Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (3): 494-500.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2023.03.001
Previous Articles Next Articles
Electroacupuncture alleviates water avoidance stress-induced irritable bowel syndrome in mice by improving intestinal barrier functions and suppressing the expression of inflammatory cytokines
SUN Mengzhu1, ZHANG Yujie1, SONG Yafang1, GUO Jing1, WANG Yuhang1, XIN Chen1, GU Dongmei1, SUN Jianhua2( ), PEI Lixia2(
), PEI Lixia2( )
)
- 1 Department of acupuncture, Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University of Chinese Meidicne, Nanjing 210023, China
2 Department of acupuncture, Jiangsu Province Hospital of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210029, China
-
Received:2021-02-12Accepted:2021-05-07Online:2023-06-15Published:2023-04-28 -
Contact:SUN Jianhua, Department of acupuncture, Jiangsu Province Hospital of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210029, China. drjhsun@sina.com. Telephone: +86-13851402838; +86-13914722816
PEI Lixia, Department of acupuncture, Jiangsu Province Hospital of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210029, China. plx11801758@163.com -
Supported by:Research and Practice Innovation Program for Postgraduates of Jiangsu Province (Mechanism of Electroacupuncture Regulating Bile Acid Receptor to Alleviate Visceral Hypersensitivity in Irritable Bowel Syndrome)(KYCX20_1469);National Natural Science Fund (Mechanism of Electroacupuncture Regulating CRF-NLRP6 Inflammasome-Related Pathways in Intestinal Flora Immune Dialogue)(81804193);Leading Talents Project of Jiangsu Provincial Administration of TCM (Clinical Effect and Mechanism of Acupuncture and Moxibustion on Irritable Bowel Syndrome)(SLJ0206);Peak Talent Project of Jiangsu Province Hospital of TCM (Clinical Effect and Mechanism of Acupuncture and Moxibustion in the Treatment of Functional Gastrointestinal Diseases)(y2018rc05)
Cite this article
SUN Mengzhu, ZHANG Yujie, SONG Yafang, GUO Jing, WANG Yuhang, XIN Chen, GU Dongmei, SUN Jianhua, PEI Lixia. Electroacupuncture alleviates water avoidance stress-induced irritable bowel syndrome in mice by improving intestinal barrier functions and suppressing the expression of inflammatory cytokines[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(3): 494-500.
share this article
Figure 1 Schematic presentation of the experimental procedures Mice in the model group were subjected to WAS while mice in the EA group were subjected to both WAS and EA. WAS: water avoidance stress; EA: electroacupuncture.
| Gene name | Primer sequence (5′?3′) | Amplicon size (bp) | Tm |
|---|---|---|---|
| IL-8-F | ATGCGTAGCTAGTCAGTCATTG | 175 | 54 ℃ |
| IL-8-R | GACCGGTTTAACTGCTAGCTGAT | ||
| TNF-α-F | GCTACGTACTGATCTGACACC | 272 | 54 ℃ |
| TNF-α-R | TCGTGCTAGTTGCACCTGGAGTACC | ||
