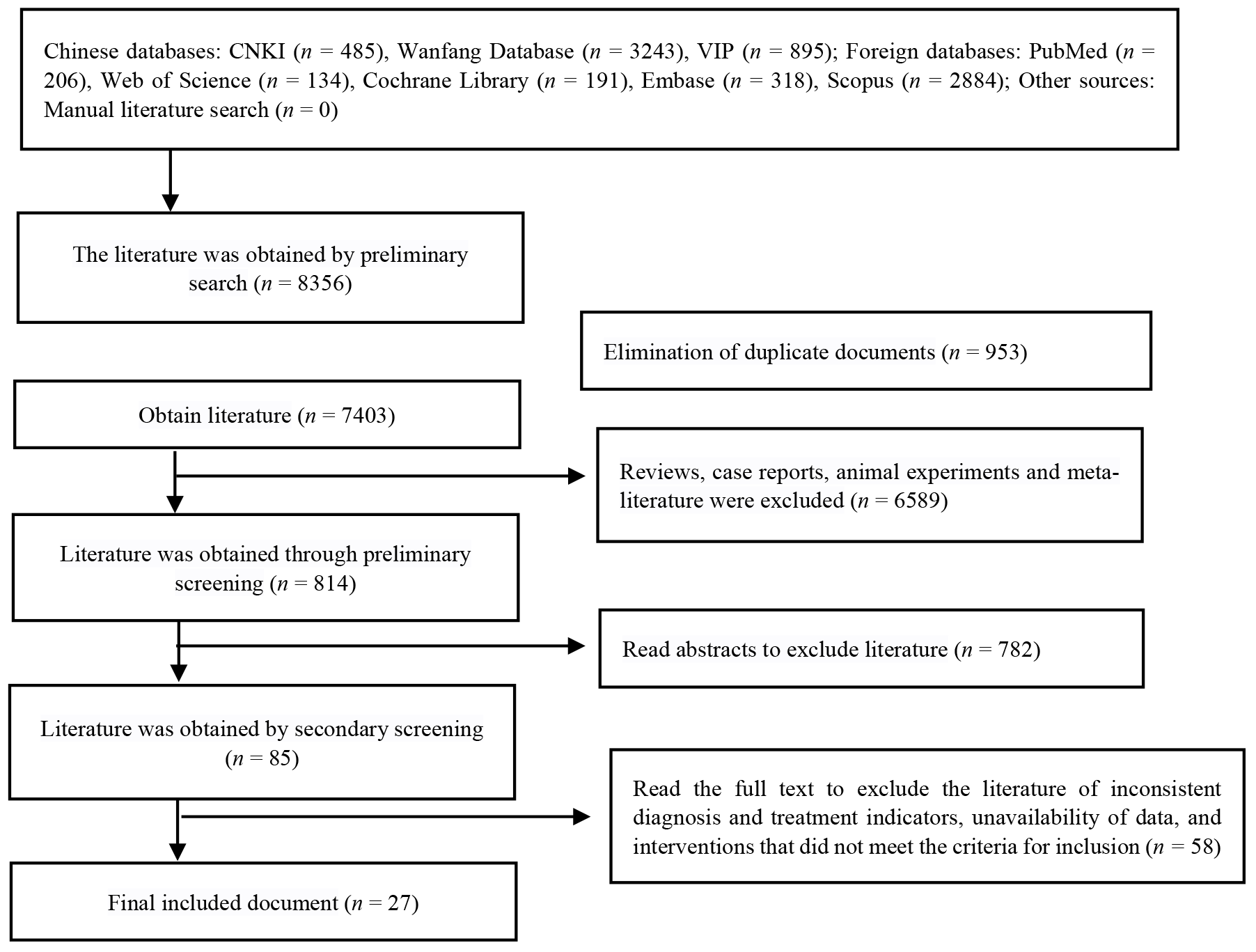
Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (4): 711-719.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2025.04.001
• Meta-analysis • Next Articles
Seven Traditional Chinese Medicine external treatments combined with rehabilitation training on the functional recovery of limbs in patients with cerebral hemorrhage: a network Meta-analysis
CHEN Ziying1, ZHAO Xiaoping3, FAN Xiaoxuan3, TANG Didi2, SUN Wen2, LYU Jing2, HUANG Lan2, QI Fan2
- 1 Department of emergency, the Fifth Clinical Medical College of Shaanxi University of Chinese Medicine, Xi'an Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Xi'an 710000, China
2 Affiliated Hospital of Shaanxi University of Chinese Medicine, Xianyang 712000, China
3 Department of brain surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Shaanxi University of Chinese Medicine, Xianyang 712000, China
-
Received:2024-06-12Accepted:2024-10-22Online:2025-07-25Published:2025-07-25 -
Supported by:Key Research and Development Plan Project of Shaanxi Province: Standardized Diagnosis and Treatment Protocol for Cerebral Hemorrhage with Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine and Research on its Therapeutic Mechanisms(2019ZDLSF04-06-01);National Key Research and Development Plan Project: Development and Implementation of a Clinical Research Information Sharing System for Traditional Chinese Medicine(2017YFC1703500);National Key Research and Development Plan Project: Development and Implementation of a Clinical Research Information Sharing System for Traditional Chinese Medicine(2017YFC1703502);Discipline Innovation Team Building Project of Shaanxi University of Chinese Medicine: Innovative Research Team for the Construction of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine Cerebrovascular Disease Diagnosis and Treatment System and Its Clinical Application(2019-YL15)
Cite this article
CHEN Ziying, ZHAO Xiaoping, FAN Xiaoxuan, TANG Didi, SUN Wen, LYU Jing, HUANG Lan, QI Fan. Seven Traditional Chinese Medicine external treatments combined with rehabilitation training on the functional recovery of limbs in patients with cerebral hemorrhage: a network Meta-analysis[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(4): 711-719.
share this article
| Study | n | Experimental group | Control group | Evaluation index | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| t | Age | N (Male/Female) | t | Age | n (Male/Female) | |||||
| Liao HY et al 2021 | 38 | A | 58.19±4.92 | 19 (11/8) | B | 57.35±4.57 | 19 (10/9) | FMA, BI | ||
| Ta CF et al 2013 | 60 | A | 62.3±7.87 | 30 (18/12) | B | 63.1±7.04 | 30 (19/11) | FMA, BI | ||
| Li TS et al 2021 | 86 | A | 58.20±11.03 | 43 (25/18) | B | 57.31±10.1 | 43 (23/20) | FMA | ||
