin for targeting human breast cancer cells [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2019, 39(04): 474-481. |
| [14] | Su Rui, Fan Jiping, Li Tao, Cao Xindong, Zhou Jie, Han Zhenyun, Ma Yan. Jiawei Xiaoyao capsule treatment for mild to moderate major depression with anxiety symptoms: a randomized, double-blind, double-dummy, controlled, multicenter, parallel-treatment trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2019, 39(03): 410-417. |
| [15] | Wei Guining, Chu Shifeng, Su Qibiao, Su Hua, Lin Meiyu, He Fei, Lu Wenjie, Lu Guoshou, Huang Zhoufeng, Tan Xiao, Lin Xiao, Zeng Xianbiao, Wei Baowei, Chen Naihong. Antidepressant-like effect of active fraction of Polyrhachisvicina Roger in a rat depression model [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2018, 38(01): 12-21. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