| INF-γ-F | GGTTCATGCTGACTGACTGAA | 281 | 54 ℃ |
| INF-γ-R | TGGGTGGGCCGGCGCGATGGCAA | ||
| ZO-1-F | TTACAGTGCTGATAGCTAGCA | 175 | 54 ℃ |
| ZO-1-R | CGTTAGCTACCGCCCAGTCATGCA | ||
| Claudin-1-F | CATGTCGTACTGTCATGGATGC | 243 | 54 ℃ |
| Claudin-1-R | CTTGGTAAACGTTTCCGATCGTACG | ||
| Occludin-F | TAACCTGTGCGACGTACCATG | 167 | 54 ℃ |
| Occludin-R | CTGGTTAACCGTAACTTGAACACT | ||
| GAPDH-F | GCCTTCCGTGTTCCTACC | 455 | 54 ℃ |
| GAPDH-R | GCCTGCTTCACCACCTTC |
Table 1 Primer sequences
| Gene name | Primer sequence (5′?3′) | Amplicon size (bp) | Tm |
|---|---|---|---|
| IL-8-F | ATGCGTAGCTAGTCAGTCATTG | 175 | 54 ℃ |
| IL-8-R | GACCGGTTTAACTGCTAGCTGAT | ||
| TNF-α-F | GCTACGTACTGATCTGACACC | 272 | 54 ℃ |
| TNF-α-R | TCGTGCTAGTTGCACCTGGAGTACC | ||
| INF-γ-F | GGTTCATGCTGACTGACTGAA | 281 | 54 ℃ |
| INF-γ-R | TGGGTGGGCCGGCGCGATGGCAA | ||
| ZO-1-F | TTACAGTGCTGATAGCTAGCA | 175 | 54 ℃ |
| ZO-1-R | CGTTAGCTACCGCCCAGTCATGCA | ||
| Claudin-1-F | CATGTCGTACTGTCATGGATGC | 243 | 54 ℃ |
| Claudin-1-R | CTTGGTAAACGTTTCCGATCGTACG | ||
| Occludin-F | TAACCTGTGCGACGTACCATG | 167 | 54 ℃ |
| Occludin-R | CTGGTTAACCGTAACTTGAACACT | ||
| GAPDH-F | GCCTTCCGTGTTCCTACC | 455 | 54 ℃ |
| GAPDH-R | GCCTGCTTCACCACCTTC |
| Group | n | AWR scores | First black stool defecation time (min) | Number of fecal particles | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 mm Hg | 30 mm Hg | 45 mm Hg | 60 mm Hg | |||||
| Normal | 10 | 0.42±0.08 | 1.51±0.24 | 2.13±0.07 | 3.05±0.09 | 115.43±11.12 | 10.76±1.18 | |
| Model | 10 | 1.18±0.17a | 2.22±0.13a | 2.67±0.16a | 3.71±0.22a | 80.07±6.24d | 13.83±0.71d | |
| EA | 10 | 0.77±0.23b | 1.69±0.20b | 2.23±0.11c | 3.26±0.21 | 107.78±10.44b | 10.88±0.84b | |
Table 2 Effects of EA on intestinal sensory and motor functions in WAS mice ($\bar{x}±s$)
| Group | n | AWR scores | First black stool defecation time (min) | Number of fecal particles | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 mm Hg | 30 mm Hg | 45 mm Hg | 60 mm Hg | |||||
| Normal | 10 | 0.42±0.08 | 1.51±0.24 | 2.13±0.07 | 3.05±0.09 | 115.43±11.12 | 10.76±1.18 | |
| Model | 10 | 1.18±0.17a | 2.22±0.13a | 2.67±0.16a | 3.71±0.22a | 80.07±6.24d | 13.83±0.71d | |
| EA | 10 | 0.77±0.23b | 1.69±0.20b | 2.23±0.11c | 3.26±0.21 | 107.78±10.44b | 10.88±0.84b | |

Figure 2 Effect of EA on colonic morphology in WAS mice A: normal group; B: model group; C: EA group. Normal group: without treatment; Model group: subjected to WAS for 1 h daily on 10 consecutive days; EA group: subjected to WAS for 1 h daily on 10 consecutive days and EA at bilateral Tianshu (ST25) and Zusanli (ST36) for 7 consecutive days. WAS: water avoidance stress; EA: electroacupuncture. Representative photomicrographs of HE staining of colon tissues in each group (magnification, ×200). The nucleus is blue and the cytoplasm is red. n = 3/ group.