| Wang MG et al 2021 | 48 | A | 52.67±8.22 | 24 (13/11) | B | 52.36±7.84 | 24 (12/12) | FMA | ||
| Wang BY et al 2018 | 90 | A | 55.5±1.0 | 45 (30/15) | B | 55.5±1.0 | 45 (28/17) | FMA | ||
| Li J et al 2018 | 66 | A | 55.98±6.76 | 33 (19/14) | B | 56.57±6.09 | 33 (20/13) | FMA | ||
| Wang XY et al 2018 | 80 | A | 58.2±10.4 | 40 (21/19) | B | 57.8±9.8 | 40 (26/14) | FMA | ||
| Zhu LL et al 2020 | 80 | A | 64.2±1.3 | 40 (25/15) | B | 63.9±1.2 | 40 (24/16) | FMA | ||
| Liu X et al 2019 | 94 | A | 57±4 | 47 (25/22) | B | 57±4 | 47 (26/21) | FMABI | ||
| Lin B et al 2017 | 76 | A | 60.5±10.2 | 38 (24/14) | B | 58.1±11.3 | 38 (26/12) | FMA, BI | ||
| Wang HQ et al 2020 | 134 | A | 55.76±7.66 | 67 (46/21) | B | 57.69±7.9 | 67 (41/26) | FMA, | ||
| Li L et al 2021 | 60 | C | 57±12.81 | 30 (20/10) | B | 58.1±10.97 | 30 (19/11) | BI | ||
| Wang CH et al 2005 | 60 | C | 55.3±10.8 | 30 (23/7) | B | 54.7±10.2 | 30 (20/10) | FMA, BI | ||
| Mao Y et al 2018 | 104 | C | 60.28±12.23 | 52 | B | 60.28±12.23 | 52 | FMA | ||
| Dong RL et al 2021 | 90 | D | 64.70±5.41 | 45 (25/20) | B | 64.19±5.32 | 45 (23/22) | FMA, BI | ||
| Wu DH et al 2020 | 100 | E | 64.06±8.70 | 50 (34/16) | B | 64.11±8.67 | 50 (22/28) | BI | ||
| Chen MF et al 2015 | 90 | E | 54.48±3.27 | 45 (27/18) | B | 54.79±3.19 | 45 (30/15) | BI | ||
| Lian LL et al 2022 | 60 | E | 57.45±11.28 | 30 (16/14) | B | 56.15±12.93 | 30 (18/12) | FMA, BI | ||
| Huang CB et al 2021 | 68 | E | 54.03±11.29 | 34 (21/13) | B | 55.76±11.44 | 34 (19/15) | FMA, BI | ||
| Wang ZY et al | 86 | E | 50.5 | 44 (20/24) | B | 57.4 | 42 (19/23) | FMA, BI | ||
| Chen S et al 2022 | 68 | F | 67.53±2.71 | 34 (19/15) | B | 66.11±2.94 | 34 (20/14) | BI | ||
| Gui SZ et al 2019 | 70 | F | 60.9±7.6 | 35 (21/14) | B | 60.9±7.7 | 35 (22/13) | FMA, BI | ||
| Tang JY et al 2020 | 120 | F | 53.46±3.21 | 60 (32/28) | B | 53.09±2.97 | 60 (33/27) | FMA, BI | ||
| Xu L et al 2022 | 80 | G | 59.20±7.31 | 40 (25/15) | B | 59.47±7.27 | 40 (26/14) | BI | ||
| Zhang T et al 2016 | 40 | G | 51.2±16.5 | 20 (11/9) | B | 50.0±16.1 | 20 (13/7) | BI | ||
| Zhou LL et al 2019 | 104 | G | 55.51±11.73 | 52 (32/20) | B | 55.28±11.89 | 52 (31/21) | FMA | ||
| Huang QS et al 2014 | 83 | H | 64.1±6.2 | 42 (31/11) | B | 63. 6±5. 8 | 41 (27/14) | FMA, BI | ||
Table 1 Basic features of included studies
| Study | n | Experimental group | Control group | Evaluation index | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| t | Age | N (Male/Female) | t | Age | n (Male/Female) | |||||
| Liao HY et al 2021 | 38 | A | 58.19±4.92 | 19 (11/8) | B | 57.35±4.57 | 19 (10/9) | FMA, BI | ||
| Ta CF et al 2013 | 60 | A | 62.3±7.87 | 30 (18/12) | B | 63.1±7.04 | 30 (19/11) | FMA, BI | ||
| Li TS et al 2021 | 86 | A | 58.20±11.03 | 43 (25/18) | B | 57.31±10.1 | 43 (23/20) | FMA | ||
| Wang MG et al 2021 | 48 | A | 52.67±8.22 | 24 (13/11) | B | 52.36±7.84 | 24 (12/12) | FMA | ||