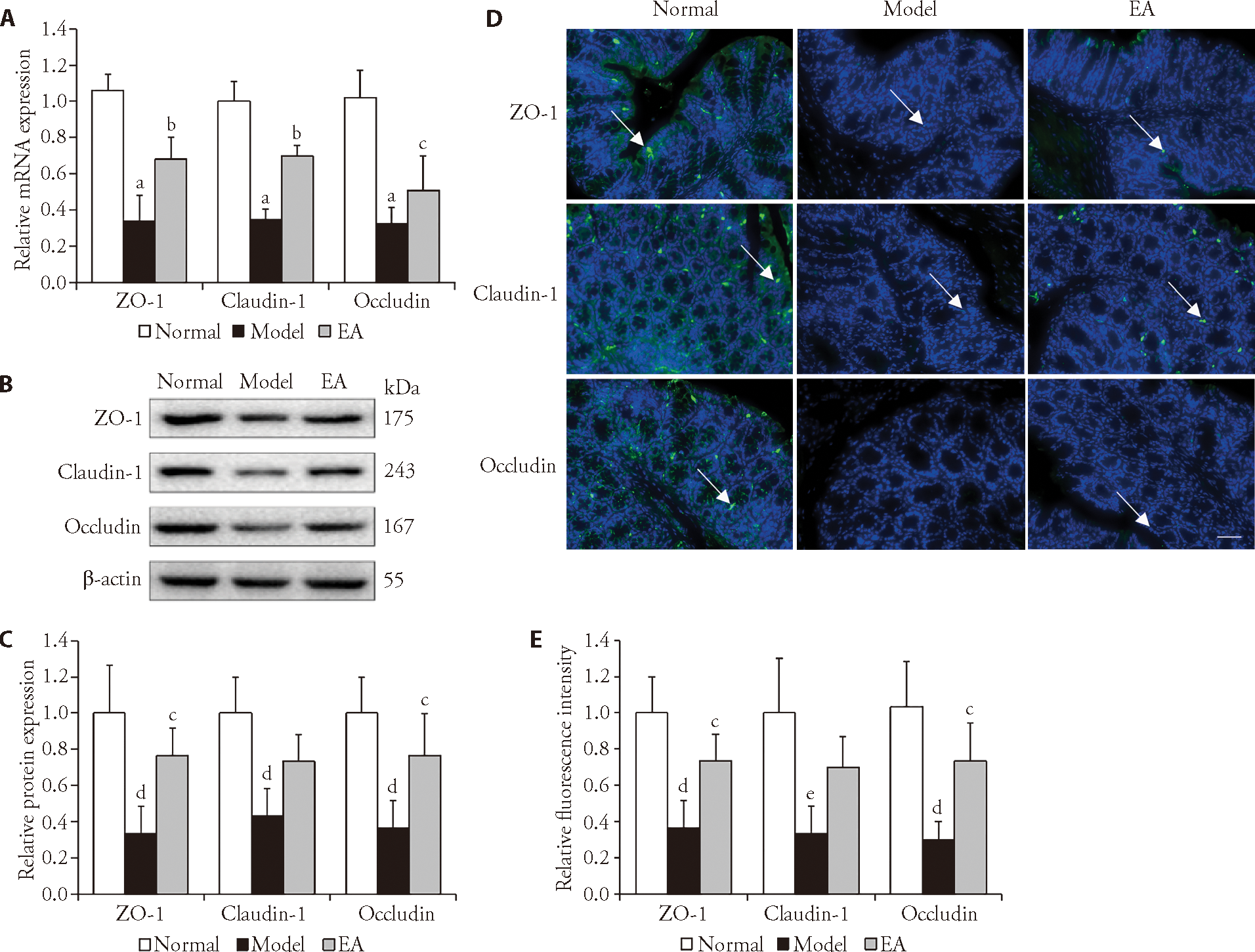
Figure 3 Effects of EA on the expression of TJPs in colon tissues A: mRNA expression levels of ZO-1, claudin-1 and occludin in each group. B: Western blot representative images of ZO-1, claudin-1 and occludin for each group. C: Protein expression levels of ZO-1, claudin-1 and occludin in each group. D: D1-D3: confocal images of ZO-1 for normal, model and EA groups as determined by immunofluorescence assays. D4-D6: confocal images of claudin-1 for normal, model and EA groups as determined by immunofluorescence assays. D7-D9: confocal images of occludin for normal, model and EA groups as determined by immunofluorescence assays. Scale bar: 50 μm. E: Relative fluorescence intensities of ZO-1, claudin-1 and occludin in each group. Normal group: without treatment; Model group: subjected to WAS for 1 h daily on 10 consecutive days; EA group: subjected to WAS for 1 h daily on 10 consecutive days and EA at bilateral Tianshu (ST25) and Zusanli (ST36) for 7 consecutive days. WAS: water avoidance stress; EA: electroacupuncture; ZO-1: zonula occludens-1. Data were presented as the mean ± standard deviation for n = 3. aP<0.001, dP<0.01, and eP<0.05 versus normal group; cP<0.05, and bP<0.001 versus model group.