| Wang BY et al 2018 | 90 | A | 55.5±1.0 | 45 (30/15) | B | 55.5±1.0 | 45 (28/17) | FMA | ||
| Li J et al 2018 | 66 | A | 55.98±6.76 | 33 (19/14) | B | 56.57±6.09 | 33 (20/13) | FMA | ||
| Wang XY et al 2018 | 80 | A | 58.2±10.4 | 40 (21/19) | B | 57.8±9.8 | 40 (26/14) | FMA | ||
| Zhu LL et al 2020 | 80 | A | 64.2±1.3 | 40 (25/15) | B | 63.9±1.2 | 40 (24/16) | FMA | ||
| Liu X et al 2019 | 94 | A | 57±4 | 47 (25/22) | B | 57±4 | 47 (26/21) | FMABI | ||
| Lin B et al 2017 | 76 | A | 60.5±10.2 | 38 (24/14) | B | 58.1±11.3 | 38 (26/12) | FMA, BI | ||
| Wang HQ et al 2020 | 134 | A | 55.76±7.66 | 67 (46/21) | B | 57.69±7.9 | 67 (41/26) | FMA, | ||
| Li L et al 2021 | 60 | C | 57±12.81 | 30 (20/10) | B | 58.1±10.97 | 30 (19/11) | BI | ||
| Wang CH et al 2005 | 60 | C | 55.3±10.8 | 30 (23/7) | B | 54.7±10.2 | 30 (20/10) | FMA, BI | ||
| Mao Y et al 2018 | 104 | C | 60.28±12.23 | 52 | B | 60.28±12.23 | 52 | FMA | ||
| Dong RL et al 2021 | 90 | D | 64.70±5.41 | 45 (25/20) | B | 64.19±5.32 | 45 (23/22) | FMA, BI | ||
| Wu DH et al 2020 | 100 | E | 64.06±8.70 | 50 (34/16) | B | 64.11±8.67 | 50 (22/28) | BI | ||
| Chen MF et al 2015 | 90 | E | 54.48±3.27 | 45 (27/18) | B | 54.79±3.19 | 45 (30/15) | BI | ||
| Lian LL et al 2022 | 60 | E | 57.45±11.28 | 30 (16/14) | B | 56.15±12.93 | 30 (18/12) | FMA, BI | ||
| Huang CB et al 2021 | 68 | E | 54.03±11.29 | 34 (21/13) | B | 55.76±11.44 | 34 (19/15) | FMA, BI | ||
| Wang ZY et al | 86 | E | 50.5 | 44 (20/24) | B | 57.4 | 42 (19/23) | FMA, BI | ||
| Chen S et al 2022 | 68 | F | 67.53±2.71 | 34 (19/15) | B | 66.11±2.94 | 34 (20/14) | BI | ||
| Gui SZ et al 2019 | 70 | F | 60.9±7.6 | 35 (21/14) | B | 60.9±7.7 | 35 (22/13) | FMA, BI | ||
| Tang JY et al 2020 | 120 | F | 53.46±3.21 | 60 (32/28) | B | 53.09±2.97 | 60 (33/27) | FMA, BI | ||
| Xu L et al 2022 | 80 | G | 59.20±7.31 | 40 (25/15) | B | 59.47±7.27 | 40 (26/14) | BI | ||
| Zhang T et al 2016 | 40 | G | 51.2±16.5 | 20 (11/9) | B | 50.0±16.1 | 20 (13/7) | BI | ||
| Zhou LL et al 2019 | 104 | G | 55.51±11.73 | 52 (32/20) | B | 55.28±11.89 | 52 (31/21) | FMA | ||
| Huang QS et al 2014 | 83 | H | 64.1±6.2 | 42 (31/11) | B | 63. 6±5. 8 | 41 (27/14) | FMA, BI | ||
| Number | Code | Intervention |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | A | Acupuncture combined rehabilitation training |
| 2 | B | Rehabilitation training |
| 3 | C | Massage combined rehabilitation training |
| 4 | D | Moxibustion combined with rehabilitation training |
| 5 | E | Electroacupuncture combined rehabilitation training |
| 6 | F | Traditional Chinese Medicine therapy combined with rehabilitation training |
| 7 | G | Acupoint sticking therapy combined with rehabilitation training |
| 8 | H | Chinese herbal fumigation combined with rehabilitation training |
Table 2 Codes corresponding to intervention measures
| Number | Code | Intervention |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | A | Acupuncture combined rehabilitation training |
| 2 | B | Rehabilitation training |
| 3 | C | Massage combined rehabilitation training |
| 4 | D | Moxibustion combined with rehabilitation training |
| 5 | E | Electroacupuncture combined rehabilitation training |
| 6 | F | Traditional Chinese Medicine therapy combined with rehabilitation training |
| 7 | G | Acupoint sticking therapy combined with rehabilitation training |
| 8 | H | Chinese herbal fumigation combined with rehabilitation training |
| Intervention measure | FMA | BI | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SUCRA | Sort | SUCRA | Sort | ||
| A | 77.9 | 1 | 65.7 | 3 | |
| C | 58.6 | 3 | 63.5 | 4 | |
| D | 45.0 | 5 | 50.2 | 5 | |
| E | 57.1 | 4 | 76.8 | 1 | |
| F | 39.3 | 6 | 27.8 | 7 | |
| G | 75.9 | 2 | 67.5 | 2 | |
| H | 32.0 | 7 | 41.5 | 6 | |
| B | 14.2 | 8 | 7.1 | 8 | |
Table 3 SUCRA probability ranking results of network Meta-analysis outcome measures
| Intervention measure | FMA | BI | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SUCRA | Sort | SUCRA | Sort | ||
| A | 77.9 | 1 | 65.7 | 3 | |
| C | 58.6 | 3 | 63.5 | 4 | |
| D | 45.0 | 5 | 50.2 | 5 | |
| E | 57.1 | 4 | 76.8 | 1 | |
| F | 39.3 | 6 | 27.8 | 7 | |
| G | 75.9 | 2 | 67.5 | 2 | |
| H | 32.0 | 7 | 41.5 | 6 | |
| B | 14.2 | 8 | 7.1 | 8 | |
| 1. | Neurology Branch of the Chinese medical association, cerebrovascular disease group of the neurology branch of the Chinese medical association. Guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of intracerebral hemorrhage in China (2019). Zhong Hua Shen Jing Ke Za Zhi 2019; 52: 994. |
| 2. | Ta CF, Wang HY, Kong J, Zhan DQ, Luo ZY, Jin YL. The influence of Quyu Shengxin acupuncture combined with bobath technique early intervention on the quality of life of patients with hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage after surgery. Jilin Zhong Yi Yao 2013; 33: 1054-6. |
| 3. | Neurology branch of the Chinese medical association, neurorehabilitation group of the neurology branch of the Chinese medical association, cerebrovascular disease group of the neurology branch of the Chinese medical association. Guidelines for Early Rehabilitation Treatment of Stroke in China. Zhong Hua Shen Jing Ke Za Zhi 2017; 50: 405-12. |
| 4. | Huang CB, Liu Y, Huang MA, et al. Clinical efficacy observation of electroacupuncture combined with functional rehabilitation training in patients with hemiplegia after cerebral hemorrhage. Hubei Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue Xue Bao 2021; 23: 85-7. |
| 5. | The 4th National Conference on Cerebrovascular Diseases. Diagnostic Key Points for Various Cerebrovascular Diseases. Zhong Hua Shen Jing Ke Za Zhi 1996; 29: 379-80. |