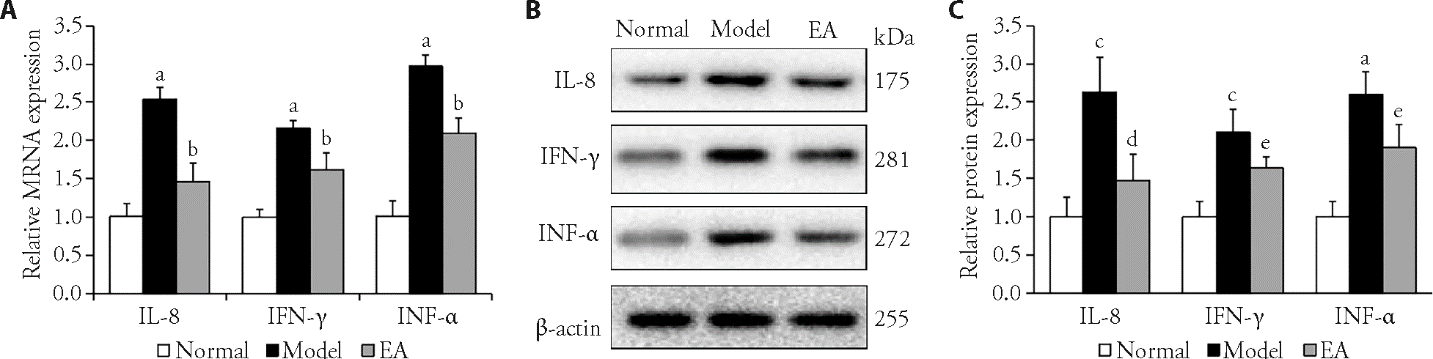
Figure 4 Effects of EA on the expression of inflammatory cytokines in colon tissues A: mRNA expression levels of IL-8, IFN-γ, and TNF-α in each group. B: Western blot representative images of IL-8, IFN-γ, and TNF-α in each group. C: Protein expression levels of IL-8, IFN-γ, and TNF-α in each group. Normal group: without treatment; Model group: subjected to WAS for 1 h daily on 10 consecutive days; EA group: subjected to WAS for 1 h daily on 10 consecutive days and EA at bilateral Tianshu (ST25) and Zusanli (ST36) for 7 consecutive days. WAS: water avoidance stress; EA: electroacupuncture; IL-8: interleukin-8; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor-α; IFN-γ: interferon-γ. Data were presented as the mean ± standard deviation for n = 3. aP<0.001, cP<0.01 versus normal group; bP<0.001,dP <0.01, eP<0.05 versus model group.
| [1] | Sultan S, Malhotra A. Irritable bowel syndrome. Ann Intern Med 2017; 166: C81-96. |
| [2] |
Posserud I, Syrous A, Lindstrom L, et al. Altered rectal perception in irritable bowel syndrome is associated with symptom severity. Gastroenterology 2007; 133: 1113-23.
DOI PMID |
| [3] |
Vancamelbeke M, Vermeire S. The intestinal barrier: a fundamental role in health and disease. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2017; 11: 821-34.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
Bertiaux-Vandaele N, Youmba SB, Belmonte L, et al. The expression and the cellular distribution of the tight junction proteins are altered in irritable bowel syndrome patients with differences according to the disease subtype. Am J Gastroenterol 2011; 106: 2165-73.
DOI PMID |
| [5] | Nozu T, Miyagishi S, Nozu R, et al. Losartan improves visceral sensation and gut barrier in a rat model of irritable bowel syndrome. Neurogastroenterol Motil 2020; 32: e13819. |
| [6] |
Nusrat A, Turner JR, Madara JL. Molecular physiology and pathophysiology of tight junctions. IV. Regulation of tight junctions by extracellular stimuli: nutrients, cytokines, and immune cells. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2000; 279: G851-7.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
Patel SR, Singh A, Misra V, et al. Levels of interleukins 2, 6, 8, and 10 in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Indian J Pathol Microbiol 2017; 60: 385-9.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
de Souza HS, Fiocchi C. Immunopathogenesis of IBD: current state of the art. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2016; 13: 13-27.
DOI PMID |
| [9] |
Neurath MF. Cytokines in inflammatory bowel disease. Nat Rev Immunol 2014; 14: 329-42.
DOI PMID |
| [10] |
Madara JL, Stafford J. Interferon-gamma directly affects barrier function of cultured intestinal epithelial monolayers. J Clin Invest 1989; 83: 724-27.
DOI PMID |
| [11] | Mullin JM, Laughlin KV, Marano CW, et al. Modulation of tumor necrosis factor-induced increase in renal (LLC-PK1) transepithelial permeability. Am J Physiol 1992; 263: F915-24. |
| [12] |
Milard M, Penhoat A, Durand A, et al. Acute effects of milk polar lipids on intestinal tight junction expression: towards an impact of sphingomyelin through the regulation of IL-8 secretion? J Nutr Biochem 2019; 65: 128-38.
DOI PMID |
| [13] |
Song YF, Geng H, Chen L, et al. Electroacupuncture relieves irritable bowel syndrome by increasing expression of nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain protein-like receptor family pyrin domain containing 6 in water-avoidance stress mice. J Tradit Chin Med 2020; 40: 407-13.
DOI PMID |
| [14] |
Fourie NH, Wang D, Abey SK, et al. Structural and functional alterations in the colonic microbiome of the rat in a model of stress induced irritable bowel syndrome. Gut Microbes 2017; 8: 33-45.
DOI PMID |
| [15] |
Ren X, Liu L, Gamallat Y, et al. Enteromorpha and polysaccharides from enteromorpha ameliorate loperamide-induced constipation in mice. Biomed Pharmacother 2017; 96: 1075-81.
DOI PMID |
| [16] |
Rojas-Macias V, Rodriguez-Fandino O, Jimenez-Ponce F, et al. External validity of a relevant model for irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) using chronic stress by water avoidance in Wistar rats. Rev Gastroenterol Mex 2010; 75: 421-6.
PMID |
| [17] |
Song YF, Pei LX, Chen L, et al. Electroacupuncture relieves irritable bowel syndrome by regulating IL-18 and gut microbial dysbiosis in a trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid-induced post-inflammatory animal model. Am J Chin Med 2020; 48: 77-90.
DOI URL |
| [18] | Chen Y, Zhao Y, Luo DN, et al. Electroacupuncture regulates disorders of gut-brain interaction by decreasing corticotropin-releasing factor in a rat model of IBS. Gastroenterol Res Pract 2019; 1759842. |
| [19] | Zhang F, Ma Z, Weng Z, et al. P2X3 receptor in primary afferent neurons mediates the relief of visceral hypersensitivity by electroacupuncture in an irritable bowel syndrome rat model. Gastroenterol Res Pract 2020; 8186106. |
| [20] |
Du MH, Luo HM, Hu S, et al. Electroacupuncture improves gut barrier dysfunction in prolonged hemorrhagic shock rats through vagus anti-inflammatory mechanism. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19: 5988-99.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
Pope JL, Bhat AA, Sharma A, et al. Claudin-1 regulates intestinal epithelial homeostasis through the modulation of Notch-signalling. Gut 2014; 63: 622-34.
DOI PMID |
| [22] |
Coeffier M, Gloro R, Boukhettala N, et al. Increased proteasome-mediated degradation of occludin in irritable bowel syndrome. Am J Gastroenterol 2010; 105: 1181-8.