| 6. | Neurology Branch of the Chinese Medical Association, Cerebrovascular Disease Group of the Neurology Branch of the Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for Diagnosis and Treatment of Intracerebral Hemorrhage in China (2014). Zhong Hua Shen Jing Ke Za Zhi 2015; 48: 435-44. |
| 7. | Eurosurgery Branch of the Chinese Medical Association, Emergency Physicians Branch of the Chinese Physicians Association, Cerebrovascular Disease Group of the Neurology Branch of the Chinese Medical Association, et al. Multidisciplinary diagnosis and treatment guidelines for hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage in China. Zhong Hua Ji Zhen Yi Xue Za Zhi 2020; 40: 689-702. |
| 8. | Liao HY. Clinical observation of acupuncture combined with rehabilitation training in the treatment of increased muscle tone in hemiplegia after cerebral hemorrhage. Xian Dai Zhong Yi Yao Yuan Cheng Jiao Yu 2021; 19: 120-2. |
| 9. | Li TS. The influence of acupuncture combined with rehabilitation training on limb function in patients during the recovery period of cerebral hemorrhage. Fan She Liao Fa Yu Kang Fu Yi Xue 2021; 2: 43-5. |
| 10. | Wang MG, Tang YF. The influence of early acupuncture combined with rehabilitation training on limb function in patients with hypertensive hemiplegia after cerebral hemorrhage. Fan She Liao Fa Yu Kang Fu Yi Xue 2021; 2: 35-8. |
| 11. | Wang BY, Sun LB, Chen Q, et al. Observation on the efficacy of daily living ability training combined with acupuncture therapy in hemiplegia after cerebral hemorrhage. Shanxi Yi Kan 2018; 47: 1808-10. |
| 12. | Li J. Promoting effect of acupuncture combined with rehabilitation training on limb function recovery in patients with cerebral hemorrhage. Zhong Guo Ji Xu Yi Xue Jiao Yu 2018; 10: 158-60. |
| 13. | Wang XY, Wang XF. Observation on the therapeutic effect of acupuncture on hand and foot Yangming meridian in patients with limb dysfunction after cerebral hemorrhage. Shi Jie Zui Xin Yi Xue Xin Xi Wen Zhai 2018; 18: 155-7. |
| 14. | Zhu LL. The influence of Traditional Chinese Medicine acupuncture combined with rehabilitation training on lower limb function recovery and quality of life in patients with hypertensive cerebral hemorrhage. Fan She Liao Fa Yu Kang Fu Yi Xue 2020; 1: 16-8. |
| 15. | Liu X, Wei Z, Xu JJ, et al. Effects of rehabilitation training combined with scalp acupuncture on motor and neurological functions in patients with spasticity after cerebral hemorrhage. Zhong Guo Yao Wu Yu Lin Chuang 2019; 19: 77-9. |
| 16. | Lin B. Effects of acupuncture combined with tourniquet movement therapy on gait function in patients with basal ganglia hemorrhage-induced hemiplegia after surgery. Zhong Guo Zhong Yi Ji Zheng 2017; 26: 1091-3. |
| 17. | Wang HQ, Hou M, Li H, et al. Effects of acupuncture treatment on motor function in patients with subacute hemorrhagic stroke: a randomized controlled study. Complement Ther Med 2020; 49: 102296. |
| 18. | Li L. Clinical observation of balance and relaxing hand technique in the treatment of spastic paralysis after stroke (cerebral hemorrhage recovery period). Hunan: Hunan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020: 1-58. |
| 19. | Wang CH, Zhang J. Effects of Tuina on rehabilitation of motor dysfunction in patients with acute hemiplegia due to cerebral hemorrhage. Zhen Ci Lin Chuang Za Zhi 2005; 21: 42-3. |
| 20. | Mao Y, Shi Y, Hu YT, et al. Effects of acupoint massage combined with passive exercise on limb motor function and muscle strength in patients with cerebral hemorrhage. Xin Li Yi Sheng 2018; 24: 81-2. |
| 21. | Dong RL. Effects of moxibustion combined with early rehabilitation training on upper limb dysfunction in patients with hemorrhagic stroke. Zhong Guo Min Jian Liao Fa 2021; 29: 53-5. |
| 22. | Wu DH. Observation on the therapeutic effect of electro-acupuncture combined with rehabilitation training in the treatment of sequelae after cerebral hemorrhage: a study of 100 cases. Shi Jie Zui Xin Yi Xue Xin Xi Wen Zhai 2020; 20: 59-60. |
| 23. | Chen MF. Application of electroacupuncture combined with neurorehabilitation techniques in the rehabilitation of limb function in patients with cerebral hemorrhage. Yi Xue Xin Xi 2015; 36: 216. |
| 24. | Lian LL, Fan XX, Zhao XP, et al. Proceedings of the 2022 annual conference of the Chinese acupuncture association; 2022 July 19; Jinan, China. Beijing: China Institute of Acupuncture and Moxibustion, 2022: 226-31. |
| 25. | Wang ZY, Lyu DC. Analysis of therapeutic effect of electroacupuncture combined with physical rehabilitation on patients with hemiplegia after cerebral hemorrhage. Henan Ke Ji Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban 2013; 31: 127-9. |
| 26. | Chen S, Ji TT, Wang QL. Effects of Traditional Chinese Medicine targeted drug therapy instrument combined with rehabilitation nursing on the rehabilitation effect of patients with cerebral hemorrhage. Yi Liao She Bei 2022; 35: 182-4. |
| 27. | Gui SZ, Wan CX, Jiang T. Observation on the therapeutic effect of Traditional Chinese Medicine targeted drug therapy on early motor function recovery after cerebral hemorrhage surgery. Zhong Guo Lao Nian Bao Jian Yi Xue 2019; 17: 138-40. |
| 28. | Tang JY, Zhong XQ, Luo HJ. Effects of traditional Chinese medicine targeted treatment combined with early limb rehabilitation training on limb function and quality of life in patients with hypertensive cerebral hemorrhage after surgery. Heilongjiang Zhong Yi Yao 2020; 49: 79-80. |