DOI PMID |
| [23] |
Piche T. Tight junctions and IBS-the link between epithelial permeability, low-grade inflammation, and symptom generation? Neurogastroenterol Motil 2014; 26: 296-302.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
Bertiaux-Vandaele N, Youmba SB, Belmonte L, et al. The expression and the cellular distribution of the tight junction proteins are altered in irritable bowel syndrome patients with differences according to the disease subtype. Am J Gastroenterol 2011; 106: 2165-73.
DOI PMID |
| [25] |
Sinagra E, Morreale GC, Mohammadian G, et al. New therapeutic perspectives in irritable bowel syndrome: targeting low-grade inflammation, immuno-neuroendocrine axis, motility, secretion and beyond. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23: 6593-627.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
Choghakhori R, Abbasnezhad A, Hasanvand A, et al. Inflammatory cytokines and oxidative stress biomarkers in irritable bowel syndrome: association with digestive symptoms and quality of life. Cytokine 2017; 93: 34-43.
DOI PMID |
| [27] |
Ji LJ, Li F, Zhao P, et al. Silencing interleukin 1alpha underlies a novel inhibitory role of miR-181c-5p in alleviating low-grade inflammation of rats with irritable bowel syndrome. J Cell Biochem 2019; 120: 15268-79.
DOI PMID |
| [28] |
Yang J, Shang B, Shi H, et al. The role of toll-like receptor 4 and mast cell in the ameliorating effect of electroacupuncture on visceral hypersensitivity in rats. Neurogastroenterol Motil 2019; 31: e13583.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
Xu D, Gao J, Gillilland MR, et al. Rifaximin alters intestinal bacteria and prevents stress-induced gut inflammation and visceral hyperalgesia in rats. Gastroenterology 2014; 146: 484-96.
DOI PMID |
| [30] |
de Magalhaes SF, Manzo LP, de Faria FM, et al. Inflammatory pain in peripheral tissue depends on the activation of the TNF-alpha type 1 receptor in the primary afferent neuron. Eur J Neurosci 2021; 53: 376-89.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
Zhen Y, Chu C, Zhou S, et al. Imbalance of tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-8 and interleukin-10 production evokes barrier dysfunction, severe abdominal symptoms and psychological disorders in patients with irritable bowel syndrome-associated diarrhea. Mol Med Rep 2015; 12: 5239-45.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Barbaro MR, Di Sabatino A, Cremon C, et al. Interferon-gamma is increased in the gut of patients with irritable bowel syndrome and modulates serotonin metabolism. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2016; 310: G439-47.
DOI URL |
| [1] | QIN Xiaoyu, WANG Chunai, XUE Jianjun, ZHANG Jie, LU Xiaoting, DING Shengshuang, GE Long, WANG Minzhen. Efficacy of electroacupuncture on myocardial protection and postoperative rehabilitation in patients undergoing cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 1-15. |
| [2] | SUN Qianhui, CHENG Kai, DAI Xingye, YANG Zhiwen, WU Xiaoling, XU Chang, QIU Xinghua, GAO Xiaofeng, LIU Daonan, YANG Qirui. Effect of electroacupuncture at Neiguan (PC6) at different time points on myocardial ischemia reperfusion arrhythmia in rats [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 113-121. |
| [3] | DU Zhongheng, CONG Wenjie, TANG Kejing, ZHENG Qiqi, SONG Zhiwei, CHEN Yong, YANG Su, ZHANG Chunwu, YE Tianshen. Electroacupuncture stimulating Zusanli (ST36), Sanyinjiao (SP6) in mice with collagen-induced arthritis leads to adenosine A2A receptor-mediated alteration of p38α mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling and inhibition of osteoclastogenesis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1103-1109. |
| [4] | JIANG Jianzhen, ZHANG Xin, LUO Zhenguo, SU Chengguo, ZHOU Haiyan, JIANG Yuqing, XIAO Xianjun, CHEN Yunfei, ZHU Jun. Efficacy of electroacupuncture stimulating Zusanli (ST36) and Xuanzhong (GB39) on synovial angiogenesis in rats with adjuvant arthritis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 955-962. |
| [5] | LI Zhihao, HAN Wenjun, SONG Xiuling, LI Yan, CHEN Yuelai. Electroacupuncture stimulating Zhongji (CV3), Guanyuan (CV4), and bilateral Dahe (KI12) attenuates inflammation in rats with chronic nonbacterial prostatitis induced by estradiol through inhibiting toll-like receptor 4 pathway [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 963-972. |
| [6] | DING Luobin, WANG Huajun, LI Yao, LI Jia, LI Ling, GAO Yangping, GUAN Jian, GENG Weiqiang. Electroacupuncture stimulating Neixiyan (EX-LE5) and Dubi (ST35) alleviates osteoarthritis in rats induced by anterior cruciate ligament transaction via affecting DNA methylation regulated transcription of miR-146a and miR-140-5p [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 983-990. |
| [7] | Minh Duc Nguyen, Thanh Van Tran, Quoc Vinh Nguyen, Cay Doan Ha, Linh Vu Phuong Dang. Effectiveness of bee venom acupuncture for patients suffering from periarthritis humeroscapularis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(4): 795-800. |
| [8] | HAN Rui, CHANG Junzhao, LIU Qianqian, LIU Haitao, LI Junwei. Efficacy of electroacupunture at Zusanli (ST36) on jumping-injured muscle based on transcriptome sequencing and genes analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(2): 322-328. |
| [9] | Minh Duc Nguyen, Thanh Van Tran, Quoc Vinh Nguyen, Ninh Khac Nguyen, Son Truong Vu, Luu Trong Nguyen, Linh Vu Phuong Dang. Effectiveness on post-stroke hemiplegia in patients: electroacupuncture plus cycling vs electroacupuncture alone [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(2): 352-358. |
| [10] | GONG Hui, LI Yang, FENG Lei, XIAO Yujie, HUANG Lizhong, MAO Dan, ZHANG Hui. Yanghe decoction (阳和汤) attenuated pain hypersensitivity induced by michigan cancer foundation-7 injection in rats with bone metastases from breast cancer by inhibiting transient receptor potential ankyrin 1 [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(6): 948-955. |
| [11] | XU Chang, LI Na, WU Xiaoling, DAI Xingye, YANG Zhiwen, SUN Qianhui, SHI Tianyu, CHAI Yemao, PANG Dandan, CHENG Kai. Effect of electroacupuncture on inflammatory signal expression in local tissues of rats with chronic pelvic pain syndrome based on purinergic 2X7 receptor/NOD-like receptor pyrin domain-containing 3 signal pathway [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(6): 965-971. |
| [12] | YANG Liping, YU Xinglin, ZHANG Chao, CHEN Pu, DUAN Xiaohua. Yajieshaba prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced intestinal barrier injury via anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptosis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(5): 707-714. |
| [13] | SUN Mengzhu, ZHANG Yujie, SONG Yafang, GUO Jing, ZHAO Tingting, WANG Yuhang, PEI Lixia, SUN Jianhua. Electroacupuncture at Tianshu (ST25) and Zusanli (ST36) alleviates stress-induced irritable bowel syndrome in mice by modulating gut microbiota and corticotropin-releasing factor [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(5): 732-740. |
| [14] | HU Xijiao, CHENG Yinglong, KANG Huanan, LI Shuoxi, WANG Yawen, LIU Jinzhe, SUN Yiming, LIU Li. Electroacupuncture attenuates chronic salpingitis via transforming growth factor-β1/p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(5): 781-787. |
| [15] | HUANG Yusi, YANG Jiju, LI Xinyi, HAO Huifeng, LI Chong, ZHANG Fan, LIN Haiming, XIE Xianfei, HE Ke, TIAN Guihua. Effectiveness and safety of electroacupuncture for the treatment of pain after laparoscopic surgery: a systematic review [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(4): 505-512. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