| 29. | Xu L. Effects of cinnamon paste applied to Yongquan acupoint combined with limb training in middle-aged and elderly patients with hemiplegia after cerebral hemorrhage. Guo Ji Hu Li Xue Za Zhi 2022; 41: 62-4. |
| 30. | Zhang T. Application of acupoint patching in the treatment of limb hemiplegia in patients with cerebral hemorrhage. Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Hu Li 2016; 2: 62-3+6. |
| 31. | Zhou LL, Gu YD, Gong PP. Effects of early limb rehabilitation training combined with acupoint patching on elderly patients with neurosurgical cerebral hemorrhage. Shi Yong Lin Chuang Yi Xue Za Zhi 2019; 23: 5-8. |
| 32. | Huang QS, Wang C. Effects of self-made fumigation therapy combined with rehabilitation exercise on walking ability in patients with hemiplegia after cerebral hemorrhage. Sichuan Zhong Yi 2014; 32: 106-8. |
| 33. | Li RW, Xia Y, Li YJ, et al. Effects of transcranial direct current stimulation with different stimulation modes on upper limb motor function and activities of daily living in stroke patients: a network Meta-analysis. Zhong Guo Kang Fu Yi Xue Za Zhi 2023; 38: 394-402. |
| 34. |
Chen XW, Shafei MN, Abdullah JM, Musa KI. Reliability of telephone interview for assessment of long-term stroke outcomes: evidence from interrater analysis. Neuroepidemiology 2019; 52: 214-9.
DOI PMID |
| 35. |
Li D, Chen QX, Zou W, et al. Acupuncture promotes functional recovery after cerebral hemorrhage by upregulating neurotrophic factor expression. Neural Regen Res 2020; 15: 1510-7.
DOI PMID |
| 36. | Chen Q, Song W, Tang Y, Tang Y, Kang Y, Zhu L. Electroacupuncture reduces cerebral hemorrhage injury in rats by improving cerebral iron metabolism. Mediators Inflamm 2022; 2022: 6943438. |
| 37. |
Wen G, Xuan LL, Hu LZ, et al. Effectiveness of Chinese herbal medicine combined with conventional medicine on acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. J Tradit Chin Med 2023; 43: 212-20.
DOI |
| 38. | Chen CX. Observation on the effects of Traditional Chinese Medicine acupuncture combined with rehabilitation therapy in the treatment of elderly patients with cerebral hemorrhage. Zhong Guo Xian Dai Yao Wu Ying Yong 2020; 14: 189-91. |
| 39. | Liu HY, Zhu LF, Xie DL, et al. A controlled study on the effects of early electroacupuncture on limb function recovery in patients with cerebral infarction. Zhong Guo Kang Fu Li Lun Yu Shi Jian 2006; 1: 26-7. |
| 40. | Guan WK, Huang L, Zhu Y, et al. Electroacupuncture enhances synaptic plasticity in hemorrhagic stroke through the mTOR/ P70S6K signaling pathway. Zhong Yao Cai 2020; 31: 505-8. |
| 41. | Peng L, Lyu J, Yan WQ, et al. Clinical study on the treatment of acute ischemic stroke with acupuncture combined with modern rehabilitation therapy. Zhong Guo Zhong Yi Ji Zheng 2007; 10: 1173-4+245 |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||